TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 5 Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership
Question 1.
Who is called Karta?
Answer:
The head of the family is known as “KARTA”.
Question 2.
What are the two schools of Hindu law?
Answer:
There are two schools of Hindu Law one is Dayabhaga law, the other is Mitakshara law.
![]()
Question 3.
Who is a called a Partner?
Answer:
The persons who enter into partnership, are individually called ‘ Partners ’ and collectively known as‘Firm’.
Question 4.
Who is a Sleeping partner?
Answer:
Such a partner contributes capital and shares in the profits or losses of the firm but does not take part in the management of the business.
Question 5.
Who is a Minor?
Answer:
A minor is a person who has not completed 18 years of age. where a guardian is appointed by a court, his age of majority extends to 21 years. Legally, a minor cannot become a partner.
![]()
Question 6.
How many types of Dissolution?
Answer:
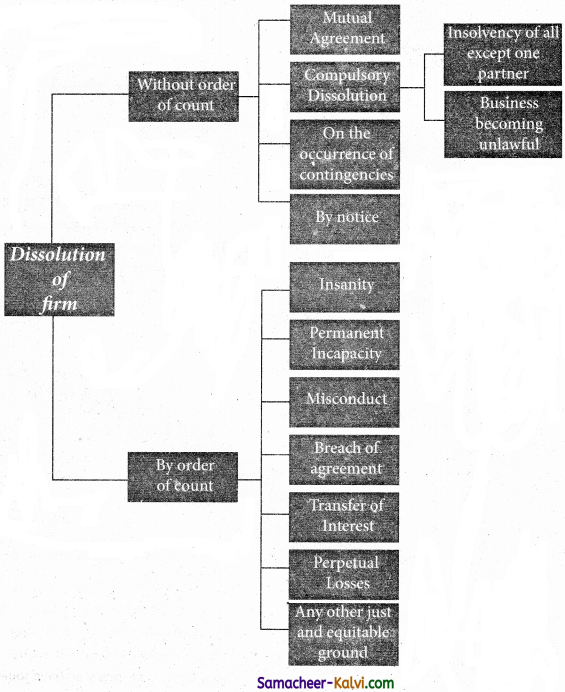
Question 7.
What is the meaning of Joint Hindu Family Business?
Answer:
- “When two or more families agree to live and work together, invest their resources and labour jointly and share profits or losses together, then this family is known as composite family or HUF” eg: C.Roy & Co (a chartered accountant firm)
- There are two schools of Hindu Law-one is Dayabhaga which is prevalent in Bengal and Assam and the other is Mitakshara prevalent in the rest of the-country.
- According to Mitakshara law, there is a son’s right by birth in the property of joint family. It means, when a son is bom in the family, he acquires an interest in the property jointly held by the family. Today Hindu succession Act 2005 is applicable to all male and female members of a HUF.
![]()
Question 8.
‘Write any three features of HUF.
Answer:
(i) Governed by Hindu Law:
The business of the Joint Hindu Family is controlled and managed under the Hindu law.
(ii) Management:
All the affairs of a Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person who is known as ‘Karta’ or ‘Manager’. The Karta is the senior most male member of the family.
(iii) Membership by Birth:
The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. As soon as a child is bom in the family, that child becomes a member. Membership requires no consent or agreement.
Question 9.
Explain the nature of liability of karta.
Answer:
Except the Karta, the liability of all other members is limited to their shares in the business. The amount of debt can be recovered from his personal property also.
Question 10.
What is the meaning of Co-parceners?
Answer:
A person who shares equally with others in the inheritance of an undivided estate. The other members are called Co-parceners.
![]()
Question 11.
Define Partnership.
Answer:
According to Spriegal, “Partnership has two or more members each of whom is responsible for the obligatory requirements of the partnership. Each of the partners may bind the others and the assets of the partners may be taken for debts of partnership”.
Question 12.
What is the minimum and maximum number of members in the partnership concern?
Answer:
There must be more than one person. The maximum number of partners has been limited to 10 in the case of banking business and 20 in the case of other business.
Question 13.
What is the meaning of Partnership Deed?
Answer:
A partnership firm can be formed through an agreement among two or more persons. In India, this agreement may be oral or in writing. But it is desirable to have it in writing to avoid any misunderstanding among the partners in future. All the terms and conditions of partnership are included inthe agreement. The partnership agreement is also known as Partnership Deed or Articles of Partnership.
![]()
Question 14.
Who is called a Secret partner?
Answer:
Secret partner is one whose name is not disclosed to outsiders. He is not known to the public. He can take part in the business.
