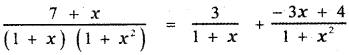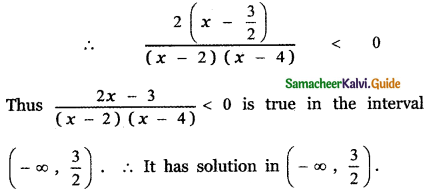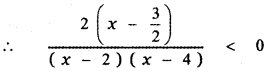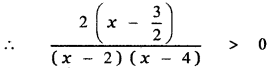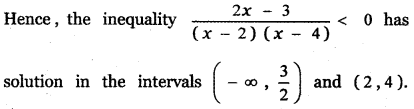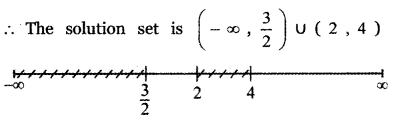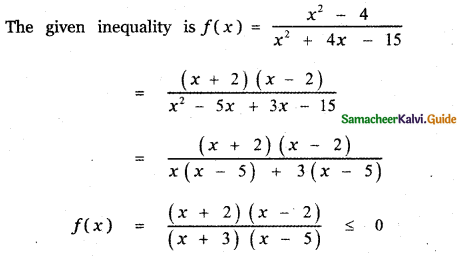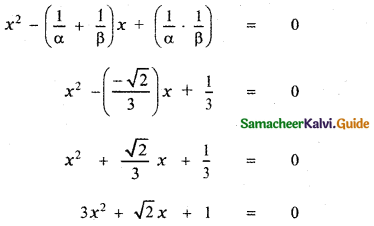Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Basic Algebra Ex 2.9 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Basic Algebra Ex 2.9
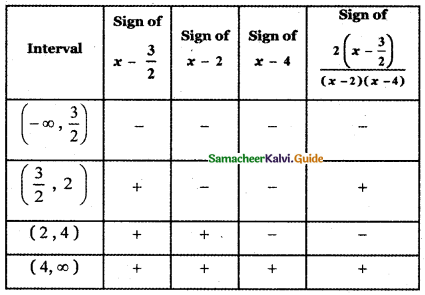
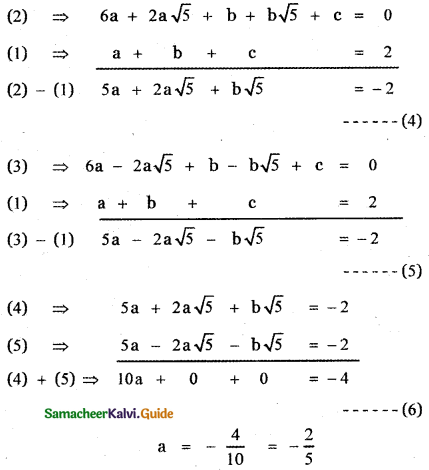
Question 1.
Resolve the following rational expressions into partial fractions : \(\frac{1}{x^{2}-a^{2}}\)
Answer:
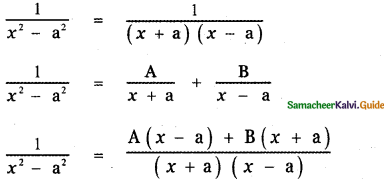
1 = A (x – a) + B (x + a) ——– (1)
Put x = a in equation (1)
1 = A (0) + B (a + a)
1 = B(2a)
⇒ B = \(\frac{1}{2 a}\)
Put x = – a in equation (1)
1 = A(- a – a) + B(- a + a)
1 = – 2a A + 0
⇒ A = \(-\frac{1}{2 a}\)
∴ The required partial fraction is
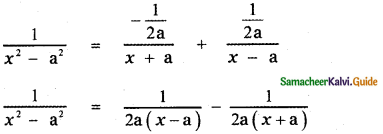
![]()
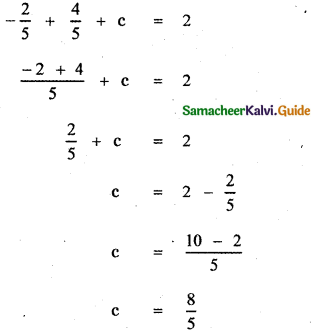
Question 2.
