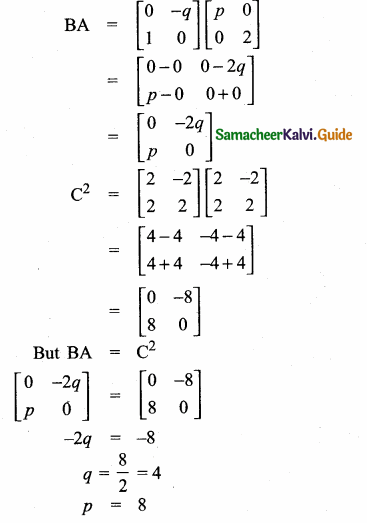
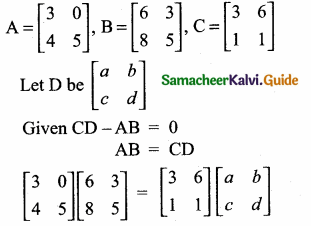
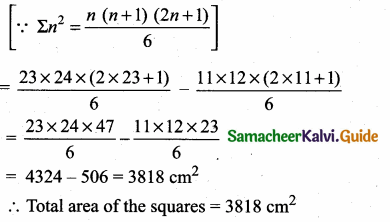
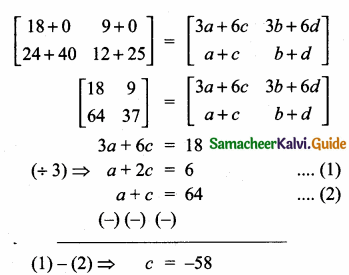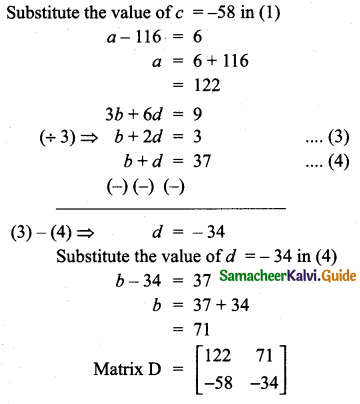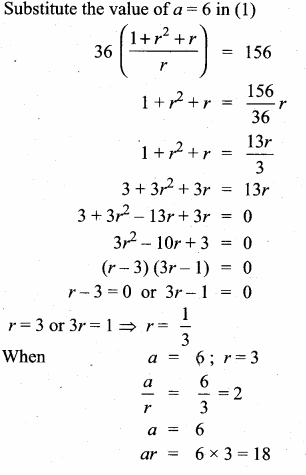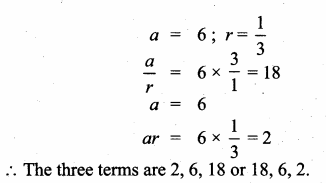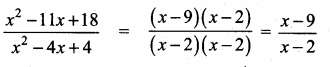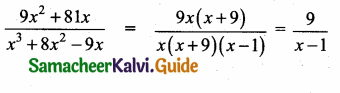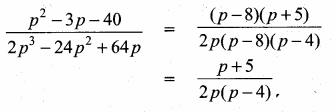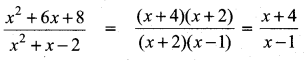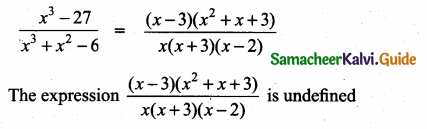Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.13 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.13
Question 1.
Determine the nature of the roots for the following quadratic equations
(i) 15x2 + 11x + 2 = 0
Answer:
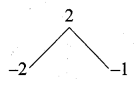
Here a = 15, b = 11, c = 2
∆ = b2 – 4ac
∆ = 112 – 4(15) × 2
= 121 – 120
∆ = 1 > 0
So the equation will have real and unequal roots
(ii) x2 – x – 1 = 0
Answer:
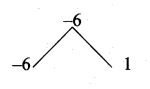
Here a = 1, b = -1, c = -1
∆ = b2 – 4ac
= (-1)2 – 4(1)(-1)
= 1 + 4 = 5
∆ = 1 > 0
So the equation will have real and unequal roots.
