Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 10 Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 10 Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
12th Bio Botany Guide Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Consider the following statements and choose the right option.
i) Cereals are members of grass family
ii) Most of the food grains come from monocotyledon
a) (i) is correct and (ii) is wrong
b) Both (i) and (ii) are correct
c) (i) is wrong and (ii) is correct
d) Both (i) and (ii) are wrong
Answer:
b) Both (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 2.
Assertion: Vegetables are important part of healthy eating.
Reason : Vegetables are succulent structures of plants with pleasant aroma and flavours.
a) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong
b) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct
c) Both are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
d) Both are correct and reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
Answer:
a) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong
Question 3.
Groundnut is native of ……………..
a) Philippines
b) India
c) North America
d) Brazil
Answer:
d) Brazil
![]()
Question 4.
Statement A : Coffee contains caffeine
Statement B : Drinking coffee enhances cancer
a) A is correct, B is wrong
b) A and B – both are correct
c) A is wrong, B is correct
d) A and B – both are wrong
Answer:
a) A is correct, B is wrong
Question 5.
Tectona grandis is coming under family.
a) Lamiaceae
b) Fabaceae
c) Dipterocaipaceae
d) Ebenaceae
Answer:
a) Lamiaceae
![]()
Question 6.
Tamarindus indica is indigenous to ……………..
a) Tropical African region
b) South India, Sri Lanka
c) South America, Greece
d) India alone
Answer:
a) Tropical African region
Question 7.
New world species of cotton
a) Gossipium arboretum
b) G. herbaceum
c) Both a and b
d) G.barbadense
Answer:
d) G. barbadense
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion : Turmeric fights various kinds of cancer.
Reason : Curcumin is an anti-oxidant present in turmeric.
a) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong
b) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct
c) Both are correct
d) Both are wrong
Answer:
c) Both are correct
Question 9.
Find out the correctly matched pair.
a) Rubber – Shorea robusta
b) Dye – Lawsonia inermis
c) Timber – Cyperus papyrus
d) Pulp – Hevea brasiliensis
Answer:
b) Dye : Lawsonia inermis
Question 10.
Observe the following statements and pick out the right option from the following.
Statement I : Perfumes are manufactured from essential oils.
Statement II : Essential oils are formed at different parts of the plants.
a) Statement I is correct
b) Statement II is correct
c) Both statements are correct
d) Both statements are wrong
Answer:
c) Both statements are correct
![]()
Question 11.
Observe the following statements and pick out the right option from the following.
Statement I : The drug sources of Siddha include plants, animal parts, ores and minerals.
Statement II: Minerals are used for preparing drugs with long shelf-life.
a) Statement I is correct
b) Statement II is correct
c) Both statements are correct
d) Both statements are wrong
Answer:
Both statements are correct
Question 12.
The active principle trans-tetra hydro canabial is present in
a) Opium
b) Curcuma
c) Marijuana
d) Andrographis
Answer:
c) Marijuana
Question 13.
Which one of the following matches is correct?
a) Palmyra – Native of Brazil
b) Saccharun – Abundant in Kanyakumari
c) Stevecide – Natural sweetener
d) Palmyra sap – Fermented to give ethanol
Answer:
c) Stevecide – Natural sweetener
![]()
Question 14.
The only cereal that has originated and domesticated from the New world.
a) Oryza sativa
b) Triticum asetumn
c) Triticum duram
d) Zea mays
Answer:
d) Zea mays
Question 15.
Write the cosmetic uses of Aloe.
Answer:
Aloe gel are used as skin tonic. It has a cooling effect and moisturizing characteristics and hence used in preparation of creams, lotions, shampoos, shaving creams, after shave lotions and allied products. It is used in gerontological applications for rejuvenation of aging skin. Products prepared from aloe leaves have multiple properties such as emollient, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal and antiseptic. Aloe vera gel is used in skin care cosmetics.
![]()
Question 16.
What is pseudo cereal? Give an example.
Answer:
- These are foods that are prepared and eaten as whole grain. Eg. quinoa (தினை) is a seed from Chenopodium quinoa plant. It belongs Amaranthaceae family.
- It is gluten free, whole grain carbohydrate.
- It is a whole protein with a essential amino acids.
- Taken for 6000 years in Andes hills.
Question 17.
Discuss which wood is better for making furniture.
Answer:
Teak wood is the ideal type of wood for making household furnitures because, it is highly durable and shows great resistance against the attack of termites and fungi. Moreover it doesnot split or crack and is a carpenter friendly wood.
![]()
Question 18.
A person got irritation while applying chemical dye. What would be your suggestion for alternative?
Answer:
- Henna is the best alternative dye.
- It is in North Africa, South west Asia. It is in Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Rajesthan.
- Orange dye henna is from leaves and shoots of
Lawsonia inermis. - Principal colouring matter is ‘lacosone’
- It is harmless causing no skin irritation.
- It is u sed to dye skin, hair and finger nails.
Question 19.
Name the humors that are responsible for the health of human beings.
Answer:
Vatam, Pittam and Kapam.
Question 20.
Give definitions for organic farming?
Answer:
- Alternative agricultural system.
- Plants and crops are cultivated in natural ways, by using biological inputs.
- It helps to maintain soil fertility and ecological balance.
- It minimizes pollution, wastage.
![]()
Question 21.
