Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Guide Pdf Chapter 15 Chemistry in Everyday Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 15 Chemistry in Everyday Life
12th Chemistry Guide Chemistry in Everyday Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – I Text Book Evaluation
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following is an analgesic?
a) Streptomycin
b) Chloromycetin
c) Asprin
d) Penicillin
Answer:
c) Asprin
Question 2.
Dettol is the mixture of
a) Chloroxylenol and bithionol
b) Chloroxylenol and a-terpineol
c) phenol and iodine
d) terpineol and bithionol
Answer:
b) Chloroxylenol and a-terpineol
Question 3.
Antiseptics and disinfectants either kill or prevent growth of microorganisms. Identify which of the following statement is not true.
a) dilute solutions of boric acid and hydrogen peroxide are strong antiseptics.
b) Disinfectants harm the living tissues.
c) A 0.2% solution of phenol is an antiseptic while 1% solution acts as a disinfectant.
d) Chlorine and iodine are used as strong disinfectants.
Answer:
a) dilute solutions of boric acid and hydrogen peroxide are strong antiseptics.
![]()
Question 4.
Saccharin, an artificial sweetener is manufactured from
a) cellulose
b) toluene
c) cyclohexene
d) starch
Answer:
b) toluene
Question 5.
Drugs that bind to the receptor site and inhibit its natural function are called
a) antagonists
b) agonists
c) enzymes
d) molecular targets
Answer:
a) antagonists
![]()
Question 6.
Aspirin is a/an
a) acetylsalicylic acid
b) benzoyl salicylic acid
c) chlorobenzoic acid
d) anthranilic acid
Answer:
a) acetylsalicylic acid
Question 7.
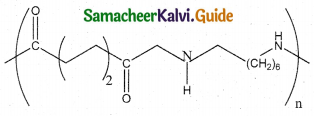
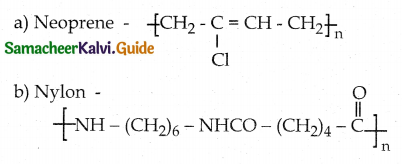
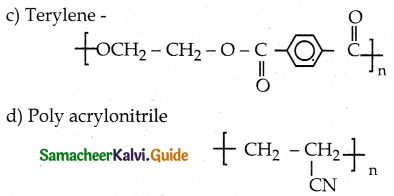
Which one of the following structures represents nylon 6,6 polymer?
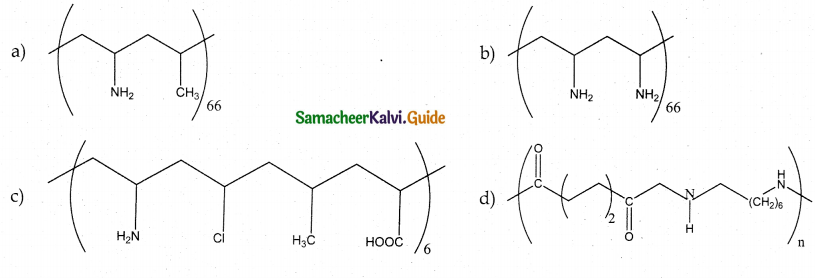
Answer:
d)
Question 8.
Natural rubber has
a) alternate cis- and trans-configuration
b) random cis- and trans-configuration
c) all cis-configuration
d) all trans-configuration
Answer:
c) all cis-configuration
![]()
Question 9.
Nylon is an example of
a) polyamide
b) polythene
c) polyester
d) poly saccharide
Answer:
a) polyamide
Question 10.
Terylene is an example of
a) polyamide
b) polythene
c) polyester
d) polysaccharide
Answer:
c) polyester
Question 11.
Which is the monomer of neoprene in the following?

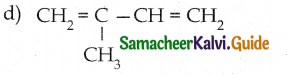
Answer:

![]()
Question 12.
Which one of the following is a biodegradable polymer?
a) HDPE
b) PVC
c) Nylon 6
d) PHBV
Answer:
d) PHBV
Question 13.
Non stick cook wares generally have a coating of a polymer, whose monomer is
a) ethane
b) prop-2-enenitrile
c) chloroethene
d) 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane
Answer:
d) 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane
Question 14.
Assertion : 2-methyl-I ,3-butadiene is the monomer of natural rubber
Reason : Natural rubber is formed through anionic addition polymerisation.
a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) assertion is true but reason is false.
d) both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
c) assertion is true but reason is false.
![]()
Question 15.
An example of antifertility drug is
a) novestrol
b) seldane
c) salvarsan
d) Chioramphenicol
Answer:
a) novestrol
Question 16.
The drug used to induce sleep is
a) paracetamol
b) bithional
c) chloroquine
d) equanil
Answer:
d) equanil
Question 17.
Which of the following is a co-polymer?
a) Orlon
b) PVC
c) Teflon
d) PHBV
Answer:
d) PHBV
![]()
Question 18.
The polymer used in making blankets (artificial wool) is
a) polystyrene
b) PAN
c) polyester
d) polythene
Answer:
b) PAN
Question 19.
Regarding cross-linked or network polymers, which of the following statement is incorrect? (NEET)
a) Examples are Bakelite and melamine
b) They are formed from bi and tri-functional monomers
c) They contain covalent bonds between various linear polymer chains
d) They contain strong covalent bonds in their polymer chain
Answer:
d) They contain strong covalent bonds in their polymer chain
Question 20.
A mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol acts as (NEET)
a) antiseptic
b) antipyretic
c) antibiotic
d) analgesic
Answer:
a) antiseptic
![]()
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
Which chemical is responsible for the antiseptic properties of Dettol.
Answer:
1. Chloroxylenol and
2. Terpineol are the chemicals responsible for the antiseptic properties of Dettol. But among these two, chloroxylenol plays a more important role. Chloroxylenol is an antiseptic and disinfectant which is used for skin disinfection and cleaning surgical instruments.
Question 2.
What are antibiotics?
Answer:
Medicines that have the ability to kill pathogenic bacteria are called antibiotics
Ex.: amoxicillin, cefixime.
Question 3.
Name one substance which can act as both analgesic and antipyretic.
Answer:
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a chemical substance which lowers body temperature (to normal) and also reduces body pain. Therefore it acts as both antipyretic and analgesic.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on synthetic detergents.
Answer:
- Synthetic detergents are formulated products containing either sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids.
- There are three types.
