Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Define Heredity.
Answer:
Heredity is defined as a process through which the inheritance of characters from parent to offspring.
Question 2.
Explain multiple alleles.
Answer:
Multiple alleles of a gene is that a particular trait is controlled by three or more alleles of a gene on the homologous chromosome of an organism.
Question 3.
What is Fischer and Race hypothesis?
Answer:
Fischer and Race hypothesis says that the Rh factor involves three different pairs of alleles, which are located on three different closely linked loci on the chromosome pair.
![]()
Question 4.
Heterogametic males- Explain.
Answer:
In this method of sex determination, the males are heterogametic, producing two types of gametes, while female is homogametic, producing similar gametes.
Question 5.
What are holandric genes?
Answer:
Holandric genes are the genes present in Y chromosomes. These genes have no corresponding allele in X chromosomes.
Question 6.
What is Karyotyping?
Answer:
Karyotyping is a technique through which a completed set of chromosomes is separated from a cell and arrange in pairs.
Question 7.
Define ideogram.
Answer:
Ideogram is the technique of diagrammatic representation of chromosomes.
Question 8.
What is meant by pedigree?
Answer:
Pedigree is a family tree, showing the inheritance path way for the specific phenotypic character, using the standard genetic symbol.
![]()
Question 9.
What is a genetic disorder?
Answer:
A genetic disorder is a disease or syndrome caused by chromosomal abnormality or change in an individual DNA.
Question 10.
What is Huntington’s chorea?
Answer:
Huntington’s chorea is a genetic disorder due to an autosomal dominant lethal gene in man. The symptoms are involuntary jerking of the body and progressive degeneration of the nervous system. Patients with this disease usually die between the age of 35 and 40.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What is the Wiener hypothesis? Explain it briefly.
Answer:
The Wiener hypothesis is proposed by Wiener and it states that at a single Rh locus, there are eight alleles (R1, R2, R0, R2, r, r1, r11, ry. The Rh-positive will be produced, when all genotypes carry a dominant ‘R’ allele (R1, R2, R0, R2), whereas the Rh-negative phenotype is expressed due to double recessive gentypes (rr, rr1, rr11, rry).
Question 2.
Explain the prevention method of Erythroblastosis foetalis.
Answer:
One of the preventive methods of Erythroblastosis foetalis is to administrate anti D antibodies to the mother at the 28th and 34th week of gestation as a prophylactic measure. This anti D antibody should be given to Rh– mother immediately after childbirth if she delivers Rh+ child. This will destroy Rh– foetal RBCs by developing passive immunity and preventing the formation of anti D antibodies in the mother’s blood; before the sensitization of the mother’s immune system.
![]()
Question 3.
What is colour blindness? Explain it briefly.
Answer:
The colour blindness is a sex-linked character in human being, who is unable to distinguish red and green colour. This allele is present in X chromosomes. The recessive form of this allele cannot produce colour sensitive cone cells. Therefore homozygous female of genotype XcXc and hemizygous XcY males cannot differentiate between red and green colour. This phenomenon is called colour blindness.
Question 4.
Give the diagrammatic representation of the human karyotype.
Answer:
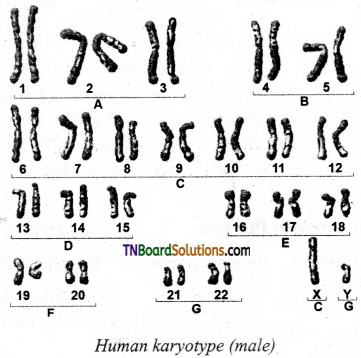
Question 5.
How does the disorder phenylketonuria occur?
Answer:
Phenylketonuria is due to the error of phenylalanine metabolism. It is an inborn disorder due to the mutation of the gene PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase gene), which controls the production of the hepatic enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase. This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine. Phenylalanine accumulates and gets converted into phenyl pyruvic acid and other derivatives in disease affected individuals who lacks phenylalanine dehydroxylase enzyme. This results in the excretion of phenylpyruvic acid through urine. The symptoms of this disorder include severe mental retardation and light pigmentation of skin and hair.

![]()
Question 6.
What are the symptoms of Patau’s syndrome?
Answer:
The symptoms of Patau’s syndrome include multiple and severe body malformation along with profound mental deficiency. The other symptoms are having a small head with small eyes, cleft palate, defective information of the brain and internal organs.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Write an account of ABO blood groups in human being.