Which is called the “King of Bitters”? Mention their medicinal importance.
Answer:
Andrographis paniculata is called as King of Bitters. Andrographis is a potent hepatoprotective agent and is widely used to treat liver disorders. Concoction of Andrographis paniculata and eight other herbs (Nilavembu Kudineer) is effectively used to treat malaria and dengue.
Question 22.
Differentiate Bio-medicines and botanical medicines.
Answer:
Bio-medicines: Medicinally useful molecules obtained from plants are marketed as drugs. These are called bio-medicines.
Botanical Medicines: Medicinal plants are marketed as powders or in other modified forms. They are called Botanical medicines.
Question 23.
Write the origin and area of cultivation of green gram and red gram.
Answer:
Origin and area of cultivation of Green Gram.
- Native of India
- Archaeological evidence is in Maharashtra.
- Cultivated in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Origin and area of cultivation of Red Gram
- The only pulse native of South India.
- Grown in Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh,
Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat.
![]()
Question 24.
What are millets? What are its types? Give example for each type.
Answer:
Millet’s: Small seeds cultivated by ancient people of Africa, Asia. Gluten-free with the less glycemic index.
Finger Millet (Ragi) (Eleusine coracana)
Came to India from East Africa. It is rich in calcium.’
Uses:
- Staple food in South Indian hills.
- Made into porridge, gruel.
- Ragi malt is a nutrient drink.
- Source of fermented beverages.
Sorghum vulgare.
Native of Africa. Major millet of the world with calcium, iron
Uses:
- Feed to poultry, birds, pigs, cattle
- Alcoholic beverage source.
Fox tail Millet (Setariaitalica)
Oldest traditional millet of India. Domesticated in China about 6000 years.
Uses: Strengthens heart, eye sight, lactation.
Kodo Millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum)
From West Africa.
Uses:
- Flour for pudding
- Diuretic, cures constipation.
- Reduce obesity, blood sugar, blood pressure.
Question 25.
If a person drinks a cup of coffee daily it will help him for his health. Is this correct? If it is correct, list out the benefits.
Answer:
Benefits of Coffee:
- Stimulates central nervous system.
- Mild diuretic
- Enhances acetyl choline release in brain.
- Enhances efficiency.
- Lower fatty liver diseases, cirrhosis, cancer.
- Reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes,
![]()
Question 26.
Enumerate the uses of turmeric.
Answer:
Turmeric is one of the most important and ancient Indian spices and used traditionally over thousands of years for culinary, cosmetic, dyeing and for medicinal purposes. It is an important constituent of curry powders. Turmeric is used as a colouring agent in pharmacy, confectionery and food industry. Rice coloured with turmeric (yellow) is considered sacred and auspicious which is used in ceremonies. It is also used for dyeing leather, fibre, paper and toys.
Curcumin extracted from turmeric is responsible for the yellow colour. Curcumin is a very good anti-oxidant which may help fight various kinds of cancer. It has anti-inflammatory, anti- ‘ diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and anti-viral activities. It stops platelets from clotting in arteries, which leads to heart attack.
Question 27.
What is TSM? How does it classify and what does it focus on?
Answer:
Traditional System of Medicines (TSM)
It is classified into
- Institutionalized (documented) system
- Non-institutionalized (oral) system
Institutionalized system:
- It includes Siddha, Ayurvedha
- It is practiced for 2000 years.
- Text with symptoms, diagnosis, drugs, preparation of drugs, dosage, diet regimen.
Non-Institutionalized system:
- Do not have any records
- Practiced by rural, tribal people of India.
- Knowledge is in oral form.
Focus of TSM:
- Healthy lifestyle
- A healthy diet for good health
- Disease reversal.
Siddha system
- Siddha is the most popular, widely practiced and culturally accepted systm in Tamil Nadu.
- Siddha is principally based on the pancabute philosophy
- This system specializes in using minerals for preparing drugs with a long shelf-life.
- This system uses about 800 herbs as source of drugs.
- Great stress is laid on disease prevention, health promotion, rejuvenation and cure.
Ayurveda system:
- Ayurveda supposed to have originated from Brahma.
- The core knowledge is documented by charaka, sushruta and vagbhata in compendiums written by them.
- This system uses more of herbs and few animal parts as drug sources.
- Plant sources include a good propertion of Himalayan plants.
- The Ayurvedic pharmacopoeia of India lists about 500 plants used as source of drugs.
Folk system of medicine
- Major tribal communities in Tamil Nadu who are known for their medicinal knowledge indued Irulas, Malayalis, Kurumbas, paliyans and kaanis.
- Folk system survive as oral traditions among innumerable rural and tribal communities of India.
![]()
Question 28.
Write the uses of nuts you have studied.
Answer:
Cashews are commonly used for garnishing sweets or curries, or ground into a paste that forms a base of sauces for curries or some sweets. Roasted and raw kernels are used as snacks.
Question 29.
Give an account of the role of Jasminum in perfuming.
Answer:
Role of Jasminum in perfuming:
- Used in India for worship, ceremonial purposes, incense, fumigants.
- For making perfumed hair oil, cosmetics and soaps.
- Essential oil for soothing relaxing, antidepressant qualities.
- Blends with other perfumes.
- Used in modern perfumery and cosmetics.
