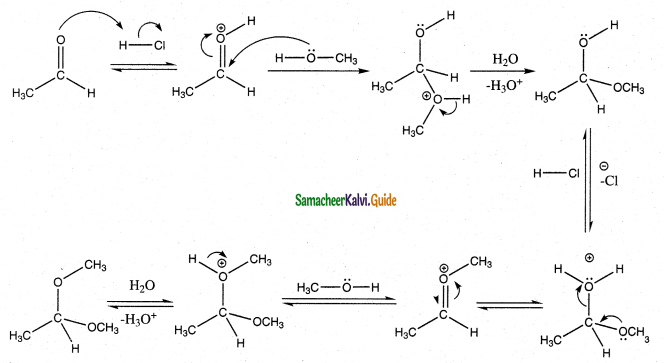
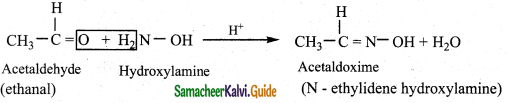
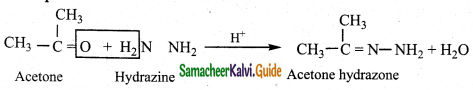
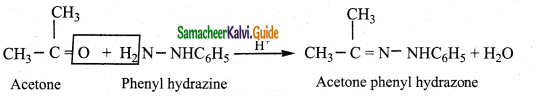
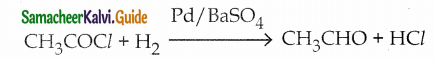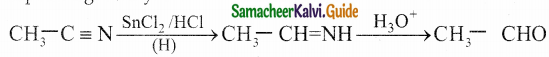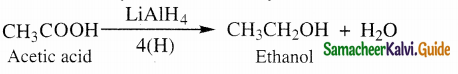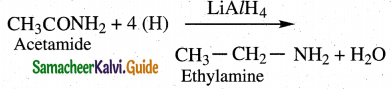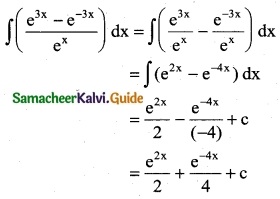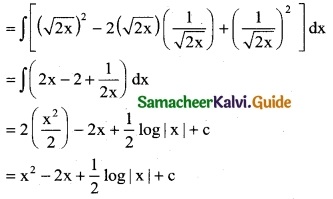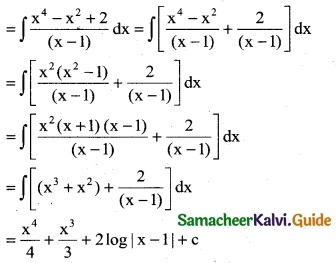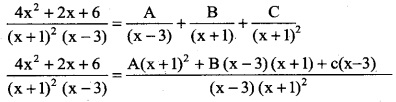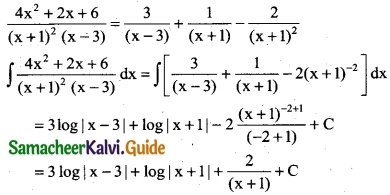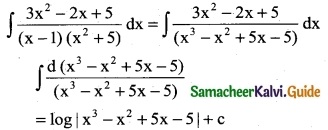Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.6 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.6
Question 1.
Integrate the following with respect to x.
\(\frac { 2x+5 }{x^2+5x-7}\)
Solution:
∫\(\frac { 2x+5 }{x^2+5x-7}\) dx
∫\(\frac { 1 }{z}\) dz
= log |z| + c
= log |x² + 5x – 7| + c
Take z = x² + 5x – 7
\(\frac { dz }{dx}\) = 2x + 5
dz = (2x + 5)dx
![]()
Question 2.
\(\frac { e^{3logx} }{x^4+1}\)
Solution:
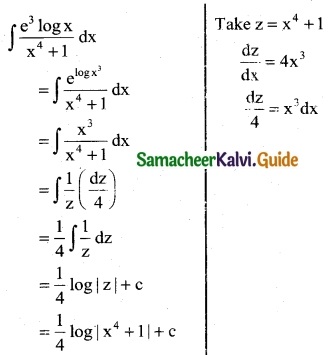
Question 3.
\(\frac { e^{2x} }{e^{2x}-2}\)
Solution:
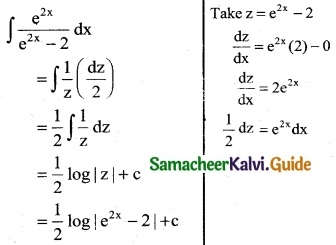
Question 4.
\(\frac { (logx)^3 }{x}\)
Solution:
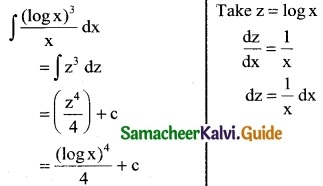
![]()
Question 5.
