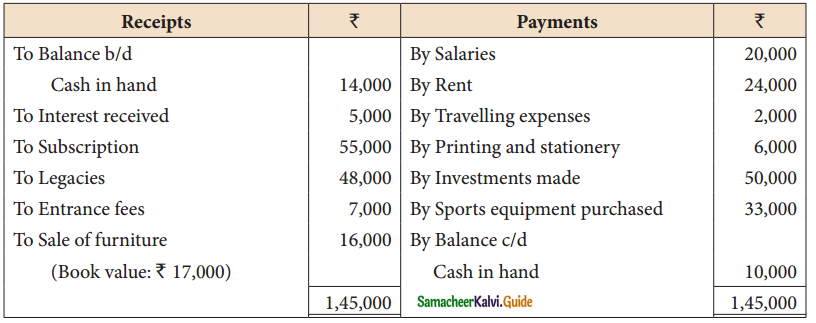
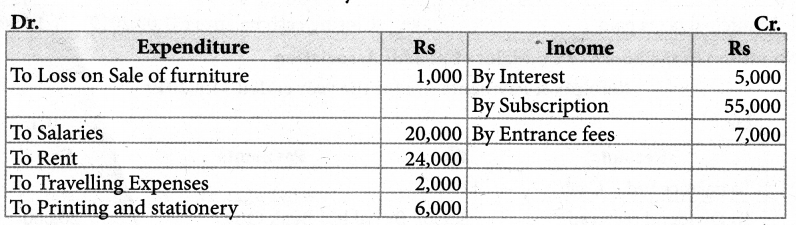
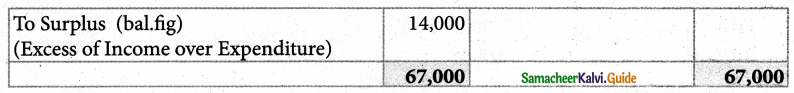
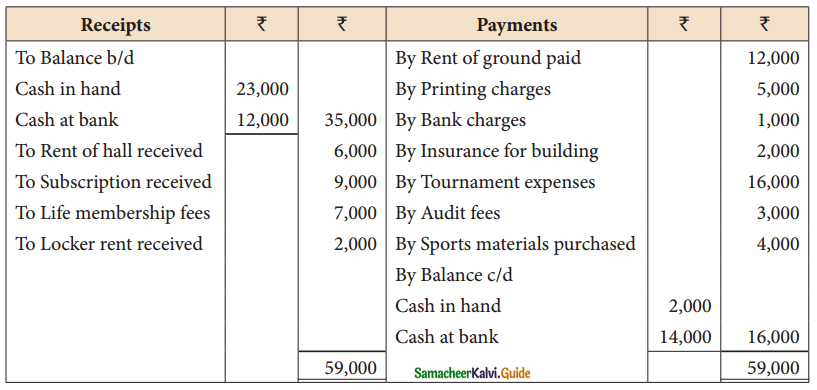
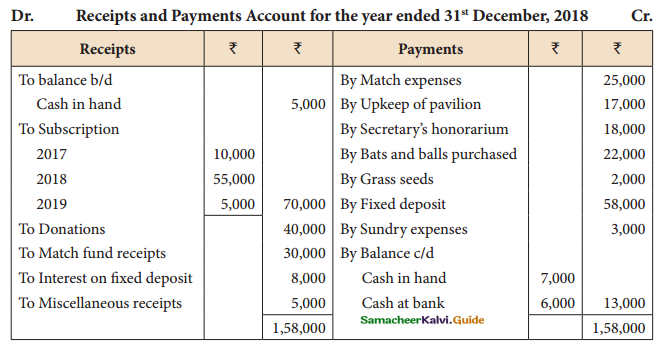
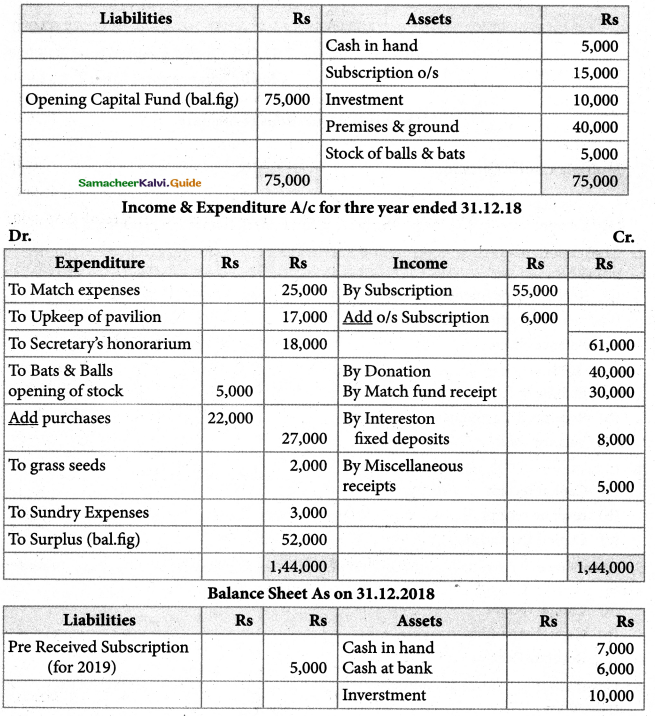
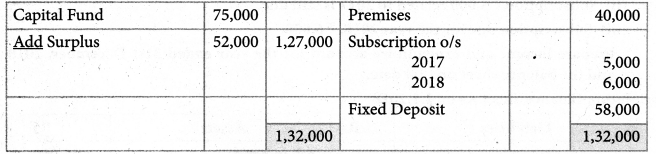
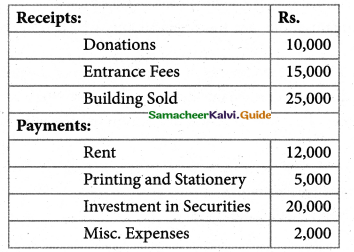
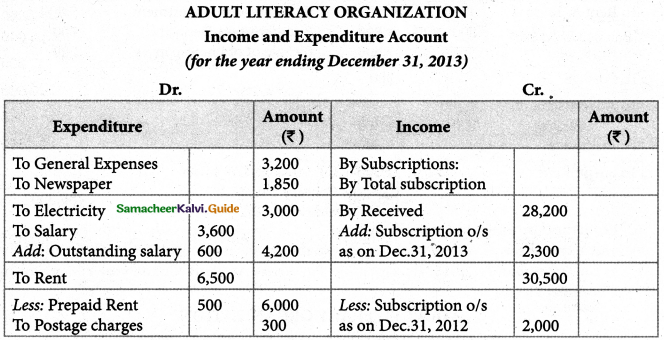
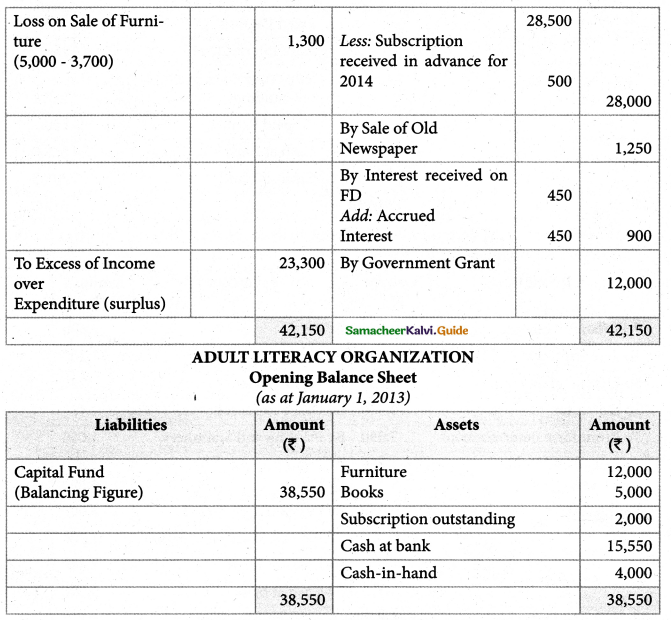
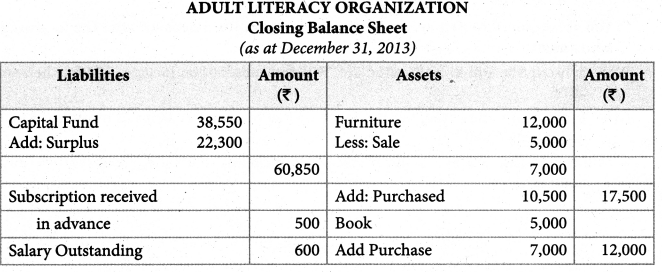
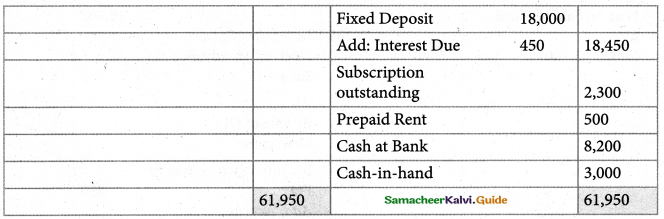
