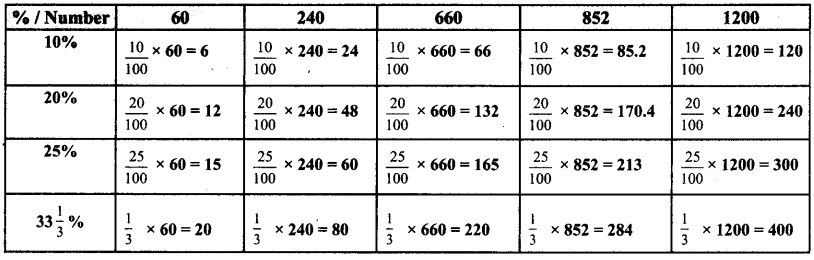
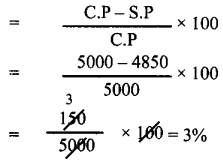
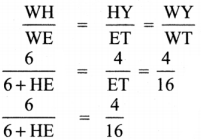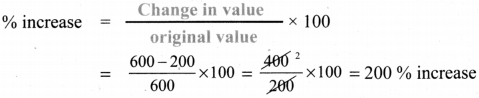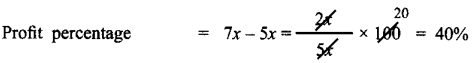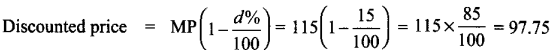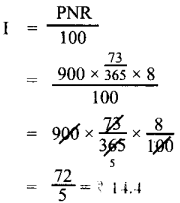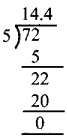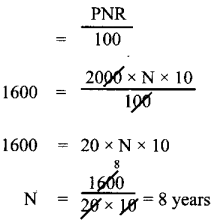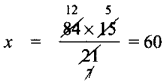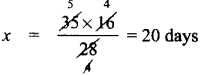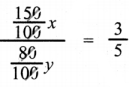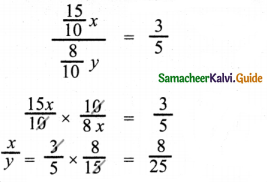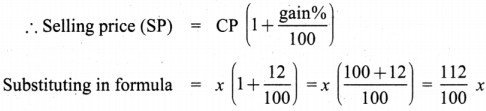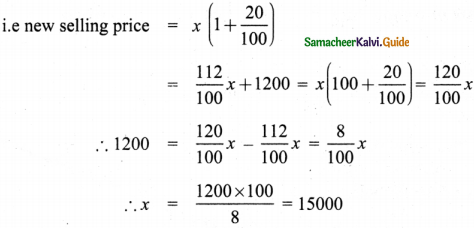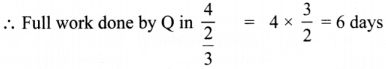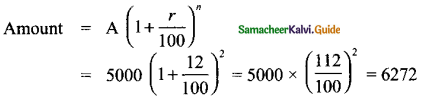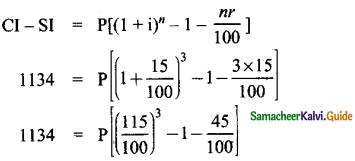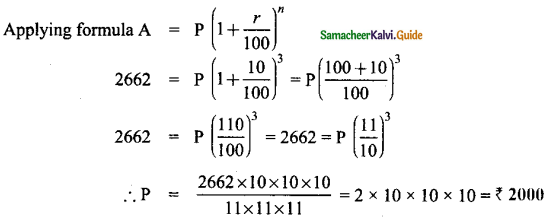Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 5 Geometry InText Questions Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Geometry InText Questions
Answer the following questions by recalling the properties of triangles:
Question 1.
The sum of the three angles of a triangle is _________ .
Answer:
180°
Question 2.
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the _______ angles to it.
Answer:
interior
![]()
Question 3.
In a triangle, the sum of any two sides is ________ than the third side.
Answer:
greater
Question 4.
Angles opposite to equal sides are ________ and vice – versa.
Answer:
Equal
Question 5.
