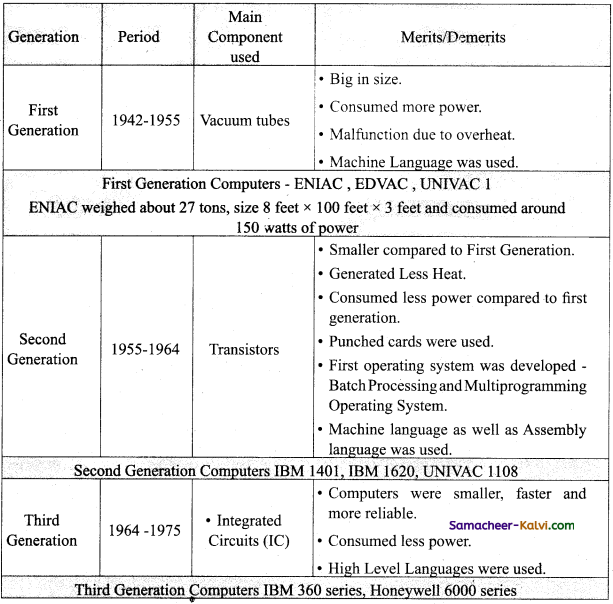
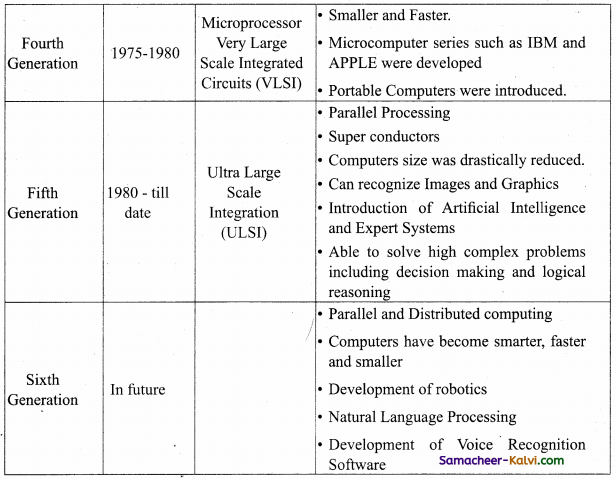
TN State Board 11th Computer Science Important Questions Chapter 5 Working with Typical Operating System (Windows & Linux)
Question 1.
What is an operating system?
Answer:
An Operating System (OS) is a system software that enables the hardware to communicate and operate with other software. It also acts as an interface between the user and the hardware and controls the
overall execution of the computer.
Question 2.
What is Desktop?
Answer:
The opening screen of Windows is called ‘Desktop’. The desktop shows the Start button, Taskbar, Notification Area and date and time.
![]()
Question 3.
What is an Icon?
Answer:
Icon is a graphic symbol representing the window elements like files, folders, shortcuts etc., It plays a vital role in GUI based applications.
Question 4.
What is window?
Answer:
Window is a typical rectangular area in an application or a document. It is an area on the screen that displays information for a specific program.
Question 5.
What is Application Window?
Answer:
It is an area on a computer screen with defined boundaries and within which information is displayed. Such windows can be resized, maximized, minimized, placed side by side, overlap, and so on.
![]()
Question 6.
What is document window?
Answer:
The smaller window, which is inside the Application Window, is called the Document window. This Window is used for typing, editing, drawing, and formatting the text and graphics.
Question 7.
Where the task bar is located? What it contains?
Answer:
A horizontal bar at the bottom of the screen is called the taskbar. This bar contains (from left to right) the Start button, shortcuts to various programs, minimized programs and in the extreme right comer you can see the system tray which consist of volume control, network, date and time etc. Next to the Start button is the quick Launch Toolbar which contains task for frequently used applications.
Question 8.
What is meant by multitasking?
Answer:
Multiple applications can execute simultaneously in Windows, and this is known as “multitasking”.
Question 9.
What is launcher?
Answer:
The vertical bar of icons on the left side of the desktop is called the Launcher. The Launcher provides easy access to applications, mounted devices and the Trash. All current applications on your system will place an icon in the Launcher.
![]()
Question 10.
How will you delete a file in Ubuntu OS?
Answer:
A file / folder created by user can be moved to j trash by using right click or by using menu.
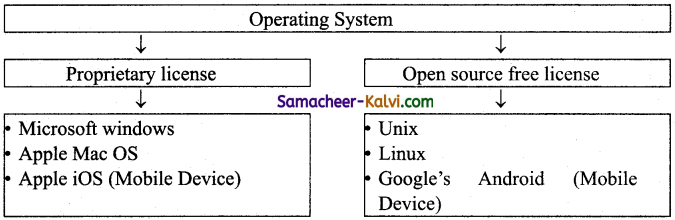
Question 11.
Define Ubuntu.
Answer:
Ubuntu is a Linux-based operating system. It is designed for computers, smartphones and network servers. The system is developed by a UK based company called Canonical Ltd.
Ubuntu was conceived in 2004 by Mark Shuttleworth, a successful South African entrepreneur.
Question 12.
Define Trash.
Answer:
Trash is the equivalent of Recycle bin of windows OS. All the deleted files and folders are moved here.
![]()
Question 13.
List the functions of an operating system.
Answer:
- Memory Management
- Process Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security Management
- Control overall system performance
- Error detecting aids
- Coordination between other software and users.
Question 14.
Write some of the most popular operating systems.
Answer:
- Windows Series – for desktop and laptop computers.
- Android – for smart phones.
- iOS – for Apple phones, i-Pad and i-Pod.
- Linux – Open source Operating System for desktop and server.
Question 15.
Write down the various mouse actions.
