TN State Board 12th Computer Applications Important Questions Chapter 17 E-Commerce Security Systems
Question 1.
What is security in E-Commerce?
Answer:
- Security has become the critical factor and core issue in any emerging E-business.
- E-Commerce security is a set of protocols that safely guide E-Commerce transactions through the Internet.
Question 2.
Define Viruses.
Answer:
Viruses cause harm to the computers. Some viruses destroy all the information stored in a computer and cause huge loss of revenue and time.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Tampering in E-Commerce?
Answer:
- E-Commerce has the problem of the authenticity and integrity -f business information.
- When hackers grasp the data transmitted on the network, there 7 destroying the authenticity and integrity- of the data.
Question 4.
What is DDo5 Attacks?
Answer:
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks is a process of taking down an E-Commerce site by sending continuous overwhelming request to its server.
Question 5.
What is Cyber squatting?
Answer:
- Cyber squatting is the illegal practice of registering an Internet domain name.
- Cyber squatters also involve in trading on the reputation and goodwill of such third parties by inducing a customer to believe that it is an official web page.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Typopiracy?
Answer:
Typopiracy is a variant of cyber squatting. Some fake websites try to take advantage of users common typographical errors in typing website address and direct users to a different website.
Question 7.
What is Hacking?
Answer:
Hacking refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. That is to say breaking security to gain access to a website illegally and intercept confidential information.
Question 8.
What is Ransomware?
Answer:
Ransomware is a type of Malware that usually encrypt all the files in a targets computer.
![]()
Question 9.
What is Encryption technology?
Answer:
- Encryption technology is an effective information security protection.
- It is defined as converting a plain text into meaningless cipher text using encryption algorithm thus ensuring the confidentiality of the data.
Question 10.
What are the types of Encryption technology?
Answer:
There are two types of Encryption Technology, they are:
- Symmetric key encryption system and
- Asymmetric key encryption system
Question 11.
What is DES?
Answer:
- DES (Data Encryption Standard) is a symmetric key data encryption method.
- DES is the typical block algorithm that takes a string of bits of clear text with a fixed length.
![]()
Question 12.
What is Asymmetric encryption?
Answer:
- Asymmetric encryption also called as RSA (Rivest – Shamir – Adleman) algorithm.
- Its uses public-key authentication and digital signatures.
Question 13.
What is a Public-key encryption method?
Answer:
A Public-key encryption method is a method for converting a plain text with a public key into a cipher text from which the plain text can be retrieved with a private key.
Question 14.
What is the main role of security certification?
Answer:
The main role of security certification is to ensure Authentication, Integrity and Non-repudiation. This can be achieved through digital signatures and digital certificates.
![]()
Question 15.
Define Digital Certificates.
Answer:
A digital certificate is an electronic document used to prove the ownership of a public key. This certificates includes the information about the sender’s identity, digital signature and a public key.
Question 16.
What is the X.509 system?
Answer:
- The X.509 system is a centralized system in which the authenticity of the key is guaranted by the hierarchy of certification authorities.
- X.509 is currently World Wide accepted certification technology.
Question 17.
Who are licensed Certifying Authority (CA) in digital certificate?
Answer:
- The digital certificate are being issued by a licensed Certifying Authority (CA).
- NIC, Safe script, TCS, MTNL, e-Mudhra are some of the authorized Certifying Authorities under Government of India.
![]()
Question 18.
What is PKI?
Answer:
- Digital signatures use a standard, World Wide accepted format, called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
- PKI to provide the highest levels of security and universal acceptance.
Question 19.
What is use of Digital signatures?
Answer:
Digital signatures are widely used for avoiding forging or tampering of important documents such as financial documents or Credit Card Data.
Question 20.
What is a Security Token?
Answer:
A security token is a hardware component that are used to identify and authenticate users.
Question 21.
What are security authentication protocols?
Answer:
There are two kinds of security authentication protocols widely used in E-Commerce. They are:
- Secure Electronic Transaction (SET), and
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
![]()
Question 22.
What is the major participants of SET purchase?
Answer:
The SET purchase involves three major participants,
- The customer
- The seller and
- The payment gateway
Question 23.
Write the guarantees of SET Protocol.
Answer:
- The SET Protocol guarantees the security of online shopping using credit cards on the open network.
- It has the advantages of ensuring the integrity of transaction data and the non-repudiation of transactions.
Question 24.
Define Secure Sockets Layers.
Answer:
- The most common cryptographic protocol is Secure Sockets Layers (SSL).
