TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities
Question 1.
Define commerce.
Answer:
According to Evelyn Thomas, “Commercial operations deal with the buying and selling of goods, the exchange of commodities and the contribution of finished products’’.
Question 2.
What do mean by industry?
Answer:
Industry refers to economic activities. The term industry is used for activities in which mechanical appliances and technical skills are involved. These include activities relating to producing or processing of goods as well as breeding and rising of animals.
![]()
Question 3.
What is trade?
Answer:
Trade is an essential part of commerce. The term ‘trade’ is used to denote buying and selling. It helps in making the goods produced available to ultimate consumers or users.
Question 4.
Write a short note on transportation.
Answer:
Selling all the goods produced at or near the production place is not possible. Hence, goods are to be sent to different places where they are demanded. The medium which , moves men and materials from one place to another is called transport.
Question 5.
Distinguish between Extractive industries and genetic industries.
Answer:
|
Extractive industries |
Genetic Industries |
| These industries extract or draw out products from natural sources. | These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. |
| Products of these industries are usually transformed into many other useful goods by manufacturing industries. Important extractive industries include farming, mining, oil drilling, hunting and fishing operations. | The seeds, nursery companies poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc are classic examples of genetic industries. |
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by tertiary industries?
Answer:
They do not produce goods. These industries produce utility services and sell them at a profit. They help trade, industry and commerce. This term also includes auxiliaries to trade like banking, insurance, warehouse, advertisement etc.
Question 7.
Write any three characteristics of commerce.
Answer:
- Economic activities: Commerce deals with all economic activities undertaken for profit.
- Exchange of goods and services: Commerce involves exchange of goods and services to earn profit.
- Profit motive: Any activity which have a aim of profit will be a part of commerce. Profit is an incentive for undertaking all commercial activities.
Question 8.
Narrate commerce with an example.
Answer:
Commerce refers to all those activities which are necessary for bringing goods from the place of production to the place of consumption such as transport, warehousing, packaging, insurance, banking arid sales promotion which are incidental or auxiliaries to trade.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the various kinds of industries on the basis of size.
Answer:
(i) Micro unit:
A unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is upto ₹ 25 lakhs in case of manufacturing and upto ₹ 10 lakhs in case of service enterprises.
(ii) Small unit:
A manufacturing unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is more than ₹ 25 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 5 Crore. In case of service enterprises these limits are ₹ 10 lakhs and 2 Crore respectively.
(iii) Medium unit:
A manufacturing unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is more than ₹ 5 Crore but does not exceed ₹ 10 Crore. In case of service enterprises, these limits are ₹ 2 Crore and ₹ 5 Crore respectively.
(iv) Large unit:
A manufacturing unit wherein investment in plant and machinery exceeds ₹ 10 Crores. In case of service unit investment in equipment exceeds ₹ 5 Crores.
Question 10.
Compare industry, commerce and trade.
Answer:
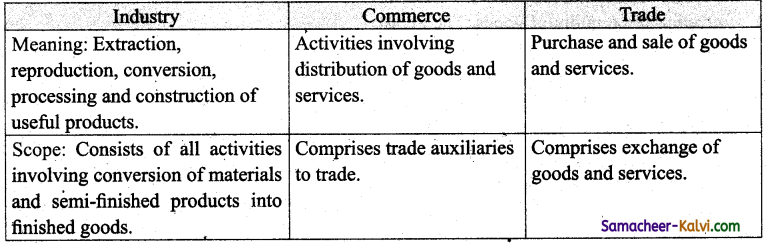
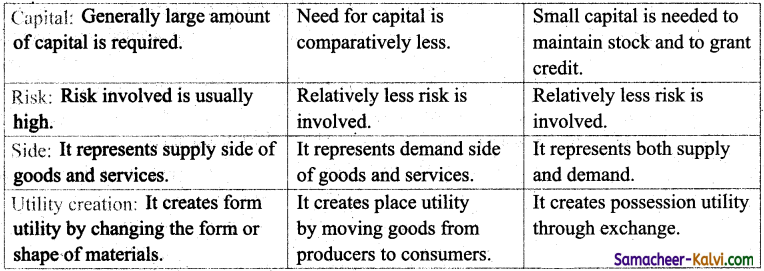
![]()
Question 11.
What are the characteristics of commerce?
Answer:
(i) Economic activities:
Commerce deals with all economic activities undertaken for profit.
(ii) Exchange of goods and services:
Commerce involves exchange of goods and services to earn profit.
(iii) Profit motive:
Any activity which have a aim of profit will be a part of commerce. Profit is an incentive for undertaking all commercial activities.
(iv) Regularity of transaction:
The transaction should be regular. No isolated transaction will be a part of commerce.