Question 15.
What is meant by Joint and Several Liability?
Answer:
The liability of a partner is joint and several. The creditors of partnership firm can claim their dues from the private assets of all the partners taken together or they can take action against private properties of any one of the partners to get back their dues.
Question 16.
What is the implied authority of Karta?
Answer:
- In a joint family firm, only Karta has the implied authority to enter into a contract for debts and pledge the property of the firm for the ordinary purpose of the businesses of the firm.
- All the affairs of the joint Hindu family is controlled and managed by the Head of the family. He is known as Karta,
- Karta is the senior most male member of the family. He alone taking decisions and controlling the whole family.
- All the members of the family have full faith and confidence in Karta.
- Karta alone entitled to deal with others.
- Other members i.e. co-parceners cannot deal with outsiders. But some times he can get permission from Karta he deal with outsiders.
- Members of Joint Hindu family liability is limited. So personal assets also liable for outside debts.
![]()
Question 17.
Can a minor is admitted in the Joint Hindu Family business. Why?
Answer:
Minor also a co-parcener:
In a Joint Hindu Family firm even a new bom baby can be a co-parcener. As soon as the child is bom in the family. The child becomes the member.
Membership by Birth: The Joint Hindu Family business can be dissolved only at the will of all the members of the family. Any single member has no right to get the business dissolved.
Question 18.
What are the contents of Partnership Deed?
Answer:
Following are the contents of Partnership Deed:
(i) Name of the Firm.
(ii) Nature of the proposed business
(iii) Duration of partnership:
Duration of the partnership business whether it is to be run for a fixed period of time or whether it is to be dissolved after completing a particular venture.
(iv) Capital contribution:
The capital is to be contributed by the partners. It must be remembered that capital contribution is not necessary to become a partner for one who contributes his organising power, business acumen, managerial skill etc., instead of capital.
(v) Withdrawal from the firm:
The amount that can be withdrawn from the firm by each partner.
(vi) Profit/loss sharing:
The ratio in which the profits or losses are to be shared. If the profit sharing ratio is not specified in the deed, all the partners must share the profits and bear the losses equally.
(vii) Interest on capital:
Whether any interest is to be allowed on capital and if so, the rate of interest. If the deed is silent on interest on capital, the rules for interest on capital in partnership act will take effect.
(viii) Rate of interest on drawing:
Whether any interest is to be allowed on drawing, the rate of interest is to be specified.
(ix) Loan from partners:
Whether loans can be accepted from the partners and if so the rate of interest payable thereom.
(x) Account keeping:
Maintenance of accounts and audit.
(xi) Salary and Commission to Partners:
Amount of salary or commission payable to partners for their services. (Unless this is specifically provided, no partner is entitled to any salary).
(xii) Retirement:
Matters relating to retirement of a partner. The arrangement to be made for paying out the amount due to a retired or deceased partner must also be stated.
(xiii) Goodwill valuation:
Method of valuing goodwill on the admission, death or retirement of a partner.
(xiv) Distribution of responsibility:
The work that is entrusted to each partner is better stated in the deed itself.
(xv) Dissolution procedure:
Procedure for dissolution of the firm and the mode of settlement of accounts thereafter.
(xvi) Arbitration of dispute:
Arbitration in case of disputes among partners. The deed should provide the method for settling disputes or difference of opinion. This clause will avoid costly litigations.
![]()
Question 19.
Explain the types of dissolution of partner-ship firm.
Answer:
The Partnership firm may be dissolved in any one of the following ways.
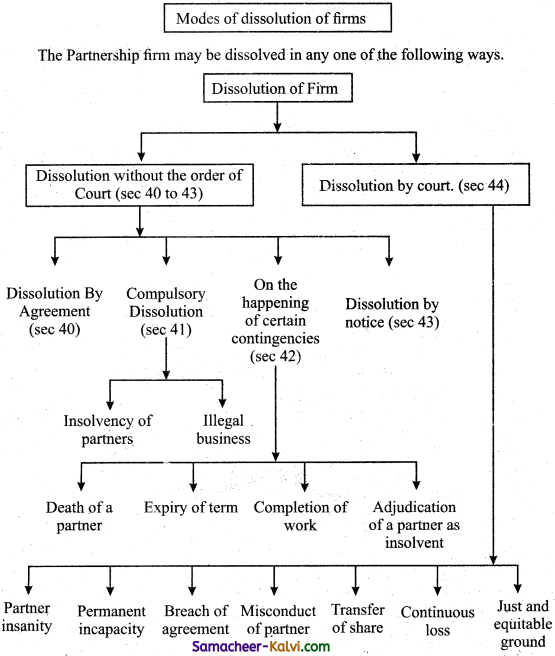
(i) Dissolution by Agreement (Sec.40):
A partnership is created and dissolved by an agreement. A firm may be dissolved by an agreement either with the consent of all partners or in accordance with the contract among the partners.