Answer:
|
Action |
Reaction |
| Point to an item | Move the mouse pointer over the item. |
| Click | Point to the item on the screen, press and release the left mouse button. |
| Right click | Point to the item on the screen, press and release the right mouse button. Clicking the right mouse button displays a pop up menu with various options. |
| Double click | Point to the item on the screen, quickly press twice the left mouse button. |
| Drag and drop | Point to an item then hold the left mouse button as you move the pointer and when you have reached the desired position, release the mouse button. |
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the icons in windows operating system.
Answer:
Icon:
It is a graphic symbol representing the window elements like files, folders, shortcuts etc. It plays a vital role in GUI based applications.
Standard Icons:
The icons which are available on desktop by default while installing Windows OS are called standard icons. The standard icons available in all Windows OS are My Computer, Documents and Recycle Bin.
Shortcut Icons:
It can be created for any application or file or folder. By double clicking the icon, the related application or file or folder will open. This represents the shortcut to open a particular application.
Disk drive icons:
The disk drive icons graphically represent five disk drive options.
- Hard disk
- CD-ROM/DVD Drive
- Pen drive
- Other removable storage such as mobile, smart phone, tablet etc.,
- Network drives if your system is connected with other system.
Question 17.
Write the difference between the application window and the document window.
Answer:
|
Application Window |
Document Window |
| The larger window is called the Application Window. | The smaller window, which is inside the Application Window is called the Document Window. |
| This window helps the user to communicate with the Application Program. | This window is used for typing, editing, drawing and formatting the text and graphics. |
![]()
Question 18.
Write the ways of creating folders in windows.
Answer:
Method I:
Step 1: Open Computer Icon.
Step 2: Open any drive where you want to create a new folder. (For example select D:)
Step 3: Click on File → New → Folder.
Step 4: A new folder is created with the default name “New folder”.
Step 5: Type in the folder name and press Enter key.
Method II:In order to create a folder in the desktop:
Step 1: In the Desktop, right click → New → Folder.
Step 2: A Folder appears with the default name “New folder” and it will be highlighted.
Step 3: Type the name you want and press Enter Key.
Step 4: The name of the folder will change.
Question 19.
Write the steps to delete a file or folders in windows.
Answer:
Select the file or folder you wish to delete.
(i) Right-click the file or folder, select Delete option from the pop-up menu or Click File → Delete or press Delete key from the keyboard.
(ii) The file will be deleted and moved to the Recycle bin.
![]()
Question 20.
Write short note on Recycle Bin.
Answer:
Recycle bin is a special folder to keep the files or folders deleted by the user, which means user still have an opportunity to recover them. The user cannot access the files or folders available in the Recycle bin without restoring it. To restore file or folder from the Recycle Bin.
- Open Recycle bin.
- Right click on a file or folder to be restored and select Restore option from the pop-up menu.
- To restore multiple files or folders, select Restore all items.
- To delete all files in the Recycle bin, select Empty the Recycle Bin.
Question 21.
Write the steps to create shortcuts on the Desktop.
Answer:
Shortcuts to your most often used folders and files may be created and placed on the Desktop to help automate your work.
- Select the file or folder that you wish to have as a shortcut on the Desktop.
- Right click on the file or folder.
- Select Send to from the shortcut menu, then select Desktop (create shortcut) from the sub-menu.
- A shortcut for the file or folder will now appear on your desktop and you can open it from the desktop in the same way as any other icon.
![]()
Question 22.
Write the significant features of Ubuntu.
Answer:
- The desktop version of Ubuntu supports all normal software like Windows such as Firefox, Chrome, VLC, etc.
- It supports the office suite called LibreOffice.
- Ubuntu has in-built email software called Thunderbird, which gives the user access to email such as Exchange, Gmail, Hotmail, etc.
- There are free applications for users to view and edit photos, to manage and share videos.
- It is easy to find content on Ubuntu with the smart searching facility.
- The best feature is, it is a free operating system and is backed by a huge open source community.
Question 23.
What is Ambiance?
Answer:
The default desktop background, or wallpaper, belonging to the default Ubuntu 16.04 theme is known as Ambiance.
Question 24.
Write the steps to create files in the windows.
Answer:
Wordpad is an in-built word processor application in Windows OS to create and manipulate text documents.
In order to create files in wordpad you need to follow the steps given below.
- Click Start → All Programs → Accessories → Wordpad or Run → type Wordpad, click OK. Wordpad window will be opened.
- Type the contents in the workspace and save the file using File → Save or Ctrl + S.
- Save As dialog box will be opened.
- In the dialog box, select the location where you want to save the file by using look in drop down list box.
- Type the name of the file in the file name textbox.
- Click save button.
![]()
Question 25.
Draw and explain the elements of windows.
Answer:
Title Bar:
The title bar will display the
name of the application and the name of the document opened. It will also contain minimize, maximize and close button.
Menu Bar:
The menu bar is seen under the title bar. Menus in the menu bar can be accessed by pressing Alt key and the letter that appears underlined in the menu title. Additionally, pressing Alt or F10 brings the focus on the first menu of the menu bar.
In Windows 7, in the absence of the menu bar, click Organize and from the drop down menu, click the Layout option and select the desired item from that list.
The Workspace:
The workspace is the area in the document window to enter or type the text of your document.
Scroll bars:
The scroll bars are used to scroll the workspace horizontally or vertically. Comers and borders:The comers and borders of the window helps to drag and resize the windows. The mouse pointer changes to a double headed arrow when positioned over a border or a comer. Drag the border or comer in the direction indicated by the double headed arrow to the desired. The window can be resized by dragging the comers diagonally across the screen.
![]()
Question 26.
Write the steps to log off / shut down the computer.
Answer:
(i) Click start → log off (click the arrow next to Shut down) or Start → Shutdown.
(ii) If any programs are opened, then it will be asked to close them or windows will Force shut down, user will lose any un saved information if you do this.