\(\frac{3 x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}\)
Answer:
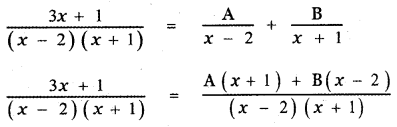
3x + 1 = A(x + 1) + B (x – 2) ——— (1)
Put x = 2 in equation (1)
3(2) + 1 = A (2 + 1) + B (2 – 2)
6 + 1 = 3A + 0
⇒ A = \(\frac{7}{3}\)
Put x = – 1 in equation (1)
3(-1) + 1 = A (-1 + 1 ) + B (- 1 – 2)
– 3 + 1 = A × 0 – 3B
– 2 = 0 – 3B
⇒ B = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
∴ The required partial fractions are
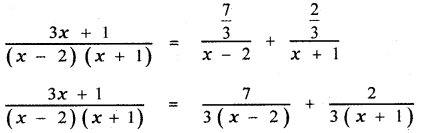
![]()
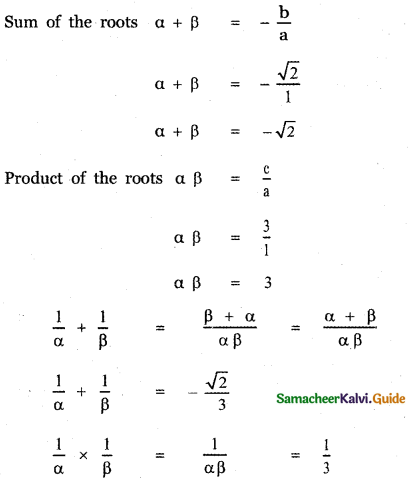
Question 3.
\(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)(x+2)}\)
Answer:
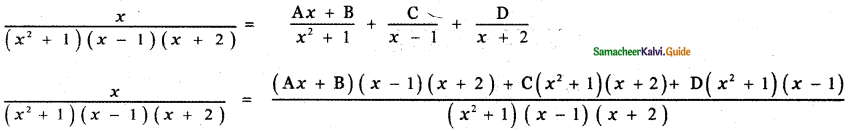
x = Ax (x + 1) (x + 2) + B(x – 1)(x + 2) + C(x2 + 1)(x + 2) + D(x2 + 1)(x – 1) ——— (1)
Put x = 1 in equation (1)
1 = A(1)(1 – 1) (1 + 2) + B ( ( 1 – 1 ) (1 + 2) + C(12 + 1 ) ( 1 + 2) + D(12 + 1) (1 – 1)
1 = A × 0 + B × 0 + C(2)(3) + D × 0
1 = 6C
⇒ C = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Put x = – 2 in equation (1)
-2 = A(- 2)(- 2 – 1)(- 2 + 2) + B(- 2 – 1)(- 2 + 2) + C ((- 2)2 + 1) (- 2 + 2) + D((-2)2 + 1 ) (- 2 – 1)
– 2 = A × 0 + B × 0 + C × 0 + D(4 + 1)(-3)
-2 = D(5)(-3)
⇒ – 2 = – 15 D
⇒ D = \(\frac{2}{15}\)
Put x = 0 in equation (1)
0 = A(0) (0 – 1) (0 + 2) + B(0 – 1)(0 + 2)+ C(02 + 1) (0 + 2) + D(02 + 1) (0 – 1)
0 = 0 + B (- 2 ) + C (2) + D (- 1)
0 = – 2B + 2C – D
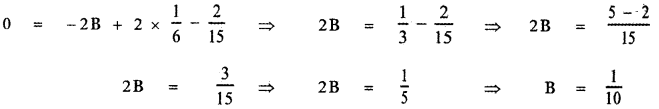
In equation (1), equate the coefficient of x3 on both sides
0 = A + C + D
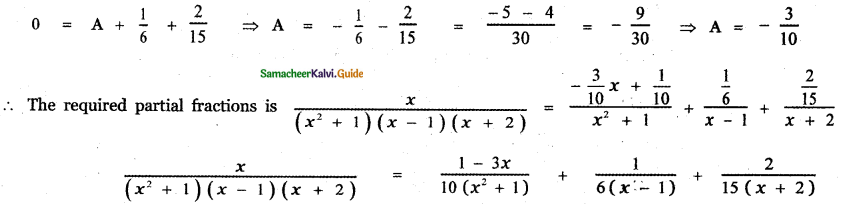
![]()
Question 4.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{3}}\)