Answer:
Four types of blood groups are noticed in human being namely A, B, AB and O groups. These groups differ from person to person, as they are different on the basis of the presence of antigens on the membrane of RBC and epithelial cells. The antigen ‘A’ and ‘B’ on the surface of RBCs of human blood were discovered by Karl Landsteiner. Three kinds of blood groups were recognized based on these antigens. The blood group A individuals have A antigen, while individuals having B blood group have ‘B’ antigen. The individuals with A and B antigens are grouped under AB blood group, which is a rare group. The individuals having O blood group do not have antigen and this group is known as a universal donor. When two incompatible blood groups are mixed agglutination of erythrocytes (RBCs) occurs.
Question 2.
Explain the disorder of Erythroblastosis foetalis.
Answer:
Erythroblastosis foetalis is caused by the Rh factor incompatibility in childbirth. If an Rh-negative woman carries an Rh-positive man, the foetus may be Rh-positive inherited from its father. The mother having Rh-positive foetus in her womb becomes immune logically sensitized. The mother’s blood recognizes the Rh antigen, due to damages of blood vessels during childbirth. This causes the sensitized mother to produce Rh antibodies. This IgG type of antibodies are small molecule and can cross the placenta and enter the foetal circulation. The child is delivered before these processes of anti ‘D’ antibody production by the sensitized mother. Hence there is no effect associated with the exposure of the mother to Rh-positive antigen during first childbirth. But in subsequent pregnancy by the same mother, the child is exposed to antibodies produced by the mother against Rh antigen, which is carried across the placenta into foetal circulation that causes haemolysis of foetal RBCs. This results in anaemia or haemolytic jaundice, which is called Erythroblastosis foetalis or Haemolytic disease of new born (HDN).
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the Lygaeus type of sex determination in Drosophila.
Answer:
The Lygaeus type of sex determination is otherwise called XX-XY type, commonly found in Drosophila and human being. In Drosophila, the females are homogametic with XX chromosomes and produce only one type of gamete with X chromosome while the males are heterogametic with XY chromosomes and produce two types of gametes, one with one X chromosome and the other with a Y chromosome. The sex of the progeny depends on the fertilizing sperm. An egg, which is fertilized by a sperm with an X chromosome will develop into a female, while an egg, which is fertilized with a sperm having a Y chromosome will develop into a male.
Question 4.
Explain the inheritance of colour blindness in a marriage of a colour blind woman with a normal man.
Answer:
When a colour blind woman with two recessive genes (XcXc) marries a normal man (X+Y) among the progenies, all the sons are colour blind and all the daughters are normal, but carriers this gene in F1 generation.
If marriage between this F1 female with a colour blind man takes place among progenies, normal visioned carrier daughters and colour blind daughters and males of colour blindness and normal vision will be expected in the F2 generation.
Question 5.
Differentiate Down’s syndrome from Turner’s syndrome.
Answer:
| Down’s Syndrome | Turner’s Syndrome |
| Down’s syndrome is due to Trisomic-21 condition. | Turner’s syndromes due to loss of a X chromosome. |
| The symptoms include severe mental retardation and defective development of CNS. | Persons with this syndrome have 44AA+XO chromosomes. |
| Other symptoms include increased separation between eyes, flattened nose, malformed ears. | The females are sterile. |
| Mouth is always open and the tongue protrudes. | The symptoms include low stature, webbed neck, under developed breast, rudimentary gonads ack of menstrual cycle during puberty. |
![]()
Multiple choice questions
1. Match the following:
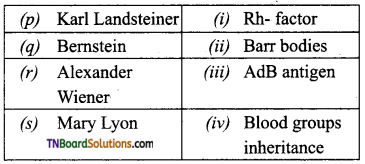
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iv)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
2. Match the following:
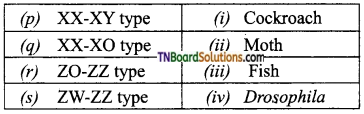
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
3. Match the following:
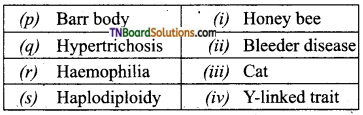
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
![]()
4. Match the following:
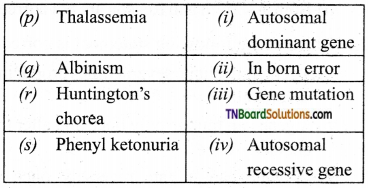
(a) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
5. The unit of heredity is known as:
(a) Chromosome
(b) Nucleus
(c) Gene
(d) RNA
Answer:
(c) Gene
6. The inheritance of different blood groups in human being is determined by:
(a) 3 autosomal alleles
(b) 3 sex linked alleles
(c) 4 autosomal alleles
(d) 4 Sex linked alleles
Answer:
(a) 3 autosomal alleles
7. What is the causative factor for Erythroblastosis foetails?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Virus
(c) Rh- factor
(d) Phenylalanine
Answer:
(c) Rh- factor
![]()
8. The method of sex determination in honey bee is:
(a) XX-XY type
(b) Haplodiploidy
(c) ZW-ZZ type
(d) Heterochromatic
Answer:
(b) Haplodiploidy
9. Y-chromosome linked character in human being includes:
(a) Phenylketonuria
(b) Colour blindness
(c) Albinism
(d) Hypertrichosis
Answer:
(d) Hypertrichosis
10. Choose the odd one out (sex-determination):
(a) Honey bee
(b) Drosophila
(c) Human being
(d) Monkey
Answer:
(a) Honey bee
11. Find out the odd one:
(a) Thalassemia
(b) Phenylketonuria
(c) Hypertrichosis
(d) Albinism
Answer:
(c) Hypertrichosis
12. Indicate the odd one:
(a) Blood group A
(b) Blood group B
(c) Rh positive
(d) Blood group AB
Answer:
(c) Rh positive
![]()
13. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Chromosome mapping
(b) Recombination frequency
(c) Linkage of genes
(d) Karyotyping
Answer:
