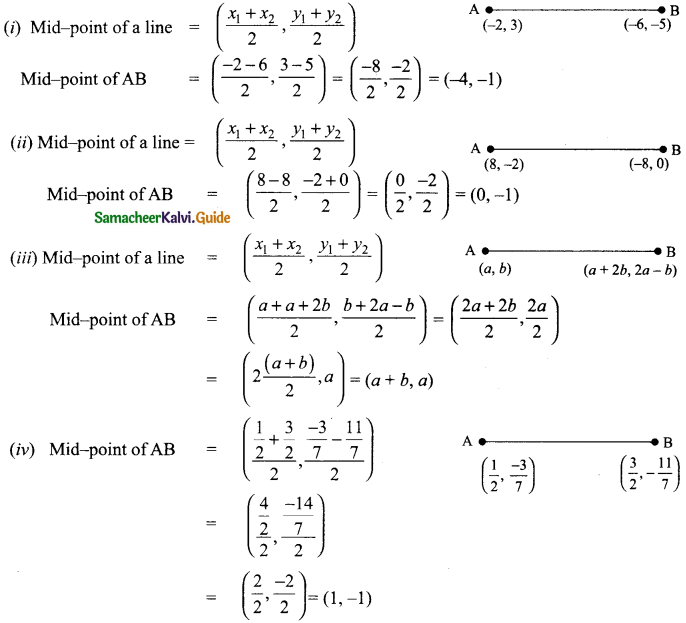
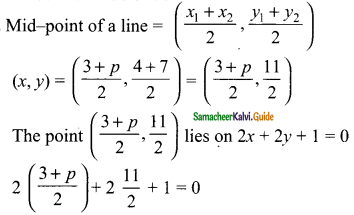
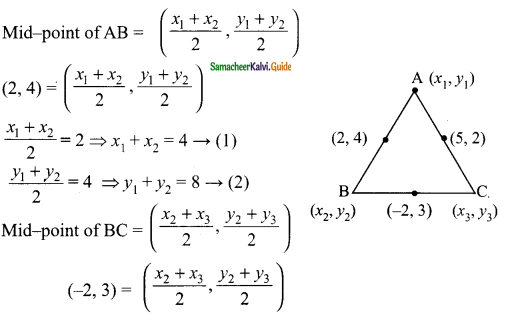
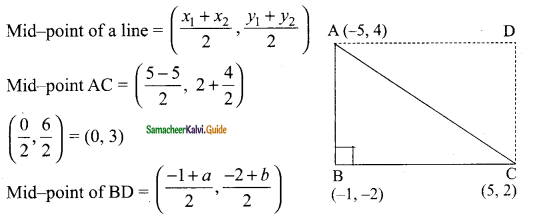
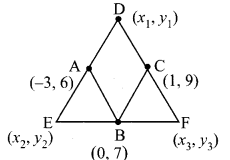
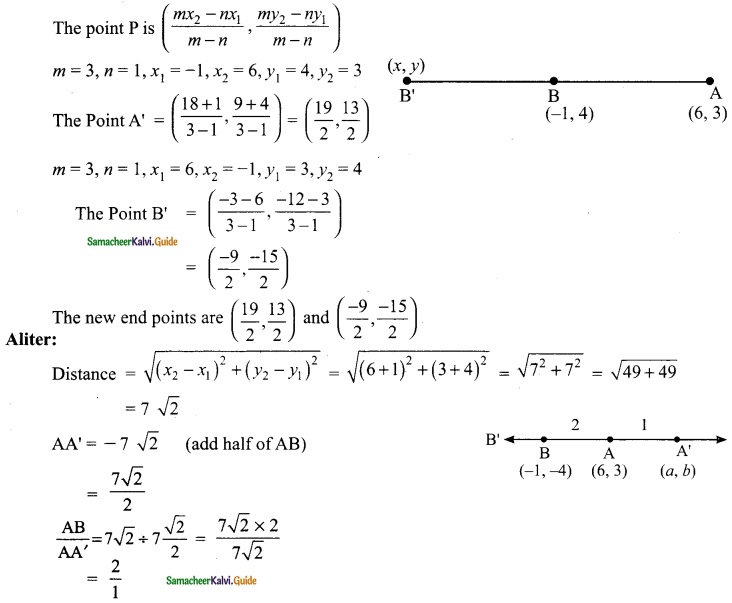
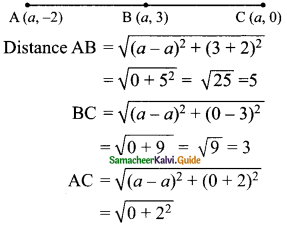
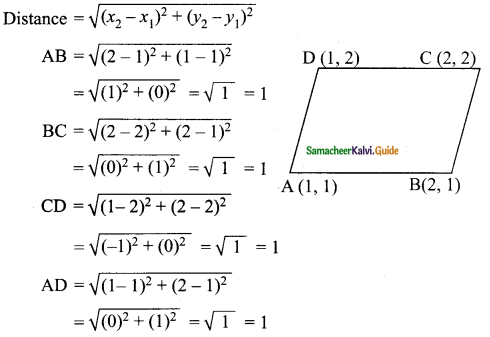
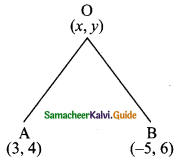
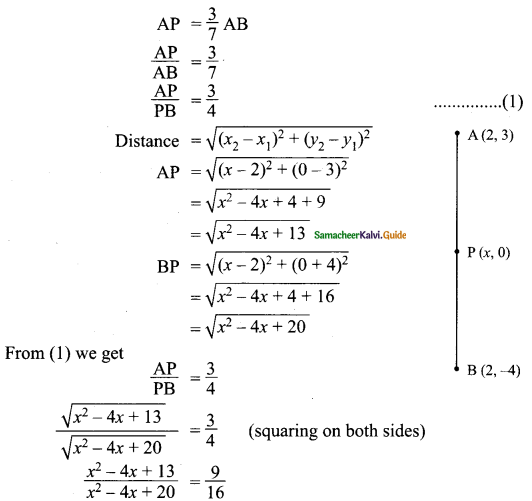
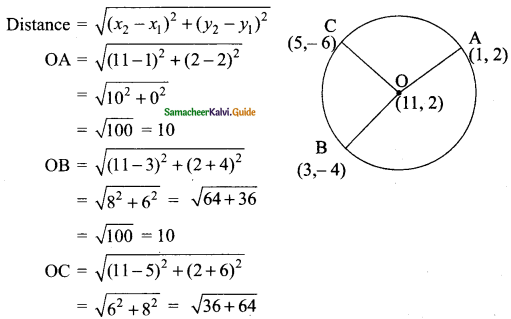