- Popular in air fresheners, antiperspirants, talcum powder, shampoo, and deodorants.
Rose:
The average oil yield is a little less than 0.5 g from lOOOg of flowers.
Uses:
- Rose oil is largely used in perfumes, scenting
soaps, flovouring soft drinks, liqueurs, and certain types of tobacco, particularly snuff of chewing tobacco. - In India, water is much used in eye lotions
and eyewashes. - Rosewater (panner) containing much of phenyl ethyl alcohol and other compounds in dissolved confectioneries syrups and soft drinks.
- In addition, it is sprinkled on guests as a ceremonial welcome.
![]()
Question 30.
Give an account of active principle and medicinal values of any two plants you have studied.
Answer:
A) Medical importance of Keezhanelli (Phyllanthus amarus):
Active principle: Phyllanthus is a major chemical component.
Medical Importance:
- Hepatoprotective.
- Used in Tamil Nadu for jaundice treatment.
- Effective against hepatitis B virus.
B) Nilavembu (Andrographis paniculata) (King of Bitters)
Active principle: Andrographolides.
Medicinal Importance:
- Potent hepatoprotective
- Treats liver disorders.
- A concoction of Andrographis + 8 herbs
(Nilavembu Kudineer) treats malaria, dengue.
Question 31.
Write the economic importance of rice.
Answer:
Rice is the easily digestible calorie rich cereal food which is used as a staple food in Southern and North East India. Various rice products such as Flaked rice (Aval), Puffed rice / parched rice (Pori) are used as breakfast cereal or as snack food in different parts of India. Rice bran oil obtained from the rice bran is used in culinary and industrial purposes. Husks are used as fuel, and in the manufacture of packing material and fertilizer.
Question 32.
Which TSM is widely practiced and culturally accepted in Tamil Nadu? explain.
Answer:
Siddha system of Medicine:
- It is widely practiced and culturally accepted in Tamil Nadu.
- Based on text of 18siddhars.
- Knowledge is documented as Tamil poems.
- Based on Pancabuta philosophy.
- Vatam, Pittam, Kapam are 3 humors. They are responsible for the health.
- Drug sources are plant, animal parts, marine products, minerals.
- Minerals are used for preparing drugs with long self life.
- 800 herbs are source of drugs.
- Disease prevention, health promotion, rejuvenation and cure are important.
![]()
Question 33.
What are psychoactive drugs? Add a note of Marijuana and Opium.
Answer:
Phytochemicals or drugs from some of the plants alter an individual’s perceptions of mind by producing hallucination are known as psychoactive drugs.
- Marijuana: Marijuana is obtained from Cannabis sativa. The active principle in Marijuana is trans – tetrahydrocannabinol (TCH). It is used as pain killer and reduce hypertension. It is also used in the treatment of Glaucoma, cancer radiotherapy and asthma, etc.
- Opium: Opium is obtained from the exudates of the fruits of papaver somniferum (poppy plants). It is used to induce sleep and relieve pain. Opium yields morphine which is used as a strong analgesic in surgeries.
Question 34.
What are the King and Queen of Spices? Explain about them and their uses.
Answer:
Queen of Spices: Cardamom (Elettaria Cardamomum)
Origin and area of cultivation:
- Indigenous to Southern India and Sri Lanka.
- Main cash crop in the Western Ghats, North-Eastern India.
Uses:
- For flavouring confectionaries, Bakery products, beverages.
- Seeds are used in curry powder, pickles and cakes.
- Medicinally, a stimulant and carminative (a drug for flatulence)
- Chewed as mouth fresheners.
King of Spices: Black Pepper (Piper nigrum)
Origin and area of cultivation:
- Indigenous to western ghats.
- Black gold of India.
- Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are top producers in India.
- Pungency is due to alkaloid piperine.
- 2 types (Black pepper, white pepper)
Uses:
- Flavouring sauce, soup, curry, and pickles
- Aromatic stimulant for salivary gastric secretions as a stomachic.
- Pepper enhances the absorption of medicines.
![]()
Question 35.
How will you prepare an organic pesticide for your home garden with the vegetables available from your kitchen?
Answer:
Preparation of Organic Pesticide:
Step 1: Mix 120 g of hot chilies with 110 g of garlic or onion. Chop them thoroughly.
Step 2: Blend the vegetables together manually or using an electric grinder until it forms a thick paste.
Step 3: Add the vegetable paste to 500 ml of warm water. Give the ingredients a stir to thoroughly mix them together.
Step 4: Pour the solution into a glass container and leave it undisturbed for 24 hours. If possible, keep the container in a sunny location. If not, at least keep the mixture in a warm place.
Step 5: Strain the mixture. Pom- the solution through a strainer, remove the vegetables and collect the vegetable-infused water and pour into another container. This filtrate is the pesticide. Either discard the vegetables or use it as a compost.
Step 6: Pour the pesticide into a squirt bottle. Make sure that the spray bottle has first been cleaned with warm water and soap to get rid it of any potential contaminants. Use a funnel to transfer the liquid into the squirt bottle and replace the nozzle.
Step 7: Spray your plants with the pesticide. Treat the infected plants every 4 to 5 days with the solution. After 3 or 4 treatments, the pest will be eliminated. If the area is thoroughly covered with the solution, this pesticide should keep bugs away for the rest of the season.