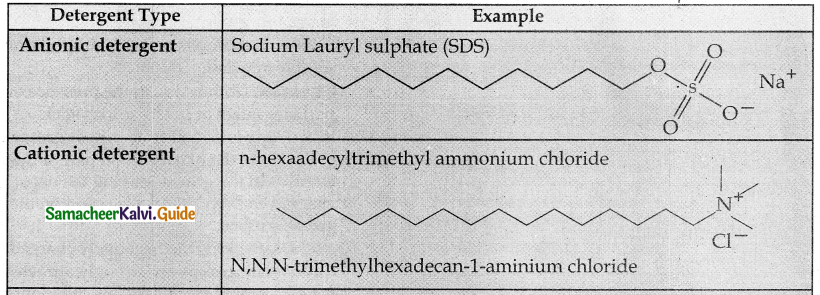
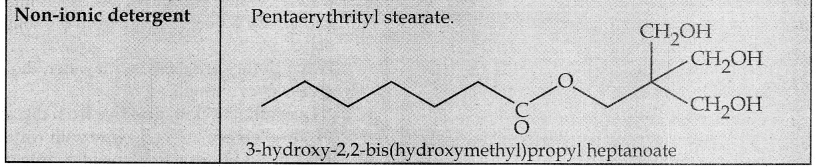
Question 5.
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
Answer:
| Antiseptics | Disinfectants |
| Stop or slow down the growth of microorganisms applied to living tissue | Stop or slow down the growth of microorganisms generally used on inanimate objects. |
| Eg: H202Povidone – iodine | Eg: Chlorine compounds alcohol, Hydrogen peroxide |
Question 6.
What are food preservatives?
Answer:
Food preservatives are chemical substances are capable of inhibiting, regarding, or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other decomposition of food by growth of microorganisms.
Examples:
- Acetic acid is used mainly as a preservative for the preparation of pickles.
- Sodium meta suiphite is used as a preservative for fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Sodium benzoate is used as a preservative for juices.
![]()
Question 7.
Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
- Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions.
- When soaps are dissolved in hard water, calcium and magnesium ions displace sodium or potassium ion from soaps forming insoluble calcium or magnesium salts of fatty acids.
- These insoluble salts separate as scum.
- So soaps do not work in hard water.
Question 8.
What are drugs? How are they classified?
Answer:
A drug is a substance that is used to modify or explore physiological systems or pathological states for the benefits of the recipient. it is used for the purpose of diagnosis, prevention cure or relief of a disease.
Classification of drugs:
Drugs care classified based on their proportions such as chemical structure, pharmacological effect, target system, site of action etc.
1. Classification based on the chemical structure:
In this classification, drugs with a common chemical skelton are classified into a single group. For example, ampicillin, amoxicillin, methiceillin etc. all have similar structure and are classified into a single group called penicillin.
Similarly we have other group of drugs such as opiates, steroids, catecholamines etc. Compounds having similar chemical structure are expected to have similar chemical properties. However, their biological actions are not always similar.
2. Classification based on the pharmacological effect:
- In this classification, the drugs are grouped based on their biological effect that they produce on the recipient.
- For example, the medicines that have the ability to kill the pathogenic bacteria are grouped as antibiotics.
- This kind of grouping will provide the full range of drugs that can be used for a particular disease.
3. Classification based on the target system:
- In this classification, the drugs are grouped based on the biological system (or) process that they target in the recipient.
- This classification is more specific than the pharmacological classification.
- For example, the antibiotics streptomycin and erythromycin inhibit the protein synthesis (target) in bacteria and are classified in a same group. However their mode of action is different.
- Streptomycin inhibits the initiation of protein synthesis, while erythromycin prevents the incorporation of new aminoacids to the protein.
4. Classification based on the site of action:
- The drug molecule interacts with biomolecules such as enzymes, receptors etc, which are referred as drug targets.
- We can classify the drug based on the drug target with which it binds.
- This classification is highly specific compared to the others. These compounds often have a common mechanism of action, as the target is the same.
![]()
Question 9.
How the tranquilizers work in body.
Answer:
They are neurologically active drugs tranquilizers act on the central nervous system by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain.
Ex: Major tranquilizers : Haloperidol, Clozapine.
Mine tranquilizers : Diozepam (Valium), alprazolam.
Question 10.
Write the structural formula of aspirin. Structural formula of aspirin :
(Acetyl Salicylic Acid) C9 H8 O4
Answer:
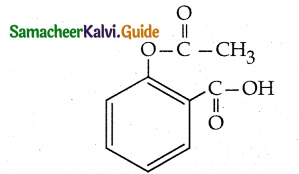
Question 11.
Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soaps and detergents
Answer:
- An example for soap is sodium palmitate.
- The cleansing action of soap is directly related to the structure of carboxylate ions (palmitate ions) present in soap.
- The structure of palmitate exhibit dual polarity

- Hydrocarbon portion is non polar, hydrophobic and soluble in oils and greases but not in water.
- Carboxyl portion is polar, hydrophilic and soluble in water.
- Dirt in the cloth is due to the presence of dust particles intact or grease which stick.
- When soap is added to an oily or greasy part of the cloth, the hydrocarbon part of the soap dissolve in the grease, leaving the negatively charged carboxylate end exposed on the grease surface.
- At the same time the negatively charged carboxylate groups are strongly attracted by water, forming small droplets called micelles and grease is floated away from the solid object.
- When clothes are rinsed with water, the grease goes with it.
- As a result, the doth gets free from dirt and the droplets are washed away with water.
- The micelles do not combine into large drops because their surfaces are all negatively charged and repel each other.
- The cleansing action of soap depends upon its tendency to act as an emulsifying agent between water and water insoluble greases.
- The cleansing action of detergents are similar to the cleansing action of soaps.
![]()
Question 12.
Which sweetening agent are used to prepare sweets for a diabetic patient?
Answer:
Artificial sweetening agents such as saccharin, Alitame, Aspartame can be used in preparing sweets for diabetic patients.
Question 13.
What are narcotic and non – narcotic drugs. Give examples.
Answer:
| Narcotic drugs | Non – narcotic drugs |
| 1. Relieve pain and produce sleep. These are addictive. In poisonous dose, these produces coma arid ultimate death. | Alleviate pain by reducing local inflammatory responses. |
| 2. Used for either short-term or long-term relief of severe pain. | Used for short-term pain relief. |
| 3. Mainly used for post-operative pain, pain of terminal cancer | Used for modest pain like headache, muscle strain, bruising or arthritis. |
| 4. Ex.: Morphine, Codeine | Ex: Ibuprofen, Aspirin |
Question 14.
What are anti-fertility drugs? Give examples.
Answer:
Artificially drugs are chemical substances which suppress the action of hormones that promote pregnancy. These drugs actually reduce the chances of pregnancy and act as a protection. Antifertility drugs are made up of derivatives of synthetic progesterone or a combination of derivatives of oestrogen and progesterone. Example : Ethynylestradiol, menstranol and norcthynodrel etc.
![]()
Question 15.
Write a note on copolymer
Answer:
- A polymer containing two or more kinds of monomer units is called a copolymer.
- Ex: SBR rubber (Buna-S). This contains styrene and butadiene monomer units.
- Co-polymers have properties quite different from homopolymers.
- Mixture of styrene and 1, 3 butadiene to form a copolymer (Buna-S).
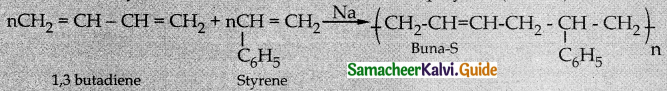
Question 16.
