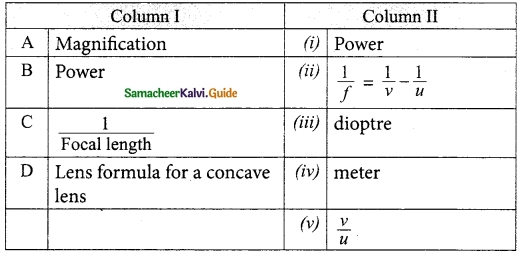
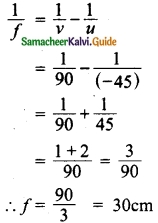
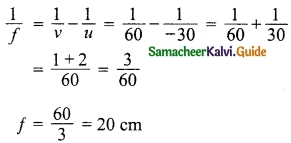
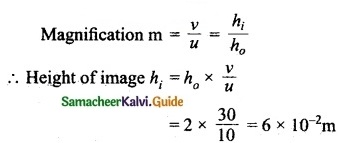
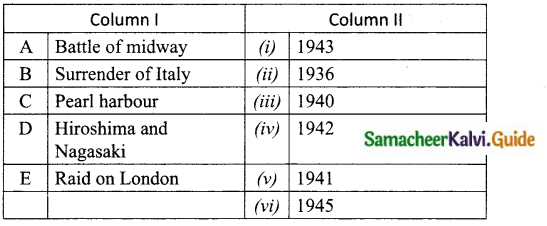
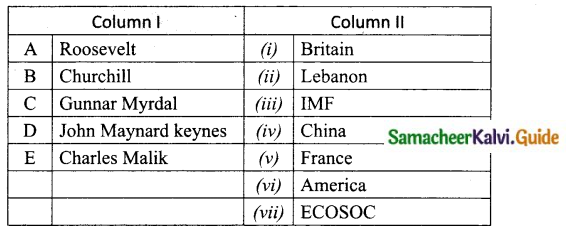
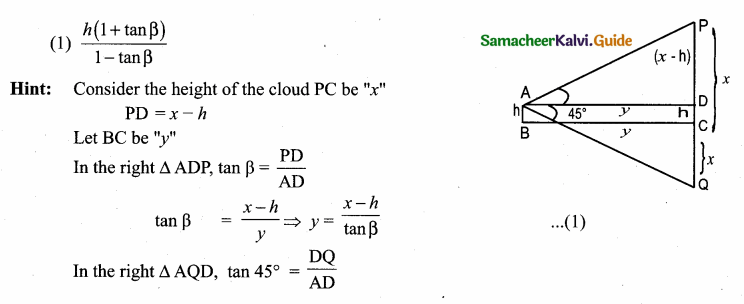
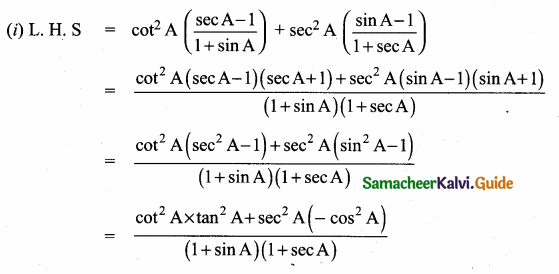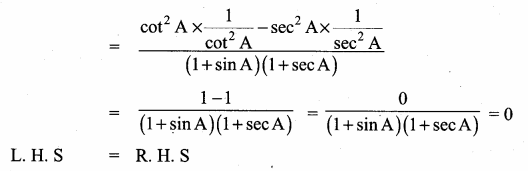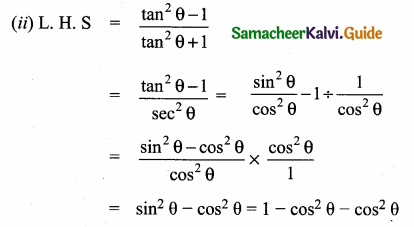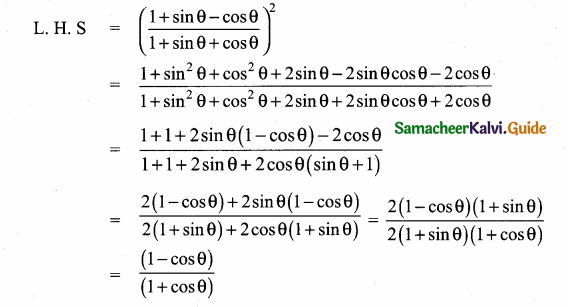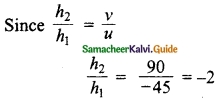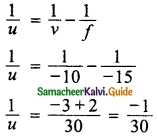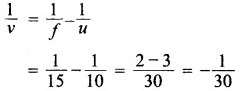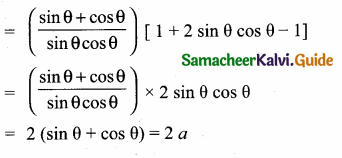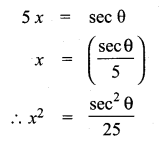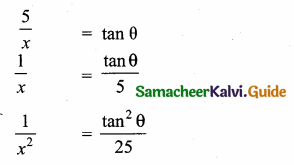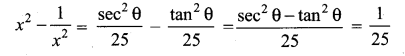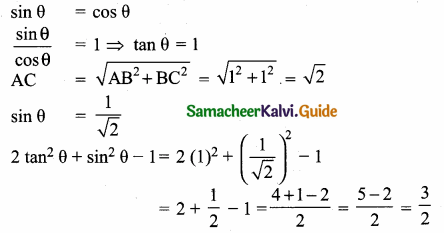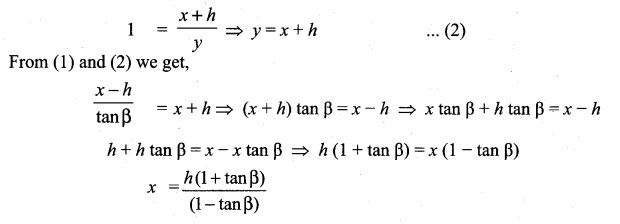Students can download Maths Chapter 6 Trigonometry Additional Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Trigonometry Additional Questions
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
(1 – sin2 θ) sec2 θ = …………
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) tan2 θ
(4) cos2 θ
Answer:
(2) 1
Hint: (1 – sin2 θ) sec2 θ = cos2 θ sec2 θ = cos2 θ \(\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} \theta}\) = 1
![]()
Question 2.
(1 + tan2 θ) sin2 θ = ………….
