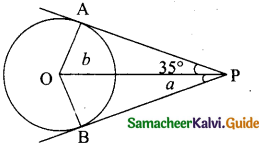
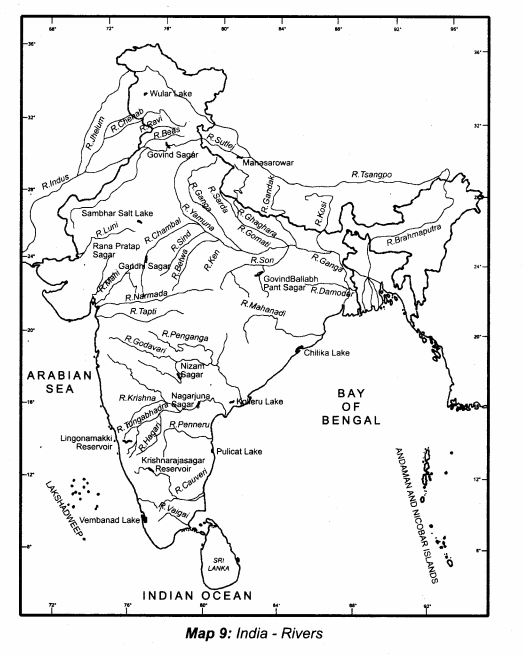
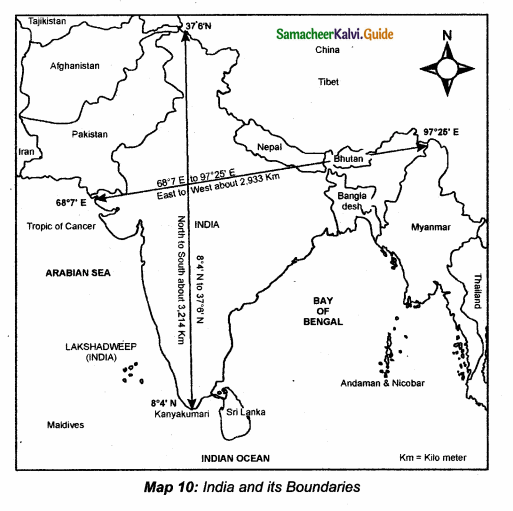
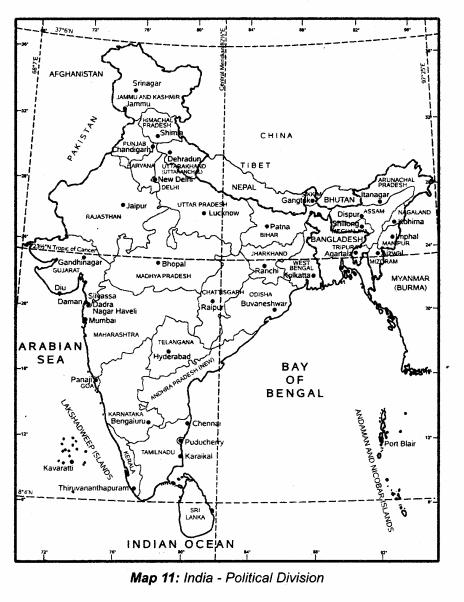
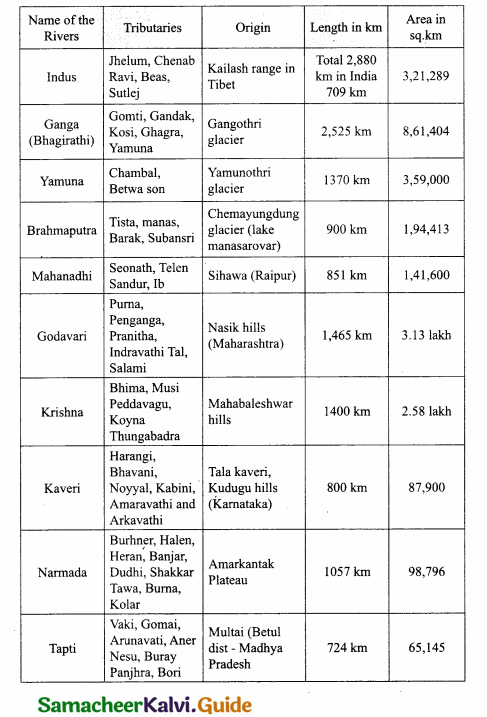
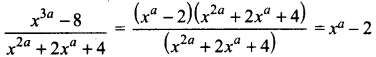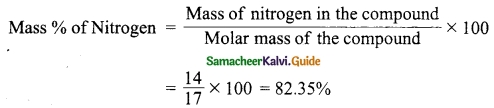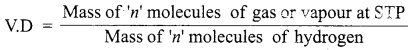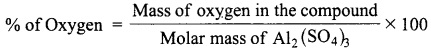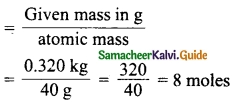Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 12 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code. - Question numbers 13 to 22 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 23 to 32 in Part III are of four marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 33 to 35 in Part IV are of seven marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 75
Part – I
(i) Answer all the questions. [12 × 1 = 12]
(ii) Choose the most suitable answer and write the code with the corresponding answer.
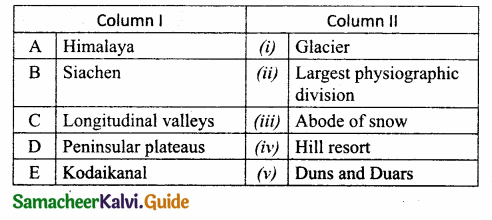
Question 1.
To produce a displacement _______ is required.
(a) Acceleration
(b) Force
(c) velocity
(d) Momentum
Answer:
(b) Force
Question 2.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Rate of change of charge is electrical power
(b) Rate of change of charge is current
(c) Rate of change of energy is current
(d) Rate of change of current is charge
Answer:
(b) Rate of change of charge is current
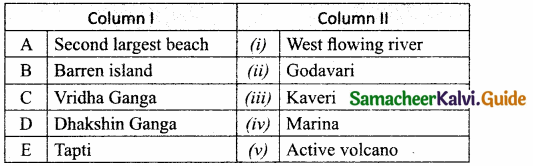
Question 3.
_______ aprons are used to protect us from gamma radiations.
(a) Lead oxide
(b) Iron
(c) Lead
(d) Aluminium
Answer:
(c) Lead
![]()
Question 4.
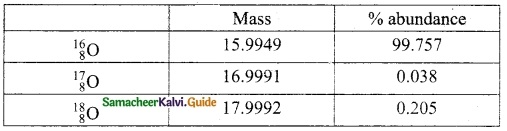
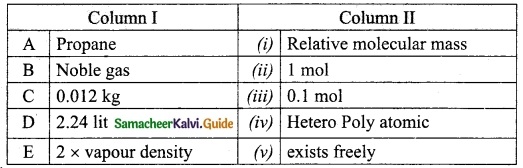
The gram molecular mass of oxygen molecule is _______.
(a) 16 g
(b) 18 g
(c) 32 g
(d) 17 g
Answer:
(d) 17 g
Question 5.
When pressure is increased at constant temperature the solubility of gases in liquid _______.
(a) No change
(b) increases
(c) Decreases
(d) No reaction
Answer:
(b) increases
Question 6.
The normal pH of human blood is _______.
(a) 7.4
