TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 6 Joint Stock Company
Question 1.
What are the different types of companies?
Answer:
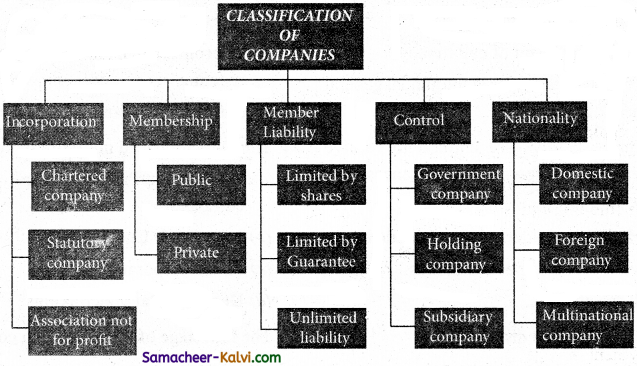
Question 2.
Define a Company.
Answer:
“A company is an association of many persons who contribute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade or business, and who share the profit and loss (as the case may be) arising there from.”
– James Stephenson
“A company is an artificial person created by law having a separate entity with a perpetual succession and a common seal”.
– Sec 2 of Companies Act 2013
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by Limited liability?
Answer:
The liability of the members of the company is called limited liability. When once the full value of the shares is paid up there is no more liability of the shareholders. This feature attracts large number of investors.
Question 4.
Exlain any two characteristics of a company.
Answer:
(i) Capacity to Sue and being sued:
A company can sue or be sued in its own name as distinct from its members.
(ii) Separate Management:
A company is administered and managed by its managerial personnel i.e. the Board of Directors. The shareholders are simply the holders of the shares in the company and need not necessarily the managers of the company.
(iii) Limited liability:
The liability of the members of the company is called limited liability. When once the full value of the shares is paid up there is no more liability of the shareholders. This feature attracts large number of investors.
![]()
Question 5.
What is meant by Chartered Company?
Answer:
Chartered companies are established as a result of charter granted by the King or Queen of a country, eg: East Indian Company, Bank of England, Hudson’s Bay Company.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of Companies?
Answer:
(i) Large Capital:
A company can secure large capital compared to a sole trader or partnership. Large amount of capital is necessary for conducting business on a large scale, eg: Reliance has invested more than ^ 25,000 Crore in its telecom venture. Raising such huge amount of funds would be utter impossible in a sole-tradership or partnership.
(ii) Limited Liability:
The liability of a shareholder is limited. In the case of a company limited by guarantee, his liability is restricted to the amount that he has guaranteed to contribute in the event of winding up of the company.
(iii) Transferability of Shares:
Transaction of Shares between two individuals is easy. So there is liquidity of investment. Any shareholder can easily convert his shares into money by selling his shares.
![]()
Question 7.
What is meant by Private Company?
Answer:
Private limited company is a company which has minimum” paidup capital of rupees one lakh or such higher paid up capital as may be prescribed. The Articles may prescribe the following:
- Cannot transfer the shares.
- Cannot issue prospectus.
- Minimum 2 members maximum 50 members.
- The company must end with the word ‘private limited’.
Question 8.
What is meant by perpetual succession?
Answer:
Perpetual Succession – continuity of life:
“Members may come and go but the company can go on forever” (Lord Gower). This is because company’s existence does not depend upon the existence of even promoters who were instrumental in its formation. Neither change in the membership of the company nor the death of its members has any impact on the continuity of its life.
Question 9.
What do you mean by issue of shares at a discount?
Answer:
When shares are issued at a price less than its face value, it is called issue of shares at a discount. When a share of face value of ₹ 10 is issued for ₹ 8, share is said to be issued at a discount of ₹ 2.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the significance of the common seal of the company?
Answer:
Though the separate personality of the company is legally recognised, it needs human agency to act. Obviously it cannot sign. Any contract entered into by a company, to be valid, must bear the official seal of the company.
Question 11.
What are economies of large scale?
Answer:
In view of the suitability of the company form of organisation for undertaking large sized industries, it can reap all the economies of large scale operation. Further there is scope for tremendous growth as raising of capital is not a problem for sound companies.
Question 12.
What are registered companies? Give examples.
Answer:
Companies which are registered under The Companies Act, 1956 are called registered companies. Tata Motors Limited, Satyam Computer Services Ltd, EID Parry Ltd, etc belong to this category.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the contents of Memorandum of Association?
