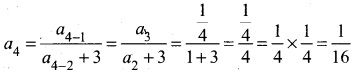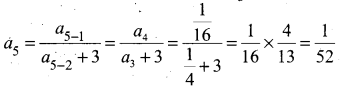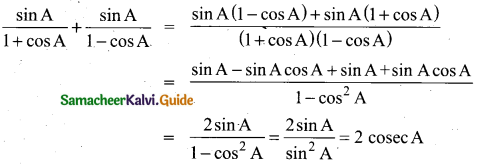Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 1 Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 1
நேரம்: 3.00 மணி
மதிப்பெண்கள் : 100
(குறிப்புகள்:
- இவ்வினாத்தாள் ஐந்து பகுதிகளைக் கொண்டது. அனைத்து பகுதிகளுக்கும் விடையளிக்க – வேண்டும். தேவையான இடங்களில் உள் தேர்வு வினாக்கள் கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. காக
- பகுதி I, II, III, IV மற்றும் Vல் உள்ள அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்குத் தனித்தனியே விடையளிக்க வேண்டும்.
- வினா எண். 1 முதல் 15 வரை பகுதி-1ல் தேர்வு செய்யும் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. ஒவ்வொரு வினாவிற்கும் ஒரு மதிப்பெண். சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து குறியீட்டுடன் எழுதவும்.
- வினா எண் 16 முதல் 28 வரை பகுதி-IIல் இரண்டு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன: ஏதேனும் 9 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
- வினா எண் 29 முதல் 37 வரை பகுதி-IIIல் மூன்று மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. –
ஏதேனும் 6 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும். - வினா எண் 38 முதல் 42 வரை பகுதி-IVல் ஐந்து மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. ஏதேனும் 5 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
- வினா எண் 43 முதல் 45 வரை பகுதி-Vல் எட்டு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. அனைத்து வினாவிற்கும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
பகுதி – 1 (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 15)
(i) அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
(ii) கொடுக்கப்பட்ட நான்கு விடைகளில் சரியான விடையினைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்துக் குறியீட்டுடன் விடையினையும் சேர்த்து எழுதுக. [15 x 1 = 15]
(குறிப்பு: விடைகள் தடித்த எழுத்தில் உள்ளன.)
Question 1.
தமிழினத்தை ஒன்றுபடுத்தும் இலக்கியமாக ம.பொ.சி. கருதியது…………..
(அ) திருக்குறள்
(ஆ) புறநானூறு
(இ) கம்பராமாயணம்
(ஈ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
Answer:
(ஈ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
Question 2.
கரும்பின் அடி……………… என அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
அ) தூறு
(ஆ) கழி
(இ) கழை
(ஈ) தட்டு
Answer:
(ஆ) கழி
![]()
Question 3.
கேட்டவர் மகிழப் பாடிய பாடல் இது’ – தொடரில் இடம்பெற்றுள்ள தொழிற்பெயரும் வினையாலணையும் பெயரும் முறையே ……………
(அ ) பாடிய ; கேட்டவர்
(ஆ) பாடல் ; பாடிய
(இ) கேட்டவர் ; பாடிய
(ஈ) பாடல் ; கேட்டவர்
Answer:
(ஈ) பாடல் ; கேட்டவர்
Question 4.
ஒப்புடன் முகம் மலர்ந்தே உபசரித்து உண்மை பேசி என்னும் அடிகள் இடம் பெறும் நூல்…………..
(அ) விவேகசிந்தாமணி
(ஆ) புறநானூறு –
(இ) காசிகாண்டம்
(ஈ) மலைபடுகடாம்
Answer:
(அ) விவேகசிந்தாமணி
Question 5.
பூக்கையைக் குவித்துப் பூவே புரிவொடு காக்க என்று ………….. ,………………வேண்டினார்.
(அ) கருணையன் எலிசபெத்துக்காக
(ஆ) எலிசபெத் தமக்காக
(இ) கருணையன் பூக்களுக்காக
(ஈ) எலிசபெத் பூமிக்காக
Answer:
(அ) கருணையன் எலிசபெத்துக்காக
Question 6.
‘உனதருளே பார்ப்பன் அடியேனே’ – யாரிடம் யார் கூறியது?
(அ) குலசேகராழ்வாரிடம் இறைவன்
(ஆ) இறைவனிடம் குலசேகராழ்வார்
(இ) மருத்துவரிடம் நோயாளி
(ஈ) நோயாளியிடம் மருத்துவர்
Answer:
(ஆ) இறைவனிடம் குலசேகராழ்வார்
![]()
Question 7.
ஒரு தொடரில் வேற்றுமை உருபுகள் மறைந்து வந்து பொருள் உணர்த்துவது………….. எனப்படும்.
(அ) வேற்றுமைத் தொகை
(ஆ) வினைத்தொகை
(இ) உவமைத்தொகை
(ஈ) உம்மைத் தொகை
Answer:
(ஈ) உம்மைத் தொகை
Question 8.
இடை க்காடனாரின் பாடலை இகழ்ந்தவர் ……………. இடைக்காடனாரிடம் அன்பு வைத்தவர்…………..
(அ) அமைச்சர். மன்னன்
(ஆ) அமைச்சர், இறைவன்
(இ) இறைவன். மன்னன்
(ஈ) மன்னன், இறைவன்
Answer:
(ஈ) மன்னன், இறைவன்
Question 9.
உரிச்சொல்லுடன் பெயரோ வினையோ தொடர்வது ………………..
(அ) பெயரெச்சத் தொடர்
(ஆ) விளித்தொடர்
(இ) உரிச்சொல் தொடர்
(ஈ) அடுக்குத்தொடர்
Answer:
(இ) உரிச்சொல் தொடர்
Question 10.
தொடக்கம் முதல் முடிவு வரை நேராகப் பொருள் கொள்வது…………
(அ) கொண்டு கூட்டுப் பொருள்கோள்
(ஆ) ஆற்றுநீர் பொருள்கோள்
(இ) எதிர் நிரல்நிறைப் பொருள்கோள்
(ஈ) நிரல்நிறைப் பொருள்கோள்
Answer:
(ஆ) ஆற்றுநீர் பொருள்கோள்
Question 11.
கோசல நாட்டில் கொடை இல்லாத காரணம் என்ன?
(அ) நல்ல உள்ளம் உடையவர்கள் இல்லாததால்,
(ஆ) ஊரில் விளைச்சல் இல்லாததால்
(இ) அரசன் கொடுங்கோல் ஆட்சி புரிவதால்
(ஈ) அங்கு வறுமை இல்லாததால்
Answer:
(ஈ) அங்கு வறுமை இல்லாததால்
பாடலைப் படித்துப் பின்வரும் வினாக்களுக்கு (12, 13, 14, 15) விடை தருக.
“விசும்பில் ஊழி ஊழ் ஊழ் செல்லக்
கரு வளர் வானத்து இசையில் தோன்றி,
உரு அறிவாரா ஒன்றன் ஊழியும்;
உந்து வளி கிளர்ந்த ஊழி ஊழ் ஊழியும்”
Question 12.
விசும்பில் என்பதன் பொருள் யாது?
(அ) வானத்தில்
(ஆ) புவியில்
(இ) காற்றில்
(ஈ) நீரில்
Answer:
(அ) வானத்தில்
![]()
Question 13.
வளி கிளர்ந்த ஊழி என்பது யாது?
(அ) காற்று தோன்றா உலகம்
(ஆ) பரிபாடல்
(இ) ஆற்றுப்படை
(ஈ) காற்று தோன்றிய உலகம்
Answer:
(ஈ) காற்று தோன்றிய உலகம்
Question 14.
இப்பாடலில் அமைந்துள்ள மோனைச் சொற்களை எழுதுக.
(அ) ஊழி – ஊழ்
(ஆ) கரு, உரு
(இ) விசும்பு, உந்து
(ஈ) தோன்றி, ஊழியும்
Answer:
(அ) ஊழி – ஊழ்
Question 15.
இப்பாடலில் அமைந்துள்ள எதுகைச் சொற்களை எழுதுக.
(அ) அறிவாரா, ஊழியும்
(ஆ) கரு, உரு
(இ) விசும்பு, உந்து
(ஈ) தோன்றி, ஊழியும்
Answer:
(ஆ) கரு, உரு
பகுதி – II (மதிப்பெண்க ள்: 18)
பிரிவு – 1
எவையேனும் நான்கு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் குறுகிய விடையளிக்க.
21 ஆவது வினாவிற்குக் கட்டாயமாக விடையளிக்க வேண்டும். [4 x 2 = 8)
Question 16.