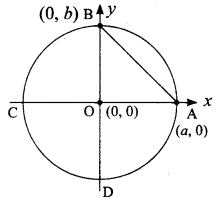
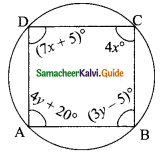
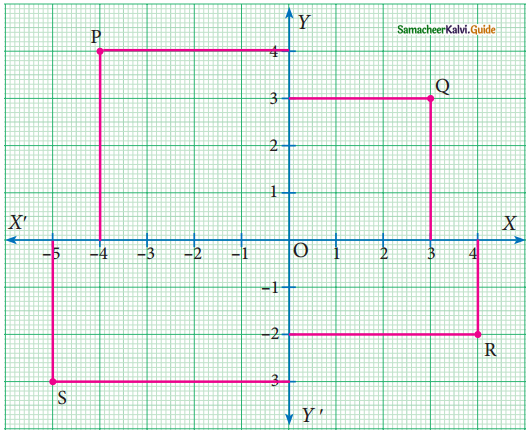
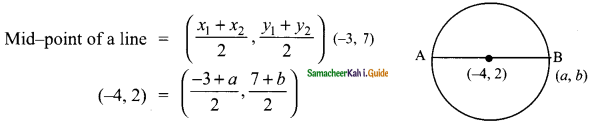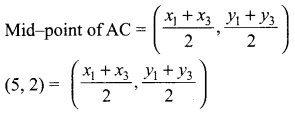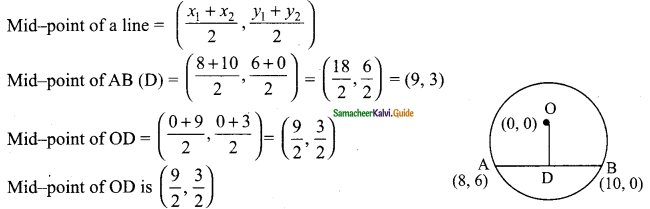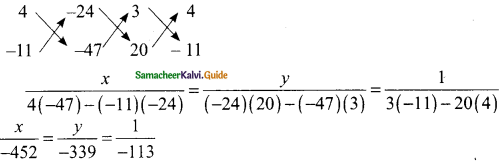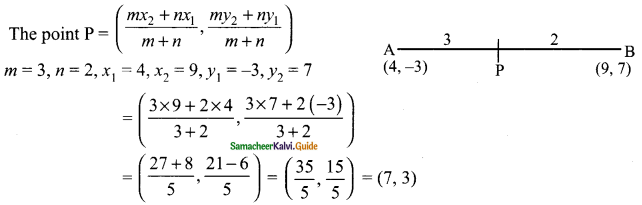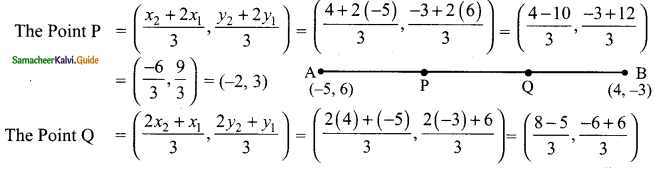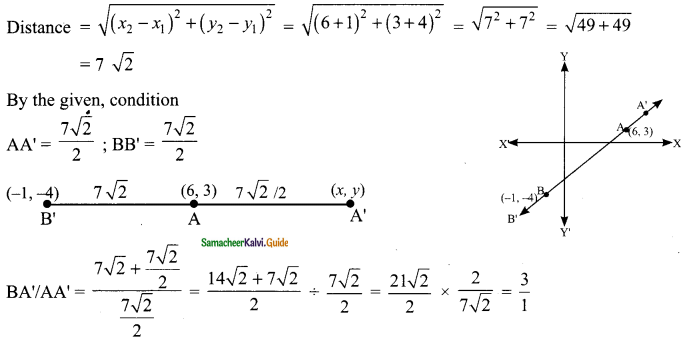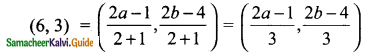