(1) sin2 θ
(2) cos2 θ
(3) tan2 θ
(4) cot2 θ
Answer:
(3) tan2 θ
Hint: (1 + tan2 θ) sin2 θ = sec2 θ sin2 θ = \(\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} \theta}\) sin2 θ = \(\frac{\sin ^{2} \theta}{\cos ^{2} \theta}\) = tan2 θ
Question 3.
(1 – cos2 θ) (1 + cot2 θ) = ………..
(1) sin2 θ
(2) 0
(3) 1
(4) tan2 θ
Answer:
(3) 1
Hint: (1 – cos2 θ) (1 + cot2 θ) = sin2 θ cosec2 θ = sin2 θ. \(\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} \theta}\)= 1
Question 4.
sin (90° – θ) cos θ + cos (90° – θ) sin θ = …………..
(1) 1
(2) 0
(3) 2
(4) -1
Answer:
(1) 1
Hint: sin (90° – θ) cos θ + cos (90° – θ) sin θ = cos θ cos θ + sin θ sin θ = cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1
![]()
Question 5.
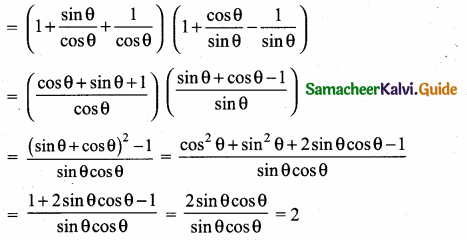
1 – \(\frac{\sin ^{2} \theta}{1+\cos \theta}\) = ……………….
(1) cos θ
(2) tan θ
(3) cot θ
(4) cosec θ
Answer:
(1) cos θ
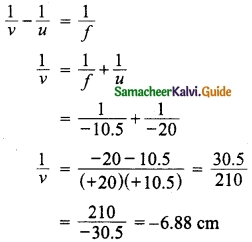
Hint:
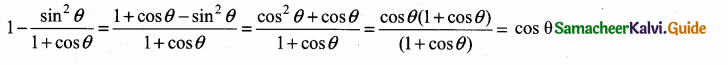
Question 6.
cos4 x – sin4 x = ……………
(1) 2 sin2 x – 1
(2) 2 cos2 x – 1
(3) 1 + 2 sin2 x
(4) 1 – 2 cos2 x
Answer:
(2) 2 cos2 x – 1
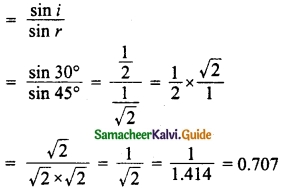
Hint:
cos4 x – sin4 x (cos2 x)2 – (sin2 x)2
= (cos2 x + sin2x) (cos2 x – sin2x)
= 1 (cos2 x – sin2 x)
= cos2 x – (1 – cos2 x)
cos2 x – 1 + cos2 x
= 2 cos2 x – 1.
Question 7.
If tan θ = \(\frac { a }{ x } \) , then the value of \(\frac{x}{\sqrt{a^{2}+x^{2}}}\) = ………………
(1) cos θ
(2) sin θ
(3) cosec θ
(4) sec θ
Answer:
(1) cos θ
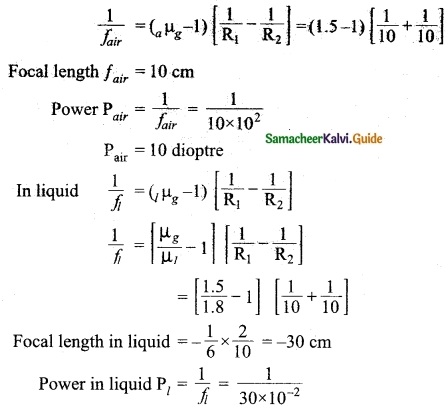
Hint:
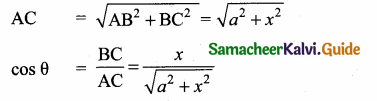
Question 8.
If x = a sec θ, y = b tan θ, then the value of \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = ………………..
(1) 1
(2) -1
(3) tan2 θ
(4) cosec2 θ
Answer:
(1) 1
Hint:
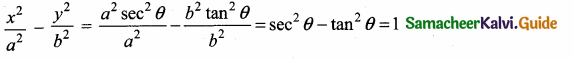
![]()
Question 9.
\(\frac{\sec \theta}{\cot \theta+\tan \theta}\) = ………..
(1) cot θ
(2) tan θ
(3) sin θ
(4) – cot θ
Answer:
(3) sin θ
Hint:
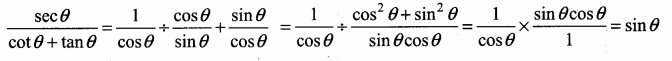
Question 10.
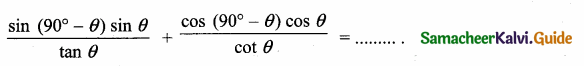
Answer:
(1) tan θ
(2) 1
(3) -1
(4) sin θ
Answer:
(2) 1
Hint:
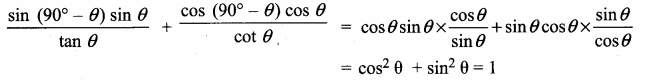
Question 11.
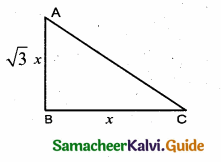
In the adjoining figure, AC = ………….
(1) 25m
(2) 25 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
(3) \(\frac{25}{\sqrt{3}}\)
(4) 25 \(\sqrt { 2 }\) m
Answer:
(2) 25 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
Hint:
tan θ = \(\frac { AC }{ AB } \) ⇒ tan 60° = \(\frac { AC }{ 25 } \) ⇒ AC = 25 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
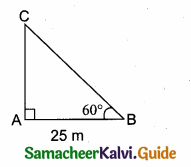
Question 12.
In the adjoining figure ∠ABC =
(1) 45°
(2) 30°
(3) 60°
(4) 50°
Answer:
(3) 60°
Hint:
tan B = \(\frac { AC }{ AC } \) = \(\frac{100 \sqrt{3}}{100}\) = \(\sqrt { 3 }\) ⇒ ∴ tan B = \(\sqrt { 3 }\) ⇒ ∠B = 60°
![]()
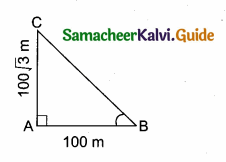
Question 13.
A man is 28.5 m away from a tower. His eye level above the ground is 1.5 m. The angle of elevation of the tower from his eyes is 45°. Then the height of the tower is …………..
(1) 30 m
(2) 27.5 m
(3) 28.5 m
(4) 27 m
Answer:
(1) 30 m
Hint:
tan 45° = \(\frac { AB }{ BC } \)
1 = \(\frac { x }{ 28.5 } \) ⇒ x = 28.5
Height of tower = 28.5 + 1.5 = 30 m
Question 14.