- SSL is a hybrid encryption protocol for securing transaction over the Internet.
![]()
Question 25.
Who was developed by SSL Standard?
Answer:
The SSL standard was developed by Netscape in Collaboration with Master Card, Bank of America, MCI and Silicon Graphics.
Question 26.
What is the principle of Secure Socket Layers?
Answer:
The Secure Socket Layers (SSL) principle is to establish a secure communication channel between a client and a server after an authentication step.
Question 27.
What is 3-D Secure?
Answer:
- 3-D Secure is a Secure Payment Protocol on the Internet.
- It was developed by visa to increase the level of transaction security, and ft has been adapted by Master Card.
![]()
Question 28.
What is the basic concept of XML based protocol?
Answer:
The basic concept ofXML based protocol is to link the financial authorization process with an online authentication system.
Question 29.
Write the types of 3-D Secure authentication model.
Answer:
The authentication model comprise three domains which are:
- The Acquirer Domain
- The Issuer Domain
- The interoperability Domain
Question 30.
Write the types of payment frauds.
Answer:
The different types of payment frauds are:
- Friendly Fraud – When customer demands false reclaim or refund.
- Clean Fraud – When a stolen credit card is used to make a purchase.
- Triangulation fraud – Fake online shops offering cheapest price and collect credit card data.
![]()
Question 31.
Write a note on Malicious code threats.
Answer:
- An E-Commerce site, there are multiple vulnerable areas that can serve as an intrusion point for a hac
- Using Malware, cross site scripting or SQL Injection, an attracker will extract the credit card information and sell the acquired data on black markets.
- Fraud is then committed to extract the greatest value possible through E-Commerce transactions or ATM withdrawals etc.,
Question 32.
Write the key features of SET system.
Answer:
SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) system incorporates the following key features:
- Using public key encryption and private key encryption ensure data confidentiality.
- Use information digest technology to ensure the integrity of information.
- Dual signature technology to secure the identity of both parties in the transaction.
![]()
Question 33.
Explain the types of E-Commerce Threats.
Answer:
E-Commerce business would face the following specific threats. Information Leakage: The leakage of trade secrets in E-Commerce in two types.
- The content of the transaction between the vendor and customer is stolen by the third party.
- The documents provided by the merchant to the customer or vice versa are illegally used by the another.
Tampering:
E-Commerce has the problem of the authenticity and integrity of business information. When hackers grasp the data transmitted on the network, thereby destroying the authenticity and integrity of the data.
Payment frauds:
Payment frauds have subsets like Friendly fraud, clean fraud, Triangulation fraud etc.,
Malicious code threats:
Within an E-Commerce site, there are multiple vulnerable areas that can serve as an intrusion point for a hacker to gain payment and user information. Using malware, Cross Site Scripting or SQL Injection, an attacker will extract the credit card information and sell the acquired data on black markets.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks:
It is a process of taking down an E-Commerce site by sending continuous overwhelming request to its server. DDoS attacks is also called as network flooding.
Cyber Squatting:
Cybersquatting is the illegal practice of registering an Internet domain name. Cyber squatters also involve in trading on the reputation and goodwill of such third parties by inducing a customer to believe that it is an official web page.
Typopiracy:
Typopiracy is a variant of Cyber Squatting. Some fake websites try to take advantage of users’ common typographical errors in typing a website address and direct users to a different website.
![]()
Question 34.
Write the steps difference between Symmetric key Encryption and Asymmetric key Encryption.
Answer:
| Symmetric Key Encryption | Asymmetric Key Encryption |
| Same key is used for both encryption and decryption. | Different keys are used for encryption and decryption |
| Speed of encryption or decryption is very fast. | Speed of encryption or decryption is comparatively slow. |
| Plain text and cipher text are of same size. | The size of cipher text is always greater than plain text. |
| Algorithms like DES, AES, RC4 uses symmetric key encryption. | Algorithms like RSA, ECC, DSA use asymmetric key encryption. |
| Provides confidentiality. | Provides confidentiality, authenticity and non repudiation. |
| The number of key used grows exponentially with the number of users. | The number of key used grows linearly with the number of users. |
![]()
Question 35.
Write about information leakage in E-Commerce.
Answer:
The leakage of trade secrets in E-Commerce mainly two aspects:
(i) The content of the transaction between the vendor and customer is stolen by the third party.
(ii) The documents provided by the merchant to the customer or viceversa are illegally used by another.
This intercepting and stealing of Online documents is called information leakage.