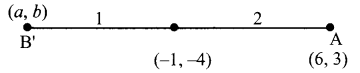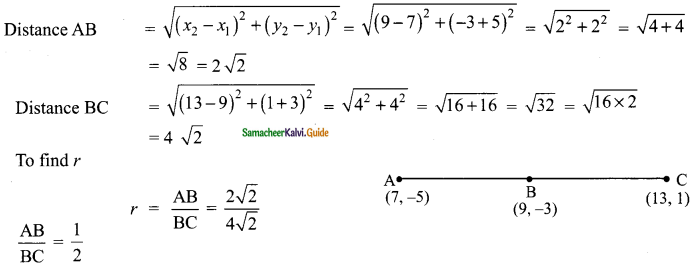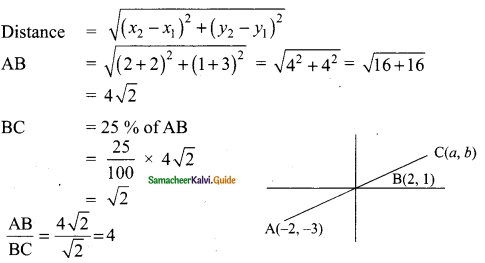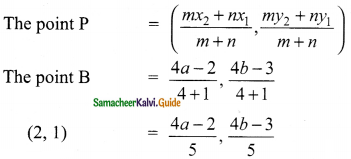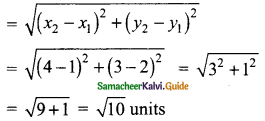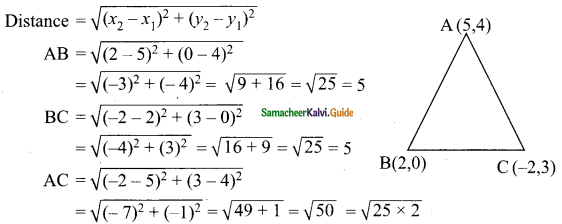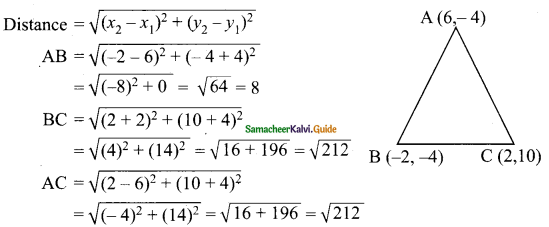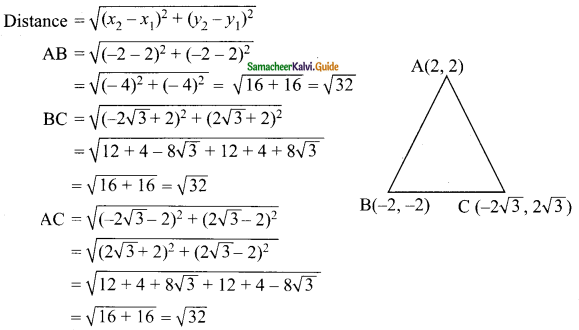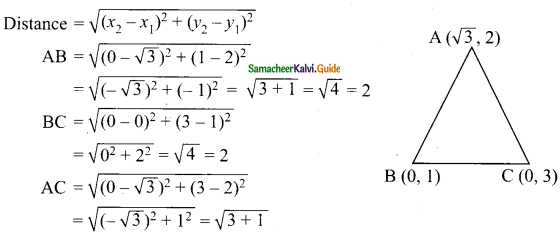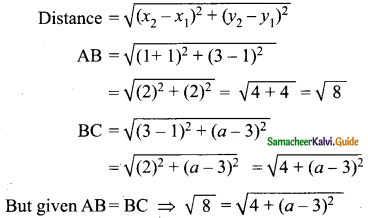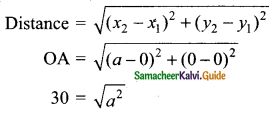