Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Guide Pdf Chapter 14 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 14 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11th Chemistry Guide Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Textbook Evaluation:
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
The IUPAC name of 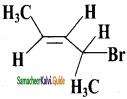 is
is
a) 2 – Bromo pent – 3 – ene
b) 4 – Bromo pent – 2 – ene
c) 2 – Bromo pent – 4 – ene
d) 4 – Bromo pent – 1 – ene
Answer:
b) 4 – Bromo pent – 2 – ene
Question 2.
Of the following compounds, which has the highest boiling point?
a) n – Butyl chloride
b) Isobutyl chloride
c) t – Butyl chloride
d) n – Propyl chloride
Answer:
a) n – Butyl chloride
Question 3.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their density
A) CCl4
B) CHCl3
C) CH2Cl2
D) CH3Cl
a) D < C < B < A
b) C > B > A > D
c) A < B < C < D
d) C > A > B > D
Answer:
a) D < C < B < A
Question 4.
With respect to the position of – Cl in the compound CH3 – CH = CH – CH2 – Cl, it is classified as
a) Vinyl
b) Allyl
c) Secondary
d) Aralkyl
Answer:
b) Allyl
Question 5.
What should be the correct IUPAC name of diethyl chloromethane?
a) 3 – Chloro pentane
b) 1 – Chloropentane
c) 1 – Chloro – 1, 1 – diethyl methane
d) 1- Chloro-1-ethyl propane
Answer:
a) 3 – Chloro pentane
![]()
Question 6.
C – X bond is strongest in
a) Chloromethane
b) Iodomethane
c) Bromomethane
d) Fluoromethane
Answer:
d) Fluoromethane
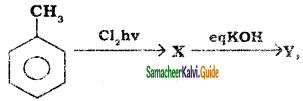
Question 7.
In the reaction 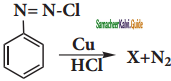 X is ______.
X is ______.
Answer:
b) 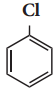
Question 8.
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH– ion?
i) 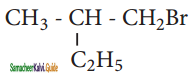
ii) 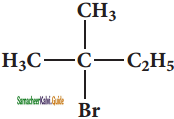
iii) 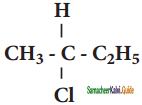
a) (i)
b) (ii) and (iii)
c) (iii)
d) (i) and (ii)
Answer:
c) (iii)
Question 9.
The treatment of ethyl formate with excess of RMgX gives
a) 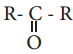
b) 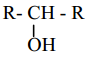
c) R – CHO
d) R – O – R
Answer:
c) R – CHO
Question 10.
Benzene reacts with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3 and in absence of sunlight to form
a) Chlorobenzene
b) Benzyl chloride
c) Benzal chloride
d) Benzene hexachloride
Answer:
a) Chlorobenzene
![]()
Question 11.
The name of C2F4C12 is
a) Freon – 112
b) Freon – 113
c) Freon – 114
d) Freon – 115
Answer:
c) Freon – 114
Question 12.
Which of the following reagent is helpful to differentiate ethylene dichloride and ehtylidene chloride?
a) Zn / methanol
b) KQH / ethanol
c) aqueous KOH
d) ZnCl2 / Con HCl
Answer:
c) aqueous KOH
Question 13.
Match the compounds given in Column I with suitable items given in Column II:
| Column I (Compound) | Column II (Uses) |
| A. Iodoform | 1. Fire extinguisher |
| B. Carbon tetra chloride | 2. Insecticide |
| C. CFC | 3. Antiseptic |
| D. DDT | 4. Refrigerants |
Code
a) A → 2 B → 4 C → 1 D → 3
b) A → 3 B → 2 C → 4 D → 1
c) A → 1 B → 2 C → 3 D → 4
d) A → 3 B → 1 C → 4 D → 2
Answer:
d) A → 3 B → 1 C → 4 D → 2
Question 14.
Assertion:
Inmonohaloarenes, electrophilic substitution occurs at ortho and para positions.
Reason:
Halogen atom is a ring deactivator.
Assertion and Reason type questions.
Directions:
In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R) mark the correct choice as
(i) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(iii) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(iv) If both assertion and reason are false.
a) (i)
b) (ii)
c) (iii)
d) (iv)
Answer:
b) (ii)
Question 15.
Consider the reaction,
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN → CH3CH2CH2CN + NaBr This reaction will be the fastest in
a) ethanol
b) methanol
c) DMF (N, N’ – dimethyl formamide)
d) water
Answer:
c) DMF (N, N’ – dimethyl formamide)
![]()
Question 16.
Freon – 12 manufactured from tetrachloro methane by
a) Wurtz reaction
b) Swarts reaction
c) Haloform reaction
d) Gattermann reaction
Answer:
b) Swarts reaction
Question 17.
The most easily hydrolysed molecules under SN1 condition is
a) allyl chloride
b) ethyl chloride
c) isopropyl chloride
d) benzyl chloride
Answer:
a) allyl chloride
Question 18.
The carbon cation formed in SN1 reaction of alkyl halide in the slow step is
a) sp3 hybridized
b) sp2 hybridized
c) sp hybridized
d) none of these
Answer:
b) sp2 hybridized
Question 19.
The major products obtained when chlorobenzene is nitrated with HNO3 and con H2SO4
a) 1 – chloro – 4 – nitrobenzene
b) 1 – chloro – 2 – nitrobenzene
c) 1 – chloro – 3 – nitrobenzene
d) 1 – chloro – 1 – nitrobenzene
Answer:
a) 1 – chloro – 4 – nitrobenzene
Question 20.
Which one of the following is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction?
a) ![]()
b) 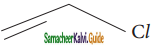
c) 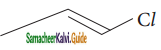
d) ![]()
Answer:
d) ![]()
![]()
Question 21.
Ethylidene chloride on treatment with aqueous KOH gives
a) acetaldehyde
b) ethylene glycol
c) formaldehyde
d) glycoxal
Answer:
a) acetaldehyde
Question 22.
The raw material for Raschig process
a) chloro benzene
b) phenol
c) benzene
d) anisole
Answer:
c) benzene
Question 23.
Chloroform reacts with nitric acid to produce
a) nitro toluene
b) nitro glycerine
c) chloropicrin
d) chloropicric acid
Answer:
c) chloropicrin
Question 24.
Acetone 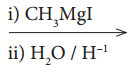 X, X is
X, X is
a) 2 – propanol
b) 2 – methyl – 2 – propanol
c) 1 – propanol
d) acetonol
Answer:
b) 2 – methyl – 2 – propanol
Question 25.
Silverpropionate when refluxed with Bromine in carbon tetrachloride gives
a) propionic acid
b) chloroethane
c) Bromo ethane
d) chloro propane
Answer:
c) bromo ethane
![]()
II. Write brief answer to the following questions:
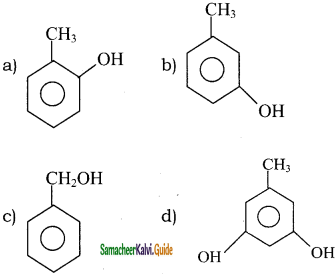
Question 26.
Classify the following compounds in the form of alkyl, allylic, vinyl, benzylic halides.
i) CH3 – CH = CH – Cl
ii) C6H5CH2I
iii) 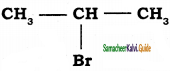
iv) CH2 = CH – Cl
Answer:
i) CH3 – CH = CH – Cl = Allylic halide
ii) C6H5CH2I = Benzylic halide
iii)  = Alkyl halide
= Alkyl halide
iv) CH2 = CH – Cl = Vinyl halide
Question 27.
Why chlorination of methane is not possible in dark?
Answer:
The reaction of chlorine and methane is a free radical reaction under the influence of light energy. Chlorine molecule first split into two Cl atoms or radicals. These are both very reactive species in contact with methane they form methyl radical and HCl.
Methyl radical further reacts with Cl to give CH3Cl and another Cl atom thus of a chain reaction. So this reaction takes place only under the influence of light. Hence the reaction does not take place in dark condition.
Question 28.
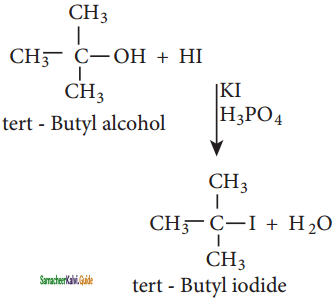
How will you prepare n propyl iodide from n – propyl bromide?
Answer:
Finkelstein reaction,
nCH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br + NaI ![]() n – CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – I + NaBr
n – CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – I + NaBr
n – propyl iodide n- propyl bromide
Question 29.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair is
i) chiral
ii) undergoes faster SN2 reaction?

Answer:
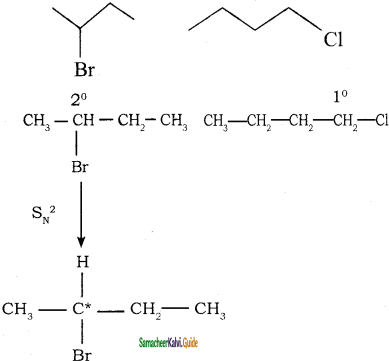
It contains one chiral carbon atom.
2 – bromo butane undergoes SN2 mechanism faster than 1- Chloro butane.
Question 30.
How does chlorobenzene react with sodium in the presence of ether? What is the name of the reaction?
Answer:
Haloarenes react with sodium metal in dry ether, two aryl groups combine to give biaryl products.
This reaction is called fittig reaction.
C6H5Cl + 2Na + Cl – C6H5 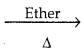 C6H5 – C6H5 + 2NaCl
C6H5 – C6H5 + 2NaCl
Chlorobenzene Biphenyl
![]()
Question 31.
Give reasons for polarity of C – X bond in halo alkane.