\(\frac { 6x+7 }{\sqrt{3x^2+7x-1}}\)
Solution:
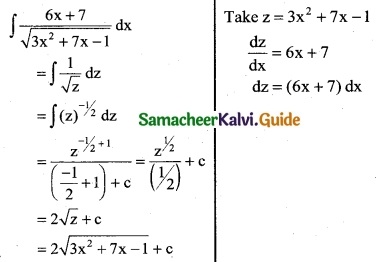
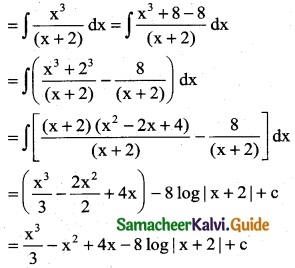
Question 6.
(4x + 2) \(\sqrt {x^2+x+1}\)
Solution:
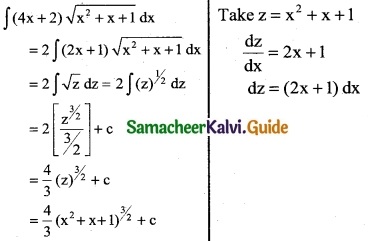
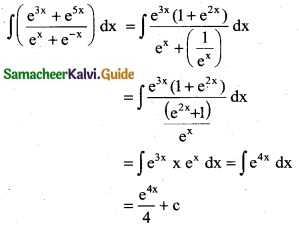
Question 7.
x8 (1 + x9)5
Solution:
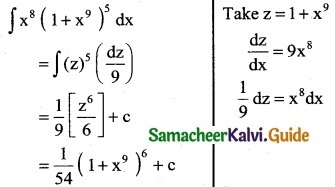
![]()
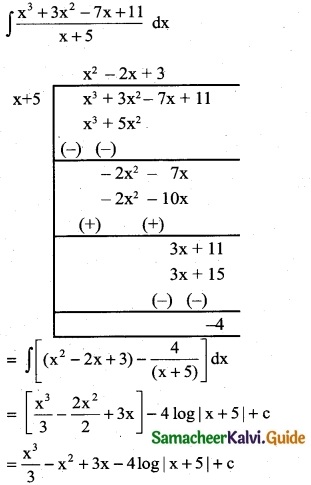
Question 8.
\(\frac { x^{e-1}+e^{x-1} }{x^e+e^x}\)
Solution:
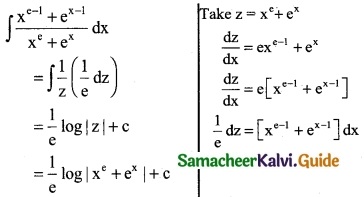
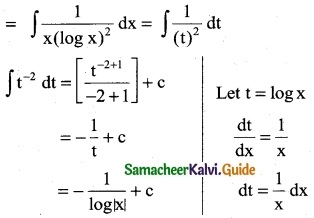
Question 9.
\(\frac { 1 }{x log x}\)
Solution:
∫\(\frac { 1 }{x log x}\) dx
∫\(\frac { 1 }{z}\) dz
= log |z| + c
= log |log x| + c
Take z = log x
\(\frac { 1 }{z}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{x}\)
dz = \(\frac { 1 }{x}\) dx
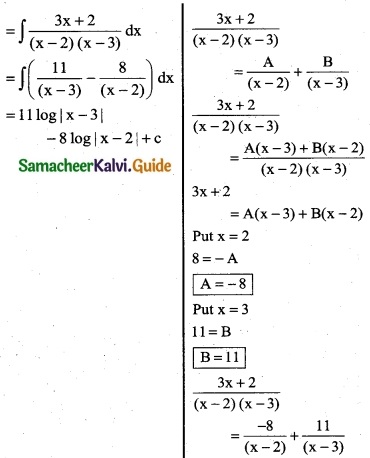
Question 10.
\(\frac { x }{2x^4-3x^2-2}\)
Solution:
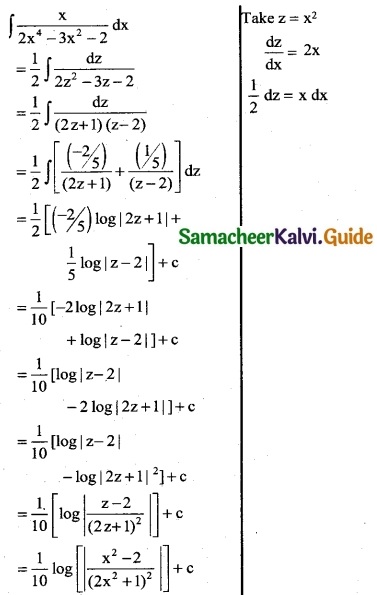
![]()
Question 11.
ex (1 + x) log (xex)
Solution:
ex (1 + x) log(x ex) = (ex + x ex) log (x ex)
Let z = x ex, Then dz = d(x ex)
dz = (x ex + ex) dx (Using product rule)
So ∫ ex (1 + x) log (x ex) dx
= ∫ log (x ex) (ex + x ex) dx
= ∫ log z dz
= z (log z – 1) + c
= x ex [log (x ex) – 1] + c

Question 12.