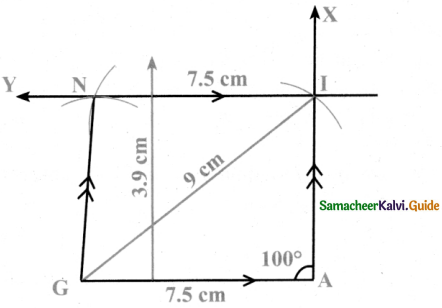
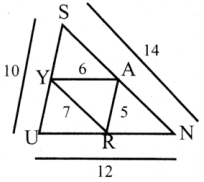
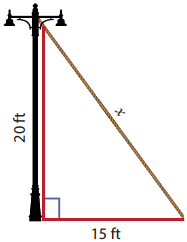
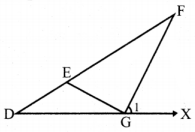
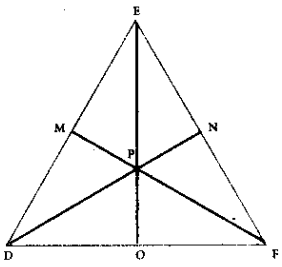
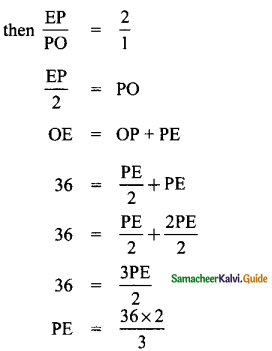
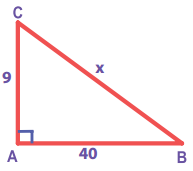
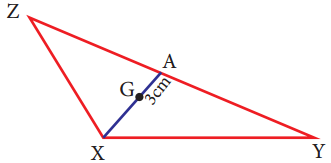
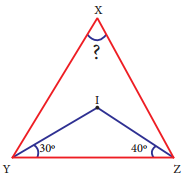
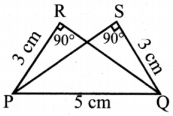
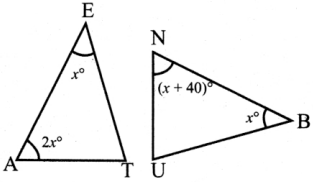
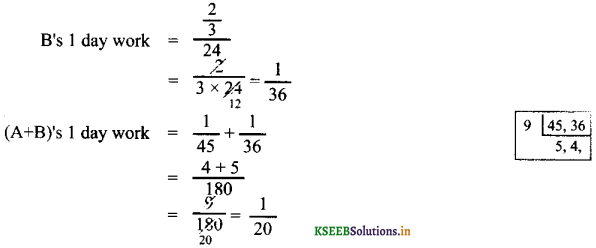
What is ∠A in the triangle ABC?
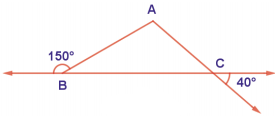
Answer:
The exterior angle = sum of interior opposite angles.
∴ ∠A + ∠C = 1500 in ∆ABC
But ∠C = 40°
[∵Vertically opposite angler are equal]
∴ ∠A + ∠C = 150°
⇒ ∠A + ∠40° = 150°
∠A = 150° – 40°
∠A = 1100
![]()
Try These (Text Book page No. 157)
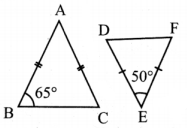
Identify the pairs of figures which are similar and congruent and write the letter pairs.