விடைக்கேற்ற வினா அமைக்க.
(அ) ‘எனது போராட்டம்’ என்னும் ம.பொ.சிவஞானத்தின் வரலாற்று நூலில்
இருந்து தொகுக்கப்பட்டது.
(ஆ) அறிவு விளக்கம் பெறுவதற்கான வழிகள் (1) கல்வி, (2) கேள்வி ஆகும்.
Answer:
விடை:
(அ) ம.பொ.சி. பற்றியக் கட்டுரை எந்நூலினின்று தொகுக்கப்பட்டது?
(ஆ) அறிவு விளக்கம் பெறுவதற்கான வழிகள் யாவை?
Question 17.
வாழ்வில் தலைக்கனம், தலைக்கனமே வாழ்வு’ என்று நாகூர்ரூமி யாருடைய வாழ்வைக் குறித்துக் கூறுகிறார்?
Answer:
ஏழைத் தொழிலாளியான ஒரு சித்தாளின் வாழ்வைக் குறித்துக் கூறுகிறார்.
Question 18.
பைங்கூழ் நாற்று குறிப்பு எழுதுக.
Answer:
பைங்கூழ் : நெல், சோளம் முதலியவற்றின் பசும் பயிர்
நாற்று : நெல், கத்தரி முதலியவற்றின் இளநிலை ஆகும். தகைவததககா மாமா மாமான கார்க்கம் மாதிரி வினாத்தாள்-10 – 167
Question 19.
மு.கு ஜகந்நாத ராஜா அவர்கள் மொழிபெயர்ப்பு பற்றி கூறுவது என்ன?
Answer:
“ஒரு மொழி வளம்பெறவும் உலகத்துடன் உறவு கொள்ளவும் மொழிபெயர்ப்பு இன்றியமையாததாகும்; உலக நாகரிக வளர்ச்சிக்கும் பொருளியல் மேம்பாட்டிற்கும் மொழி
பெயர்ப்பும் ஒரு காரணமாகும்” என்கிறார் மு.கு. ஜகந்நாத ராஜா.
Question 20.
கல்வியில் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு காண்க.
Answer:
- ஒரு காலத்தில் வாழ்க்கையில் முன்னேறுவதற்கு எழுதப் படிக்கத் தெரிந்த கல்வியறிவே போதுமானதாக இருந்தது.
- கல்வியறிவுடன் மின்னணுக் கல்வியறிவையும் மின்னணுச் சந்தைப்படுத்துதலையும் அறிந்திருப்பது வாழ்க்கையை எளிதாக்கவும் வணிகத்தில் வெற்றியடையவும் உதவுகிறது.
- எதிர்காலத்தில் தொழிற்புரட்சியின் தொழில் நுட்பங்களைப் பயன்படுத்தும் அறிவே நம்மை
வளப்படுத்த உதவும்.
Question 21.
‘செயல்’ என முடியும் குறள்.
Answer:
செயற்கை அறிந்தக் கடைத்தும் உலகத் தியற்கை அறிந்து செயல்.
![]()
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் ஐந்து வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் குறுகிய விடையளிக்க. [5 x 2 = 10)
Question 22.
மரபுத் தொடருக்கான பொருளறிந்து தொடரில் அமைக்கவும்.
அள்ளி இறைத்தல்
Answer:
விடை: நம்மிடம் பணம் இருக்கும் போது அள்ளி இறைத்தால் நம்மிடம் பணம் இல்லாத போது
கடினப்பட நேரிடும்.
Question 23.
பொருத்தமானவற்றை சொற்பெட்டியில் கண்டு எழுதுக.
(தோற்பவை, தோற்பாவை, விருது, விருந்து)
Answer:
விடை:
1. வாழ்க்கையில் தோற்பவை மீண்டும் வெல்லும் – இதைத்
தத்துவமாய்த் தோற்பாவைக் கூத்து சொல்லும்.
2. தெருக்கூத்தில் நடிகருக்குக் கைதட்டலே விருது – அதில்
வரும் காசு குறைந்தாலும் அதுவே அவர் விருந்து.
Question 24.
இரு சொற்களையும் ஒரே தொடரில் அமைக்கவும்.
சிறு – சீரு
Answer:
விடை:
சிறுகச் சிறுகச் சேமித்தால் சீரும் சிறப்புமாக வாழ முடியும்.
Question 25.
கலைச்சொற்கள் தருக.
Answer:
Myth – தொன்மம்
Terminology – கலைச்சொல்
Question 26.
பிறமொழிச் சொற்களுக்குரிய தமிழ்ச்சொற்களை எழுதுக.
ஷேத்திரங்கள் தோறும் சென்று விக்கிரகங்களை வழிபடுக.
Answer:
புனிதத்தலங்கள் தோறும் சென்று தெய்வச்சிலைகளை வழிபடுக.
Question 27.
பொருத்தமான நிறுத்தற் குறிகளை இடுக.
யாரப்பா நீ எங்கே வந்தே என்று முகத்தில் வெறுப்பைப் பூரணமாகக் காட்டிக் கொண்டு கேட்டேன்
Answer:
விடை: யாரப்பா நீ? எங்கே வந்தே? என்று முகத்தில் வெறுப்பைப் பூரணமாகக் காட்டிக் கொண்டு கேட்டேன்.
Question 28.
பொழிந்த – பகுபத உறுப்பிலக்கணம் தருக.
Answer:
பொழிந்த = பொழி + த்(ந்) + த் + அ
பொழி – பகுதி
த் – சந்தி ‘ந்’ ஆனது விகாரம்
த் – இறந்த கால இடைநிலை
அ – பெயரெச்ச விகுதி
பகுதி – III (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 18)
பிரிவு – 1
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 29.
ஜெயகாந்தன் தம் கதைமாந்தர்களின் சிறந்த கூறுகளைக் குறிப்பிடத் தவறுவதில்லை என்று அசோகமித்திரன் கூறுகிறார். இக்கூற்றை மெய்ப்பிக்கும் செயல் ஒன்றைத் ‘தர்க்கத்திற்கு அப்பால்’ கதை மாந்தர் வாயிலாக விளக்குக.
Answer:
- தோல்வி நிச்சயம் என்ற மனப்பான்மையுடன் போன. நான் வழக்கத்திற்கு மாறாக அன்று தோற்றுப்போனேன்.
- ல்வி நிச்சயம் என்ற என் மனப்போக்கு தோற்றது. என் வாழ்க்கையே நிர்ணயிக்கப்பட்டது.
- பிச்சைக்காரனுக்கு பிச்சை போட்டதில் நாலணாவில் அந்த நல்லநாளைக் கொண்டாடிவிட்ட நிறைவு பிறந்தது.
- காலணாதான் கடன் தரலாம் தருமத்தைத் தரமுடியுமா? தருமத்தை யாசித்துத் தந்தால்தான் பெற முடியும்.
- ஒருவனுக்கு என்ன கிடைக்க வேண்டுமோ அதுதான் கிடைக்கும் நாம் எப்படி முயற்சி செய்தாலும் நமக்குக் கிடைப்பதுதான் கிடைக்கும்.
Question 30.
‘சுற்றுச்சூழலைப் பேணுவதே இன்றைய அறம்’ என்ற தலைப்பில், பெற்றோர் ஆசிரியர் கூட்டத்தில் பேசுவதற்கான உரைக்குறிப்பு ஒன்றை உருவாக்குக.
(குறிப்பு – சுற்றுச்சூழல் மாசுபடுவதைத் தடுக்கச் சட்டங்கள் இயற்றப்பட்டிருந்தாலும், ஒவ்வொருவரின் உள்ளத்திலும் ஏற்படும் மாற்றமே சுற்றுச்சூழலைப் பாதுகாக்கும்)
Answer:
சுற்றுச்சூழல் :
‘சுத்தம் சுகம் தரும்’, ‘சுத்தம் சோறு போடும்’, ‘சுத்தம் கடவுள் தன்மைக்கு ஒப்பானது’ என்னும் பழமொழிகள் தூய்மையாக இருக்க வேண்டும் என்பதை வலியுறுத்துகின்றன.
புறந்தூய்மை நீரான் அமையும் அகந்தூய்மை
வாய்மையால் காணப் படும்
என்கிறார் திருவள்ளுவர். உடலின் தூய்மை நீரால் அமைவதுபோல உள்ளத்தின் தூய்மை வாய்மையால் அமைகிறது என்பது இக்குறளின் பொருள். அதுபோல வீட்டையும் வீட்டின் சுற்றுப்புறத்தையும் நாம் தூய்மையாக வைத்துக்கொள்ள வேண்டும்.