\(\frac { 1 }{x(x^2+1)}\)
Solution:
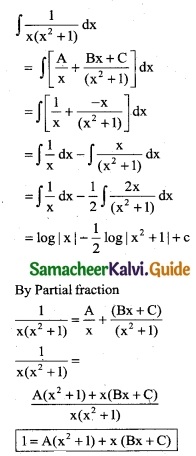
Put x = 0
1 = A(1)
A = 1
Put x = 1
1 = A(2) + 1(B + C)
1 = (1)2 + B + C
B + C = -1 …….. (1)
Put x = -1
1 = A[(-1)² + 1] + (-1)[B(-1) + C]
1 = A(2) – (-B + C)
1 = 2A + B – C
1 = 2(1) + B – C
B – C = -1 ………. (2)
Adding (1) & (2)
2B = -2
B = -1
C = 0
![]()
Question 13.
ex [ \(\frac { 1 }{x^2}\) – \(\frac { 2 }{x^3}\) ]
Solution:
∫ex [ \(\frac { 1 }{x^2}\) – \(\frac { 2 }{x^3}\) ] dx
= ∫ex [f(x) + f'(x)] dx
= ex f(x) + c
= ex [ \(\frac { 1 }{x^2}\) ] + c
Take
f(x) = \(\frac { 1 }{x^2}\)
f'(x) = \(\frac { -2 }{x^3}\)
Question 14.