![]()
(iii) \(\sqrt { 2 }\) t2 – 3t + 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\) = 0
Answer:
Here a = \(\sqrt { 2 }\) , b = -3, c = 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)
∆ = b2 – 4ac
= (-3)2 – 4(\(\sqrt { 2 }\)) (3\(\sqrt { 2 }\))
= 9 – 24 = -15
∆ = -15 < 0
So the equation will have no real roots.
(iv) 9y2 – 6\(\sqrt { 2y }\) + 2 = 0
Answer:
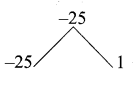
Here a = 9, b = -6\(\sqrt { 2 }\), c = 2
∆ = b2 – 4ac
= (-6\(\sqrt { 2 }\))2 – 4(9) (2)
= 72 – 72
= 0
So the equation will have real and equal roots.
(v) 9a2b2x2 – 24abcdx + 16c2d2 = 0, a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0
Answer:
Here a = 9a2b2; b = -24 abed, c = 16c2d2
∆ = b2 – 4ac
= (-24abcd)2 – 4(9a2b2) (16c2d2)
= 576a2b2c2d2 – 576a2b2c2d2
∆ = 0
So the equation will have real and equal roots.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the value(s) of ‘k’ for which the roots of the following equations are real and equal.
(i) (5k – 6)2 + 2kx + 1 = 0
(ii) kx2 + (6k + 2)x + 16 = 0
Solution:
(5k – 6)x2 + 2kx + 1 :
a = (5k – 6), b = 2, c = 1
Δ = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (2k)2 – 4 (5k – 6)(1)
⇒ 4k2 – 20k + 24 = 0 [∵ Since the roots are real and equal)
⇒ k2 – 5k + 6 = 0
⇒ (k – 3)(k – 2) = 0
k = 3, 2
(ii) kx2 + (6k + 2)x + 16 = 0
a = k, b = (6k + 2), c = 16
Δ = b2 – 4ac [∵ the roots are real and equal)
⇒ (6k + 2)2 – 4 × k × 16 = 0
⇒ 36k2 + 24k + 4 – 64k = 0
⇒ 36k2 – 40k + 4 =0
⇒ 36k2 – 36k – 4k + 4 =0
⇒ 36k (k – 1) – 4 (k – 1) = 0
⇒ 4 (k – 1) (9k – 1) =0
⇒ k = 1 or k = \(\frac{1}{9}\)
![]()
Question 3.
If the roots of (a – b)x2 + (b – c)x + (c – a) = 0 are real and equal, then prove that b, a, c are in arithmetic progression.
Answer:
(a – b) x2 + (b – c) x + (c – a) = 0
Here a = (a – b);b = b – c ; c = c – a
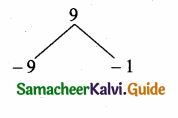
Since the equation has real and equal roots ∆ = 0
∴ b2 – 4ac = 0
(b – c)2 – 4(a – b)(c – a) = 0
b2 + c2 – 2bc -4 (ac – a2 – bc + ab) = 0
b2 + c2 – 2bc – 4ac + 4a2 + 4bc – 4ab = 0
b2 + c2 + 2bc -4a (b + c) + 4a2 = 0
(b + c)2 – 4a (b + c) + 4a2 = 0
[(b+c) – 2a]2 = 0 [using a2 – 2ab + b2 = (a – b)2]
b + c – 2a = 0
b + c = 2a
b + c = a + a
c – a = a – b (t2 – t1 = t3 – t2)
b,a,c are in A.P.
![]()
Question 4.
If a, b are real then show that the roots of the equation (a – b)2 – 6(a + b)x – 9(a – b) = 0 are real and unequal.