வீட்டில் எப்போதும் தூய்மை இல்லாமை, காற்றோட்டம் இன்மை, போதிய வெளிச்சம் இன்மை, கெட்டுப்போன பொருள்களை உண்ணல், நோயாளியுடன் இருத்தல், அழுக்கு ஆடைகளை உடுத்துதல், இயற்கைச் சூழல் இன்மை ஆகிய காரணங்களால் நமக்கு நோய்கள் வருகின்றன.
அரசியல் தலைவர்களோ, அறிஞர்களோ கலந்து கொள்ளும் ஒவ்வொரு விழாவின் போதும் கட்டாயமாக ஒரு மரக்கன்றை நட்ட பின்னரே விழா நிகழ்ச்சியில் கலந்து கொள்ள வேண்டும். வீடுகளைச் சுற்றிலும் மரங்களை வளர்க்க வேண்டும்.
‘நோயற்ற வாழ்வே குறைவற்ற செல்வம்’ என்னும் பழமொழிக்கு எடுத்துக்காட்டாய் வாழ வேண்டும். சுற்றுப்புறம் தூய்மையாக இருத்தல் வேண்டும். குப்பைக் கூளங்கள் இல்லாமல் எல்லா இடங்களிலும் இயற்கை அன்னை கொலு வீற்றிருக்கச் செய்தல் வேண்டும்.
![]()
Question 31.
உரைப்பத்தியைப் படித்து வினாக்களுக்கு விடை தருக.
Answer:
பன்னெடுங்காலமாக மக்களால் விரும்பப்படும் மரபார்ந்த கலைகளில் ஒன்றே கரகாட்டம். கரகம் என்னும் பித்தளைச் செம்பையோ, சிறிய குடத்தையோ தலையில் வைத்துத் தாளத்திற்கு ஏற்ப ஆடுவது, கரகாட்டம். இந்த நடனம் கரகம், கும்பாட்டம் என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது. கரகச் செம்பின் அடிப்பாகத்தை உட்புறமாகத் தட்டி, ஆடுபவரின் தலையில் நன்கு படியும்படி செய்கின்றனர். தலையில் செம்பு நிற்கும் அளவு எடையை ஏற்றுவதற்குச் செம்பில் மணலையோ பச்சரிசியையோ நிரப்புகின்றனர். கண்ணாடியாலும் பூக்களாலும் அழகூட்டிய கரகக் கூட்டின் நடுவில், கிளி பொம்மை பொருத்திய மூங்கில் குச்சியைச் செருகி வைத்து ஆடுகின்றனர்.
(அ) கரகாட்டத்தின் போது எவற்றை தலையில் வைப்பர்?
Answer:
பித்தளை செம்பையோ, சிறிய குடத்தையோ தலையில் வைத்துத் தாளத்திற்கு ஏற்ப ஆடுவர்.
(ஆ) கரகாட்டத்தின் மறுபெயர் என்ன?
Answer:
கும்பாட்டம்
(இ) கரகத்தின் நடுவில் எதனை வைப்பர்?
Answer:
கரகக் கூட்டின் நடுவில் கிளி பொம்மை பொருத்திய மூங்கில் குச்சியை செருகி வைத்து ஆடுவர்.
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க.
34 ஆவது வினாவிற்குக் கட்டாயமாக விடையளிக்க வேண்டும். (2 x 3 = 6)
Question 32.
மலைபடுகடாம் குறிப்பு எழுதுக.
Answer:
- பத்துப்பாட்டு நூல்களுள் ஒன்று ‘மலைபடுகடாம்’ 583 அடிகளைக் கொண்ட இது கூத்தராற்றுப்படை எனவும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
- மலையை யானையாக உருவகம் செய்து மலையில் எழும் பலவகை ஓசைகளை அதன் மதம் என்று விளக்குவதால் இதற்கு மலைபடுகடாம் எனக் கற்பனை நயம் வாய்ந்த பெயர் சூட்டப்பட்டுள்ளது.
- நன்னன் என்னும் குறுநில மன்னனைப் பாட்டுடைத் தலைவனாகக் கொண்டு இரணிய முட்டத்துப் பெருங்குன்றூர் பெருங்கௌசிகனார் பாடியது மலைபடுகடாம்.
Question 33.
முகம்மதுரஃபி ஆசிரியர் குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
- முகம்மதுரஃபி என்னும் இயற்பெயரைக் கொண்ட நாகூர்ரூமி தஞ்சை மாவட்டத்தில்
பிறந்தவர். - இவர் எண்பதுகளில் கணையாழி இதழில் எழுதத் தொடங்கியவர்.
- கவிதை, குறுநாவல், சிறுகதை, மொழிபெயர்ப்பு எனப் பலதளங்களில் இவர் தொடர்ந்து
இயங்கி வருபவர். - மீட்சி, சுபமங்களா, புதிய பார்வை, குங்குமம், கொல்லிப்பாவை, இலக்கிய வெளிவட்டம், குமுதம் ஆகிய இதழ்களில் இவரது படைப்புகள் வெளியாகியுள்ளன.
- இதுவரை நதியின் கால்கள், ஏழாவது சுவை, சொல்லாத சொல் ஆகிய மூன்று கவிதைத் தொகுதிகள் வெளியாகியுள்ளன.
- மொழிபெயர்ப்புக் கவிதைகள், சிறுகதைத்தொகுதிகள் ஆகியவற்றுடன் ‘கப்பலுக்குப் போன மச்சான்’ என்னும் நாவலையும் படைத்துள்ளார்.
Question 34.
அடிபிறழாமல் எழுதுக.
(அ) “வெய்யோன் ஒளி” எனத் தொடங்கும் ‘கம்பராமாயணப் பாடலை எழுதுக.
Answer:
வெய்யோன் ஒளி தன் மேனியில் விரி சோதியில் மறையப்
பொய்யோ எனும் இடையாளொடும் இளையானொடும் போனான்;
மையோ? மரகதமோ? மறிகடலோ? மழை முகிலோ?
ஐயோ இவன் வடிவு என்பது ஓர் அழியா அழகு உடையான். (- கம்பர்)
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) “அருளைப் பெருக்கி” எனத் தொடங்கும் ‘நீதிவெண்பா ‘ பாடல்.
Answer:
அருளைப் பெருக்கி அறிவைத் திருத்தி
மருளை அகற்றி மதிக்கும் தெருளை
அருத்துவதும் ஆவிக்கு அருத்துணையாய் இன்பம்
பொருத்துவதும் கல்வியென்றே போற்று (- கா.ப. செய்குதம்பிப் பாவலர்)
![]()
பிரிவு – 3
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 35.
வேற்றுமைத்தொடர் என்றால் என்ன? எடுத்துக்காட்டுடன் விளக்குக.
Answer:
வேற்றுமை உருபுகள் வெளிப்பட அமையும் தொடர்கள் வேற்றுமைத் தொகாநிலைத் தொடர்கள் ஆகும்.
(எ.கா.)
கதையைப் படித்தான் – இத்தொடரில் ‘ஐ’ என்னும் வேற்றுமை உருபு வெளிப்படையாக வந்து பொருளை உணர்த்துகிறது.
(எ.கா.)
வளையலுக்குப் பொன் – இத்தொடரில் ‘கு’ என்னும் வேற்றுமை உருபு வெளிப்படையாக வந்து பொருளை உணர்த்துகிறது.
Question 36.
‘குற்றம் இலனாய்க் குடி செய்த வாழ்வானைச்
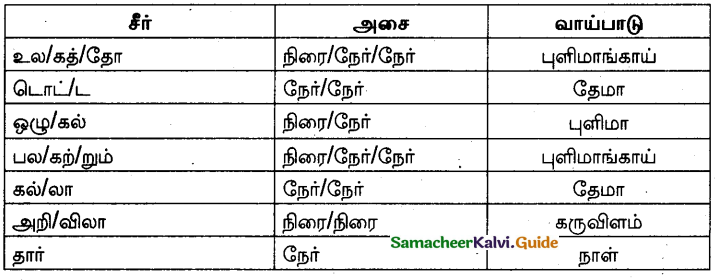
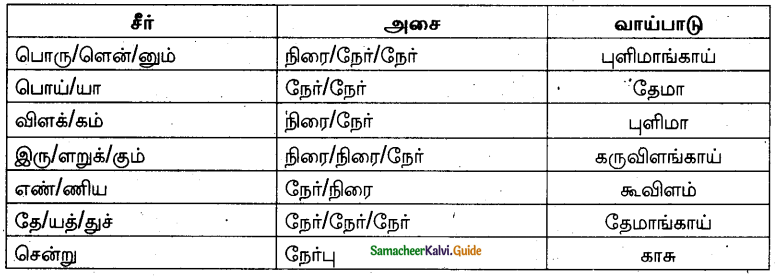
சுற்றமாச் சுற்றும் உலகு’ – இக்குறட்பாவினை அலகிட்டு வாய்பாடு தருக.