(b) 0.74
(c) 7.04
(d) 70.4
answer:
(a) 7.4
Question 7.
Active transport involves _______.
(a) movement of molecules from lower to higher concentration
(b) expenditure of energy
(c) it is an uphill task
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate secretion of adrenalin. The component causing this could be _______.
(a) Nicotine
(b) Tannic acid
(c) Curcumin
(d) Leptin
Answer:
(a) Nicotine
![]()
Question 9.
The segments of leech are known as _______.
(a) Metameres
(b) Proglottids
(c) Strobila
(d) Ganglion
Answer:
(a) Metameres
Question 10.
Vomiting centre is located in _______.
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Medulla oblongata
(d) Hypothalamus
Answer:
(c) Medulla oblongata
Question 11.
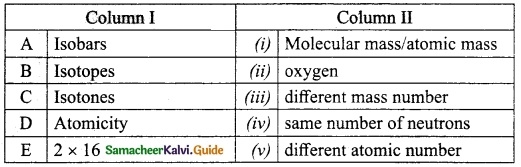
Which one of the following organ in man is not Vestigeal?
(a) Vermiform appendix
(b) Epiglottis
(c) Nictitating membrane
(d) Ear muscles
Answer:
(b) Epiglottis
![]()
Question 12.
Pusa Komal is a disease resistant variety of _______.
(a) Cow pea
(b) Sugarcane
(c) Rice
(d) Maize
Answer:
(a) Cow pea
Part – II
Answer any seven questions. (Q.No: 22 is compulsory) [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 13.
Define Raman Scattering.
Answer:
Raman Scattering is defined as “The interaction of light ray with the particles of pure liquids or transparent solids, which leads to a change in wavelength or frequency”.
Question 14.
How does an astronaut float in a space shuttle?
Answer:
An astronaut float in a space shuttle because both are in the state of weightlessness. Both are – experiencing equal acceleration towards earth as free fall bodies. Astronauts are not floating but falling freely.
![]()
Question 15.
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Answer:
Convex lens:
- The lens which is thicker at the centre that at the edges.
- It is called as converging lens.
Concave Lens:
- The lens which is thinner at the centre than at the edges.
- It is called as diverging lens.
Question 16.