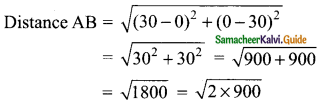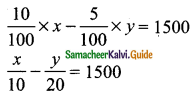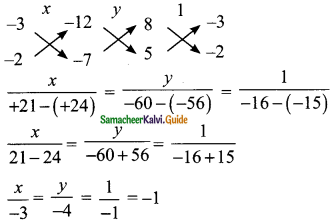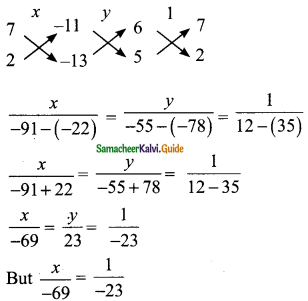Students can download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.1 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.1
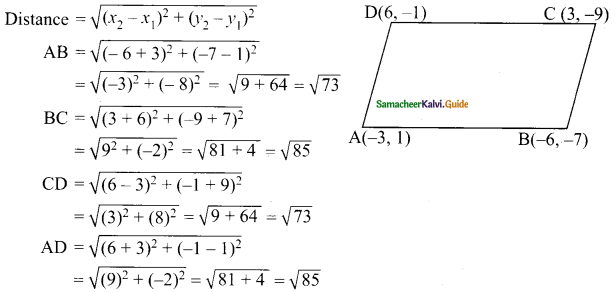
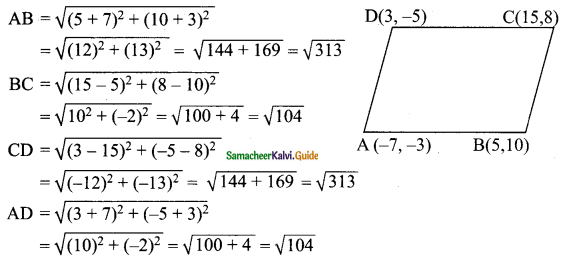
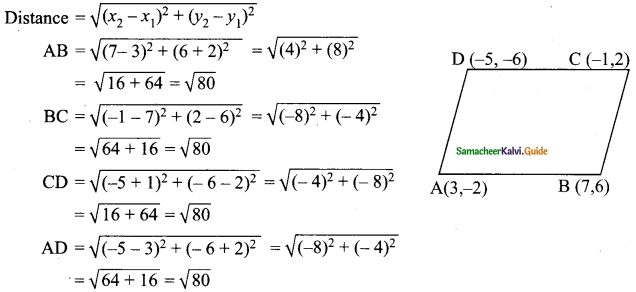
Question 1.