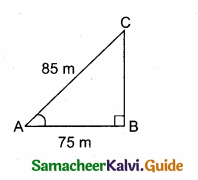
In the adjoining figure, sin θ = \(\frac { 15 }{ 17 } \) Then BC = ………….
(1) 85 m
(2) 65 m
(3) 95 m
(4) 75 m
Answer:
(4) 75 m
Hint:
sin θ = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \) ⇒ \(\frac { 15 }{ 17 } \) = \(\frac { BC }{ 85 } \) ⇒ BC = \(\frac{85 \times 15}{17}\) = 75 m
Question 15.
(1 + tan2 θ) (1 – sin θ) (1 + sin θ) = …………..
(1) cos2 θ – sin2 θ
(2) sin2 θ – cos2 θ
(3) sin2 θ + cos2 θ
(4) 0
Answer:
(3) sin2 θ + cos2 θ
Hint:
(1 + tan2 θ) (1 – sin θ) (1 + sin θ) = (1 + tan2 θ) (1 – sin2 θ) = sec2 θ × cos2 θ = sec2 θ × cos2 θ = sec2 θ × \(\frac{1}{\sec ^{2} \theta}\) = 1 = sin2 θ + cos2 θ
![]()
Question 16.
(1 + cot2 θ) (1 – cos θ) (1 + cos θ) = ………………….
(1) tan2 θ – sec2 θ
(2) sin2 θ – cos2 θ
(3) sec2 θ – tan2 θ
(4) cos2 θ – sin2 θ
Answer:
(3) sec2 θ – tan2 θ
Hint:
(1 + cot2 θ) (1 – cos θ) (1 + cos θ) = (1 + cot2 θ) (1 – cos2 θ) = cosec2 θ. sin2 θ
= \(\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} \theta}\) sin2 θ = 1 = sec2 θ – tan2 θ.
Question 17.
(cos2 θ – 1) (cot2 θ + 1) + 1 = ……………….
(1) 1
(2) -1
(3) 2
(4) 0
Answer:
(4) 0
Hint:
(cos2 θ – 1) (cot2 θ + 1) + 1 = – sin2 θ (cosec2 θ) + 1 = – sin2 θ \(\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} \theta}\) + 1 = -1 + 1 = 0
Question 18.
\(\frac{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}{1+\cot ^{2} \theta}\) = …………….
(1) cos2 θ
(2) tan2 θ
(3) sin2 θ
(4) cot2 θ
Answer:
(2) tan2 θ
Hint:
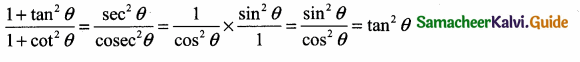
Question 19.
Sin2 θ + \(\frac{1}{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\) …………
(1) cosec2 θ + cot2 θ
(2) cosec2 θ – cot2 θ
(3) cot2 θ – cosec2 θ
(4) sin2 θ – cos2 θ
Answer:
(2) cosec2 θ – cot2 θ
Hint:
sin2 θ + \(\frac{1}{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\) = sin2 θ + \(\frac{1}{\sec ^{2} \theta}\) = sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1 cosec2 θ – cot2 θ
Question 20.
9 tan2 θ – 9 sec2 θ = ……..
(1) 1
(2) 0
(3) 9
(4) -9
Answer:
(4) -9
Hint:
9 tan2 θ – 9 sec2 θ = 9(tan2 θ – sec2 θ) = 9(-1) = -9
![]()
Question 21.
The length of shadow of a tower on the plane ground is \(\sqrt { 3 }\) times the height of the tower. The angle of elevation of sum is …………..
(1) 45°
(2) 30°
(3) 60°
(4) 90°
Ans.
(2) 30°
Hint: Let the height of the tower be “x”
Lenght of the shadow is \(\sqrt { 3 }\) x
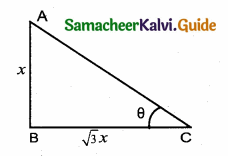
In the right ∆ ABC, tan θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{x}{\sqrt{3} x}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
= tan 30°
θ = 30°
Question 22.
A ladder makes an angle of 60° with the ground, when placed against a wall. If the foot of the ladder is 2m away from the wall, then the length of the ladder (in metres) is …………
(1) \(\frac{4}{\sqrt{2}}\) m
(2) 4 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
(3) 2 \(\sqrt { 2 }\) m
(4) 4 m
Answer:
(4) 4 m
Hint:
Let the length of the ladder be x.
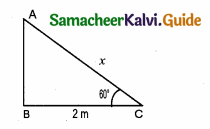
In ∆ ABC, cos 60° = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ x } \)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ x } \) ⇒ x = 4m
Question 23.
The angle of depression of a car parked on the road from the top of a 150m high tower is 30°. The distance of the car from the tower (in metres) is ……….
(1) 150 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
(2) 150 \(\sqrt { 2 }\)
(3) 75 cm
(4) 50 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
Answer:
(4) 50 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
Hint:
Let the distance of the car from the tower is “x” m
In ∆ ABC, tan 30° = \(\frac { AB }{ BC } \)
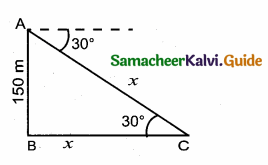
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac { 150 }{ x } \) ⇒ x = 150 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
![]()
Question 24.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower at a point on the ground 50 m away from the foot of the tower is 45°. Then the height of the tower (in meters) is ……….
(1) 50 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
(2) 50 m
(3) \(\frac{50}{\sqrt{2}}\) m
(4) \(\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\) m
Answer:
(4) \(\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\) m
Hint:
Let the height of the AB be “x”
On ∆ ABC
tan 45° = \(\frac { AB }{ BC } \)
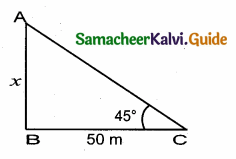
1 = \(\frac { x }{ 50 } \) ⇒ x = 50 m
Question 25.
If x = a cos θ and y = b sin θ, then b2x2 + a2y2 = ……………
(1) a2b2
(2) ab
(3) a4b4
(4) a2 + b2
Answer:
(1) a2b2
Hint:
b2a2 cos2 θ + a2 b2 sin2 θ = a2b2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = a2b2 × 1 = a2b2
II. Answer The Following Questions.
Question 1.
Prove that sec2 θ + cosec2 θ = sec2 θ cosec2 θ
Answer:
L.H.S = sec2 θ + cosec2 θ
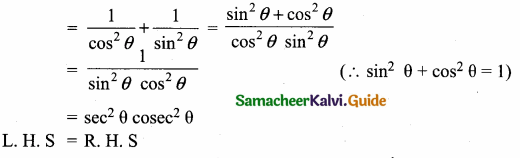
Question 2.