ex [ \(\frac { x-1 }{(x+1)^3}\) ]
Solution:
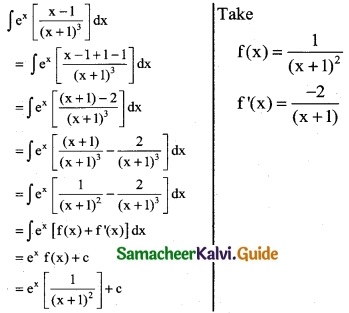
Question 15.
e3x [ \(\frac { 3x-1 }{9x^2}\) ]
Solution:
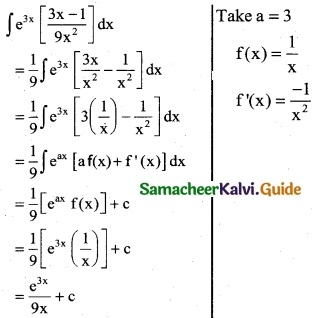
![]()
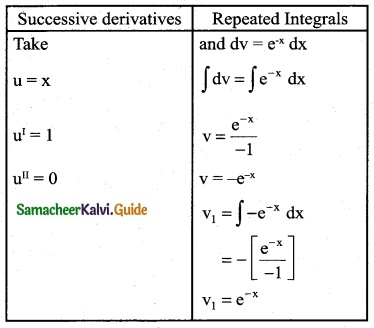
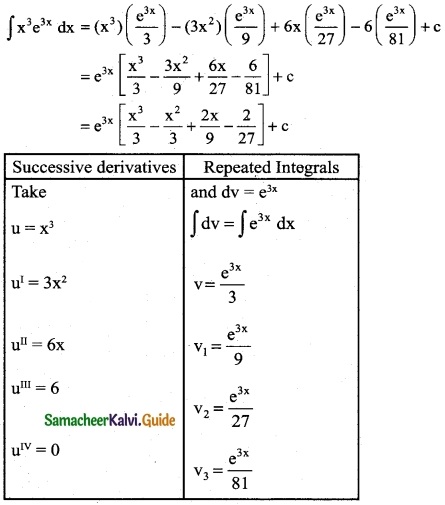
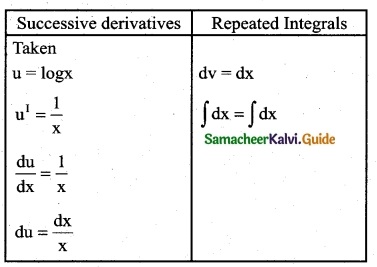
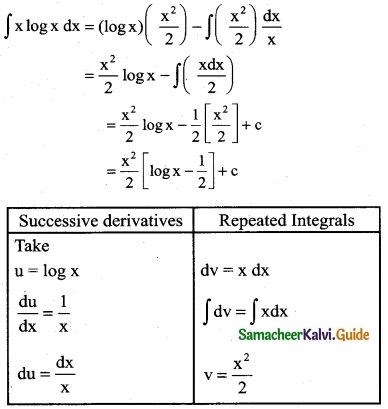
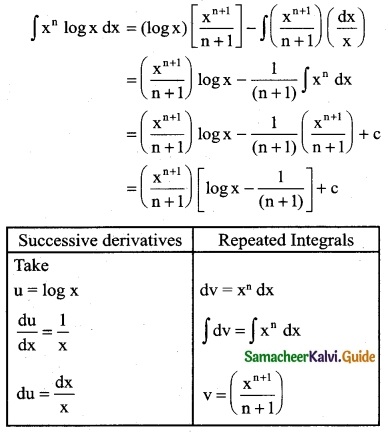
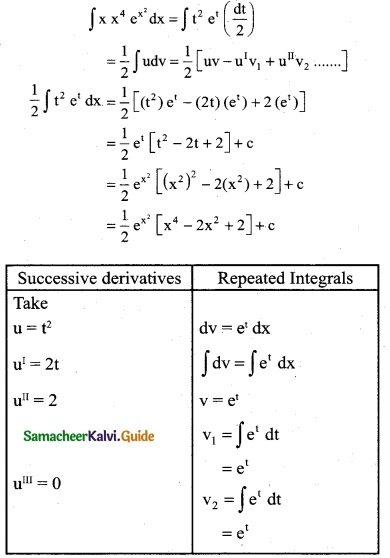
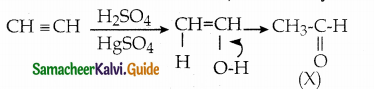
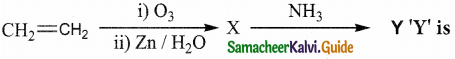
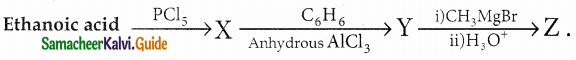
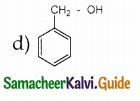
