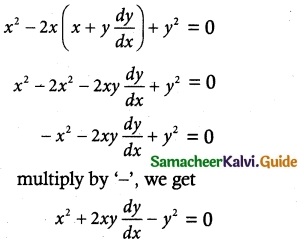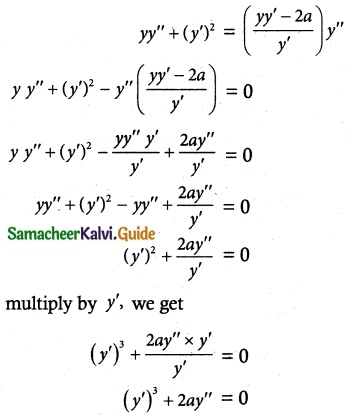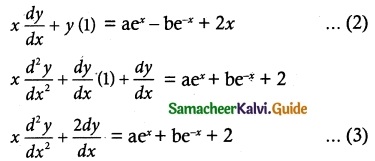Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.5 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.5
Question 1.
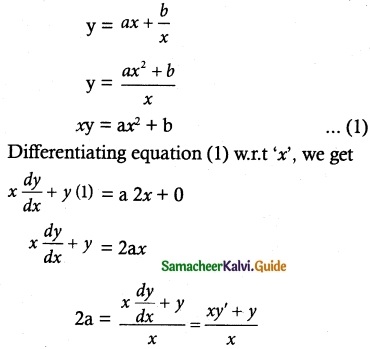
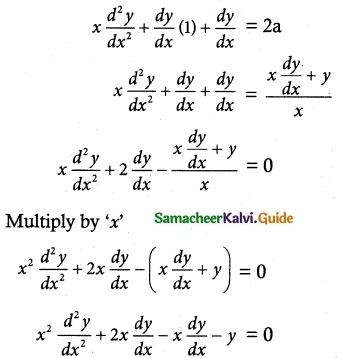
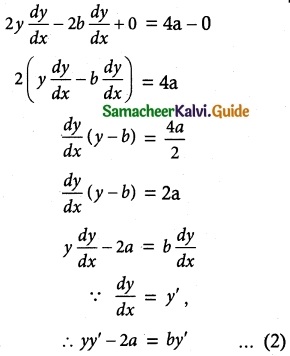
If F is the constant force generated by the motor of an automobile of mass M, its velocity V is given by M \(\frac { dV }{ dt }\) = F – kV, where k is a constant. Express V in terms of t given that V = 0 when t = 0.
Solution:
Given differential equation is M \(\frac { dV }{ dt }\) = F – kV
The given equation can be written as
\(\frac { dV }{ F-kV }\) = \(\frac { dt }{ M }\)
Now Integrating, we get
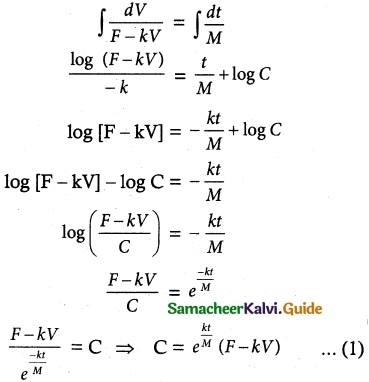
Initial condition:
Given V = 0 When t = 0
C = e\(\frac { k(0) }{ M }\) [F – k (0)]
= e° [F – 0]
C = F
∴ (1) ⇒ F = (F – kV)e\(\frac { kt }{ M }\)
![]()
Question 2.
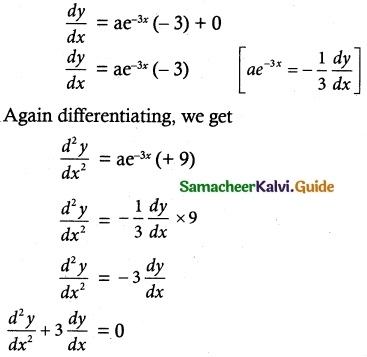
The velocity v, of a parachute falling vertically satisfies the equation v\(\frac { dv }{ dx }\) = g(1 – \(\frac { v^2 }{ k^2 }\)) where g and k are constants. If v and are both initially zero, find v in terms of x.