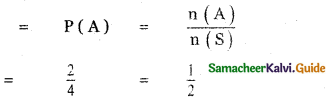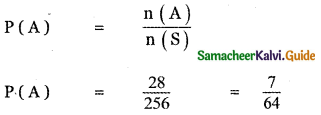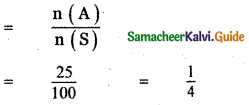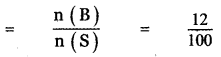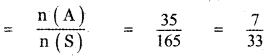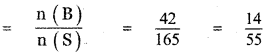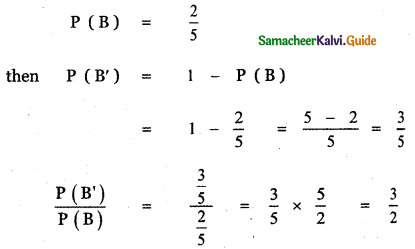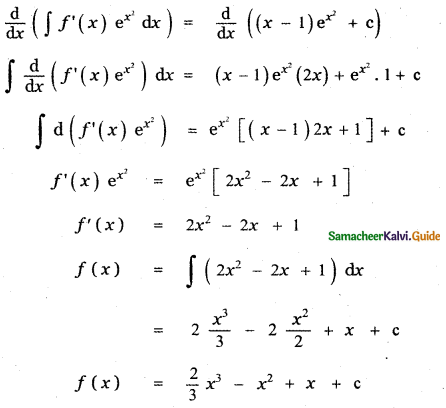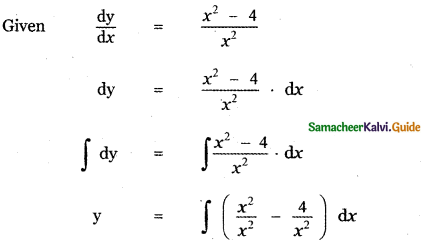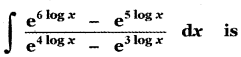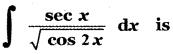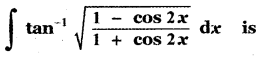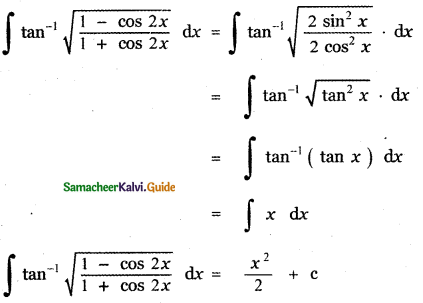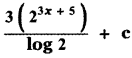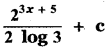