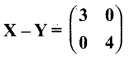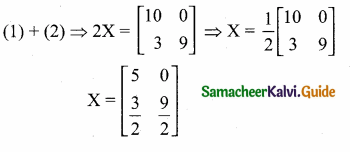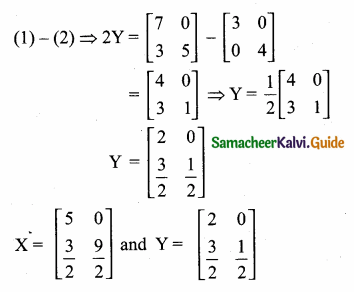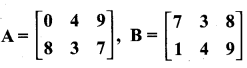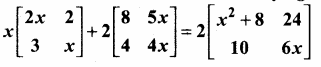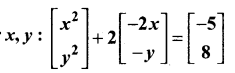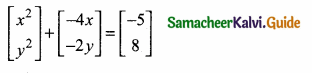Students can download Maths Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.4
Question 1.
Find the next three terms of the following sequence.
(i) 8, 24, 72,…
(ii) 5, 1, -3, …
(iii) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { 2 }{ 9 } \), \(\frac { 3 }{ 16 } \)
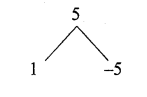
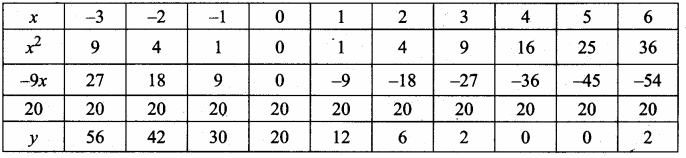
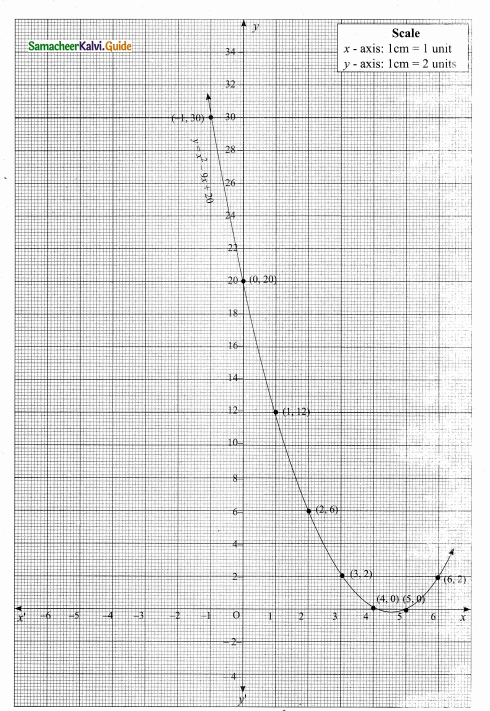
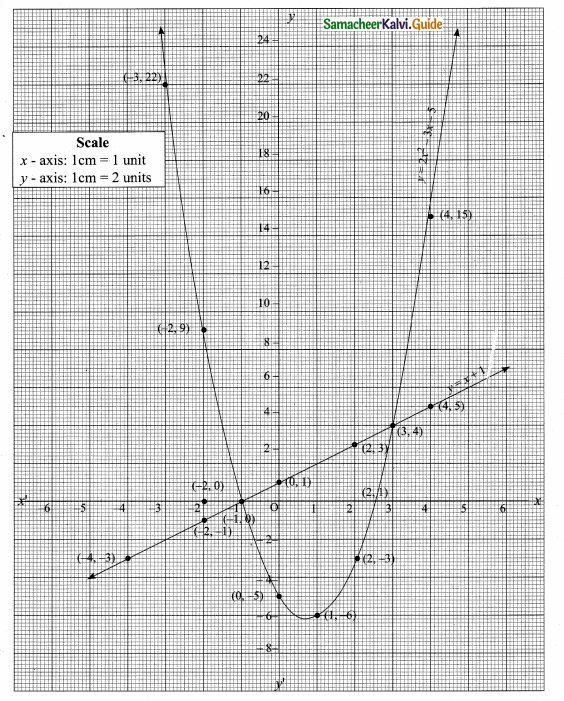
(i) 216, 648, 1944 (This sequence is multiple of 3)
Next three terms are 216, 648, 1944
(ii) Next three terms are -7, -11, -15
(adding -4 with each term)
(iii) Next three terms are \(\frac { 4 }{ 25 } \),\(\frac { 5 }{ 36 } \) and \(\frac { 6 }{ 49 } \)
[using \(\frac{n}{(n+1)^{2}}\)]
![]()
Question 2.
Find the first four terms of the sequences whose nth terms are given by
(i) an = n3 – 2
(ii) an = (-1)n+1 n(n+1)
(iii) an = 2n2 – 6
Solution:
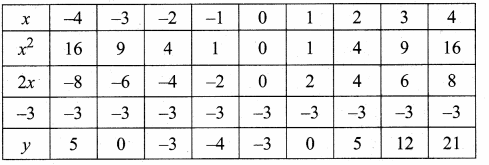
tn = an = n3 -2
(i) a1 = 13 – 2 = 1 – 2 – 1
a2 = 23 – 2 = 8 – 2 = 6
a3 = 33 – 2 = 27 – 2 = 25
a4 = 43 – 2 = 64 – 2 = 62
∴ The first four terms are -1, 6, 25, 62, ……….
(ii) an = (-1)n+1 n(n + 1)
a1 = (-1)1+1 (1) (1 +1)
= (-1)2 (1) (2) = 2
a2 = (-1)2+1 (2) (2 + 1)
= (-1)3 (2) (3)= -6
a3 = (-1)3+1 (3) (3 + 1)
= (-1)4 (3) (4) = 12
a4 = (-1)4+1 (4) (4 + 1)
= (-1)5 (4) (5) = -20
∴ The first four terms are 2, -6, 12, -20,…
(iii) an = 2n2 – 6
a1 = 2(1)2 – 6 = 2 – 6 = -4
a2 = 2(2)2 – 6 = 8 – 6 = 2
a3 = 2(3)2 – 6 = 18 – 6 = 12
a4 = 2(4)2 – 6 = 32 – 6 = 26
∴ The first four terms are -4, 2, 12, 26, …
![]()
Question 3.