Question 36.
Write a short note on typopiracy.
Answer:
Typopiracy is a variant of cyber squatting. Some fake websites try to take advantage of users common typographical errors in typing a website address and d: eei users to a different website.
Question 37.
Define non-repudiation.
Answer:
- Non-repudiation refers to a situation where a statements author cannot successfully dispute its authorship or the validity of an associated contract.
- Non-repudiation that prevention against violation agreement after the deal.
![]()
Question 38.
List the different types of security technologies in E-Commerce.
Answer:
The security technologies in E-Commerce transactions are classified into:
- Encryption technology
- Authentication technology
- Authentication protocols
Question 39.
Write about digital signature.
Answer:
Digital Signature is a mechanism that is used to verify that a particular digital document, message or transaction is authentic.
Question 40.
Write a note on certification authorities (CA).
Answer:
- Digital certificates function is similar to the function of identification cards such as passports and driving licenses.
- Digital certificates are issued by recognized Certification Authorities (CA).
- When someone requests a digital certificate, the authority verifies the identity of the requester, and if the requester fulfills all requirements, the authority issues it.
- When the sender uses a certificate to sign a document digitally, receiver can trust the digital signature.
![]()
Question 41.
List some E-Commerce Security Threats.
Answer:
Information Leakage:
The intercepting and stealing of online document is called information leakage.
Tampering:
E-Commerce has the problem of the authenticity and integrity of business information.
Payment frauds:
Payment frauds have subsets like friendly fraud, clean fraud, triangulation fraud etc.,
Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDoS):
This attack will be conducted from numerous unidentified computers using botnet.
Cyber Squatting:
Cyber squatting is the illegal practice of registering an Internet domain name.
Question 42.
Differentiate asymmetric and symmetric algorithms.
Answer:
| Asymmetric | Symmetric |
| Different keys are used for encryption and decryption. | Same key is used for both encryption and decryption |
| Speed of encryption or decryption is comparatively slow. | Speed of encryption or decryption is very fast. |
| Algorithms like RSA, ECC, DSA use asymmetric key encryption. | Algorithms like DES, AES, RC4 uses symmetric key encryption. |
![]()
Question 43.
Write a note on PGP.
Answer:
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) is developed by Phil Zimmermann in 1991.
- It is a decentralized encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication.
- PGP encryption uses a serial combination of bashing, data compression, symmetric – key cryptography and asymmetric – key cryptography and works on the concept of ‘Web of Trust’.
Question 44.
Explain 3D secure payment protocols.
Answer:
- 3-D secure is a secure payment protocol on the Internet.
- It was developed by visa to increase the level of transaction security, and it has been adapted by Master card.
- It gives a better authentication of the holder of the Payment Card, during purchases made on websites.
- The basic concept of this protocol is to link the financial authorization process with an online authentication system.
![]()
Question 45.
Write about dimensions of E-Commerce Security.
Answer:
The dimensions of E – Commerce security elements are:
- Authenticity – Conforming genuineness of data shared.
- Availability – Prevention against data delay or removal.
- Completeness – Unification of all business information.
- Confidentiality – Protecting data against unauthorized disclosure.
- Effectiveness – Effective handling of hardware, software and data.
- Integrity – Prevention of the data being unaltered or modified.
- Non – repudiation – Prevention against violation agreement after the deal.
- Privacy – Prevention of customers personal data being used by others.
- Reliability – Providing a reliable identification of the individuals or businesses.
- Review ability – Capability of monitoring activities to audit and track the operations.
Question 46.
Explain encryption technology.
Answer:
Encryption technology is an effective information security protection.
- It is defined as converting a plain text into meaningless cipher text using encryption algorithm thus ensuring the= confidentiality of the data.
- The encryption or decryption process use a key to encrypt or decrypt the data.
- Now, two encryption technologies are widely used. They are symmetric key encryption system and an asymmetric key encryption system.
- The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric key data encryption method.
- DES is the typical block algorithm that takes a string of bits of clear’ text with a fixed length and through a series of complicated operations, transforms it into another encrypted text of the same length.
- Asymmetric encryption also called as RSA (Rivest – Shamir – Adleman) algorithm.
- RSA uses public – key authentication and digital signatures.
![]()
Question 47.
Differentiate digital signatures and digital certificates.