Solution:
(a – b)x2 – 6(a + b)x – 9(a – b) = 0
Δ = b2 – 4ac
= (-6(a + b)2 – 4(a – b)(-9(a – b))
= 36(a + b)2 + 36(a – b)2
= 36 (a2 + 2ab + b2) + 36(a2 – 2ab + b2)
= 72a2 + 12b2
= 72(a2 + b2) > 0
∴ The roots are real and unequal.
![]()
Question 5.
If the roots of the equation (c2 – ab)x2 – 2(a2 – bc)x + b2 – ac = 0 are real and equal prove that either a = 0 (or) a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
Answer:
(c2 – ab)x2 – 2(a2 – bc)x + b2 – ac = 0
Here a = c2 – ab ; b = – 2 (a2 – bc); c = b2 – ac
Since the roots are real and equal
∆ = b2 – 4ac
[-2 (a2 – bc)]2 – 4(c2 – ab) (b2 – ac) = 0
4(a2 – bc)2 – 4[c2 b2 – ac3 – ab3 + a2bc] = 0
Divided by 4 we get
(a2 – bc)2 – [c2 b2 – ac3 – ab3 + a2bc] = 0
a4 + b2 c2 – 2a2 bc – c2b2 + ac3 + ab3 – a2bc = 0
a4 + ab3 + ac3 – 3a2bc = 0
= a(a3 + b3 + c3) = 3a2bc