Answer:
Carbon halogen bond is a polar bond as halogens are more electro negative than carbon. The carbon atom exhibits a partial positive charge (δ+) and halogen atom a partial negative charge (δ–)
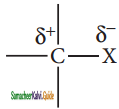
The C -X bond is formed by overlap of sp3 orbital of carbon atom with half-filled p- orbital of the halogen atom. The atomic size of halogen increases from fluorine to iodine, which increases the C – X bond length. Larger the size, greater is the bond length, and weaker is the bond formed. The bond strength of C – X decreases from C – F to C – I in CH3X.
Question 32.
Why is it necessary to avoid even traces of moisture during the use of Grignard reagent?
Answer:
Grignard reagents are mostly reactive and react with the source of product to give hydrocarbons. Even alcohols, amines, H2O are sufficiently acidic to convert them to corresponding hydrocarbons.
R Mg X + H2O → RH + 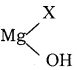
Due to its high reactivity, it is necessary to avoid even traces of moisture from Grignard reagent.
Question 33.
What happens when acetyl chloride is treated with an excess of CH3MgI?
Answer:
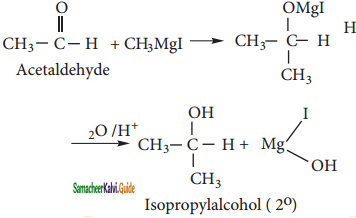
Question 34.
Arrange the following alkyl halide in increasing order of bond enthalpy of RX.
CH3Br, CH3F, CH3Cl, CH3I
Answer:
The order is:
CH3I < CH3Br < CH3Cl < CH3F.
Question 35.
What happens when chloroform reacts with oxygen in the presence of sunlight?
Answer:
2 CHCl3 + O2 → 2 COCl2 + 2 HCl
![]()
Question 36.
Write down the possible isomers of C5H11Br and give their IUPAC and common names.
Answer:
C5H11Br – Possible isomers
1. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – Br → 1 – bromo pentane
2. 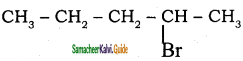 → 2 – bromo pentane
→ 2 – bromo pentane
3. 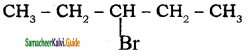 → 3 – bromo pentane
→ 3 – bromo pentane
4. 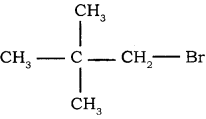 → 1 – bromo 2, 2 – dimethyl propane
→ 1 – bromo 2, 2 – dimethyl propane
5. 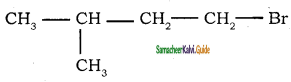 → 1 – bromo 3 – methyl butane
→ 1 – bromo 3 – methyl butane
6. 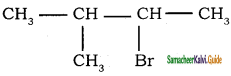 → 2 – bromo 3 – methyl butane
→ 2 – bromo 3 – methyl butane
7. 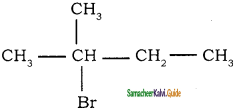 → 2 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
→ 2 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
8. 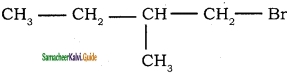 → 1 – bromo 2- methyl butane
→ 1 – bromo 2- methyl butane
9. 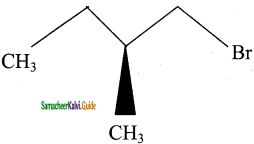 → (2S) – 1 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
→ (2S) – 1 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
10. 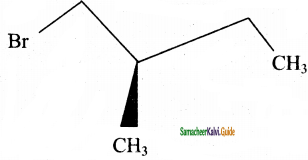 → (2R) – 1 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
→ (2R) – 1 – bromo 2 – methyl butane
Question 37.
Mention any three methods of preparation of haloalkanes from alcohols.
Answer:
Haloalkanes are prepared by the following methods.
1) From alcohols:
Alcohols can be converted into halo alkenes by reacting it with any one of the following reagent.
1. Hydrogen halide
2. Phosphorous halides
3. Thionyl chloride.
a) Reaction with hydrogen halide:
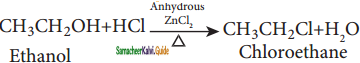
Mixture of con. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2 is called Lucas Reagent.
The order of reactivity of halo acids with alcohol is in the order HI > HBr > HCl.
The order of reactivity of alcohols with halo acid is tertiary > secondary > primary.
b) Reaction with phosphorous halides:
Alcohols react with PX5 or PX3 to form haloalkanes.
Example:
CH3CH2OH + PCl5 → CH3CH2Cl + POCl3 + HCl
Ethane Chloro ethane
3CH3CH2OH + PCl3 → 3 CH3CH2Cl + H3PO3
Ethanol Chloro ethane
c) Reaction with Thionyl chloride(Sulphonyl Chloride)
CH3CH3OH + SOCl2 ![]() CH3CH2Cl + SO2↑ + HCl↑
CH3CH2Cl + SO2↑ + HCl↑
Ethanol Chloro ethane
Question 38.
Compare SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms.
Answer:
| SN1 | SN2 | |
| Rate law | Unimolecular (Substrate only) | Biomolecular (substrate and nucleophile) |
| “Big Barrier” | Carbocation stability | Steric hindrance |
| Alkyl halide (electrophile) | 3° > 2° > 1° | 1° > 2° > 3° |
| Nucleophile | Weak (generally neutral) | Strong (generally bearing a negative charge) |
| Solvent | Polar protic (e.g., alcohols) | Polar aprotic (e.g., DMSO, acetone) |
| Stereo Chemistry | Mix of retention and inversion | inversion |
Question 39.
Reagents and the conditions used in the reactions are given below. Complete the table by writing down the product and the name of the reaction.
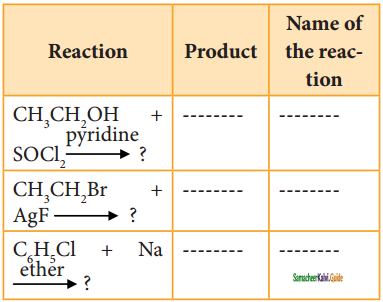
Answer:
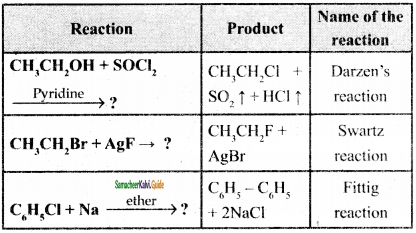
Question 40.
Discuss the aromatic nucleophilic substitutions reaction of chlorobenzene.
Answer:
The halogen of haloarenes can be substituted by OH–, NH2– or CN– with appropriate nucleophilic reagents at high temperature and pressure.
Example:
(i) Chlorobenzene reacts with ammonium at 250 and at 50 atm to give aniline.
C6H5Cl + 2NH3 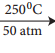 C6H5NH2 + NH4Cl
C6H5NH2 + NH4Cl
Chlorobenzene Aniline
(ii) Chlorobenzcne reacts with CuCN in presence of pyridine at 250 to give phenyl cyanide.
C6H5Cl + CuCN ![]() C6H5CN + CuCl
C6H5CN + CuCl
Chlorobenzene Phenyl cyanide
(iii) Dows process:
C6H5Cl + NaOH ![]() C6H5OH + NaCl
C6H5OH + NaCl
Chlorobenzene Phenol
This reaction is known as Dow’s process.
![]()
Question 41.
Account for the following:
(i) t – butyl chloride reacts with aqueous KOH by SN1 mechanism while n – butyl chloride reacts with SN2 mechanism.
(ii) p – dichloro benzene has higher melting point than those of o – and m – dichloro benzene.
Answer:
(i) t – butyl chloride reacts with aqueous KOH by SN1 mechanism while n – butyl chloride reacts with SN2 mechanism.
It general, SN1 reaction proceeds through the formation, of carbocation, The tert- butyl chloride readily loses Cl ion to form stable 3° carbocation. Therefore, it reacts with aqueous KOH by SN1 mechanism as:
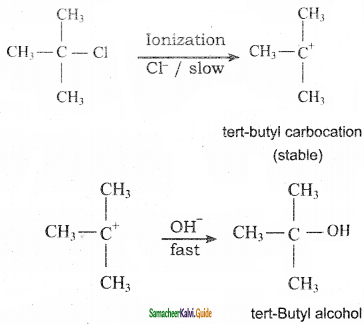
On the other hand n-Butyl chloride does not undergo ionization to form n-Butyl carbocation (1°) because it is not stable. Therefore, it prefers to undergo reaction by SN2 mechanism, which occurs is one step through a transition state involving nucleophilic attack of OH– ion from the backside with simultaneous expulsion of Cl– ion from the front side.
SN1 mechanism follows the reactivity order as 3° > 2°> 1° while SN2 mechanism follows the reactivity order as 1° > 2° > 3°. Therefore, tert-butyl chloride (3°) reacts by SN1 mechanism while n-butyl chloride (1°) reacts by SN2 mechanism. (ii) p – dichloro benzene has higher melting point than those of o – and m – dicholoro benzene. The higher melting point of p – isomer is due to its symmetry which leads to more close packing of its molecules in the crystal lattice and consequently strong intermolecular attractive force which requires more energy for melting. p – Dihalo benzene > o – Dichloro benzene> m – Dichioro benzene
Melting point: 323 K 256 K 249 K
Question 42.
In an experiment methyl iodide in ether is allowed to stand over magnesium pieces. Magnesium dissolves and product is formed.
a) Name of the product and write the equation for the reaction.
b) Why all the reagents used in the reaction should be dry? Explain.
c) How is acetone prepared from the product obtained in the experiment?
Answer:
a) Name of the product and write the equation for the reaction.
CH3I + Mg ![]() CH3MgI
CH3MgI
b) Why all the reagents used in the reaction should be dry? Explain.
All the reagents used in the reaction should be dry because reagent reacts with H20 to produce alkane. This is the reason that everything has to be very dry during the preparation of Grignard reagents.
