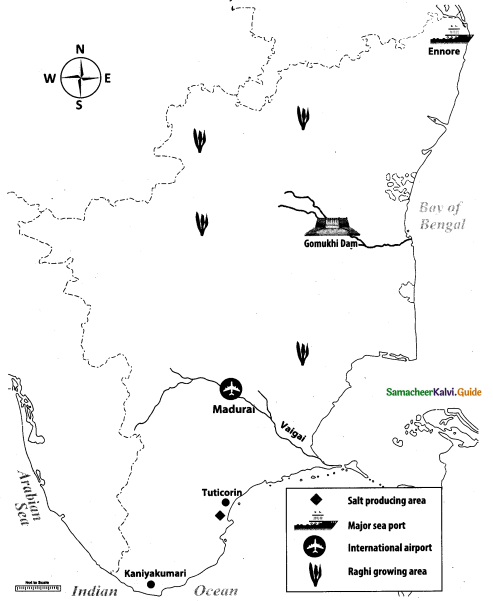
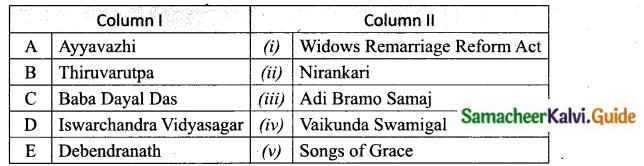
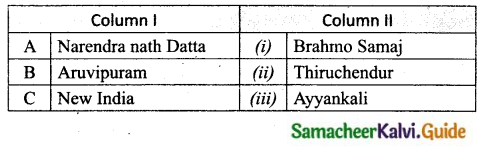
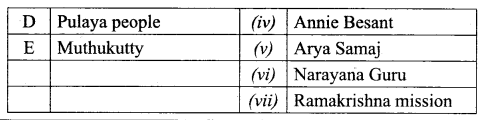
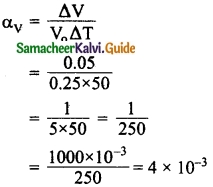
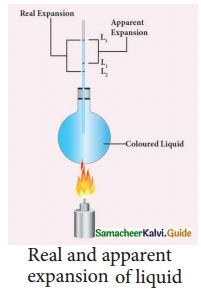
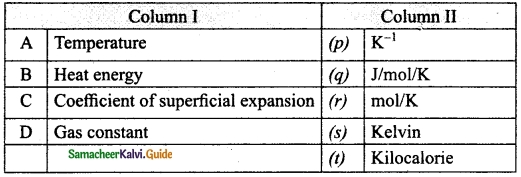
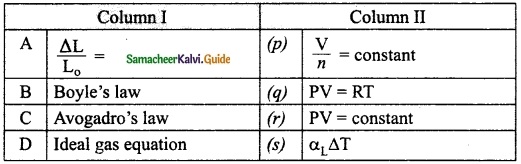
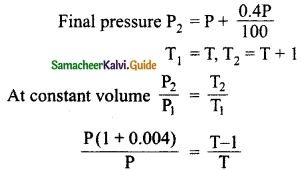
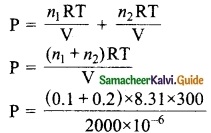
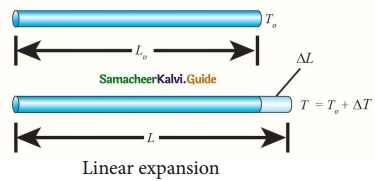
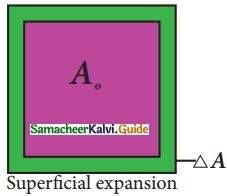
Expert Teachers at SamacheerKalvi.Guru has created Tamil Nadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers 2020-2021 Pdf Free Download of TN SSLC Class 10th Tamil Model Question Papers, Previous Year Question Papers, Sample Papers are part of Samacheer Kalvi 10th Model Question Papers 2021 Tamilnadu.
Here we have given the Government of TN State Board Samacheer Kalvi 10th Std Tamil Model Question Papers with Answers 2020-21 Pdf. Students can view or download the Samacheer Kalvi Class 10th Tamil New Model Question Papers 2021 Tamil Nadu Pdf for their upcoming TN SSLC board examinations. Students can also read Tamilnadu Samcheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Guide.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers 2020 2021
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers with Answers 2021 Tamil Nadu
- Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 1
- Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 2
- Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 3
- Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 4
- Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 5
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper Design 2020-2021 Tamil Nadu
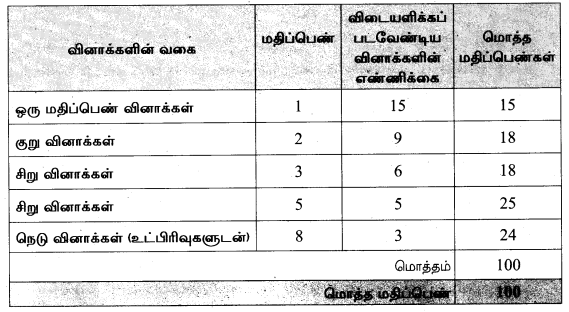
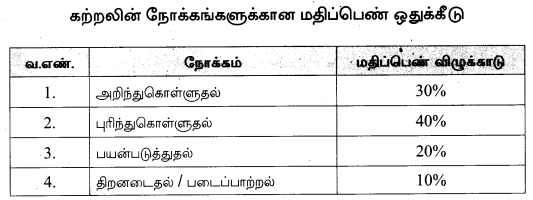
It is necessary that students will understand the new pattern and style of Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers 2021 Answer Keys according to the latest exam pattern. These State Board 10th Standard Tamil Public Exam Model Question Papers 2020-21 Tamil Nadu are useful to understand the pattern of questions asked in the board exam. Know about the important concepts to be prepared for TN SSLC Board Exams and Score More marks.
We hope the given Tamil Nadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi Class 10th Tamil Model Question Papers 2020 2021 Pdf Free Download will help you.
If you have any queries regarding the Government of TN State Board Samacheer Kalvi SSLC 10th Standard Tamil Model Question Papers with Answers 2020 21, Sample Papers, Previous Year Question Papers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.