Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Principles of Management Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 1 Principles of Management
12th Commerce Guide Principles of Management Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Management is what a……………..does?
a) Manager
b) Subordinate
c) Supervisor
d) Superior
Answer:
a) Manager
![]()
Question 2.
Management is an …………………
a) Art
b) Science
c) Art and Science
d) Art or Science
Answer:
c) Art and Science
Question 3.
Scientific management is developed by
a) Fayol
b) Taylor
c) Mayo
d) Jcob
Answer:
b) Taylor
Question 4.
Dividing the work into small tasks is known as
a) Discipline
b) Unity
c) Division of work
d) Equity
Answer:
c) Division of work
![]()
Question 5.
With a wider span, there will be …………… hierarchical levels.
a) More
b) Less
c) Multiple
d) Additional
Answer:
b) Less
II. Very short answer questions.
Question 1.
What is Management?
Answer:
Management is part and parcel of our day to day life. So management is goal oriented and it is an art of getting things done with and through others.
Question 2.
List out the management tools. (BASED)
Answer:
- Business Law
- Accounting
- Statistics
- Economics
- Data processing
![]()
Question 3.
Who is a manager?
Answer:
A manager is a dynamic and life giving element in every business. Without efficient management it cannot be possible to secure the best allocation and utilisation of human, material and financial resources.
Question 4.
State the meaning of Authority.
Answer:
“Authority” means the right of a superior given to his subordinate to get work from him.
Question 5.
What do you mean by the span of management?
Answer:
The Span of Management refers to the number of subordinates who can be managed efficiently by a superior. Simply, the manager having the group of subordinates who report him directly is called as the span of management.
III. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Define the term management.
Answer:
“Management is a multi-purpose organ that manages a business, and manages manager and manages workers and work”. – PETER F. DRUCKER.
Question 2.
Is management an Art or Science?
Answer:
Management is neither a science nor an art, but a combination of both requiring people holding managerial positions to apply the scientific management principles and displaying popular managerial skills to accomplish the organizational goals as efficiently and as quickly as possible so as to be competitive in the globalized environment of business.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate management from Administration. MA CARD
Answer:
| Basis of Difference | Management | Administration |
| 1 Meaning | An organized way of managing people and things of a business organization is called the ‘Management’ | The process of administering an organization by a group of people is known as the ‘Administration |
| 2 Authority | Middle and Lower level. | TOP level |
| 3 Concerned with | Policy implementation | Policy formulation |
| 4 Area of operation | It works under the administration | It has full control over the activities of the organization. |
| 5 Role | Executive | Decisive |
| 6 Decides | Who will do the work? and How it will be done? | What should be done? When it should be done? |
Question 4.
What are the principles of Taylor?
Answer:
- Science, not a Rule of Thumb.
- Harmony, not Discord.
- Mental Revolution
- Cooperation, not Individualism
- Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity.
Question 5.
What determines the span of management?
Answer:
The Span of Management has two implications:
- Influences the complexities of the individual manager’s job.
- Determine the shape or configuration of the organization.
- There is a wide and a narrow span of management.
![]()
IV. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain the concept of management.
Answer:
The substance of management should be identified as a process. A process is something that what a person does in the context of his individual duties and responsibilities assigned by his or her immediate higher authority.
There are twin purposes of the management process:
- Maximum productivity or profitability
- Maximum human welfare and satisfaction.
There are five parts of management as a process:
- Co-ordination of resources: The manager of an enterprise must effectively coordinate all activities and resources of the organization, namely, men, machines, materials, and money, the four M’s of management.
- Management is a Process: The manager achieves proper coordination of resources by means of the managerial functions of planning, organizing, staffing, directing (or leading and motivating), and controlling.
- Management is a Purposive Process: It is directed toward the achievement of predetermined goals or objectives. Without an objective, we have no destination to reach or a path to follow to arrive at our destination, i.e., a goal, both management, and organization must be purposive or goal-oriented.
- Management is a Social Process: It is the art of getting things done through other people.
- Management is a Cyclical Process: It represents a planning-action-control-replanning cycle, i.e., an ongoing process to attain the planned goals.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the management process in detail.
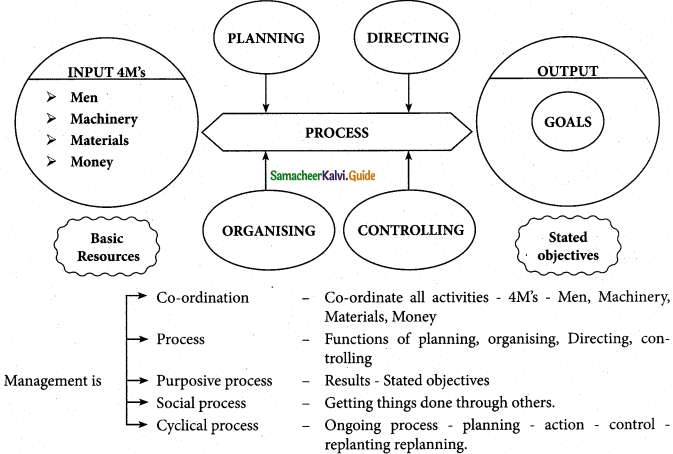
Question 3.