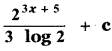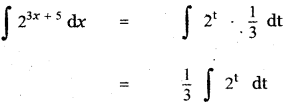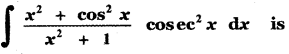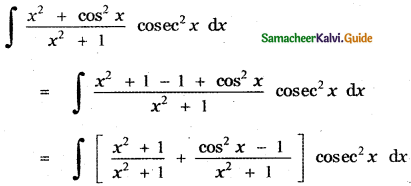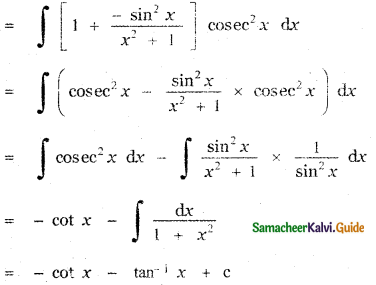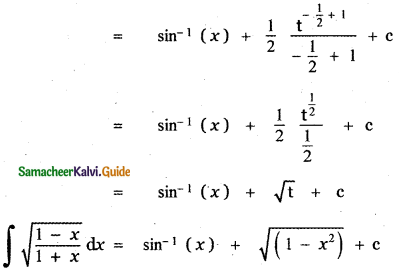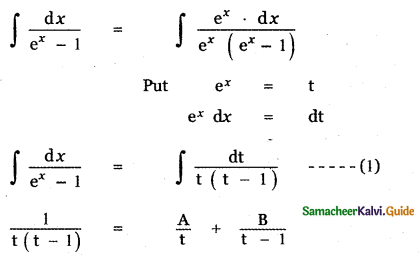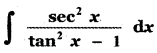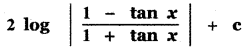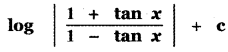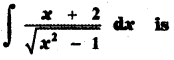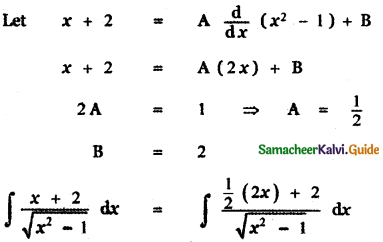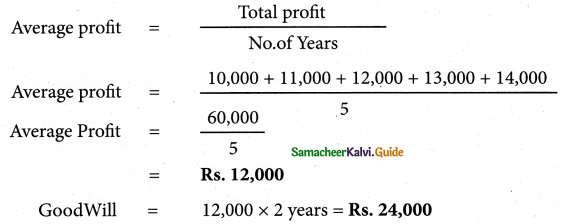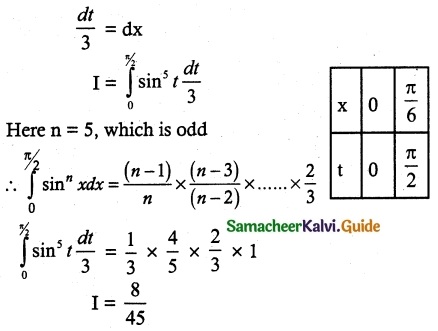