State two condition necessary for rusting of iron.
Answer:
- The presence of water and oxygen is essential for the rusting of iron.
- Impurities in the iron, the presence of water vapour, acids, salts and carbon dioxide hastens rusting.
Question 17.
Define combination reaction.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which 2 or more reactants combine to form a single product, the reaction is known as combination reaction.
Question 18.
Which hormone is known as stress hormone in plants ? Why?
Answer:
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a growth inhibitor which regulate abscission and dormancy. It increases tolerance of plants to various kind of stress. Hence, it is called as stress hormone. It is found in the chloroplast of plants.
Question 19.
Distinguish between,
(а) Somatic gene therapy and germ line gene therapy.
(b) Undifferentiated cells and differentiated cells.
Answer:
(a)
Somatic gene therapy:
Somatic gene therapy is the replacement of defective gene in somatic cells.
Germ line gene therapy:
Germ line gene therapy is the replacement of defective gene in germ cell (egg and sperm).
(b)
Undifferentiated cells:
The cells which have not become specialized are called undifferentiated cells.
Eg. Cells in early embryos
Differentiated cells:
The cells which have become specialised for doing certain job.
Eg. Nerve cell
![]()
Question 20.
What is Natural selection?
Answer:
During the struggle for existence, the organisms which can overcome the challenging situation, survive and adapt to the surrounding environment. Organism which are unable to face the challenges are unfit to survive and disappear. The process of selection of organisms with favourable variation is called as Natural selection.
Question 21.
What is Heparin?
Answer:
Heparin is an anticoagulating substance produced in leech by its salivary gland.
Question 22.
The refractive index of glass is 1.50, and the speed of light in air is 3 x 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in glass.
Answer:

