Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Guide Pdf History Chapter 6 The Middle Ages Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Important Questions, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Solutions History Chapter 6 The Middle Ages
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science The Middle Ages Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
_______ was the old religion of Japan.
(a) Shinto
(b) Confucianism
(c) Taoism
(d) Animism
Answer:
(a) Shinto
![]()
Question 2.
_______ means great name-lord.
(a) Daimyo
(b) Shogun
(c) Fujiwara
(d) Tokugawa
Answer:
(a) Daimyo
Question 3.
The Arab General who conquered Spain was__________
(a) Tariq
(b) Alaric
(c) Saladin
(d) Mohammad the Conqueror
Answer:
(a) Tariq
Question 4.
Harun-al-Rashid was the able emperor of ____________.
(a) Abbasid dynasty
(b) umayyad dynasty
(c) Sassanid dynasty
(d) Mongol dynast
Answer:
(a) Abbasid dynasty
Question 5.
feudalism centred around _________
(a) vassalage
(b) slavery
(c) serfdom
(d) land
Answer:
(a) vassalage
II. Fill in the blanks:
- ______ were the original inhabitants of Japan.
- ______ was the original name of Japan.
- _______ was the original name of Medina.
- _______ were the barbarians posing a threat to the Chinese in the north.
- ________established Ottoman supremacy in the Balkans.
Answer:
- Aious
- yamoto
- madinat-un-nabi
- Mongols
- Mohammad II
III. Find out the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) ChengizKhan was an intolerant person in religion.
(ii) Mongols destroyed the city of Jerusalem
(iii) Crusades weakened the Ottoman Empire
(iv) Pope Gregory succeeded in making King Henry IV to abdicate the throne by means of Interdict
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (ii) is correct
(c) (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(d) (iv) is correct
Question 2.
(i) Mangu Khan was the Governor of China.
(ii) Mongol court in China impressed Marco Polo.
(iii) The leader of Red Turbans was Hung Chao.
(iv) Mongols established their rule in China in the name of Yuan dynasty
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (ii) is correct
(c) (ii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (iv) is correct
Answer:
(c) (ii) and (iv) are correct
![]()
Question 3.
(i) Boyang and Changon were built during the Sung dynasty.
(ii) Peasant uprisings led to the collapse of the Tang dynasty.
(iii) Seljuq Turks were a tribe of Tartars.
(iv) Mongols established their rule in China in the name of the Yuan dynasty
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (ii) is correct
(c) (iii) is correct
(d) (iv) is correct
Answer:
(ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Buddhism went to China from India
Reason (R): The earliest Indian inhabitants in China were the followers of Buddhism
(a) A is correct; R is wrong
(b) Both A & R are wrong
(c) Both A & R are correct
(d) A is the wrong R is irrelevant to A
Answer:
(a) A is correct; R is wrong
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The fall of Jerusalem into the hands of Seljuk Turks led to the Crusades. Reason (R): European Christian pilgrims were denied access to Jerusalem.
(a) A is correct; R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) A and R are correct
(c) A and R are wrong
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
Answer:
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
IV. Match the following:
- Red Turbans – (i) Kamakura
- Seljuk Turks – (ii) Mohammad II
- First Shogunate – (iii) City of Arabian Nights
- Baghdad – (iv) Chu Yuan Chang
- Capture of Constantinople – (v) Central Asia
Answer:
- – (iv)
- – (v)
- – (i)
- – (iii)
- – (ii)
V. Answer the following briefly:
Question 1.
The Great Wall of China.
Answer:
- The Great Wall of China was built between the 8th and 7th centuries B.C. to protect themselves from enemies of the North.
- During the Chin (Qin) Dynasty, the separate walls were connected and consequently from east to west for about the wall stretched about 5000 kilometers.
- One of the Seven Wonders of the world is the Great wall of China.
- Now it is 6,700 kilometers in length.
Question 2.
Impact of Crusades.
Answer:
- Crusades ended the feudal relations.
- Increasing demand for products of the East led to the expansion of trade.
- Venice, Genoa, and Pisa emerged as important commercial centers in the Mediterranean region
- Constantinople ceased to be the middle man in the trade between the East and the West.
- Pope and Papacy lost their prestige.
![]()
Question 3.