Prove that \(\frac{\sin \theta}{1-\cos \theta}\) = cosec θ + cot θ.
Answer:
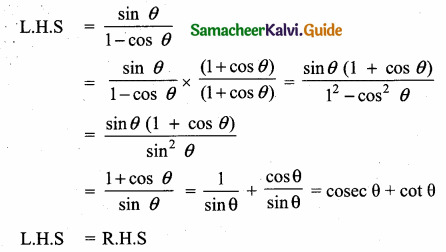
![]()
Question 3.
Prove that \(\frac{\cos \theta}{\sec \theta-\tan \theta}\) = 1 + sin θ
Answer:
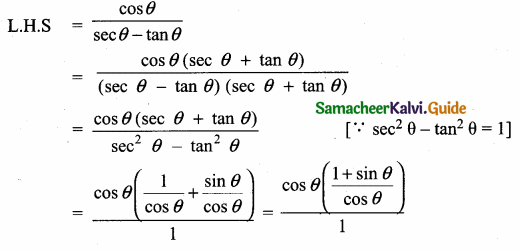
= 1 + sin θ = R.H.S
L.H.S = R.H.S
Question 4.
Prove that sec θ (1 – sin θ) (sec θ + tan θ) = 1
Answer:
L.H.S = sec θ (1 – sin θ) (sec θ + tan θ)
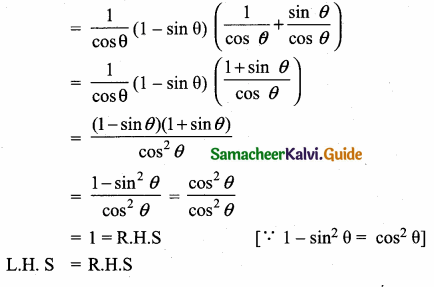
Question 5.
Prove that \(\frac{\sin \theta}{\csc \theta+\cot \theta}=1\) – cos θ
Answer:
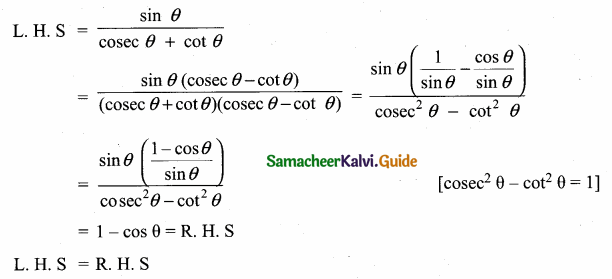
Question 6.
Prove the identify \(\frac{\sin \theta}{\csc \theta}+\frac{\cos \theta}{\sec \theta}=1\)
Answer:
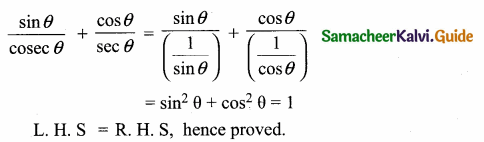
Question 7.
Prove the identify \(\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos \theta}{1+\cos \theta}}\) = cosec θ – cot θ
Answer:
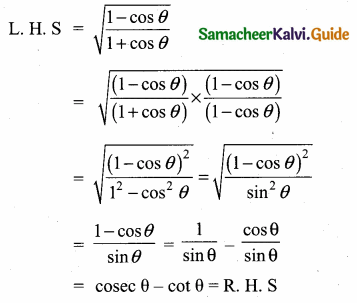
(∵ 1 – cos2 θ = sin2 θ)
L.H.S = R.H.S
![]()
Question 8.
Prove the identity [cosec (90° – θ) – sin (90° – θ)] [cosec θ – sin θ] [tan θ + cot θ] = 1
Answer:
Now, [cosec (90° – θ) – sin (90° – θ)] [cosec θ – sin θ] [tan θ + cot θ]
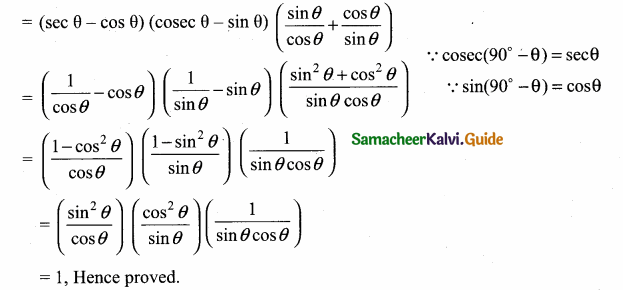
Question 9.
A kite is flying with a string of length 200 m. If the thread makes an angle 30° with the ground, find the distance of the kite from the ground level. (Here, assume that the string is along a straight line.)
Answer:
Let h denote the distance of the kite from the ground level.
In the figure, AC is the string
Given that ∠CAB = 30° and AC = 200 m.
In the right ∆ CAB,
sin 30 = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \)
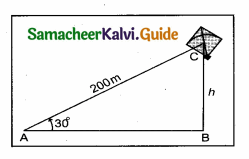
sin 30 = \(\frac { h }{ 200 } \)
⇒ h = 200 sin 30°
∴ h = 200 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = 100 m
Hence the distance of the kite from the ground level is 100 m.
Question 10.
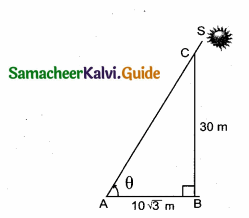
Find the angular elevation (angle of elevation from the ground level) of the Sun when the length of the shadow of a 30 m long pole is 10 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m.
Answer:
Let S be the position of the Sun and BC be the pole.
Let AB denote the length of the shadow of the pole.
Let the angular elevation of the Sun be θ.
Given that AB = 10 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m and BC = 30 m
In the right ∆ CAB,tan θ = \(\frac { BC }{ AB } \) = \(\frac{30}{10 \sqrt{3}}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{3}}\)
⇒ tan θ = \(\sqrt { 3 }\)
∴ θ = 60°
Thus, the angular elevation of the Sun from the ground level is 60°
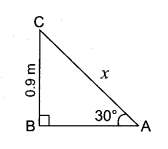
Question 11.
A ramp for unloading a moving truck, has an angle of elevation of 30°. If the top of the ramp is 0.9 m above the ground level, then find the length of the ramp.
Answer:
Let AC be the length of the ramp and AC = “x” metre
In the right angled ∆ ABC,
∠A = 30° and BC = 0.9 m
sin 30° = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 0.9 }{ x } \)
x = 0.9 × 2 = 1.8 m
∴ Length of the ramp x = 1.8 m
![]()
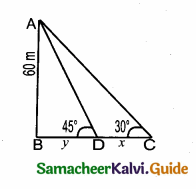
Question 12.
