TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 21 Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) and Self Help Groups (SHGs)
Question 1.
What do you understand by the manufacturing enterprises?
Answer:
Manufacturing enterprises refer to the enterprises engaged in the manufacturing or production of goods pertaining to any industry specified in the first schedule to the Industries (Development and Regulation) Act, 1951. The manufacturing enterprises are defined in terms of investment in plant and machinery.
Question 2.
Give some examples for micro enterprises.
Answer:
The limit for investment in plant and machinery does not exceed 25 lakhs. Micro enterprises engaged in small scale activities. Such as fruit and vegetable venders, cottage industries, fire works, handicrafts, clay pot making etc.
Question 3.
What is the aim of NEEDS?
Answer:
Government of Tamil Nadu launched “New Entrepreneur-cum-Enterprise Development Scheme (NEEDS)” with a view to encouraging the educated youth to become the first generation entrepreneurs.
The Scheme envisages providing entrepreneurship development training to educated young entrepreneurs, preparing business plans and helping them to tie up with financial institutions to set up new business ventures, besides linking them with major industrial clients.
Question 4.
What is a Self Help Group?
Answer:
- Self help group is a small informal voluntary association created for the purpose of enabling members to reap economic benefit out of mutual help, solidarity, and joint responsibility.
- The benefits include mobilization of savings and credit facilities for the pursuit of group enterprise activity, eg: (self help women group).
Question 5.
State the investment limit for small enterprise in manufacturing and service sector.
Answer:
- Size of enterprise: Small enterprises.
- Manufacturing sector: More than ₹ 25 lakhs but not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
- For service sector: More than ₹ 10 lakhs but not exceeding ₹ 2 crores.
Question 6.
State the investment limit for medium enterprise engaged in Manufacturing and service sector.
Answer:
- Size of enterprise: Medium-enterprises
- Manufacturing sector: More than ₹ 5 Crores but not exceeding ₹ 10 Crores.
- For service sector: More than ₹ 2 Crores but not exceeding ₹ 5 Crores.
Question 7.
List out the products produced by MSME in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
In Tamil Nadu MSMEs sector produces a wide variety of products in almost all fields. The prominent among them are the textile, electronic products, engineering products, auto ancillanes, leather products, chemicals, plastics, garments, jewellery etc. There are 12.94 Lakh registered number of units of MSMEs in the State, providing an employment opportunities to about 81 Lakh people. (source cms.tn.gov.in – 12.12.2017)
Question 8.
What is the role and significance of MSMEs in Indian Economy?
Answer:
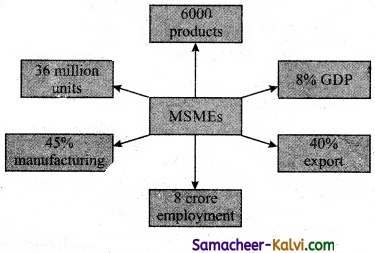
This Sector consists of 36 million units and provides employment to over 8 Crore people. MSME provides employment opportunity to the people of India. It helps towards industrialisation of rural and backward areas. This sector reduces regional imbalance. It provides equal distribution of national income and wealth.
Question 9.
Explain any three features of Self Help Group.
Answer:
- The motto of every group members should be “saving first – credit latter”.
- Self Help Group is homogeneous in terms of economic status.
- The ideal size of a Self Help Group ranges between 10 and 20 members.
Question 10.
What are the different ways in which banks fund Self Help Groups?
Answer:
- There are three distinct modes of credit to SHGs, under the first mode, banks lend directly to the SHGs.
- In the second mode banks provide loans to the NGOs for toward lending to the SHGs and ultimately to micro entrepreneurs.
- Under the third mode, banks extend credit to the SHGs with the NGOs serving as facilitators.
- Out of these three methods, the last method of direct lending by bank with NGOs facilitation is widely practised.
Question 11.
What is the definition of MSME?
Answer:
In accordance with the provisions of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development Act 2006, the micro, small and medium enterprises are classified into two classes.
(i) Manufacturing Enterprises:
They refer to the enterprises engaged in the manufacturing or production of goods pertaining to any industry specified in the first schedule to the Industries (Development and Regulation) Act, 1951. The manufacturing enterprises are defined in terms of investment in plant and machinery.
(ii) Service Enterprises:
They refer to the enterprises engaged in providing or rendering of services.
Question 12.
Explain the advantages of MSMEs?
Answer:
(i) Employment Potential:
MSMEs generate more employment opportunities than large business concerns.
(ii) Low Production Cost:
MSMEs do not require skilled labourers or professionals to run the organisation. It employs cheap labour and thus minimizes the overhead.
(iii) Low Investment:
MSMEs do not require a huge capital to start the unit. It can employ locally available resources within the reach of the owner.
(iv) Quick Decision Making:
MSMEs need not hire professional managers to run the management on a day to day basis.
(v) Supplementary Role:
MSMEs play a complementary role to serve as a feeder to large scale industries.