In the figure, AB is parallel to CD, find x.
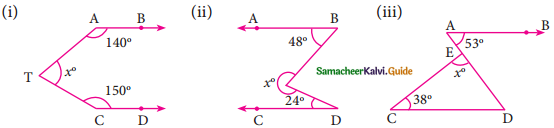
Solution:
(i) Through T draw TE || AB.
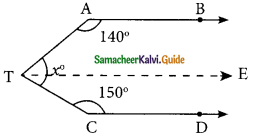
∴ ∠BAT + ∠ATE = 180° (AB || TE)
140° + ∠ATE = 180°
∠ATE = 180°- 140° = 40°
Similarly ∠ETC + ∠TCD = 180° (TE || CD)
∠ETC+150° = 180°
∠ETC = 180°- 150° = 30°
x = ∠ATE + ∠ETC
= 40°+ 30° = 70°
x = 70°
![]()
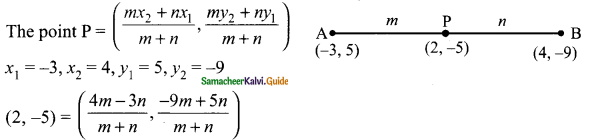
(ii) Draw TE || AB.
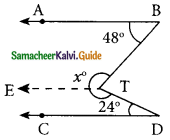
∠ABT + ∠ETB = 180° (AB || TE)
48° + ∠ETB = 180°
∠ETB = 180° – 48° = 132°
Similarly ∠CDT + ∠DTE = 180°
24° + ∠DTE = 180°
∴ ∠DTE = 180° – 24°
= 156°
∴ ∠BTE + ∠ETD = 132° + 156°
= 288°
x = 288°
![]()
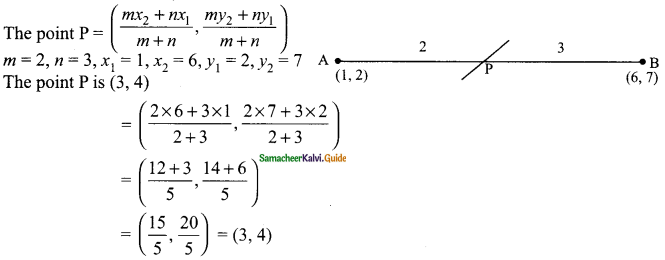
(iii) In the given figure AB || CD, AD is the transversal.
∠CDA = ∠BAD
= 53° (alternate angles are equal)
In ΔECD, ∠D = ∠A = 53° (Alternate angles are equal)
∠E + ∠C + ∠D = 180° (sum of the angles of a triangle)
x° + 38° + 53° = 180°
x° = 180°- 91°
= 89°
x = 89°
Question 2.
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3, find the measure of each angle of the triangle.
Solution:
The ratio of the angles of a triangle = 1 : 2 : 3.
Let the angles of a triangle be x, 2x and 3x.
x + 2x + 3x = 180° (Total angle of a triangle is 180°)
6x = 180°
x = \(\frac{180°}{6}\)
= 30°
x = 30°; 2x = 2 × 30° = 60°; 3x = 3 × 30° = 90°
Measures of the angles of a triangle = 30°, 60° and 90°.
![]()
Question 3.