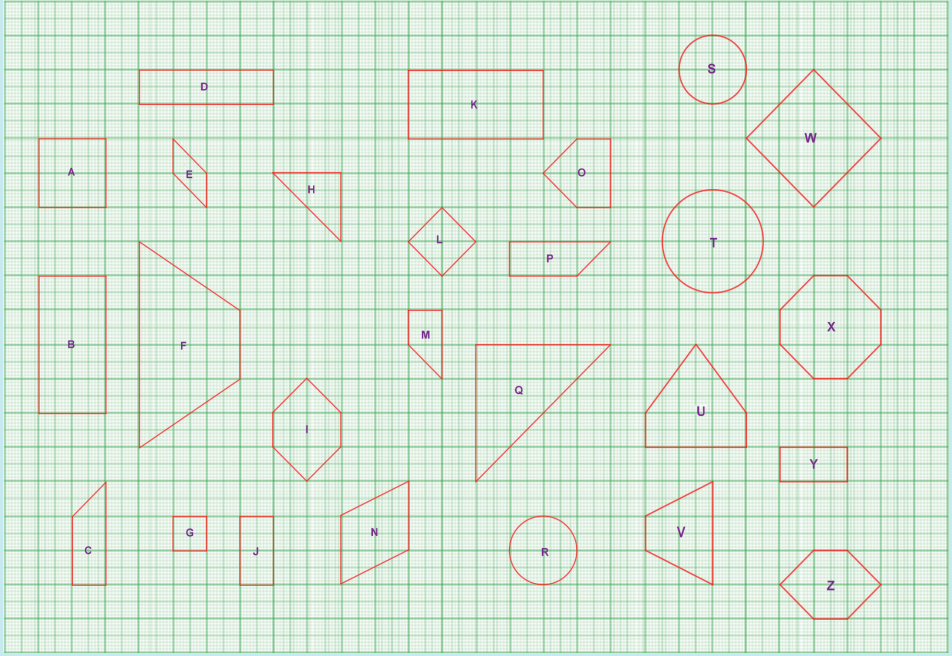
Answer:
Similar shapes:
(i) Wand L
(ii) B and J
(iii) A and G
(iv) B and J
(v) B and Y
(vi) E and N
(vii) H and Q
(viii) R and T
(ix) S and T
Congruent shapes:
(i) Z and I
(ii) J and Y
(iii) C and P
(iv) B and K
(v) R and S
(vi) I and Z
You can find more.
![]()
Try These (Text Book page No. 158)
Question 1.
Match the following by their congruence property
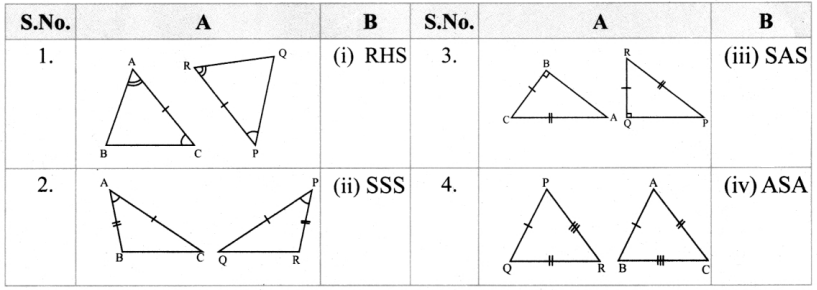
Answer:
1. – (iv),
2. – (iii),
3. – (i),
4. – (ii)
![]()
Think (Text Book page No. 160)
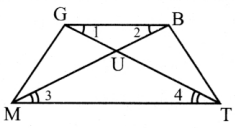
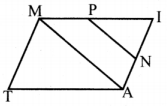
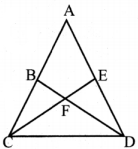
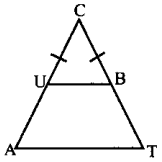
In the figure, DA = DC and BA = BC. Are the triangles DBA and DBC congruent? Why?
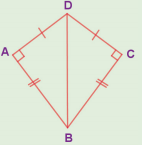
Answer:
Here AD = CD
AB = CB
DB = DB (common)
∆DB ≡ ∆DBC
[∵ By SSS congruency]
Also RHS rule also bind here to say their congruency.
![]()
Activity (Text Book page No. 169)
Question 1.
We can construct sets of Pythagorean triplets as follows.
Let m and n be any two positive integers (m > n):
(a, b, c) is a Pythagorean triplet if a = m2 – n2, b = 2mn and c = m2 + n2 (Think, why?)
Complete the table.

Answer:
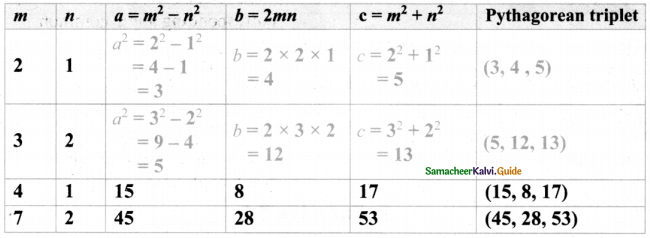
![]()
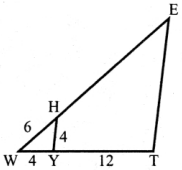
Question 2.
Find all integer-sided right angled triangles with hypotenuse 85.
Answer:
(x + y)2 – 2xy = 852

Think (Text Book page No. 173)
Question 1.