What are biodegradable polymers? Give examples.
Answer:
- The materials that are readily decomposed by microorganisms in the environment are called biodegradable.
- Natural polymers degrade on their own after certain period of time but the synthetic polymers do not.
- The biopolymers which disintergrates by themselves in biological systems during a
- certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis and to some extent by oxidation are called biodegradable polymers.
Examples:
- Polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB)
- Polyhydroxy butyrate – co – hydroxyl valerate (PHBV)
- Polylactic acid (PLA)
Question 17.
How is terylene prepared?
Answer:
- Monomers – Ethylene glycol and terepathalic acid (or) dimethyl terephthalate.
- Catalyst – Zinc acetate / antimony trioxide.
- Temperature – 500K
- Product – Terylene
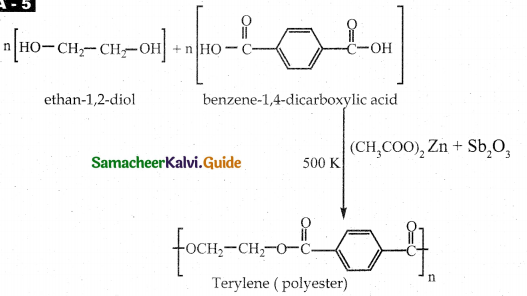
![]()
Question 18.
Write a note on vulcanization of rubber
Answer:
- Natural rubber is very soft and brisky. it has high water absorption capacity and low tensile strength. Its properties can be improved by a process called vulcanization.
- Natural rubber is mixed with 3 – 5% sulphur and heated at 100 – 150°C causes cross-linking of the cis – 1, 4 polyisoprene chains through disuiphide ( – S – S – ) bonds.
- The physical properties of rubber can be altered by controlling the amount of sulphur that is used for vulcanization. When 3 to 10% sulphur is used the resultant rubber is somewhat harder but flexible.
- Following properties of rubber CH3
Question 19.
Classify the following as linear, branched or cross-linked polymers
a) Bakelite
b) Nylon
c) polythene
Answer:
| Polymer | Type |
| a) Bakelite | Cross-linked polymer |
| b) Nylon | Linear polymer |
| c) Polythene (HOPE) | Linear polymer |
| d) Polythene (LDPE) | Branched polymer |
![]()
Question 20.
Differentiate thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
| Thermoplastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| 1. Linear polymers with weak van der walls forces acting in various chains. | Cross-linked polymer. |
| 2. When heated, they melt and form a fluid which sets into a hard mass on cooling. | When heated, they become hard and infusible due to the cross-linking between the polymer chains |
| 3. They can be remoulded and reused. | They can not be remoulded. |
| 4. Formed by addition polymerisation. | Formed by condensation polymerisation. |
| 5. They are of low strength. | They are of high strength. |
| 6. Ex: Polythene, polystyrene | Ex: Bakelite, melamine-formaldehyde resin. |
12th Chemistry Guide Chemistry in Everyday Life Additional Questions and Answers
Part – II – Additional Questions
I. Choose the best answer
Question 1.
An ideal drug is the one which is
(i) non-toxic
(ii) bio-compatible
(iii) bio-degradable
(iv) should not have any side effects .
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (i) & (iii)
c) (i), (ii) & (iv)
d) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
Answer:
d) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
Question 2.
A drag is safer when its therapeutic index is ………………..
a) lower
b) higher
c) one
d) zero
Answer:
b) higher
Question 3.
Which among the following belongs to the group penicillin?
a) Ampicillin
b) Amoxicillin
c) Methicillin
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 4.
Which among the following is an antibiotic?
a) Atenolol
b) Cefixime
c) Amlodipine
d) All the above
Answer:
b) Cefixime
Question 5.
Which among the following is an anti-hypertensive drug?
a) Ampicillin
b) Cefixime
c) Atenolol
d) Cefpodoxime
Answer:
c) Atenolol
Question 6.
Proteins which act as biological catalysts are called.
a) Antibiotics
b) Enzymes
c) Tranquilizers
d) Analgesics
Answer:
b) Enzymes
![]()
Question 7.
Penicillin is an example of
a) Analgesics
b) Antibiotic
c) Anaesthetic
d) Antacid
Answer:
b) Antibiotic
Question 8.
Drugs which act on the central nervous system by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain are called.
a) Analgesics
b) Antacids
c) Tranquilizers
d) Antihistamines
Answer:
c) Tranquilizers
Question 9.
Diazepam is an example of ……………..
a) analgesics
b) antacids
c) tranquilizer
d) antihistamine
Answer:
c) tranquilizer
![]()
Question 10.
Which among the following is not a non-narcotic analgesic?
a) Aspirin
b) Ibuprofen
c) Acetaminophen
d) Morphine
Answer:
d) Morphine – A narcotic analgesic
Question 11.
Which among the following is an inhalational general anesthetics?
a) lidocaine
b) Isoflurane
c) Propofol
d) Procaine
Answer:
b) Isoflurane
Question 12.
Which among the following is used as an antacid?
a) Sodium hydroxide
b) Potassium hydroxide
c) Aluminium hydroxide
d) Calcium carbonate
Answer:
c) Aluminium hydroxide
![]()
Question 13.
The drugs which provide relief from allergic effects are called.
a) Antimicrobials
b) Antacids
c) Opioids
d) Antihistamines
Answer:
d) Antihistamines
Question 14.
Neomycin belongs to …………………
a) beta-lactams
b) aminoglycosides
c) tetracyclines
d) fluoroquinolones
Answer:
b) aminoglycosides
Question 15.
Benzalkonium chloride is used as an ………………………
a) disinfectant
b) antibiotic
c) antiseptic
d) antifertility drug
Answer:
c) antiseptic
![]()
Question 16.
Which drug suppresses ovulation/fertilisation?
a) Oxytetracycline
b) Terfenadine
c) Menstranol
d) Minocycline
Answer:
c) Menstranol
Question 17.
The drug which inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis is ……………….
a) macrolide
b) beta-lactams
c) fluoroquinolone
d) tetracycline
Answer:
b) beta-lactams
Question 18.
The drug which targets bacterial ribosomes and prevents protein production is …………………
a) macrolide
b) beta-lactam
c) fluoroquinolone
d) tetracycline
Answer:
a) macrolide
![]()
Question 19.
Which among the following are food additives?
(i) Food colours
(ii) Antioxidants
(iii) Stabilizers
(iv) Preservatives
a) (i), (ii) & (iv)
b) (i), (iii) & (iv)
c) (i), (ii) & (iii)
d) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
Answer:
d) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
Question 20.
The preservative used for the preparation of pickles is ………………..
a) benzoic acid
b) sorbic acid
c) acetic acid
d) hydroxybenzoic acid
Answer:
c) acetic acid
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the following not correctly matched
Answer:
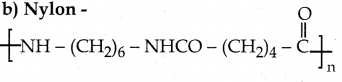
Question 22.