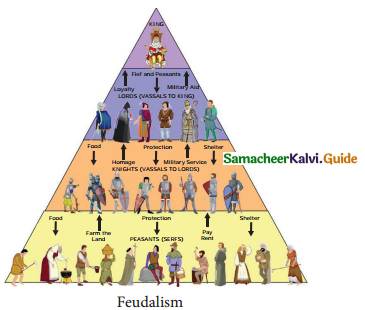
How was Feudalism organized in the Middle Ages?
Answer:
- The king was at the head of the feudal regime.
- Next to him were the great nobles, known as dukes, counts, earls.
- The relationship was one of a vassal.
- The nobles in turn had vassals of their own, dividing and distributing their fief to lesser nobles called viscounts or barons.
- Last in this order were the knights, whose fiefs could not be divided.
- At the bottom were the villeins or serfs.
Question 4.
Write about the two instruments used by the Medieval Pope to assert his authority.
Answer:
The two instruments used by the Medieval Pope to assert his authority were
(a) Excommunication
(b) Interdict.
(a) Excommunication:
- Excommunication means depriving a person of all the privileges of a Christian.
- He was denied the right to sacraments in Church.
- His or her body could not be buried in the consecrated ground.
(b) Interdict:
- Interdict means was to deny the benefits of religion to a ruler’s subject.
- It was intended to kindle their resentment against him.
VI. Answer all the questions given under each caption.
Question 1.
Shogunate in Japan
(a) Name the two Daimyo families that fought for power in Japan.
(b) Who emerged successful in the fight?
(c) What was the title given by the Emperor to the victorious?
(d) Where was the capital of the first Shogunate established?
Answer:
(a) Tara and Minamoto.
(b) Yoritomo emerged successful in the fight.
(c) In A.D 1192, the emperor gave him the high sounding title of Sei-i-tai-Shogun, which means the Barbarian-subduing-Great-General
(d) Yoritomo established his military capital at Kamakura.
![]()
Question 2.
Rule of Abbasids
(a) Who were Abbasids?
(b) What was the title assumed by Abbasid Caliph?
(c) Where did they have their new capital?
(d) In whose period was the Abbasid Empire at the height of its glory?
Answer:
(a) The branch which descended from Prophet Mohammad’s uncle Abbas were called Abbasids.
(b) Abbasid Caliph assumed the title of “The Commander of the Faithful”
(c) The capital was shifted from Damascus to Baghdad in Iraq.
(d) The Abbasid Empire was at the height of its glory during the reign of Harun-al-Rashid.
VII. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Write about crusades and its impact.
Answer:
- The Pope and the Church called upon all the Christian peoples of Europe to march to the rescue of the “holy city” (Jerusalem).
- The Crusaders had to fight against the Seljuq Turks who controlled those parts.
- The struggle between Christianity and Islam beginning in 1095 continued for nearly 200 years and is called the Crusades.
- The Crusades did not achieve the desired end.
- Jerusalem continued to remain in Ottoman hands for another 700 years.
Impact of Crusades:
- Crusades ended the feudal relations. Many of the nobles who went to East to take part in the Crusades either stayed too long a period or did not return.
- The serfs took advantage of their absence to break away from their bondage to the soil. Increasing demand for products of the East led to expansion of trade.
- Venice, Genoa and Pisa emerged as important commercial centres in the Mediterranean region.
- The elimination of powerful nobles had its influence in strengthening the monarchy in France and England.
- One notable outcome of Crusades was the loss of prestige suffered by Pope and Papacy.
![]()
Question 2.
Who were the Mongols? How did they rule China?
Answer:
- Mongols were nomads from the Steppes of Asiatic Russia.
- They were herdsmen but experts in warfare.
- Their remarkable chief, Chengiz Khan.
- In China after the Sung Dynasty , the Mongols established their rule in the name of Yuan dynasty.
- Mangu Khan became the Great Khan in 1252.
- Kublai Khan was appointed the Governor of China.
- The Mongol presence from one end of Eurasia to the other played a key role in spreading Chinese technological advances to the less developed societies in the west.
- Marco Polo, a foreigner was very much impressed seeing the Mongol court in Beijing,
- But the peasants were suffering due to poverty.
- There were revolts of religious sects and secret societies.
- Finally, the leader of “Red Turbans” Chu Yuan Chang took the Mongol capital Beijing and proclaimed himself emperor in 1369.