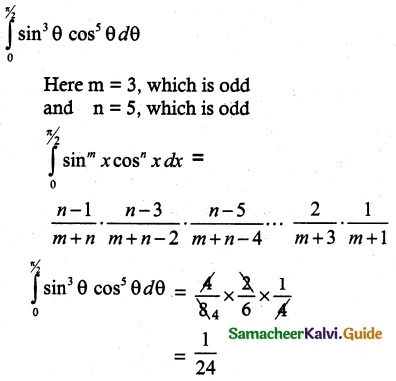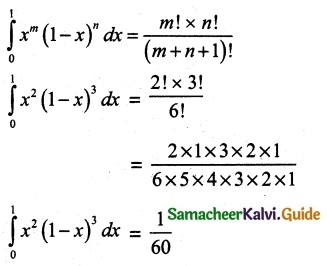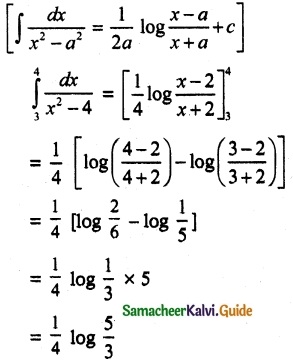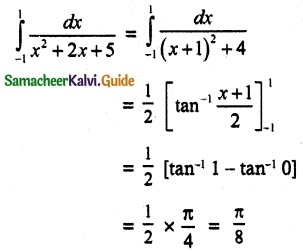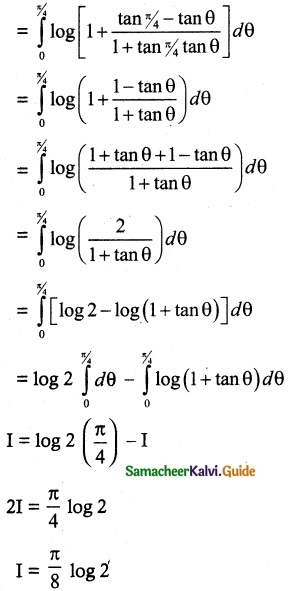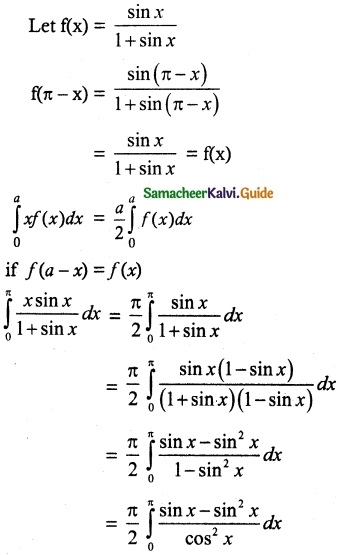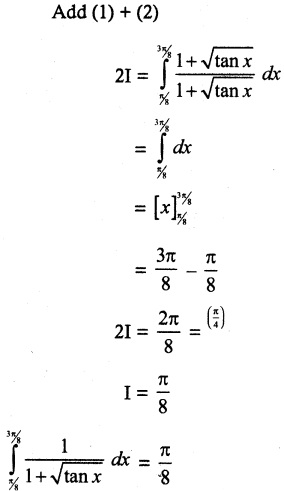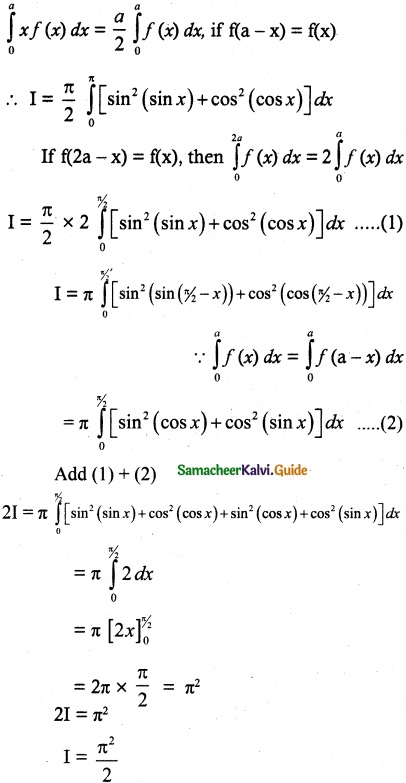Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 12 Introduction to Probability Theory Ex 12.2 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Introduction to Probability Theory Ex 12.2
Question 1.