(iii) Switch User: Switch to another user account on the computer without closing open programs and Windows processes.
(iv) Log Off: Switch to another user account on the computer after closing all open programs and Windows processes.
(v) Lock: Lock the computer while you’re away from it.
(vi) Restart: Reboot the computer. (This option is often required as part of installing new software or Windows update.)
(vii) Sleep: Puts the computer into a low- power mode that retains all miming programs and open Windows in computer memory for a super-quick restart.
(viii) Hibernate (found only on laptop computers): Puts the computer into a low-power mode after saving all miming programs and open windows on the machine’s hard drive for a quick restart.
Question 27.
Explain the different method of renaming files and folders.
Answer:
There are number of ways to rename files or folders. You can rename using the File menu, left mouse button or right mouse button.
Method I: Using the FILE Menu
- Select the File or Folder to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
Method II:Using the Right Mouse Button
- Select the file or folder to rename.
- Click the right mouse button over the file or folder.
- Select Rename from the pop-up menu.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
- The folder “New Folder” is renamed as C++.
Method III: Using the Left Mouse Button
- Select the file or folder to rename.
- Press F2 or click over the file or folder. A surrounding rectangle will appear around the name.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
![]()
Question 28.
What are the different method of copying files and folders to removable disk.
Answer:
There are several methods of transferring files to or from a removable disk.
(i) Copy and Paste
(ii) Send To
Method I: Copy and Paste
(a) Plug the USB flash drive directly into an available USB port.
(b) If the USB flash drive or external drive folder does NOT open automatically, the following steps are followed.
(c) Click Start → Computer.
(d) Double-click on the Removable Disk associated with the USB flash drive.
(e) Navigate to the folders in computer containing files to be transfered.
Right-click on the file to copy, then select Copy.
Return to the Removable Disk window, right- click within the window, then select Paste.
Method II: Send To
(a) Plug the USB flash drive directly into an available USB port.
(b) Navigate to the folders in computer containing files to be transfered.
(c) Right-click on the file transfer to removable disk.
(d) Click Send To and select the Removable Disk associated with the USB flash drive.
Question 29.
Explain the indicators in the menubar of Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
(i) Network indicator:
This manages network connections, allowing user to connect to a wired or wireless network.
(ii) Text entry settings:
This shows the current keyboard layout (such as En, Fr,Ku, and so on) . If more than one keyboard layout is shown, it allows to select a keyboard layout out of those choices. The keyboard indicator menu contains the following menu items: Character Map, Keyboard Layout Chart, and Text Entry Settings.
(iii) Messaging indicator:
This incorporates your social applications. From here, user can access instant messenger and email clients.
(iv) Sound indicator:
This provides an easy way to adjust the volume as well as access the music player.
(v) Clock:
This displays the current time and provides a link to calendar and time and date settings.
(vi) Session indicator:
This is a link to the system settings, Ubuntu Help and session options (like locking your computer, user/guest session, logging out of a session, restarting the computer or shutting down completely).
(vii) Title bar:
The title bar shows the name of the currently selected directory. It also contains the Close, Minimize, and Maximize buttons.
(viii) Toolbar:
The toolbar displays user directory browsing history (using two arrow buttons), location in the file system, a search button and options for current directory view.
![]()
Question 30.
How will you move files and folders?
Answer:
Method I: CUT and PASTE
To move a file or folder, first select the file or
folder and then choose one of the following:
(i) Click on the Edit → Cut or Ctrl + X or right click → cut from the pop-up menu.
(ii) To move the filets) or folder(s) in the new location, navigate to the new location and paste it using Click Edit → Paste from edit menu or Ctrl + V using keyboard.
(in) Or Right click → Paste from the pop-up menu. The file will be pasted in the new location.
Method II: Drag and Drop
In the disk drive window, there are two panes called left and right panes. In the left pane, the files or folders are displayed like a tree structure. In the right pane, the files inside the specific folders in the left pane are displayed with various options.
(i) In the right pane of the Disk drive window, select the file or folder to be moved.
(ii) Click and drag the selected file or folder from the right pane, to the folder list on the left pane.
(iii) Release the mouse button when the target folder is highlighted (active).
(iv) File or folder will now appear in the new area.
Question 31.
How will you copy files and folders in windows?
Answer:
There are variety of ways to copy files and folders:
Method I: COPY and PASTE
To copy a file or folder, first select the file or folder and then choose one of the following:
(i) Click Edit → Copy or Ctrl + C or right click → Copy from the pop-up menu.
(ii) To paste the file(s) or folder(s) in the new location, navigate to the target location then do one of the following:
(iii) Click Edit → Paste or Ctrl + V.
(iv) Or Right click → Paste from the pop-up menu.
Method II: Drag and Drop
(i) In the RIGHT pane, select the file or folder to be copied.
(ii) Click and drag the selected file and/or folder to the folder list on the left, and drop it where to copy the file and/or folder.
(iii) File(s) and folder(s) will now appear in the new area.
![]()
Question 32.
Start the application Wordpad using Start menu and Run option.
Answer:
Click, Run option on the Start menu, the Run dialog box appears. Type the “Word Pad” in the open window box, then press OK button. Now, wordpad window is opened.
Close the Wordpad application using File
menu.
Click, File → Exit (or) File → Close.
Question 33.
Create a Folder in My Documents with your name using any one of the methods discussed.
Answer:
(i) Open My Computer or Computer icon.
(ii) Open any drive where you want to create a new folder, (eg: select D drive)
(iii) Click on File → New → Folder.
(iv) Now, a new folder is created with the default name “New Folder”.
(v) Type in the New Folder for your name and press Enter key. Now, Folder name created for you name.
Question 34.
Open the Wordpad application and save it under a folder created with your name in My Document.