Activities for Students
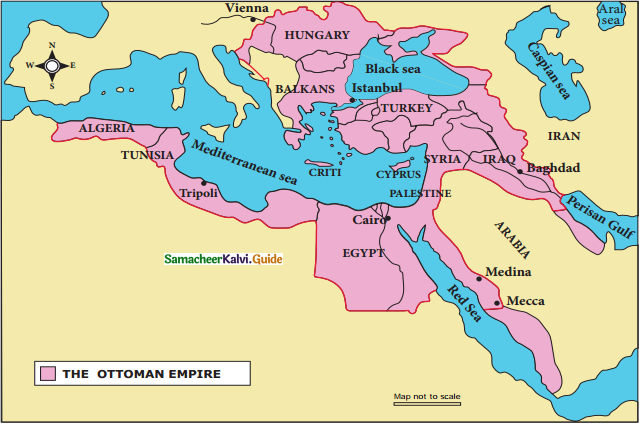
Question 1.
In an outline map of Europe, the students are to sketch the extern of Ottoman Empire at height of its glory.
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science The Middle Ages Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answers
Question 1.
The centreal or high Middle Ages witnessed ______
(a) rapid development
(b) territorial expansion
(c) urban growth
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 2.
Seljuq Turks came from ________
(a) Central America
(b) Central Asia
(c) Central Australia
(d) Central Europe
Answer:
(b) Central Asia
![]()
Question 3.
Li Yuan belong to ________ dynasty
(a) Tang
(b) Sui
(c) Sung
(d) Ming
Answer:
(a) Tang
Question 4.
Trade and industry flourished during the reign of ________ dynasty
(a) Shogun
(b) Yuan
(c) Sung
(d) Ming
Answer:
(c) Sung
Question 5.
In ceramics _____ excelled
(a) Japan
(b) Arabia
(c) Spain
(d) China
Answer:
(d) China
Question 6.
Shotuku Taishi was the leader of _________
(a) Soga
(b) Fujiwaras
(c) Daimyos
(d) Shogunate
Answer:
(a) Soga
Question 7.
Hideyoshi was a _________
(a) Noble
(b) Trader
(c) Peasant
(d) Warrior
Answer:
(c) Peasant
Question 8.
General Tang was a / an ______
(a) Chinese
(b) Japanese
(c) Roman
(d) Arab
Answer:
(d) Arab
Question 9.
After conquering Egypt, the Ottomans assumed the title of _________
(a) King
(b) Caliph
(c) Emperor
(d) Raja
Answer:
(b) Caliph
Question 10.
The theory of sacraments increased the power of the _________
(a) Commoners
(b) Emperor
(c) Nobler
(d) Clergy
Answer:
(d) Clergy
II. Find out the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) Sung dynasty was overthrown by the Seljuq Turks
(ii) China followed Japan in all walks of life.
(iii) Kamakura Shogunate was founded by a military general.
(iv) Abbasids ruled from Baghdad.
(a) (i), (ii) are correct
(b) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (iii) is correct
(d) (iv) is correct
Answer:
(b) (iii) and (iv) are correct
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Feudal System involved lords and vassals.
(ii) Seljuq Turks took over the holy city of Jerusalem.
(iii) Ummayads ruled from Damascus.
(iv) Saracenic architecture was developed by the Arabs.
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (ii), (iii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct]
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Iron and Steel industries became highly organized.
Reason (R): The quantity of iron, China produced in 1078 A.D., exceeded 114,000 tons,
(a) A is correct; R is wrong
(b) Both A & R are wrong
(c) Both A & R are correct
(d) A is wrong R is irrelevant to A
Answer:
(c) Both A & R are correct
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Many pious Christians began to resent Pope’s intrusion into state affairs.
Reason (R): Pope Innocent III forced King John to recognize England and Ireland as fiefs of the papacy.
(a) A is correct; R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) A & R are correct
(c) A & R are wrong
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
Answer:
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 5.
Statement (i): Kyoto was replaced by Tokyo as Capital.
Statement (ii): Arab physicians and surgeons earned a great reputation.
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are wrong
(c) (i) and (ii) are correct
(d) (i) is wrong, (ii) is correct
Answer:
(c) (i) and (ii) are correct
III. Fill in the blanks
- Seljuq Turks were a tribe of _______ from Central Asia
- Hung Ch’ao and his followers brought downfall to _____ empire
- Chu Yuan Chang was the leader of ______
- Japan remained in _______ for many centuries.
- During the Tang dynasty, there were constant contacts between China and ______
- Fujiwara family emperors in later years retired to _______
- The title Sei-i-tai-Shogun meant _______
- Kamakura Shogunate was followed by _______ Shogunate.