Find the nth term of the following sequences
(i) 2, 5, 10, 17, ……
Answer:
(12 + 1);(22 + 1),(32 + 1),(42 + 1)….
nth term is n2 + 1
an = n2 + 1
(ii) 0,\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \),\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) ……
Answer:
(\(\frac { 1-1 }{ 1 } \)), (\(\frac { 2-1 }{ 2 } \)), (\(\frac { 3-1 }{ 3 } \)) …..
nth term is \(\frac { n-1 }{ n } \)
an = \(\frac { n-1 }{ n } \)
(iii) 3,8,13,18,…….
Answer:
[5(1) -2], [5(2) – 2], [5(3) – 2], [5(4) – 2] ….
The nth term is 5n – 2
an = 5n – 2
![]()
Question 4.
Find the indicated terms of the sequences whose nth terms are given by
(i) an = \(\frac { 5n }{ n+2 } \) ; a6 and a13
Answer:
an = \(\frac { 5n }{ n+2 } \)
a6 = \(\frac { 5(6) }{ 6+2 } \) = \(\frac { 30 }{ 8 } \) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 4 } \)
a13 = \(\frac { 5(13) }{ 13+2 } \) = \(\frac{5 \times 13}{15}\) = \(\frac { 13 }{ 3 } \)
a6 = \(\frac { 15 }{ 4 } \), a13 = \(\frac { 13 }{ 3 } \)
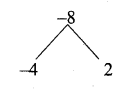
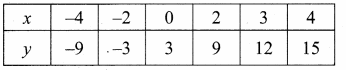
(ii) an = – (n2 – 4); a4 and a11
Answer:
an = -(n2 – 4)
a4 = -(42 – 4)
= – (16 – 4)
= -12
a11 = -(112 – 4)
= – (121 – 4)
= – 117
a4 = -12 and a11 = -117
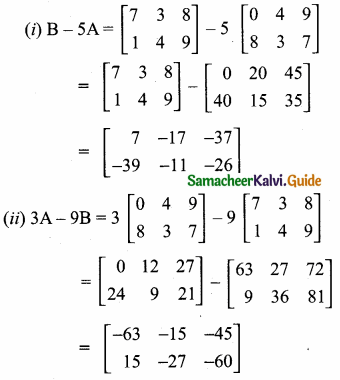
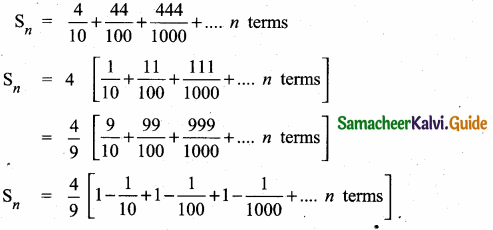
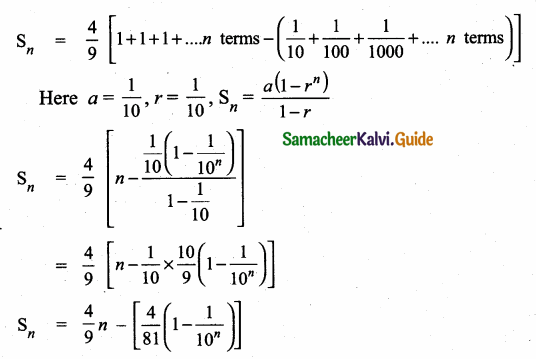
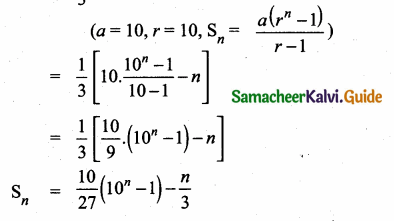
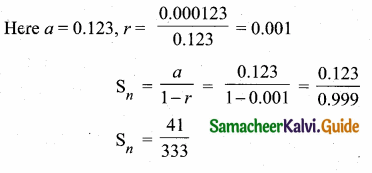
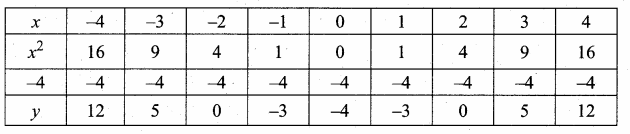
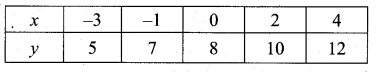
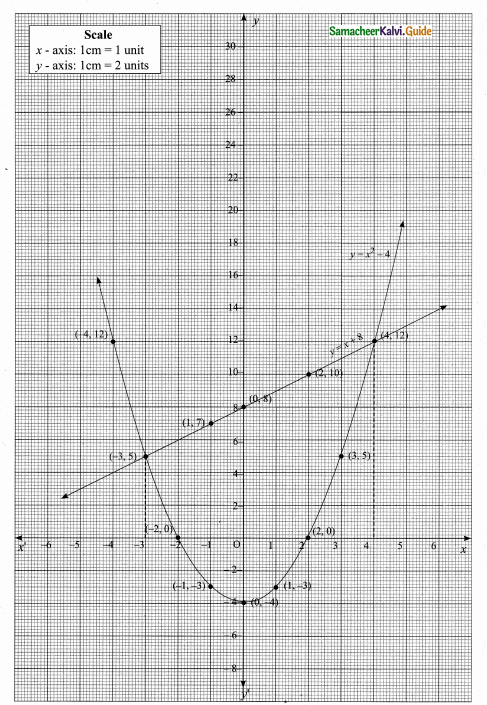
Question 5.
Find a8 and a15 whose nth term is an
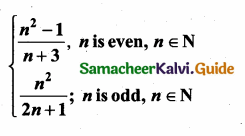
Answer:
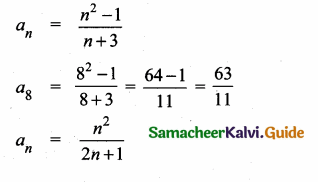
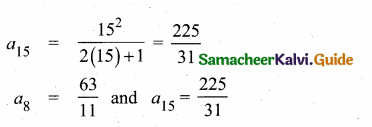
![]()
Question 6.
If a1 = 1, a2 = 1 and an = 2an-1 + an-2, n > 3, n ∈ N, then find the first six terms of the sequence.