Describe the principles of scientific management. (S) (HM) (CD)
Answer:
Science, not Rule of Thumb:
- Rule of thumb means decisions taken by managers as per their personal judgements.
- Taylor says, even a small production activity like loading – iron sheets into box cars can be scientifically planned.
- It saves time and energy of human.
Harmony, not Discard:
- Taylor emphasized that there should be complete harmony between the workers and the management.
- If there is any conflict between the two, it will not be beneficial either for workers or for management.
Mental Revolution:
- Taylor suggested complete mental revolution on the part of both workers and Management.
- It means that there should be complete change in the attitude and out look of both workers and management.
- It becomes possible – Teamwork – Sharing profits – Division of work etc.
Co-operation, not Individualism:
- It is an extension of principle of “Harmony, not discord”.
- It lays stress on mutual co-operation between workers and the management.
- Both workers and management should realize the importance of each other.
Development of Each and Every person:
- Efficiency of any organisation also depends on the skills and capabilities of its employees to a great extent.
- Thus, providing to the workers was considered essential in order to learn the best method.
- It helps to attain the efficiency and property for both workers and management.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the principles of modern management.
Answer:
The Father of Modem Management is Mr.Henry Fayol, and according to him, there are 14 major principles of management which every manager has to practice for the success of the organization.
- Division of Work: According to this principle the whole work is divided into small tasks. This leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of labour.
- Authority and Responsibility: This is the issue of commands followed by responsibility for their consequences.
- Discipline: It is obedience, proper conduct in relation to others, respect of authority, etc. It is essential for the smooth functioning of all organizations.
- Unity of Command: This principle states that each subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only one superior.
- Unity of Direction: All related activities should be put under one group, there should be one plan of action for them, and they should be under the control of one manager.
- Subordination of Individual Interest to Mutual Interest: The management must put aside personal considerations and put company objectives firstly.
- Remuneration: Workers must be paid sufficiently as this is a chief motivation of employees and therefore greatly influences productivity.
- The Degree of Centralization: The amount of power wielded with the central management depends on company size.
- Line of Authority/Scalar Chain: This refers to the chain of superiors ranging from top management to the lowest rank.
- Order: Social order ensures the fluid operation of a company through the authoritative procedure.
- Equity: Employees must be treated kindly, and justice must be enacted to ensure a just workplace.
- Stability of Tenure of Personnel: Stability of tenure of personnel is a principle stating that in order for an organization to run smoothly, personnel (especially managerial personnel) must not frequently enter and exit the organization.
- Initiative: Using the initiative of employees can add strength and new ideas to an organization.
- Esprit de Corps/Team Spirit: This refers to the need of managers to ensure and develop morale in the Workplace; individually and communally.
12th Commerce Guide Principles of Management Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1
_______ is a global and universal concept.
(a) Management
(b) Process
(c) Art
(d) Science
Answer:
(a) Management
![]()
Question 2.
To manage is to forecast, to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control said by ……………………
a) Henry Fayol
b) Peter F. Drucker
c) Taylor
d) NOTA
Answer:
a) Henry Fayol
Question 3.
“To manage is to forecast, to plan, to organise, to command, to co-ordinate and to control.” said by _______
(a) Henry Fayol
(b) Peter F. Drucker
(c) Walker
(d) Carter
Answer:
(a) Henry Fayol
Question 4.
What should be done? and when is should be done decided by ……………
a) Management
b) Supervisor
c) Director
d) Administrator
Answer:
d) Administrator
![]()
Question 5.
Executive and governing functions are done by ……………..
a) Manager
b) Supervisor
c) Worker
d) Administrator
Answer:
a) Manager
Question 6.
The father of Modem Management is _______
(a) F.W. Taylor
(b) Henry Fayol
(c) Peter F. Drucker
(d) Louis A. Allen
Answer:
(b) Henry Fayol
Question 7.
The Authority of Top-level is ………………
a) Management
b) Administration
c) Both
d) NOTA
Answer:
b) Administration
![]()
Question 8.
One employee should receive an order from only one boss is known as ………………
a) Unity of command
b) Unity of objective
c) Unity of direction
d) Unity of strength
Answer:
a) Unity of command
Question 9.
Superiors ranging from top management to the lowest rank is called …………….
a) Responsibility
b) Authority
c) Remuneration
d) Scalar chain
Answer:
d) Scalar chain
Question 10.
With the narrow span, the hierarchical levels……………..
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Ups and downs
d) Stagnant
Answer:
b) Increases
![]()
Question 11.
Find the odd one out:
a) Harmony, Not Discord
b) Mental Revaluation
c) Cooperation, not individualization
d) Order
Answer:
d) Order
Question 12.
Find the odd one out:
a) Division of work
b) Scalar chain
c) Equity
d) Science not thum of Rule
Answer:
d) Science not thum of Rule
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
a) Business law – Management Tool
b) Specialisation – Highly qualified
c) Code of conduct – Social conscience
d) Behavioural school – Process of planning
Answer:
d) Behavioural school – Process of planning
Question 14.