Answer:
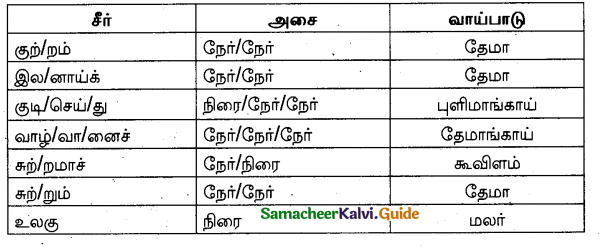
Question 37.
கவிஞர் தாம் கூற விரும்பும் கருத்திற்கு ஏற்றவாறு தற்குறிப்பேற்ற அணி அமைவதை எடுத்துக்காட்டுக.
Answer:
தற்குறிப்பேற்ற அணி:
இயல்பாய் நிகழும் நிகழ்ச்சியின் மீது கவிஞன் தன் குறிப்பை ஏற்றிக் கூறுவது தற்குறிப்பேற்ற அணி எனப்படும்.
(எ.கா.) ‘போருழந் தெடுத்த ஆரெயில் நெடுங்கொடி
வாரல் என்பனபோல் மறித்துக்கை காட்ட’
பொருள்:
கோட்டை மதில் மேல் இருந்த கொடியானது வரவேண்டாம் எனத் தடுப்பதுபோல, கை காட்டியது என்பது பொருள்.
அணிப்பொருத்தம் :
கோவலனும், கண்ணகியும் மதுரை மாநகருக்குள் சென்றபோது மதிலின் மேலிருந்த கொடிகள் காற்றில் இயற்கையாக அசைந்தன. ஆனால், இளங்கோவடிகள் கோவலன் மதுரையில் கொலை செய்யப்படுவான் எனக்கருதி அக்கொடிகள் கையை அசைத்து, ‘இம்மதுரைக்குள் வரவேண்டா’ என்று தெரிவிப்பது போலக் காற்றில் அசைவதாகத் தம் குறிப்பைக் கொடியின் மீது ஏற்றிக் கூறுகிறார். இவ்வாறு இயல்பாக நிகழும் நிகழ்ச்சியின் மீது கவிஞன் தன் குறிப்பை ஏற்றிக் கூறுவது தற்குறிப்பேற்ற அணி எனப்படும்.
![]()
பகுதி – IV (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 25)
அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விடையளிக்க. [ 5 x 5 = 25 ]
Question 38.
(அ) பாடப்பகுதியில் இடம்பெற்றுள்ள மெய்க்கீர்த்திப் பாடலின் நயத்தை விளக்குக.
Answer:
- இந்திரன் முதலாகத் திசைபாலகர் எட்டுப்பேரும் ஓருருவம் பெற்றது போல் ஆட்சி செலுத்தினான் சோழன்.
- அவன் நாட்டில் யானைகள் மட்டுமே பிணிக்கப்படுவன (மக்கள் பிணிக்கப்படுவதில்லை). சிலம்புகள் மட்டுமே புலம்புகின்றன (மக்கள் புலம்புவதில்லை). ஓடைகள் மட்டுமே கலக்கமடைகின்றன (மக்கள் கலக்கமடைவதில்லை).
- புனல் மட்டுமே அடைக்கப்படுகின்றது (மக்கள் அடைக்கப்படுவதில்லை). • மாங்காய்கள் மட்டுமே வடுப்படுகின்றன (மக்கள் வடுப்படுவதில்லை.
- மலர்கள் மட்டுமே பறிக்கப்படுகின்றன (மக்கள் உரிமைகள் பறிக்கப்படுவதில்லை ). காடுகள் மட்டுமே கொடி உடையனவாக – அதாவது கொடி உடையனவாக உள்ளன (மக்கள் கொடியவராய் இல்லை ).
- வண்டுகள் மட்டுமே கள் – அதாவது தேன் உண்ணுகின்றன (மக்கள் கள் உண்பதில்லை).
- மலை மூங்கில் மட்டுமே உள்ளீடு இன்றி வெறுமையாய் இருக்கின்றது (மக்களிடையே வெறுமை இல்லை). வயலில் நெற்கதிர்கள் மட்டுமே போராக எழுகின்றன (வேறு போர் இல்லை ).
- நீண்ட மலைகளே இருள் சூழ்ந்திருக்கின்றன (நாட்டில் வறுமை இருள் இல்லை).
- இளமான்களின் கண்களே மருள்கின்றன (மக்கள் கண்களில் மருட்சியில்லை). குளத்து மீன்களே பிறழ்ந்து செல்கின்றன (மக்கள் நிலை பிறழ்வதில்லை).
- செவிலித்தாயாரே சினங் காட்டுவர் (வேறு யாரும் சினம் கொள்வதில்லை). புலவர் பாட்டில் மட்டுமே பொருள் பொதிந்து (மறைந்து இருக்கின்றது. (யாரும் பொருளை மறைப்பதில்லை ).
- இசைப்பாணரே தெருவில் கூடி ஆடிப்பாடுவர் (தேவையற்று வேறு யாரும் அவ்வாறு செய்வதில்லை). இராசராசன் காக்கும் திரு நாட்டின் இயல்பு இது.
அவன் நெறியோடு நின்று காவல் காக்கின்றான். தந்தையில்லாதோருக்குத் தந்தையாய் இருக்கின்றான். தாயில்லாதோருக்கு தாயாய் இருக்கின்றான். - மகனில்லாததோருக்கு மகனாக இருக்கின்றான். உலகில் உயிர்களுக்கு எல்லாம் உயிராக இருக்கின்றான்.
- விழிபெற்ற பயனாகவும் மெய் பெற்ற அருளாகவும் மொழி பெற்ற பொருளாகவும் புகழ் பெற்ற நூல் போலவும் திகழ்கிறான். புகழ் அனைத்திற்கும் தலைவனாகி யாதும் புரிகின்றான்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் என்பது அன்றைக்குப் புலவர்களையும் கலைஞர்களையும் வள்ளல்களை நோக்கி நெறிப்படுத்துவதாக இருந்தது. அது இன்றைய நிலையில் ஒரு வழிகாட்டுதலாக மாறியிருப்பதை விளக்குக.
Answer:
- ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் என்பது வள்ளலை நாடி எதிர்வருபவர்களை அழைத்து யாம் இவ்விடத்தைச் சென்று இன்னவெல்லாம் பெற்று வருகின்றோம். . நீயும் அந்த வள்ளலிடம் சென்று வளம்பெற்று வாழ்வாயாக என்று கூறுதல் ஆற்றுப்படை
ஆகும். - ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் என்பது இன்றைய நிலையில் ஒரு வழிகாட்டுதலாக இருக்கிறது.
- தன்னிடம் இல்லை என்றோ அல்லது தெரியாது என்றோ யார் வந்தாலும் அவர்களுக்கு வழிகாட்டுதலாகவும் இருக்கிறது.
- அவர்களுக்கு அறிவுரை கூறி அவர்களை வழிகாட்டுகின்றனர். அன்றைய ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் இன்றைய வழிகாட்டுதலாக மாறியுள்ளது.
- இது ஒவ்வொரு நிலையிலும் மாற்றம் அடைந்துள்ளது. உதவி தேவைப்படுபவர்களுக்கு பெரும் உதவியாக இருந்து வருகிறது.
- இதுவே இன்றைய ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் ஆகும்.
Question 39.
(அ) மாநில அளவில் நடைபெற்ற “மரம் இயற்கையின் வரம்” எனும் தலைப்பிலான கட்டுரைப் போட்டியில் வெற்றி பெற்று முதல் பரிசு பெற்ற தோழனை வாழ்த்தி மடல் எழுதுக.