- Abu Bakr and Omar laid the foundation for an _______ Empire.
- Islam advocated simplicity and _______
- The two sects of Islam were and _______
- The arches, the pillars, and the minarets and domes represented _______ architecture.
- Umayyads were overthrown by _______
- The Arabs had a scientific spirit of _______
- Chengiz Khan was a great _______
- The Ottomans conquest Constantinople in _______
- Fief was a _______ given to someone by their lord.
- New elements like ______ and _____ were included in Chiristian theology
Answer:
- Tartars
- Tang
- Red Turbans
- isolation
- Japan
- Monasteries
- The Barbarian-subduing-Great-General
- Ashikaga
- Islamic
- Equality
- Sunnis and Shias
- Saracenic
- Abbasids
- Inquiry
- Military genius
- 1453
- Piece of land
- Theory of Priesthood and Theory of Sacraments
IV. Match the following
- Mongol court – (i) Tokyo
- Kyoto – (ii) Damascus
- Ummayads – (iii) Beijing
- Abbasids – (iv) Venice
- Commercial centres – (v) Baghdad
Answer:
- – (iii)
- – (i)
- – (ii)
- – (v)
- – (iv)
![]()
V. Answer all questions given under each heading
Question 1.
Middle Ages
(a) Which period is named as Middle Ages?
(b) What is meant by early Middle Ages?
(c) Explain the Central or high Middle Ages.
(d) What represented the later Middle Ages?
Answer:
(a) Historians call the period between the end of the Roman Empire in 476 A.D. and the capture of Constantinople by the Turks in 1453 A.D. as the Middle Ages
(b) In the early Middle Ages, Christianity, followed by Islam, began to establish themselves as dominant religions of continental Europe.
(c) The central or high Middle Ages witnessed rapid development, marked by territorial
expansion, demographic and” urban growth, and the restructuring of secular and ecclesiastical institutions.
(d) The later Middle Ages was represented by the feudal system. This was followed by a period of decline and decay.
Question 2.
Tang dynasties
(a) Name the two Capital Cities built by Tang dynasties.
(b) How were the aristocratic class counter balanced?
(c) Mention the sources of revenue.
(d) Who led a mutiny and what was the result?
Answer:
(a) Tang dynasty built the two Capital cities Boyang and Chang-on.
(b) Scholar officials, trained in Confucius Philosophy, were appointed to counterbalance the landowning aristocratic class.
(c) Mention the sources of revenue.
- Land was divided into small peasant holdings.
- As a result, the agricultural surplus went to the state as taxes.
- State monopoly of salt, and tea added to its revenues.
(d) A mutiny was led by a frontier general An Lu-shan, which led to years of turmoil. The imperial authority was very much reduced during this period.
Question 3.
Great wall of China
(a) When was the Great wall of China built?
(b) Why was it built?
(c) Mention the contribution of Chin (Qin) Dynasty towards the Great Wall of China.
(d) How long is it now?
Answer:
(a) Between 8th and 7th centuries B.C. (BCE), the warring states in China built defensive walls.
(b) It was built to protect themselves from enemies from the north.
(c) During Chin (Qin) Dynasty, the separate walls were connected and consequently the wall stretched from east to west for about 5000 kilometres. This wall, considered to be one of the wonders of the world, served to keep nomadic tribes out.
(d) Now it is 6,700 kilometres in length.
![]()
Question 4.
Sung Dynasty
(a) What sounded death knell to Tang empire?
(b) What happened to the empire?
(c) What about the achievements of the Sung Dynasty?
(d) What was the end of the Sung Dynasty?
Answer:
(a) The rebellion of hard-pressed peasantry under the leadership of Hung Ch’ao dealt a death knell to Tang empire.
(b) The empire split into five rival states, until it was reunited under the Sung Dynasty.
(c) Trade and industry flourished. Iron and steel industries became highly organized. It was a period of great prosperity to the landowning class, officials and rich merchants.
(d) The peasants that suffer alone to poverty. Before any internal crisis could develop, there were two external invasions from the north that ended the Sung dynasty.
Question 5.
Yuan Dynasty
(a) Who formed the Yuan Dynasty?
(b) Who was Mangu Khan?
(c) Who was appointed as the Governor of China?
(d) Who captured the Mangoi Capital in 1369?
Answer:
(a) The Mongols established their rule in China with the name of Yuan Dynasty.
(b) Mangu Khan became the Great Khan in 1252.