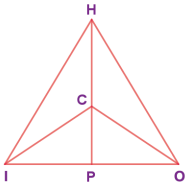
In any acute angled triangle, all three altitudes are inside the triangle. Where will be the orthocentre? In the interior of the triangle or in its exterior?
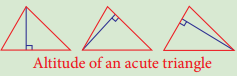
Answer:
Interior of the triangle
Question 2.
In any right angled triangle, the altitude perpendicular to the hypotenuse is inside the triangle; the other two altitudes are the legs of the triangle. Can you identify the orthocentre in this case?
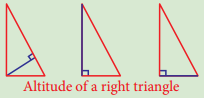
Answer:
Vertex containing 90°
![]()
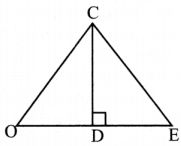
Question 3.
In any obtuse angled triangle, the altitude connected to the obtuse vertex is inside the triangle, and the two altitudes connected to the acute vertices are outside the triangle. Can you identify the orthocentre in this case?
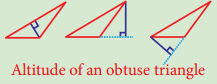
Answer:
Exterior of the triangle.
Try These (Text Book page No. 177)
Identify the type of segment required in each triangle:
(median, altitude, perpendicular bisector, angle bisector)
(i)
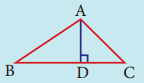
AD = _______
Answer:
AD = Altitude
(ii)
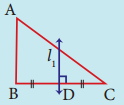
l1 = _______
Answer:
l1 = perpendicular bisector
![]()
(iii)
BD = _______
Answer:
BD = Median
(iv)
CD = _______
Answer:
CD = Angular bisector
Think (Text Book page No. 187)
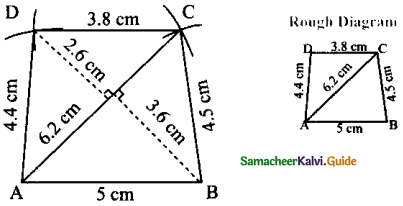
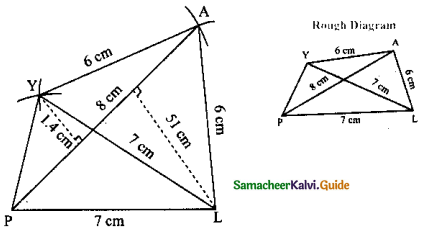
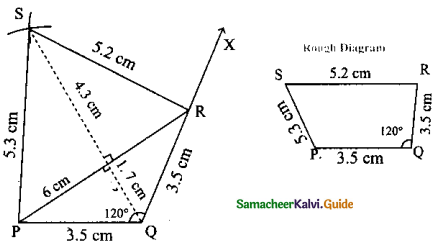
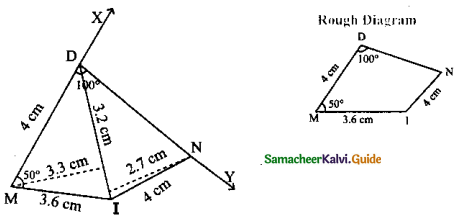
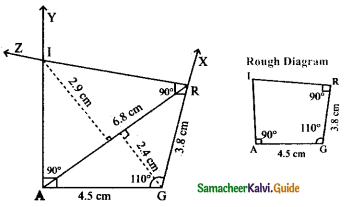