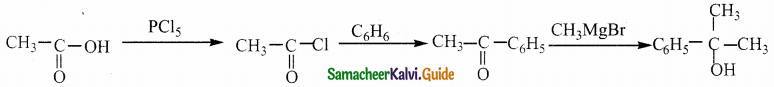
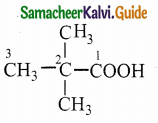
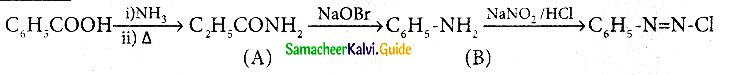
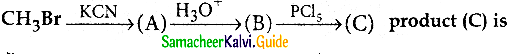
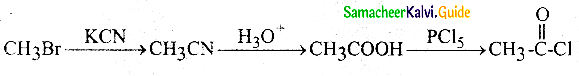
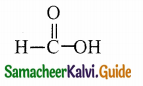
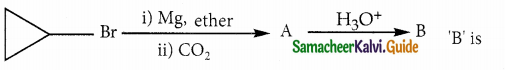
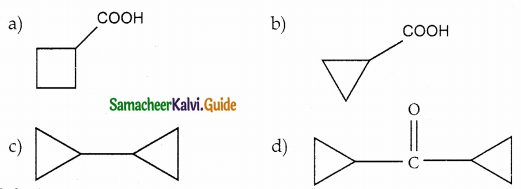
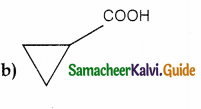
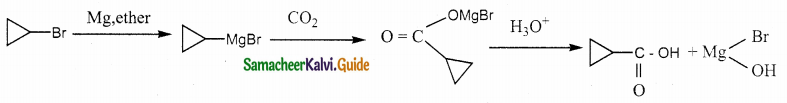
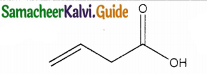
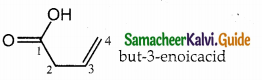
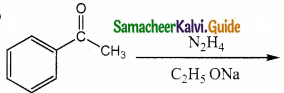
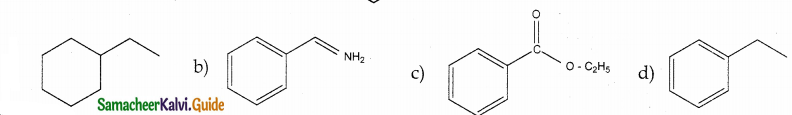 Answer:
Answer: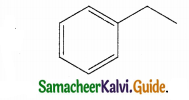