(d) Karyotyping
14. Which of the following is the correct pair?
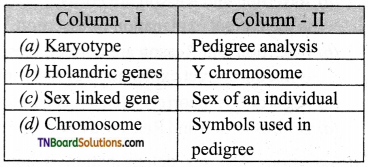
Answer:
(b)
15. Find out the incorrect pair:
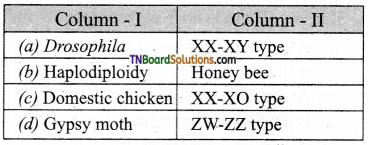
Answer:
(c)
16. Indicate the correct pair:
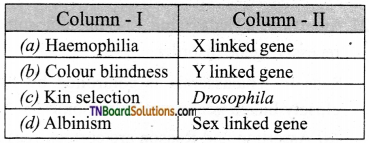
Answer:
(a)
17. Choose the correct pair:
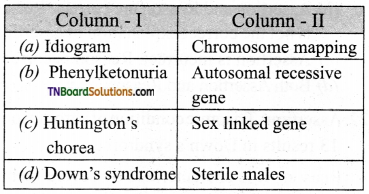
Answer:
(b)
![]()
18. Assertion: Blood group O is called a universal donor.
Reason: Because no agglutination antigen is present in ‘O’ blood group.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
(d) Both assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
19. Assertion: An individual having D antigen are Rh-positive (Rh+).
Reason: Rhesus factor in the blood is inherited as a dominant trait.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
(d) Both assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
20. Assertion: The sex determination is a honey bee is of XX-XO type.
Reason: There is no Y chromosome in a male.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
(d) Both assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(d) Both assertion and Reason are not correct.
21. Assertion: Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
Reason: Thalassemia is controlled by two closely linked genes on chromosome 16.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
![]()
22. Assertion: Trisomic condition of chromosome 13 results in Down’s syndrome.
Reason: It is characterized by severe mental retardation.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
(d) Both assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct.
23. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A gene can mutate several times producing several alternative forms.
(b) A gene can mutate only once and alter the character once.
(c) A gene can mutate reversely once in a lifetime.
(d) A gene can mutate thrice in a lifetime.
Answer:
(a) A gene can mutate several times producing several alternative forms.
24. Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) In the homogametic female system of sex determination, the males produce two types of gametes.
(b) In the homogametic female system of sex determination, females produce only one type of gamete.
(c) In the female heterogametic type, the females produce only one type of gametes.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) In the female heterogametic type, the females produce only one type of gametes.
25. Indicate the correct statement:
(a) Kin selection is normally seen in moth.
(b) Kin selection is normally seen in honey bees.
(c) Kin selection is normally seen in butterflies.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Kin selection is normally seen in honey bees.
![]()
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Haemophilia is commonly known as bleeder’s disease.
(b) This disease was first discovered by John Cotto in 1803.
(c) This disease is more common in female than male human.
(d) This is caused by a sex-linked gene.
Answer:
(c) This disease is more common in female than male human.
27. Choose the correct statement:
(a) Turner’s syndrome is caused by a trisomic condition.
(b) Turner’s syndrome is due to the loss of an X chromosome in female.
(c) Turner’s syndrome is due to the presence of an additional copy of the X chromosome.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Turner’s syndrome is due to the loss of an X chromosome in female.