Part – III
Answer any seven questions (Q.No: 32 is compulsory) [7 × 4 = 28]
Question 23.
State the universal law of gravitation and derive its Mathematical expression.
Answer:

This law states that every other particle of matter in this universe attracts every other particle with a force. This force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centres of there masses. The direction of the force acts along the line joining the masses.
Derivation: Let m1 and m2 be the masses of two bodies A and B placed at r metre apart in space.
Force, F ∝ m1 x m2, F ∝ \(\frac{1}{r^{2}}\)
On combining the above two expressions,

Where G is the universal gravitational constant. Its value is SI unit is 6.674 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2.
![]()
Question 24.
(i) What are the causes of ‘Myopia’?
Answer:
- Myopia, also known as short sightedness, occurs due to the lengthening of eye ball.
- Nearby objects can be seen clearly but distant objects Cannot be seen clearly.
- The focal length of the eye lens is reduced or the distance between eye lens and retina increases.
- Due to this, the image of distant objects are formed before the retina.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram, a ray is passing parallel to the optic axis of convex lens.
Answer:

Question 25.
(i) State Joule’s law of heating:
Answer:
H = I2RT
Joule’s law of heating states that the heat produces in any resistor is:
- Directly proportional to the square of the current passing through the resistor.
- Directly proportional to the resistance of he resistor.
- Directly proportional to the lime for which the current is passing through the resistor.
(ii) An alloy of nickel and chromium is used as the heating element. Why?
Answer:
- It has high resistivity
- It has a high melting point
- It is not easily oxidized.
(iii) What happens to the resistance, as the conductor is made thicker?
Answer:
The resistance decreases as the conductor is made thicker.
Reason: Resistance is inversely proportional to area of cross section A.
(i.e) R ∝ 1/A – here, A = πr²
Where, r is the radius which determines the thickness.
Question 26.
(i) (a) Identify the bond between H and F in HF molecule.
Answer:
The nature of bond in HF molecule is ionic.
(b) What property forms the basis of identification?
Answer:
Electronegativity
(c) How does the property vary in periods and in groups?
Answer:
Along the period, from left to right in the periodic table the electronegativity increases because of the increase in the nuclear charge which in turn attracts the electrons more strongly. On moving down a group, the electronegativity of the elements decreases because of the increased number of energy level.
(d) Name the acid that renders aluminium passive. Why?
Answer:
Dilute or concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) renders aluminium passive. Because nitric acid does not attack aluminium but it renders aluminium passive due to the formation of an oxide film on its surface.
Question 27.
What are the methods preventing corrosion?
Answer:
(i) Alloying: The metals can be alloyed to prevent the process of corrosion. E.g: Stainless Steel.
(ii) Surface Coating: It involves application of a protective coating over the metal. It is the following types:
- Galvanization: It is the process of coating zinc on iron sheets by using electric current.
- Electroplating: It is the method of coating one metal over another metal by passing electric current.
- Anodizing: It is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable and corrosion resistant. Aluminium is widely used for anodizing process.
- Cathodic Protection: It is the method of controlling corrosion of a metal surface protected is coated with the metal which is easily corrodible. The easily corrodible metal is called Sacrificial metal to act as anode ensuring cathodic protection.
![]()
Question 28.
What are the functions of the following?
(a) Thalamus (b) Hypothalamus (c) Cerebellum (d) Pons
Answer:
(a) Thalamus – acts as relay station
(b) Hypothalamus – Temperature control, thirst, hunger, urination, important link between nervous system and endocrine system.
(c) Cerebellum – Maintenance of posture and balance, co-ordinate voluntary, muscle activity
(d) Pons – Role in sleep – awake cycle
Question 29.
(a) Why is euploidy considered to be advantageous to both plants and animals?
Answer:
In euploidy condition, the individual bears more than the usual number of diploid chromosomes.
- Triploid plants (3n) and animals are typically sterile.
- The tetraploid plants, (4n), often result in increased fruit and flower size.
(b) How are arteries and veins structurally different from one another?
Answer:
Artery:
- Distributing vessel.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery.
- Arteries are made up of thick walls.
- Deep location.
Vein:
- Collecting vessel.
- Veins carries deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein.
- Veins are made up of thin walls.
- Superficial in location.
Question 30.
Write a short note on mesophyll.
answer:
The tissue present between the upper and lower epidermis is called mesophyll. It is differentiated into:
(a) Palisade Parenchyma: It is found just below the upper epidermis. The cells are elongated. These cells have more number of chloroplasts. The cells do not have intercellular spaces and they take part in photosynthesis.
(b) Spongy Parenchyma: It is found below the palisade parenchyma tissue. Cells are almost spherical or oval and are irregularly arranged. Cells have intercellular spaces. It helps in gaseous exchange.
Question 31.
(a) Mention the diseases caused by tobacco smoke.
Answer:
Lung cancer, bronchitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, emphysema and hypoxia are some of the diseases caused by tobacco smoke.
(b) Name two make hybrids rich in amino acid lysine.
Answer:
Protina, Shakti and Rathna are lysine rich maize hybrids which are developed in India.
![]()
Question 32.
(i) Write the application of echo.
Answer:
- Some animals communicate with each other over long distance and also locate object by sending the sound signals and receiving the echo as reflected from targets.
- The principle of echo is used in obstetric ultrasonography, which is used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the mother’s uterus. This is a safe testing tool, as it does not use any harmful radiations.
- Echo is used to determine the velocity of sound waves in any medium.
(ii) Write the characteristics of hydrocarbons.
Answer:
- Lower hydrocarbons are gases at room temperature.
- Alkanes are least reactive where alkynes are most reactive due to presence triple bond.
- Alkanes are saturated whereas alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated.
- They are insoluble in water.
Part – IV
(1) Answer all the questions. [3 × 7 = 21]
(2) Each question carries seven marks.
(3) Draw diagram wherever necessary.
Question 33.
(i) Explain the construction of simple microscope and derive its magnification power.
Answer:
Simple Microscope: Simple microscope is a convex lens of short focal length. It is held near the eye to get enlarged image of small B’ objects.