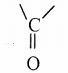
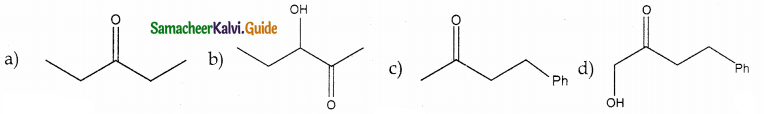
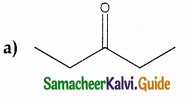
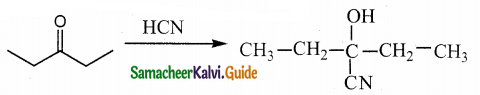
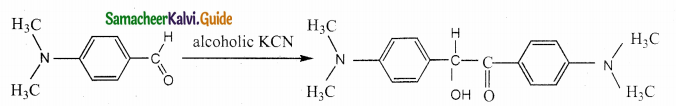
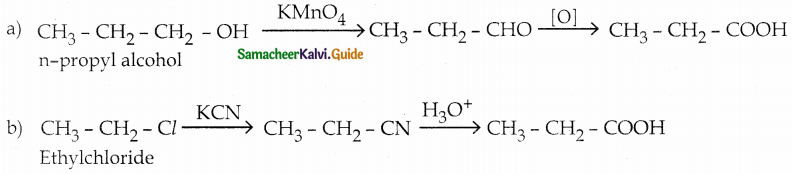
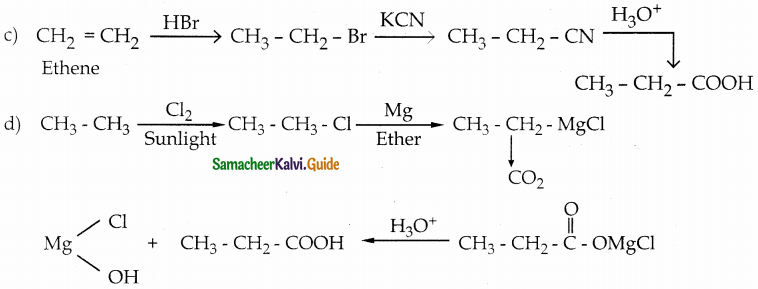
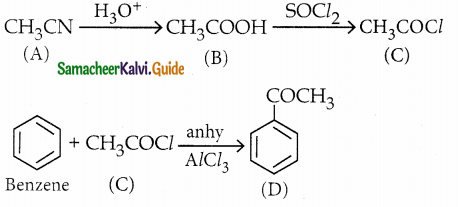
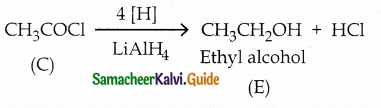
 Answer:
Answer:
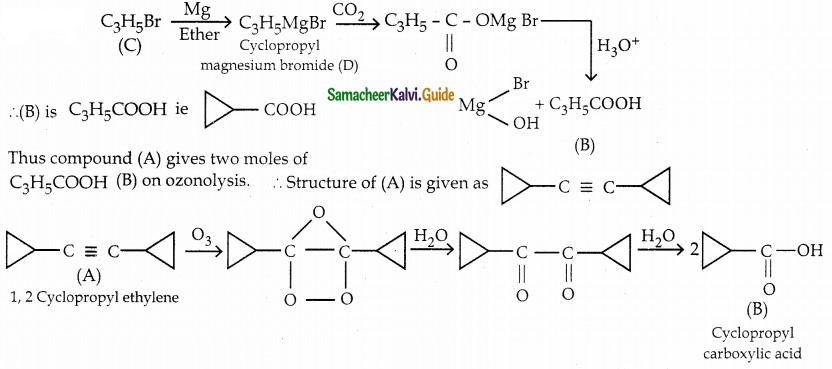
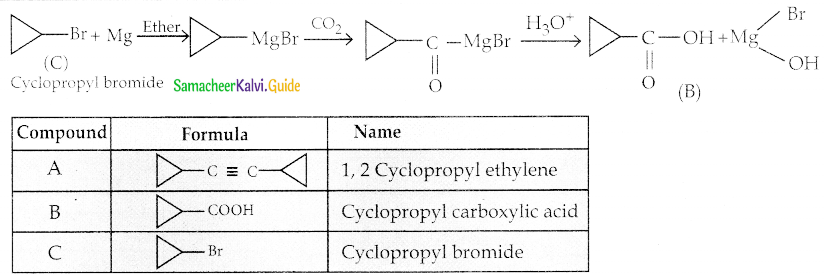
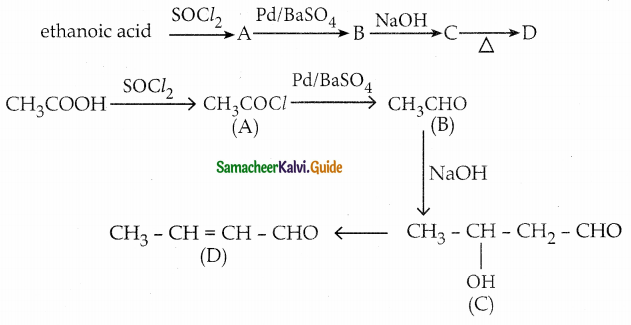
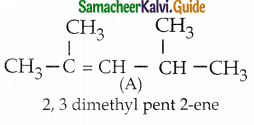
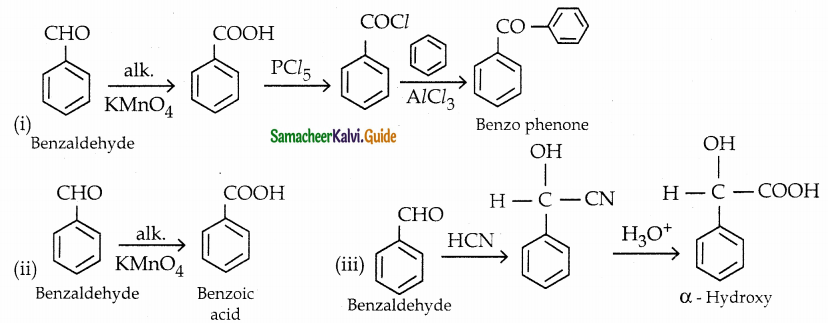