Answer:
- Click Start → All programs → Accessories → Wordpad (or) Run → type Wordpad, click OK. Wordpad window will be opened.
- Type the contents in the workspace and save the file using File → save or Ctrl + S.
- Save As dialog box will be opened.
- In this dialog box, select the drive name and folder name, where you want to save the file.
- Now, type the name of the file in the file name text box.
- Click save button.
![]()
Question 35.
Find the file created in Workshop-3 using the above procedure.
Answer:
- Click computer icon from desktop or from start menu.
- The computer disk drive screen will be appear and at the top right comer of that screen, there is a search box.
- Type the name of File / Folder you want I to search. Even if you give the part of the File or Folder name. It will displays the list of files or folders starting with the specified name.
- Just click and open that file or the folder.
Question 36.
Rename the file created by you using the File menu, left mouse button or right mouse button.
Answer:
Method 1:
- Select the file or folder to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name as you desired.
- Press Enter key.
Method 2:
- Select the file or folder to rename.
- Click the right mouse button over the file or folder.
- Select Rename from the pop-up menu.
- Type in the new name.
- Press Enter key.
Question 37.
Find the file created in Workshop-3 using the above procedure.
Answer:
- Click computer icon from desktop or from start menu.
- The computer disk drive screen will be appear and at the top right comer of that screen, there is a search box.
- Type the name of File / Folder you want I to search. Even if you give the part of the File or Folder name. It will displays the list of files or folders starting with the specified name.
- Just click and open that file or the folder.
![]()
Question 38.
Rename the file created by you using the File menu, left mouse button or right mouse button.
Answer:
Method 1:
- Select the file or folder to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name as you desired.
- Press Enter key.
Method 2:
- Select the file or folder to rename.
- Click the right mouse button over the file or folder.
- Select Rename from the pop-up menu.
- Type in the new name.
- Press Enter key.
Question 39.
Move the file created by you in My Documents to Drive D:.
Answer:
There are variety of ways to copy files and folders.
Drag and drop method:
- Open computer icon.
- In the disk drive window, there are two panes called left and right panes. In the left pane, the files or folders are displayed like a tree structure. In the right pane, the files inside the specific folders in the left pane are displayed with various options.
- In the right pane of the disk drive window, select My Documents with created your file name.
- Click filename and drag to drive D: in the left pane.
- Release the mouse button, now file name is moved from My Documents to Drive D.
- Drive D: to a removable Disk.
* Copy the file created by you from drive D: to a removable disk.
- Plug the USB flash drive directly into an available USB port, (or)
- Click start → Computer.
- Click Drive D: Select file name you want to move.
- Click the right mouse button, send to option and select the Removable Disk with the USB flash drive.
![]()
Question 40.
Delete the file created by you after duplicating the same under My Documents.
Answer:
- Select My Documents, then click to delete.
- Right-click the file created. Select Delete Option from the pop-up menu (or) Click File → Delete (or) Press Delete key from the keyboard.
- The file will be deleted from the My Documents and moved to the Recycle bin.
Question 41.
Differentiate cut and copy options.
Answer:
|
Cut |
Copy |
| When an object is cut from a document it is completely removed and placet into a clipboard. | When an object is copied a duplicate of it is placed into a clipboard while the original remains in place. |
| Ctrl + X and Ctr + V is the shortcul command for cul and paste. | Ctrl + C and Ctrl + V is the shortcul command for copy and paste. |
Question 42.
What is the use of a file extension?
Answer:
The extension of the file name simply says the format in which the data in the file is stored.
Eg: If a file is named letter.doc, the .doc is the file extension, and it tells windows that
![]()
Question 43.
Differentiate Files and Folders.
Answer:
|
Files |
Folders |
| A file is a collection of data on a single unit. It can be anything from a word file to a music, video or photo file. | Folders are places where files are stored. Folders can contain folders inside them. |
| Files have a size ranging from a few bytes to several giga bytes. | Folders take up no space on hard drive. |
Question 44.
Differentiate save and save as option.
Answer:
|
Save |
Save as |
| The ‘save’ simply saves our work by updating the Iasi saved version o1 the file to match the current version we see on our screen. | The ‘save as’ brings upto save our work as a file with a different name. |
Question 45.
What is Open Source?
Answer:
- Open Source refers to a program or software in which the source code is available in the web to the general public free of cost.
- Open Source code is typically created as a collaborative effort in which programmers continuously improve upon the source code in the web and share the changes within the community.
![]()
Question 46.
What are the advantages of open source?
Answer:
The advantages of open sources are better security, better quality, more control, no vendor dependence, easier licence management.
Question 47.
Mention the different server distributions in Linux OS.
Answer:
- Ubuntu Linux
- Linux Mint
- Arch Linux
- Deepin
- Fedora
- Debian
- CentOS
Question 48.
How will you log off from Ubuntu OS?
Answer:
When you have finished working on your computer, you can choose to Log Out, Suspend or Shut down through the Session Indicator on the far right side of the top panel.
![]()
Question 49.
Analyse:
Why the drives are segregated?
Answer:
A drive is a computer component used to store data. Partitioning a hard drive essentially tells the computer to treat portions of that drive as separate entities. It can be for a variation for reasons, keeping things organized, creating a backup and recovery partition.
(i) Multiple file systems:
If we require
different file systems on our computer for specific action then we make multiple partition and assign one type of file system to one of the partitions and another to one of the other partitions.
(ii) Partition size:
If we have more storage space on a hard drive, we would need to create other partitions, to utilize this unused space.
(iii) Multiple operating system:
If we went to use two operating systems on the same computer then we could make two partitions, one for each operating system.
(iv) Wasted disk space:
By having multiple partitions of smaller size, we can reduce the amount of waste that file systems may create.
(v) Separate system files from users files:
By creating a partition we can store system files in one partition and users data to another partition to avoid causing problem.