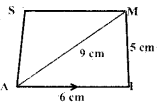
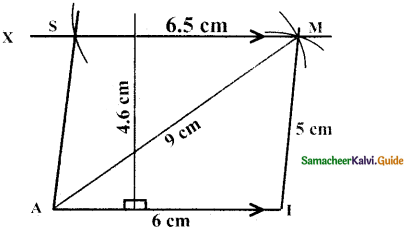
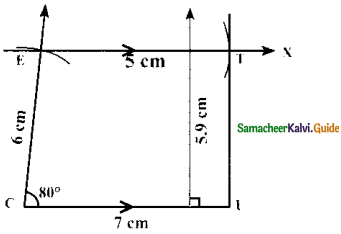
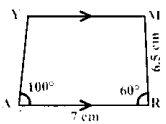
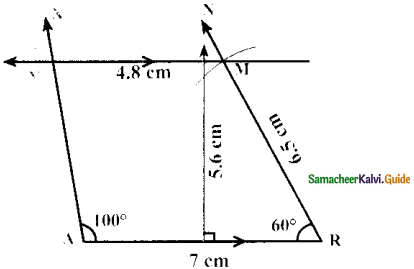
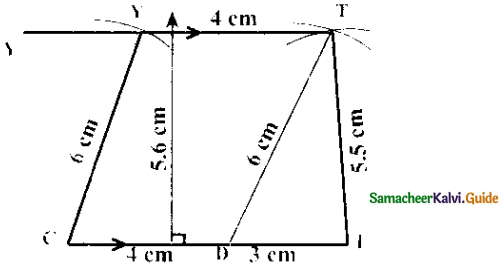
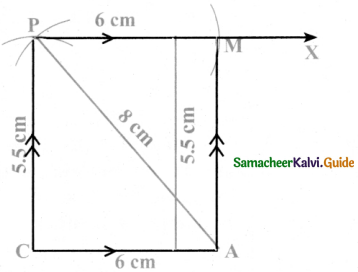
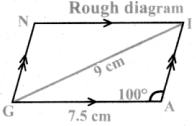
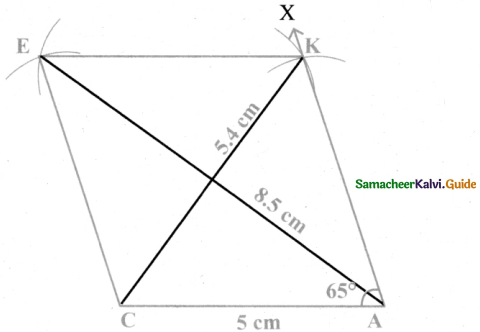
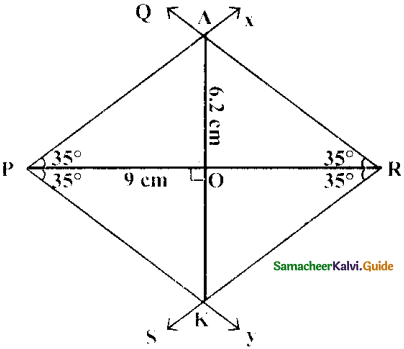
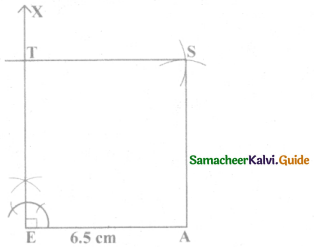
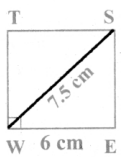
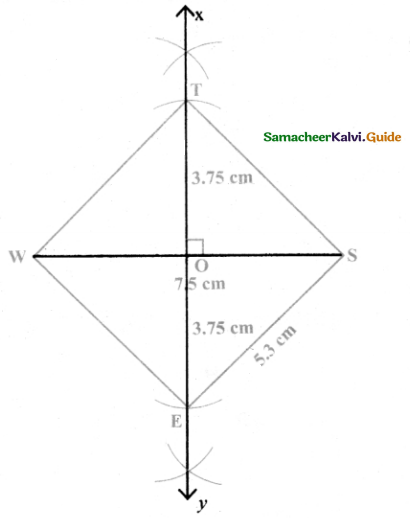
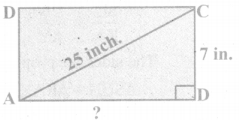
Is it possible to construct a quadrilateral PQRS with PQ = 5 cm, QR = 3cm, RS = 6cm, PS = 7cm and PR = 10cm. If not,why?
Answer:
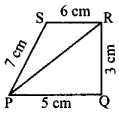
The lower triangle cannot be constructed as the sum of two sides 5 + 3 = 8 < 10 cm. So this quadrilateral cannot be constructed,
![]()
Try These (Text Book page No. 187)
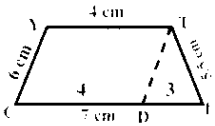
Question 1.
The area of the trapezium is ________ .
Answer:
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × h × (a + b) sq. units
Question 2.
The distance between the parallel sides of a trapezium is called as ________ .
Answer:
its height
Question 3.
If the height and parallel sides of a trapezium are 5cm, 7cm and 5cm respectively, then
its area is ________ .
Answer:
30
Hints:
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × h × (a + b) sq. units
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 5 × (7 + 5) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 5 × 12 = 30 sq. cm
![]()
Question 4.
