TN State Board Kalvi 12th Commerce Notes Chapter 5 Capital Market
Question 1.
What is Capital Market?
Answer:
Capital Market is a market where buyers and sellers engage in trade of financial securities like bonds, and stocks. The buying and selling is undertaken by participants such as individuals and institutions.
Question 2.
Write a note on OTCEI.
Answer:
The OTCEI was set up by a premier financial institutions to allow the trading of securities across the electronic counters throughout the country. The strength of OTCEI are transparency of transactions, quick deals, faster settlements and better liquidity.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Mutual Fund?
Answer:
- Financial Institution that provide facilities for channeling savings of small investors into avenues of productive investments are called “Mutual Funds”.
- A mutual fund company invests the funds pooled from shareholders to investment portfolio and a reasonable return.
Question 4.
Who are the participants in a Capital Market?
Answer:
The participants of the Capital Market include individuals, Corporate Sectors, Government, banks and other financial institutions.
Question 5.
How is price determined in a Capital Market?
Answer:
The price of the Securities is determined based on the demand and supply prevailing in the capital market for securities.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the various kinds of Capital Market? Explain.
Answer:
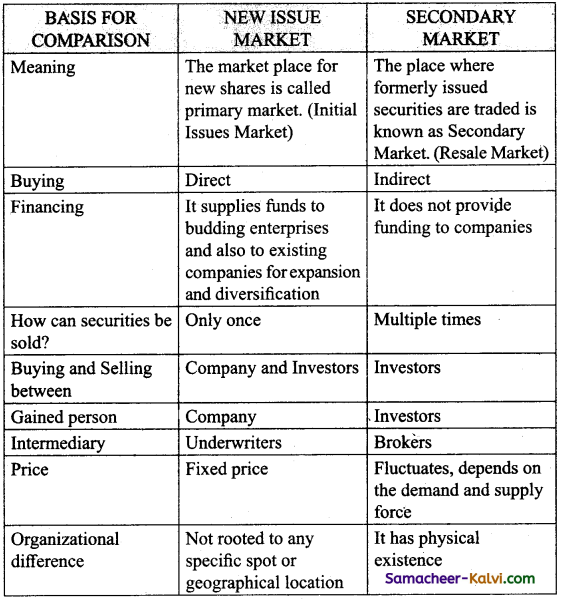
The capital market is divided into two
(i) Primary Market
(ii) Secondary Market
(i) Primary Market:
The Primary Market deals with securities which are issued to the public for the first time. In the Primary Market borrowers exchange new financial securities for long term funds. Primary Market facilitates capital formation.
There are three ways by which a company may raise capital in a Primary Market
(i) Public Issue,
(ii) Rights issue
(iii) Private placement
(ii) Secondary Market:
Secondary Market may be defined as the market for old securities which are previously issued in the Primary Market are traded here. The trading takes place between investors who follow the original issue in the Primary Market. It covers both stock exchange and over-the-counter market.
Question 7.
Explain any two functions of Capital Market.
Answer:
Savings and Capital Formation:
In capital market, various types of securities help to mobilize savings from various sectors of population (Individual, Corporate, Government etc.,) People to invest in securities at a reasonable return and liquidity in stock exchange. This accelerates the capital formation in the country.
Industrial Growth:
The stock exchange is a central market through which resources are transferred to the industrial sector of the economy institution encourage people to invest in productive channels. Thus it stimulates industrial growth and economic development of the country by mobilizing funds for investment in the Corporate Securities.
![]()
Question 8.
Write a note on National Clearance and Depository System (NCDS).
Answer:
Under the scripless trading system settlement of transactions relating to securities takes place through a book entry. The entire scripless trading system comprises. The following three segments:
- National Trade comparison and Reporting system which prescribes the terms and conditions of contract for the securities market.
- National Clearing system which aims at determining the net cash and stock liability of each broker on a settlement date.
- National Depository system which arranges to provide for the transfer of ownership of securities in exchange on payment by book entry on electronic ledgers without any physical movement of transfer deed.
Question 9.
Discuss about evolution and growth of Indian Capital Market.
Answer:
- The period between 1947 and 1973 marked the development of infrastructure for Capital Market. During this period, a network of development financial institutions (IFCI, ICICI, IDBI, UTI, SFC and SIDC)
- The period between 1980 and 1992 debenture emerged as a powerful instrument of resource mobilization in the Primary Market. A number of stock exchanges came into existence.
- SEBI emerged as an effective regulatory body for the Primary and Secondary Market.
- A number of committees were constituted inorder to suggest measures to revamp and restructure the working of the Secondary Market and cause in the Primary Market.
- A High Powered Study Group on Establishment of New Stock Exchange, A Committee on Trading in Public Sector Bonds and Units of Mutual Funds.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain about Factoring and Venture Capital Institutions.