If A and B are mutually exclusive events P(A) = \(\frac{3}{8}\) and P(B) = \(\frac{1}{8}\), then find
(i) P(A̅)
(ii) P(A ∪ B)
(iii) P(A̅ ∩ B)
(iv) P(A̅ ∪ B̅)
Answer:
(i) P(A̅)
P(A̅) = 1 – P(A)
= 1 – \(\frac{3}{8}\)
P(A̅) = \(\frac{8-3}{8}\) = \(\frac{5}{8}\)
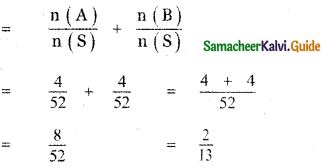
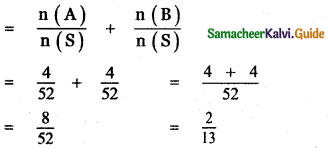
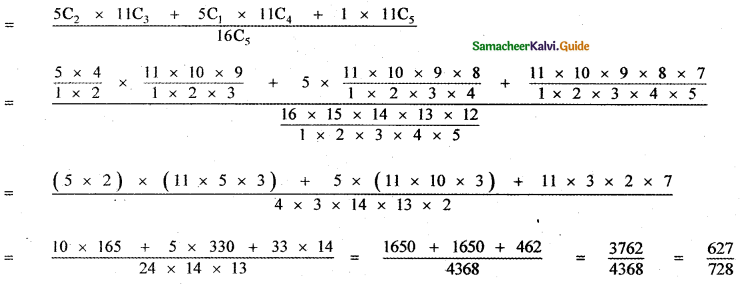
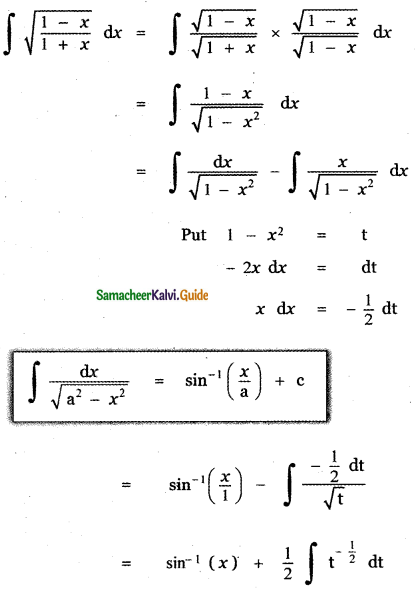
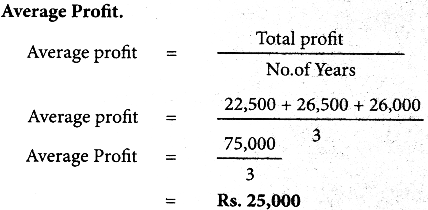
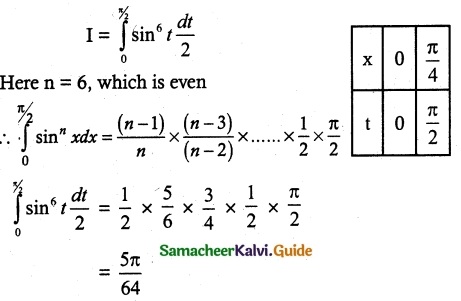
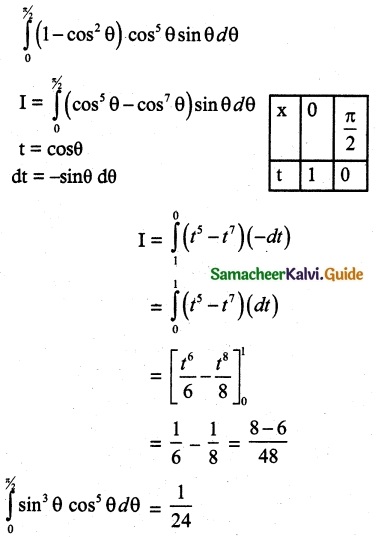
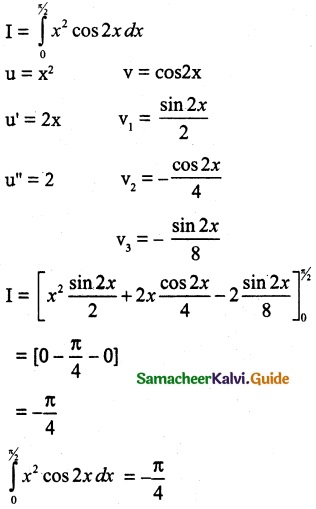