Solution:
a1 = 1, a2 = 1, an = 2an-1 + an-2
a3 = 2a(3-1) + a(3-2)
= 2a2 + a1
= 2 × 1 + 1 = 3
a4 = 2a(4-1) + a(4-2)
= 2a3 + a2
= 2 × 3 + 1 = 7
a5 = 2a(5-1) + a(5-2)
= 2a4 + a3
= 2 × 7 + 3 = 17
a6 = 2a(6-1) + a(6-2)
= 2a5 + a4
= 2 × 17 + 7
= 34 + 7
= 41
∴ The first six terms of the sequence are 1, 1, 3, 7, 17, 41 ………..
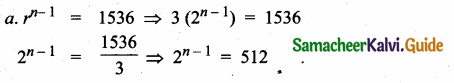
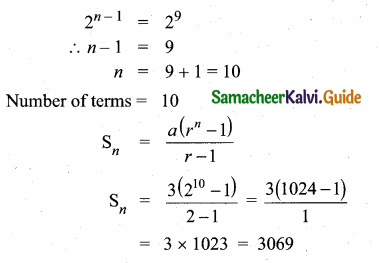
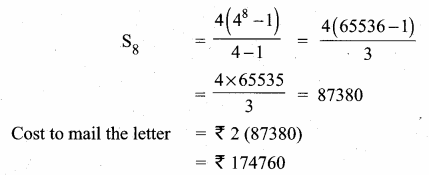
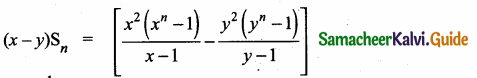
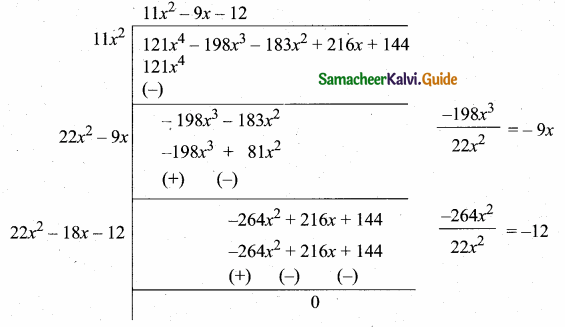
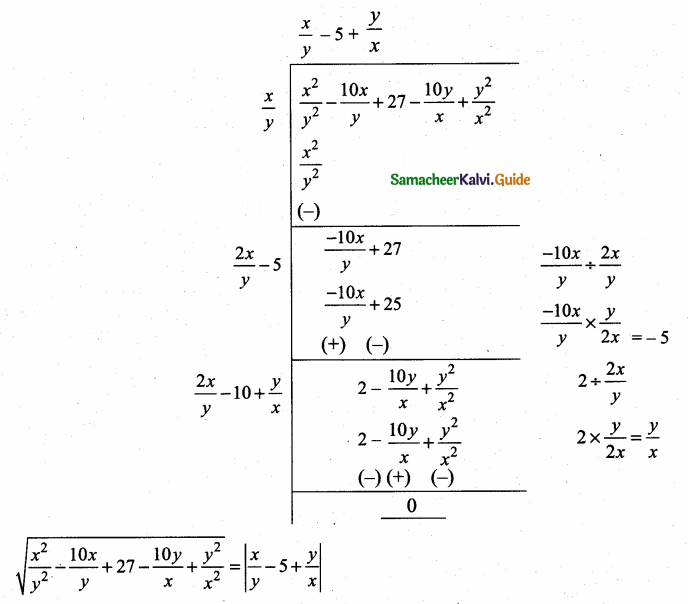
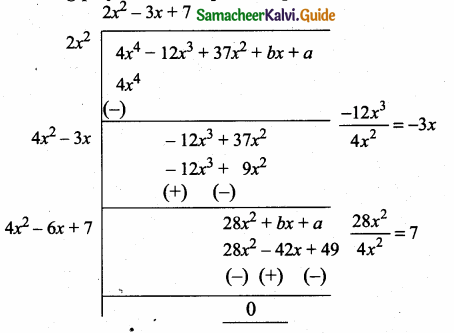
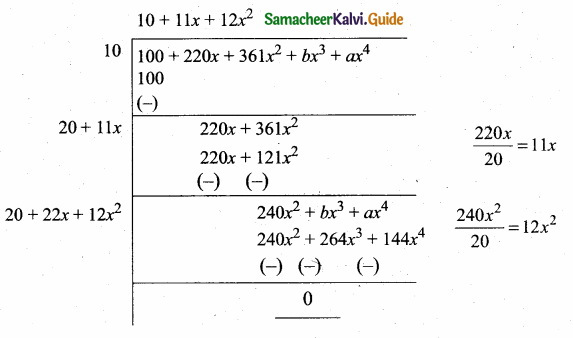
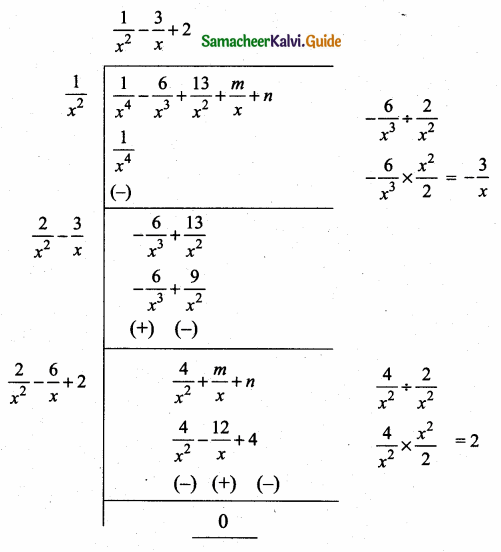
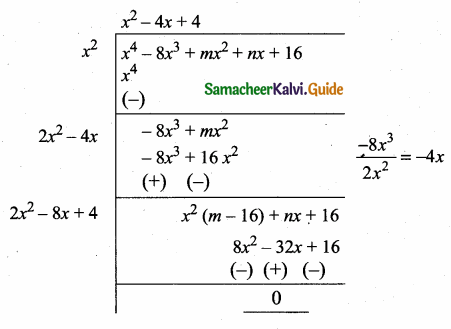
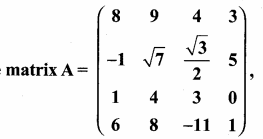
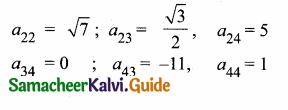

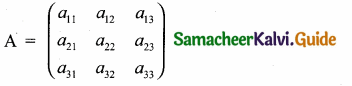
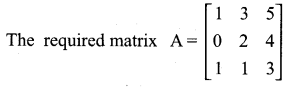
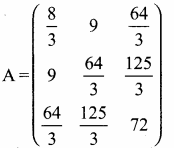
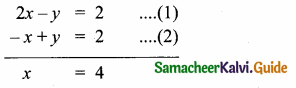
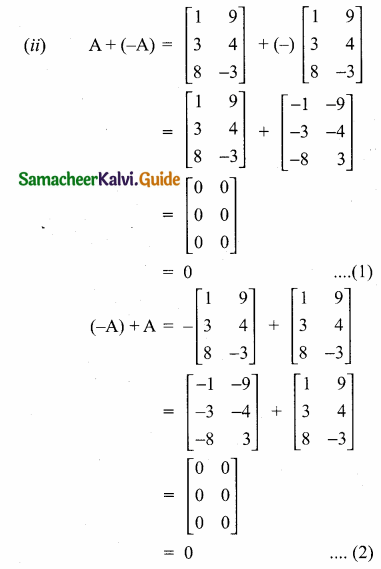
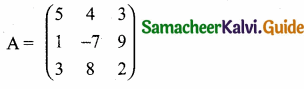 then find the tranpose of A.