Answer:
| Digital Signature |
Digital Certificate |
| A digital signature is a mechanism that is used to verify that a particular digital document, message or transaction is authentic. | A digital certificate is a computer file which officially approves the relation between the holder of the certificate and a particular public key. |
| These are used to verify the trustworthiness of the data being sent. | These are used to verify the trustworthiness of the sender. |
| This is to ensure that a data remain secure from the point. | It binds a digital signature to an entity. |
| It provides authentication, non repudiation and integrity. | It provides authentication and security. |
| A digital signature is created using a Digital Signature Standard (DSS). | A digital certificate works on the principles of public key cryptography standards (PKCS). |
| The document is encrypted at the sending end and decrypted at the receiving end using asymmetric keys. | A digital certificate consist of certificate’s owner name and public key, expiration date, a Certificate Authority’s name , a Certificate Authority’s digital signature. |
![]()
Question 48.
Define Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) and its features.
Answer:
- Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a security protocol for electronic payments with credit cards, in particular via the Internet.
- SET was developed in 1996 by VISA and Master Card, with the participation of GTE, IBM, Microsoft and Netscape.
- SET is based on the use of digital signatures and the encryption of transmitted data with asymmetric and symmetric encryption algorithms.
- SET system incorporates the following key features.
(a) Using public key encryption and private key encryption ensure data confidentiality.
(b) Use information digest technology to ensure the integrity of information.
(c) Dual signature technology to ensure the identity of both parties in • the transaction.
Question 49.
Briefly explain SSL.
Answer:
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layers) is the most common cryptographic protocol..
- SSL is a hybrid encryption protocol for securing transactions over the Internet.
- The SSL Standard was developed by Netscape in collaboration with Master card, Bank of America, MCI and Silicon Graphics.
- The SSL system acts as an additional layer, to ensure the security of data, located between the application layer and the transport layer in TCP.
- All browsers in the market support SSL and most of the secure communications are proceeded through this protocol.
- SSL works completely hidden for the user, who does not have to intervene in the protocol.
- The user has to do is make sure the URL starts with http:// instead of http:// where S-means secured.
![]()
Question 50.
Identifying the security protocols used in the particular payment gateway.
• Create a chart for a payment process.
Answer:
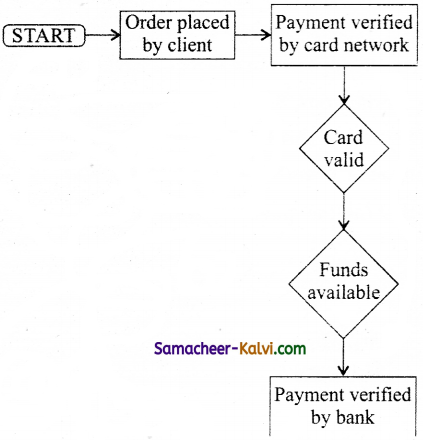
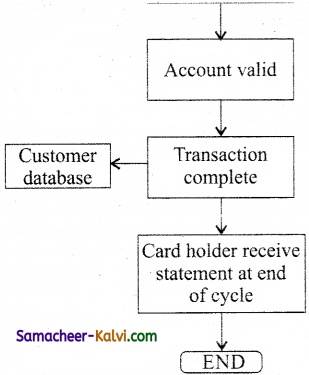
![]()
Question 51.
Describe the security technology used in that payment method.
Answer:
To secure online payments:
(i) SSL Protocol:
The SSL protocol in our website shows website is secure.
(ii) PCI Compliance:
PCI Compliance helps improve security. They decrease the risk of payment and data fraud.
(iii) Tokenization:
It is the technology that makes it easier to improve payment security and provide payment process without vulnerabilities.
(iv) 3D Secure:
It helps prevent fraud in online credit and debit card transactions. It will be extra protection with many benefits.
(v) Address Verification Service:
It requires customers to provide the billing address associated with their credit card.
• Repeat the process for few other payment process.
Mobile E-Wallet (online) payment process:
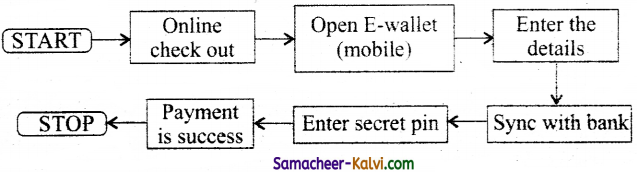
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which transaction based on network resources have been accepted by the public?
(a) E-Commerce
(b) E-Business
(c) E-sales
(d) Commerce
Answer:
(a) E-Commerce
Question 2.
Which security threats not only result in loss of revenue but also in reputation?