In an isosceles trapezium, the non-parallel sides are _________ in length.
Answer:
equal
Question 5.
To construct a trapezium, _________ measurements are enough.
Answer:
Four
Question 6.
If the area and sum of the parallel sides are 60 cm2 and 12 cm, its height is ________ .
Answer:
10 cm
Hint:
Area of the trapezium = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × h (a + b)
60 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × h × (12)
∴ h = \(\frac{60 \times 2}{12}\) = 10cm
![]()
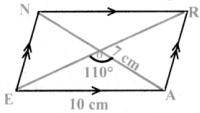
Activity (Text Book page No. 193 & 194)
Question 1.
A pair of identical 30° – 60° – 90° set-squares are needed for this activity. Place them as shown in the figure.
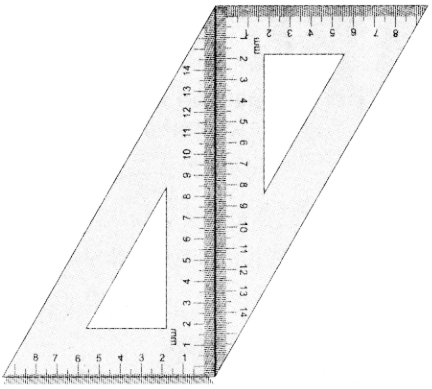
(i) What is the shape we get? It is a parallelogram.
Answer:
(ii) Are the opposite sides parallel?
Answer:
Yes
(iii) Are the opposite sides equal?
Ans:
Yes
(iv) Are the diagonals equal?
Answer:
No
(v) Can you get this shape by using any other pair of identical set-squares?
Answer:
Yes
![]()
Question 2.
We need a pair of 30° – 60° – 90° set- squares for this activity. Place them as shown in the figure.
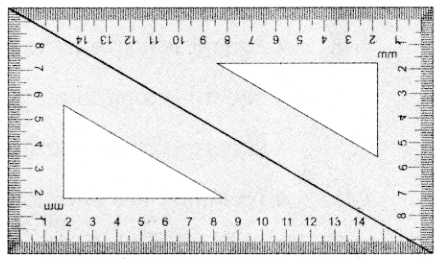
(i) What is the shape we get’?
Ans:
Rectangle
(ii) Is it a parallelogram?
Answer:
Yes
(iii) It is a quadrilateral; infact it is a rectangle. (How?)
Ans:
Opposits sides are equal.
All angles = 90°
(iii) What can we say about its lengths of sides, angles and diagonals?
Discuss and list them out.
Answer:
Opposite sides are equal
All angles are equal and are = 90°
Diagonals arc equal
![]()
Question 3.
Repeat the above activity, this time with a pair of 45° – 45° – 90° set-squares.
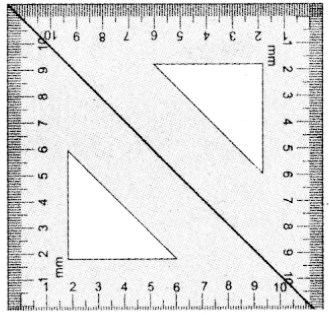
(i) How does the figure change now? Is it a parallelogram? It becomes a square! (How did it happen?)
Ans:
All sides are equal
(ii) What can we say about its lengths of sides, angles and diagonals? Discuss and list them out.
Answer:
All sides are equal
All angles = 90°
Diagonals equal
(iii) How does it differ from the list we prepared for the rectangle?
Answer:
All sides are equal.
Diagonals bisects each other.
![]()
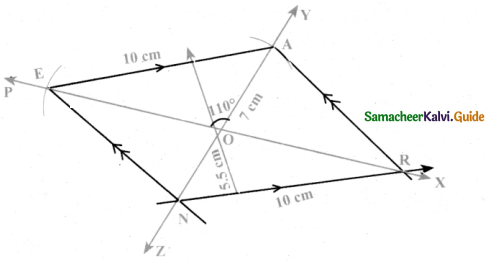
Question 4.
We again use four Identical 30° – 60° – 90° set- squares for this activity.
Note carefully how they are placed touching one another.