Which among the following is used as an emulsifier?
a) Sodium metabisulphite
b) Alkyl ester of hydroxybenzoic acid
c) Sucrose ester with palmitic acid
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Sucrose ester with palmitic acid
Question 23.
Antioxidants are …………….
a) butyl hydroxy toluene
b) butylated hydroxy anisole
c) both (a) & (b)
d) none of the above
Answer:
c) both (a) & (b)
![]()
Question 24.
Sulphur dioxide acts as ……………….
a) antimicrobial agent
b) antioxidant
c) enzyme inhibitor
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 25.
Artificial sweetening agent is ……………….
a) Butyl hydroxytoluene
b) Butylated hydroxyanisole
c) alitame
d) all the above
Answer:
c) alitame
Question 26.
Softsoap is ……………..
a) Sodium palmitate
b) Potassium palmitate
c) Sodium methylbenzene sulphonate
d) Methyl hydrogen sulphate
Answer:
b) Potassium palmitate
Question 27.
For a good soap, its TFM value should be ………………..
a) higher
b) lower
c) minimum
d) zero
Answer:
a) higher
![]()
Question 28.
As per BIS standards, grade -1 soaps should have a minimum TFM of
a) 60%
b) 70%
c) 76%
d) 50
Answer:
c) 76%
Question 29.
An example of anionic detergent is ………………..
a) n-hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride
b) Sodium lauryl sulphate
c) Pentaerythrityl stearate
d) Sodium stearate
Answer:
b) Sodium lauryl sulphate
Question 30.
Which among the following is a natural polymer?
a) Cellulose diacetate
b) Cellulose
c) Polythene
d) Viscose rayon
Answer:
b) Cellulose
![]()
Question 31.
Which among the following is a synthetic polymer?
a) Cellulose diacetate
b) Cellulose
c) Polythene
d) Viscose rayon
Answer:
c) Polythene
Question 32.
Which among the following is a semi-synthetic polymer?
a) Cellulose diacetate
b) Cellulose
c) Polythene
d) Polyvinyl chloride
Answer:
a) Cellulose diacetate
Question 33.
Which among the following is a linear polymer?
a) LDPE
b) HDPE
c) Polypropylene
d) Bakelite
Answer:
b) HDPE
![]()
Question 34.
Which among the following is a branched polymer?
a) LDPE
b) HOPE
c) PVC
d) Bakelite
Answer:
a) LDPE
Question 35.
Which among the following is a cross-linked polymer?
a) LDPE
b) HDPE
c) PVC
d) Bakelite
Answer:
d) Bakelite
Question 36.
Which among the following is an elastomer?
a) Nylon 6,6
b) Polythene
c) Neoprene
d) Polystyrene
Answer:
c) Neoprene
![]()
Question 37.
Which among the following polymer belongs to fibers?
a) Nylon 6,6
b) Polythene
c) Neoprene
d) Polystyrene
Answer:
a) Nylon 6,6
Question 38.
Which among the following is a thermoplastic?
a) Nylon 6,6
b) Polythene
c) Neoprene
d) Buna-N
Answer:
b) Polythene
Question 39.
Which among the following is a thermosetting plastic?
a) Nylon 6,6
b) Polythene
c) Neoprene
d) Bakelite
Answer:
d) Bakelite
![]()
Question 40.
Which among the following is a condensation polymer?
a) PVC
b) Nylon 6,6
c) Polythene
d) Teflon
Answer:
b) Nylon 6,6
Question 41.
Which is used as a free radical initiator?
a) Benzyl acetate
b) Benzyl alcohol
c) Benzoyl peroxide
d) Benzyl nitrate
Answer:
c) Benzoyl peroxide
Question 42.
The catalyst used in the preparation of LDPE is …………………
a) Hydrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Zeigler-Natta catalyst
d) Wilkinson catalyst
Answer:
b) Oxygen
![]()
Question 43.
The catalyst used in the preparation of HDPE is ………………….
a) Hydrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Zeigler-Natta catalyst
d) Wilkinson catalyst
Answer:
c) Zeiglar-Natta catalyst
Question 44.
Zeiglar-Natta catalyst is ………………….
a) ZnCl2+(C2H5)3Al
b) TiCl4+(C2H5)3Al
c) AlCl3+(C25)3Al
d) CuCl2+(C2H5)3Al
Answer:
b) TiCl4+(C2H2)3Al
Question 45.
The monomer used in the manufacture of Teflon is ………………..
a) Tetra fluoro methane
b) Tetra chloromethane
c) Tetra fluoro ethylene d) Vinyl cyanide
Answer:
c) Tetra fluoro ethylene
![]()
Question 46.
The chemical name of orlon is ……………….
a) Polyethylene terephthalate
b) Polyacrylonitrile
c) Poly hexamethylene adipamide
d) Poly tetrafluoroethylene
Answer:
b) Polyacrylonitrile
Question 47.
The monomer of nylon 6 is ………………
a) Hexan-l,6-dioic acid
b) Hexan-1, 6-diamine
c) Caprolactam
d) both (a) & (b)
Answer:
c) Caprolactam
Question 48.
The monomer of nylon 6,6 is …………………..
a) Hexan-1,6-dioic acid
b) Hexan-1, 6-diamine
c) Caprolactam
d) both (a) & (b)
Answer:
d) both (a) & (b)
![]()
Question 49.
Terylene is an example of ………………….
a) Poly amide
b) Polyester
c) Polyene
d) Poly acid
Answer:
b) Polyester
Question 50.
The polymer used to make unbreakable crockery is ………………
a) Novolac
b) Bakelite
c) Melamine formaldehyde
d) Urea formaldehyde
Answer:
c) Melamine formaldehyde
Question 51.
Natural rubber is a polymer of ………………..
a) Chloroprene
b) 2-methyl buta-1,3-diene
c) 2-chloro buta-1, 3-diene
d) acrylonitrile
Answer:
b) 2-methyl buta-1, 3-diene
![]()
Question 52.
Which is used in vulcanization of rubber?
a) Carbon
b) Nitrogen
c) Sulphur
d) Chlorine
Answer:
c) Sulphur
Question 53.
The polymer used in the manufacture of conveyer belts is ………………….
a) Buna – N
b) Buna – S
c) Neoprene
d) Chloroprene
Answer:
c) Neoprene
Question 54.
Which among the following is not a copolymer?
a) Neoprene
b) Buna – N
c) Buna – S
d) all the above
Answer:
a) Neoprene
![]()
Question 55.
Which among the following is a biodegradable polymer?
a) PCA
b) Nylon-6
c) PVC
d) HDPE
Answer:
a) PGA
II. Pick out the correct statements
Question 1.
(i) All drugs belonging to penicillin group have same biological action.
(ii) The drug molecule interacts with biomolecules such as enzymes, receptors etc., which are referred as drug targets.
(iii) In all living systems, the biochemical reactions are catalysed by hormones.