Answer:
(i) Name Clause:
The name clause requires to state the legal and recognized name of the company. The company name is allow to be registered if it does not bear any similarities with the name of an existing company, companies only.
(ii) Situation Clause:
The registered office clause requires to show the physical location of the registered office of the company. It is required to keep all the company registers in this office. The registered office should be established prior to commencing business activities.
(iii) Objective Clause:
The objective clause requires to summarize the main objectives for establishing the company with reference to the requirements for shareholding and use of financial resources. It is required to state the ancillary objectives; that is, those objectives that are required to facilitate the achievement of the main objectives.
(iv) Liability Clause:
The liability clause requires to state the extent to which shareholders of the company are liable to the debt obligations of the company in the event of the company dissolving. There are companies limited by shares and limited by guarantee.
(v) Capital Clause:
The capital clause requires to state the company’s authorized share capital, the different categories of shares and the nominal value (the minimum value per share) oftheshares.lt is also required to list the company’s assets under this clause.
(vi) Association Clause:
The association clause confirms that shareholders bound by the MO A are willingly associating and forming a company. It is required seven members to sign an MOA for a public company and not less than two people for a MOA of a private company. The signing must be done in the presence of witness who must also append his signature.
![]()
Question 14.
What are the contents of Articles of Association?
Answer:
- Amount of shares, capital, value and type of shares.
- Rights of each class of shareholders regarding voting, dividend, return of capital.
- Rules regarding issue of shares and debentures.
- Procedures as well as regulations in respect of making calls on shares.
- Manner of transfer of shares.
- Declaration of dividends.
- Borrowing powers of the company.
- Rules regarding the appointment, remuneration, removal of directors.
- Procedure for conducting proxy, quorum, meetings etc.,
- Procedures concerning keeping of books and audits.
- Seal of the company. %
- Procedures regarding the winding up of the company.
Question 15.
What is meant by Prospectus?
Answer:
According to Section 2(36) of the Companies Act, any document inviting the public to buy its shares or debentures comes under the definition of prospectus. It also applies to advertisements inviting deposits from the public.
- The main objectives of the company.
- The names, addresses, description and occupations of the signatories to memorandum and the number of shares subscribed by each of them.
- The kinds of shares with their total numbers and rights attaching to each class of shares.
- Qualification shares which a member must hold in order to be eligible for election as director. It is fixed by the Articles.
- The names, addresses, descriptions and occupations, the interest, rights and remuneration of the directors, managing directors and the secretaries and treasures.
![]()
Question 16.
What is meant by Multi National Company?
Answer:
Multi National Companies: A Multi National Company (MNC) is a huge industrial organisation which,
(i) Operates in more than one country.
(ii) Carries out production, marketing and research activities on international Scale in those countries.
(iii) Seeks to maximise profits world over.
A domestic company or a foreign company can be a MNC.
eg: Microsoft Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Nestle, Coca-Cola, International Business Machine, Pepsico, Sony Corporation.
Question 17.
What is meant by Holding and Subsidiary company?
Answer:
Holding Companies:
As per Section 2(87) “subsidiary company” or “subsidiary”, in relation to any other company (that is to say the holding company), means a company in which the holding company.
(i) Controls the composition of the Board of Directors; or
(ii) Exercises or controls more than one-half of the total share capital either at its own or together with one or more of its subsidiary companies:
Provided that such class or classes of holding companies as may be prescribed shall not have layers of subsidiaries beyond such numbers as may be prescribed.
Subsidiary Companies:
“Subsidiary company” or “Subsidiary”, in relation to any other company (that is to say the holding company), means a company in which the holding company.
(i) Controls the composition of the Board of Directors; or
(ii) Exercises or controls more than one-half of the total share capital either at its own or together with one or more of its subsidiary companies:
eg: H Ltd., holds more than 50% of the equity share capital of S Ltd. Now H Ltd., is the holding company of S Ltd., and S Ltd., is the subsidiary of H Ltd.
![]()
Question 18.
Name any 2 Government owned Joint Stock Company.
Answer:
- Indian Telephone Industries.
- TamilNadu State Transport Corporation Limited.
- TamilNadu Agro Industries Corporation.
Question 19.
Name any 2 Joint stock company with private ownership.
Answer:
- Nokia
- Nestle
Question 20.
Name any 2 Private ownership with Foreign participants.
Answer:
- Marathi Suzuki.
- Ford.
- Hundai.
![]()
Question 21.
Collect advertisements of three different companies inviting the public to subscribe their shares. Compare their contents regarding following points.