Answer:
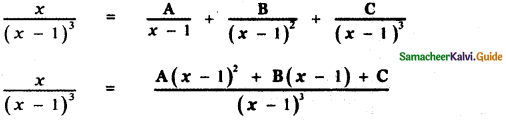
X = A(x – 1)2 + B(x – 1) + C ——— (1)
Put x = 1 in equation (1)
⇒ 1 = A(1 – 1)2 + B(1 – 1) + C
1 = 0 + 0 + C
⇒ C = 1
In equation (1), equating the coefficient of x2 on both sides
0 = A ⇒ A = 0
Put x = 0 in equation (1) ⇒ 0 = A(0 – 1)2 + B(0 – 1) + C
⇒ 0 = A – B + C
0 = 0 – B + 1
⇒ B = 1
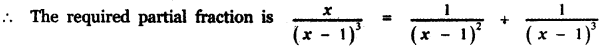
![]()
Question 5.
\(\frac{1}{x^{4}-1}\)
Answer:
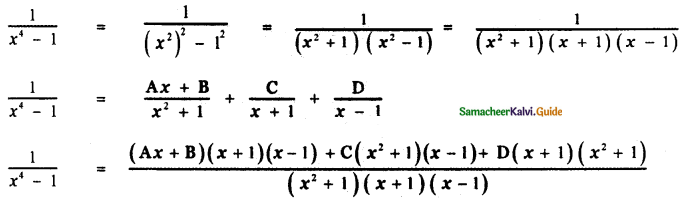
1 = Ax (x + 1)(x – 1) + B (x + 1) (x – 1) + C (x<sup2 + 1)(x – 1) + D(x + 1)(x2 + 1) —— (1)
Put x = 1 in equation (1)
1 = A(1 ) (1 + 1) (1 – 1) + B(1 + 1) (1 – 1) + C(1<sup2 + 1) (1 – 1) + D(1 + 1) (1<sup2 + 1)
1 = A × 0 + B × 0 + C × 0 + D(2)(2)
⇒ 1 = – 4D
⇒ D = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Put x = -1 in equation (1)
1 = A(- 1)(- 1 + 1)(- 1 – 1) + B(- 1 + 1)(- 1 – 1) + C ((- 1)2 + 1)(- 1 + 1) + D(- 1 + 1)((-1)2 + 1)
1 = A × 0 + B × 0 + C (2) (-2) + D × 0
⇒ 1 = -4C
⇒ C = \(-\frac{1}{4}\)
Put x = 0 in equation (1)
I = A(0) (0 + 1 )(0 – 1) + B(0 + 1 )(0 – 1) + C(02 + 1 )(0 – 1) + D(0 + 1)(02 + 1)
1 = A × O + B(-1) + C(- 1) + D(1)
⇒ 1 = – B – C + D
1 = – B + \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
⇒ B = \(\frac{1}{2}\) – 1 = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ B = – \(\frac{1}{4}\)
In equation (1), equate the coefficient of x3 on both sides
0 = A + C + D
⇒ 0 = A – \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}\)
⇒ A = 0
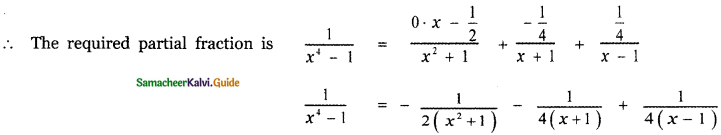
![]()
Question 6.