12th Bio Botany Guide Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Staple food of North India is ………………….
a) Sorghum
b) Millet
c) Paddy
d) Wheat
Answer:
d) Wheat
Question 2.
Folk system of medicine is popular in ………………
a) Nigeria
b) USA
c) India
d) UK
Answer:
c) India
Question 3.
State not growing black gram
a) Uttar Pradesh
b) Tamil Nadu
c) Chattisgarh
d) Karnataka
Answer:
b) Tamil Nadu
![]()
Question 4.
The very common rubber yielding plant of Tamilnadu is ……………………
a) Manihot esculenta
b) Ficus elastica
c) Hevea benthamiana
d) Hevea brasiliensis
Answer:
d) Hevea brasiliensis
Question 5.
Not a major cultivar mango in India
a) Alphonsa
b) Neelam
c) Malgova
d) Salem Mango
Answer:
d) Salem Mango
Question 6.
Toddy is from ……………… tree
a) Palmyra
b) Coconut
c) Mango
d) Sugar cane
Answer:
a) Palmyra
![]()
Question 7.
Chillies are a good source of:
a) Vitamin A, C and E
b) Vitamin K
c) Vitamin D
d) Vitamin B complex and Vitamin D
Answer:
a) Vitamin A, C and E
Question 8.
Gingeelly or sesame is originated in ……………………..
a) Asia
b) Africa
c) China
d) Europe
Answer:
b) Africa
Question 9.
Coffee is native of ……………….
a) Nigeria
b) Cuba
c) Ethiopia
d) Egypt
Answer:
c) Ethiopia
![]()
Question 10.
India is the largest producer of
a) Chilly
b) Tamarind
c) Turmeric
d) Pepper
Answer:
c) Turmeric
Question 11.
World’s largest turmeric market is in ………………. of Tamil Nadu
a) Coimbatore
b) Erode
c) Madurai
d) Nagercoil
Answer:
b) Erode
Question 12.
Asia contributes …………… % of latex in world production.
a) 80
b) 90
c) 70
d) 50
Answer:
b) 90
![]()
Question 13.
……………….. is the largest producer of latex
a) Kerala
b) Karnataka
c) Andhra
d) Delhi
Answer:
a) Kerala
Question 14.
…………….. is native of Sudan
a) Henna
b) Aloe
c) Jasmine
d) Turmeric
Answer:
b) Aloe
Question 15.
Thovalai of Tamil Nadu produces ………………..
a) Aloe
b) Tamarind
c) Turmeric
d) Jasmine
Answer:
d) Jasmine
![]()
Question 16.
Paste of this plant is used in bone fracture
a) Ocimum
b) Phyllanthus
c) Cissus
d) Acalypha
Answer:
c) Cissus
Question 17.
Find the Matching Pair
a) Ocimum – Antiseptic
b) Phyllanthus – Ringworm disease
c) Acalypha – Immune modulator
d) Aegle marmelos – Bone fracture
Answer:
a) Ocimum – Antiseptic
Question 18.
Capsaicin is in ……………..
a) Chilly
b) Pepper
c) tea
d) coffee
Answer:
a) Chilly
![]()
Question 19.
Veldt grape is the common name of …………….
a) Ocimum
b) I’hyllanthus
c) Acalypha
d) Cissus
Answer:
d) Cissus
Question 20.
Find the Mismatching Pair
a) Pappaver somniferum – Opium
b) Cannabis sativa – Marijuana
c) Phyllanthus amarus – Keezhanelli
d) Andrographis paniculata – Turmeric
Answer:
d) Andrographis paniculata – Turmeric
Question 21.
Match
| A. Rice | 1. East Africa |
| B. Wheat | 2. Africa |
| C. Ragi | 3. Crescent Region |
| D. Sorghum | 4. South East Asia |
a) A-4, B-3, C-l, D-2
b) A-l, B-2, C-3, D-4
c) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-l
d) A-2, B-l, C-4, D-3
Answer:
a) A-4, B-3, C-l, D-2
![]()
Question 22.
Vigna mungo is the botanical name of ………………..
a) Black gram
b) Red gram
c) Green gram
d) Brown gram
Answer:
a) Black gram
Question 23.
Match
| A. Sesamum indicum | 1. Sugar cane |
| B. Arachis hypogea | 2. Palmyra |
| C. Borassus flabellifer | 3. Peanut |
| D. Saccharum officinarum | 4. Gingelly |
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-l
b) A-l, B-2, C-3, D-4
c) A-2, B-l, C-4, D-3
d) A-3, B-l, C-2, D-4
Answer:
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-l
Question 24.
Which one of the following is an incorrect pair?
a) Turmeric – Erode
b) Cardamom – Queen of spices
c) Rubber – Kerala
d) Banana – National fruit of India
Answer:
d)Banana – National fruit of India
![]()
Question 25.
Assertion (A): Rice is the staple food for most of people in the world.
Reason (R): It is easily digestible and calorie-rich food.
a) (A) correct; (R) wrong
b) (A) wrong; (R) correct
c) (A) correct; (R) correct; but (R) does not explain (A)
d) (A) correct; (R) correct; (R) explains (A)
Answer:
d) (A) correct; (R) correct; (R) explains (A)
Question 26.
………………… is the largest consumer of coffee in India?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Andhra
c) Kerala
d) Karnataka
Answer:
a) Tamil Nadu
Question 27.