A girl of height 150 cm stands in front of a lamp-post and casts a shadow of length 150 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) cm on the ground. Find the angle of elevation of the top of the lamp-post.
Answer:
The height of the girl (BC) = 150 cm
Length of the shadow = 150 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) cm
Let θ be the angle of elevation of the lamp post.
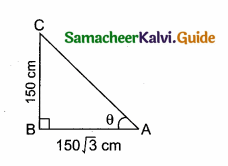
In θ = \(\frac{150}{150 \sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
tan 30° = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) ⇒ ∴ θ = 30°
∴ Angle of elevation of the lamp post = 30°
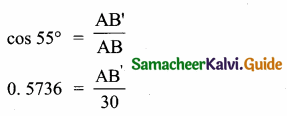
Question 13.
Prove that \(\sqrt{\cot ^{2} \theta-\cos ^{2} \theta}\) = cot θ . cos θ
Answer:
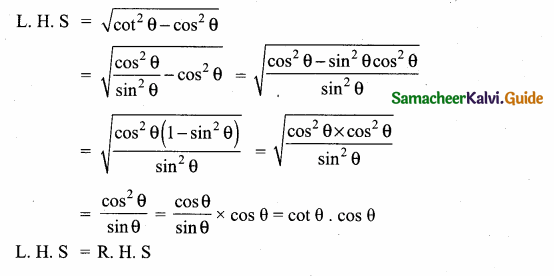
![]()
Question 14.
Prove that \(\frac{1+\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}+\frac{\cos \theta}{1+\sin \theta}\) = 2 sec θ
Answer:
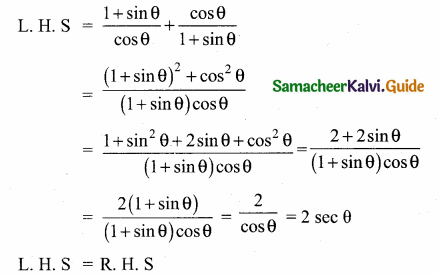
Question 15.
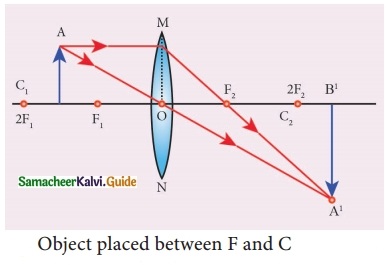
A tower is 100 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) metres high. Find the angle of elevation of its top from a point 100 metres away from its foot.
Answer:
Let MN be the tower of height 100 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
“O” be the point of observation such that OM = 100 m
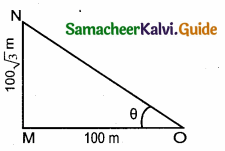
Let 0 be the angle of elevation
In the right ∆ OMN, we have
tan θ = \(\frac { MN }{ OM } \) = \(\frac{100 \sqrt{3}}{100}\)
tan θ = \(\sqrt { 3 }\) = tan 60°
∴ θ = 60°
Hence the angle of elevation is 60°
Question 16.
If sin θ = x and sec θ = y, then find the value of cot θ
Answer:
Given sin θ = x
y = sec θ = \(\frac{1}{\cos \theta}\)
∴ cos θ = \(\frac { 1 }{ y } \) ⇒ cot θ = \(\frac{\cos \theta}{\sin \theta}=\frac{1}{y} \div x\)
cot θ = \(\frac { 1 }{ xy } \)
Question 17.
A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is 30° ( see figure).
Answer:
In the figure, let AC is the rope and AB is the pole. In right ∆ ABC, we have
\(\frac { AB }{ AC } \) = sin 30°
But, sin 30° = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
\(\frac { AB }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ⇒ \(\frac { AB }{ 20 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
[∵ AC = 20 m]
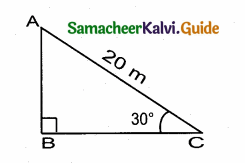
AB = 20 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = 10 m
Thus, the required height of the pole is 10 m.
Question 18.
A kite is flying at a height of 60 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
Answer:
Let in the right ∆ AOB,
OB = Length of the string
AB = 60 m = Height of the kite.
In the right ∆ OAB
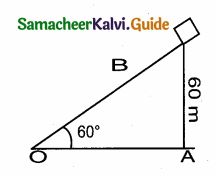
sin 60° = \(\frac { AB }{ OB } \)
\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) = \(\frac { 60 }{ OB } \)
\(\sqrt { 3 }\) × OB = 120
OB = \(\frac{120}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{120 \times \sqrt{3}}{3}\)
Lenght of the string = 40 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) = 40 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m
![]()
Question 19.
Prove that sin6 θ + cos6 θ + 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1
Answer:
L. H. S = sin6 θ + cos6 θ + 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ
= (sin2 θ)3 + (cos2 θ)3 + 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ
= (sin2 θ + cos2 θ)3 – 3 × sin2 θ cos2 θ (sin2 θ + cos2 θ) + 3 × sin2 θ cos2 θ
[Using a3 + h3 = (a + h)3 – 3 ab (a + h)]
= 13 – 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ (1) + 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ
= 1 – 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ + 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ
= 1
L.H. S = R. H. S
III. Answer The Following Questions.
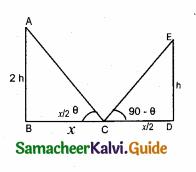
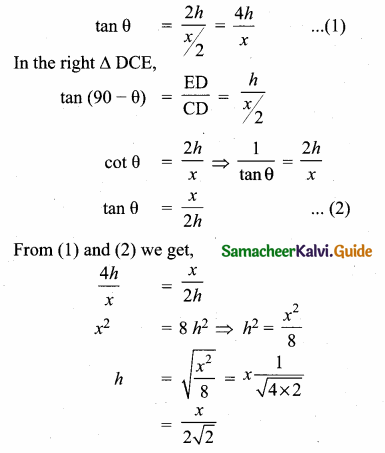
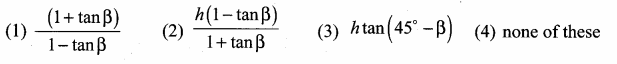
Question 1.