\(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{x^{3}+x}\)
Answer:
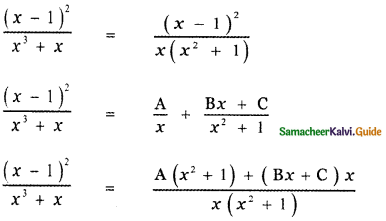
(x – 1)2 = A(x2 + 1) + Bx2 + Cx ——- (1)
Put x = 0 in equation (I)
(0 – 1)2 = A(02 + 1) + B × 0 + C × 0
1 = A + 0 + 0
⇒ A = 1
Equating the coefficient of x2 on both sides
1 = A + B
1 = 1 + B
⇒ B = 0
Put x = 1 in equation (1)
(1 – 1)2 = A(12 + 1) + B × 12 + C × 1
0 = 2A + B + C
0 = 2 × 1 + 0 + C
⇒ C = – 2
∴ The required partial fraction is
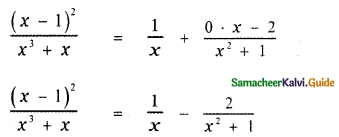
![]()
Question 7.
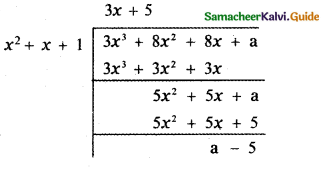
\(\frac{x^{2}+x+1}{x^{2}-5 x+6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{x^{2}+x+1}{x^{2}-5 x+6}\)
Here the degree of the numerator is equal to the degree of the denominator. Let us divide the numerator by the
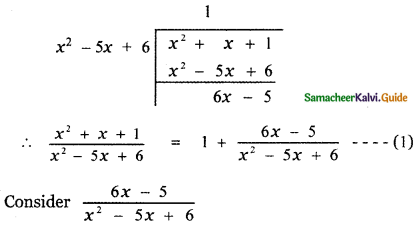
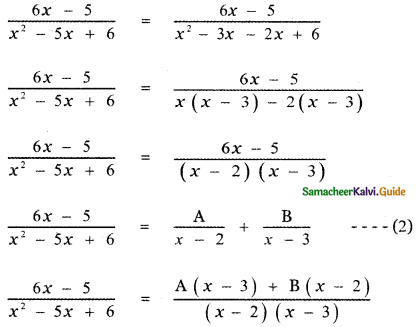
6x – 5 = A(x – 3) + B(x – 2) ——- (3)
Put x = 3 in equation (3)
6(3) – 5 = A(3 – 3) + B(3 – 2)
18 – 5 = 0 + B
⇒ B = 13
Put x = 2 in equation (3)
6(2) – 5 = A(2 – 3) + B(2 -2)
12 – 5 = – A + 0
7 = -A
⇒ A = – 7
Substituting the values of A and B in equation (2)
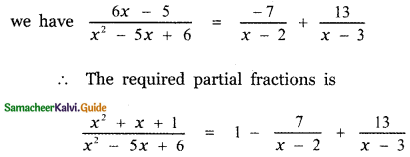
![]()
Question 8.
\(\frac{x^{3}+2 x+1}{x^{2}+5 x+6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{x^{3}+2 x+1}{x^{2}+5 x+6}\)
Since the numerator is of degree greater than that of the denominator divide the numerator by the denominator.