Consider the given pairs of triangles and say whether each pair is that of congruent triangles. If the triangles are congruent, say ‘how’; if they are not congruent say ‘why’ and also say if a small modification would make them congruent:
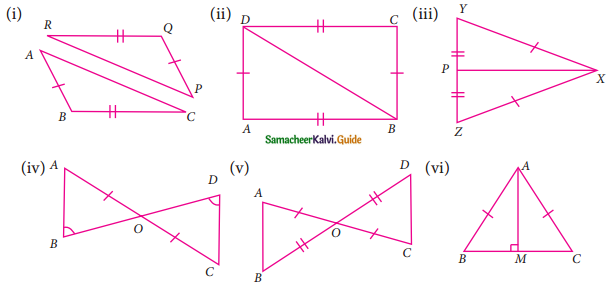
(i) In ΔPQR and ΔABC
PQ = AB (Given)
RQ = BC (Given)
ΔABC is not congruent to ΔPQR.
If PR = AC then ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
(ii) In ΔABD and ΔCDB
AB = CD (Given)
AD = BC (Given)
BD is common
By SSS congruency
ΔABD ≅ ΔCDB
![]()
(iii) In ΔPXY and ΔPXZ
PX is common.
XY = XZ (Given)
PY = PZ (Given)
By SSS congruency
ΔPXY ≅ ΔPXZ
(iv) In the given figure BD bisect AC
In ΔAOB and ΔOCD
OA = OC (Given)
∠AOB = ∠DOC (vertically opposite angles)
∠B = ∠D (Given)
By ASA congruency ΔAOB ≅ ΔOCD
(v) In the given figure AC and BD bisect each other at O.
∴ OA = OC (Given); OB = OD (Given)
∠AOB = ∠COD (vertically opposite angles)
By SAS congruency
ΔAOB ≅ ΔOCD
![]()
(vi) In the given figure
AB = AC (Given)
BM = MC (AM is the median of the ΔABC)
AM is common (By SSS congruency)
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔACM
Question 4.
ΔABC and ΔDEF are two triangles in which AB = DF, ∠ACB = 70°, ∠ABC = 60°; ∠DEF = 70° and ∠EDF = 60°. Prove that the triangles are congruent.
Solution:
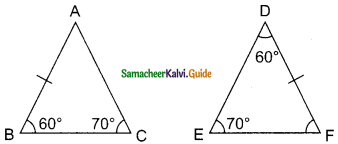
In ΔABC ∠B = 60° and ∠C = 70°
∴ ∠A = 180° – (60° + 70°)
= 180° – 130°
= 50°
In ΔDEF ∠E = 70° and ∠D = 60°
∠F = 180° – (70° + 60°)
= 180° – 130°
= 50°
∠A = ∠F = 50°
∠B = ∠D = 60°
∠C = ∠E = 70°
By AAA congruency
ΔABC ≅ ΔFDE
(or)
∠B = ∠D = 60°
∠C = ∠E = 70°
AB = FE
By ASA congruency
ΔABC ≅ ΔFDE
![]()
Question 5.
Find all the three angles of the ΔABC.
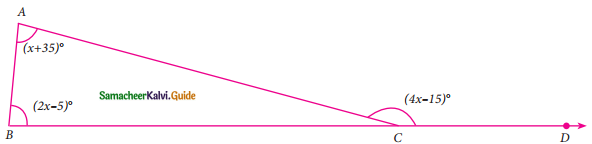
Solution:
∠A + ∠B = ∠ACD (An exterior angle of a triangle is sum of its interior opposite angles)
x + 35 + 2x – 5 = 4x – 15
3x + 30 = 4x – 15
30 + 15 = 4x – 3x
45° = x
∠A = x + 35°
= 45° + 35°
= 80°
∠B = 2x – 5
= 2(45°) – 5°
= 90° – 5°
= 85°
∠ACD = 4x – 15
= 4 (45°) – 15°
= 180° – 15°
= 165°
∠ACB = 180° – ∠ACD
= 180° – 165°
= 15°
∠A = 80°, ∠B = 85° and ∠C = 15°.
![]()