![]()
Question 50.
If you are working on multiple files at a time, sometimes the system may hang. What is the reason behind it. How can you reduce it?
Answer:
When each program or files are opened, computer takes some of the computer resources to keep it running. If too many programs are opened to one time, computer If we have too many programs open at one time, our computer may be low on resources and it slows down or it may hang. Try only one program running at a time to make sure our hang-ups is not being caused by multiple programs running at the same time.
To determine computer in this situation is by pressing the Num Lock button on the keyboard and watching the Num Lock to see if it turns off and on. To get the light to turn off and on, press Ctrl + Alt + Del and End Task for the hang-up files.
Question 51.
Are drives such as hard drive and floppy drives represented with drive letters? If so why, if not why?
Answer:
The drive letters plays an important role in telling windows where to look. All the computers with a hard drive will always have that default hard drive assigned to a C: and for floppy drivers has a drive letter of A:.
Question 52.
Write the specific use of Cortana.
Answer:
Cortana – the personal assistant feature from windows phone. This has become a major part of windows 10 doing double duty as a web search and a start merfu / windows search. Plus the ability to search by voice.
Uses:
(i) It is used to set reminder in our PC.
(ii) It can alert you whenever you miss a call on your phone.
(iii) It can also help find the latest news.
![]()
Question 53.
List out the major differences between Windows and Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
|
Windows OS |
Ubuntu OS |
| It is a GUI based operating system. | It is a Linux based operating system. |
| It is a closed source (proprietary software). | It is an open source operating system. |
| It is strictly Microsoft company based. | It is based around the company canonical and is also community based. |
Question 54.
Are there any difficulties you face while using Ubuntu? If so, mention it with reasons.
Answer:
Yes, Many difficulties are there while using Ubuntu operating system.
- A lack of familiarity and shared experiences fragments users they do not have a shared any points.
- Many Linux newbies start with Ubuntu. This should not take away from Ubuntu, it is a testament to its smart design and ease of use.
- Ubuntu has come a long way regarding hardware compatibility and some accessory hardware will not have the needed software to interface.
![]()
Question 55.
Differentiate Thunderbird and Firefox in Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
|
Thunderbird |
Firefox |
| Ubuntu has in – built email software called Thunderbird. | Firefox is a internet browser, you can directly browse the internet. |
| It gives the user Access to email such as Gmail, Hotmail etc., | It is the fastest browser and numerous features that protect you, from viruses and other common exploits. |
| There are free applications for users to view and edit photos, to manage and share videos. | Fire fox has some advanced security measures that guard against the spyware and viruses. |
Question 56.
Differentiate Save, Save As and Save a Copy in Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
Save:
This will save the document without asking for a new name or location. It will over-write the original.
SaveAs:
This will prompt user to save the document using a dialog box. User will have the ability to change the file name or location.
Save a Copy:
This will prompt user to save a copy using the same dialog box as save as. User will have the ability to change the file name or location. If the name or location of the document is changed user will be working on the original document not the copy. That means if user make additional changes and then hit save the original will be overwritten with new changes, but the copy user saved earlier will be left at the state of the ‘save a copy.
![]()
Question 57.
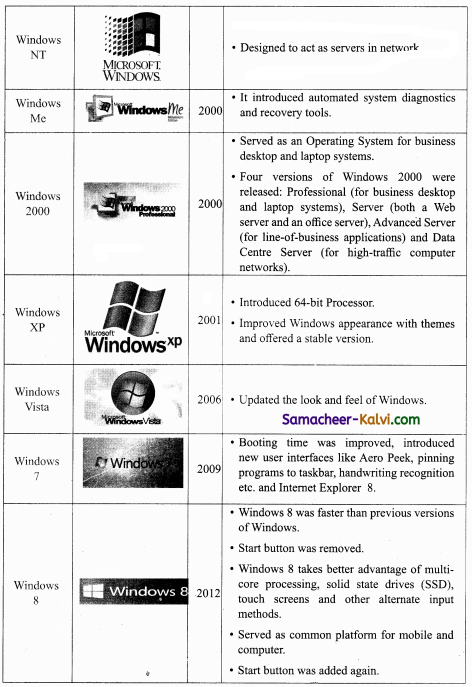
Explain the versions of Windows Operating System.
Answer:
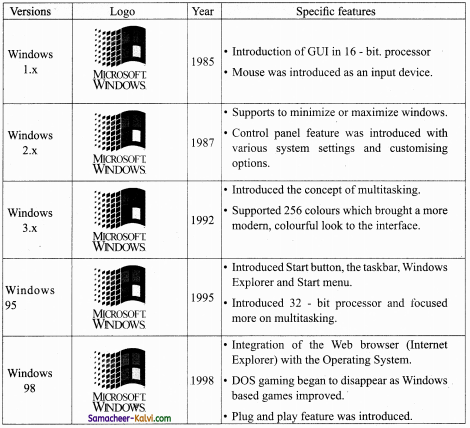


![]()
Question 58.
Draw and compare the icon equivalence in Windows and Ubuntu.
Answer:
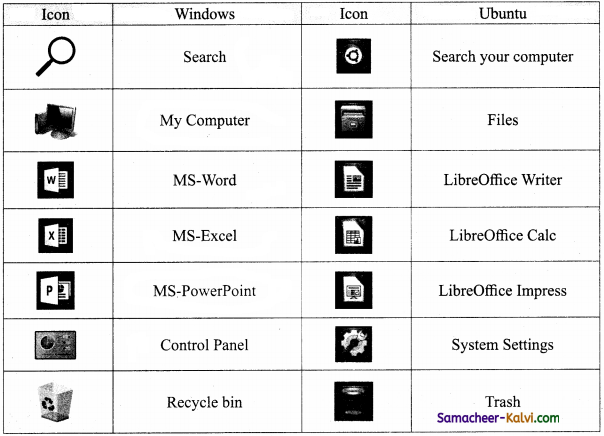
Question 59.