CH3 – MgI + H2O → CH4 +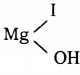
Methane
c) How is acetone prepared from the product obtained in the experiment?
Question 43.
Write a chemical reaction useful to prepare the following.
i) Freon – 12 from Carbon tetrachloride
ii) Carbon tetrachloride from carbon disulphide.
Answer:
i) Freon – 12 from Carbon tetrachloride:
Freon – 12 is prepared by the action of hydrogen fluoride on carbon tetrachloride in the presence of catalytic amount of antimony pentachloride.
CCl4 + 2HF ![]() 2HCl + CCl2F2
2HCl + CCl2F2
Carbon tetrachloride Freon – 12
ii) Carbon tetrachloride from carbon disulphide.
Carbon disulphide reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 as catalyst giving carbon tetra chloride.
CS2 + 3 Cl2  CCl4 + S2Cl2
CCl4 + S2Cl2
Carbon disulfide Carbon tetrachloride
Question 44.
What are Freons? Discuss their uses and environmental effects.
Answer:
The chloro fluoro derivatives of methane and ethane are called freons.
Nomenclature:
Freon is represented as Freon – cba
Where a = number of carbon atoms – 1;
b = number of hydrogen atoms + 1
a = total number of fluorine atoms
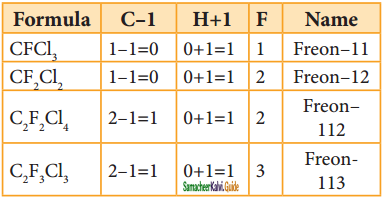
Uses:
i) Freons are used as a refrigerants in refrigerators and air conditioners.
ii) It is used as a propellant for aerosols and foams
iii) It is used as propellant for foams to spray out deodorants, shaving creams, and insecticides.
Question 45.
Predict the products when bromo ethane is treated with the following.
i) KNO2 ii) AgNO2
Answer:
i) KNO2:
Bromo ethane reacts with alcoholic solution of NaNO2 or KNO2 to form ethyl nitrite.
CH3CH2Br + KNO2 → CH3CH2 – O – N = O + KBr
Bromoethane Ethyl nitrite
ii)AgNO2:
Bromo ethane reacts with alcoholic solution of AgNO2 to form nitro ethane.
CH3CH2Br + AgNO2 → CH3CH2 NO2 + AgBr
Bromoethane Nitro ethane
![]()
Question 46.
Explain the mechanism of SN1 reaction by highlighting the stereochemistry behind it.
Answer:
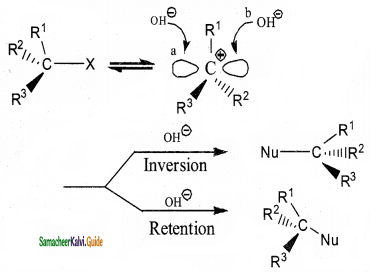
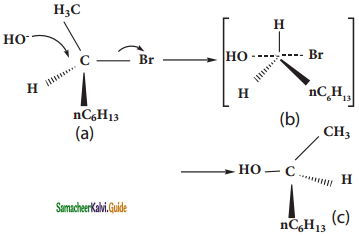
In SN1 reactions, if the alkyl halide is optically active, the product obtained in a racemic mixture. The intermolecular carbocation formed in slowest step being sp2 hybridised is planar species. Therefore the attack of the nucleophile OH on it, can occur from both the faces with equal case forming a mixture of two enantiomers. Thus SN1 reaction of optically active alkyl halides are accompained by racemisation.
Question 47.
Write short notes on the following.
i) Raschig process
ii) Dows process
iii) Darzen’s process
Answer:
i) Raschig process:
Chloro benzene is commercially prepared by passing a mixture of benzene vapour, air and HCl overheated cupric chloride, this reaction is called the Raschig process,
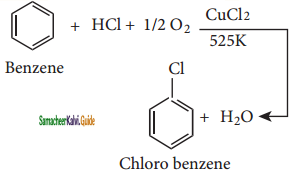
ii) Dows Process:
C6H5Cl + NaOH ![]() C6H5OH + NaCl
C6H5OH + NaCl
This reaction is known as Dows process.
iii) Darzen’s process:
CH3CH2OH + SOCl ![]() CH3CH2Cl + SO2↑ + HCl↑
CH3CH2Cl + SO2↑ + HCl↑
Ethanol Chloro ethane
This reaction is known as Darzen’s process.
Question 48.
Starting from CH3MgI, How will you prepare the following?
i) Acetic acid
ii) Acetone
iii) Ethyl acetate
iv) Iso propyl alcohol
v) Methyl cyanide
Answer:
i) Acetic acid:
Solid carbon dioxide reacts with methyl magnesium iodide to form addition product which on hydrolysis yields aceti acid.
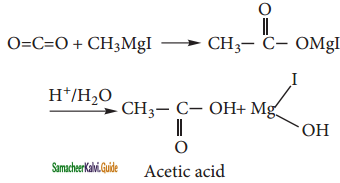
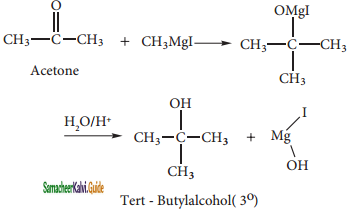
ii) Acetone:
Acetyl chloride reacts with methyl magnesium iodide and followed by acid hydrolysis to give acetone.
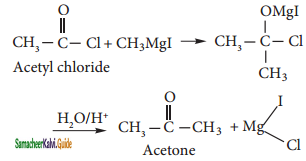
iii) Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl chloroformate reacts with methyl magnesium iodide to form ethyl acetate.
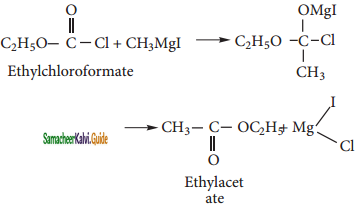
iv) Isopropyl alcohol:
Aldehydes (Acetaldehyde) other than formaldehyde, react with methyl magnesium iodide to give addition product which on hydrolysis yields isopropyl alcohol.
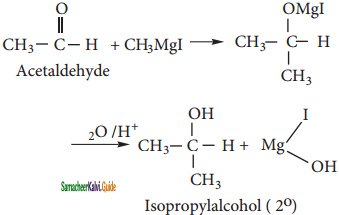
v) Methyl cyanide:
Methyl magnesium iodide reacts with cyanogen chloride to give methyl cyanide.
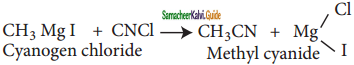
![]()
Question 49.
Complete the following reactions.
i) CH3 – CH = CH2 + HBr ![]()
ii) CH3 – CH2 – Br + NaSH 
iii) C6H5Cl + Mg ![]()
iv) CHCl3 + HNO3 ![]()
v) CCl4 + H2O ![]()
Answer :
i) CH3 – CH = CH2 + HBr ![]() CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br
Propene n – propyl bromide
ii) CH3 – CH2 – Br + NaSH  CH3 – CH2 – SH + NaBr
CH3 – CH2 – SH + NaBr
Propyl bromide Ethanethiol
iii) C6H5Cl (Chloro benzene) + Mg ![]() C6H5MgCl (Phenyl magnesium chloride)
C6H5MgCl (Phenyl magnesium chloride)
iv) CHCl3 + HNO3 ![]() CCl3NO2 + H
CCl3NO2 + H
Chloroform Chloropicrin
v) CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride) + H2O ![]() COCl2 (Carbonyl chloride) + 2HCl
COCl2 (Carbonyl chloride) + 2HCl
Question 50.
Explain the preparation of the following compounds.
i) DDT
ii) Chloroform
iii) Biphrnyl
iv) Chloropicrin
v) Freon – 12
Answer:
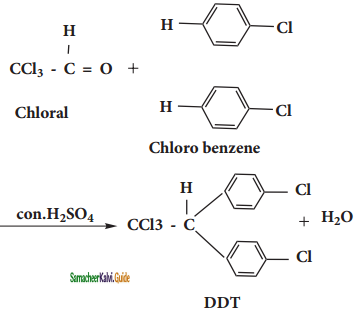
i) DDT:
DDT can be prepared by heating a mixture of chlorobenzene with chloral (Trichloro acetaldehyde) in the presence of con.H2SO4.
ii) Chloroform:
Preparation:
Chloroform is prepared in the laboratory by the reaction between ethyl alcohol with bleaching powder followed by the distillation of the product chloroform. Bleaching powder act as a source of chlorine and calcium hydroxide. This reaction is called haloform reaction. The reaction proceeds in three steps as shown below.
Step – 1: Oxidation
CH3CH2OH + Cl2 → CH3CHO + 2HCl
Ethyl alcohol Ethanal (Acetaldehyde)
Step – 2: Chlorination
CH3CHO + 3Cl2 → CCl3CHO + 3HCl
Acetaldehyde Trichloro acetaldehyde
Step – 3: Hydrolysis
2CCl3CHO + Ca(OH)2 → 2CHCl3 + (HCOO)2 Ca
Chloral chloroform
iii) Biphenyl:
Chloro benzene react with sodium metal in dry ether, to give biphenyl. This reaction is called fitting reaction.
C6H5Cl + 2 Na + Cl – C6H5  C6H5 – C6H5 + 2NaCl
C6H5 – C6H5 + 2NaCl
Chloro benzene Biphenyl
iv) Chloropicrin:
Chloroform reacts with nitric acid to form chloropicrin. (Trichloro nitro methane)
CHCl3 + HNO3 ![]() CCl3NO2 + H2O
CCl3NO2 + H2O
Chloroform Chloropicrin
v) Freon – 12
Freon – 12 is prepared by the action of hydrogen fluoride on carbon tetrachloride in the presence of catalytic amount of antimony pentachloride
CCl4 + 2 HF  2 HCl + CCl2F2
2 HCl + CCl2F2
Carbon tetrachloride Freon – 12
![]()
Question 51.