(iv) The substrate molecule binds to the active site of the enzymes by means of strong covalent bonding.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
a) (i) & (ii)
Correct Statements:
(iii) In all living systems, the biochemical reactions are catalysed by enzymes.
(iv) The substrate molecule binds to the active site of the enzymes by means of weak hydrogen bonding.
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Many drugs exert their physiological effects by binding to a specific molecule called a messenger.
(ii) Receptors bind to the active site of messengers.
(iii) Compounds that carry messages to cells are called chemical messengers.
(iv) Most receptors are chiral and hence different enantiomers of a drug can have different effect.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (iii) & (iv)
Correct Statements:
(i) Many drugs exert their physiological effects by binding to a specific molecule called a receptor.
(ii) Messengers bind to the active site of receptors.
Question 3.
(i) Aspirin prevents platelet coagulation and hence useful in the prevention of heart attacks.
(ii) Lidocaine is used for major surgical procedures.
(iii) Procaine block pain perception that is transmitted via peripheral nerve fibres to the brain.
(iv) Fluoro quinolones increase the activity of bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (i) & (iii)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (i) & (iii)
Correct Statements:
(ii) Lidocaine is used for minor surgical procedures.
(iv) Fluoro quinolones inhibits the activity of bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase.
![]()
Question 4.
(i) In soap manufacture common salt is added to the reaction mixture to increase the solubility of soap which helps the precipitation of soap from the aqueous solution.
(ii) In soap the hydrocarbon portion is non-polar and the carboxyl portion is polar
(iii) In soap the hydrocarbon portion is water soluble and the carboxyl portion is soluble in oil or grease.
(iv) The cleansing ability of a soap depends upon its tendency to act as an emulsifying agent between water and water insoluble grease.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (ii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (ii) & (iv)
Correct Statements:
(i) In soap manufacture common salt is added to the reaction mixture to decrease the solubility of soap which helps the precipitation of soap from the aqueous solution.
(iii) In soap the hydrocarbon portion is soluble in oil or grease and the carboxyl portion is water soluble.
![]()
III. Pick out the incorrect statements
Question 1.
(i) Natural polymers are obtained from plants or animals.
(ii) Natural polymers modified by chemical treatment are called synthetic polymers.
(iii) Addition polymers are formed by the polymerisation of monomers without the elimination of any by product.
(iv) Thermosetting plastics can be remoulded,
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (ii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
c) (ii) & (iv)
Correct Statements:
(ii) Natural polymers modified by chemical treatment are called semi-synthetic polymers
(iv) Thermo plastics can be remoulded (or) Thermosetting plastics cannot be remoulded.
Question 2.
(i) Polyethene is obtained by condensation polymerisation.
(ii) In the preparation of HDPE peroxides formed from oxygen acts as a free radical initiator.
(iii) The monomer of teflon is tetrafluoroethylene.
(iv) Orion is polyacrylonitrile.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
a) (i) & (ii)
Correct Statements:
(i) Polyethene is obtained by addition polymerisation.
(ii) In the preparation of LDPE peroxides formed from oxygen acts as a free radical initiator.
![]()
Question 3.
(i) Proteins which act as biological catalysts are called enzymes.
(ii) Proteins which are important for communication systems are called receptors.
(iii) Allosteric inhibitors do not change the active site geometry of enzymes.
(iv) When allosteric inhibitors bind to the allosteric site, the substrate can also bind to the enzyme.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (iii) & (iv)
Correct Statements:
(iii) Allosteric inhibitors change the active site geometry of enzymes.
(iv) When allosteric inhibitors bind to the allosteric site, the substrate can not bind to the enzyme.
Question 4.
(i) For the treatment of stress, anxiety, depression tranquilizers are used.
(ii) Non-narcotic analgesics are mainly used for post operative pain, pain of terminal cancer.
(iii) In the treatment of peptic ulcer aminoglycosides are used.
(iv) Rabeprazole is used as an antacid,
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
b) (ii) & (iii)
Correct Statements:
(ii) Narcotic analgesics are mainly used for post operative pain, pain of terminal cancer.
(iii) In the treatment of peptic ulcer tetracyclines are used.
![]()
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion : The quality of soap is described in terms of total fatty matter (TFM value)
Reason : As per BIS Standards, Grade-I soaps should have 60% minimum TFM value.
a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) Assertion is true but reason is false
d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
c) Assertion is true but reason is false
Question 2.
Assertion : Paracetamol and aspirin are both antipyretics.
Reason : Both paracetamol and aspirin are controlled and reversible loss of concionsness by affecting central nervous system.
a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
b) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation for assertion,
c) Assertion is true but reason is false
d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
c) Assertion is true but reason is false
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Soaps are superior to detergents.
Reason (R): Detergents can be used even in hard water,
a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, (R) explains (A)
b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct
Answer:
d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct Correct Assertion (A): Detergents are superior to soaps.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Nylon 6,6 is a condensation polymer.
Reason (R): Addition polymers are formed by the polymerisation of monomers without the elimination of any product.
a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, (R) explains (A)
b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct
Answer:
b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
![]()
V. Match the following
Question 1.
| Anaesthetics | Example |
| 1. Ester-linked local anaesthetic | a. Propofol |
| 2. Amide-linked local anaesthetic | b. Isoflurane |
| 3. Intravenous general anaesthetic | c. Lidocaine |
| 4. Inhalational general anaesthetic | d. Procaine |
Answer:
1. – d. Procaine
2. – c. Lidocaine
3. – a. Propofol
4. – b. Isoflurane
Question 2.
| Drug | Example |
| 1. Tranquilizer | a. Erythromycin |
| 2. Non-narcotic analgesic | b. Menstranol |
| 3. Opioid | c. Benzalkonium chloride |
| 4. Antihistamine | d. Alprazolam |
| 5. Antimicrobial | e. Cetirizine |
| 6. Antiseptic | f. Ibuprofen |
| 7. Antifertility drug | g. Codeine |
Answers:
1. – d. Alprazolam
2. – f. Ibuprofen
3. – g. Codeine
4. – e. Cetirizine
5. – a. Erythromycin
6. – c. Benzalkonium chloride
7. – b. Menstranol
![]()
Question 3.
| Monomer | Polymer |
| 1. Butadiene & styrene | a. Bakelite |
| 2. 3 – hydroxybutanoic acid &
3 – hydroxypentanoic acid |
b. Buna-N |
| 3. Vinyl Chloride | c. Buna-S |
| 4. Butadiene & Acrylonitrile | d. PHBV |
| 5. Phenol & formaldehyde | e. PVC |
Answers:
1. – c. Buna-S
2. – d. PHBV
3. – e. PVC
4. – b. Buna-N
5. – a. Bakelite
VI. Two mark questions
Question 1.
What is called as medicine?
Answer:
The drug which interacts with macromolecular targets such as proteins to produce a therapeutic and useful biological response is called medicine.
Question 2.