Complete the following matrix:
Answer:
|
Navigational method |
Located on |
Ideally suited for |
| Start Button | Task bar | Quick access to common applications and settings. |
| My Computer | Desktop | Exploring your disk drives and using system tools. |
| Windows Explorer | Task bar | Seeing hierarchy of all computer contents and resources in one window. |
| Quick Launch | Task bar | Enables a user the ability to launch their programs. |
![]()
Question 60.
Observe the figure and mark all the window elements. Identify the version of the Windows OS.
Answer:
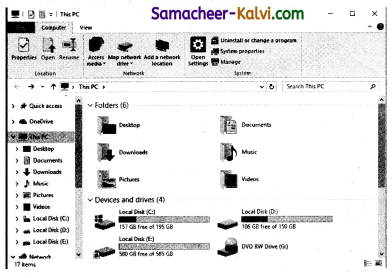
All the Window elements are same. The version of OS is Windows 10.
Question 61.
Write the procedure to create, rename, delete and save a file in Ubuntu OS. Compare it with Windows OS.
Answer:
The procedure to create, rename, delete and save a file in Ubuntu OS is similar to windows OS. User can create, rename, delete and save the files and folders with the same procedure by clicking files icon. The some related figure on the desktop represents creating a file or folder by right clicking in the Desktop.
A New Folder can also be created by using menus in the files icon.
A document created by user can be moved to ‘trash’ by using right click or by using menus as in windows.
All the other options like rename, cut, copy can be performed by using right click or by using menus as windows.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Microsoft windows is a based operating system.
(a) GUI
(b) command driven
(c) window
(d) menu driven
Answer:
(a) GUI
Question 2.
Multiple applications which can execute simultaneously in windows is known as :
(a) multi programming
(b) multi tasking
(c) time sharing
(d) based on priority
Answer:
(b) multi tasking
Question 3.
________ is used to interact windows by clicking its elements.
(a) Keyboard
(b) Light pen
(c) Mouse
(d) Scanner
Answer:
(c) Mouse
![]()
Question 4.
_______ is used to enter alphabets and characters.
(a) Light pen
(b) Mouse
(c) Notes taker
(d) Keyboard
Answer:
(d) Keyboard
Question 5.
Multiple desktop is available in :
(a) windows XP
(b) windows vista
(c) windows 8
(d) windows 10
Answer:
(d) windows 10
Question 6.
The opening screen of windows is called :
(a) desktop
(b) icons
(c) windows
(d) documents
Answer:
(a) desktop
![]()
Question 7.
The __________ is an area on the screen that displays information for a specific program.
(a) desktop
(b) icons
(c) window
(d) document
Answer:
(c) window
Question 8.
The larger window is called the:
(a) document window
(b) application window
(c) workspace
(d) scroll bar
Answer:
(b) application window
Question 9.
The first level in a multilevel or hierarchical directory system is:
(a) root directory
(b) additional directory
(c) sub directories
(d) directories
Answer:
(a) root directory
![]()
Question 10.
The shortcut keyboard command to cut is:
(a) Ctrl + X
(b) Ctrl + C
(c) Ctrl + V
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + X
Question 11.
The shortcut keyboard command to copy is:
(a) Ctrl + X
(b) Ctrl + C
(c) Ctrl + V
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(b) Ctrl + C
Question 12.
The shortcut keyboard command to paste is:
(a) Ctrl + X
(b) Ctrl + C
(c) Ctrl + V
(d) Ctrl + A
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + V
![]()
Question 13.
The paste option is on ______ menu.
(a) edit
(b) file
(c) view
(d) tools
Answer:
(a) edit
Question 14.
______ switches to another user account on the computer without closing the open programs and windows processes.
(a) Log off
(b) Restarting the computer
(c) Shut down
(d) Switch user
Answer:
(d) Switch user
Question 15.
__________ shows the name of the currently selected directory.
(a) Tool bar
(b) Menu bar
(c) Task bar
(d) Title bar
Answer:
(d) Title bar
![]()
Question 16.
__________ displays your directory browsing history, location in the file system, a search button and options for the current directory view.
(a) Tool bar
(b) Menu bar
(c) Task bar
(d) Title bar
Answer:
(a) Tool bar
Question 17.
Windows 7 was released in :
(a) October 2012
(b) September 2014
(c) October 2009
(d) October 2015
Answer:
(c) October 2009
Question 18.
A horizontal bar at the very bottom of the screen is called the:
(a) tool bar
(b) menu bar
(c) task bar
(d) title bar
Answer:
(c) task bar
![]()
Question 19.
We can select multiple files by holding down the _____ key.
(a) Alt
(b) Shift
(c) Ctrl
(d) Home
Answer:
(c) Ctrl
Question 20.
________ is located at the top of the screen.
(a) Tool bar
(b) Menu bar
(c) Task bar
(d) Title bar
Answer:
(b) Menu bar
Question 21.
The graphic symbol representing the window elements is:
(a) Icon
(b) Desk
(c) Start
(d) Task
Answer:
(a) Icon
![]()
Question 22.
Which shortcut key is used to move the desktop anytime?
(a) Winkey + M
(b) Winkey + V
(c) Winkey + D
(d) Winkey + C
Answer:
(c) Winkey + D
Question 23.
Which is not available in the windows standard icon?
(a) My computer
(b) Documents
(c) Recycle Bin
(d) Paint icon
Answer:
(d) Paint icon
Question 24.
Shortcut icons can be created for any:
(a) application
(b) file
(c) folder
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
![]()
Question 25.
How many disk drive options are graphically represented?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
Question 26.