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C2H5Cl reacts with KOH gives compounds (B) and with alcoholic KOH gives compound (C). Identify (A), (B), (C).
Answer:
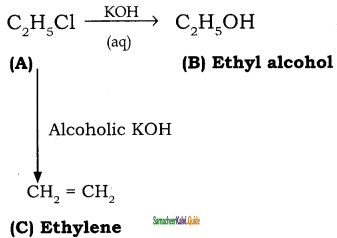
Question 52.
Simplest alkene (A) reacts with HCl to form compound (B). Compound (B) reacts with ammonia to form compound (C) of molecular formula C2H7N. Compound (C) undergoes carbylamine test. Identify (A),
(B) and (C).
Answer:
CH2 = CH2 + HCl → C2H5Cl
(A) Ethylene (B) Ethyl chloride
C2H5Cl + NH3 → C2H5NH2 + HCl
(C) Ethyl chloride (B) Ethyl amine
Question 53.
A hydrocarbon C3H6(A) reacts with HBr to form compound (B). Compound (B) reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide to give (C) of molecular formula C3H6O. What are the (A), (B) and (C). Explain the reactions.
Answer:
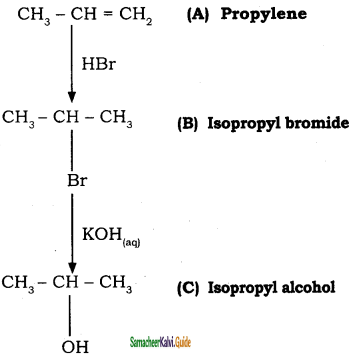
Question 54.
Two isomers (A) and (B) have the same molecular formula C2H4Cl2. Compound (A) reacts with aqueous KOH gives compound (C) of molecular formula C2H4O. Compound (B) reacts with aqueous KOH gives compound (D) of molecular formula C2H6O2. Identify (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Answer:
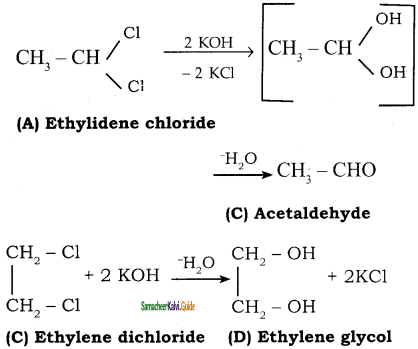
![]()
11th Chemistry Guide Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Which of the following is 1° alkyl halide
a) R – CH2 – X
b) R2CHX
C) R3C – X
d) R – H
Answer:
a) R – CH2 – X
Question 2.
2° halide among the following
a) isopropyl chloride
b) iso – butyl chloride
c) n – propyl chloride
d) n – butyl chloride
Answer:
a) isopropyl chloride
Question 3.
Ethylidene dibromide is
a) CH3CH2Br
b) Br – CH2 – CH2 – Br
c) CH3 – CHBr2
d) CH2 = CH Br
Answer:
c) CH3 – CHBr2
Question 4.
Which of the following is gemdihalide?
a) CH3CHBrCH2Br
b) CH3CHBr2
c) CH3CHBrCH2CH2Br
d) BrCH2CH2Br
Answer:
b) CH3CHBr2
Question 5.
Vicinal dihalide is
a) CH3CH2Br
b) Br – CH2 – CH2 – Br
c) CH3 – CHBr2
d) CH2 = CHBr
Answer:
b) Br – CH2 – CH2 – Br
![]()
Question 6.
The reagent used to get alkyl halide from alcohol
a) PCl5
b) SOCl2
c) Both a and b
d) Cl2
Answer:
c) Both a and b
Question 7.
For the preparation of alkyl halides from alcohols which among the following cannot be used
a) PCl5
b) SOCl2
c) PCl3
d) NaCl
Answer:
d) NaCl
Question 8.
In the preparation of alkyl halide from alkane and halogen which of the following reaction involved
a) Electrophilic addition
b) Nucleophilic addition
c) Electrophilic substitution
d) Nucleophilic substitution
Answer:
a) Electrophilic addition
Question 9.
In the preparation of alkyl halide from alkane and halogen which of the following reaction involved
a) Free radical substitution
b) Nucleophilic addition
c) Electrophilic substitution
d) Nucleophilic substitution
Answer:
a) Free radical substitution
Question 10.
Grignard reagent is formed when alkyl halide reacts with which one of the following
a) Mg in alcohol
b) Mg in acid
c) Mg in dry ether
d) MgO
Answer:
c) Mg in dry ether
![]()
Question 11.
When alkyl halide reacts with moist Ag2O gives
a) alcohol
b) ether
c) alkane
d) Alkene
Answer:
a) alcohol
Question 12.
Alkyl halide on reduction with Zn + HCl gives
a) alcohol
b) alkene
c) alkane
d) ether
Answer:
c) alkane
Question 13.
Cyanide is formed as the major product of the reaction when alkyl halide is treated with one of the following :
a) AgNO2
b) KNO2
c) AgCN
d) KCN
Answer:
c) AgCN
Question 14.
Which of the reactions are most common in alkyl halides
a) Nucleophilic addition
b) Electrophilic addition
c) Nucleophilic substitution
d) Electrophilic substitution
Answer:
c) Nucleophilic substitution
Question 15.
Treatment of ammonia with excess of ethyl chloride will yield
a) Diethyl amine
b) Ethane
c) Tetra ethyl ammonium chloride
d) methyl amine
Answer:
c) Tetra ethyl ammonium chloride
![]()
Question 16.
In chloro ethane the carbon bearing halogen is bonded to ________.
a) three, primary
b) two, secondary
c) one, tertiary
d) two, primary
Answer:
d) two, primary
Question 17.
Which of the fallowing is used as refrigerant?
a) CH3COCH3
b) CCl4
c) C2H5Cl
d) CF4
Answer:
c) C2H5Cl
Question 18.
SN1reaction occurs through the intermediate formation of
a) carbocation
b) carbanion
c) free radicals
d) transition
Answer:
a) carbocation
Question 19.
The rate of SN2 reaction is maximum when the solvent is
a) Methyl alcohol
b) Water
c) Dimethyl sulphoxide
d) Benzene
Answer:
c) Dimethyl sulphoxide
Question 20.
The most reactive nucleophile among the following is
a) CH3O–
b) C6H5O–
c) (CH3)2CHO–
d) (CH3)3CO–
Answer:
a) CH3O–
![]()
Question 21.
The correct order of reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction is
a) CH3F > CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3I
b) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3F
C) CH3I > CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3F
d) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3F > CH3Cl
Answer:
b) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3F
Question 22.
In SN2 reactions the order of reactivity of the halides.
CH3X, C2H5X , n – C3H7X, n- C4H9X is
a) CH3X > C2H5X > n – C3H7X > n – C4H9X
b) C2H5X > n – C3H7X > n – C4H9X > CH3X
c) C2H5X > n – C3H7X > n – C4H9X < CH3X
d) n – C4H9X > n – C3H7X > C2H5X > CH3X
Answer:
a) CH3X > C2H5X > n – C3H7X > n – C4H9X
Question 23.
SN2 mechanism proceeds through the formation of a
a) carbocation
b) transition state
c) free radical
d) carbanion
Answer:
b) transition state
Question 24.
In Dow’s process the starting raw material is
a) Phenol
b) Chloro benzene
c) Aniline
d) Diazobenzene
Answer:
b) Chloro benzene
Question 25.
Chloro benzene is prepared commercially by
a) Dow’s process
b) Decon’s process
c) Raschig process
d) Etard’s process
Answer:
c) Raschig process
![]()
Question 26.
Chloro benzene is ________ reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution and directs incoming electrophile to the ______ position.
a) more, ortho & para
b) less, ortho & para
c) more, meta
d) less, meta
Answer:
b) less, ortho & para
Question 27.
The raw material for raschig; process is
a) chloro benzene
b) phenol
c) benzene
d) anisol
Answer:
c) benzene
Question 28.
Chloro benzene on treatment with sodium in dry ether gives diphenyl. The name of the reaction is
a) Fitting reaction
b) Wurtz fittig reaction
c) Wurtz reaction
d) Sandmeyer reaction
Answer:
a) Fitting reaction
Question 29.
An organic compound which produces a bluish green coloured flame on heating in the presence of copper is,
a) chloro benzene
b) benzaldehyde
c) aniline
d) benzoic acid
Answer:
a) chloro benzene
Question 30.
The raw materials for the commercial manufacture of DDT are
a) chloro benzene and chloroform
b) chloro benzene and chloro methane
c) chloro benzene and chloral
d) chloro benzene and iodoform
Answer:
c) chloro benzene and chloral
![]()
Question 31.
Iodoform is used as
a) anaesthetic
b) antiseptic
c) analgesic
d) anti febrin
Answer:
b) antiseptic
Question 32.
The following is used in paint removing
a) CHCl3
b) CH2Cl2
c) CCl4
d) CH3CI
Answer:
b) CH2Cl2
Question 33.
In fire extinguishers, following is used
a) CHCl3
b) CS2
c) CCl4
d) CH2Cl2
Answer:
c) CCl4
Question 34.
The following is used for metal cleaning and finishing
a) CHCl3
b) CHI3
c) CH2Cl2
d) C6H6
Answer:
c) CH2Cl2
Question 35.
First chlorinated insecticide
a) DDT
b) Gammaxene
c) Iodoform
d) Freon
Answer:
a) DDT
![]()
Question 36.
The following is used as anaesthetic
a) C2H4
b) CHCl3
c) CH2Cl2
d) DDT
Answer:
b) CHCl3
Question 37.
Freon – 12 is
a) CF3Cl
b) CHCl2F
c) CF2Cl2
d) DDT
Answer:
c) CF2Cl2
Question 38.