………………… is the largest coffee producing estate in India
a) Kerala
b) Karnataka
c) Tamil Nadu
d) Andhra
Answer:
b) Karnataka
![]()
Question 28.
Curcumin is extracted from
a) Turmeric
b) Chilly
c) Cardamom
d) Tamarind
Answer:
a) Turmeric
Question 29.
Vilvum belongs to ……………………
a) Lamiaceae
b) Rutaceae
c) Vitaceae
d)Euphorbiaceae
Answer:
b) Rutaceae
Question 30.
Dr. Thyagarajan of university of Madras proved effect of Phyllanthus amarus against
a) Hepatitis-B
b) Cirrhosis
c) Cancer
d) Typhoid
Answer:
a) Hepatitis-B
![]()
Question 31.
Which one of the following is highly effective against jaundice?
a) Nilavembu
b) Opium poppy
c) Marijuana
d) Phyllanthus
Answer:
d) Phyllanthus
Question 32.
……………… Are gluten free with less Glycemic indess
a) pulses
b) gram
c) vegetables
d) millets
Answer:
d) millets
Question 33.
…………….. is native to tropical region of Africa.
a) Sugar cane
b) Palmyra
c) Peanut
d) Sesame
Answer:
b) Palmyra
![]()
Question 34.
Nuts contain ……………. Oil
a) 54%
b) 45%
c) 44%
d) 54%
Answer:
c) 44%
Question 35.
The medicinal plant commonly known as “King of Bitters” is ……………………
a) Nilavembu
b) Holy basil
c) Adathodai
d) Turmeric
Answer:
a) Nilavembu
Question 36.
Pungency of cayenne pepper is ……………….. Scoville Heat Units (SHU)
a) 30,000 to 50,000
b) 1,349,000
c) 2,200,000
d) 1,200,000
Answer:
a) 30,000 to 50,000
![]()
Question 37.
Foxtail millet is domesticated in China ……………….. years ago
a) 4000
b) 3000
c) 5000
d) 6000
Answer:
d) 6000
Question 38.
Setaria italica is the scientific name of ……………………
a) kodo millet
b) foxtail millet
c) sorghum
d) finger millet
Answer:
b) foxtail millet
Question 39.
Lady’s finger is not grown in abundance in ……………..
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Assam
c) Maharashtra
d) Gujarat
Answer:
a) Tamil Nadu
![]()
Question 40.
Which is the temperature region fruit?
a) Mango
b) Jack
c) Banana
d) plum
Answer:
c) Banana and d) plum
Question 41.
The following are the activities of entrepreneurship
a) Mushroom cultivation
b) Single cell protein production
c) Organi farming
d) Above all
Answer:
d) Above all
Question 42.
…………………. is a bio-pest repellent
a) Tamarind
b) Chilly
c) Sesame
d) Neem
Answer:
d) Neem
![]()
Question 43.
Indigenous to western ghats of India
a) Black pepper
b) Cardamom
c) Turmeric
d) Red pepper
Answer:
a) Black pepper
Question 44.
Endosperm of ………………… is a refreshing summer food
a) Coconut
b) Groundnut
c) Gingelly
d) Palmyra
Answer:
d) Palmyra
Question 45.
……………….. Enhances salivary and gastric secretions
a) Cardamom
b) Black pepper
c) Red pepper
d) Turmeric
Answer:
b) Black pepper
![]()
Question 46.
………………… is used in gerontological applications
a) Aloe
b) Turmeric
c) Jasmine
d) Phyllanthus
Answer:
a) Aloe
Question 47.
Lacosone (Colouring Matter) is in ……………………
a) Aloe
b) Jasminum
c) Henna
d) Turmeric
Answer:
c) Henna
Question 48.
Paper pulp is made from ………………
a) Eucalyphis
b) Casuarina
c) Neolamarkia
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
![]()
Question 49.
Eco friendly packaging material is ……………………
a) cotton
b) latex
c) wood pulp
d) jute
Answer:
d) jute
Question 50
……………….. is a ingredient of Ponga I of Tamil Nadu
a) Green gram
b) Red gram
c) Black gram
d) Brown gram
Answer:
a) Green gram
II Two Marks
Question 1.
Name the 3 grass species of food plants?
Answer:
Rice, Wheat, Maize.
Question 2.
What are the nutrients provided by cereals?
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins, fibres, vitamins and minerals.
![]()
Question 3.
Classify cereals based on size? Give example.
Answer:
- Major Cereals. Eg. Rice, Wheat
- Minor Cereals. Eg. Millet’s, Sorghum
Question 4.
Comment on Maida?
Answer:
- Processed wheat flour is called Maida.
- It is used in making Parota, Naan and Bakery products.
Question 5.
Explain the rice products?
Answer:
- Flaked rice (Aval)
- Puffed rice (Pori) are used as breakfast cereal (or) snack food in India.
Question 6.
What are millet’s?
Answer:
A variety of very small seeds. These were originally cultivated by ancient people in Africa. It is gluten free, less glycemic index.
![]()
Question 7.
Enlist the uses of finger millet?
Answer:
- Rich in calcium
- Staple food of south hilly regions in India.
- Ragi is made into porridge and gruel.
- Ragi malt is a nutrient drink
- It is the source of fermented beverage.
Question 8.