Let an object (AB) of height ‘h’ is placed at a point within the principal focus (u < f ) of the convex lens and the observer’s eye is placed just behind the lens. As per this position the convex lens produces an erect, virtual and enlarged image (A’B’). The image formed in the same side of the object and the distance equal to the least distance of distinct vision (D).
Magnification power (M): Ratio of the height of the image produced by the microscope (h2) to the original height of the object (h1) is called Magnification.

Magnification can also be defined as the ratio of the distance of image (v) to the distance of object (u).
![]()
Since the image is virtual and erect; the magnification (M) is taken as positive,
In simple microscope,
When the image is formed at the near point
M = 1 + \(\frac{D}{f}\)
When the image is formed at infinity
M= \(\frac{D}{f}\)
(ii) Write the uses of simple microscope.
Answer:
- By watch repairers and jewellers.
- To read small letters clearly.
- TO observe parts of flower, insects etc.
- To observe finger prints in the field of forensic science.
[OR]
(b) Find the final temperature of a copper rod. Whose area of cross section changes from 10 m2 to 11 m2 due to heating. The copper rod is initially kept at 90 K. (Coefficient of superficial expansion is 0.0021 K)
Answer:
Given:
Area of copper rod, A = 10 m2
After expansion A2 = 11 m2
Initial temperature T1 = 90K
Coefficient of superficial expansion αA= 0.0021/K
Final temperature, T2 = ?

T2 = \(\frac{1}{0.021}\) + 90 = 47.6 + 90
Final temperature, T2 = 137.6 K
(ii) Calculate the energy consumed by 120 W toaster in 4 hours.
Answer:
Given:
Power of toaster P = 120 W
Time t =4 h
Energy consumed by toaster E = P × t
= 120 × 4
E = 480 Wh
![]()
Question 34.
(a) (i) Calculate the number of water molecule present in one drop of water which weighs 0.18 g.
Answer:
Mass of water = 0.18 g