The name of DDT
a) p, p’ – dichloro diphenyl trichloro ethane
b) p, p’ – dichloro diphenyl trichloro ethene
C) p, p’ – dichloro diphenyl tnchloro benzene
d) p, p’ – tetra chloro ethane
Answer:
a) p, p’ – dichloro diphenyl trichloro ethane
Question 39.
Freon R – 22 is
a) CHClF2
b) CCl2F2
c) CH3Cl
d) CH2Cl2
Answer:
a) CHClF2
Question 40.
Molecular formula of DDT has
a) 5 Cl atoms
b) 4 Cl atoms
c) 3 Cl atoms
d) 2 Cl atoms
Answer:
a) 5 Cl atoms
![]()
Question 41.
What is DDT among the following
a) Green house gas
b) A fertilizer
c) Bio degradable pollutant
d) Non – Bio degradable pollutant
Answer:
d) Non – Bio degradable pollutant
Question 42.
The IUPAC name of (CH3)3CHCH2Br is
a) 1 – bromo – 2 – methyl propane
b) 2 – bromo – 2 -methyl propane
c) 1 – bromo – 1 – methyl propane
d) 2 – bromo – 1 -methylpropane
Answer:
a) 1 – bromo – 2 – methyl propane
Question 43.
IUPAC name of allyl chloride is
a) 1 – chloro ethane
b) 3 – chloro- 1 – propyne
c) 3 – chloro – 1 – propene
d) 1 – chloro propane
Answer:
c) 3 – chloro – 1 – propene
Question 44.
The number of structural isomers possible with the formula C4H9Cl are
a) 5
b) 4
c) 3
d) 2
Answer:
b) 4
Question 45.
Density is highest for
a) CH3Cl
b) CH2Cl2
c) CHCl3
d) CCl4
Answer:
d) CCl4
![]()
Question 46.
C2H5OH ![]() X. In this reaction ‘X’ is
X. In this reaction ‘X’ is
a) Ethanol
b) Ethylene chloride
c) ethylidene chloride
d) ethyl chloride
Answer:
d) ethyl chloride
Question 47.
Thionyl chloride is preferred in the preparation of chloro compound from alcohol since
a) Both the byproducts are gases and they escape out leaving product in pure state
b) It is a chlorinating agent
c) It is an oxidising agent
d) All other reagents are unstable
Answer:
a) Both the byproducts are gases and they escape out leaving product in pure state
Question 48.
The only alkene which gives primary alkyl halides on hydro halogenation
a) C2H4
b) C3H6
c) C4H8
d) C5H10
Answer:
a) C2H4
Question 49.
– OH cannot be replaced by – Cl if we use
a) PCl5
b) PCl3
c) S2Cl2
d) SOCl2
Answer:
c) S2Cl2
Question 50.
In the hydrohalogenation of ethylene for adding HCl, the catalyst used is
a) Anhydrous AlCl3
b) Conc. Sulphuric acid
c) Dilute Sulphuric acid
d) Anhydrous ZnCl2
Answer:
a) Anhydrous AlCl3
![]()
Question 51.
Which one of the following has the lowest boiling point?
a) CH3Cl
b) C2H5Cl
c) C2H5Br
d) C2H5I
Answer:
a) CH3Cl
Question 52.
Chloroethane is reacted with alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The product formed is
a) C2H6O
b) C2H6
c) C2H4
d) C2H4O
Answer:
c) C2H4
Question 53.
What is X in the following reaction? C2H5Cl + X → C2H5OH + KCl
a) KHCO3
b) alc. KOH
c) aq. KOH
d) K2CO3
Answer:
c) aq. KOH
Question 54.
Which of the following acids will give maximum yield of alkyl chloride in Hunsdiecker reaction
a) CH3CH2CH2COOH
b) (CH3)2CHCOOH
c) (CH3)3CCOOH
d) C6H5CH (CH3)COOH
Answer:
a) CH3CH2CH2COOH
Question 55.
In the reaction sequence
C2H5Cl + KCN X. What is the molecular formula of X is
a) C2H5CN
b) C2H5NC
c) C2H5OH
d) C2H4O
Answer:
a) C2H5CN
![]()
Question 56.
Ethyl chloride on heating with silver cyanide forms a compound X. The functional isomer of X is
a) C2H5NC
b) C2H5NCN
c) H3C – NH – CH3
d) C2H5NH2
Answer:
b) C2H5NCN
Question 57.
With Zn – Cu couple and C2H5OH, ethyl Iodide reacts to give
a) ethers
b) diethyl ether
c) Iodoform
d) Ethane
Answer:
d) Ethane
Question 58.
Ethyl bromide on boiling with alcoholic solutions of sodium hydroxide forms
a) Ethane
b) ethylene
c) ethyl alcohol
d) all of these
Answer:
b) ethylene
Question 59.
Following major compound is formed when ethyl chloride react with silver nitrite
a) Nitro ethane
b) Ethyl nitrite
c) Ethylene
d) Acetaldehyde
Answer:
b) Ethyl nitrite
Question 60.
Which of the following represents Williamson’s synthesis?
a) CH3COOH + PCl3 →
b) CH3 – CH2 – Cl + CH3COOH →
c) CH3 – CH2 – ONa + CH3 – CH2 – Cl →
d) CH3 – CH2 – OH + Na →
Answer:
c) CH3 – CH2 – ONa + CH3 – CH2 – Cl →
![]()
Question 61.
The reaction of alkyl halide with benzene in presence of anhydrous A1Cl3 gives alkyl benzene the reaction is known as
a) Friedel – craft’s reaction
b) Carbylamine reaction
c) Gattermann reaction
d) Wurtz reaction
Answer:
a) Friedel – craft’s reaction
Question 62.
A Grignard’s reagent reacts with water to give
a) ether
b) alkanes
c) amine
d) Alcohol
Answer:
b) alkanes
Question 63.
C2H5Cl + Mg → C2H5 MgCl in this reaction the solvent is
a) C2H5OH
b) Water
c) Dry ether
d) Acetone
Answer:
c) Dry ether
Question 64.
For a nucleophilic substitution reaction the rate was found in the order RI > RBr > RCl > RF then the reaction could be
a) SN1 only
b) SN2 only
c) Either SN1 or SN2
d) Neither SN1 or SN2
Answer:
c) Either SN1 or SN2
Question 65.
SN2 reaction leads to
a) inversion of configuration
b) retention of configuration
c) partial racemisation
d) no racemisation
Answer:
a) inversion of configuration
![]()
Question 66.
Which of the following alkyl halide is hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism
a) CH3Cl
b) CH3 – CH2 – Cl
c) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Cl
d) (CH3)3CCl
Answer:
d) (CH3)3CCl
Question 67.
SN1 reaction is favoured by
a) non – polar solvents
b) Bulky group on the carbon atom attached to the halogen atom
c) Small groups on the carbon atom attached to halogen atom
d) All of the above
Answer:
b) Bulky group on the carbon atom attached to the halogen atom
Question 68.
Which of the following is not stereospecific
a) SN1
b) SN2
c) E2
d) Addition of Br2 to ethylene in CCl4
Answer:
a) SN1
Question 69.
Which of the following factors does not favour SN1 mechanism
a) Strong base
b) Polar solvent
c) Low. conc. of nucleophile
d) 3° halide
Answer:
c) Low. conc. of nucleophile
Question 70.
The order of reactivity of various alkyl halides toward SN1 reaction is
a) 3° > 2° > 1°
b) 1° > 2° > 3°
c) 3° = 2° = 1°
d) 1° > 3° > 2°
Answer:
a) 3° > 2° > 1°
![]()
Question 71.
In aryl halides carbon atom holding halogen is
a) sp2 hybridised
b) sp hybridised
c) sp3 hybndised
d) sp3d hybridised
Answer:
a) sp2 hybridised
Question 72.
Chloro benzene can be prepared by reacting benzene diazonlum chloride with
a) HCl
b) Cu2Cl2 / HCl
c) Cl2 / AlCl3
d) HNO2
Answer:
b) Cu2Cl2 / HCl
Question 73.
 + Cl2
+ Cl2 ![]() X, X is
X, X is
a) Chloro benzene
b) m – dichloro benzene
c) benzene hexachioride
d) p – dichlorobenzene
Answer:
a) Chloro benzene
Question 74.
The following is an example of Sandmeyer reaction
a) C6H5N2+ Cl– ![]() C6H5Cl
C6H5Cl
b) C6H5N2+ Cl– ![]() C6H5OH
C6H5OH
c) C6H5N2+ Cl– ![]() C6H5F
C6H5F
d) C6H5N2+ Cl– ![]() C6H5Cl
C6H5Cl
Answer:
a) C6H5N2+ Cl– ![]() C6H5Cl
C6H5Cl
Question 75.
Chlorobenzene on reaction with CH3Cl in presence of AlCl3 gives
a) toulene
b) m – chloro toulene
c) only o – chloro toulene
d) mixture of o – and p – chlorotoulene
Answer:
d) mixture of o – and p – chlorotoulene
![]()
Question 76.
2C6H5Cl + 2Na → X, X is
a) toulene
b) biphenyl
C) phenyl ethane
d) 1 – chloro – 2 – phenyl ethane
Answer:
b) biphenyl
Question 77.
Chlorobenzene on fusing with solid NaOH gives
a) benzene
b) benzoic acid
c) phenol
d) benzene chloride
Answer:
c) phenol
Question 78.
Chlorobenzene on nitration gives major product of
a) 1 – chloro – 4 – nitro benzene
b) 1 – chloro – 3 – nitro benzene
c) 1, 4 – dinitro benzene
d) 2, 4, 6 – tri nitro benzene
Answer:
a) 1 – chloro – 4 – nitro benzene
Question 79.
The reaction C6H5I + 2 Na + CH3I → C6H5CH3 + 2 NaI is
a) Wurtz reaction
b) Fittig reaction
c) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
d) Sandmeyer reaction
Answer:
c) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Question 80.