Answer:
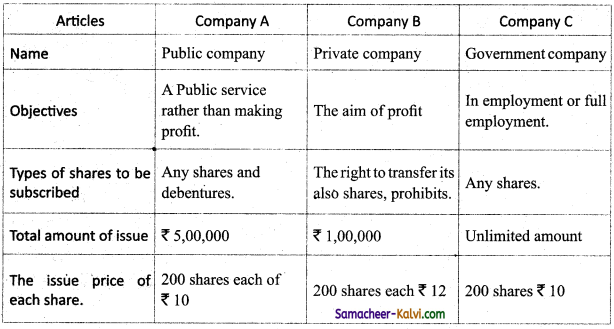
Question 22.
Ashok is an industrial designer by training. He had the opportunity to learn the technology of fibre glass manufacture while he was in Germany for his training. He plans to set up a plant for the manufacture of fibre glass in India and is able to interest some financiers and technologists. It is estimated that the initial investment in the plant will be of the order of ₹ 50 lakhs.
Ashok and others decide to set up a company for the purpose. Should they set up a public limited company for the purpose? If so, how should I they go about it? If not, what alternative would you suggest? What formalities will be required of Ashok and his associates if they choose the alternative form of organization suggested by you?
Answer:
Ashok started public limited company with a capital of ₹ 50 lakhs.
Incorporation:
(a) Registration,
(b) Approval for the proposed name.
Filling documents:
(a) Memorandum of Association,
(b) Articles of Association,
(c) List of directors,
(d) Written consent to act as a director,
(e) Statutory declaration,
(f) Registrar check all the documents,
(g) Prospectus,
(h) Minimum subscription,
(i) Statement in lies of prospectus,
(j) Filing further documents.
Ashok followed above rules regarding to form a company.
![]()
Question 23.
Collect any 10 items of daily use (Packed items} and list the names of the companies manufacturing those items. Classify those companies as public and private limited companies. Which of them are Multinational Companies?
Answer:
- Sakthi Masala – Private Limited.
- Aachi Masala – Private Limited.
- Aavin milk – Government of Tamil Nadu.
- Arokia – Private Limited.
- Coca Cola – Multinational company.
- Nestle chocolate – Multinational company.
- Pepsico – Multinational company.
- Bovanto – Private Limited company.
- Dairy Milk – Private Limited company.
- Colgate – Private Limited company.
- Hamam Soap – Multinational company.
![]()
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
The relationship between outsiders and the company is defined in:
(a) prospectus
(b) articles of association
(c) memorandum of association
(d) certificate of Incorporation
Answer:
(a) prospectus
Question 2.
Table A of the Companies Act is a:
(a) model minutes book
(b) model form of balance sheet
(c) model of AOA
(d) model of MOA
Answer:
(c) model of AOA
Question 3.
Which of the following is created by a Special Act of Parliament or in State Assemblies?
(a) Chartered company
(b) Foreign company
(c) Government company
(d) Statutory company
Answer:
(d) Statutory company
![]()
Question 4.
The Board of directors of a company is elected by:
(a) creditors
(b) debtors
(c) debenture holders
(d) share holders (members)
Answer:
(d) share holders (members)
Question 5.
Companies established as a result of a charter granted by the King or Queen of a country is called:
(a) chartered companies
(b) statutory companies
(c) registered companies
(d) foreign companies
Answer:
(a) chartered companies
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 6 Joint Stock Company
→ A company is a long shadow of the boss” with the advent of industrial revolution and the factory system of production. Large scale production has become the order of the day. To meet the ever-expanding needs of the fast growing population. Large sized industrial organisation has become indispensable.
→ The traditional forms of business units, namely, sole proprietary concerns, and partnership firms, with their limited financial resources and managerial capability, cannot meet the challenges forced by the need for massive production and speedy distribution. Joint stock company form of organisation provides to key to this problem.
→ This is better suited for mobilising large capital resources and ensuring highly sophisticated managerial skills for running giant sized industrial enterprises. The term company refers to “ body corporate.”
→ Joint stock company is distinct type of business organisation evolved to overcome the limitations of sole trader and partnership concern.
→ The act came into force on 12 September 2013 with few changes like earlier private companies maximum number of members was 50 and now it will be 200. A new class of company is “one person company ” is included in this act that will be private limited company public limited company minimum 7 maximum unlimited members. To learn kinds of companies memorandum and its contents articles and its contents, prospectus and its contents.