then find the tranpose of A.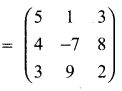
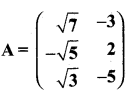 then find the tranpose of – A
then find the tranpose of – A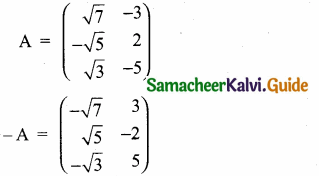
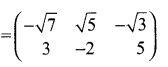
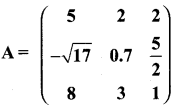 then verify (AT)T = A
then verify (AT)T = A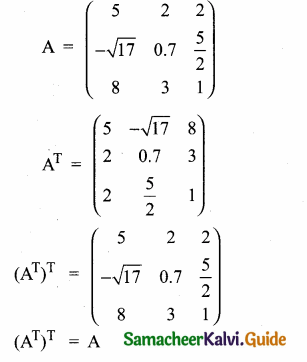
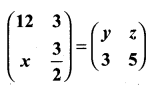
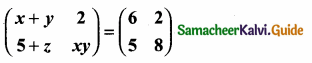
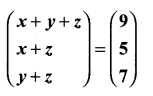
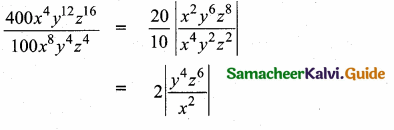
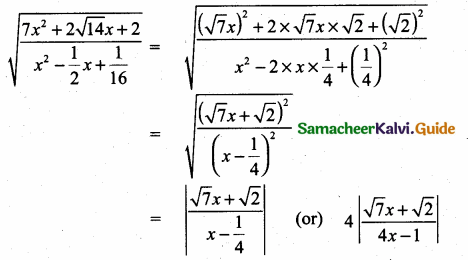
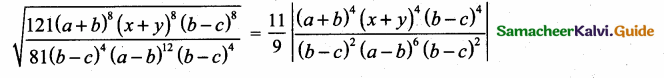
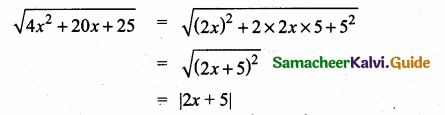
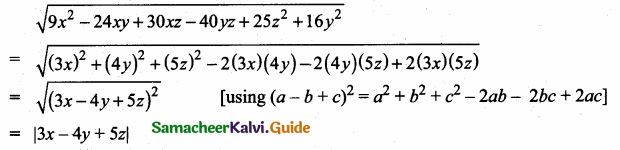