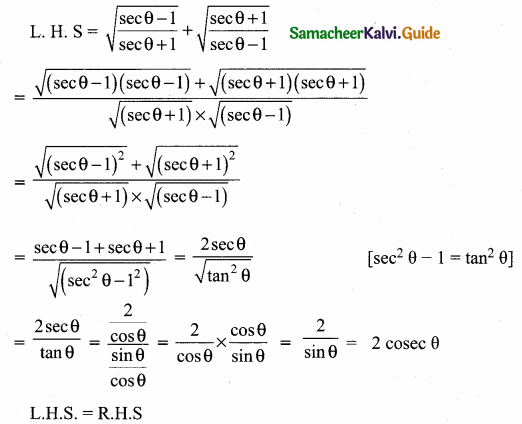
Prove that \(\sqrt{\frac{\sec \theta-1}{\sec \theta+1}}+\sqrt{\frac{\sec \theta+1}{\sec \theta-1}}=2\) cosec θ
Answer:
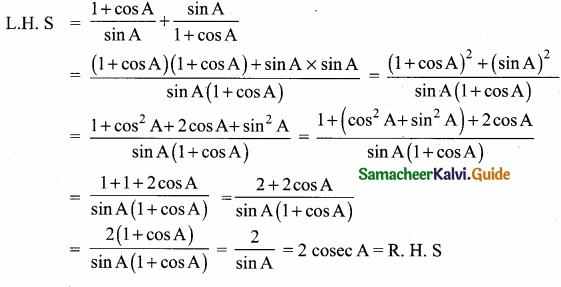
Question 2.
Prove that \(\frac{1+\cos A}{\sin A}+\frac{\sin A}{1+\cos A}\) = 2 cosec A.
Answer:
Question 3.
Prove that 2 (sin6 θ + cos6 θ) – 3 (sin4 θ + cos4 θ) + 1 = θ
Answer:
consider, sin6 θ + cos6 θ
= (sin2 θ)3 + (cos2 θ)3
[Using a3 + b3 = (a + b)3 – 3 ab(a + b)]
= (sin2 θ + cos2 θ)3 – 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ (sin2 θ + cos2 θ)
= 1 – 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ
Now sin4 θ + cos4 θ = (sin2 θ)2 + (cos2 θ)2 (a2 + b2 = (a + b)2 – 2 ab)
= (sin2 θ + cos2 θ)2 – 2 (sin2 θ cos2 θ)
= 1 – 2 (sin2 θ cos2 θ)
L. H. S = 2 (sin6 θ + cos6 θ) – 3 (sin4 θ + cos4 θ) + 1
= 2(1 – 3 sin2 θ cos2 θ) – 3 (1 – 2 sin2 θ cos2 θ) + 1
= 2 – 6 sin2 θ cos2 θ – 3 + 6 sin2 θ cos2 θ + 1
= 3 – 3 = 0
L.H.S. = R.H.S
![]()
Question 4.
Prove that \(\frac{\sin \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)}{1+\sin \theta}+\frac{\cos \theta}{1-\cos \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)}\) = 2 sec θ
Answer:
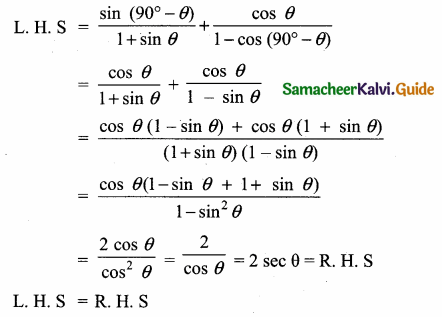
Question 5.
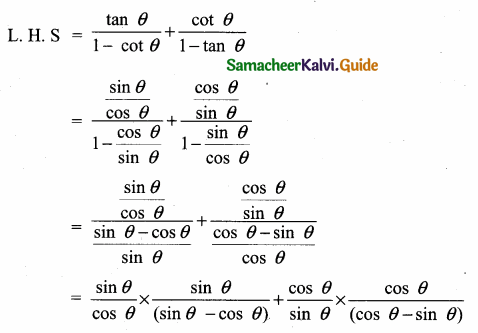
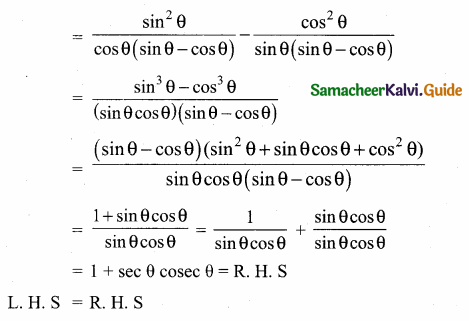
Prove that \(\frac{\tan \theta}{1-\cot \theta}+\frac{\cot \theta}{1-\tan \theta}\) = 1 + sec θ cosec θ
Answer:
Question 6.
Prove that \(\frac{\sin \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)}{1-\tan \theta}+\frac{\cos \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)}{1-\cot \theta}\) = cos θ + sin θ
Answer:
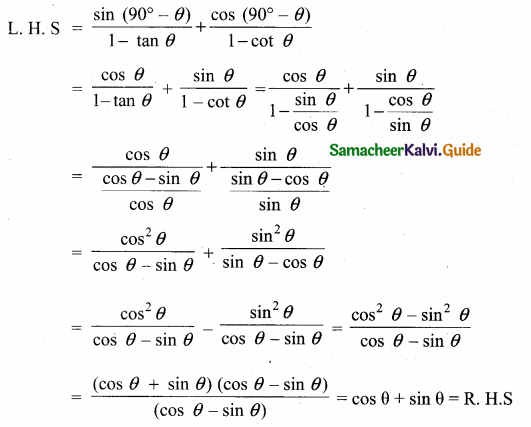
L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence Proved
Question 7.
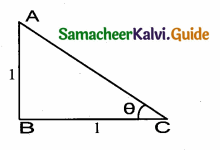
Prove that \(\frac{\tan \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)}{\csc \theta+1}+\frac{\csc \theta+1}{\cot \theta}\) = 2 sec θ
Answer:
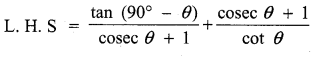
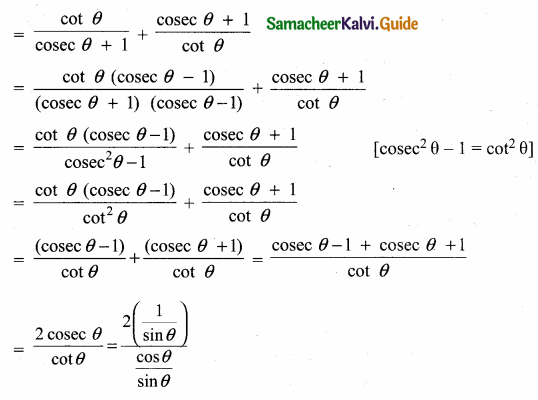
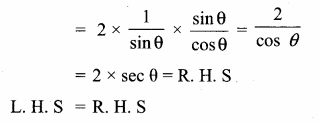
![]()
Question 8.