(a) E-Commerce
(b) E-Business
(c) E-sales
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) E-Business
Question 3.
Which security threats can be accidental or intentional?
(a) E-Commerce
(b) E-Business
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) E-Commerce
![]()
Question 4.
Which is cause harm to the computers there by harms the efficient and smooth functioning of E-commerce?
(a) Frauds
(b) Cyber squatting
(c) Viruses
(d) Phishing
Answer:
(c) Viruses
Question 5.
Which has turned to be the best medium for the spread of viruses?
(a) Network
(b) Internet
(c) E-Business
(d) E-Commerce
Answer:
(b) Internet
Question 6.
The intercepting and stealing of online document is called
(a) Information Leakage
(b) Tampering
(c) Payment frauds
(d) Cyber squatting
Answer:
(a) Information Leakage
![]()
Question 7.
Which is a E-Commerce thread in which a target is contacted by e-mail, telephone or text message?
(a) Frauds
(b) Cyber squatting
(c) Viruses
(d) Phishing
Answer:
(d) Phishing
Question 8.
Which will extract the credit card information and sell the acquired data on black markets?
(a) Malware
(b) SQL
(c) Attacker
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 9.
Which is committed to extract the greatest value possible through ATM withdrawals?
(a) Fraud
(b) Malware
(c) SQL
(d) Attacker
Answer:
(a) Fraud
![]()
Question 10.
What is a process of taking down an E-Commerce site by sending continuous overwhelming request to its server?
(a) DDoS Attack
(b) Fraud
(c) Tampering
(d) Malware
Answer:
(a) DDoS Attack
Question 11.
Which attack will be conducted from numerous unidentified computers using botnet?
(a) DDoS
(b) Fraud
(c) Tampering
(d) Malware
Answer:
(a) DDoS
Question 12.
Which attacks is also called as network flooding?
(a) DDoS
(b) Fraud
(c) Tampering
(d) Malware
Answer:
(a) DDoS
![]()
Question 13.
Which is the illegal practice of registering an Internet domain name?
(a) Tampering
(b) Frauds
(c) Threats
(d) Cyber squatting
Answer:
(d) Cyber squatting
Question 14.
Which is also involve in trading on the reputation and goodwill of such third parties?
(a) Tampering
(b) Cyber squatters
(c) Frauds
(d) Threats
Answer:
(b) Cyber squatters
Question 15.
Which is a variant of cyber squatting?
(a) Tampering
(b) Cyber squatters
(c) Frauds
(d) Typopiracy
Answer:
(d) Typopiracy
![]()
Question 16.
Which refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer?
(a) Hacking
(b) Viruses
(c) Threats
(d) Malware
Answer:
(a) Hacking
Question 17.
Which is conforming genuineness of data shared in E-Commerce security?
(a) Authenticity
(b) Availability
(c) Completeness
(d) Confidentiality
Answer:
(a) Authenticity
Question 18.
Which is the prevention against data delay or removal?
(a) Authenticity
(b) Availability
(c) Completeness
(d) Confidentiality
Answer:
(b) Availability
![]()
Question 19.
Which is the unification of all business information in E-Commerce security0
(a) Authenticity
(b) Availability
(c) Completeness
(d) Confidentiality
Answer:
(c) Completeness
Question 20.
Which is protecting data against unauthorized disciosura in E-Comrr-“-ce security?
(a) Authenticity
(b) Availability
(c) Completeness
(d) Confidentiality
Answer:
(d) Confidentiality
Question 21.
Which is the effective handling of hardware, software and data in E-Commerce security?
(a) Effectiveness
(b) Integrity
(c) Non-repudiation
(d) Privacy
Answer:
(a) Effectiveness
![]()
Question 22.
Which is the prevention of the data being unaltered or modified in E-Commerce security?
(a) Effectiveness
(b) Integrity
(c) Non-repudiation
(d) Privacy
Answer:
(b) Integrity
Question 23.
Which is the prevention against violation agreement after the deal in E-Commerce security?
(a) Effectiveness
(b) Integrity
(c) Non-repudiation
(d) Privacy
Answer:
(c) Non-repudiation
Question 24.
Which is the prevention of customers’ personal data being used by others in E-Commerce security?
(a) Effectiveness
(b) Integrity
(c) Non-repudiation
(d) Privacy
Answer:
(d) Privacy
![]()
Question 25.
Which is providing a reliable identification of the businesses in E-Commerce security?