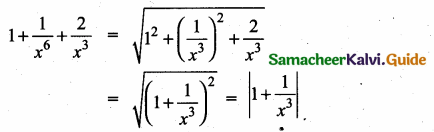
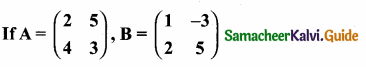
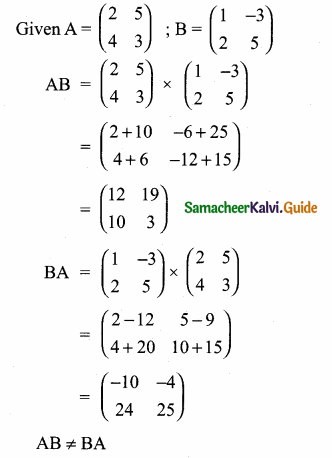
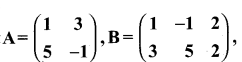
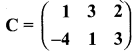
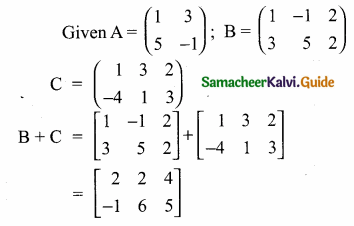
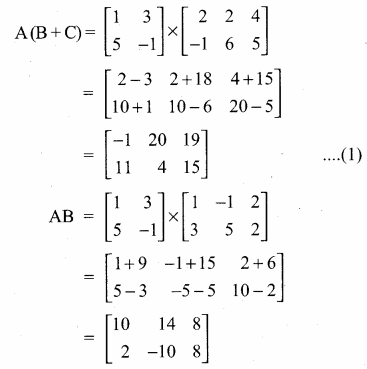
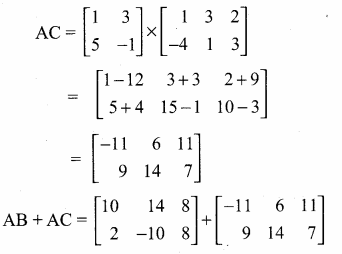
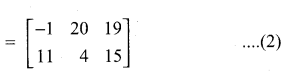
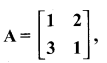
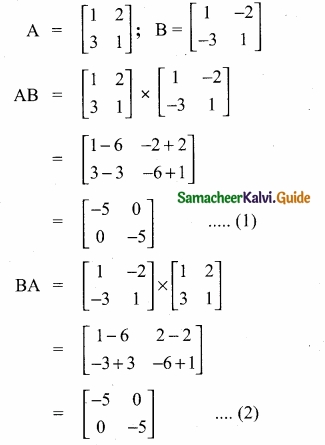
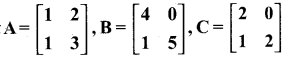
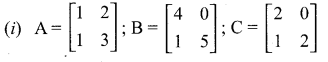
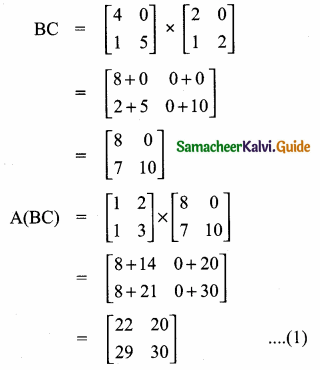
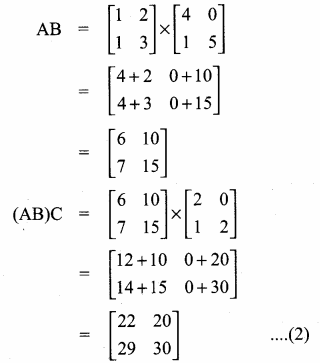
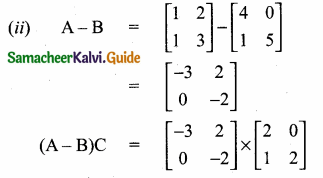
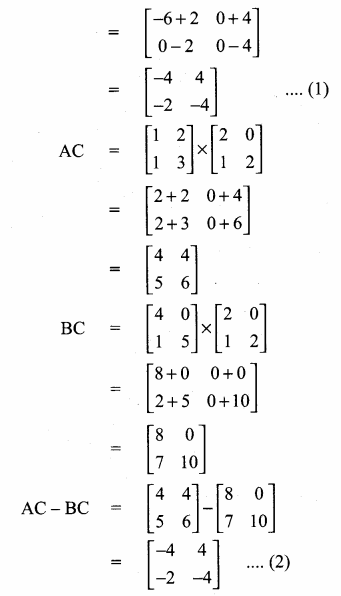
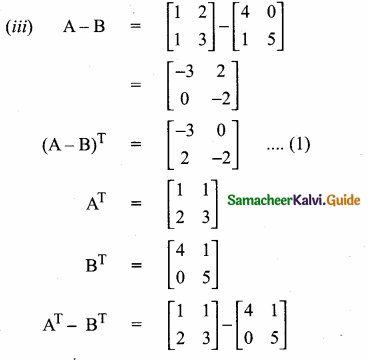