Solution:
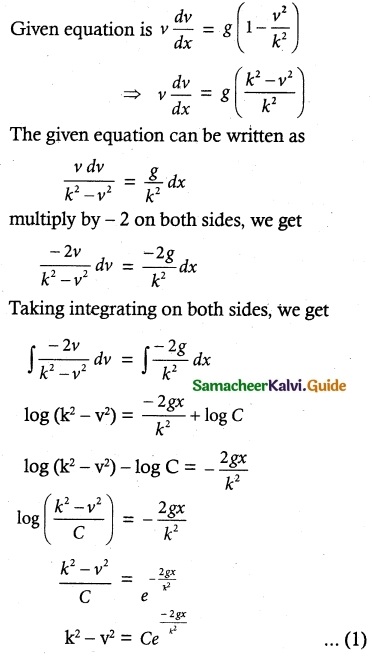
Initial condition:
Given V = 0 when x = 0, we get
k²(0)² = Ce\(\frac { -2g(0) }{ k^2 }\)
k² = Ce°
k² = C
(1) ⇒ k² – v² = k² e\(\frac { -2gx }{ k^2 }\)
k² – k² e\(\frac { -2gx }{ k^2 }\) = v²
k² [1 – e\(\frac { -2gx }{ k^2 }\)] = v²
![]()
Question 3.
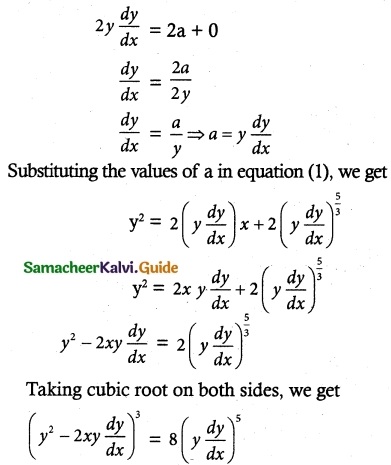
Find the equation of the curve whose slope is \(\frac { y-1 }{ x^2+x }\) and which passes through the point (1, 0).
Solution:
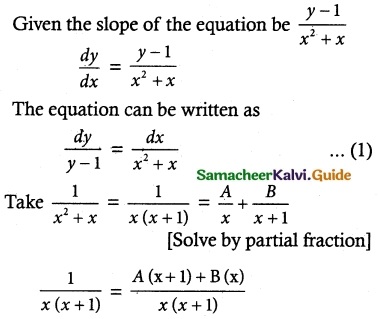
1 = A(x + 1) + B(x)
Put x = -1; Put x = 0
1 = A (0) + B (-1) ; 1 = A(0 + 1) + B(0)
1 = -B; 1 = A
B = -1; A = 1
∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ x^2+x }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ x+1 }\) ……. (2)
Substituting equation (2) in equation (1), we get
\(\frac { dy }{ y-1 }\) = \(\frac { dx}{ x }\) + \(\frac { dx }{ x+1 }\)
Taking integrating on both sides, we get
log (y – 1) = log x – log (x + 1) + log C
log (y – 1) = log C + log x – log (x + 1)
= log Cx – log (x + 1)

![]()
Question 4.