Number of molecules = Number of moles × Avogadro number
= 0.01 × 6.023 × 1023
= 0.06023 × 1023
= 6.023 × 1021 molecules
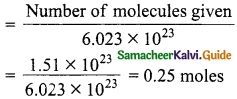
(ii) Calculate the number of moles in 1.51 × 1023 molecules of NH4Cl.
Answer:

= 0.25 mole
(iii) Calculate the gram of 5 moles of sulphur molecule, S8.
Answer:
5 moles of sulphur molecule S8
Molecular mass of sulphur molecule = 32 × 8 = 256
Mass = No of moles × molecular mass
= 5 × 256
= 1280 g
[OR]
(b) (i) Explain the classification based on the direction of the reaction.
Answer:
Reversible reaction : A reversible reaction is a reaction that can be reversed, i.e., the products can be converted back to the reactants.
A reversible reaction is represented by a double arrow with their heads in the direction opposite to each other. Thus a reversible reaction can be represent

Explanation:
The compound ‘AB’ undergoes decomposition to form the products ‘A’ and ‘B’. It is the forward reaction. As soon as the products are formed, they combine together to form ‘AB’. It is the backward reaction.
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Irreversible Reactions:
The reaction that cannot be reversed is called irreversible reaction. Consider the combustion of coal into carbon-di-oxide and water.

In this reaction, solid coal bums with oxygen and gets converted into carbon dioxide gas and water. As the product is a gas, as soon as it is formed it escapes out of the reaction container. It is hard to decompose a gas into a solid. Thus, the backward reaction is not possible in this case. So, it is an irreversible reaction.
(ii) What happens during a chemical change?
Answer:
- In a chemical reaction, the atoms of the reacting molecules or elements are rearranged to form new molecules.
- Old chemical bonds between atoms are broken and new chemical bonds are formed.
- Bond breaking absorbs energy where as bond formation releases energy.
![]()
Question 35.
(a) (i) What are the hormones secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland? Mention the tissues on which they exert their effect.
Answer:
Vasopressin and Oxytocin are the hormones secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
In kidney tubules, the vasopressin hormone increases the reabsorption of water. Its deficiency caused Diabetes insipidus.
Oxytocin helps in the contraction of the smooth muscles of uterus at the time of child birth and milk ejection from the mammary gland after child birth.
(ii) How are e-wastes generated?
Answer:
E-wastes are generally called as electronic wastes, includes the spoiled, outdated, non-repairable electrical and electronic devices.
(iii) Define fertilization?
Answer:
The process of Fusion of male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (ovum) is known as fertilization. It results in the formation of Zyote.
[OR]
(b) (i) Why are leucocytes classified as granulocytes and agranulocytes? Name each cell and mention its functions.
Answer:
White blood corpuscles or Leucocytes:
Based on the presence of granules in the cytoplasm of leucocytes it is classified into two categories,
(i) Granulocytes
(ii) Agranulocytes.
(i) Granulocytes: They contain granules in their cytoplasm. Their nucleus is irregular or lobed. They are classified into three types,
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
(1) Neutrophils: Their numbers are increased during infection and inflammation.
(2) Eosinophils: Their number increases during conditions of allergy and parasitic infections. It also brings about detoxification of toxins.
(3) Basophils: They release chemicals during the process of inflammation.
(ii) Agranulocytes: Granules are not found in the cytoplasm of these cells. The agranulocytes are of two types: (a) Lymphocytes (b) Monocytes
(a) Lymphocytes: They produce antibodies during bacterial and viral infections.
(b) Monocytes: They are phagocytic and can engulf bacteria.
(ii) Biofortification may help in removing hidden hunger. How?
Answer:
Biofortification is the scientific process of developing crop plants enriched with high levels of desirable nutrients like vitamins, proteins and minerals.
Example:
- Protina, Shakti and Rathna are lysine rich maize hybrids
- Atlas 66, a protein rich wheat variety.
- Iron rich fortified rice variety.
- Vitamin A enriched carrots, pumpkin and spinach.
- By this way, Biofortification may help in removing hidden hunger.