What are the characteristics of an ideal drug?
Answer:
Characteristics of an ideal drug:
- Non-toxic > Bio-compatible .
- Bio-degradable
- Should not have any side effects
- Bio-compatible .
![]()
Question 3.
What is therapeutic index? How is it related to the safety of the drug.
Answer:
- Therapeutic index is defined as the ratio between the maximum tolerated dose of a drug (above which it become toxic) and the minimum curative dose (below which the drug is ineffective).
- Therapeutic index = \(\frac {Maximum tolerated dose of the drug}{Minimum curative dose of the drug}\)
- Higher the value of therapeutic index, safer is the drug.
Question 4.
What are competitive inhibitors?
Answer:
- When a drug molecule that has a similar shape as the substrate is administered, it can also bind to the enzyme and inhibit its activity.
- In other words, the drug acts as an inhibitor to the enzyme catalyst.
- These type of inhibitors are called competitive inhibitors.
Question 5.
Write the mode of action and uses of antacids. Give example.
Answer:
- Substances which neutralize the acid in the stomach that causes acidity are called antacids.
- Uses: To relieve symptoms such as burning sensation in the chest/throat area (heartburns) caused by acid reflux.
- Ex.: Milk of Magnesia, Aluminium hydroxide
![]()
Question 6.
What are antihistamines? Give example.
Answer:
Drugs which block histamine release from histamine-1-receptors.
Question 7.
What are food additives?
Answer:
The substances which are not naturally a part of the food and added to improve the quality of food are called food additives.
Question 8.
Write the important categories of food additives.
Answer:
- Aroma compounds
- Preservatives
- Artificial Sweeteners
- Buffering substances
- Vitamins and minerals
![]()
Question 9.
What are the advantages of food additives?
Answer:
- Preservatives reduce the product spoilage and extend the shelf-life of food.
- Vitamins and minerals reduce the mall nutrient.
- Flavouring agents enhance the aroma of the food.
- Antioxidants prevent the formation of potentially toxic oxidation products of lipids and other food constituents.
Question 10.
What are sugar substituents? Give example.
Answer:
- Compounds that are used like sugars for sweetening, but are metabolised without the influence of insulin are called sugar substituents.
- Ex.: Sorbitol, Xylitol, Mannitol
Question 11.
What are artificial sweetening agents? Give example.
Answer:
- Synthetic compounds which imprint a sweet sensation and possess no or negligible nutritional value are called artificial sweeteners.
- Ex.: Saccharin, Aspartame, sucralose, alitame
![]()
Question 12.
Define soap and detergent.
Answer:
- Soap is the sodium or potassium salt of higher fatty acids.
- Detergent is the sodium salt of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or alkyl benzene sulphonic acids.
Question 13.
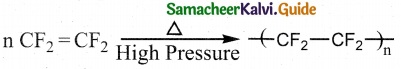
How is teflon prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction : Addition polymerisation
- Monomer: Tetrafluroethylene
- Catalyst: Oxygen (or) ammonium persulphate
- Polymer : Teflon
- Use : Coating non-stick utensils.
![]()
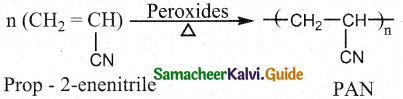
Question 14.
How is orlon prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction : Addition polymerisation
- Monomer : Vinylcyanide (acrylonitrile)
- Catalyst: Peroxide initiator
- Polymer : Polyacrylonitrile – PAN (Orlon)
- Use : Substitute of wool for making blankets, sweaters etc…
Question 15.
Differentiate addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation.
Answer:
| Addition polymerisation | Condensation polymerisation |
| 1. Polymerisation of monomers containing double or triple bonds. | Polymerisation of monomers with the elimination of small molecules such as water alcohol, hydrogen chloride. |
| 2. Chain growth polymerization. | Step growth polymerisation. |
| 3. One type of monomer is involved. | More than one type of monomer is involved. |
Question 16.
What are Antiseptics ? Give an example.
Answer:
- Chemicals that stop or slowdown the growth of microorganisms are called antiseptics.
- They are applied to living tissues.
- Ex.: Hydrogen peroxide, povidone – iodine, benzalkonium chloride.
![]()
VII. Three mark questions
Question 1.
Write notes on antagonists and agonists.
Answer:
- Many drugs exert their physiological effects by binding to a specific molecule called a receptor.
- Drugs which bind to the receptor site inhibiting its natural functions are called antagonists.
- Drugs which mimic the natural messenger by switching on the receptor are called agonists. Agonists are used when there is lack of chemical messenger.
- Ex .: when adenosine binds to the adenosine receptors, it induces sleepiness. But the antagonist drug caffeine binds to the adenosine receptor making it inactive. This results in reduced sleepiness.
- The agonist drug, morphine used as a pain killer, binds to the opioid receptors activating them. This suppresses the neurotransmitters that cause pain.
Question 2.
Write about antioxidants.
Answer:
- Antioxidants are substances which retard the oxidative deteriorations of food.
- Food containing fats and oils is easily oxidized and turn rancid.
- To prevent the oxidation of the fats and oils, BHT (butylhydroxytoluene), BHA (Butylated hydroxyanisole) are added as food additives.
- They are generally called antioxidants.
- These materials readily undergo oxidation by reacting with free radicals generated by the oxidation of oils, thereby stop the chain reaction of oxidation of food.
- Sulphur dioxide and sulphites are also used as food additives.
- They act as anti-microbial agents, antioxidants and enzyme inhibitors
![]()
Question 3.
Write about the preparation of soaps.
Answer:
- Animal fats or vegetable oils contain glyceryl esters of long-chain fatty acids.
- When the glycerides are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide soap (sodium or potassium salt of fatty acids) and glycerol are obtained.
- This is known as saponification.
- Common salt is added to the reaction mixture to decrease the solubility of soap and it helps to precipitate out soap from the aqueous solution.
- Soap is then mixed with desired colours, perfumes and chemicals of medicinal importance.
Question 4.
Write a note on total fatty matter (TFM) of soap
Answer:
- The quality of a soap is described in terms of total fatty matter (TFM value).
- It is defined as the total amount of fatty matter that can be separated from a sample after splitting with mineral acids.
- Higher the TFM value of the soap better is its quality.
- As per BIS standards, minimum TFM value of Grade-1 soaps is 76% , Grade-2 soap is 70%, Grade-3 soap is 60%.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the preparation of LDPE and HDPE.
Answer:
Question 6.