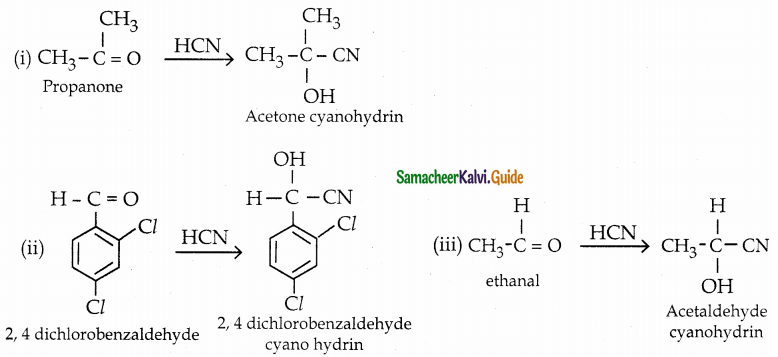
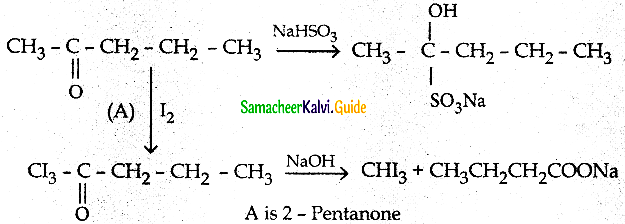
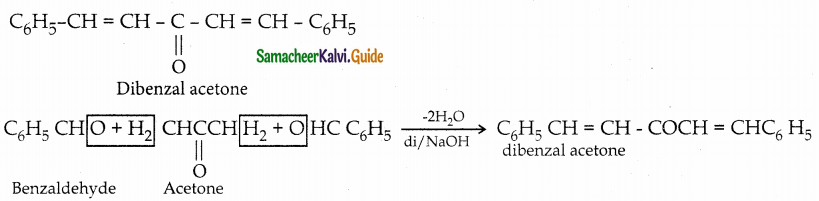
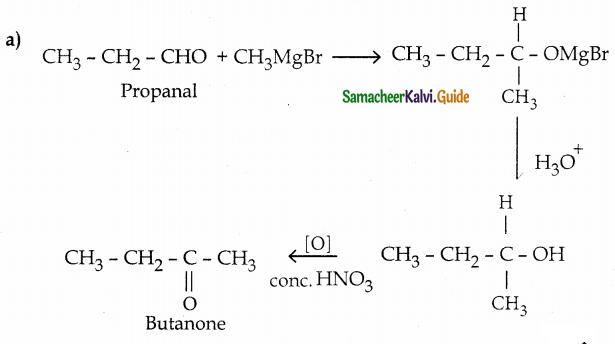
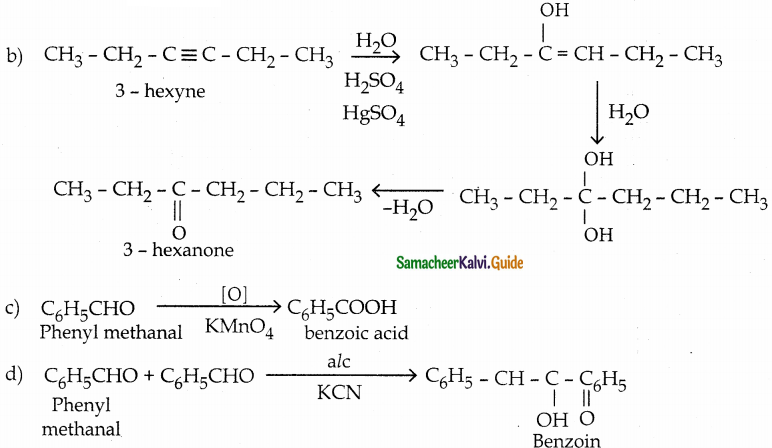

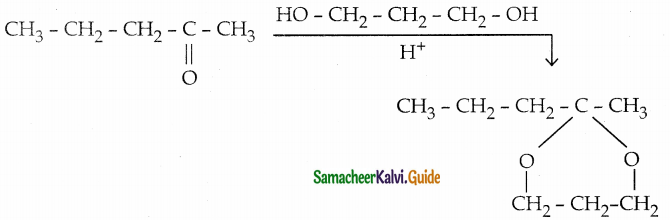
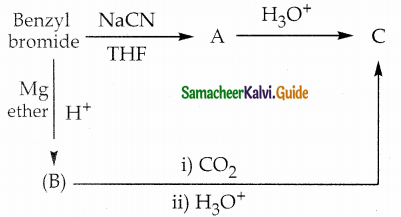
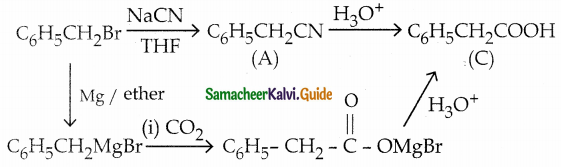
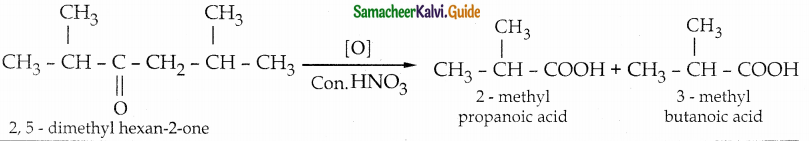
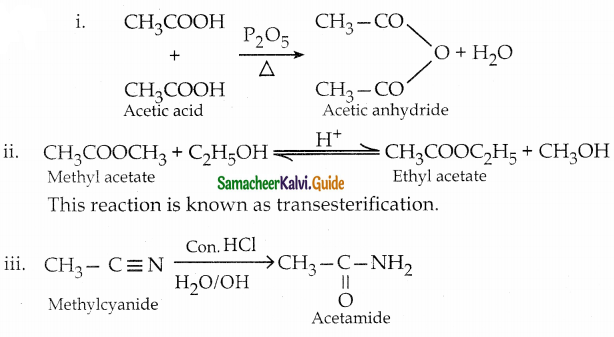
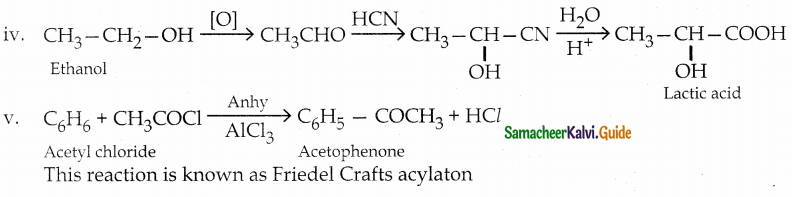
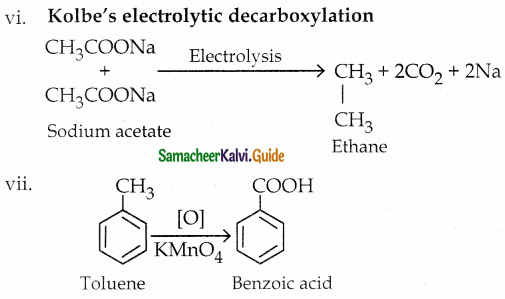
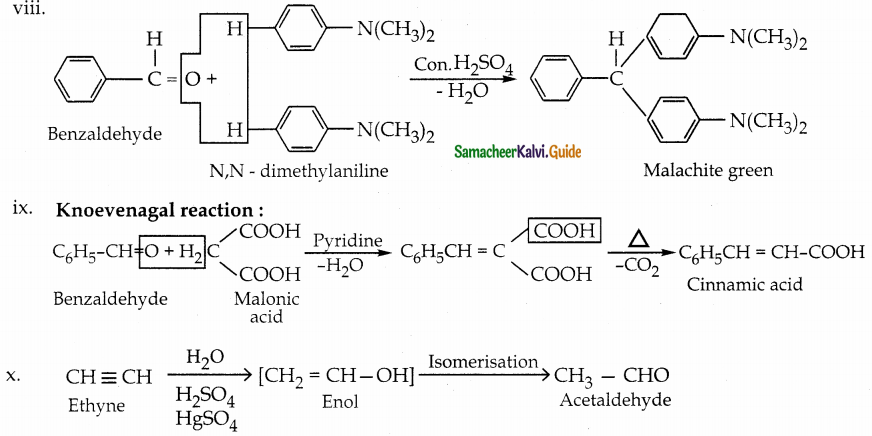
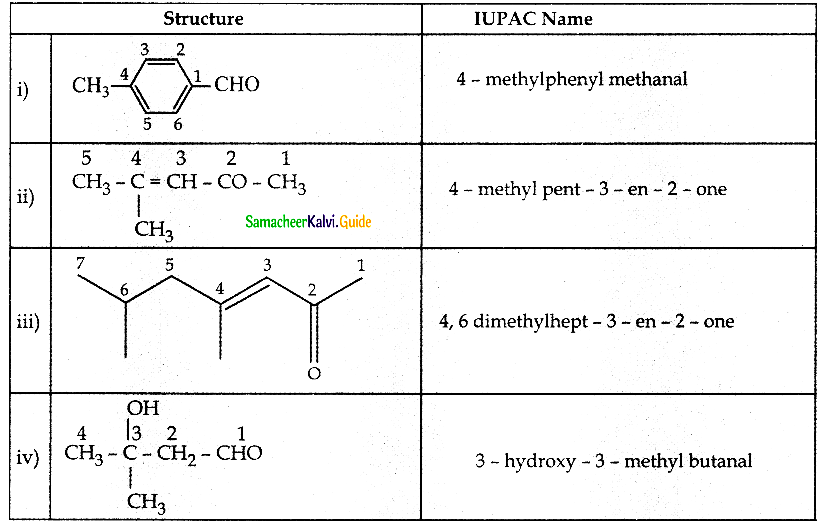
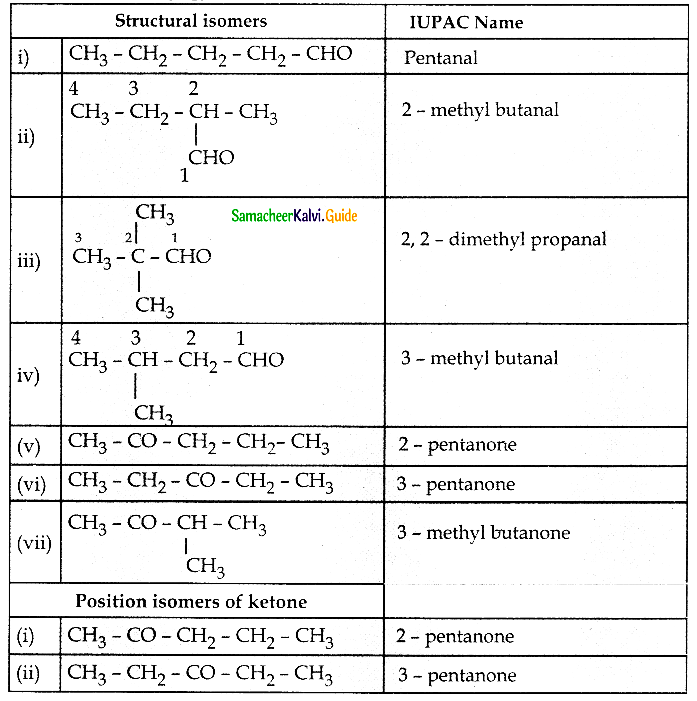