(ii) Compulsory dissolution (Sec.41):
A firm is compulsorily dissolved either by the agreement of all the partners or on the insolvency of all the partners except one. It may also be dissolved on the happening of an event which makes the object of the firm unlawful. Example, the passing of Prohibition Act, declaration of war with another country.
(ii) Dissolution on the happening of certain contingencies (Sec.42):
A partnership may be dissolved on the happening of the following contingencies (a) Death of a partner, (b) Expiry of the time, if partnership is for a fixed period, (c) Completion of the venture for which the firm was formed. (d) Adjudication of a partner as an insolvent.
(iv) Dissolution by notice of partnership-at-will (Sec43):
Where the partnership is at will, the firm may be dissolved by any partner by giving a notice in writing to all the other partners of his intention to dissolve the firm.
(v) Dissolution through Court (Sec.44):
Any partner may bring a suit in a court of law to get the partnership dissolved on any of the following grounds.
(a) Partner’s Insanity:
If any partner becomes insane, the court may order dissolution.
(b) Permanent Incapacity:
When a partner becomes permanently incapable of doing business the court may order dissolution.
(c) Persistent Breach of Agreement:
If a partner persistently violates the agreement and the other partner finds it impossible to do business in partnership with him, then the other partner can move for dissolution.
(d) Misconduct of a Partner:
If any partner is guilty of misconduct (misuse of money) then any partner can file a suit for dissolution of the firm.
(e) Transfer of Share:
When a partner transfers his share in the business to a third party without the consent of other partners, then the other partners can move the court for dissolution.
(f) Continuous Loss:
When the business of the firm cannot be carried on except at a loss, the court order for dissolution.
(g) Just and equitable grounds:
When the court feels that it is just and equitable, it may order for dissolution of the firm, eg: If A and B are partners but do not speak to each other, the court may order for dissolution.
![]()
Question 20.
Write any three differences between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm.
Answer:
| Dissolution of Partnership |
Dissolution of Firm |
| One or more of the partners terminate their connections with the firm. | All the partners terminate their connections with the firm. |
| May or may not bring the business of the firm to an end. | Bring the business of the firm to an end. |
| Business will continue even after dissolution. | Business cannot be continued. |
| Need not necessarily results in the dissolution of the firm. | Results in the dissolutions of the partnership. |
Question 21.
What is the procedure for Registration of a Firm?
Answer:
A statement should be prepared stating the following particulars.
(i) Name of the firm.
(ii) The principal place of business.
(iii) Name of other places where the firm carried on business.
(iv) Names and addresses of all the partners.
(v) The date on which each partner joined the firm.
(vi) The duration of the firm.
This statement signed by all the partners should be produced to the Registrar of Firms along with the necessary registration fee. Any change in the above, particulars must be communicated to the Registrar within 14 days of such alteration.
![]()
Question 22.
Raman with members of his extended family established a Joint Hindu Family business of Handicrafts. Raman being the head of family controlled the business as ‘Karta’. He had authority to take all decisions for the business. Many times, he sold goods for cash without informing other members of the family business. This resulted in lesser profits. He also sold one of the family properties and gave money to his daughter as a wedding gift. What values did Karta ignored in the above case?
Answer:
Raman want to discuss all business matters. Because he is Karta.
Question 23.
Palani is an Electronics Engineer. He has met two businessmen who wish to enter into a partnership with him for the manufacture of tape-recorders. They are prepared to make the investment and offer a fourth share in profits to Palani. Would you have any special words of advice for Palani?
Answer:
No, special words of advice for Palani. Because he needs extra money to manufacture of tape recorders. He knows the field of product manufacturing of tape recorders.
Question 24.
Write any 2 HUF run Hospitals in your nearest place.
Answer:
- Apollo Hospitals
- Billroth Hospitals
- Dr. Agarwal’s eye Hospitals.
![]()
Question 25.
How will you run a HUF for export business?
Answer:
In HUF ‘ family including more members each member take response regarding export business.
Question 26.
How will you run a HUF Bus operating business?
Answer:
This type of business need more employees. So, bus operating business suitable to HUF.
Question 27.