a3 + b3 + c3 = \(\frac{3 a^{2} b c}{a}\)
a3 + b3 + c3 = 3 abc
Hence it is proved
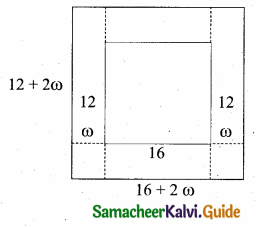
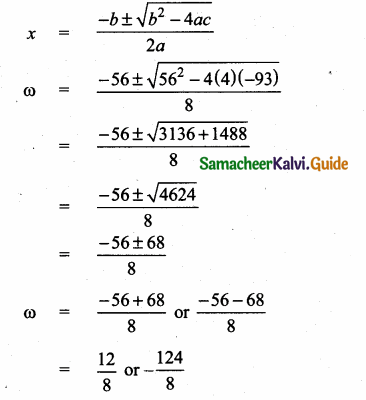
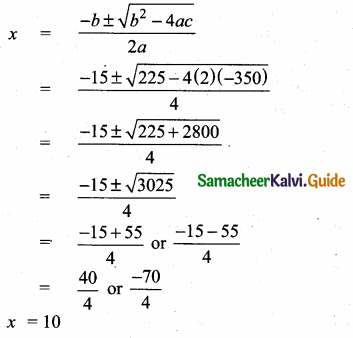
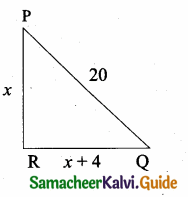
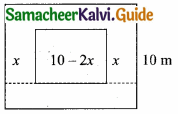
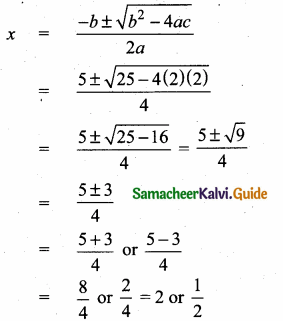
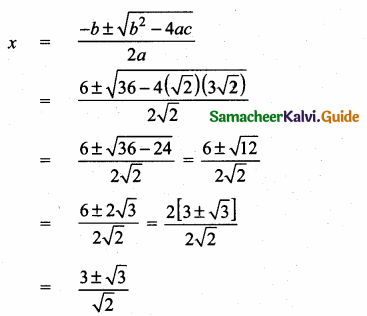
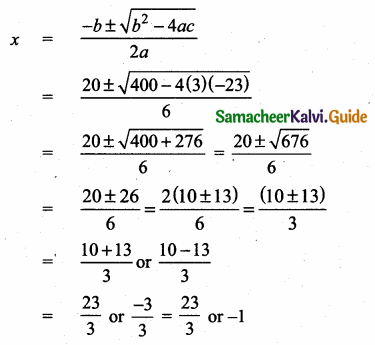
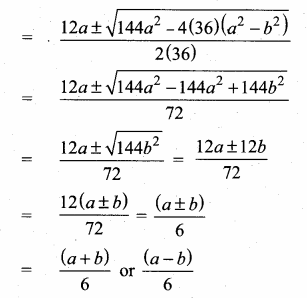
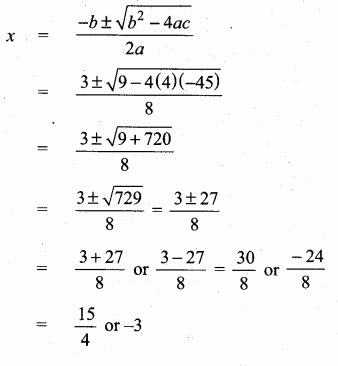



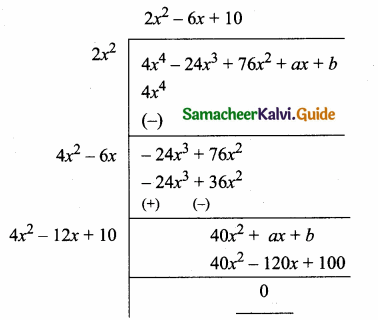
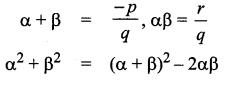
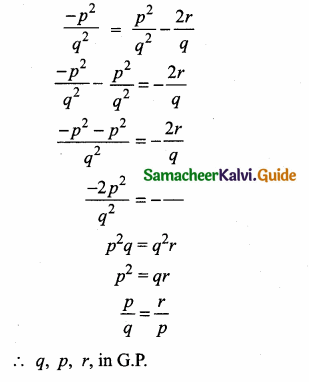
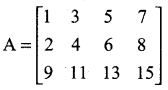
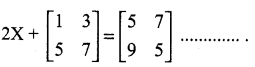


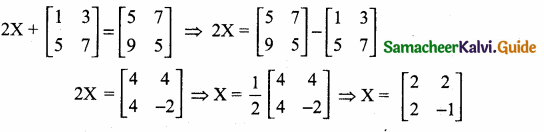
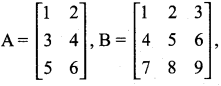
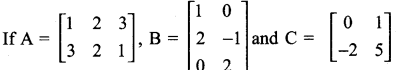