(a) Integrity
(b) Privacy
(c) Reliability
(d) Review ability
Answer:
(c) Reliability
Question 26.
Which is the capability of monitoring activities to audit and track the operations in E-Commerce security?
(a) Integrity
(b) Privacy
(c) Reliability
(d) Review ability
Answer:
(d) Review ability
Question 27.
Which is a type of Malware that usually encrypt ail the files in a target’s “computer?
(a) Ransomware
(b) Virus
(c) Malware
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Ransomware
![]()
Question 28.
How many types of E-Commerce transactions are classified?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 29.
Which is the technology an effective information security protection?
(a) Encryption
(b) Authentication
(c) Authentication protocols
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Encryption
Question 30.
At present, How many types of encryption technologies used?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 31.
Which is a symmetric key data encryption method?
(a) Data Encryption Standard (DES)
(b) Encryption
(c) Authentication
(d) Protocol
Answer:
(a) Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Question 32.
Expansion of FIPS:
(a) First Information Processing Standard
(b) Federal Information Processing Standard
(c) File Information Processing Standard
(d) Format Information Processing Standard
Answer:
(b) Federal Information Processing Standard
Question 33.
How many bits are apparently used in Data Encryption Standard (DES) key?
(a) 64
(b) 32
(c) 16
(d) 128
Answer:
(a) 64
![]()
Question 34.
Which method is a method for converting a plain text with a public key?
(a) Public key Encryption
(b) Symmetric Encryption
(c) Asymmetric Encryption
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Public key Encryption
Question 35.
Which can be achieved through digital signatures and digital certificates?
(a) Authentication
(b) Integrity
(c) Non-repudiation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 36.
Which key is same key is used for both encryption and decryption?
(a) Symmetric key
(b) Asymmetric key
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(a) Symmetric key
![]()
Question 37.
Which is different keys are used for encryption and decryption?
(a) Symmetric key
(b) Asymmetric key
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) Asymmetric key
Question 38.
Which is also known as Public Key Certificate?
(a) Digital certificates
(b) Digital signature
(c) Digital banner
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Digital certificates
Question 39.
Which is an electronic document used to prove the ownership of a public key?
(a) Digital cash
(b) Digital Signature
(c) Digital Certificates
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Digital Certificates
![]()
Question 40.
Which function is similar to the functions of identification cards such as driving licenses?
(a) Digital cash
(b) Digital Signature
(c) Digital Certificates
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Digital Certificates
Question 41.
Digital certificates are issued by recognized
(a) Certification Authorities (CA)
(b) System Analyst
(c) Special Officer (SO)
(d) Digital Department
Answer:
(a) Certification Authorities (CA)
Question 42.
Which is a mechanism that is used to verify that a particular digital document?
(a) Digital signature
(b) Digital certificates
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(a) Digital signature
![]()
Question 43.
Which format to provide the highest levels of security and universal acceptance?
(a) Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
(b) Private key
(c) Common key
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Question 44.
Which are widely used for avoiding forging or tampering of important documents?
(a) Digital certificates
(b) Digital signatures
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) Digital signatures
Question 45.
Which is used as dual signatures to ensure the privacy?
(a) PKI
(b) GTE
(c) SET
(d) SSL
Answer:
(c) SET
![]()
Question 46.
The most common cryptographic protocol is
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
(b) Transport Layer Security (TLS)
(c) Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
(d) Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
Answer:
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
Question 47.
Which is a hybrid encryption protocol for securing transactions over the Internet?
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
(b) Transport Layer Security (TLS)
(c) Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
(d) Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
Answer:
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
Question 48.
Which system acts as an additional layer, to ensure the security of data?
(a) PGP
(b) SET
(c) TLS
(d) SSL
Answer:
(d) SSL
![]()
Question 49.
Which was renamed as Transport Layer Security (TLS) in 2001?
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
(b) Transport Layer Security (TLS)
(c) Secure Electronic Transactions (SET)
(d) Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
Answer:
(a) Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
Question 50.
Which is a secure payment protocol on the Internet?
(a) 2-D secure
(b) 3-D secure
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) 3-D secure
Question 51.
Which was developed by visa to increase the level of transaction security?
(a) 2-D secure
(b) 3-D secure
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) 3-D secure
![]()
Question 52.
Which is an additional security layer for online credit or debit card transactions?
(a) 2-D secure
(b) 3-D secure
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) 3-D secure
Question 53.
Which is the encrypted data usually the output of an encryption algorithm?
(a) 3-D secure
(b) Cipher text
(c) Decipher
(d) Cracker
Answer:
(b) Cipher text
Question 54.