(v) Creation of utilities:
Commerce creates form, place and time utility in goods. By conversion of raw material into finished products the form utility is created. For e.g., when a carpenter makes furniture out of wood the goods may not be consumed at the place of production. This may be needed in different places. The goods are taken to those places where they are needed. Transportation facilities help in creating place utility of goods.
The goods are also needed in different periods of time. It may not be possible to produce the goods whenever they are demanded. The producers go on producing goods as per their capacity. The goods are stored up to the time till they are demanded. The production is done at one time and the consumer gets them as per their need. The storage facilities create time utility of goods.
![]()
Question 12.
Write short notes on:
(i) Analytical Industry,
(ii) Genetic Industry and
(iii) Construction Industry.
Answer:
(i) Analytical Industry:
Analytical Industry which analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery.
(ii) Genetic Industry:
These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. The seeds, nursery companies’ poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc are classic examples of genetic industries.
(iii) Construction Industry:
These industries are involved in the construction of building, dams, bridges, roads, as well as tunnels and canals.
![]()
Question 13.
Briefly explain the auxiliaries to trade.
Answer:
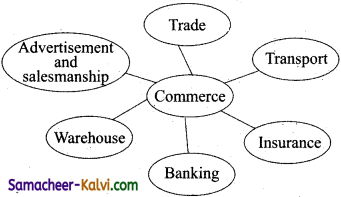
(i) Trade:
Trade removes hindrance of person, through wholesalers, retailers and mercantile agents. Goods are owned and possessed by those who produce them. Ownership and possession of goods must pass on from the producers to the ultimate consumers. Then only consumers can enjoy these goods. This is made possible by the organisation of trade. Wholesale traders take goods from the producers. From the wholesale traders, retail traders take the goods to the consumers. Thus trade, through traders removes hindrance of person.
(ii) Transport:
Transport removes place hindrance. Goods may be produced at places where their demand is less. These goods are to be taken to the place of consumption with the help of transport which creates places utility in goods. The place utility helps the producer to increase the production and earn remunerative price. The consumer is also helped with the supply of goods. Various modes of transport i.e., road, rail, sea, air have helped the growth of commerce and industry.
(iii) Warehousing:
Warehousing removes hindrance of time. Many goods such as cotton, jute, food grains, sugar, etc. are produced during particular seasons of the year. But they are needed throughout the year. To make them available throughout the year arrangement must be made for their proper storage. This is done with the help of warehousing; s
(iv) Banking:
There is also difficulty of finance. There is always a time – gap between the time of production and consumption. During this time-gap, traders need funds to cany on their trade. These funds are made available by commercial banks and other financial institutions.
(v) Advertisement and Salesmanship:
The consumers may not be aware of the availability of various goods in the market. The producer will also like to have more consumers. Advertisement and salesmanship in informing the consumers about the availability and usefulness of various products. With the advent of TV, FM Radio, Internet, etc., Consumer awareness is increasing.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The industries engaged in extraction of iron ore are known as:
(a) construction industries
(b) manufacturing industries
(c) extraction industries
(d) genetic industries
Answer:
(c) extraction industries
Question 2.
Auxiliaries to trade is also called as:
(a) trade
(b) advertisement
(c) warehousing
(d) aids to trade
Answer:
(d) aids to trade
Question 3.
Production which involves several stages for manufacturing finished products is known as:
(a) analytical industry
(b) synthetic industry
(c) processing industry
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) processing industry
![]()
Question 4.
Normally high level risk involved in:
(a) industry
(b) commerce
(c) trade
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(a) industry
Question 5.
Commerce is mainly concerned with:
(a) connecting producer and consumer
(b) pricing of goods
(c) buying and selling of goods
(d) manufacturing of goods
Answer:
(a) connecting producer and consumer
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities
→ The manufacturers produce the goods for the consumers at one point of location.
→ They distribute the goods to final consumer through intermediaries like wholesalers, retailers distributors and the like.
→ All these process taking place from the point of production to the point of consumption are collectively called as business activities.
→ All business activities can be classified into two broad categories (i.e.) Industry and commerce.
→ Three important inventions viz. Fire, wheel, and money made a remarkable turning point in the history of human life and civilisation.
→ Before invention of money goods were exchanged for goods.
![]()
→ Due to the growth of civilization production activities developed leading to the gradual expansion of business.
→ What is blood circulation to a human body so, is commercial activity to a business concern.
→ The volume and velocity of business / commercial activities determines the level of employment, income, demand, consumption, profit etc. of an econoihy.
→ Economic growth, which naturally implies growth of business, warrants a high level of commercial activities.
→ Wherein aspects such as industries, transport’ trade, warehousing, advertisement, communication etc. Plays an important role.