Answer:
Factoring Institutions:
‘Factoring’ is an arrangement whereby a financial institution provides financial-accommodation on the basis of assignment and sale of account receivable. The factoring institutions collect the book debts for and onbehalf of its clients. Factoring Institutions operating in India SBI Factors and commercial services Private Limited, Canbank Factors Limited, a subsidiary of Canara Bank.
Venture Fund Institutions:
Venture capital funds bring into force the hi- technology projects which are converted into commercial production. Many specialized financial institutions have promoted their own Venture Capital Funds. They include Risk Capital Foundation of IPCI, Venture Fund of IDBI, SIDBI, Technology Development and infrastructure Corporation of India TDICI.
Question 11.
Discuss the characters of a Capital Market.
Answer:
- Securities Market: The dealings in a capital.market are done through the securities like shares, debentures etc., The capital market is also called Securities Market.
- Price: The price of the securities is determined based on the demand and supply prevailing in the capital market for securities.
- Participants: The participants of the Capital Market include individuals, Corporate Sectors, Government, Banks and other financial institutions.
- Location: Capital market is not confined to certain specific locations. Markets are concentrated in certain well known centres known as Stock Exchanges.
- Market for Financial Assets: Capital market provides a transactions platform for long term financial assets.
![]()
Question 12.
Briefly explain the functions of capital market.
Answer:
(i) Savings and Capital Formation:
In capital market various types of securities help to mobilize savings from various sectors of population (Individuals, Corporate, Govt etc.,)
(ii) Permanent Capital:
The existence of a capital market and stock exchange enables companies to raise permanent capital. The investors cannot commit their funds for a permanent period but companies require funds permanently.
(iii) Industrial Growth:
The stock exchange is a central market through which resources are transferred to the industrial sector of the economy.
(iv) Ready and Continuous Market:
The stock exchange provides a central convenient place where buyers and sellers can easily purchase and sell securities.
(v) Reliable Guide to Performance:
The capital market serves as a reliable guide to the performance and financial position of corporate and thereby promotes efficiency.
(vi) Provision of Variety of Services:
The financial institutions provide a variety of services such as grant of long term and medium term loans to entrepreneurs, Provision of Underwriting facilities, Participation in equity capital.
(vii) Foreign Capital:
Capital Market makes possible to generate foreign capital. Government has liberalized Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the country, Foreign technology which is important for economic development of the country.
(viii) Easy Liquidity:
With the help of secondary market investors can sell off their holdings and convert them into liquid cash.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the various types of New Financial Institutions.
Answer:
A number of institutions of finance have been established to cater to the credit requirements of various segments of industry and needs.
(i) Venture Fund Institutions: Venture Capital financing is a form of equity financing designed especially for funding new and innovative project ideas. Specialized financial institution have promoted their own venture capital funds. Venture Fund of IDBI, SIDBI, Risk Capital Foundation of IFCI.
(ii) Mutual Funds:
A mutual fund company invests the funds pooled from shareholders and gives them the benefit of diversified investment portfolio and a reasonable return.
(iii) actoring Institution:
The factoring institutions collect the book debts for and on behalf of its clients some of the factoring institutions operating in India. SBI Factors and commercial services Private Limited.
(iv) Over the Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI):
The OTCEI was set up by a premier financial institution to allow the trading of securities across the electronic counters throughout the country.
(v) National Stock Exchange of India (NSEI):
NSEI was established in 1992 to function as a model Stock Exchange. The exchange aims at providing the advantage of nation-wide electronic screen based “Scripless” and “Floorless” trading system in securities.
(vi) National clearance and Depository System (NCDS):
Under scripless trading system settlement of transaction relating to securities take place through a book entry.
(vii) National Securities Depositories Limited:
The (NSDL) was set up in the year 1996 for achieving a time bound dematerialization as well as rematerialization of shares.
(viii) Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL):
Aims at serving as a central securities depository in respect of transactions on stock exchange. The corporation also take up the administration of clearing functions at a national level.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Capital market do not provide:
(a) Short term Funds
(b) Debentuire Funds
(c) Equity Funds
(d) Long term Funds
Answer:
(a) Short term Funds
Question 2.
When the NSEI was established:
(a) 1990
(b) 1992
(c) 1998
(d) 1997
Answer:
(b) 1992
![]()
Question 3.
Primary market is a Market where securities are traded in the:
(a) First Time
(b) Second Time
(c) Three Time
(d) Several Times
Answer:
(a) First Time
Question 4.
Participants in the capital market includes:
(a) Individuals
(b) Corporate
(c) Financial Institutions
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 5.
How many times a security can be sold in a secondary market?
(a) Only One Time
(b) Two Time
(c) Three Times
(d) Multiple Times
Answer:
(d) Multiple Times