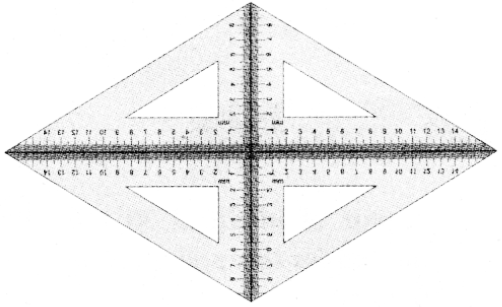
(j) Do we get a parallelogram now?
Answer:
Yes
(ii) What can we say about its lengths of sides, angles and diagonals’?
Answer:
All sides equal.
opposite sides arc equal and parallel.
(iii) What is special about their diagonals?
Answer:
Diagonals bisects perpendicularly.
![]()
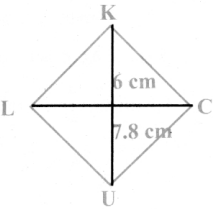
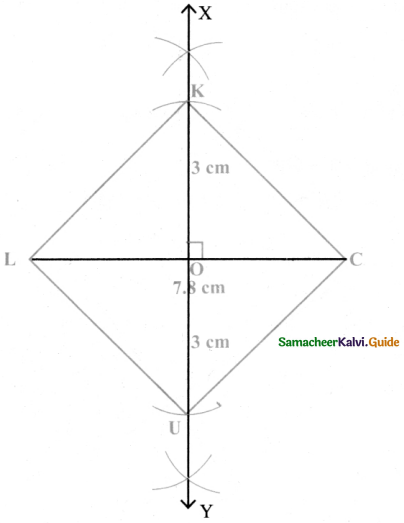
Try These (Text Book Page No. 195 & 196)
Question 1.
Say True or False:
(a) A square is a special rectangle.
Answer:
True
(b) A square is a parallelogram.
Answer:
True
(c) A square is a special rhombus.
Answer:
True
(d) A rectangle is a parallelogram
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 2.
Name the quadrilaterals
(a) Which have diagonals bisecting each other.
Answer:
Square, rectangle, parallelogram, rhombus.
(b) In which the diagonals are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Answer:
Rhombus and square.
(c) Which have diagonals of different lengths.
Answer:
Parallelogram and Rhombus
(d) Which have equal diagonals.
Answer:
Rectangle, square.
(e) Which have parallel opposite sides.
Answer:
Square, Rectangle. Rhombus, parallelogram.
(f) In which opposite angles are equal.
Answer:
Square, rectangle. rhombus, parallelogram
![]()
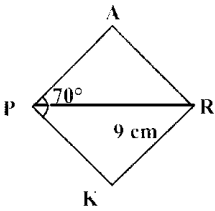
Question 3.
Two sticks are placed on a ruled sheet as shown. What figure is formed if the four corners of the sticks are joined?
(a)
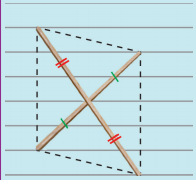
Two unequal sticks. Placed such that their midpoints coincide.
Answer:
parallelogram
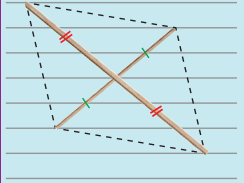
(b)
Two equal sticks. Placed such that their midpoints coincide.
Answer:
Rectangle
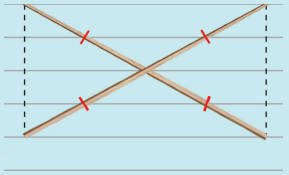
(c)
Two unequal sticks. Placed intersecting at mid points perpendicularly.
Answer:
Rhombus
![]()
(d)
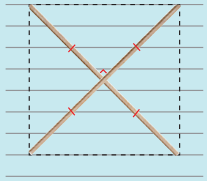
Two equal sticks. Placed intersecting at mid points perpendicularly.
Answer:
Square
(e)
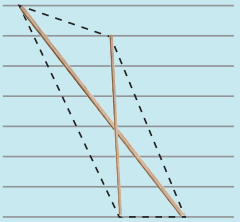
Two unequal sticks. Tops are not on the same ruling. Bottoms on the same ruling. Not cutting at the mid point of either.
Answer:
Quadrilateral
![]()
(f)
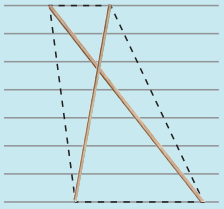
Two unequal sticks. Tops on the same ruling. Bottoms on the same ruling. Not necessarily cutting at
the mid point of either.
Answer:
Trapezium