Prove that
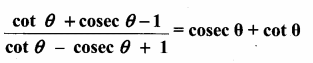
Answer:
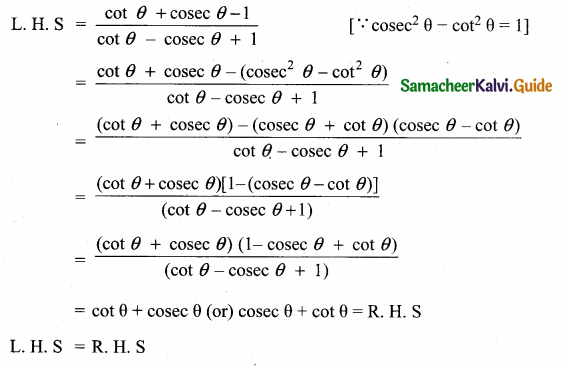
Question 9.
Prove that (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) (1 + tan θ + sec θ) = 2
Answer:
L.H.S = (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) (1 + tan θ + sec θ)
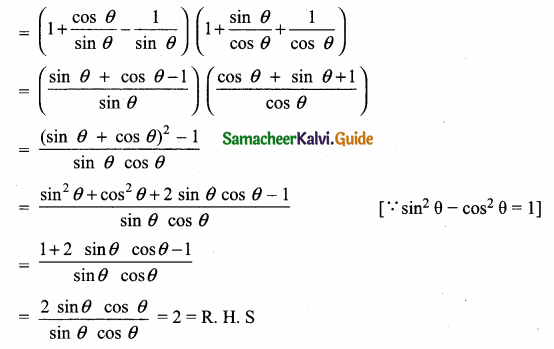
L. H. S = R. H. S
Hence proved
Question 10.
Prove that \(\frac{\sin \theta-\cos \theta+1}{\sin \theta+\cos \theta-1}=\frac{1}{\sec \theta-\tan \theta}\)
Answer:
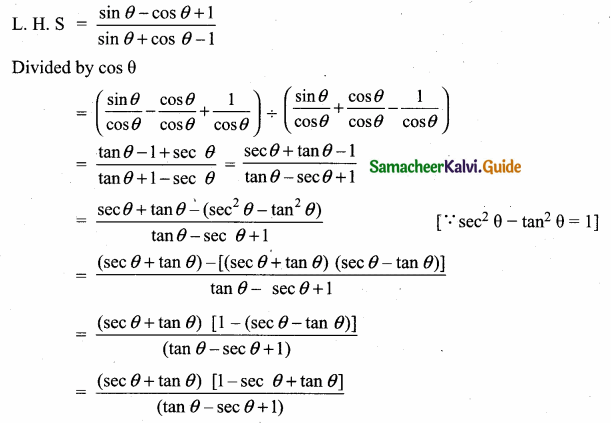
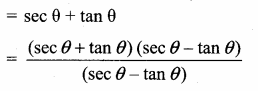
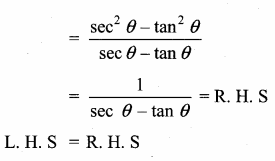
![]()
Question 11.
Prove that
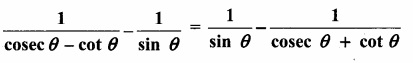
Answer:
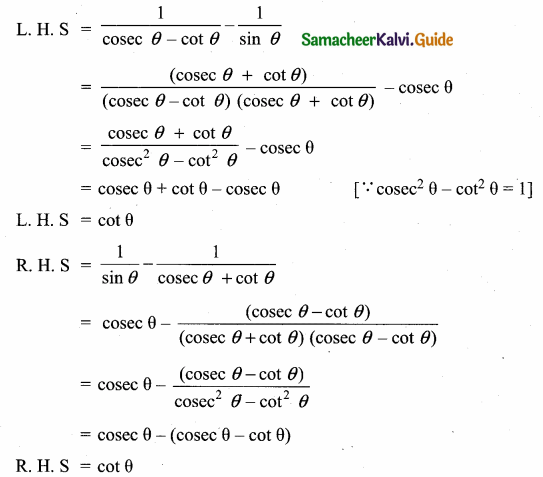
LHS = RHS
Hence proved
Question 12.
If tan θ = n tan α and sin θ = m sin α, then prove that cos2 θ = \(\frac{m^{2}-1}{n^{2}-1}, n \neq \pm 1\)
Answer:
Given tan θ = n tan α and sin θ = m sin α
Let us eliminate using cosec2 α – cot2 α = 1
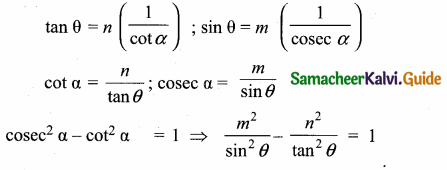
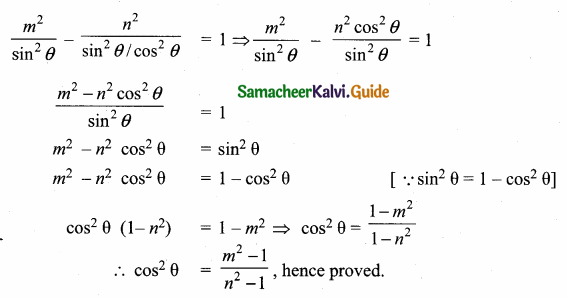
Question 13.
If sin θ, cos θ and tan θ are in G. P., then prove that cot6 θ – cot2 θ = 1.
Answer:
Given, sin θ, cos θ, tan θ are in G. P., To prove cot6 θ – cot2 θ = 1
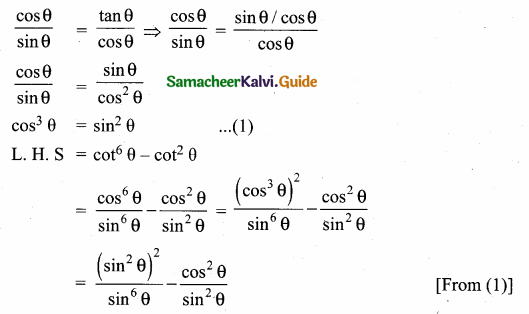
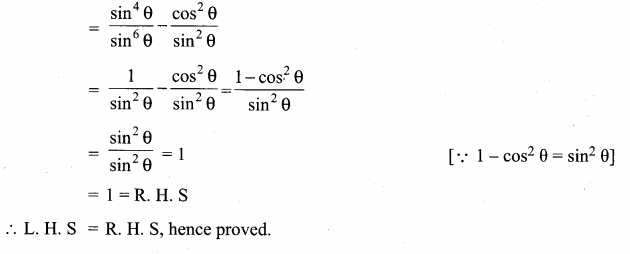
Question 14.