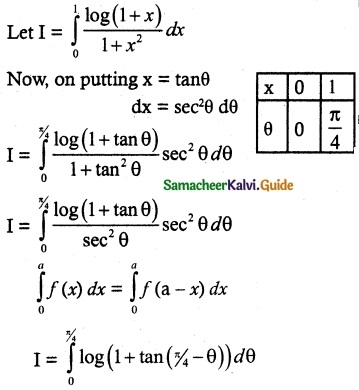
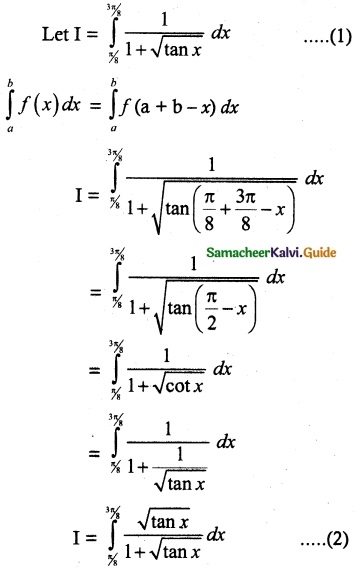
(ii) P(A ∪ B)
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B)
since A and B are mutually exclusive events.

![]()
(iii) P(A̅ ∩ B)
P(A̅ ∩ B) = P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
Since A and B are mutually exclusive we have A ∩ B = Φ
∴ P(A ∩ B) = 0
∴ P(A̅ ∩ B) = p(B)
= \(\frac{1}{8}\)
(iv) P(A̅ ∪ B̅)
P(A̅ ∪ B̅) = P\((\overline{A \cup B})\)
= 1 – P(A ∩ B)
Since A and B are mutually exclusive we have A ∩ B = Φ
∴ P(A ∩ B) = 0
P(A̅ ∪ B̅) = 1 – 0 = 1
Question 2.