(c) Kublai Khan was appointed as Governor of China.
(d) The leader of “Red Turbans” Chu Yuan Chang took the Mongol capital Beijing and proclaimed himself emperor in 1369.
![]()
Question 6.
Kamakura Shogunate
(a) Who were called Kamakura Shogunate?
(b) Who were samurai?
(c) What was the end of the Kamakura Shogunate?
(d) Name the new line of Shogunate which came into power.
Answer:
(a) Yoritomo established his military capital at Kamakura. Therefore, the first Shogunate was called the Kamakura Shogunate.
(b) The government was a feudal military Shogunate government administered by samurai or warriors.
(c) The decline of the ruling dynasty started and in 1338 A.D. the Kamakura Shogunate ended.
(d) A new line of Shogunate canie into power was Ashikaga Shogunate that lasted for 235 years.
Question 7.
Islam
(a) How did Islam have a great appeal to the people of the world?
(b) Explain the term Hijrat?
(c) Who laid the foundation for Islamic empire?
(d) What happened to the city of Jerusalem?
Answer:
(a) Islam gave a message of brotherhood. Mohammad laid stress on the equality of all those who were Muslims. This message of equality and brotherhood had great appeal not only for the Arabs but to people in other parts of the world.
(b) When faced with persecution in his place of birth, Mohammad and his followers moved to the city of Yethrib (Medina). The flight of Mohammad from Mecca in 622 AD (CE) is called Hijrat in Arabic.
(c) Abu Bakr and Omar who succeeded Prophet Mohammad as Khalif or Caliph laid the foundation for an Islamic Empire.
(d) Jerusalem, the holy city of Jews and Christians, was won by the Arabs.
Question 8.
Umayyad dynasty
(a) How long did the Umayyad rule?
(b) Name their Capital.
(c) What type of new achievement did the Umayyad introduced ?
(d) By whom were the Umayyad over thrown?
Answer:
(a) Umayyads ruled for about 100 years.
(b) Damascus was their capital.
(c) They developed a new style of architecture known as Saracenic architecture. The arches, the pillars, and the minarets and domes came to India later and blended with Indian ideas.
(d) Umayyads were thrown by Abbasids.
Question 9.
Crusades
(a) What is meant by Crusades?
(b) What resulted in Crusades?
(c) How long was Jerusalem in Ottoman hands?
(d) What was the end of Abbasid Empire?
Answer:
(a) The struggle between Christianity and Islam beginning in 1095 continued for nearly 200 years and is called the Crusades.
(b) The Christian pilgrims to the holy city of Jerusalem were put to a lot of hardships by the Turks. This resulted in Crusades.
(c) Jerusalem continued to remain in Ottoman hands for another 700 years.
(d) The destruction of Baghdad in 1258 A.D. by the Mongols, put an end to the Abbasid Empire.
Question 10.
Feudalism
(a) Wo was the head of the feudal regime?
(b) What is meant by fief?
(c) Who formed the socio-political structure?
(d) What was the role played by the merchants and artisans?
Answer:
(a) The king was at the head of the feudal regime.
(b) Fief was a piece of land given to someone by their lord, to whom they had a duty to provide particular services in return.
(c) The Bishops, Abbots and Cardinals and the Church came under this socio-political structure.
(d) The merchants and artisans formed guilds and groups. In course of time they became wealthy enough to defy even the nobles and the kings. This development led to the end of feudal system.
![]()
Question 11.
The Huns
(a) What happened to Europe after the collapse of Roman empire?
(b) Who involved North-East Asia?
(c) Mention the names of two well known Hun rulers in India?
(d) Who ended the rule of the Huns in India?
Answer:
(a) Europe fragmented into multiple small Germanic kingdoms after the collapse of Roman Empire.
(b) The Huns (white), a fierce and warlike people from Central Asia, invaded Northeast India.
(c) Toramana and Mihirakula were the two well known Hun rulers in India.
(d) Yasodharman of Malwa is credited to have ended the rule of Huns in India around 528 A.D.
Question 12.
The Chalukyas
(a) When did the Chalukyas kingdom exist?
(b) Write about Khusrau II?
(c) Name the capital of the Chalukya kingdom.
(d) What is remarked by Hiuen Tsang, the Chinese traveller, about the Chalukyas?
Answer:
(a) The Chalukya kingdom existed contemporaneously with the rule of Sassanid dynasty in
Persia.