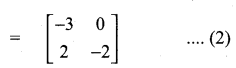
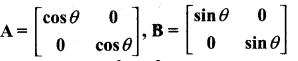
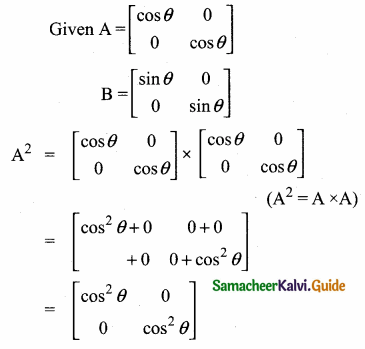
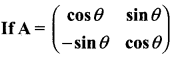
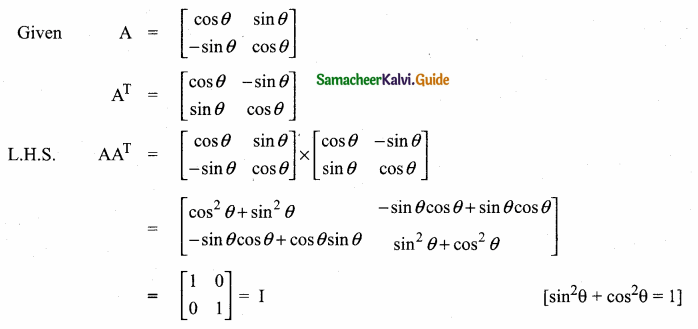
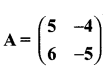
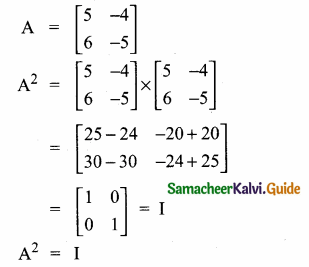
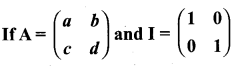
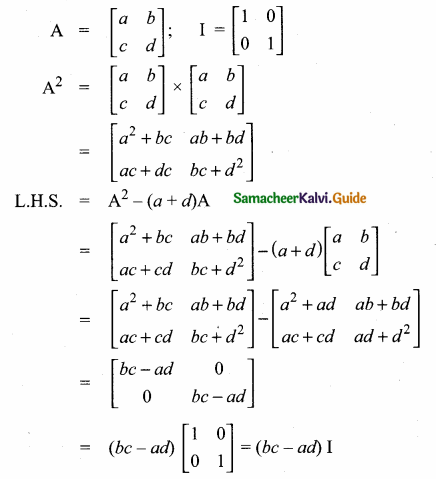
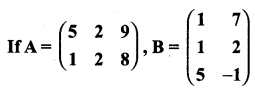
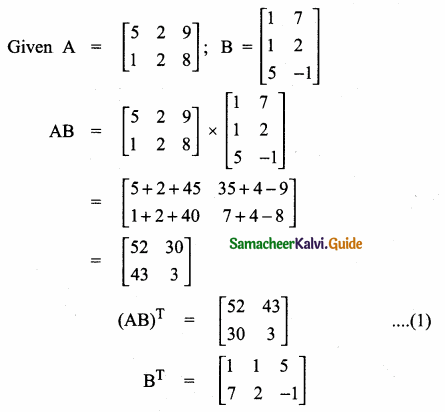
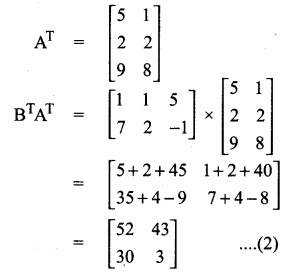
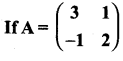
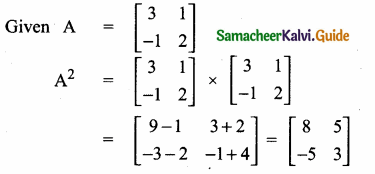
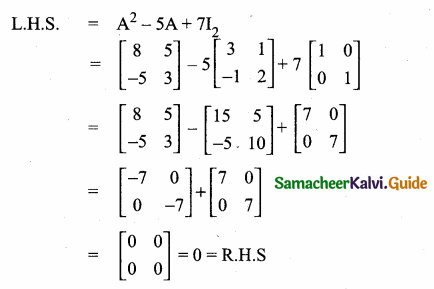
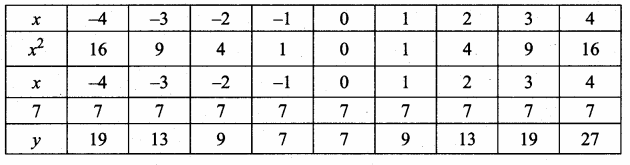
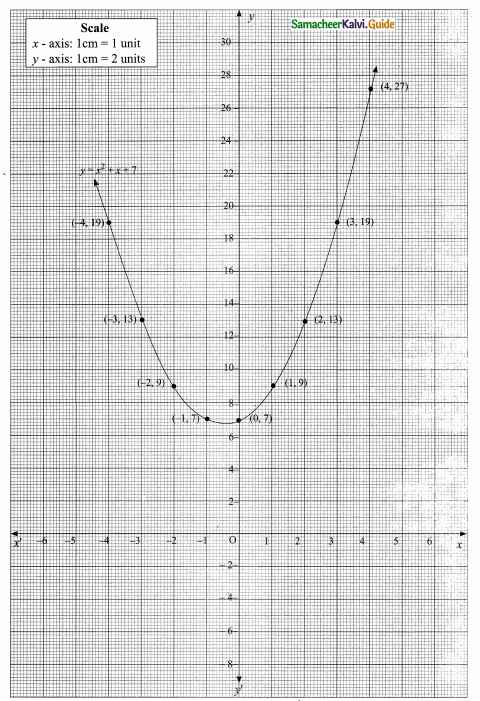
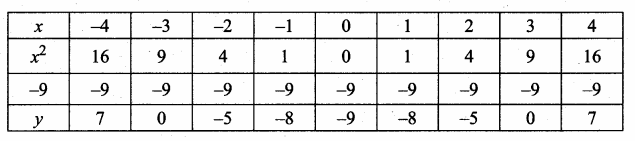