Solve the following differential equations:
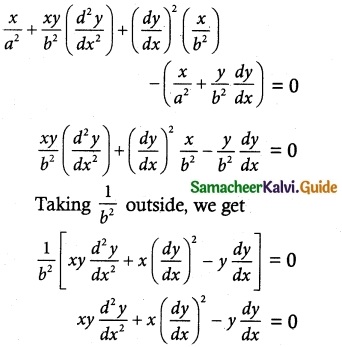
(i) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = \(\sqrt { 1-y^2 }{ 1-x^2 }\)
(ii) ydx + (1 + x²) tan-1 x dy = 0
(iii) sin \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = a, y (0) = 1
(iv) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\)ex+y + x³, ey
(v) (ey + 1) cos x dx + ey sin x dy = 0
(vi) (ydx – xdy) cot (\(\frac { x }{ y }\)) = ny² dx
(vii) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) – x\(\sqrt { 25-x^2 }\) = 0
(viii) x cos y dy = ex (x log x + 1) dx
(xi) tan y \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
(x) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = tan² (x + y)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = \(\sqrt { 1-y^2 }{ 1-x^2 }\)
The equation can be written as
\(\frac { dy }{ \sqrt {1-y^2} }\) = \(\frac { dx }{ \sqrt {1-x^2} }\)
Taking Integration on both sides, we get
∫ \(\frac { dy }{ \sqrt {1-y^2} }\) = ∫ \(\frac { dx }{ \sqrt {1-x^2} }\)
sin-1y = sin-1 x + C
![]()
(ii) ydx + (1 + x²) tan-1 x dy = 0
ydx = – (1 + x²) tan-1 x dy
Take t = tan-1 x
dt = \(\frac { 1 }{ 1+x^2 }\) dx
The equation can be written as
\(\frac { dx }{ (1+x^2)tan^{-1}x }\) = –\(\frac { dy }{ y }\)
\(\frac { dt }{ t }\) = –\(\frac { dy }{ y }\)
Taking Integration on both sides, we get
∫ \(\frac { dt }{ t }\) = ∫ \(\frac { dy }{ y }\)
log t = – log y + log C
log (tan-1 x) = – log y + log C
log (y(tan-1 x)) + log y = log C
y tan-1 x = C
(iii) sin \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = a, y (0) = 1
sin \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = a
sin \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = sin-1 (a)
The equation can be written as
dy = sin-1 (a) dx
Taking integration on both sides, we get
∫ dy = ∫ sin-1 (a) dx
y = sin-1 a ∫ dx
y = sin-1 (a) x + C ……… (1)
Initial condition:
Since y (0) = 1, we get
y = sin-1 (a) x + C
1 = sin-1 (a) (0) + C
0 + C = 1
C = 1
Equation (1) ⇒ y = sin-1 (a) x + 1
y – 1 = sin-1 (a) x
\(\frac { y-1 }{ x }\) = sin-1 (a)
sin(\(\frac { y-1 }{ x }\)) = a
![]()
(iv) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\)ex+y + x³, ey
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\)ex+y + x³, (ey)
= ey [ex + x³]
\(\frac { dy }{ e^y }\) = dx(ex + x³)
The equation can be written as
\(\frac { dy }{ e^y }\) = (ex + x³) dx
