Students can download Maths Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.6 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.6
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
If n(A × B) = 6 and A= {1, 3} then n (B) is ………….
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 6
Answer:
(3) 3
Hint: n(A × B) = 6
n(A) = 2
n(A × B) = n(A) × n(B)
6 = 2 × n(B)
n(B) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) = 3
![]()
Question 2.
A = {a, b, p}, B = {2, 3}, C = {p, q, r, s} then n[(A ∪ C) × B] is
(1) 8
(2) 20
(3) 12
(4) 16
Answer:
(3) 12
Hint:
A = {a, b, p}, B = {2, 3}, C = {p, q, r, s}
n (A ∪ C) × B
A ∪ C = {a, b, p, q, r, s}
(A ∪ C) × B = {{a, 2), (a, 3), (b, 2), (b, 3), (p, 2), (p, 3), (q, 2), (q, 3), (r, 2), (r, 3), (s, 2), (s, 3)
n [(A ∪ C) × B] = 12
Question 3.
If A = {1,2}, B = {1,2, 3, 4}, C = {5,6} and D = {5, 6, 7, 8} then state which of the following statement is true ……………….
(1) (A × C) ⊂ (B × D)
(2) (B × D) ⊂ (A × C)
(3) (A × B) ⊂ (A × D)
(4) (D × A) ⊂ (B × A)
Answer:
(1) (A × C) ⊂ (B × D)
Hint: n(A × B) = 2 × 4 = 8
(A × C) = 2 × 2 = 4
n(B × C) = 4 × 2 = 8
n(C × D) = 2 × 4 = 8
n(A × C) = 2 × 2 = 4
n(A × D) = 2 × 4 = 8
n(B × D) = 4 × 4 = 16
∴ (A × C) ⊂ (B × D)
![]()
Question 4.
If there are 1024 relations from a set A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} to a set B, then the number of elements in B is
(1) 3
(2) 2
(3) 4
(4) 6
Answer:
(2) 2
Hint:
n(A) = 5
n(B) = x
n(A × B) = 1024 = 210
25x = 210
⇒ 5x = 10
⇒ x =2
Question 5.
The range of the relation R = {(x, x2) a prime number less than 13} is ……………………
(1) {2, 3, 5, 7}
(2) {2, 3, 5, 7, 11}
(3) {4, 9, 25, 49, 121}
(4) {1, 4, 9, 25, 49, 121}
Answer:
(3) {4, 9, 25, 49, 121}
Hint:
Prime number less than 13 = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11}
Range (R) = {(x, x2)}
Range = {4, 9, 25, 49, 121} (square of x)
![]()
Question 6.
If the ordered pairs (a + 2, 4) and (5, 2a + b)are equal then (a, b) is
(1) (2, -2)
(2) (5, 1)
(3) (2, 3)
(4) (3, -2)
Answer:
(4) (3, -2)
Hint:
(a + 2, 4), (5, 2a + b)
a + 2 = 5
a = 3
2a + b = 4
6 + b = 4
b = -2
Question 7.
Let n(A) = m and n(B) = n then the total number of non-empty relations that can be defined from A to B is ……………..
(1) mn
(2) nm
(3) 2mn – 1
(4) 2mn
Answer:
(4) 2mn
Question 8.
If {(a, 8),(6, b)}represents an identity function, then the value of a and b are respectively
(1) (8, 6)
(2) (8, 8)
(3) (6, 8)
(4) (6, 6)
Answer:
(1) (8, 6)
Hint:
{{a, 8), (6, b)}
a = 8
b = 6
![]()
Question 9.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {4, 8, 9, 10}.
A function f: A → B given by f = {(1, 4), (2, 8),(3,9),(4,10)} is a ……………
(1) Many-one function
(2) Identity function
(3) One-to-one function
(4) Into function
Answer:
(3) One-to-one function
Hint:
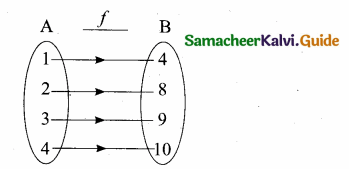
Different elements of A has different images in B.
∴ It is one-to-one function.
Question 10.
If f (x) = 2x2 and g(x) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3x } \), then fog is …………..
(1) \(\frac{3}{2 x^{2}}\)
(2) \(\frac{2}{3 x^{2}}\)
(3) \(\frac{2}{9 x^{2}}\)
(4) \(\frac{1}{6 x^{2}}\)
Answer:
(3) \(\frac{2}{9 x^{2}}\)
Hint:
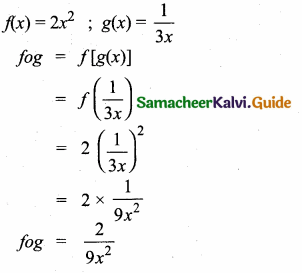
![]()
Question 11.
If f: A → B is a bijective function and if n(B) = 7, then n(A) is equal to
(1) 7
(2) 49
(3) 1
(4) 14
Answer:
(1) 7
Hint:
In a bijective function, n(A) = n(B)
⇒ n(A) = 7
Question 12.
Let f and g be two functions given by
f = {(0,1),(2, 0),(3-4),(4,2),(5,7)}
g = {(0,2),(1,0),(2, 4),(-4,2),(7,0)}
then the range of f o g is …………………
(1) {0,2,3,4,5}
(2) {-4,1,0,2,7}
(3) {1,2,3,4,5}
(4) {0,1,2}
Answer:
(4) {0,1,2}
Hint: f = {(0, 1)(2, 0)(3, -4) (4, 2) (5, 7)}
g = {(0,2)(l,0)(2,4)(-4,2)(7,0)}
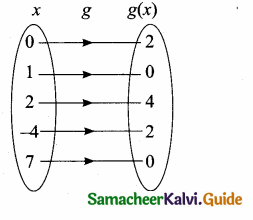
fog = f[g(x)]
f [g(0)] = f(2) = 0
f [g(1)] = f(0) = 1
f [g(2)] = f(4) = 2
f[g(-4)] = f(2) = 0
f[g(7)] = f(0) = 1
Range of fog = {0,1,2}
![]()
Question 13.
Let f(x) = \(\sqrt{1+x^{2}}\) then
(1) f(xy) = f(x),f(y)
(2) f(xy) ≥ f(x),f(y)
(3) f(xy) ≤ f(x).f(y)
(4) None of these
Answer:
(3) f(xy) ≤ f(x).f(y)
Hint:
\(\sqrt{1+x^{2} y^{2}} \leq \sqrt{\left(1+x^{2}\right)} \sqrt{\left(1+y^{2}\right)}\)
⇒ f(xy) ≤ f(x) . f(y)
Question 14.
If g= {(1,1),(2,3),(3,5),(4,7)} is a function given by g(x) = αx + β then the values of α and β are
(1) (-1,2)
(2) (2,-1)
(3) (-1,-2)
(4) (1,2)
Answer:
(2) (2, -1)
Hint: g (x) = αx + β
g(1) = α(1) + β
1 = α + β ….(1)
g (2) = α (2) + β
3 = 2α + β ….(2)
Solve the two equations we get
α = 2, β = -1
![]()
Question 15.
f(x) = (x + 1)3 – (x – 1)3 represents a function which is
(1) linear
(2) cubic
(3) reciprocal
(4) quadratic
Answer:
(4) quadratic
Hint:
f(x) = (x + 1)3 – (x – 1)3
= x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 -[x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 1]
= x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 – x3 + 3x2 – 3x + 1 = 6x2 + 2
It is a quadratic function.