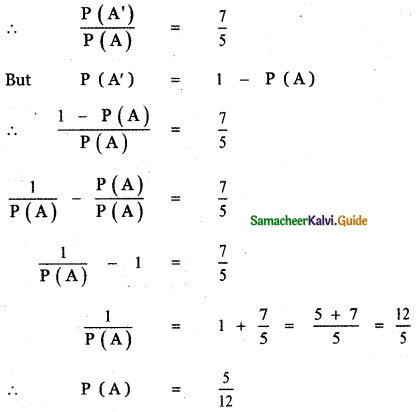
If A and B are two events associated with a random experiment for which P (A) = 0.35, P (A or B ) = 0.85 , and P (A and B) = 0.15 find (i) P (only B) (ii) P (B) (iii) P (only A)
Answer:
Given P (A) = 0.35 ,
P (A and B) = P(A ∩ B) = 0.15
P(A or B) = P(A ∪ B) = 0.85
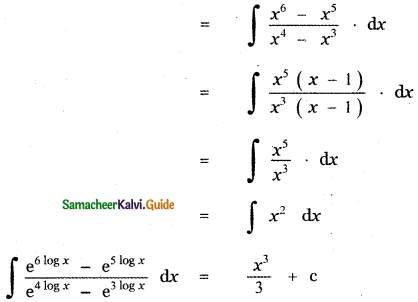
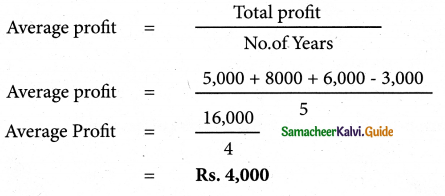
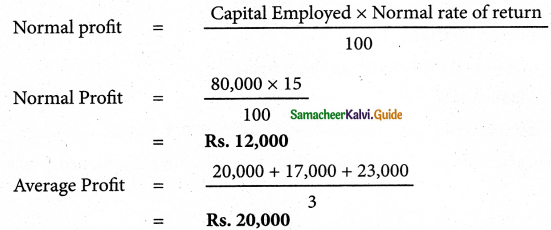
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
0.85 = 0.35 + P (B) – 0.15
0.85 + 0.15 – 0.35 = P(B)
P(B) = 1 – 0.35
P(B) = 0.65
![]()
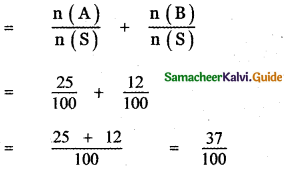
(i) P (only B)
P (only B) = P(A̅ ∩ B)
= P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.65 – 0.15
P (only B) = 0.50
(ii) P (B̅)
P (B̅) = 1 – P(B)
= 1 – 0.65
P (B̅) = 0.35
(iii) P (only A)
P (only A) = P(A ∩ B̅)
= P(A) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.35 – 0.15
P (only A) = 0.20
Question 3.
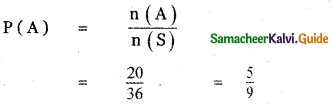
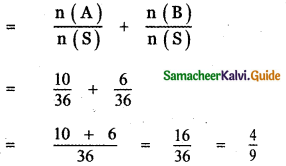
A die is thrown twice. Let A be the event, ‘First die shows 5’ and B be the event , ‘second
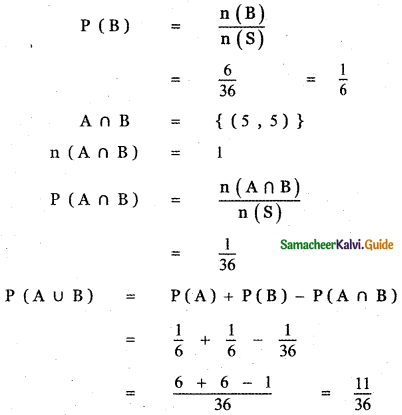
die shows 5’. Find P(A ∪ B).