How will you organise a partnership business with your friends according to a law?
Answer:
According to Indian partnership Act 1932 (Sec.4)”. The relation between persons who have agreed to share profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.
- According to above law to organise a partnership business.
- A written agreement is necessary because to avoid future misunderstandings.
Question 28.
Name a Partnership firm in your town (Nearest).
Answer:
Mothers world Departmental Stores, Mohan Agencies, Parvathy Stores, Vision eye care opticals.
![]()
Question 29.
A father had self acquired agricultural land. He transferred the said land in the name of his three sons. The revenue records reflect the names of the three sons with 1/3rd share against each name. Father died recently. However physical partition of the said land amongst the three brothers has not been done as they have mutually decided against it. Eldest son has started managing the land since fathers demise. Is the land in question. ancestral property of the three brothers? Can the three brothers claim to a HUF? If yes, then since when are they HUF – after fathers demise or since the date land transferred in their names?
(i) Is the land is Ancestral property,
Yes, father self acquired agricultural land.
(ii) Can, three brothers claim to HUF?
Answer:
Yes, brothets can claim to HUF. After father’s death. They can get. land from fathers name to son’s name.
Question 30.
Draw a family tree diagram as you think. Just imagine you are running a business under the Joint Hindu Family system.
Answer:
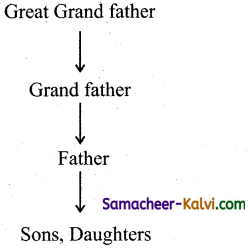
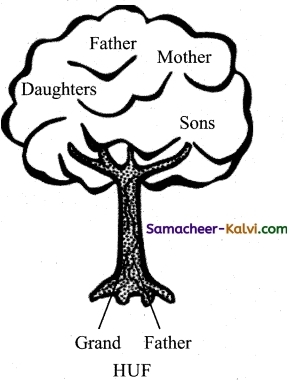
![]()
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
The firm of Hindu Undivided Family is managed by whom?
(a) Owner
(b) Karta
(c) Manager
(d) Partner
Answer:
(b) Karta
Question 2.
In the firm of Hindu Undivided Family, how one gets the membership?
(a) By agreement
(b) By birth
(c) By investing capital
(d) By managing
Answer:
(b) By birth
Question 3.
The members in the joint hindu family are called:
(a) karta
(b) coparceners
(c) generations
(d) partners
Answer:
(b) coparceners
![]()
Question 4.
‘Only the male members in the family get the right of inheritance by birth’ as:
(a) hindu law
(b) mitakshara law
(c) dayabhaga law
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) mitakshara law
Question 5.
A partnership is formed by:
(a) agreement
(b) relationship among persons
(c) the direction of government
(d) friendship
Answer:
(a) agreement
Question 6.
Registration of partnership is:
(a) compulsory
(b) Optional
(c) not necessary
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) Optional
![]()
Question 7.
A temporary partnership which is formed to complete a specific job doing a specified period of time is called:
(a) partnership-at-will
(b) particular partnership
(c) limited partnership
(d) joint venture
Answer:
(a) partnership-at-will
Question 8.
The partnership deed also called:
(a) articles of association
(b) articles of partnership
(c) partnership act
(d) partnership
Answer:
(b) articles of partnership
Question 9.
A partnership is registered with:
(a) registrar of companies
(b) registrar of co-operatives
(c) registrar of firms
(d) district collector
Answer:
(c) registrar of firms
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 5 Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership
→ The joint hindu family business is a distinct from of organisation peculiar to India joint hindu family firm is created by the operation of law.
→ It does not have any separate and distinct legal entity from that of its members. The business of joint hindu family is controlled under the hindu law. The membership in this form of business organisation can be acquired only by birth or by marriage to a male person who is already a member of joint hindu family.
→ India is unique in the system of joint hindu family.
→ Introduction to partnership:
The need for partnership form of organisation arose from the limitations of sole proprietorship. In sole tradership financial resources is limited, individual capacity is limited skill. It is at this stage need for associating more persons arises so more are associated to form groups to carry on business.
![]()
→ The partnership form of organisation comes into existence in two ways. It may come into existence either as a result of expansion of the scale trading concern or two or more persons joining together through an agreement to form a partnership.
→ History reveals that the partnership organisation was started with the enactment of partnership act in 1907 in England. In india the act was approved in 1932. The act governs the formation, management and control of various partnership firms in the country. Examples of partnership firms are running a cinema theatre, a book shop chit funds etc.
→ “Coming together is a beginning” “keeping together is progress” “working together is success”.