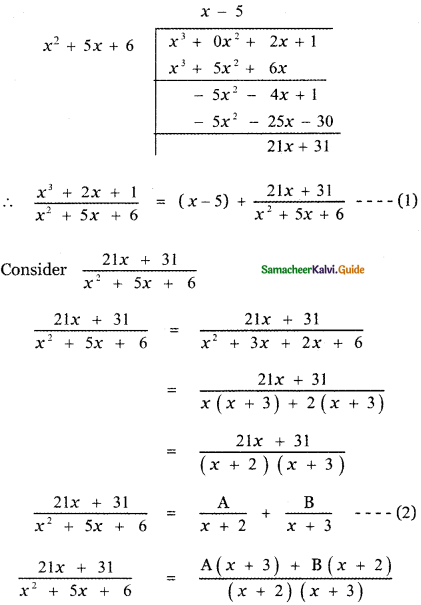
21x + 31 = A(x + 3) + B(x + 2) ——- (3)
Put x = – 3 . in equation (3)
21(- 3) + 31 = A(- 3 + 3) + B(- 3 + 2)
– 63 + 31 = 0 – B
– 32 = – B
⇒ B = 32
Put x = – 2 , in equation (3)
21(- 2) + 31 = A(- 2 + 3) + B(- 2 + 2)
– 42 + 31 = A + 0
⇒ A = – 11
Substituting the values of A and B in equation (2)
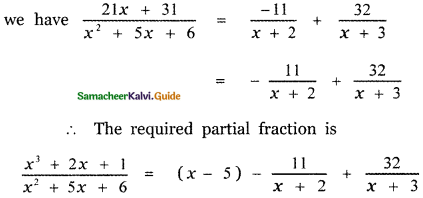
![]()
Question 9.
\(\frac{x+12}{(x+1)^{2}(x-2)}\)
Answer:
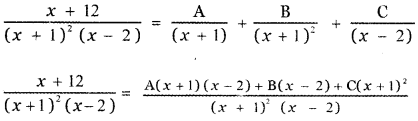
x + 12 = A(x + 1 ) (x – 2) + B(x – 2) + C(x + 1)2 ——– (1)
Put x = 2 in equation (l)
2 + 12 = A(2 + 1 ) (2 – 2) + B(2 – 2) + C(2 + 1)2
14 = A(3) (0) + B × 0 + C (3 )2
4 = 0 + 0 + 9C
⇒ C = \(\frac{14}{9}\)
Put x = – 1 in equation (1)
-1 + 12 = A(- 1 + 1)(- 1 – 2) + B(- 1 – 2) + C(- 1 + 1)2
11 = A × 0 + B (- 3 ) + C × 0
11 = -3 B
⇒ B = \(-\frac{11}{3}\)
Put x = 0 in equation (1)
0 + 12 = A (0 + 1)(0 – 2) + B(0 – 2) + C(0 + 1)2
12 = – 2A – 2B + C
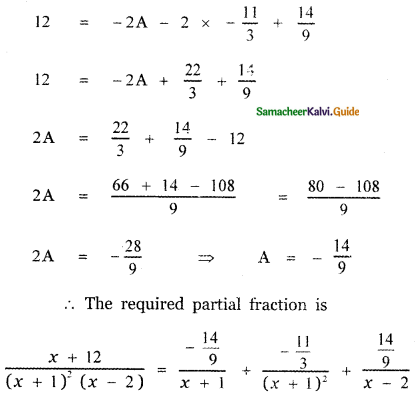
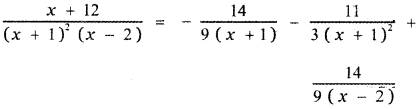
![]()
Question 10.
\(\frac{6 x^{2}-x+1}{x^{3}+x^{2}+x+1}\)
Answer:
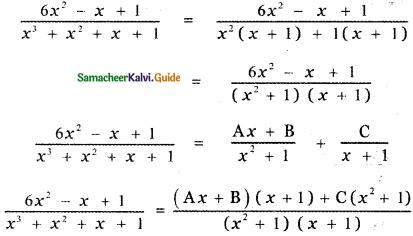
6x2 – x + 1 = Ax (x + 1) + B (x + 1) + C(x2 + 1) ——— (1)
Put x = – 1 in equation (1)
6 x (- 1)2 – (- 1) + 1 = A (- 1 ) (- 1 + 1 ) + B(- 1 + 1) + C ( (- 1)2 + 1 )
6 + 1 + 1 = A × 0 + B × 0 + C (2)
8 = 2C
⇒ C = 4
Put x = 0 in equation (1)
6 × 02 – 0 + 1 = A(0)(0 + 1 ) + B(0 + 1) + C(02 + 1)
1 = 0 + B + C
1 = B + 4
B = 1 – 4 = – 3
Equating the coefficient of x2 in equation (1) we have
6 = A + C
6 = A + 4
⇒ A = 6 – 4
⇒ A = 2
∴ The required partial fraction is
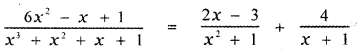
![]()
Question 11.