Answer:
A die is thrown twice. Let S be the sample space
s = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3 ,2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2) ,(5, 3 ) ,(5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6) }
n(S) = 36
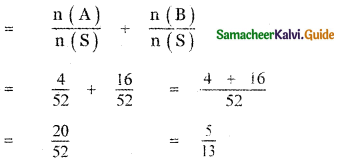
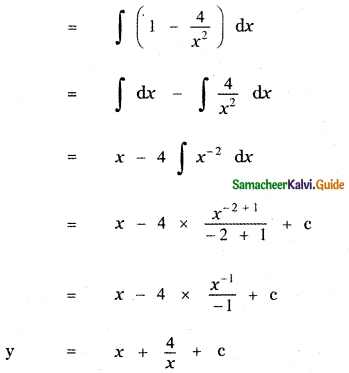
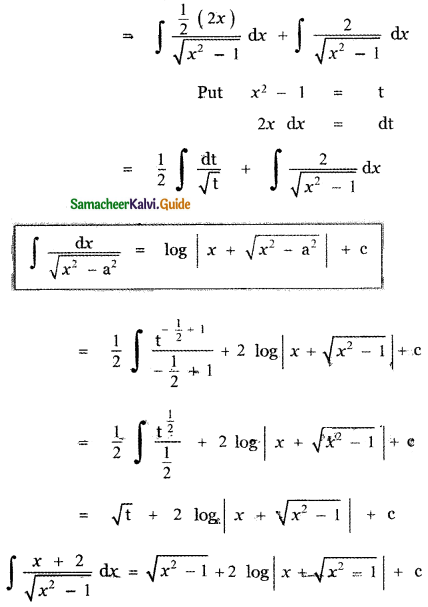
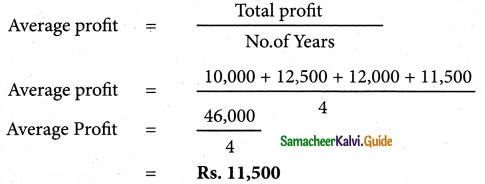
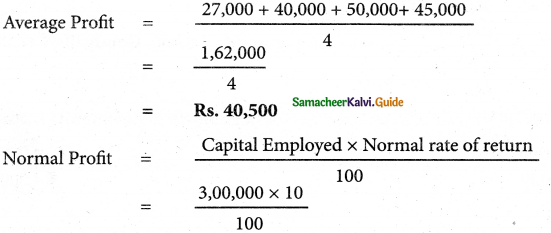
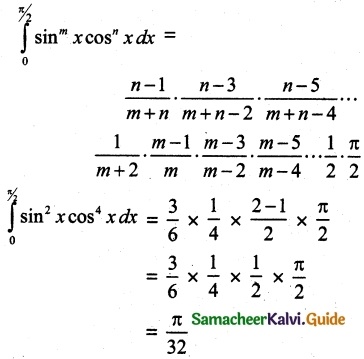
Let A be the event ‘First die shows 5’
A = {(5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5,0)}
n(A) = 6
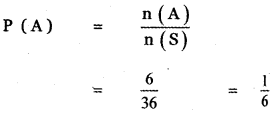
Let B be the event ‘Second die shows 5’
B = {(1, 5), (2, 5), (3, 5), (4, 5), (5, 5), (6, 5)}
n(B) = 6
![]()
Question 4.
The probability of an event A occurring is 0.5 and B occurring is 0.3. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then find the probability of
(i) P(A∪B)
(ii) P(A ∩ B̅)
(iii) P(A̅ ∩ B)
Answer:
P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.3
Here A and B are mutually exclusive.
(i) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B)
= 0.5 + 0.3 = 0.8
(ii) P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∪ B) = 0.5 + 0.3 – 0.8
P(A ∩ B) = 0
P(A ∩ \(\overline{B}\)) = P(A) – P(A ∩ B) = 0.5 – 0 = 0.5
(iii) P(\(\overline{A}\) ∩ B) = P(B) – P(A ∩ B) = 0.3 – 0 = 0.3
Question 5.
A town has 2 fire engines operating independently. The probability that a fire engine is available when needed is 0.96.
(i) What is the probability that a fire engine is available when needed?
(ii) What is the probability that neither is available when needed?
Answer:
A be the event of availability of a fire B be the event of a fire engine when needed. Availability of a second fire engine when needed.
Given P(A) = 0.96, P(B) = 0.96
Then A̅ is the event of non-availability of the first fire engine and B̅ is the event of non-availability of second fire engine when needed.
P (A̅) = 1 – P(A)
= 1 – 0.96
= 0.04
Also P(B) = 0.04
(i) P(atleast one engine is available) = (1 – probability of no engine available)
= 1 – P(A’ ∩ B’)
= 1 – P (A’) P(B’)
= 1 – (0.04) (0.04)
= 1 – 0.0016
= 0.9984
(ii) P (A’ ∩ B’) = P (A’) P(B’)
= 0.04 × 0.04
= 0.0016
Question 6.
The probability that a new railway bridge will get an award for its design is 0.48, the probability that it will get an award for the efficient use of materials is 0.36, and that it will get both awards is 0.2. What is the probability, that
(i) it will get at least one of the two awards
(ii) it will get only one of the awards.
Answer:
(i) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.48 + 0.36 – 0.2
= 0.64.
(ii) P (Getting only one award)
= P(A) – P(A ∩ B) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= (0.48 – 0.2) + (0.36 – 0.2)
= 0.28 + 0.16
= 0.44.