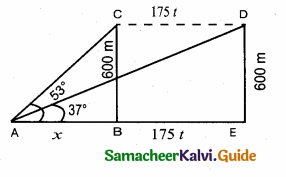
A person in an helicopter flying at a height of 700 m, observes two objects lying opposite to each other on either bank of a river. The angles of depression of the objects are 30° and 45°. Find the width of the river. (\(\sqrt { 3 }\) = 1. 732)
Answer:
Let C be the point of observation.
The objects A and B lying opposite to each other on either bank of a river.
Width of the river AB = AD + BD
In the right ∆ ACD,
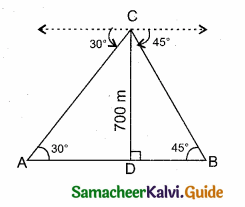
tan 30° = \(\frac { CD }{ AD } \) ⇒ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac { 700 }{ AD } \)
∴ AD = 700 \(\sqrt { 3 }\)
In the right ∆ BCD tan 45° = \(\frac { CD }{ BD } \)
1 = \(\frac { 700 }{ BD } \) ⇒ BD = 700 m
∴ Width of the river = AD + BD
= 700 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) + 700 = 700 (\(\sqrt { 3 }\) + 1)
= 700 (1.732 + 1) = 700 × 2.732 m
= 1912.400 m
∴ Width of the river = 1912.4 m
![]()
Question 15.
A person X standing on a horizontal plane, observes a bird flying at a distance of 100 m from him at an angle of elevation of 30°. Another person Y standing on the roof of a 20 m high building, observes the bird at the same time at an angle of elevation of 45°. If X and Y are on the opposite sides of the bird, then find the distance of the bird from Y.
Answer:
Let the position of the bird be “B”
Given, AY = 20 m, CD = 20 m, BX = 100 m, ∠BXD = 30° and ∠BYC = 45°
In the right ∆ BXD, sin 30° = \(\frac { BD }{ BX } \)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { BD }{ 100 } \) ⇒ BD = \(\frac{100 \times 1}{2}\) = 50 m
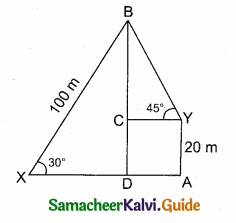
BC = BD – DC
BC = 50 m – 20 m = 30 m
In the right ∆ YBC, sin 45° = \(\frac { BC }{ BY } \)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) = \(\frac { 30 }{ BY } \) ⇒ BY = 30\(\sqrt { 2 }\)
∴ Distance of the bird from the person Y is 30\(\sqrt { 2 }\) m
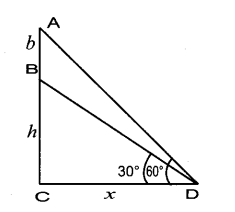
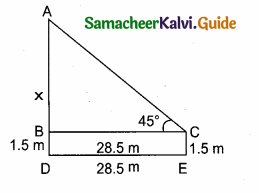
Question 16.
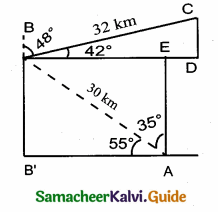
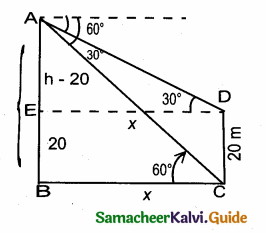
A boy is standing at some distance from a 30 m tall building and his eye level from the ground is 1.5 m. The angle of elevation from his eyes to the top of the building increases from 30° to 60° as he walks towards the building. Find the distance he walked towards the building.
Answer:
In the given figure A, B, C is a horizontal at the level of the boy
AD = A’D – AA’
AD = 30 – 1.5 = 28.5 m
Let the distance walked by the student CB is ‘x’ m.
Let AB be ‘y’ m
In the right ∆ ABD,tan 60° = \(\frac { AD }{ AB } \)
\(\sqrt { 3 }\) = \(\frac { 28.5}{ y } \)
y =\(\frac{28.5}{\sqrt{3}}\) …….(1)
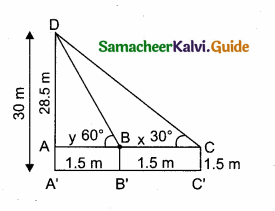
In the right ∆ ACD,tan 30° = \(\frac { AD }{ AC } \)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{28.5}{x+y}\) ⇒ x + y = 28.5 \(\sqrt { 3 }\)
y = 28.5 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) – x ………..(2)
From (1) and (2) we get,
\(\frac{28.5}{\sqrt{3}}\) = 28.5 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) – x
28.5 = 28.5 × 3 – \(\sqrt { 3 }\) x
\(\sqrt { 3 }\) x = 28.5 × 3 – 28.5
\(\sqrt { 3 }\) x = 28.5 × (3 – 1) = 28.5 × 2
\(\sqrt { 3 }\) x = 57.0 m
x = \(\frac{57}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{57 \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}\) ⇒ x = \(\frac{57 \times \sqrt{3}}{3}\) = 19 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m.
∴ The distance walked by the boy = 19 \(\sqrt { 3 }\) m.
![]()
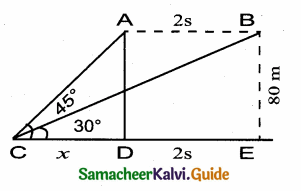
Question 17.
A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing on the top of the tower spots a van at an angle of depression of 30°. The van is approaching the tower with a uniform speed. After 6 minutes, the angle of depression of the van is found to be 60°. How many more minutes will it take for the van to reach the tower?
Answer:
Let A be the point of observation. B and C be the positions of the van. Let the height of the tower AD be x. Let the speed of the van be “s”. C is the position of van after 6 minutes.
Time taken by the van from B to C be minutes.
Distance BC = 6 × s = 6 s (speed × time)
Let distance between CD be t s (time × speed)
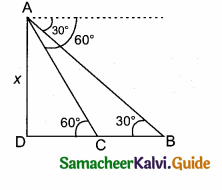
In the right ∆ ABD, tan 30° = \(\frac { AD }{ DB } \)
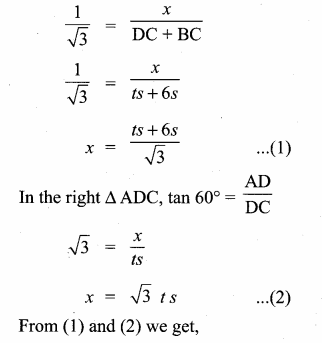
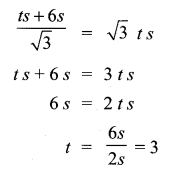
∴ 3 more minutes will be taken by the van to reach the tower.