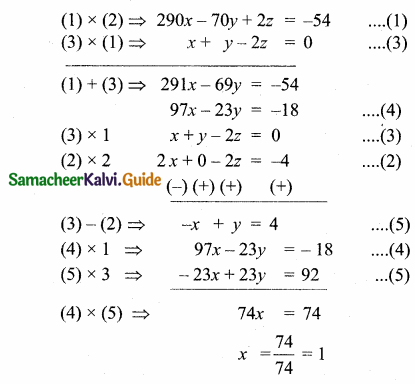
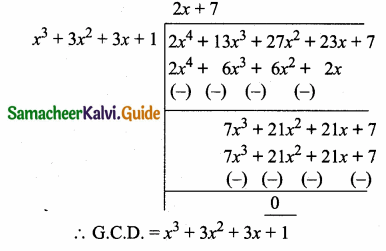
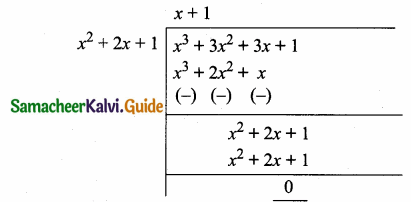
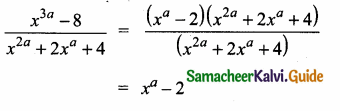
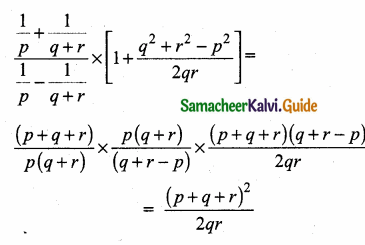
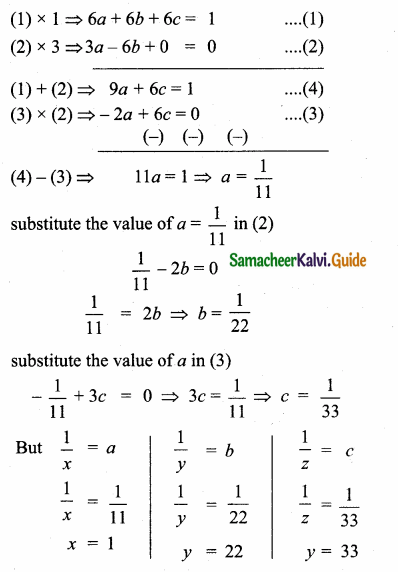

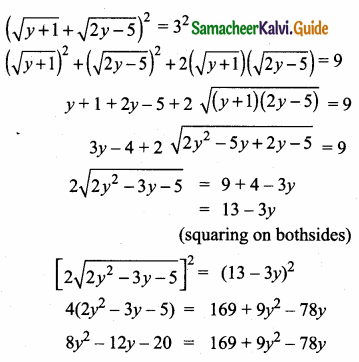

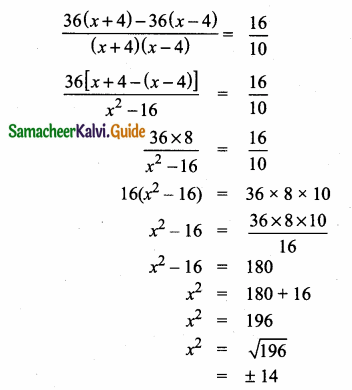
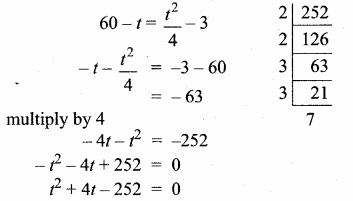
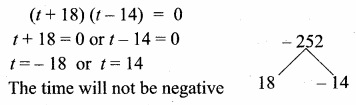
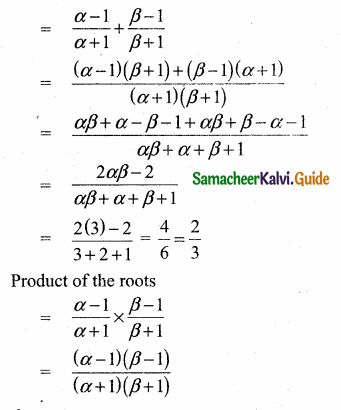
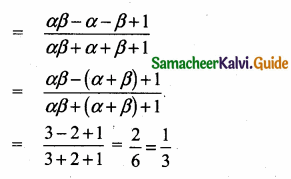
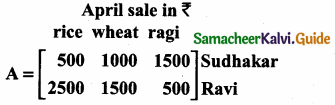


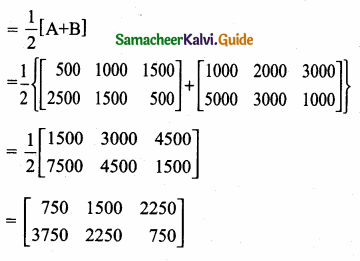
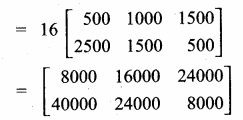
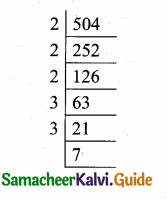
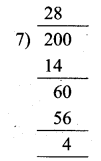
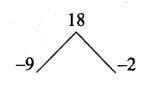
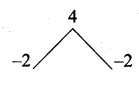
 = I2, find x.
= I2, find x.