A person who breaks computer network’s security maliciously to gain access to critical data ________
(a) Cipher text
(b) Cryptanalysis
(c) Cracker
(d) Cyber squatting
Answer:
(c) Cracker.
![]()
Question 55.
Which is standard algorithm for decrypting data?
(a) Cipher text
(b) Cryptanalysis
(c) Cracker
(d) Desipher
Answer:
(d) Desipher
Question 56.
Match the following: (E-Commerce Threats)
| (A) Payment Fraud | (i) ATM withdrawals |
| (B) Fraud | (ii) Network flooding |
| (C) DDoS | (iii) Friendly Fraud |
| (D) Typopiracy | (iv) Cyber squatting |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii): (D) – (iv)
(b) (A) – (i); (B) – (ii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
(c) (A) – (ii): (B) – (iii): (C) – (i); (D) – (iv)
(d) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
Answer:
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii): (D) – (iv)
Question 57.
Match the following:
| (A) Encryption technology | (i) Data Encryption Standard |
| (B) Symmetric key | (ii) Security protection |
| (C) Asymmetric key | (iii) Non repudiation |
| (D) Authentication technology | (iv) Public key |
(a) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
Answer:
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
![]()
Question 58.
Match the following:
| (A) Digital certificates | (i) Hardware |
| (B) Digital signature | (ii) Phil Zimmermann |
| (C) Pretty Good Privacy | (iii) Digital document |
| (D) Security token | (iv) Certification Authority |
(a) (A) – (iv); (B) – (ii); (C) – (iii); (B) – (i)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (iii); (D) – (i)
Answer:
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
Question 59.
Match the following:
| (A) Secure Electronic Transaction | (i) Secure Socket Layer |
| (B) Secure Sockets Layer | (ii) VISA |
| (C) Transport Layer Security | (iii) Security protocol |
| (D) 3 – D Secure | (iv) Hybrid encryption |
(a) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (iii); (D) – (i)
(b) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (i); (D) – (ii)
(d) (A) – (iii); (B) (i); (C) – (ii); (D) – (iv)
Answer:
(c) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (i); (D) – (ii)
Question 60.
Match the following:
| (A) Message digest | (i) Input Chip |
| (B) One Time Password (OTP) | (ii) Hashing formula |
| (C) PIN (Personal Identification Number) | (iii) Dynamic password |
| (D) Plain text | (iv) Static number |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (i); (D) – (ii)
(b) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (i); (D) – (ii)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
Answer:
(b) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (I)
![]()
Question 61.
Choose the Incorrect pair:
(a) Phishing – Threat
(b) OTP – Password
(c) Malware – Viruse type
(d) Botnet – Tampering
Answer:
(d) Botnet – Tampering
Question 62.
Choose the Incorrect pair:
(a) Ransomware – Hardware
(b) domain – google.com
(c) Typopiracy – Cyber squatting
(d) Hacking – Intrusion
Answer:
(a) Ransomware – Hardware
Question 63.
Choose the Incorrect pair:
(a) Clear text – Plain text
(b) Triple DES – DESede
(c) Same key – Asymmetric key
(d) RSA – Algorithm
Answer:
(c) Same key – Asymmetric key
![]()
Question 64.
Choose the correct pair:
(a) e-muthra – Symmetric key
(b) Safe script – Asymmetric key
(c) Digital signature – Public key Infrastructure
(d) SET – Cracker
Answer:
(c) Digital signature – Public key Infrastructure
Question 65.
Choose the correct pair:
(a) Secured Sockets Layers – Transport Layers Security
(b) 3-D Secure – URL
(c) Decipher – Website Address
(d) Domain name – Algorithm
Answer:
(a) Secured Sockets Layers – Transport Layers Security
Question 66.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Friendly fraud mean when customer demands false reclaim or refund.
(b) Clean fraud mean when a stolen credit card is used to make a purchase.
(c) Triangulation fraud mean fake online shops offering cheapest price and collect credit card data
(d) Cyber squatting is the legal practice of registering an Internet domain – name.
Answer:
(d) Cyber squatting is the legal practice of registering an Internet domain – name.
![]()
Question 67.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a asymmetric encryption algorithm.
(b) Encryption technology is an effective information security protection.
(c) Cipher text using encryption algorithm.
(d) The encryption or decryption process use a key to encrypt or decrypt the data.
Answer:
(a) The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a asymmetric encryption algorithm.