\(\frac{2 x^{2}+5 x-11}{x^{2}+2 x-3}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2 x^{2}+5 x-11}{x^{2}+2 x-3}\)
Since the degree of the numerator is equal to the degree of the denominator divide the numerator by the denominator
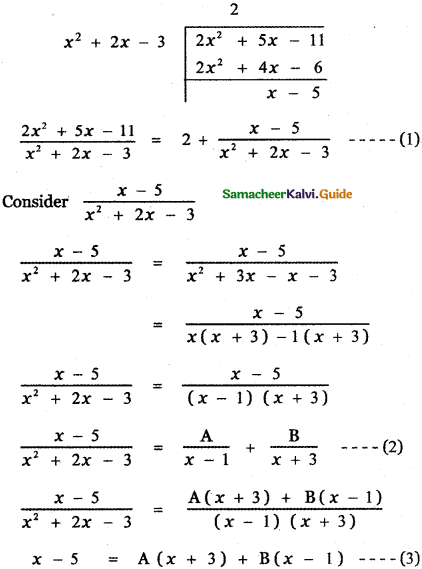
Put x = 1 in equation (3)
1 – 5 = A(1 + 3) + B(1 – 1)
– 4 = 4A + 0
⇒ A = – 1
Put x = – 3 in equation (3)
– 3 – 5 = A (- 3 + 3) + B(- 3 – 1)
– 8 = 0 – 4B
⇒ B = 2
Substituting the values of A and B in equation (2) we have
![]()
∴ The required partial fraction is
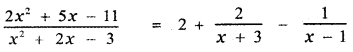
![]()
Question 12.
\(\frac{7+x}{(1+x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
Answer:
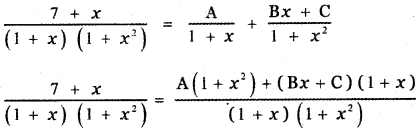
7 + x = A( 1 + x2) + Bx (1 + x) + C(1 + x) ——- (1)
Put x = -1 , in equation (1)
7 – 1 = A(1 + (-1)2) + B (- 1) (1 – 1) + C(1 – 1)
6 = A(1 + 1) + 0 + 0
A = \(\frac{6}{2}\) = 3
⇒ A = 3
Put x = 0 , in equation (1)
7 + 0 = A(1 + 02) + B × 0 (1 + 0) + C(1 + 0)
7 = A + 0 + C
7 = 3 + C
⇒ C = 4
Equating the coefficient of x2 in equation (I) we have
0 = A + B
0 = 3 + B
⇒ B = – 3
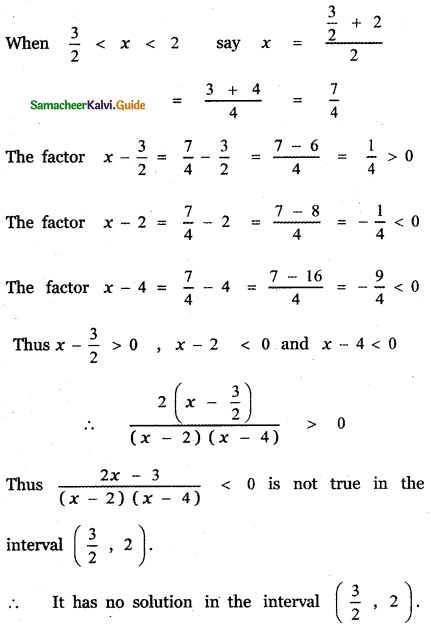
∴ The required partial fraction is