Taking integration on both sides, we get
∫ e-y dy = ∫ (ex + x³) dx
\(\frac { e^y }{ -1 }\) = ex + \(\frac { x^4 }{ 4 }\) + C
[Where – C = C, Which is also constant].
∴ ex + e-y + \(\frac { x^4 }{4 }\) = -C = C
∴ ex + e-y + \(\frac { x^4 }{4 }\) = C
(v) (ey + 1) cos x dx + ey sin x dy = 0
Solution:
(ey + 1) cos x dx + ey sin x dy = 0
ey sin x dy = – (ey + 1) cos x dx
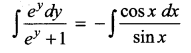
log (ey + 1) = – log sin x + log c
log [(ey + 1) + log sin x = log c
log (ey +1) sin x] = log c
(ey+ 1) sin x = c
![]()
(vi) (ydx – xdy) cot (\(\frac { x }{ y }\)) = ny² dx
equation can be written as
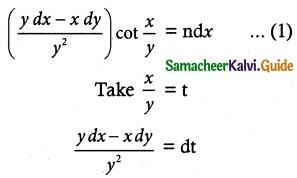
Substituting these values in equation (1), we get
dt cot t = ndx
cot t dt = ndx
Taking integration on both sides, we get
∫ cot t dt = n∫ dx
log (sin t) = n x + c
sin t = enx+c
∴ sin(\(\frac { x }{ y }\)) = enx+c [∵ t = \(\frac { x }{ y }\) ]
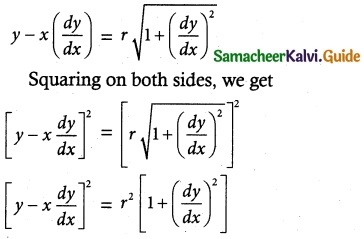
(vii) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) – x\(\sqrt { 25-x^2 }\) = 0
The equation can be written as
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) – x\(\sqrt { 25-x^2 }\) …….. (1)
Take 25 – x² = t
-2x dx = dt
x dx = –\(\frac { dt }{ 2 }\)
Substituting these values in equation (1), we get
dy = x\(\sqrt { 25-x^2 }\) dx
dy = -√t \(\frac { dt }{ 2 }\)
Taking integration on both sides, we get
∫ dy = –\(\frac { dt }{ 2 }\) ∫ t\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) dt
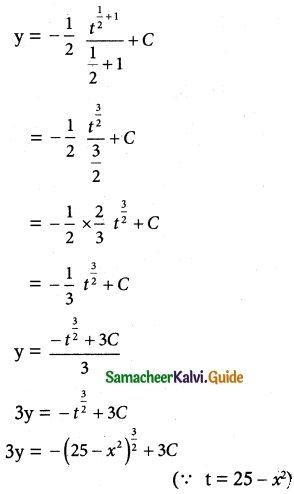
(viii) x cos y dy = ex (x log x + 1) dx
The equation can be written as
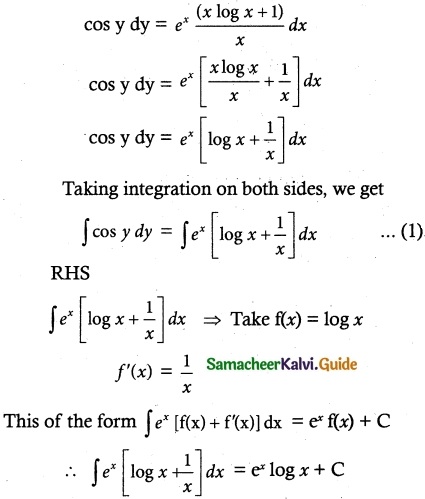
Substituting in (1), we get
sin y = ey log x + C
![]()
(ix) tan y \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
The equation can be written as
tan y \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
[W.K.T cos (A + B) + cos (A – B) = 2 cos A cos B
Here A = x, B = y]
∴ tan y\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = 2 cos x cos y
\(\frac { tany }{ cosy }\) dy = 2 cos x dx
Taking integration on both sides, we get
∫ \(\frac { tany }{ cosy }\) dy = 2 ∫ cos x dx
2 ∫ tan y sec y dy = 2 ∫ cos x dx
sec y = 2 sin x + C
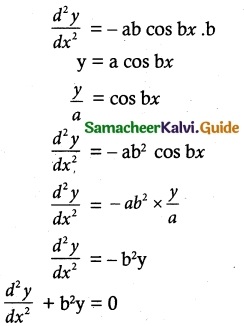
(x) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = tan² (x + y)
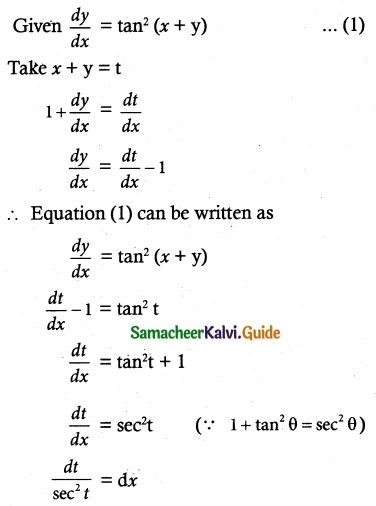
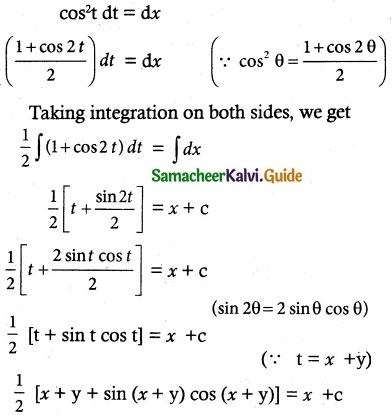
![]()