(vi) Establishment of Socialistic Pattern of Society:
MSME sector contributes towards the establishment of socialistic , pattern of society by reducing the concentration of income and wealth.
(vii) Balanced Regional Development:
By encouraging MSMEs in industrially backward areas of India, balanced development can be achieved across all regions.
(viii) Promotion of Self Employment and Self Reliance Spirit:
MSMEs help to a great deal in developing a class of entrepreneurs. It promotes self employment and a spirit of self reliance in the society, thereby contributing an increase in per capita income or economic development.
(ix) Higher Contribution to Manufacturing and Export:
MSMEs contribute 45% to the total manufacturing output and 40% to the exports from the country. It helps in earning precious foreign exchange in various countries across the world.
Question 13.
What are the objectives of SHGs?
Answer:
(i) Focusing on empowerment of women.
(ii) Saving people from the clutches of money lenders.
(iii) Building capacity of women and to enable them to participate in generating activities.
(iv) Creating the habit of saving in the minds of the people who are economically backward.
(v) Promoting entrepreneurship skills among women.
(vi) Creating awareness about the importance of credit circle or revolving credit and the payment of the circle.
(vii) Elevating the economic standard of the member’s families.
(viii) Developing skills and facilitating credit linkages for eventual economic empowerment.
(ix) Promoting awareness among the members about finding solutions for their economic problems.
(x) Identifying the common interest of the group members and carrying out their operations in the most efficient and economic way.
(xi) Enabling the members to overcome all social and economic barriers.
(xii) Promising and ensuring human rights to women at all stages of their life cycle.
Question 14.
Role of women as entrepreneurs.
Answer:
One of the famous Indian women entrepreneurs is Indira Nooyi. She was bom in Chennai and had her bachelor’s degree in Madras Christian College. Master’s Degree in public management from Yale University. Masters in Finance and Marketing from IIM, Kolkata.
Occupation:
Joined pepsico in 1994 and became CFO in 2001. Earlier she held Senior executive positions in Motorola and Asia Brown Boveri. She was product manager at Johnson and Johnson and then textile firm mettur Beardsell. Awarded PadmaBushan for her business achievements and being an inspiration to India’s corporate leadership. She helped the company to complete 30 billion dollars worth of crucial deals within the last couple of years.
Question 15.
Income-tax exemption for Start-up initiatives.
Answer:
The Government of India has launched Mudra Bank with a capital amount of ₹ 20,000 Crore and credit guarantee corpus of ₹ 3000 Crore to help MSMEs and startups to resolve problems relating to income tax exemption and financing.
Question 16.
World Association of Small & Medium enterprises (WASME).
Answer:
UNICTAD, ITC, WIPO, UNESCO, UNESCAP, global non profit organisation head quarters – Noida (India).
Question 17.
Ministry of MSME and its functions.
Answer:
Ministry of MSME. Its function is honoured the people those who are producing quality goods. Gandhimathi appliances are honoured by Ministry of MSME. National Award 2010. Quality product in Micro and «* small enterprises for LPG operated stoves / appliance.
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
MSMED Act was enacted in the year:
(a) 2004
(b) 2007
(c) 2006
(d) 2008
Answer:
(c) 2006
Question 2.
MSMEs are important for the nation’s economy because they significantly contribute to:
(a) industrial production
(b) exports
(c) employment
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 3.
Self help groups convert the savings into a common fund known as:
(a) common fund
(b) group corpus fund
(c) group fund
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) group corpus fund
Question 4.
There are _______ distinct modes of credit to Self Help Groups.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 5.
Investment limit of a micro enterprise under manufacturing sector does not exceed ______ lakhs.
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 50
Answer:
(c) 25
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 21 Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) and Self Help Groups (SHGs)
→ Entrepreneurship is the key for economic development of any country By empowering entrepreneurs, MSME sector provides more employment opportunities to the people of India. It helps towards the industrialization of rural and backward areas. This sector reduces regional imbalances. It provides equitable distribution of national income and wealth.
→ Micro enterprises are engaged in low scale activities such as clay pot making, fruits and vegetable vendors, transport (three wheeler tempos and autos), repair shops, cottage industries, small industries, handlooms handicraft works etc.
→ Rural development is one of the main pillars of progress of India. It has lagged behind in many aspects of development even after six decades of the independence of India. According to 2011 population census, rural and urban India accounts for 33.8 per cent and 20.09 per cent of people below the poverty line respectively.
→ Self Help Group has emerged as a new model for combating poverty. This concept mainly demonstrates the significance of togetherness. The Self Help Group represents an association of people formed to attain certain common goals.
→ Self Help Group is a small informal voluntary association created for the purpose of enabling members to reap economic benefit out of mutual help, solidarity, and joint responsibility. The benefits include mobilization of savings and credit facilities for the pursuit of group enterprise activity.
→ National Bank for Agricultural & Rural Development (NABARD) has defined Self Help Group as “a homogenous group of rural poor voluntarily formed to save whatever amount they can conveniently save out of their earnings and mutually agree to contribute to a common fund of the group to be lent to the members for meeting their productive and emergent credit needs”.