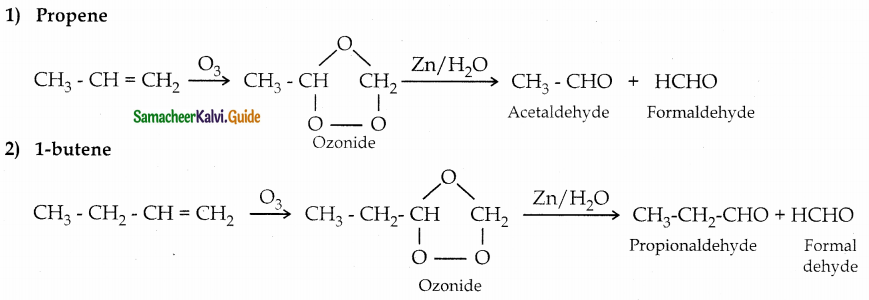
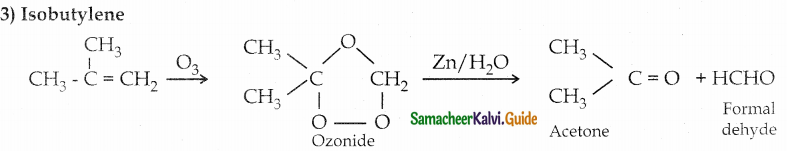
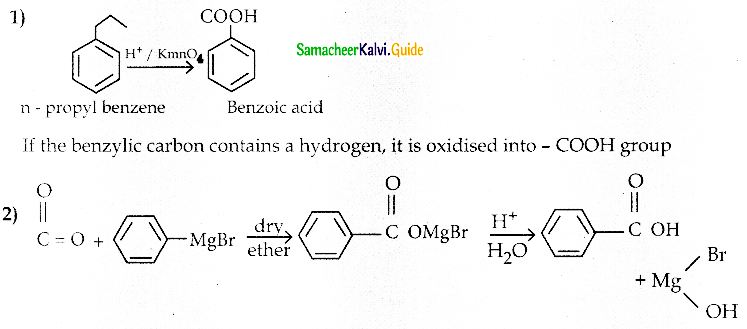

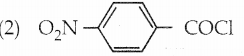
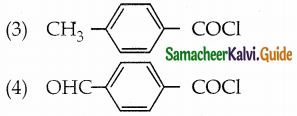
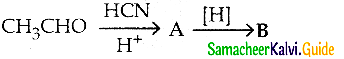

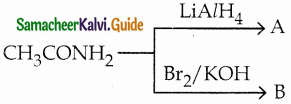
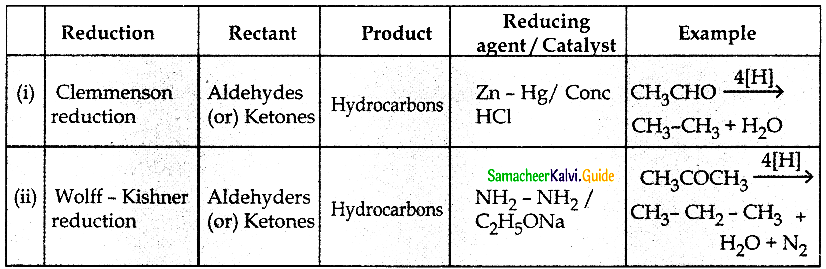
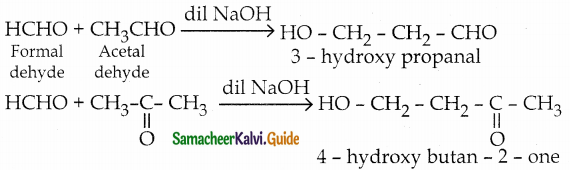
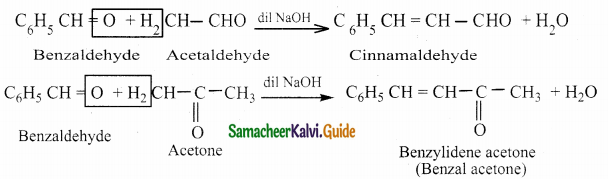
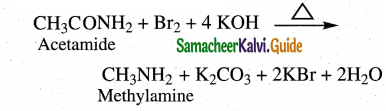
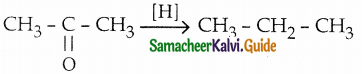 The reducing agent used in this reaction is
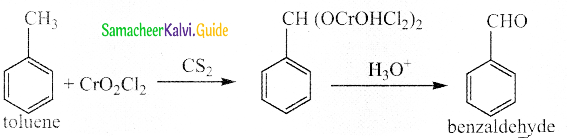
The reducing agent used in this reaction is