How is Sorghum useful?
Answer:
- It is used to feed poultry, birds, pigs, cattle.
- Source of fermented alcoholic beverage.
Question 9.
Discuss the medicinal uses of Fox tail millet?
Answer:
- Strengthens heart
- Improves eye sight
- Thinai porridge is given to lactating mother.
Question 10.
Kodo Millet is medicinally useful – Discuss?
Answer:
- It is a good diuretic
- It cures constipation
- It reduces obesity, blood sugar, blood pressure.
![]()
Question 11.
Which is the only pulse native to southern India? Give it’s uses?
Answer:
Red gram (Pigeon pea) Cajanus cajan is the only pulse native to south India.
Uses:
- Major ingredient of Sambar
- Roasted, salted, unsalted seeds are snacks.
- Young pods are cooked and consumed.
Question 12.
Enlist the nutrients in vegetables?
Answer:
Potassium, fibre, folic acid, vitamin A, E, C
Question 13.
Molecular farming plants are different from natural medicinial plants. How?
Answer:
| Molecular farming | Natural medicinal plants |
| It is a bio-technological method of production of valuable pharmaceutical products from transgenete plants. | Natural method of extraction of medicine from cultivated medicinal plants. |
| Large scale production at cheaper cost bus need bi-technological experts | Simple but can’t produce on very large scale, due to lack of man power, at higher cost. |
![]()
Question 14.
What are the major cultivating states of okra in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Coimbatore, Dharmapuri, Vellore.
Question 15.
Classify fruits based on the climatic region in which they grow?
Answer:
- Temperate Eg. Apple, Pear, Plum
- Tropical fruits Eg. Mango, Jack, Banana.
Question 16.
Which is the National fruit of India? Give its origin and area of cultivation?
Answer:
Mango (Mangifera Indica)
Origin and area of cultivation.
- Native of southern Asia, Burma and Eastern India.
- Mango producing states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat and Karnataka.
- Salem, Krishnagiri, Dharmapuri are major mango producing districts of Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the Major Cultivars of Mango in India.
Answer:
Alphonsa, Banganapalli, Neelam, Malgova.
Question 18.
Which food is the source of antioxidants?
Answer:
Dry fruits with hard shell and edible kernel are nuts. They are the good source of health fat, fibre, protein, vitamin, mineral, antioxidants.
Question 19.
Name the plants ideal for the extraction of commercial sugar?
Answer:
Sugar Cane, Palmyra
![]()
Question 20.
What is sugar?
Answer:
It is the generic name for sweet tasting soluble carbohydrate. They are used in food, beverages.
Question 21.
Give the sources of sugar?
Answer:
Roots of Sugar beet, Stems of Sugar cane, Fruits of Apple, Palmyra sap.
Question 22.
How is cultivated Saccharum officinarum evolved?
Answer:
By repeated back crossing of Saccharum officinarum of new guinea with wild Saccharum Spontaneum.
Question 23.
Toddy-Comment?
Answer:
The sap from Palmyra inflorescence is fermented to get toddy.
![]()
Question 24.
Name the 2 kinds of oils?
Answer:
- Essential oil
- Vegetable, fatty oil
Question 25.
Define Essential oil?
Answer:
They evaporate or volatilize in contact with air. So, they are called volatile oils.
Question 26.
Give the sources of essential oils?
Answer:
Flowers of jasmine, fruits of orange and roots of ginger.
Question 27.
Comment on vegetable oil?
Answer:
These are non-volatile oils or fixed oils. They do no evaporate. Eg. Whole seeds or endosperm are the sources.
![]()
Question 28.
What are spices?
Answer:
Aromatic plant products. They are of sweet or bitter taste. They give flavour and improve the palatability of food.
Question 29.
Comment on condiments?
Answer:
Flavouring substances with sharp taste. They are added to food after cooking Eg. Curry leaves.
Question 30.
Dates of India – Discuss.
Answer:
Tamarindus is an Arabian word. It means dates of India (Tamar – Taste; Indus – India)
![]()
Question 31.
Write any two uses of THC.
Answer:
THC is used in treating Glaucoma a condition in which presšure develops in the eyes.
- THC is also used in reducing nausea of cancer patients under going radiation and chemotherapy.
- It is an effective pain reliever and reduces hypertension.
III. Three Marks
Question 1.
Suggest the 4 commercial cotton species?
Answer:
- G. hirsutum
- G. barbadense
- G. arboreum
- G. herbaceum
Question 2.
Give the uses of cotton?
Answer:
Manufacturing of textile, hosiery products, toys. UsedinFlospitals.
Question 3.
Name the 2 species of plants from which Jute is derived?
Answer:
- Corchorus capsularis (Indo – Burmese origin)
- Corchorus olitorius (African origin)
![]()
Question 4.
Define Vulcanization?
Answer:
Heating rubber with sulphur under pressure at 150°C. It overcomes defect in rubber articles. (Vulcan is the Roman god of fire)
Question 5.
Name the woods used for making paper pulp?
Answer:
- Wood of Melia azadirachta.
- Neolamarkia chienensis
- Cauarinaspe, Eucalyptus spe.
Question 6.
Dyeing is in use since that ancient times? Substantiate?
Answer:
- Authentic records of dyeing is in the tomb painting of ancient Egypt.
- Colouring of mummy cements (wrapping) included saffron and indigo.