R – Cl + Nal ![]() R – I + NaCl. This reaction is
R – I + NaCl. This reaction is
a) Wurtz reaction
b) Fittig reaction
c) Finkelstein reaction
d) Frankland reaction
Answer:
c) Finkelstein reaction
![]()
Question 81.
C2H5OH + SOCl2 ![]() x + y + z. In this reaction x, y and z respectively are
x + y + z. In this reaction x, y and z respectively are
a) C2H4Cl2, SO2, HCl
b) C2H5Cl, SO2, HCl
c) C2H5Cl, SOCl, HCl
d) C2H4, SO2, Cl2
Answer:
b) C2H5Cl, SO2, HCl’
Question 82.
C2H5Cl + AgOH → A + AgCl.
A + CH3COCl → C + HCl. “C” is
a) Ethyl acetate
b) Methyl acetate
c) butanone – 2
d) propanone
Answer:
a) Ethyl acetate
Question 83.
The compound (B) in the below reaction is:
C2H5Cl ![]() A
A ![]() B
B
a) ethylene chloride
b) acetic acid
c) propionic acid
d) ethyl cyanide
Answer:
c) propionic acid
Question 84.
Chloro ethane reacts with X to form diethyl ether. What is X?
a) NaOH
b) H2SO4
c) C2H5ONa
d) Na2S2O3
Answer:
c) C2H5ONa
Question 85.
1 – chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives
a) 1 – butene
b) 1 – butanol
c) 1 – butyne
d) 2 – butanol
Answer:
a) 1 – butene
![]()
Question 86.
Propane nitrile may be prepared by heating
a) Propyl alcohol with KCN
b) ethyl chloride with KCN
c) Propyl chloride with KCN
d) ethyl chloride with KCN
Answer:
d) ethyl chloride with KCN
Question 87.
CH3CH = CH2 ![]() A
A  B, B is
B, B is
a) propanol – 2
b) propanal – 1
c) propanol – 1
d) propanal – 2
Answer:
c) propanol – 1
Question 88.
 Y is
Y is
Answer:
c) 
Question 89.
The correct order of increasing boiling points is
a) 1 – chloropropane < isopropylchloride < 1 – chlorobutane
b) isopropylchloride < 1 – chloropropane < 1 – chlorobutane
c) 1 – chlorobutane < isopropylchloride < 1 – chloropropane
d) 1 – chlorobutane < 1 – chloropropane < isopropylchloride
Answer:
b) isopropylchloride < 1 – chloropropane < 1 – chlorobutane
Question 90.
The correct order of decreasing SN2 reactivity
a) RCH2X > R2CHX > R3CX
b) RCH2X > R3CX > R2CHX
c) R2CHX > R3CX > RCH2X
d) R3CX > R2CHX > RCH2X
Answer:
a) RCH2X > R2CHX > R3CX
![]()
II. Very short question and answer (2 Marks):
Question 1.
What are haloalkanes? Give example.
Answer:
Mono halogen derivatives of alkanes are called haloalkanes. Haloalkanes are represented by general formula R – X, Where, R is an alkyl group (CnH2n + 1) – and X is a halogen atom (X = F, Cl, Br or I). Haloalkanes are further classified into primary, secondary, tertiary haloalkane on the basis of type of carbon atom to which the halogen is attached.
Example:
Question 2.
How will you convert methane into tetra chloro methane?
Answer:
Chlorination of methane gives different products which have differences in the boiling points. Hence, these can be separated by fractional distillation.
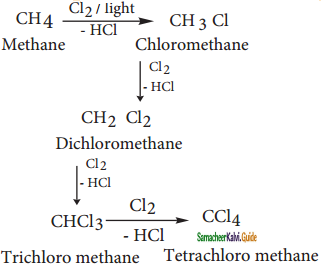
Question 3.
What is Finkelstein reaction?
Answer:
Chloro or bromoalkane on heating with a concentrated solution of sodium iodide in dry acetone gives iodo alkanes. This reaction is called as Finkelstein reaction.
CH3CH2Br + NaI 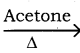 CH3CH2I + NaI
CH3CH2I + NaI
Bromo ethane Iodoethane
Question 4.
What is Swartz reaction?
Answer:
Chloro or bromo alkanes on heating with metallic fluorides like AgF or SbF3 gives fluoro alkanes. This reaction is called Swarts reaction.
CH3CH2Br + AgF ![]() CH3CH2F + AgBr
CH3CH2F + AgBr
Bromo ethane Fluoro ethane
Question 5.
What is Hunsdiecker reaction?
Answer:
Silver salts of fatty acids when refluxed with bromine in CCl4 gives bromo alkane.
CH3CH2COOAg + Br2 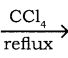 CH3CH2Br + CO2 + AgBr
CH3CH2Br + CO2 + AgBr
Silver propionate Bromo ethane
![]()
Question 6.
How is ehtyl magnesium bromide prepared from ethyl bromide?
Answer:
When a solution of ethyl bromide in ether is treated with magnesium, we get ethyl magnesium bromide.
CH3 – CH2 – Br + Mg ![]() CH3CH2MgBr
CH3CH2MgBr
Ethyl bromide Ethyl magnesium bromide
Question 7.
How will you convert ethyl bromide into ethyl lithium?
Answer:
Ethyl bromide reacts with active metals like sodium, lead etc in the presence of dry ether to form ethyl lithium.
CH3 CH2 Br + 2Li ![]() CH3 CH2Li + LiBr
CH3 CH2Li + LiBr
Ethyl bromide Ethyl Lithium
Question 8.
How is TEL prepared from ethyl bromide?
Answer:
When ethyl bromide reacts with Na / Pb alloy to give TEL.
4CH3 CH2 Br + 4Na/Pb → (CH3CH2)4Pb + 4NaBr + 3Pb
Ethyl bromide Sodium-lead alloy Tetra ethyl lead (TEL)
Question 9.
What are organic metallic compounds? Give example.
Answer:
Organo metallic compounds are organic compounds in which there is a direct carbon-metal bond
Example:
CH3 Mg I – Methyl magnesium iodide
CH3CH2Mg Br – Ethyl magnesium bromide
Question 10.
How is methane prepared from Grignard reagent?
Answer:
Compounds like water, alcohols and amines which contain active hydrogen atom react with Grignard reagents to form alkanes.
CH3MgI + HO – H → CH4 + Mg I (OH)
CH3MgI + C2H5OH ![]() CH4 + MgI (OC2H5)
CH4 + MgI (OC2H5)
Ethyl alcohol Methane
![]()
Question 11.
What are Haloarenes? Give a suitable example.
Answer:
Haloarenes are the compounds in which the halogen is directly attached to the benzene ring.
Example:
Question 12.
How is chloro benzene prepared from benzene by direct halogenation?
Answer:
Chloro benzene is prepared by the direct chlorination of benzene in the presence of lewis acid catalyst like FeCl3.
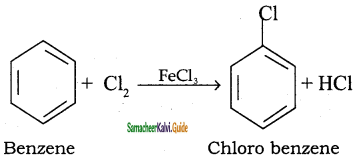
Question 13.
Write a note on Sand Meyer reaction.
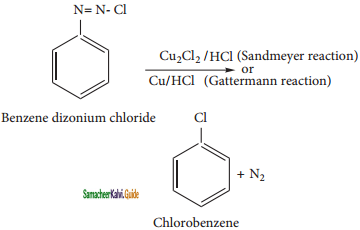
Answer:
When aqueous solution of benzene diazonium chloride is warmed with Cu2Cl in HCl gives chioro benzene.
Question 14.
How is Iodo benzene prepared from benzene diazonium chloride?
Answer:
Iodo benzene is prepared by warming benzene diazonium chloride with an aqueous KI solution.
C6H5N2Cl + Kl ![]() C6H5I + N2 + KCl
C6H5I + N2 + KCl
Benzene dizonium chloride Iodo benzene
Question 15.
What happens when ethylidene dichloride is treated with Zinc dust in methanol?
Answer:
Gem dihalides and vic – dihalides on treatment with zinc dust in methanol give alkenes.
CH3 – CHCl2 + Zn ![]() CH2 = CH2 + ZnCl2
CH2 = CH2 + ZnCl2
Ethylidene dichloride Ethylene
![]()
Question 16.
How will you convert chloroform into methylene chloride?
Answer:
a) Reduction of chloroform in the presence of Zn + HCl gives methylene chloride.
CHCl3 (chloroform) 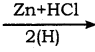 CH2Cl (Methylene chloride) + HCl
CH2Cl (Methylene chloride) + HCl
b) Reduction of chloroform using H2/Ni
CHCl3 (chloroform) ![]() CH2Cl2 (Methylene chloride) + HCl
CH2Cl2 (Methylene chloride) + HCl
Question 17.
Write the chlorination reaction of methane.
Answer:
Chlorination of methane gives methylene chloride
CH4 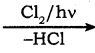 CH3Cl
CH3Cl 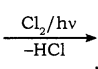 CH2Cl2
CH2Cl2
Methane Methylene chloride
Question 18.
How is chloroform prepared from carbon tetrachloride?
Answer:
Carbon tetrachloride is reduced by iron powder in dilute HCl medium to form chloroform
CCl4 (carbon tetrachloride) + 2[H]  CHCl3 (chloroform) + HCl
CHCl3 (chloroform) + HCl
![]()
III. Short question and answers (3 Marks):
Question 1.
write IUPAC name of the following.
i) 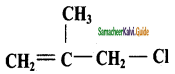
ii) 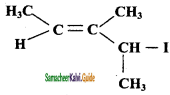
iii) 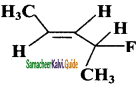
Answer:
i) 
ii) 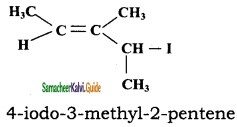
iii) 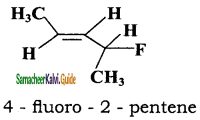
Question 2.