Question 68.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Same key is used for both encryption and decryption in symmetric key encryption.
(b) The speed of encryption or decryption is very slow in symmetric key encryption.
(c) Plain text and cipher text are of same size in symmetric key encryption.
(d) Symmetric key encryption that provides confidentiality.
Answer:
(b) The speed of encryption or decryption is very slow in symmetric key encryption.
Question 69.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) A digital certificate also known as Public Key Certificate.
(b) Digital certificates are issued by Government of India.
(c) Digital signature is to ensure that a data remain unsecure.
(d) A digital signature is created using digital documents.
Answer:
(a) A digital certificate also known as Public Key Certificate.
![]()
Question 70.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) 3-D secure is a Unsecure Payment Protocol on the Internet.
(b) The most common cryptographic protocol is Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
(c) The SSL Standard was developed by windows.
(d) TLS and SSL are the same in the generation of symmetric keys.
Answer:
(b) The most common cryptographic protocol is Secure Sockets Layers (SSL)
Question 71.
Assertion (A):
Viruses cause harm to the computers.
Reason (R):
Viruses destroy all the information stored in a computer.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A
Question 72.
Assertion (A):
Hacking refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer.
Reason (R):
Typopiracy is a variant of cyber squatting.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
![]()
Question 73.
Assertion (A):
Ransomware is a type of Malware.
Reason (R):
A person who breaks computer network security is called cipher text.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Answer:
(c) A is true, But R is false.
Question 74.
Assertion (A):
Digital certificates are provides non-repudiation and integrity.
Reason (R):
Digital certificates provides authentication and security.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Answer:
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Question 75.
Assertion (A):
PIN is a dynamic password that is valid for one login session.
Reason (R):
OTP is a static number that is assigned to consumers.
(a) Both A and R are true.
(b) Both A and R are false.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is True.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are false.
![]()
Question 76.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) TDES
(b) 3DES
(c) DESede
(d) DDoS
Answer:
(d) DDoS
Question 77.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Hacking
(b) Ransomware
(c) Tampering
(d) Malware
Answer:
(c) Tampering
Question 78.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) DES
(b) RSA
(c) ECC
(d) DSA
Answer:
(a) DES
![]()
Question 79.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) NIC
(b) AES
(c) e-mudhra
(d) MTNL
Answer:
(b) AES
Question 80.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Domain Name
(b) Acquirer Domain
(cj Issuer Domain
(d) Interoperability Domain
Answer:
(a) Domain Name
Question 81.
In E-Commerce, when a stolen credit card is used to make a purchase it is termed as:
(a) Friendly fraud
(b) Clean fraud
(c) Triangulation fraud
(d) Cyber squatting
Answer:
(b) Clean fraud
![]()
Question 82.
Which of the following is not a security element involved in E-Commerce?
(a) Authenticity
(b) Confidentiality
(c) Fishing
(d) Privacy
Answer:
(c) Fishing
Question 83.
Asymmetric encryption is also called as:
(a) Secure Electronic Transaction
(b) Certification Authority
(c) RSA algorithm
(d) Payment Information
Answer:
(c) RSA algorithm
Question 84.
The security authentication technology does not include:
(i) Digital Signatures
(ii) Digital Time Stamps
(iii) Digital Technology
(iv) Digital Certificates
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii)
![]()
Question 85.
PGP stands for:
(a) Pretty Good Privacy
(b) Pretty Good Person
(c) Private Good Privacy
(d) Private Good Person
Answer:
(a) Pretty Good Privacy
Question 86.
__________ for securing crsen cards transactions via the Internet.
(a) Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
(b) Credit Card Verification
(c) Symmetric Key Encryption
(d) Public Key Encryption
Answer:
(a) Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
Question 87.
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) was developed in:
(a) 1999
(b) 1996
(c) 1969
(d) 1997
Answer:
(b) 1996
![]()
Question 88.
The websites secured by Secure Socket Layer protocols can be identified using:
(a) html:/7 .
(b) http://
(c) htmls://
(d) https://
Answer:
(d) https://
Question 89.
3-D Secure, a protocol was developed by:
(a) Visa
(b) Master
(c) Rupay
(d) PayTM
Answer:
(a) Visa
![]()
Question 90.
Which of the following is true about Ransomware?
(a) Ransomware is not a subset of malware
(b) Ransomware deletes the file instantly
(c) Typopiracy is a form of ransomware
(d) Hackers demand ransom from the victim
Answer:
(b) Ransomware deletes the file instantly