- Found in rock paintings of India.
![]()
Question 7.
Give the significance of Henna?
Answer:
- Orange dye henna is from the leaves and shoots of Lawsonia intermis.
- The colouring matter Lacosone is harmless and causes no skin irritation.
- This dye is used for skin, hair and finger nails.
- It is used for colouring leather for tails of horses and in hair dyes.
Question 8.
What do the south Indian people traditionally for skin and hair care?
Answer:
People of South India use turmeric, green gram powder, henna, sigaikai and usilai for skin, hair care.
Question 9.
What does the word’perfume’mean?
Answer:
- ‘Perfume’ is a word derived from Latin.
- Per (through) and fumus (to smoke) means through smoke.
- Age old tradition of burning scented woods at religious ceremonies.
Question 10.
Give an account of NCB?
Answer:
The Narcotics Control Bureau is the drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India. It is responsible for drug trafficking and abuse of illegal substances.
![]()
Question 11.
Can we create new business using plant resources?
Answer:
Entrepreneurial botany is the study of new business created using plant resources.
Question 12.
What is entrepreneurship?
Answer:
Developing ideas to create new ventures among young people.
Question 13.
What is the role of an Entrepreneur?
Answer:
- One who works to create a product or service that people will buy
- He builds an organization to support the sales.
Question 14.
Discuss about ‘Capsaicin’
Answer:
- It is an active component of chillies.
- It has pain relieving properties.
- It gives pungency or spicy taste to chillies.
- Pungency is measured in Scoville Heat Unit (SHU)
- Eg. Naga piper is the hottest chilly of India with 1,349,000 SHU.
![]()
Question 15.
Name some plants used in making paper pulp?
Answer:
- Melia azadirachta
- Neolamarkia chinensis
- Casuarina spe
- Eucalyptus spe
Question 16.
Give the uses of purified dissolving pulp?
Answer:
It helps to manufacture rayon, artificial silk, fabrics, transparent films (cellophane, cellulose, acetate films), plastic. Viscose process of making rayon is common.
Question 17.
Which the second geographical Indication tag after Mysore Malli? How?
Answer:
- Madurai Malli is the second GI Tag.
- It has thick petals, long stalk.
- Distinct fragrance is due to chemicals like jasmine, alpha terpineol.
![]()
Question 18.
Name the major tribal communities in Tamil Nadu known for their medicinal knowledge?
Answer:
Irulas, Malayalis, Kurumbas, Paliyans and Kaanis
Question 19.
Discuss the origin and area of cultivation of black gram?
Answer:
- Archeo botanical evidence show the presence of black gram 3500 years ago.
- India gives 80 % of global production.
- Black gram is grown in Uttar Pradesh, Chattisgarh and Karnataka.
Question 20.
Suggest the nutrients in fruits?
Answer:
Potassium, dietary fibre, folic acid, vitamins.
![]()
Question 21.
What is rayon?
Answer:
- Rayon is purified dis solving pulp is used as a basic material in the manufacture of rayon or artificial silk, fabrics, transport films (cellophane), cellulose, acetate films), plastics.
- This viscose process of making rayon is the most common process.
Question 22.
What is known as sustainable development of agriculture?
Answer:
- Use of biofertilizers is one of the important components of integrated organic farm management, as they are cost effective and renewable source of plant nutrients to supplement the chemical fertilizers for sustainable agriculture.
IV . Five Marks
Question 1.
What kind of cereal can be eaten as a whole grain? Discuss?
Answer:
- Pseudocereal can be eaten as wholegrain.
- These are botanical outliers from grasses.
- Eg. Seed from the Chenopodium quinoa (Family: Amaranthaceae)
- Gluten-free, whole grain carbohydrate, whole protein with all essential amino acids.
- Eaten for 6000 years in Andes hill region.
![]()
Question 2.
Suggest the attributes of cereals as food plants?
Answer:
- Adaptability and colonisation on every type of habitat.
- Ease of cultivation.
- Tillering property gives high yield per unit area.
- Compact dry grains are easily handled, transported, stored without spoilage.
- High-calorie value provides energy.
Question 3.
How will you prepare a Bio-pest repellent?
Answer:
- Neem tree leaves are plucked.
- Put chopped leaves in 50 litre container half-filled with water. Leave it for 3 days to brow.
- Strain the mixture and spray on plants.
- 100 ml of cooking oil is added to make the repellent stick to the plants.
- Soap water is added to break down the oil.
- A stewed leaf mixture can be composted around the base of the plant.
Question 4.
Tabulate the uses of common medicinal plants?
Answer:
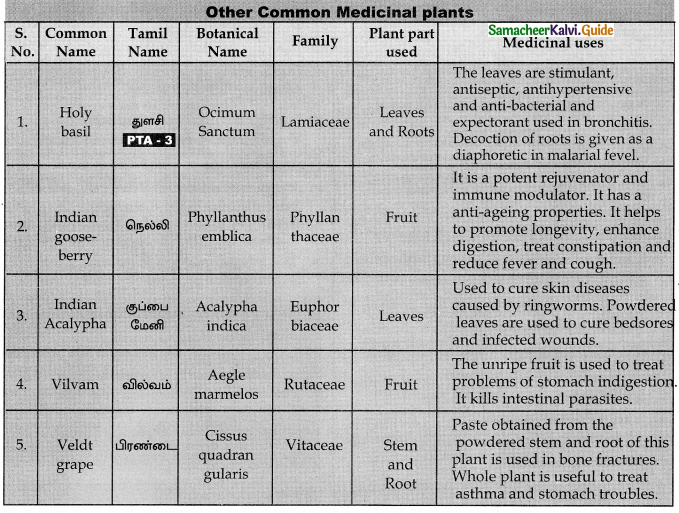
![]()
Question 5.