Write the structure of the following compounds.
i) 1 – Bromo – 4 – ethyl cyclohexane
ii) 1, 4 – Dichlorobut – 2 – ene
iii) 2 – chloro – 3 – methyl pentane
Answer:
i) 1 -Bromo – 4 – ethyl cyclohexane:
ii) 1, 4 – Dichlorobut – 2 – ene
– Cl – CH2 – CH = CH – CH2 – Cl
iii) 2 – chloro – 3 – methyl pentane
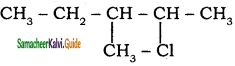
Question 3.
Write any three methods of preparation of chloro ethane from ethanol.
Answer:
a) Reaction with hydrogen halide:
Ethanol is heated with HCl in presence of anhydrous ZnCl2 to give ethyl chloride.
CH3CH2OH + HCl ![]() CH3CH2Cl + H2O
CH3CH2Cl + H2O
Ethanol Chloroethane
b) Reaction with phosphorous halides:
Ethanol reacts with PCl5 or PCl3 it gives ethyl chloride.
CH3CH2OH + PCl5 → CH3CH2Cl + POCl3 + HCl
Ethanol Chloro ethane
3 CH3CH2OH + PCl3 → 3CH3CH2Cl + H 3PO3
Ethanol Chloro ethane
C) Reaction with thionyl chloride (Sulphonyl chloride):
When ethanol reacts with SOCl2 in presence of pyridine, it gives chloro ethane.
CH3CH2OH + SOCl2 ![]() CH3CH2Cl + SO2 + HCl
CH3CH2Cl + SO2 + HCl
Ethanol Chloro ethane
Question 4.
What happens when haloalkane reacts with aqueous alkali or most silver oxide?
Answer:
Ethyl bromide reacts with aqueous solution of KOH or moist silver oxide (Ag2O/H2O) to form ethanol.
CH3 – CH2 – Br + KOH (aq) ![]() CH3CH2 – OH + KBr
CH3CH2 – OH + KBr
Bromoethane Ethyl alcohol
CH3 – CH2 – Br + AgOH(aq) ![]() CH3CH2 – OH + AgBr
CH3CH2 – OH + AgBr
Bromoethane Moist silver oxide Ethanol
Question 5.
Explain the ammonolysis reaction of bromo ethane.
Answer:
Ethyl bromide reacts with alcoholic ammonia solution to form ethylamine.
CH3 – CH2 – Br + H – NH2 → CH3 CH2 – NH2 + HBr
Bromo ethane Ethyl amine
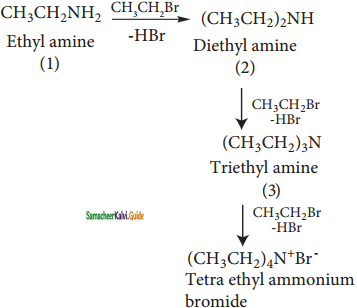
However, with excess of ethyl bromide, secondary and tertiary amines along with quaternary ammonium salts are obtained.
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when bromoethane reacts with alcoholic KCN and alcoholic AgCN?
Answer:
Reaction with alcoholic KCN:
Ethyl bromide reacts with alcoholic KCN solution to form ethyl cyanides.
CH3 – CH2 – Br + KCN → CH3 – CH2 – CN + KBr
Bromoethane Ethyl cyanide
Reaction with alcoholic AgCN:
Haloalkanes react with alcoholic AgCN solution to form alkyl isocyanide.
CH3CH2Br + AgCN → CH3CH2NC + AgBr
Bromoethane Ethyl isocyanide
Question 7.
How are the following compounds prepared from bromo ethane?
i) Ethane thiol
(ii) Diethyl ether
Answer:
i) Ethane thiol:
Ethyl bromide reacts with sodium or potassium hydrogen sulphide to form thio alcohols.
CH3CH2Br 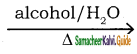 CH3CH2SH + NaBr
CH3CH2SH + NaBr
Bromo ethane Ethane thiol
ii) Diethyl ether:
Ethyl bromide, when boiled with sodium alkoxide gives diethyl ether. This method can be used to prepare mixed (unsymmetrical) ethers also.
CH3 – CH2Br + NaOCH2CH3 ![]() CH3CH2 – O – CH2CH3 + NaBr
CH3CH2 – O – CH2CH3 + NaBr
Bromo ethane Sodium ethoxide diethyl ether
Question 8.
How is ethane prepared from the following compounds?
i) Bromo ethane ii) Iodo ethane
Answer:
i) From bromo ethane:
Ethyl bromide is reduced to ethane by treating with H2 in the presence of metal catalyst like nickel, palladium etc or with hydroiodic acid in the presence of red phosphrous.
Ni(or)Pd
CH3CH2Br + H2 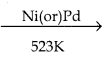 CH3 – CH3 + HBr
CH3 – CH3 + HBr
Bromo ethane Ethane
ii) From iodo ethane:
Iodo ethane is reduced with H2 in presence of Red P it gives ethane.
CH3CH2I + HI ![]() CH3 – CH3 + I2
CH3 – CH3 + I2
Iodo ethane Ethane
Question 9.
Write the uses of carbon tetra chloride.
Answer:
- Carbon tetrachloride is used as dry cleaning agent.
- It is used as a solvent for oils, fats and waxes
- As the vapour of CCl4 is non-combustible, it is used under the name pyrene for extinguishing the fire in oil or petrol.
Question 10.
Write the uses of Grignard reagents.
Answer:
- Grignard reagents are synthetically very useful compounds. These reagents are converted to various organic compounds like alcohols, carboxylic acids, aldehydes and ketones.
- The alkyl group being electron rich acts as a carbanion or a nucleophile.
- They would attack polarized molecules at a point of low electron density. The following reactions illustrate the synthetic uses of Grignard reagent.
![]()
Question 11.
What is Balz – Schiemann reaction?
Answer:
Fluoro benzene is prepared by treating benzene diazonium chloride with fluoro boric acid. This reaction produces diazonium fluoroborate which on heating produces fluorobenzene. This reaction is called Balz – schiemann reaction.
C6H5N2Cl + HBF4 ![]() C6H5N2 + BF4–
C6H5N2 + BF4– ![]() C6H5 F + BF3 + N2
C6H5 F + BF3 + N2
Benzene diazonium chloride Fluorobenzene
Question 12.
Write the uses of chloro benzene.
Answer:
- Chloro benzene is used in the manufacture of pesticides like DDT
- It is used as high boiling solvent in organic synthesis.
- It is used as fibre – swelling agent in textile processing.
Question 13.
How is ethylidene dichloride prepared from
(i) Acetaldehyde
(ii) Acetylene
Answer:
i) Treating acetaldehyde with PCl5:
CH3CHO (Acetaldehyde) + PCl5 → CH3CHCl2 (Ethylidene dichloride) + POCl
ii) Adding hydrogen chloride to acetylene
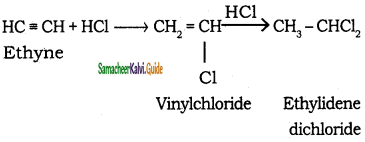
Question 14.
How is ethylene dichloride prepared from (i) Chloride (ii) PCl5?
Answer:
i) Addition of chlorine to ethylene
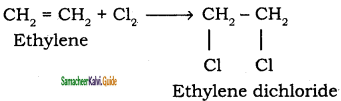
ii) Action of PCl5 (or HCl) on ethylene glycol
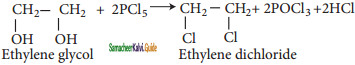
Question 15.
What happens when the following compounds are treated with alcoholic KOH?
i) Ethylidene dichloride
ii) Ethylene dichloride
Answer:
i) Ethylidene dichloride:
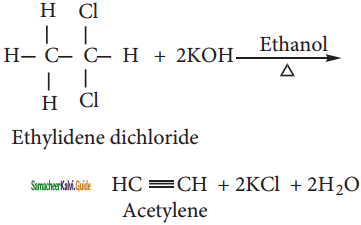
ii) Ethylene dichloride:
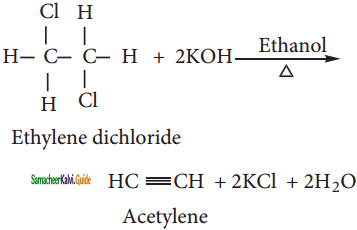
![]()
Question 16.
Write the uses of methylene chloride.
Answer:
Methylene chloride is used as
- aerosol spray propellant
- solvent in paint remover
- process solvent in the manufacture of drugs
- a metal cleaning solvent
Question 17.
How are the following compounds prepared from chlorobenzene?
i) Benzene
ii) Phenyl magnesium chloride
Answer:
i) C6H6 (Benzene):
Chlorbenzene undergoes reduction with Ni – Al alloy in the presence of NaOH gives benzene.
C6H5Cl + 2(H) 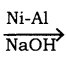 C6H6 + HCl
C6H6 + HCl
Chloro benzene Benzeneide
ii) Phenyl Magnesium chloride:
Chloro benzene reacts with magnesium to form phenyl magnesium chloride in tetra hydrofuran (THF).
C6H5Cl (Chloro benzene) + Mg  C6H5MgCl (Phenyl magnesium chloride)
C6H5MgCl (Phenyl magnesium chloride)
![]()
IV. Long question and answers (5 Marks):
Question 1.
Explain the SN2 mechanism of haloalkanes with suitable example.
Answer:
S2 stands for bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
“S” stands for substitution
“N” stands for nucleophilic
“2” stands for bimolecular (two molecules are involved in the rate determining step)
The rate of SN2 reaction depends upon the concentration of both alkyl halide and the nucleophile.
Rate of reaction = k2 [alkyihalide] [nucleophile]
This SN2 reaction follows second order kinetics and occurs in one step.