Answer:
எண், 20/3 மாடவீதி,
மதுரை,
5.5.2019
அன்புள்ள நவீன்குமார்,
நாங்கள் அனைவரும் இங்கு நலம். நீயும் உன் குடும்பத்தாரும் எப்படி இருக்கிறீர்கள்? சென்ற மாதம் தமிழக அரசின் சார்பில் நடைபெற்ற இலக்கிய மன்றக் கட்டுரைப் போட்டியில் கலந்து கொண்டு “மரம் இயற்கையின் வரம்” என்ற தலைப்பில் நீ எழுதிய கட்டுரை அனைவரிடமும் இயற்கையைக் காப்பாற்ற வேண்டும், மரங்களை நட்டு வளர்க்க வேண்டும் என்ற அவசியத்தை உணர்த்தியுள்ளது. ஆகவே உன் ஈடுபாட்டைப் பார்த்து எனக்கும் கட்டுரைப் போட்டியில் கலந்து கொள்ள * ஆர்வம் வருகிறது. பல போட்டிகளில் நீ பெற்ற பரிசுப்பொருள்கள் உன் வீட்டில் ஏராளமாகக் குவிந்து கிடக்கின்றன. அனைத்தையும் பார்த்து நான் பலமுறை வியந்துள்ளேன்.
உன்னை நண்பனாக அடைந்ததற்கு நான் மிகவும் பெருமைப்படுகிறேன். நீ இன்னும் பல போட்டிகளில் கலந்து கொண்டு வெற்றிகளைப் பெற வாழ்த்துகிறேன். நீ அடுத்தமுறை போட்டியில் கலந்து கொள்ளும்போது எனக்குத் தெரியப்படுத்து. நான் நீ எவ்வாறு போட்டிக்குத் தயாராகிறாய் என்பதை அறிந்து கொள்கிறேன். உன் பதிலுக்காகக் காத்திருக்கிறேன்.
இப்படிக்கு,
உன் அன்புள்ள,
ப. அன்பரசன்.
உறைமேல் முகவரி
பெறுநர்
க. நவீன்குமார்,
5. காளையார் கோவில்
முத்தமிழ் நகர்,
ஈரோடு – 638 001.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) உணவு விடுதியொன்றில் வழங்கப்பட்ட உணவு தரமற்றதாகவும், விலை கூடுதலாகவும் இருந்தது குறித்து உரிய சான்றுகளுடன் உணவுப் பாதுகாப்பு ஆணையருக்குக் கடிதம் எழுதுக.
Answer:
அனுப்புநர்
கபிலன்,
பாரதியார் தெரு,
மதுரை.
பெறுநர்
உணவுப் பாதுகாப்பு ஆணையர்,
உணவுப் பாதுகாப்பு அலுவலகம்,
மதுரை.
ஐயா,
பொருள் : உணவு தரமில்லை, விலை கூடுதல் புகார் அளித்தல் – சார்பு. வணக்கம்.
நான் காலையில் சுந்தர பவன் உணவு விடுதிக்குச் சாப்பிடச் சென்று இருந்தேன். நான்கு இட்லிகள் மட்டும்தான் சாப்பிட்டேன். அதற்கு ரூ 50/- விலை போட்டார்கள். அந்த அளவிற்கு இட்லியின் தரமும் இல்லை. இட்லிக்குச் சாம்பார் மட்டும் தான் கொடுத்தார்கள். சட்னி கொடுக்கவில்லை கேட்டால் பொறுப்பற்ற முறையில் பதில் கூறுகின்றனர். அதனால் ஐயா அவர்கள் அந்த உணவு விடுதியின் மீது நடவடிக்கை எடுக்குமாறு கேட்டுக் கொள்கிறேன்.
நன்றி
இடம் : மதுரை
தேதி : 18.05.2019
இங்ஙனம்,
தங்கள் உண்மையுள்ள, .
கபிலன்.
குறிப்பு
1. உணவு விடுதியின் பில்
2. அவர்கள் பேசிய ஆடியோ
3. புகைப்படம்
உறைமேல் முகவரி
உணவுப் பாதுகாப்பு ஆணையர்,
உணவுப் பாதுகாப்பு அலுவலகம்;
மதுரை – 625 001.
![]()
Question 40.
படம் உணர்த்தும் கருத்தை நயமுற ஐந்து தொடர்களில் எழுதுக.
Answer:

மழை என்று பெய்யும்
என் வாழ்வு என்று விடியும் என
விடியலுக்காகக் காத்திருக்கிறேன்
எனக்கு மட்டும் விடிவேயில்லை !
மாதம் மும்மாரி பெய்த நாளெங்கே?
வானம் பார்த்த பூமி மட்டும் இங்கே!
உழவனின் இதயமும் பாளமாய்!
பாளம், பாளமாய் வெடித்த நிலம் கண்டு,
விடியல் எப்போது? காத்திருக்கிறேன்!
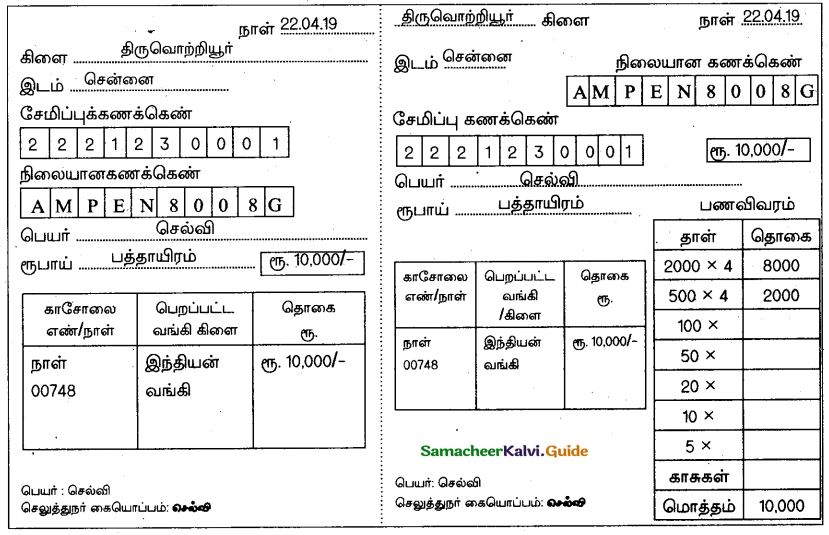
Question 41.
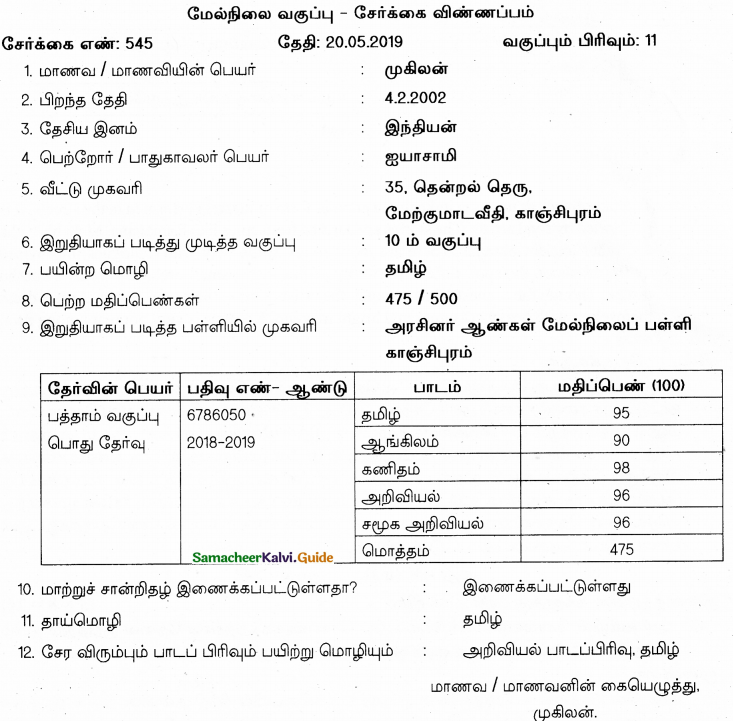
விண்ண ப்பப் படிவத்தை நிரப்புக.
Answer:
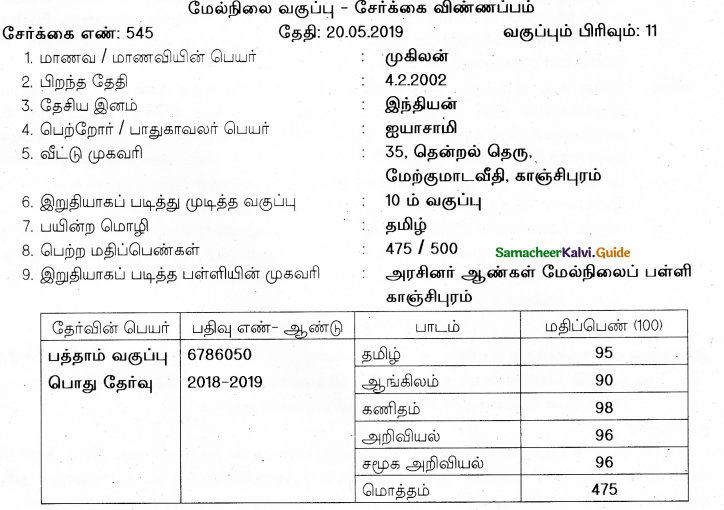

Question 42.
(அ) பள்ளியிலும் வீட்டிலும் நீ செய்ய விரும்புவனவற்றை எழுதுக. Answer:
பள்ளியில் நான் :
- நேரத்தைச் சரியாகக் கடைப்பிடிப்பேன்.
- உடன் பயிலும் மாணவரின் திறமையைப்
- பாராட்டுவேன். பாடத்தைக் கவனமாகக் கவனிப்பேன்.
- யாரிடமும் சண்டை போடமாட்டேன்.
வீட்டில் நான் :
- வீட்டுப் பணிகளைப் பகிர்ந்து செய்வேன்.
- வீட்டைத் தூய்மையாக வைத்திருப்பேன்.
- தன்வேலைகளைத் தானே செய்வேன்.
- என் தாய்க்கு உதவியாக இருப்பேன்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) மொழிபெயர்க்க.
Respected ladies and gentlemen, I am Ilangovan studying tenth standard. I have come here to say a few words about our Tamil culture. Sangam literature shows that Tamils were best in culture and civilization about two thousand years ago. Tamils who have defined grammar for language have also defined grammar for life. Tamil culture is rooted in the life styles of Tamils throughout India. Srilanka, Malaysia, Singapore, England and Worldwide. Though our culture is very old, it has been updated consistently. We
should feel proud about our culture. Thank you one and all.
Answer:
விடை :
இங்கு கூடி இருக்கும் அனைவருக்கும் என் மனமார்ந்த வணக்கம். என் பெயர் இளங்கோவன். நான் 10 ஆம் வகுப்பு படிக்கிறேன். தமிழ்க் கலாச்சாரத்தைப் பற்றி சில வார்த்தைகள் கூற வந்துள்ளேன். இரண்டாயிரம் ஆண்டுகளுக்கு முன்னமே தமிழன் கலாச்சாரத்திலும், நாகரிகத்திலும் மேம்பட்டு இருந்தான் என்பதைச் சங்க இலக்கியங்கள் புலப்படுத்துகின்றன. தமிழ் மொழிக்கு இலக்கணம் வகுத்த தமிழன் வாழ்க்கை நெறிக்கும் இலக்கணம் வகுத்துள்ளான். தமிழ்க் கலாச்சாரம் இலங்கை, சிங்கப்பூர், இங்கிலாந்து மற்றும் உலகளாவிய இந்தியத் தமிழ் மக்களின் வாழ்வாதாரங்களில் வேரூன்றி நிற்கிறது. நம் கலாச்சாரம் பழமை வாய்ந்ததாக இருப்பினும் அது தொடர்ச்சியாகப் புதுபித்த வண்ணமே இருக்கின்றன. நாம் நம் கலாச்சாரத்தைப் பற்றி பெருமை கொள்ள வேண்டும். அனைவருக்கும் நன்றி.
![]()
பகுதி – V
(மதிப்பெண்கள்: 24) அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விரிவாக விடையளிக்க. [3 x 8 = 24]
Question 43.
(அ) தமிழின் சொல்வளம் பற்றியும் புதிய சொல்லாக்கத்திற்கான தேவை குறித்தும் தமிழ்
மன்றத்தில் பேசுவதற்கான உரைக் குறிப்புகளை எழுதுக.
Answer:
முன்னுரை:
கால வெள்ளத்தில் கரைந்துபோன மொழிகளுக்கிடையில் நீந்தி தன்னை நிலை நிறுத்திக் கொண்டுள்ளது. தமிழ் சொல்வளம் இலக்கியச் செம்மொழிகளுக்கெல்லாம் பொது என்றாலும் தமிழ் மட்டுமே அதில் தலை சிறந்ததாகும். தமிழின் சொல் வளத்தை நாம் பலதுறைகளிலும் காணலாம்.
தமிழின் சொல் வளம்:
ஆங்கிலம் போன்ற மொழிகளில் இலையைக் குறிக்க ஒரே ஒரு சொல் மட்டுமே உள்ளது. ஆனால் தமிழ்மக்கள் இலையை அதன் வன்மை, மென்மை இவற்றைக் கொண்டு இலை, தோகை, ஓலை என பாகுபாடு செய்துள்ளனர். இதுமட்டுமன்றி தாவரங்கள், மணிவகை, இளம்பயிர்வகை, காய்கனி வகை, அடி, கிளை கொழுந்து என அனைத்து உறுப்புகளுக்கும் சொற்களைப் பகுத்து வைத்துள்ளனர்.
பூவின் நிலைகளைக் குறிக்கும் சொற்கள்:
அரும்பு: பூவின் தோற்றநிலை போது, பூ விரியத் தொடங்கும் நிலை மலர், பூவின் மலர்ந்த நிலை, வீ: மரம், செடியிலிருந்து பூ கீழே விழுந்த நிலை செம்மல், பூ வாடின நிலை
தமிழின் பொருள் வளம்:
தமிழ்நாடு எத்துணைப் பொருள் வளமுடையது என்பது அதன் வினைபொருள் வகைகளை நோக்கினாலே விளங்கும். தமிழ்நாட்டு நெல்லில் செந்நெல் வெண்ணெல், கார்நெல் என்றும், சம்பா, மட்டை, கார் என்றும் பல வகைகள் உள்ளன. அவற்றில் சம்பாவில் மட்டும் ஆவிரம் பூச்சம்பா, ஆனைக் கொம்பன் சம்பா, குண்டு சம்பா, குதிரை வாலிச்சம்பா, சிறுமணிச்சம்பா, சீரகச்சம்பா முதலிய அறுபது உள் வகைகள் உள்ளன. இவற்றோடு வரகு, காடைக்கண்ணி-குதிரைவாலி முதலிய சிறு கூலங்கள் தமிழ் நாட்டிலன்றி வேறெங்கும் விளைவதில்லை.
முடிவுரை:
பண்டைத் தமிழ் மக்கள் தனிப்பெரும் நாகரிகத்தை உடையவராக இருந்திருக்கின்றனர். ஒரு நாட்டாரின் அல்லது இனத்தாரின் நாகரிகத்தை அளந்தறிவதற்கு உதவுவது மொழியேயாகும். ஆகவே “நாடும் மொழியும் நமதிரு கண்கள்” என்ற கூற்றின்படி பொருட்களைக் கூர்ந்து நோக்கி நுண்பொருட் சொற்களை அமைத்துக் கொள்வது நம் தலையாய கடமையாகும்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) உங்கள் இல்லத்துக்கு வந்த உறவினருக்கு நீங்கள் செய்த விருந்தோம்பலை அழகுற விவரித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
- எங்கள் இல்லத்திற்கு என் தந்தையின் நண்பர்கள் பொங்கல் திருநாளன்று வந்தனர் .
- நாங்கள் அவர்களை அன்போடு வரவேற்றோம். வந்தவர்களை வாருங்கள் என்று அழைத்து அவர்களுக்குக் குடிக்கத் தண்ணீர் கொடுத்தோம்.
- அவர்களை அமரவைத்து அவர்களிடம் நலம் விசாரித்தும் என் தாய், தந்தையர் பேசிக் கொண்டு இருந்தனர்.
- சிறிது நேரம் கழித்து அவர்கள் குடிக்கப் பழச்சாற்றினைக் கொடுத்தோம்.
- பிறகு அவர்கள் உணவருந்த சுவையான உணவு சமைத்து வைத்திருந்தோம்.
- வந்தவர்களை உணவருந்த அழைத்து வந்து வாழையிலை போட்டு கூட்டு, பொரியல் இனிப்பு, வடை, பாயசம் என்று அறுசுவை உணவைப் படைத்தோம்.
- அவர்கள் உண்டபின் அவர்களுக்கு வெற்றிலை பாக்கு கொடுத்து இளப்பாற வைத்தோம்.
- பின் அவர்கள் வீட்டிற்குச் சொல்லும் போது அவர்களுக்குப் பரிசுப்பொருள் கொடுத்து வீட்டின் வாசல் வரை சென்று வழி அனுப்பி வைத்தோம்.
Question 44.
(அ) அன்னமய்யா என்னும் பெயருக்கும் அவரின் செயலுக்கும் உள்ள
பொருத்தப்பாட்டினைக் கோபல்லபுரத்து மக்கள் கதைப்பகுதி கொண்டு விவரிக்க.
Answer:
கதைக்கரு:
கிராமத்து மனிதர்கள் காட்டும் விருந்தோம்பல் பகிர்ந்து கொடுக்கிற நேயம்.
கதைமாந்தர்கள் :
- சுப்பையா
- கிராமத்து மக்கள் . அன்னமய்யா
- மணி
முன்னுரை:
கிராமத்து வெள்ளந்தி மனிதர்கள் காட்டும் விருந்தோம்பல் இயல்பான வரவேற்பும் எளிமையான உணவும் பசித்த வேளையில் வந்தவர்களுக்குத் தம்மிடம் இருப்பதை பகிர்ந்து கொடுக்கிற மனித நேயம் ஆகியவற்றை இக்கதைப்பகுதி எடுத்துக்கூறுகிறது.
கிராமத்து காட்சி :
அதிகாலை நேரத்தில் பாச்சல் அருகு எடுத்து முடித்துவிட்டுக் காலைக் கஞ்சியைக் குடிக்க உட்காரும் வேளையில் அன்னமய்யா யாரோ ஒரு சன்னியாசியைக் கூட்டிக் கொண்டு வருவதைக் கண்டான் சுப்பையா வரட்டும் வரட்டும். ஒரு வயிற்றுக்குக் கஞ்சி ஊற்றி நாமும் குடிப்போம் என்றார். கொத்தாளி அந்தப் புஞ்சை சாலையோரத்தில் இருந்ததால் தேசாந்திரிகள் வந்து இவர்களிடம் தண்ணீரோ, கஞ்சியோ சாப்பிட்டு விட்டுப் போவது வழக்கம்.
அன்னமய்யா கண்ட காட்சி:
நடக்க முடியாமல் உட்கார்ந்து உட்கார்ந்து எழுந்திருந்து ஆயாசமாக மெதுவாக நடந்து வந்து தாடியும் அழுக்கு ஆடையும் தள்ளாட்டமுமாக நடந்து வந்து கொண்டிருந்தவனைப் பார்க்கும் போது வயோதிகனாகவும் சாமியாரைப்போலவும் எண்ண வைத்தது. தற்செயலாக இவனைக்கண்ட அன்னமய்யா அவன் அருகில் சென்று பார்த்த பிறகுதான் தெரிந்தது அவன் ஒரு வாலிபன் என்று, கால்களை நீட்டி புளிய மரத்தில் சாய்ந்து உட்கார்ந்திருந்த அவனை நெருங்கிப் பார்த்தபோது பசியால் அவன் முகம் வாடிப்போயிருந்தது.
அன்னமய்யாவின் செயல்:
பசியால் வாடிப்போயிருந்த அவன் முகத்தில் தீட்சணியம் தெரிந்தது தன்னைப் பார்த்து ஒரு நேசப்புன்னகை காட்டிய அந்த வாலிப மனிதனைப் பார்த்துக்கொண்டே நின்றான் அன்னமய்யா. குடிக்கக் கொஞ்சம் தண்ணீர் கிடைக்குமா? என்ற அவனைத் தன்னோடு மெதுவாக நடக்க வைத்து அழைத்துச் சென்றான் அன்னமய்யா.
அன்னமய்யாவின் விருந்தோம்பல்:
வேப்பமரத்தின் அடியில் ஏகப்பட்ட மண் கலயங்கள் இருந்தன. அதில் அன்னமய்யா ஒரு கலயத்தின் மேல் வைக்கப்பட்ட கல்லை அகற்றிச் சிரட்டையைத் துடைத்துச் சுத்தப்படுத்தி அந்த கலயத்தில் பதனமான வடித்த நீரை அவனிடம் உறிஞ்சி குடிங்க எனக் கொடுத்தான். உட்கார்ந்து குடிங்க என்று உபசரித்தான். பிறகு கலயத்தைச் சுற்றி ஆட்டியதும் தெளிவு மறைந்து சோற்றின் மகுளி மேலே வந்ததும் வார்த்துக் கொடுத்தான். பிறகு அன்னமய்யா அந்த புது ஆளைச் சுப்பையாவின் வயலுக்கு அழைத்துச் சென்று கம்மஞ்சோற்றைச் சாப்பிட வைத்தான். அந்த வாலிபன் அன்னமய்யா என்ற பெயரை மனசுக்குத் திருப்பித் திருப்பிச் சொல்லிப் பார்த்துக் கொண்டான். எவ்வளவு பொருத்தம் என்று நினைத்துக் கொண்டான்.
முடிவுரை:
வந்தவனுக்கு எப்படி ஒரு நிறைவு ஏற்பட்டதோ அதை விட மேலான ஒரு நிறைவு அன்னமய்யாவுக்கு ஏற்பட்டது. வயிறு நிறைந்ததும் தூங்கிவிடும் குழந்தையைப் பார்ப்பதுபோல அவனை ஒரு பிரியத்தோடு பார்த்துக் கொண்டிருந்தான் அன்னமய்யா.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) அனுமான் ஆட்டத்தைக் கூறுக.
Answer:
- திடீரென்று மேளமும் நாதசுரமும் துரித கதியில் ஒலிக்கத் தொடங்கின.
- எதற்கென்று தெரியாமல் கூட்டம் திகைத்துப் பந்தலை நோக்குகையில் பெருங்குரல் எழுப்பியபடி அனுமார் பந்தல் கால் வழியாகக் கீழே குதித்தார். அனுமார் வாலில் பெரிய தீப்பந்தம். ஜ்வாலை புகைவிட்டுக் கொண்டு எரிந்தது. கூட்டம் தானாகவே பின்னால் நகர்ந்தது.
- அனுமார் கால்களைத் தரையில் பதித்து உடம்பை ஒரு குலுக்குக் குலுக்கினார். தீயின் ஜ்வாலை மடிந்து அலை பாய்ந்தது. கைகளைத் தரையில் ஊன்றி அனுமார் கரணமடித்தார்.
- சுருண்ட வால் இவன் பக்கமாக வந்து விழுந்தது.
- கூட்டம் அச்சத்தோடு கத்தியபடி அலைக்கழிந்தது.
அனுமார் பெரிதாகச் சிரித்துக்கொண்டு நின்றார். அனுமார் நின்றதும் கூட்டம் கொஞ்சம் அமைதியுற்றது. முன்நோக்கி நகர்ந்து வந்தது. அனுமார் நேசப்பான்மையோடு சிரித்து வாலை மேலே தூக்கிச்
சுற்றினார். - தீ வட்டமாகச் சுழன்றது.. வேகம் கூடக்கூட, கூட்டம் இன்னும் முன்னால் நகர்ந்து வந்தது.
- இவன் நெருங்கி அனுமார் பக்கம் சென்றான்.
- அனுமார் இன்னொரு பாய்ச்சல் பாய்ந்து வேகமாக ஆட ஆரம்பித்தார். வர வர ஆட்டம் துரிதகதிக்குச் சென்றது. பதுங்கியும் பாய்ந்தும் ஆடினார்.
- ஆட ஆட, புழுதி புகை போல எழுந்தது. கழுத்துமணி அறுந்து கீழே விழுந்தது.
- ஒன்றையும் பொருட்படுத்தாமல் ஆட்டத்தில் தன்னை இழந்தவராக ஆடினார்.
- மேளமும் நாதசுரமும் அவர் ஆட்டத்தோடு இணைந்து செல்ல முடியவில்லை
தடுமாறிவிட்டது. - மேல் மூச்சு வாங்க அனுமார் ஆட்டத்தை நிறுத்தினார். மேளமும் நாதசுரமும் நின்றன.
- அயர்ச்சியோடு மேளக்காரன் தோளிலிருந்து தவுலை இறக்கிக் கீழே வைத்தான்.
- ஆட்டம் முடிந்தது. தீர்மானமாகியது போல எஞ்சி இருந்த கூட்டமும் அவசர அவசரமாகக் கலைய ஆரம்பித்தது.
![]()
Question 45.
(அ) குறிப்புகளைப் பயன்படுத்திக் கட்டுரை ஒன்று தருக.
முன்னுரை – பாரதத்தில் கணினியின் வளர்ச்சி – கணினியின் பயன்கள் – பிற துறைகளில் கணினி – கல்வி நிலையங்களில் கணினி — முடிவுரை.
Answer:
இந்தியாவில் கணினிப் புரட்சி
முன்னுரை:
உலக நாடுகளிடையே இந்தியாவும் முன்னேற்றமடைந்த வளர்ச்சியுற்ற நாடாக வேண்டும். இக்கனவு நனவாகுமா? இதற்குப் பாரதம் பல துறைகளிலும் நன்கு உழைக்க வேண்டும். அவற்றுள் ஒன்றுதான் கணினிப் புரட்சி. உலக நாடுகள் அனைத்தும் கணினித் துறையில் வளர்ந்த அளவிற்கு நாமும் உயர வேண்டும் என்ற எண்ணம் தான் 1984இல் கணினியைக் கொணர்ந்தோம். அன்றைய பிரதமர் திரு. இராஜீவ் காந்தி அவர்கள் கணினிக்கு முக்கியத்துவம் கொடுத்து முதலிடம் அளித்தார்.
பாரதத்தில் கணினியின் வளர்ச்சி:
முதன் முதலாக மும்பையிலுள்ள டாடா ஆய்வு மையம் தான் 1966இல் கணினியை இயக்கத் தொடங்கியது. நம் நாட்டிலுள்ள மின்னியல் கழகம் கணினிகளை வாணிக நோக்குடன் தயாரிக்கத் தொடங்கியது. மின்னியல் துறையில் ஒரு புரட்சி ஏற்பட்டது. அப்போதைய பிரதமர் திரு. இராஜீவ் காந்தி அவர்கள் இந்தியாவிற்கு நல்ல எதிர்காலம் நல்கும் என வலியுறுத்தினார். வேலையில்லாத் திண்டாட்டத்திற்கு முற்றுப்புள்ளி வைக்கும் அளவிற்கு மின்னியல் துறையை வளர்த்தார். தற்போது நல்ல அடிப்படையுடன் கணினித் துறை பல துறைகளிலும் நிலைபெற்று விட்டது.
கணினியின் பயன்கள்:
மக்கள் சபையிலும், மாநில சட்டமன்றங்களிலும் கூட கணினி பயன்படுகிறது. தேர்தல் முடிவுகளை உடனுக்குடன் அறிவிப்பதிலும், வானொலி, தொலைக்காட்சி நிகழ்ச்சிகளைத் தயாரிப்பதிலும் கணினித் தொழில் நுட்பம் அங்கம் வகிக்கிறது. எல்லா மாநிலத் தலைநகரங்களிலும், மாவட்டத் தலைநகரங்களிலும் கணினி மயமாக்கப்பட்டுவிட்டது. போர்க்கால அடிப்படையில் வங்கிகள் யாவும் கணினியை ஏற்றுக் கொண்டுவிட்டன. தேசிய மயமாக்கப்பட்ட வங்கிகளைக் கணினியைக் கொண்டு கண்காணிக்க உதவுகிறது. தேசிய காப்பீட்டுக் கழகம் பெரிய அளவில் கணினி மயமாக்கப்பட்டு விட்டது.
பிறதுறைகளில் கணினி:
போக்குவரத்துத் துறையான விமான, இரயில் துறைகளில் இருக்கை முன்பதிவு செய்யவும், அவற்றைக் கட்டுப்பாட்டுக்குள் செயல்பட வைக்கவும் கணினி பயன்படுகிறது. குற்றவாளிகளைக் கண்டு பிடிக்கக் கூடிய முறைகள் கையாளப்படுகின்றன. மருத்துவத் துறையில் இரத்தப் பரிசோதனை, இருதய ஆய்வு, அறுவைச் சிகிச்சையிலும் கூட குறிப்பிடத்தக்க அளவில் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.
கல்வி நிலையங்களில் கணினி:
வணிகம், தொழில், தபால், தந்தி போன்ற பல துறைகளிலும் கணினிபுரட்சி ஏற்பட்டு விட்டது. கல்வி நிலையங்களில், பல்கலைக் கழகங்களில் கல்வி மேம்பாட்டுப் பணிகளைச் செய்து விடுகிறது. பலரும் கணினி பற்றிய கல்வி நிலையங்களைத் துவங்கி பட்டம், பட்டமேற்படிப்பு என வகைப்படுத்தி இந்தியாவில் அனைவருமே கணினி அறிவு பெற்றுத் திகழ வாய்ப்பினை ஏற்படுத்தி விட்டது. இதன்மூலம் நம்நாட்டு இளைஞர்கள் மேனாடுகளில் சென்று வேலைவாய்ப்பு பெற்று நிரம்பப் பொருளீட்டும் வாய்ப்பும் பெற்றுள்ளனர். கணினித் தொழில் நுட்பம் செய்திகளை அனுப்பவும், தொலைதூர நாடுகளிடையே தொடர்பு ஏற்படுத்தவும் பெரிதும் உதவுகிறது. கல்வி நிலையங்களில் கணினி ஒரு பாடத் திட்டமாக அமைந்துள்ளது. தற்கால இளைஞர்கள் கணினியை விரும்பிக் கற்று புரட்சி ஏற்படுத்துவதில் முனைந்துவிட்டனர்.
முடிவுரை:
கணினித்துறை, நம் நாட்டின் எதிர்காலத்தில் மிக விரைவாகவும், திறமையாகவும் செயல்படும் என்பதில் ஐயமில்லை. பாரதத்தின் தொழில் வளர்ச்சிக்கேற்ப கணினித் துறை பெருமளவில் வளர்ச்சி பெறுவது இயற்கை நியதிகளில் ஒன்றாகிவிடும்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) உங்கள் பகுதியில் நடைபெற்ற அரசுப் பொருட்காட்சிக்குச் சென்று வந்த நிகழ்வைக் கட்டுரையாக்குக.
Answer:
பொருட்காட்சி
முன்னுரை:
விடுமுறை தினத்தைச் சிறந்த முறையில் செலவழிப்பதற்காக நடைபெறும் பொருட்காட்சிகள் மக்களின் மனதையும் கருத்தினையும் கவரும் வகையில் அமைதல் வேண்டும். 14.1.2019 அன்று தமிழக முதல்வர் சுற்றுலா வர்த்தகப் பொருட்காட்சியைத் திறந்து வைத்தார்கள். அனைவரும் சென்று கண்டுகளித்தோம்.
கண்ணை கவரும் மாதிரிகள்:
பிற்காலச் சோழ மன்னர்களில் சிறந்து விளங்கிய இராசராச சோழன் தஞ்சையில் எழுப்பிய வியத்தகு பெரிய கோயிலின் மாதிரி, பொருட்காட்சியின் வாயிலில் அமைத்திருக்கிறார்கள். அது காண்போர் கண்ணைக் கவர்ந்து இழுக்கின்றது.
கலை பண்பாட்டு அரங்குகள்:
பொருட்காட்சியின் உள்ளே இந்திய மாநிலங்கள் ஒவ்வொன்றும் தங்கள் மாநிலத்தின் கலை, பண்பாடு, நாகரிகம் முதலியவைப் பற்றி விளக்கும் அரங்கங்கள் நம்மை வரவேற்கின்றன. குழந்தைகளுக்காகச் சிறுவர் உலகம் வரவேற்கிறது. அதன் உள்ளே ரயில் வண்டி மிகப்பெரிய இராட்டினம் ஆகியவை உள்ளன.
குழந்தைகளுக்கான அரங்குகள்:
விளையாட்டுப் போட்டிகளும், மாயாஜாலங்களும், இழுவைப் பாலமும், துப்பறியும் நாய்களின் வியத்தகு செயல்களும், கோளரங்கமும் அறிவியல் வளர்ச்சியை விளக்கும் வகையில் அமைந்துள்ளது.
அறிவியல் கூடங்கள்:
அறிவியல் வேளாண்மையில் நமது முன்னேற்றத்தை விளக்கும் அரங்கமும் அதில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ள காய் கனி வகைகளும் இழுவைப் பாலமும் போக்குவரத்துத் துறையில் நமது முன்னேற்றத்தை விளக்கும் மாதிரிகள் அடங்கிய அரங்கமும் விடுதலைக்குப் பிறகு நம் நாட்டின் முன்னேற்றத்தை விளக்கும் அரங்கமும் செயல்படுகிறது.
அங்காடி வீதிகள்:
வீட்டின் அன்றாடத் தேவைகளுக்கு உதவக்கூடிய பொருள்களை விற்கும் அங்காடிகளும் சிற்றுண்டி விடுதிகளும் நிறைந்து நம்மை மெய்மறக்கச் செய்கின்றன.
முடிவுரை:
குழந்தைகள் முதல் பெரியவர்கள் வரை அனைவருக்கும் பயன்படும் வகையில் பொருட்காட்சி அமைந்திருந்தது.