(b) Khusrau II, the last great king of Sassanid dynasty had a close relationship with the Tang dynasty in China, and the Chalukya ruler Pulakesin II. They exchanged ambassadors.
(c) Badami was their capital.
(d) According to Hiuen Tsang, ‘they are warlike and proud-spirited, grateful for favours and revengeful for wrongs’
VI. Answer the following briefly:
Question 1.
Iron and Steel industries became highly organised in China – Prove.
Answer:
- Iron and Steel industries became highly organised.
- The quantity of iron China produced in 1078 A.D. exceeded 114,000 tons (England produced only 68,000 tons even in 1788).
- China excelled in ceramics and porcelain-making.
- This technique was not known to Europe for another 700 years.
- Gun powder was in use by 1044.
Question 2.
What was the impact of the Ming empire on China?
Answer:
- The Ming Empire, which replaced the Mongol empire, consciously discouraged industry and foreign trade in order to concentrate on agriculture.
- This resulted in China lagging’behind in the 16th century. Other parts of Eurasia, building on the techniques of the Chinese, began to march ahead.
Question 3.
How did Japan get its name?
Answer:
- Japan’s name was given by a Chinese Emperor.
- In a message sent by the Chinese Emperor, the Emperor of Japan was addressed as Tai- Nyih-Pung-Kok, meaning Great Sun-Rise-Kingdom.
- The Japanese thought that this sounded better than Yamato.
- So they began calling their country “Dai Nippon”- the land of the Rising Sun.
- Nippon became Japan.
Question 4.
Who were called Saracens?
Answer:
- The Arabs easily overran many regions.
- Led by the General Tariq, the Arabs, after conquering Morocco and Africa, crossed into Europe.
- They took Spain and ruled for many hundreds of years.
- The Arabs, until then largely nomads from the deserts, became the rulers of a mighty empire.
- They were called Saracens.
Question 5.
What is mentioned by Nehru about Baghdad in his “Glimpses of World History” ?
Answer:
- Baghdad- a city known as the city of Arabian Nights, ‘was a vast city of palaces and public offices and schools and colleges, and great shops and parks and gardens.
- The merchants carried on a vast trade with the East and West.
- Visitors came to Baghdad from all over the world, especially learned men and students and artists.
Question 6.
Who were Mongol?
Answer:
- Mongols were nomads.
- They came into Europe from the steppers of Asiatic Russia.
- They were herdsmen.
- They were experts in warfare.
- They remarkable leader was Chengiz Khan.
![]()
Question 7.
Write about Chengiz Khan.
Answer:
- Mongols’ remarkable leader was Chengiz Khan.
- He was a great military genius.
- His religion was Shamanism, a worship of the “Everlasting Blue Sky”.
- Mongols’ hold over Russia for about 300 years made Russia technologically backward from the rest of Europe until the end of Middle Ages.
Question 8.
How was Ottoman supremacy established?
Answer:
- When the Seljuq Turks weakened, the Ottomans extended their power.
- They captured Bulgaria and Serbia, and made Adrianople their capital.
- The conquest of Constantinople in 1453 A.D. by Mohammad II, helped establish Ottoman supremacy in the Balkans, Black Sea and the Middle East.
- After conquering Egypt, they assumed the title of Caliph. They became a major player in the international power politics of the day.
Question 9.
During the later Middle Ages what developments did Christianity undergo?
Answer:
- Christianity underwent many significant developments during the later Middle Ages.
- The most important were in matters of doctrine and religious practices.
- New elements were included in Christian theology like theory of priesthood and the theory
of sacraments. - Excommunication and Interdict were the two instruments used against those who defied the Church.
VII. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Write about Feudalism.
Answer:
- Feudalism was bom out of chaos and disorder in the society.
- Under Feudalism the king was the head of the feudal regime.
- Immediately after him were the great nobles, known as dukes, counts, earls.
- The relationship was one of a vassal.
- The nobles in turn had vassals of their own, dividing and distributing their fief to lesser nobles called viscounts or barons.
- Last in this order were the knights, whose fiefs cannot be divided.
- At the bottom were the villeins or serfs.
- In the feudal system which centred around vassalage, there was no idea of equality or freedom.
- There were only rights and obligations.
- The Bishops, Abbots and Cardinals and the Church came under this socio-political structure.
- The nobility and the clergy did not do any physical work only peasants and artisans were taxed.
- They new class traders formed guilds, became wealthy enough to defy even the nobles and the kings.
- This development led to the end of Feudalism.