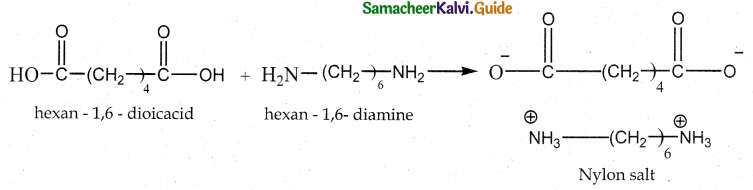
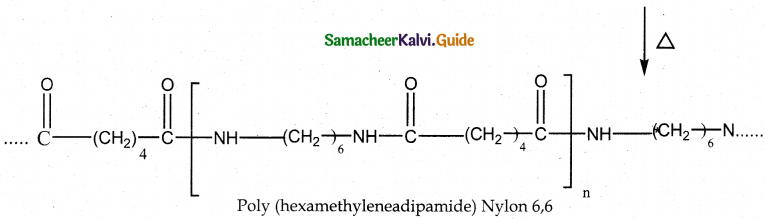
How is nylon 6,6 prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction : Condensation polymerisation
- Monomers : Equimolar adipic acid and hexamethylene – diamine
- Intermediate : Nylon salt which on heating eliminate a water molecule.
- Polymer : Poly hexamethylene adipamide (Nylon 6,6)
- Uses : Textiles, manufacture of cards
![]()
Question 7.
How is nylon 6 prepared? Mention its use. Nylon -6
Answer:
- Capro lactam (monomer) on heating at 533K in an inert atmosphere with traces of water gives ∈ amino carproic acid which polymerises to give nylon – 6
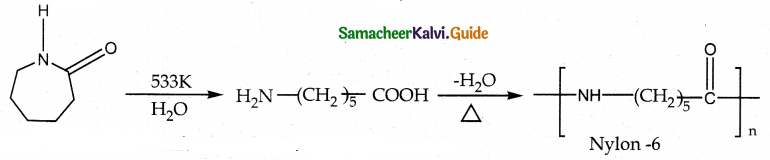
- it is used in the manufacture of tyrecards fabrics etc…
Question 8.
How is bakelite prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction: Condensation polymerization
- Monomers: Phenol and formaldehyde
- Catalyst : acid or base
- Intermediate: Ortho or para hydroxy methyl phenol which on reaction with phenol gives linear polymer novolac.
Novalac on heating with formaldehyde undergo cross linkages to form bakelite. - Polymer: Bakelite
- Uses : Navolac – in paints. Soft bakelites – making glue for binding laminated wooden planks, in varinishes Hard bakelites – combs, pens etc..
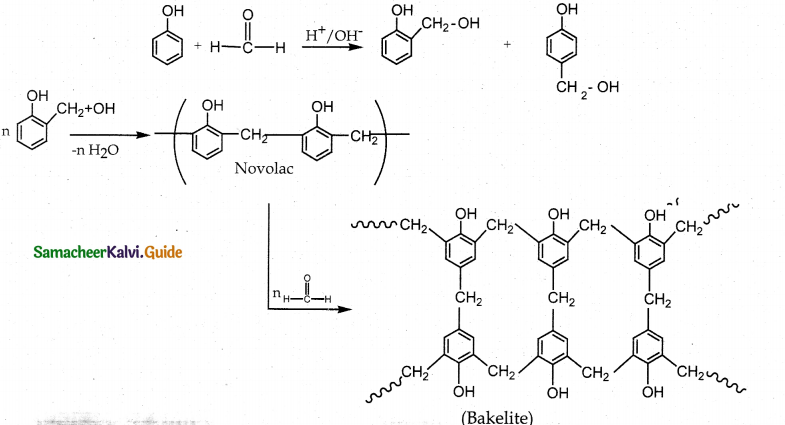
![]()
Question 9.
How is melamine formaldehyde prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction : Condensation polymerization
- Monomers : Melamine and formaldehyde
- Polymer : Melamine formaldehyde
- Uses : Making unbreakable crockery
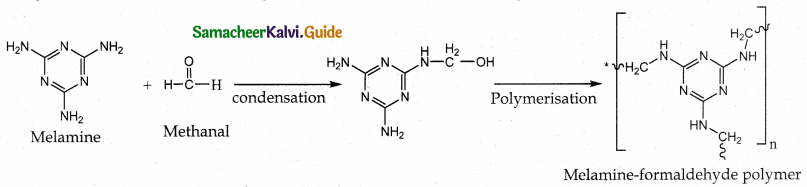
Question 10.
How is urea formaldehyde polymer is prepared?
Answer:
- Reaction : Condensation polymerization
- Monomers : Urea and formaldehyde
- Polymer: Urea formaldehyde polymer
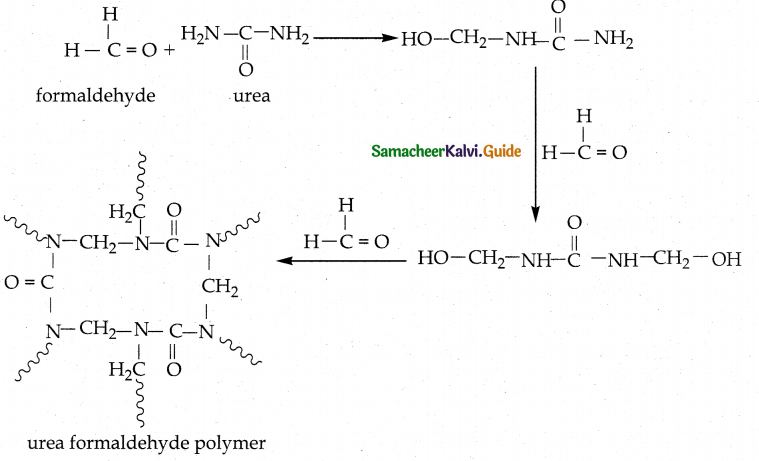
![]()
Question 11.
Differentiate natural rubber and synthetic rubber.
Answer:
| Natural rubber | Synthetic rubber |
| 1. Naturally occurring polymer. | Synthetic polymer |
| 2. Monomer is cis isoprene. | Monomer is buta-1,3-diene or its derivatives. |
| 3. Not so strong or elastic. | Stretching to a greater extent |
Question 12.
Write about Neoprene preparation? Mention its use.
Answer:
- Reaction : Free radical polymeristion
- Monomer : 2-chloro buta-1, 3-diene (chloroprene)
- Polymer : Neoprene (Superior to rubber and resistant to chemical action)
- Uses : Manufacture of chemical containers, conveyer belts.
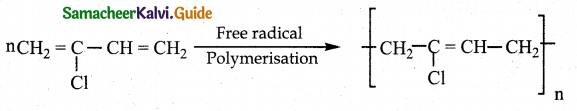
Question 13.
What is PHBV? How is it prepared? Mention its use.
Answer:
- PHBV is Poly- β -hydroxy butyrate-co- β -hydroxy valerate
- It is a co polymer.
- Monomers : 3-hydroxy butanoic acid and 3-hydroxy pentanoic acid
- Monomer units are joined by ester linkages.
- Uses : in ortho paedic devices, in controlled release of drugs.