Which is known as typical rectangular area in an application or a document?
(a) Window
(b) Icon
(c) Disk
(d) Drive
Answer:
(a) Window
Question 27.
Which will display the name of the application and name of the document in the window?
(a) Title bar
(b) Menu bar
(c) Task bar
(d) Scroll bar
Answer:
(a) Title bar
![]()
Question 28.
Which key is pressed in the menus that appears underlined in the menu title?
(a) Ctrl key
(b) Alt key
(c) Shift key
(d) Home key
Answer:
(b) Alt key
Question 29.
Which is the area in document window to type the text?
(a) Document window
(b) Application window
(c) Work space
(d) Desktop
Answer:
(c) Work space
Question 30.
The smaller window, which is inside the application window is called the:
(a) document window
(b) application window
(c) work space
(d) desktop
Answer:
(a) document window
![]()
Question 31.
The title bar will display the name of the:
(a) file
(b) document
(c) directory
(d) program
Answer:
(b) document
Question 32.
Which bars are used to scroll the workspace horizontally or vertically?
(a) Title bar
(b) Task bar
(c) Scroll bar
(d) Menu bar
Answer:
(c) Scroll bar
Question 33.
Which changes to a double headed arrow when positioned over a border or a comer?
(a) Mouse pointer
(b) Enter key
(c) Arrow keys
(d) Mouse click
Answer:
(a) Mouse pointer
![]()
Question 34.
Write the order from left to right in the taskbar contains:
(1) Network icon
(2) Volume adjustment
(3) Default language
(4) Time and Date
(a) 1, 3, 4 and 2
(b) 3, 1, 2 and 4
(c) 1, 4, 3 and 2
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer:
(b) 3, 1, 2 and 4
Question 35.
Which icon is used by windows 8 and 10 instead of My computer icon?
(a) Computer icon
(b) PC icon
(c) This PC icon
(d) My system icon
Answer:
(c) This PC icon
Question 36.
To quit an application of document click on:
(a) File → Exit
(b) File → Close
(c) ☒ Close button
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 37.
Which is an in-built word processor application in windows OS?
(a) MS word
(b) Wordpad
(c) Star writer
(d) Libre office writer
Answer:
(b) Wordpad
Question 38.
Which box on the start menu can be used to quickly search a particular folder or file in the computer?
(a) Search
(b) Find
(c) Seek
(d) Look in
Answer:
(a) Search
Question 39.
Which is the most common way of opening a file or a folder?
(a) Open
(b) Double-click
(c) Click
(d) Right click
Answer:
(b) Double-click
![]()
Question 40.
Which function key is used to change the file name or folder for selected?
(a) F1
(b) F2
(c) F3
(d) F4
Answer:
(b) F2
Question 41.
Which combination of keys are used to select multiple files or folders?
(a) Alt + Click
(b) Alt + Enter
(c) Ctrl + Click
(d) Ctrl + Enter
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + Click
Question 42.
Which keys are used to delete a file or folder permanently?
(a) Shift + Delete
(b) Shift + Enter
(c) Ctrl + Delete
(d) Ctrl + Enter
Answer:
(a) Shift + Delete
![]()
Question 43.
Recycle bin is a:
(a) folder
(b) box
(c) drive
(d) program
Answer:
(a) folder
Question 44.
Most often used folders and files may be created on the desktop in:
(a) Copy
(b) Send
(c) Shortcut
(d) Move
Answer:
(c) Shortcut
Question 45.
Which button is used to switch to another user account on the computer without closing existing account?
(a) Switch user
(b) Log off
(c) Lock
(d) Sleep
Answer:
(a) Switch user
![]()
Question 46.
Switch to another user account after closing all your open programs, if you do this:
(a) Switch user
(b) Log off
(c) Lock
(d) Sleep
Answer:
(b) Log off
Question 47.
Puts the computer into a low-power mode after saving all running programs is:
(a) Hibernate
(b) Sleep
(c) Log off
(d) Lock
Answer:
(a) Hibernate
Question 48.
Which is one of the popular Open Source versions of the UNIX operating system?
(a) LINUX
(b) MS-DOS
(c) Windows
(d) XENIX
Answer:
(a) LINUX
![]()
Question 49.
Which OS is designed for computers, smartphones and network servers?
(a) MS-DOS
(b) Uhuntu
(c) Windows
(d) UNIX
Answer:
(b) Uhuntu
Question 50.
When was Ubuntu OS conceived?
(a) 2001
(b) 2002
(c) 2003
(d) 2004
Answer:
(d) 2004
Question 51.
Who was the successful entrepreneur of Ubuntu?
(a) Mark Shuttleworth
(b) Mark Wagh
(c) John Mauchly
(d) Engelbart
Answer:
(a) Mark Shuttleworth
![]()
Question 52.
Which is the in-built email software in Ubuntu?
(a) Thunderbird
(b) Yahoo
(c) Gmail
(d) Hotmail
Answer:
(a) Thunderbir
Question 53.
Which is the default desktop background or wallpaper in Ubuntu?
(a) Natural
(b) Ambiance
(c) Elephant
(d) Peacock
Answer:
(b) Ambiance
Question 54.
Which is known as equivalent to taskbar in Ubuntu?
(a) Launcher
(b) Device
(c) Trash
(d) VBox
Answer:
(a) Launcher
![]()
Question 55.
All current applications on your system will place an icon in the:
(a) Device
(b) Launcher
(c) Trash
(d) VBox
Answer:
(b) Launcher
Question 56.
Which icon is equivalent of recycle bin of windows OS?
(a) Trash
(b) Device
(c) Launcher
(d) Vbox
Answer:
(a) Trash
Question 57.