Give a detailed account on the ‘National Fruit of India’?
Answer:
Mango (Mangifera indica) belongs to the family Anacardiaceae
Origin and area of cultivation.
- Native of southern Asia, Burma and Eastern India.
- Andhra, Bihar, Gujarat and Karnataka are mango producing states.
- Salem, Krishnagiri, Dharmapuri are mango producing districts of Tamil Nadu.
- Major cultivars of Mango are Alphonsa, Banganapalli, Neelam and Malgova.
Uses:
- Major Indian table fruit.
- Rich in beta carotenes.
- Used as dessert, canned, dried, preserves in Indian cuisine.
- Unripe mangoes are used in chutney, pickle, side dishes, eaten raw with salt, chilli.
- Pulp is made as jelly
- Aerated, non aerated soft drinks are prepared.
Question 6.
Enlist the uses of Sugar cane.
Answer:
Botanical Name : Saccharum officinarum of
Poaceae family
Uses:
- Raw material for white sugar
- Industries supported are
- Sugar mills producing refined sugar
- Distilleries producing liquor grade ethanol.
- Jaggery manufacturing unit.
- Refreshing drink can be extracted.
- Gives molasses. It is the raw material for ethyl alcohol.
![]()
Question 7.
Detail on the State Tree of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Botanical Name : Borassus flabellifer of Arecaceae family
Origin and area of cultivation
- Native of tropical Africa, Asia, New Guinea.
- All over Tamil Nadu especially in coastal districts.
Uses:
- Exudate from inflorescence gives palm sugar
- Sap of inflorescence is a healthy drink
- Processed sap gives palm sugar
- Fermented sap gives toddy
- Endosperm is a refreshing summer food
- Elongated embryo of germinated seeds is edible.
Question 8.
Enlist the uses of Chilly / Red pepper?
Answer:
Botanical Name : Capsicum annuum of
Solanaceae family
Uses:
- Capsicum annuum is less pungent
- Capsicum annuum includes large sweet bell peppers.
- Long fruit cultivars called ‘Cayenne Pepper’ are crushed, powdered and used as condiment.
- Sauce, Curry powder, pickle can be prepared.
- Capsaicin has pain relieving property. Good source of vitamins A, C, E.
![]()
Question 9.
Which plant contributes to 90% of world production by Asia? Detail the uses?
Answer:
Rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) of Euphorbiaceae.
Origin and Cultivation
- Native of Brazil
- Kerala is the largest Indian producers
Uses:
- Tyre, automobile parts consume 70% of rubber.
- To manufacture footwear, wire, cable insulation, rain coats, household, hospital goods, shock absorbers, belts, sports goods, erasers, adhesives, rubber band
- Hard rubber is used in electrical and radio engineering
- Latex makes gloves, balloons, condoms.
- Foamed latex used for the manufacture of cushion, pillow, life belts.
Question 10.
Which system of medicine originated from Brahma? Explain?
Answer:
- Ayurveda system of Medicine
- Core knowledge is documented in compendium of Charaka, Sushruta and Vagbhata.
- It is based on 3 humor principles Vatha, Pitha, Kapha.
- Herbs, few animal parts are drug sources.
- Himalayan plants are plant sources.
- Ayurvedic pharmacopoeia of India list 500 plant sources.
Question 11.
Which system of medicine survives as oral tradition? Explain?
Answer:
Folk system of Medicine:
- It is a oral tradition in rural, tribal communities.
- Document of plants used by ethnic communities was launched by Ministry of Environment and Forest, Government of India.
- The document is All India Co-ordinated Research Project on Ethnobiology.
- 8000 species of medical plants are documented.
- Major tribal communities with medicinal knowledge are Irulas, Malayalis, Kurumbas, Paliyans and Kaanis.
Question 12.
Jute Industry occupies an important place in the national economy of India. Explain?
Answer:
- One of the largest exported fibre of India.
- Used for safe packaging of natural, renewable, bio degradable, Eco-friendly products.
- Used in bagging, wrapping textile.
- 75% is used to prepare sack, bag.
- Manufacture of blanket, rag, curtain
- Used in textiles recently.
![]()
Question 13.
Organic farming is considered as the movement towards the philosophy of Back to Nature. Explain
Answer:
- Organic farming is an alternative agricultural system in which plants / crops are cultivated in natural ways by using biological inputs to maintain soil fertility and ecological balance thereby minimizing pollution and wastage
- Indians were organic farmers by default until the green revolution came in to practice.
- Use of bio-fertilizers is one of the important components of integrated organic farm management, as they are cost effective and renewable source of plant nutrients to supplement the chemical fertilizers for sustainable agriculture.
- Several microorganisms and their association with crop plants are being exploited in the production of bio-fertilizers.
- Organic farming is thus considered as the movement directed towards the philosophy of Back to Nature.