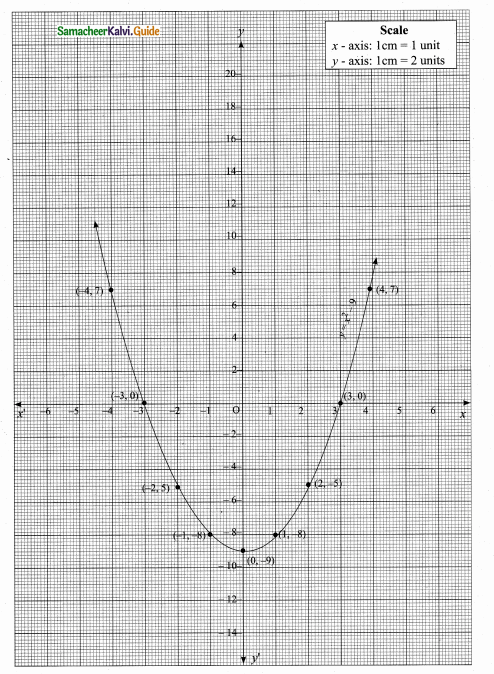
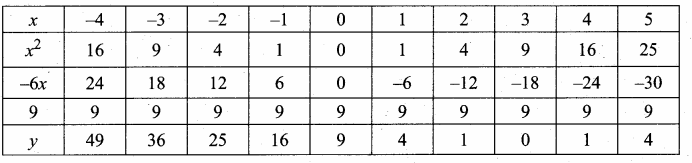
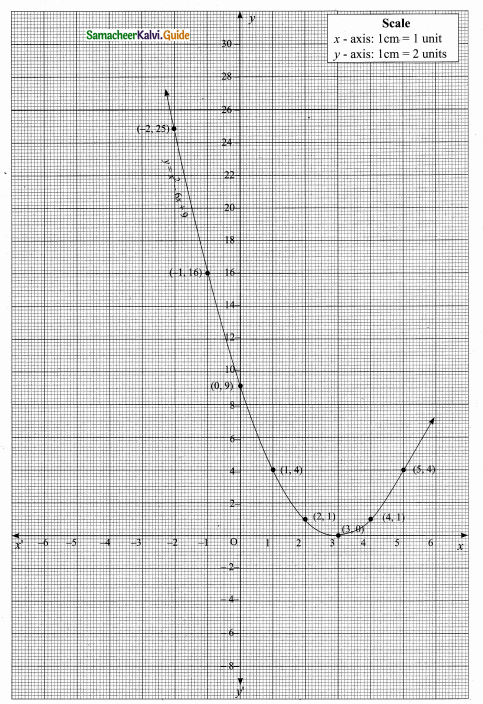
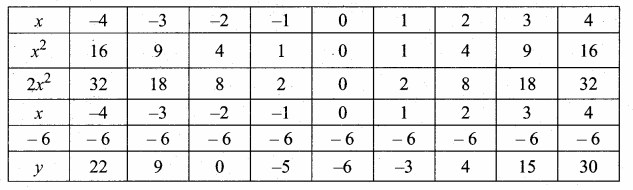
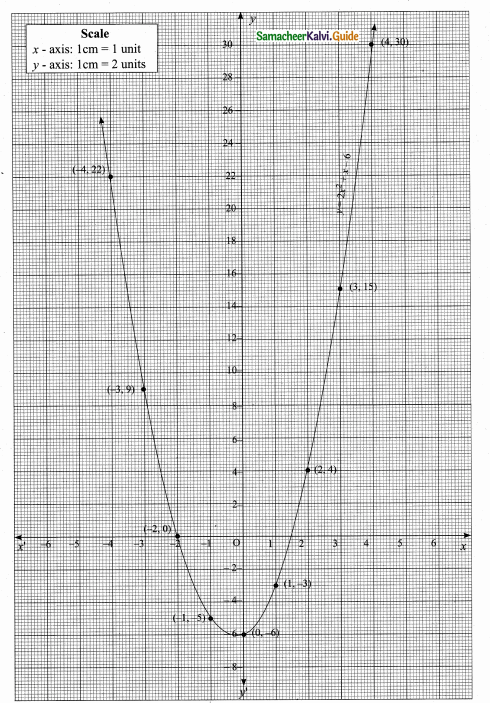
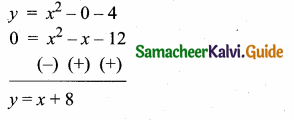
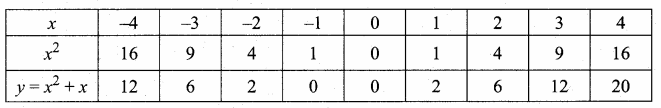
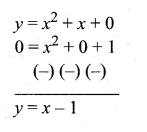
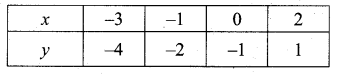
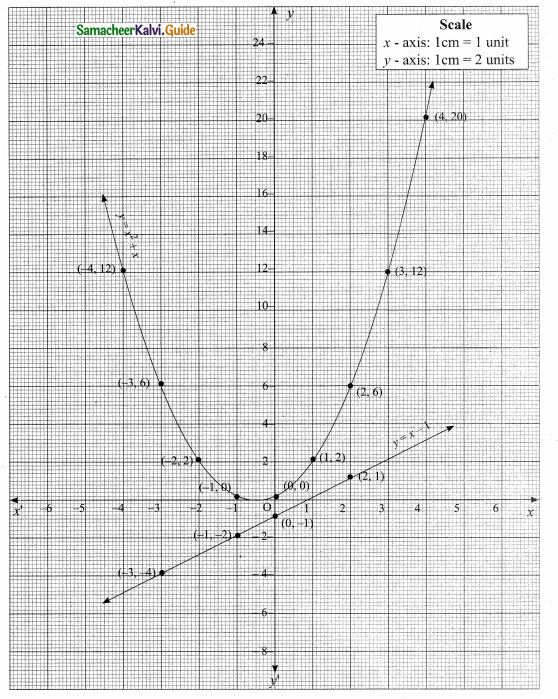
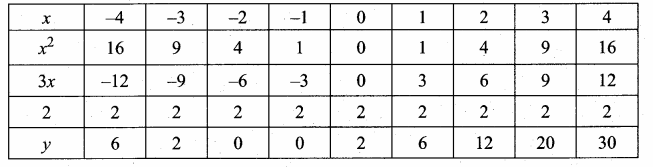
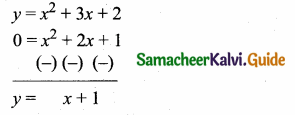
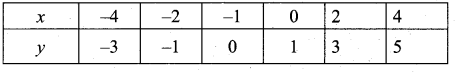
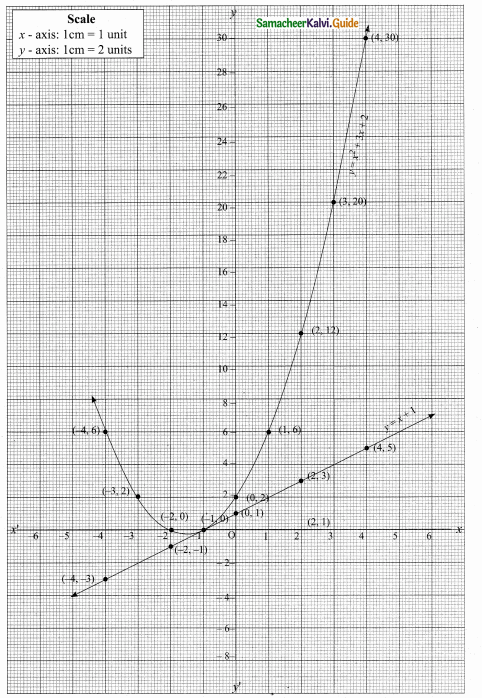
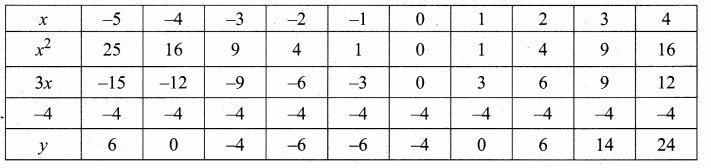
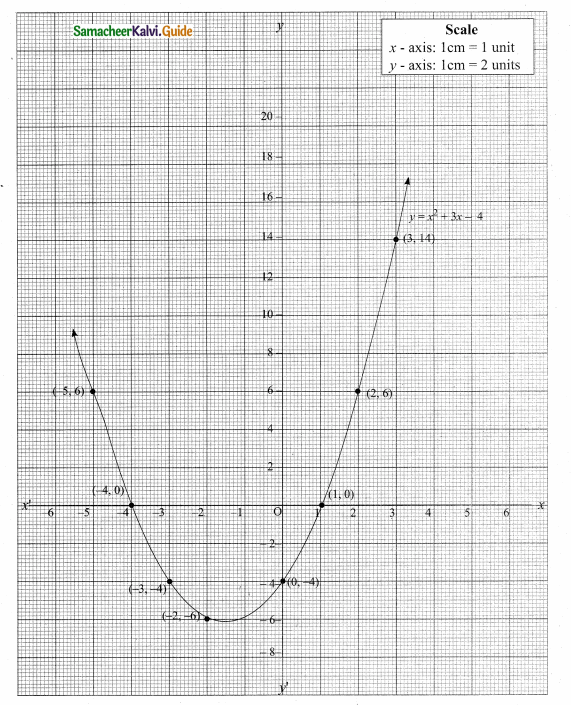
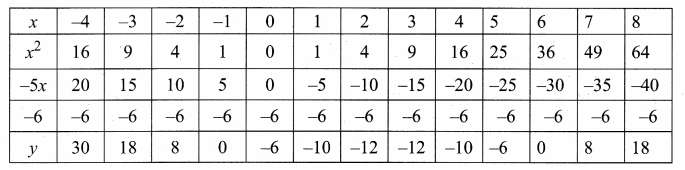