Match the following:
| (i) Windows series | (a) For Apple phones, I – pad and I – pod. |
| (ii) Android | (b) For Desktop and Laptop computers |
| (iii) iOS | (c) For smart phones |
| (iv) Linux | (d) Open source Operating System for desktop and server. |
(a) (i) – (b); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (d)
(b) (i) – (a); (ii) – (b); (iii) – (c); (iv) – (d)
(c) (i) – (b); (ii) – (a); (iii) – (c); (iv) – (d)
(d) (i) – (d); (ii) – (a); (iii) – (b); (iv) – (c)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (b); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (d)
![]()
Question 58.
Match the following:
| (i) Windows 3.x | (a) 2001 |
| (ii) Windows Me | (b) 2006 |
| (iii) Windows XP | (c) 2000 |
| (iv) Windows Vista | (d) 1992 |
(a) (i) – (d); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (b)
(b) (i) – (b); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (d)
(c) (i) – (c); (ii) – (d); (iii) – (b); (iv) – (a)
(d) (i) – (b); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (d); (iv) – (a)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (d); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (b)
Question 59.
Choose the incorrect pair:
|
Column – I |
Column – II |
| (a) Windows NT | Designed to act as servers in network. |
| (b) Windows 8 | Served as common platform for mobile and computer. |
| (c) Windows 7 | Multiple desktop |
| (d) Windows XP | Introduced 64 – bit processor. |
Answer:
(c)
Question 60.
Choose the correct pair:
| Column – I |
Column – II |
| (a) Menu bar | Displays the name of the application. |
| (b) Work space | Telps to drag and resize the windows. |
| (c) Computer icon | We can start any application. |
| (d) Task bar | Contains shortcuts to /various programs. |
Answer:
(d)
![]()
Question 61.
Choose the odd man out:
(a) Ctrl + X
(b) Ctrl + C
(c) Ctrl + S
(d) Ctrl + V
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + S
Question 62.
Assertion (A):
Recycle bin is a special folder to keep the files or folders deleted by the user.
Reason (R):
We can still have an opportunity to recover them.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
Question 63.
Match the following:
| (i) Messaging indicator | (a) To adjust the volume |
| (ii) Sound indicator | (b) Access instant messenger and email clients. |
| (iii) Session indicator | (c) Manages the network connections. |
| (iv) Network indicator | (d) Link to the system settings. |
(a) (i) – (d); (ii) – (b); (iii) – (c); (iv) – (a)
(b) (i) – (b); (ii) – (a); (iii) – (d); (iv) – (c)
(c) (i) – (a); (ii) – (b); (iii) – (c); (iv) – (d)
(d (i) – (b); (ii) – (c); (iii) – (a); (iv) – (d)
Answer:
(b) (i) – (b); (ii) – (a); (iii) – (d); (iv) – (c)
![]()
Question 64.
Identify the correct pair:
| Column – I |
Column – II |
| (a) Libre office writer | Similar to MS Excel |
| (b) Libre office calc | To prepare any presentation. |
| (c) Trash | Equivalent to Recycle bin. |
| (d) Tool bar | Contains Close, Minimize and Maximize buttons. |
Answer:
(c)
Question 65.
Identify the incorrect pair:
|
Column – I |
Column – II |
| (a) Launcher | Provides easy access to applications. |
| (b) Files | Equivalent to My computer icon. |
| (c) Software Icon | To add any additional applications. |
| (d) Menu bar | Displays the current time. |
Answer:
(d)
Question 66.
Choose the odd man out.
(a) Libre office writer
(b) Libre office calc
(c) Libre office Impress
(d) MS power point
Answer:
(d) MS power point
![]()
Question 67.
Assertion (A):
The Menu bar is located at the top of the screen.
Reason (R):
Network indicator manages network connections.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
Question 68.
From the options given below, choose the operations managed by the operating system.
(a) memory
(b) processes
(c) disks and I/O devices
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 69.
Which is the default folder for many Windows Applications to save your file?
(a) My Document
(b) My Pictures
(c) Documents and Settings
(d) My Computer
Answer:
(a) My Document
![]()
Question 70.
Under which of the following OS, the option Shift + Delete – permanently deletes a file or folder?
(a) Windows 7
(b) Windows 8
(c) Windows 10
(d) None of the OS
Answer:
(a) Windows 7
Question 71.
What is the meaning of “Hibernate” in Windows XP/Windows 7?
(a) Restart the Computer in safe mode
(b) Restart the Computer in hibernate mode
(c) Shutdown the Computer terminating all the running applications
(d) Shutdown the Computer Without closing the running applications
Answer:
(d) Shutdown the Computer Without closing the running applications
Question 72.
Which of the following OS is not based on Linux?
(a) Ubuntu
(b) Redhat
(c) CentOs
(d) BSD
Answer:
(d) BSD
![]()
Question 73.
Which of the following in Ubuntu OS is used to view the options for the devices installed?
(a) Settings
(b) Files
(c) Dash
(d) VBox_GAs_5.2.2
Answer:
(d) VBox_GAs_5.2.2
Question 74.
Identify the default email client in Ubuntu:
(a) Thunderbird
(b) Firefox
(c) Internet Explorer
(d) Chrome
Answer:
(a) Thunderbird
Question 75.
Which is the default application for spreadsheets in Ubuntu? This is available in the software launcher.
(a) LibreOffice Writer
(b) LibreOffice Calc
(c) LibreOffice Impress
(d) LibreOffice Spreadsheet
Answer:
(b) LibreOffice Calc
![]()
Question 76.
Which is the default browser for Ubuntu?
(a) Firefox
(b) Internet Explorer
(c) Chrome
(d) Thunderbird
Answer:
(a) Firefox
Question 77.
Where will you select the option to log out, suspend, restart, or shut down from the desktop of Ubuntu OS?
(a) Session Indicator
(b) Launcher
(c) Files
(d) Search
Answer:
(a) Session Indicator