Which one of the following is correctly matched?
a) Cyclical process – Ongoing process
b) Purposive process – Co-ordinate
c) Social process – Goal-oriented
d) Not Individualisation – Separation
Answer:
a) Cyclical process – Ongoing process
![]()
Question 15.
Which is the correct statement?
i) Division of work is whole work divided into small tasks.
ii) Discipline is obedience and respect for authority.
iii) Unity of direction is related activities put under many groups.
a) (i) is correct
b) (i) and (ii) are correct
c) All are correct
d) All are wrong
Answer:
b) (i) and (ii) are correct
II. Match the following.
Question 1.
Match List I with List II
| List -I |
List -II |
| i. Mental Revolution | 1 Morale in the workplace |
| ii. Scalar chain | 2 Proper conduct |
| iii. Discipline | 3 top management to the lowest rank |
| iv. Team spirit | 4 Change in attitude |
a) iv-1, iii-2, ii-3, i-4
b) iv-2, iii-1, ii-3, i-4
c) iv-3, iii-4, ii-1, i-1
d) iv-4, iii-3, ii-2, i-1
Answer:
a) iv-1, iii-2, ii-3, i-4
![]()
Question 2.
Match List I with List II
| List -I | List -II |
| i. Initiative | 1. New idea |
| ii. Social Process | 2. Key person |
| iii. Manager | 3. Done through others |
| iv. Management | 4. A multi-purpose organ |
a) i-1, ii-3, iii-2, iv-4
b) i-1, ii-2, iii-4, iv-3
c) i-1, ii-4, iii-3, iv-2
d) i-1, ii-2, iii-3, iv-4
Answer:
a) i-1, ii-3, iii-2, iv-4
III. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): line employees should recei\e orders from one superior.
Reason (R): If the receives orders from more superiors, it creates confusion and conflict,
a) both (A) and (R) are true. (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
b) both (A) and (R) are false. (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
c) Roth (A) and (R) are I rue. (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
d) (A) is true (R) is False
Answer:
a) both (A) and (R) are true. (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : All related activities should be put under one group.
Reason (R) : There should be under the control of one manager.
a) (A) is true (R) is False
b) (A) is False (R) is True
s) Both tA) and (R) are True
d) Moth (A) and iR) are False
Answer:
c) Both (A) and (R) arc True.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Equity must be treated kindly and justice.
Reason (R): Managers should be fair and partial.
a) (A) is true (R) is False
b) (A) is False (R) is True
c) t A) and (R) are I rue
d) (A) and (R’ are False
Answer:
a) (A) is True (R) is False
IV. Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is a Scalar chain or Line of Authority?
Answer:
This refers to the chain of superiors ranging from top management to the lowest rank. The principle suggests that there should be a clear line of authority from top to bottom linking all managers at all levels.
V. Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Who is a Professional Manager?
Answer:
“A professional manager is one who specializes in the work of planning, organising, leading and controlling the efforts of others and does so through the systematic use of classified knowledge, a common vocabulary, and principles and who subscribes to the standards of practice and code of ethics established by a recognized body.” – Louis A. Allen.
VI. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Formulate a new policy relating to the timing of employees.
Answer:
It has always been a struggle for people to maintain a work-life balance. Working excessive hours poses a danger to workers’ health and to their families. Earlier all the work was done manually. However, with the help of machinery and computers, in modem times certain industries don’t require as many working hours anymore. Technology has introduced new ways to increase productivity. More recently, the global trend leans toward a four-day workweek (counting one workday as eight hours).
Even the ILO standards on working time provide the framework for regulated hours of work, daily and weekly rest periods, and annual holidays. These instruments ensure high productivity while safeguarding workers’ physical and mental health. If the workers earn enough to pay for their necessities, they may opt to spend more time at home or in leisure. Countries around the globe are already experimenting and implementing shorter workweeks in varying degrees. So, in my opinion, the new policy relating to the timing of employees should be a four-day workweek.
We hope the information prevailed in this article is helpful for all the students of Class 12th. The Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 1 Principles of Management Questions and Answers And Pdf enhance your skills and score good marks in the exams. Stay tuned to get the latest information about the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 1 Principles of Management Solutions.
![]()
Question 2.
Discuss the implications of the span of management.
Answer:
Can a superior effectively manage, supervise and control how many subordinates.
It is known as “Span of Control” or “Span of Management” or “Span of Supervision”.
The span of management has two implications:
- Influences the complexities of the individual Manager’s job.
- Determine the shape or configuration of the organization.
It has two horizontal levels of span of management.
- Wider-Span
- Narrow Span
Wider-Span:
- Wider-Span-Less hierarchical levels – More subordinates – Less expensive.
- It imposes more challenges.
- It is very difficult for a superior to manage a large number of subordinates.
- In this structure, managers get reduced and remuneration saved.
Narrow Span:
- Narrow Span- more hierarchical levels – fewer subordinates – more expensive.
- With more levels of hierarchy the communication sutlers drastically.
- It takes a lot of time to reach the appropriate points and hence the actions delayed.
- In this structure, less number of subordinates under one superior requires more managers to be employed