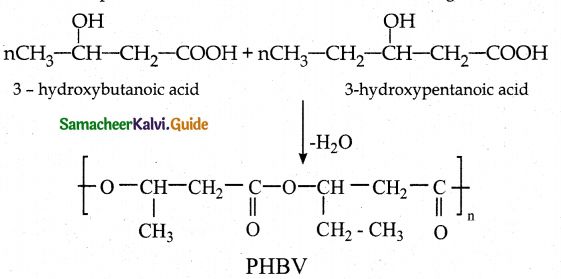
![]()
Question 14.
How is Nylon-2-Nylon-6 prepared?
Answer:
- It is a co polymer.
- Obtained by condensation polymerisation.
- Monomers – glycine and E – amino caproic acid.
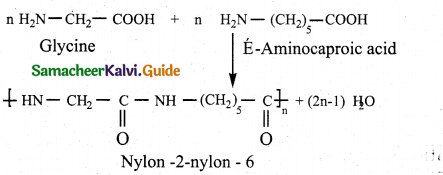
VIII. Five mark questions
Question 1.
How polymers are classified on the basis of structure and molecular formula and molecular
forces gives example one.
Answer:
(A) Classification based on structure of polymers
(i) Linear polymers:
The monomers in these are linked together to form along chain. Eg: HDPE, PVC
(ii) Branch chain polymers:
One main chain with small chains as branches. Eg: polypropylene, LDPE
(iii) Crosslinked or Network polymers:
Monomers are linked together to form a three-dimensional network. The monomers contain strong
covalent bonds as they are composed of bi-functional and tri-functional in nature. These polymers are brittle and hard.
Ex: Bakelite (used in electrical insulators), Melamine formaldehyde etc.,
(B) Classification Based on Molecular Forces
Intra molecular forces are the forces that hold atoms together within a molecule. In Polymers, strong covalent bonds join atoms to each other in individual polymer molecules. Intermolecular forces (between the molecules) attract polymer molecules towards each other. Polymers can be classified into 4 types :
i) Elastomers : (soft and stretched)
Elastomers are rubber like solid polymers, that are elastic in nature. The polymer chains are hold by the weakest intermolecular forces, hence allowing the polymer to be stretched. But as you notice removing that stress also results in the rubber band taking up its original form.
Eg: Buna-S, Buna-N neoprene.
ii) Thermoplastics : They become soft on heating and hard cooling they can be remolded . Eg: Polythene, PVC, Polystyrene
iii) Thermosetting : Do not become soft on heating but set to an infusible mass upon heating.
Eg: Bakelite, melamine formaldehyde.
iv) Fibre : They have strong inter molecules forces between the chains giving them less elasticity and high tensile strength. The intermolecular force may be hydrogen bonds or dipole-dipole interaction Eg: Nylon-6,6, Terylene.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain various types of anaesthetics.
Answer:
Drugs which produce loss of sensation are called anaesthetics.
Local anaesthetics:
- They cause loss of sensation, in the area in which they are applied without losing consciousness.
- They block pain perception that is transmitted via peripheral nerve fibres to the brain.
- Often used during minor surgical procedures.
- Ex.: Ester-linked local anaesthetic – Procaine, Amide-linked local anaesthetic – Lidocaine
General anaesthetics:
- Cause a controlled and reversible loss of consciousness by affecting central nervous system.
- They are often used for major surgical procedures.
- Ex.: Intravenous general anaesthetics: Propofol
- Inhalational general anaesthetics: Isoflurane
![]()
Question 3.
Explain about antimicrobials.
Answer:
Beta-Lactams:
- Inhibits bacterial cell wall biosynthesis.
- Used to treat skin infections, dental infections, ear infections, respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and gonorrhoea.
- Ex.: Penicillins, ampicillin, cephalosporins.
Macrolides:
- Targets bacterial ribosomes and prevent protein production.
- Used to treat respiratory tract infections, genital, gastrointestinal tract and skin infections.
- Ex.: Erythromycin, azithromycin
Fluoroquinolones:
- Inhibits bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase.
- Used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, respiratory infections (sinusitis, pneumonia, bronchitis), pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis.
- Ex.: Ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin
Tetracyclines:
- Inhibit the bacterial protein synthesis via interaction with the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome.
- Used to treat peptic ulcer, respiratory tract infections, cholera, acne vulgaris.
- Ex.: Doxycycline, minocycline, oxytetracycline
Aminoglycosides:
- Bind to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, thus stopping bacteria from making proteins.
- Used to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria
- Ex.: Kanamycin, gentamycin, neomycin
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the steps involved in free radical polymerisation.
Answer:
When alkenes are heated with free radical initiator such as benzoyl peroxide, they undergo addition polymerisation through free radical mechanism.
1. Initiation – formation of free radical
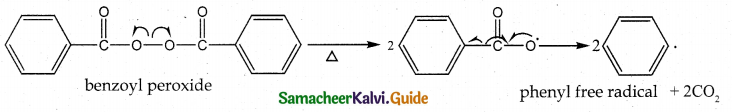
2. Propagation step
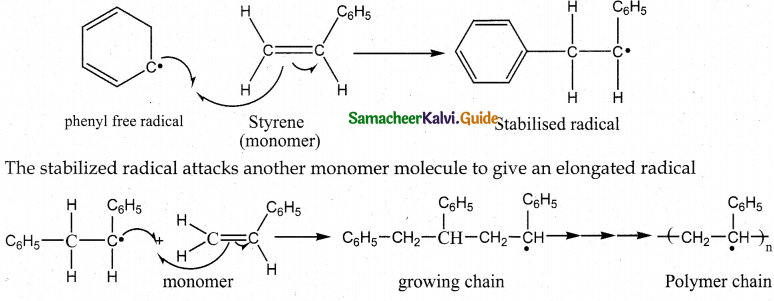
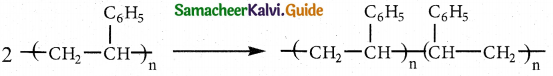
Chain growth will continue with the successive addition of several thousands of monomer units.
Termination:
The above chain reaction can be stopped by stopping the supply of monomer or by coupling of two chains or reaction with an impurity such as oxygen.
Question 5.
Write about buna rubbers.
Answer:
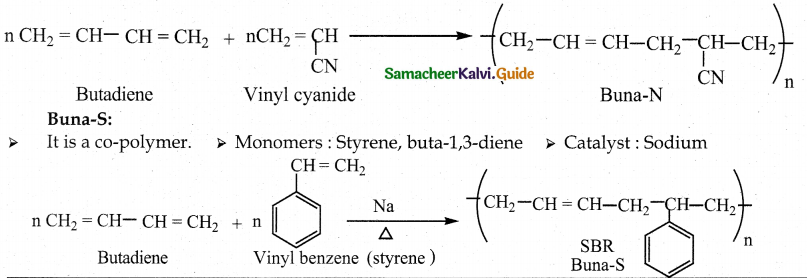
Buna-N:
- It is a co-polymer.
- Monomers : acrylonitrile, buta-1, 3-diene.
- Catalyst: Sodium
- Uses : Manufacture of hoses and tank linings.