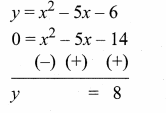
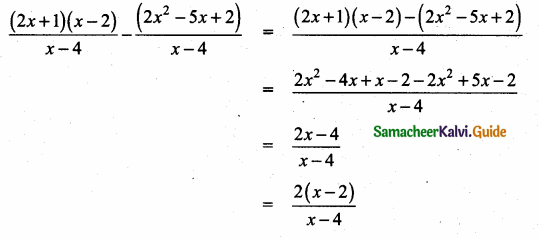
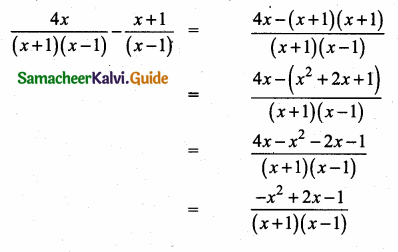
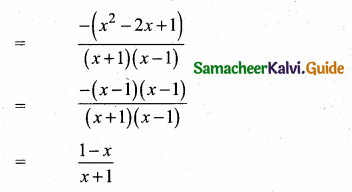
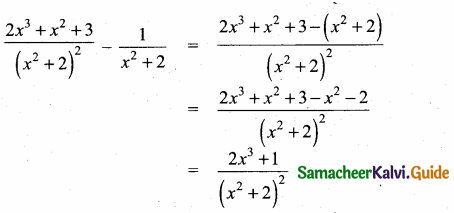
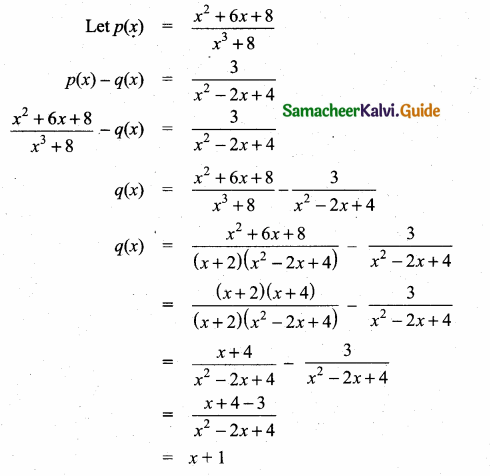
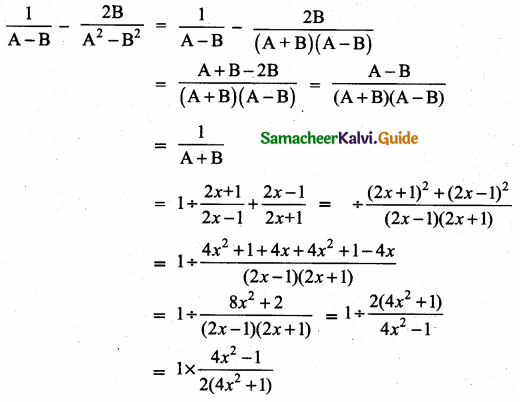
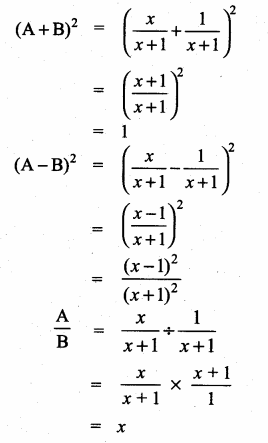
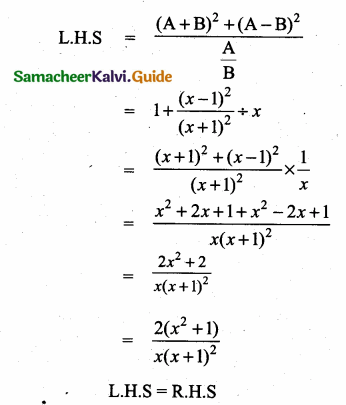
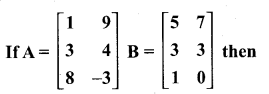
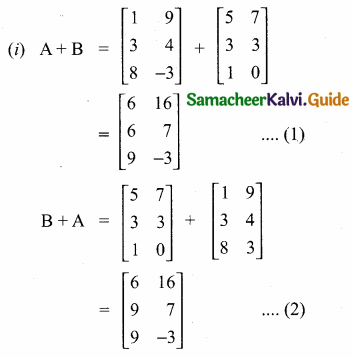
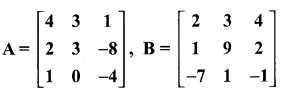
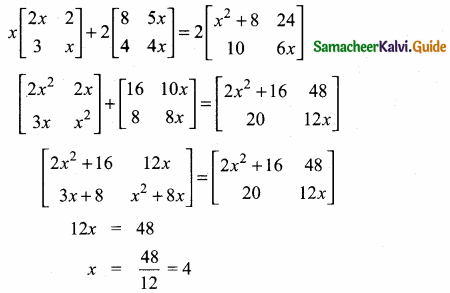
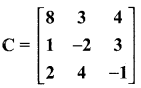 then verify that
then verify that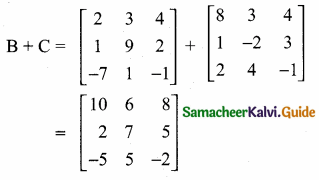
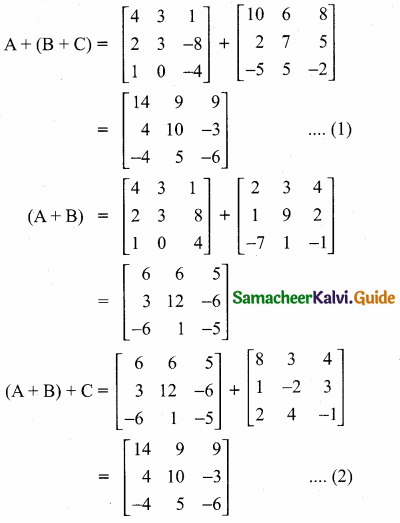
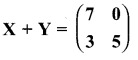 and
and