This reaction involves the formation of a transition state in which both the reactant molecules are partially bonded to each other. The attack of nucleophile occurs from the back side and the halide ion leaves from the front side. The carbon at which substitution ocurs ha inverted configuration during the course of reaction just as an umbrella has tendency to invert in a wind storm. This inversion of configuration is called Walden inversion; after paul walden who first discovered the inversion of configuration of a compound in SN2 reaction.
We understand SN2 reaction mechanism by taking an example of reaction between chloromethane and aqueous KOH. SN2 reaction of an optically active haloalkane is always accompanied by inversion of configuration at the asymmetric centre.
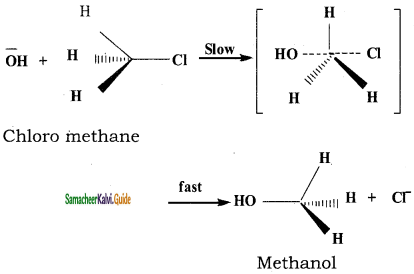
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the SN1 mechanism of haloalkanes with suitable examples.
Answer:
SN1 stands for unimolecular nucleophilic substitution
‘S’ stands for substitution
‘N’ stands for nucleophilic
‘1’ stands for unimolecular (one molecule is involved in the rate determining step)
The rate of the following SN1 reaction depends upon the concentration of aikyl halide (RX) and is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile (OH-).
Rate of the reaction = k[alkyl halide]
R – Cl + OH– → R – OH + Cl–
This SN1 reaction follows first order kinetics and occurs in two steps.
We understand SN1 reaction mechanism by taking a reaction between tertiary hutyl bromide with aqueous KOH.
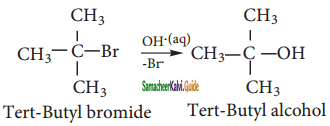
This reaction takes place in two steps aas shown below.
Step – 1:
Formation of carbocation:
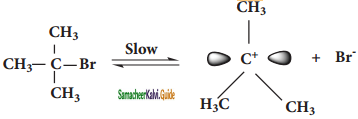
t – butyl bromide
The polar C – Br bond breaks forming a carbocation and bromide ion. This step is slow and hence it is the rate determining step.
Step 2:
Nucleophilic attack on carbocation
The carbocation immediately reacts with the nucleophile. This step is fast and hence does not affect the rate of the reactions.
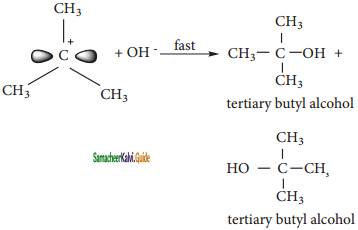
As shown above, the nucleophilic reagent OH~ can attack carbocation from both the sides, they will be mirror image of each other.
In the above example the substrate tert-butyl bromide is not optically active, hence the obtained product is optically inactive. If halo alkane substrate is optically active then, the product obtained will be optically inactive racemic mixture. As nucleophilic reagent OH- can attack carbocation from both the sides, to form equal proportion of dextro and levorotatory optically active isomers which form optically inactive racemic mixture.
Example :
Hydrolysis of optically active 2- bromo butane gives racemic mixture of ±butan-2-ol.
Question 3.
Explain the E2 reaction mechanism with suitable example.
Answer:
E2 stands for bimolecular elimination reaction
‘E’ stands for elimination
‘2’ stands for bimolecular
The rate of E2 reaction depends on the concentration of alkyl halide and base
Rate = k2 [alkyl halide] [base]
It is therefore, a second-order reaction generally primary alkyl halide undergoes this reaction in the presence of alcoholic KOH. E2 is a one-step process in which the abstraction of the proton from the p carbon and expulsion of halide from the carbon occurs simultaneously. The mechanism is shown below.
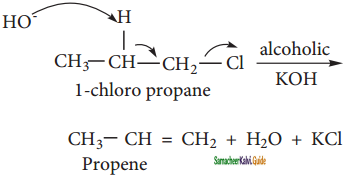
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the E1 reaction mechanism with suitable example.
Answer:
E1 stands for unimolecular elimination reaction
‘E’ stands for elimination ‘1’ stands for unimolecular
The rate of E1 reaction depends on the concentration of alkyl halide only and hence
rate = k [alkyl halide]
Generally, tertiary alkyl halide which undergoes elimination reaction by this mechanism in the presence of alcoholic KOH following first order kinetics is a two step process. The mechanism is shown by taking following example.
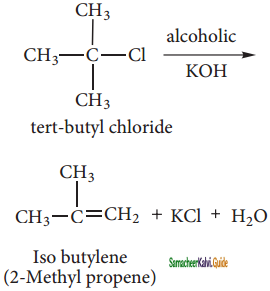
step – 1:
Heterolytic fission to yield a carbocation:
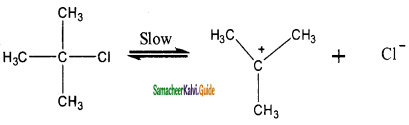
Step – 2:
Elimination of a proton from the β – carbon to produce an alkene:
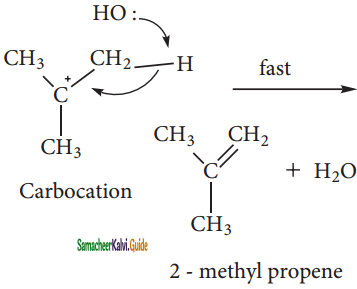
Question 5.
How are the following compounds prepared from Methyl magnesium iodide?
(i) Ethanol
(ii) Tert-butyl alcohol
(iii) Acetaldehyde
Answer:
(i) Ethanol:
Formaldehyde reacts with methyl magnesium iodide to give addition products which on hydrolysis yield ethanol.
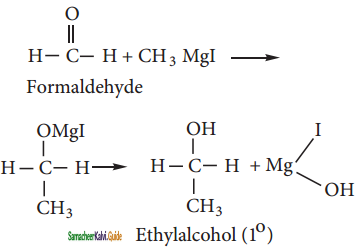
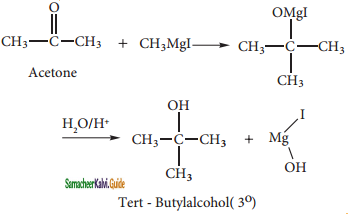
(ii) Tert-butyl alcohol:
Acetone reacts with methyl magnesium iodide to give an additional product which on hydrolysis yields tert butyl alcohol.
(iii) Acetaldehyde:
Ethyl formate reacts with methyl magnesium iodide and followed by acid hydrolysis, it forms Acetaldehyde.
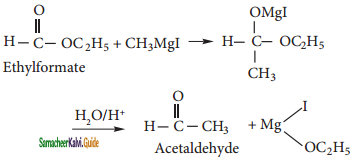
Question 6.
How is ethylene dichloride converted into
i) Acetaldehyde
ii) Ethylene glycol
ii) Ethylene
Answer:
i) Acetaldehyde:
(Hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH or KOH)
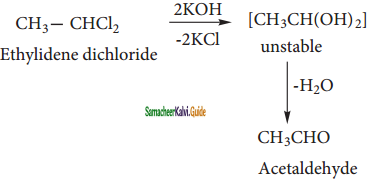
Ethylidene chloride reacts with aqueous KOH to give acetaldehyde.
ii) Ethylene glycol :
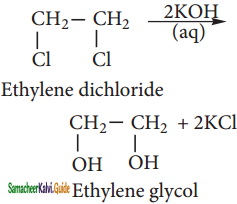
Ethylene chloride reacts with aqueous KOH, it gives glycol.
iii) Ethylene:
Ethylene dichloride is heated with Zinc in presence of methanol gives ehtylene.
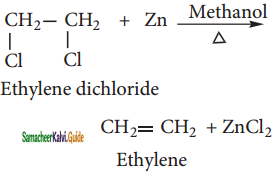
![]()
Question 7.
How are the following compounds prepared from chloroform?
(i) Phosgene
(ii) Methylene chloride
(iii) Methyl isocyanide
Answer:
(i) Phosgene:
Chloroform undergoes oxidation in the presence of light and air to form phosgene (carbonyl chloride)
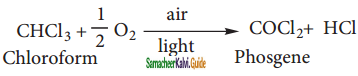
Since phosgene is very poisonous, its presence makes chloroform unfit for use as an anaesthetic.
(ii) Methylene chloride:
Chloroform undergoes reduction with zinc and HCl in the presence of ethyl alcohol to form methylene chloride.
CHCl3 (Chloroform) + 2(H) 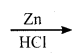 CH2Cl2 (Methylene chloride)+ Cl2
CH2Cl2 (Methylene chloride)+ Cl2
(iii) Methyl isocyanide:
Chloroform reacts with aliphatic or aromatic primary amine and alcoholic caustic potash, to give foul-smelling alkyl isocyanide (carbylamines).
CH3NH2 + CHCl2 + 3KOH → CH3NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
Methylamine Chloroform Methyl isocyanide
Question 8.
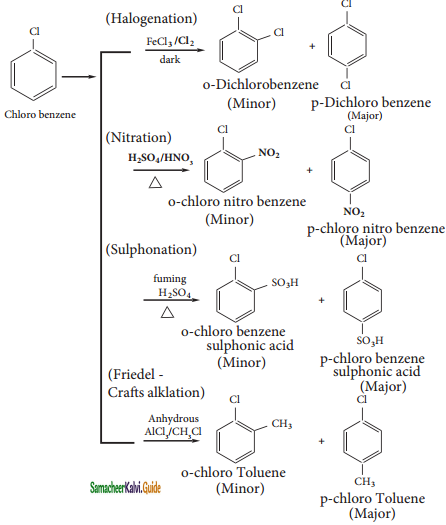
Discuss the aromatic electrophilic substitutions reaction of chlorobenzene.
Answer: