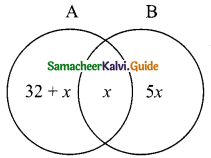
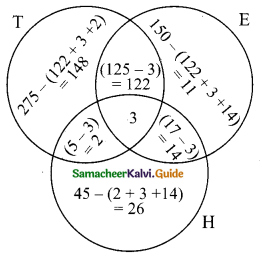
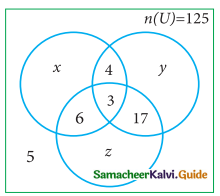
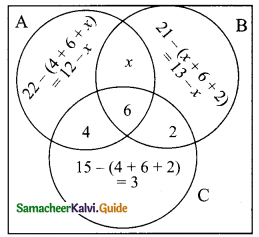
Students can download Maths Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.7 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.7
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) {7} ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
(b) 1 ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
(c) 7 ∉ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
(d) {7} ⊄ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Solution:
(b) 1 ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Question 2.
The set P = {x | x ∈ Z, -1 < x < 1} is a ……….
(a) Singleton set
(b) Power set
(c) Null set
(d) Subset
Solution:
(a) Singleton set
Hint: P = {0}
![]()
Question 3.
If U = {x | x ∈ N, x < 10} and A = {x | x ∈ N, 2 ≤ x < 6} then (A’)’ is………..
{a) {1, 6, 7, 8, 9}
(b) {1, 2, 3, 4}
(c) {2, 3, 4, 5}
(d) { }
Solution:
(c) {2, 3, 4, 5}
Hint:
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
A= {2, 3, 4, 5}; A’ = {1, 6, 7, 8, 9}
(A’)’ = U – A
(A’)’ = {2, 3, 4, 5}
Question 4.
If B⊆A then n(A∩B) is………..
(a) n(A – B)
(b) n(B)
(c) n(B – A)
(d) n(A)
Solution:
(b) n(B)
![]()
Question 5.
If A = {x, y, z} then the number of non- empty subsets of A is…………..
(a) 8
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 7
Solution:
(d) 7
Hint:
n(A) = 3; P(A) = 2m = 23 = 8
Non-empty subsets of A = 8 – 1 = 7
Question 6.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Ø ⊆ {a, b}
(b) Ø ∈ {a, b}
(c) {a} ∈ {a, b}
(d) a ⊆ {a, b}
Solution:
(a) Ø ⊆ {a, b}
Hint:
‘Q’ is a subset of every set.
![]()
Question 7.
If A∪B = A∩B then ……………
(a) A ≠ B
(b) A = B
(c) A ⊂ B
(d) B ⊂ A
Solution:
(b) A = B
Question 8.
If B – A is B, then A∩B is………….
(a) A
(b) B
(c) U
(d) Ø
Solution:
(d) Ø
![]()
Question 9.
From the adjacent diagram n[P(AΔB)] is………….
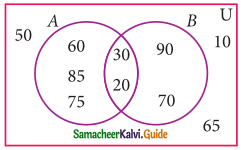
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 32
(d) 64
Solution:
(c) 32
Hint:
A – B = {60, 85, 75}
B – A = {90, 70}
AΔB = (A – B) ∪ (B – A)
= {60, 70, 75, 85, 90}
n[P(AΔB)] = 25 = 32
Question 10.
If n(A) = 10 and n(B) = 15 then the minimum and maximum number of elements in A∩B is …………
(a) (10, 15)
(b) (15, 10)
(c) (10, 0)
(d) (0, 10)
Solution:
(d) (0, 10)
![]()
Question 11.
Let A = {Ø} and B = P(A) then A∩B is………..
(a) {Ø, {Ø}}
(b) {Ø}
(c) Ø
{d) {0}
Solution:
(b) {Ø}
Hint:
A = {Ø}, B = {{ }, {Ø}}
A∩B = {Ø}
Question 12.
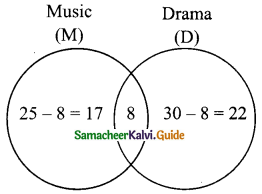
In a class of 50 boys, 35 boys play carrom and 20 boys play chess then the number of boys play both games is……..
(a) 5
(b) 30
(c) 15
(d) 10
Solution:
(a) 5
Hint:
n(A∪B) = 50, n(A) = 35, n(B) = 20
n(A∩B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A∪B)
= 35 + 20 – 50 = 5
Question 13.
If U = {x : x ∈ N and x < 10}, A = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8} and B = (2, 5, 6, 7, 9}, then n [(A∪B)’] is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Solution:
(a) 1
Hint:
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
A∪B ={1, 2, 3, 5, 8} ∪ {2, 5, 6, 7, 9}
= {1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
(A∪B)’ = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
= {4}
n(A∪B)’ = 1
![]()
Question 14.
For any three sets P, Q and R, P – (Q∩R) is ………
(a) P – (Q∪R)
(i)(P∩Q) – R
(c) (P – Q) ∪ (P – R)
(d) (P – Q) ∩ (P – R)
Solution:
(c)(P – Q) ∪ (P – R)
Question 15.
Which of the following is true?
(a) A – B = A∩B
(b) A – B = B – A
(c) (A∪B)’ = A’∪B’
(d) (A∩B)’ = A’∪B’
Solution:
(d) (A∩B)’ = A’∪B’
![]()
Question 16.
If n(A∪B∪C) = 100, n(A) = 4x, n(B) = 6x, n(C) = 5x, n(A∩B) = 20, n(B∩C) = 15 and n(A∩C) = 25, then n(A∩B∩C) = 10, then the value of x is……….
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 25
(d) 30
Solution:
(b) 15
Hint:
n(A∪B∪C) = n( A) + n(B) + n(C) – n(A∩B) – n(B∩C) – n(A∩C) + n(A∩B∩C)
100 = 4x + 6x + 5x – 20 – 15 – 25 + 10
100 = 15x – 50 ⇒ 150 = 15x ⇒ x = \(\frac{150}{15}\) = 10
Question 17.
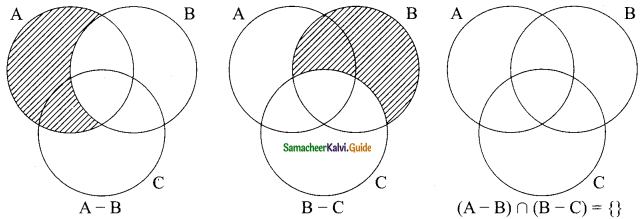
For any three sets A, B and C, (A – B) ∩ (B – C) is equal to
(a) A only
(b) B only
(c) C only
(d) \(\phi \)
Solution:
(d) \(\phi \)
![]()
Question 18.
If J = Set of three sided shapes, K = Set of shapes with two equal sides and L = Set of shapes with right angle, then J∩K∩L is………
(a) Set of isosceles triangles
(b) Set of equilateral triangles
(c) Set of isosceles right triangles
(d) Set of right angled triangles
Solution:
(c) Set of isosceles right triangles
J = Set of three sided shapes; It is a triangle
K = Set of shapes with two equal sides (Isosceles triangle)
L = Set of shapes with right angle (One angle is right angle)
∴ J∩K∩L = Set of isosceles right triangles
Question 19.
The shaded region in the Venn diagram is
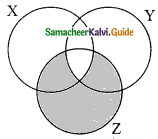
(a) Z – (X∪Y)
(b) (X∪Y) ∩ Z
(c) Z – (X∩Y)
(d) Z ∪ (X∩Y)
Solution:
(c) Z – (X∩Y)
![]()
Question 20.
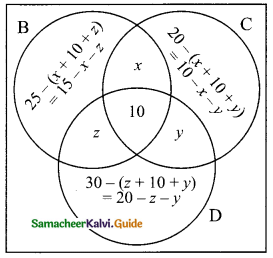
In a city, 40% people like only one fruit, 35% people like only two fruits, 20% people like all the three fruits. How many percentage of people do not like any one of the above three fruits?
(a) 5
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 15
Solution:
(a) 5