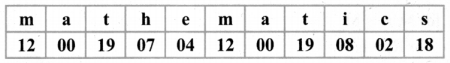
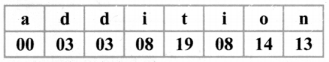
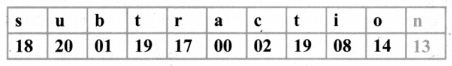
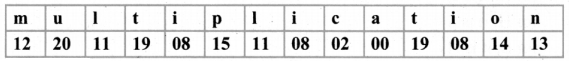
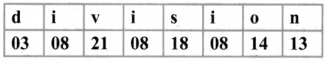
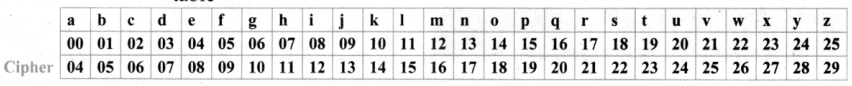
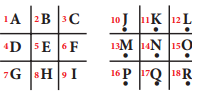
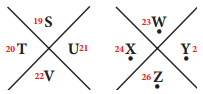
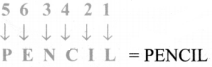
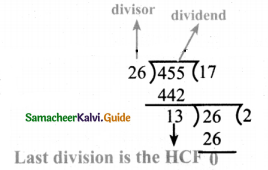
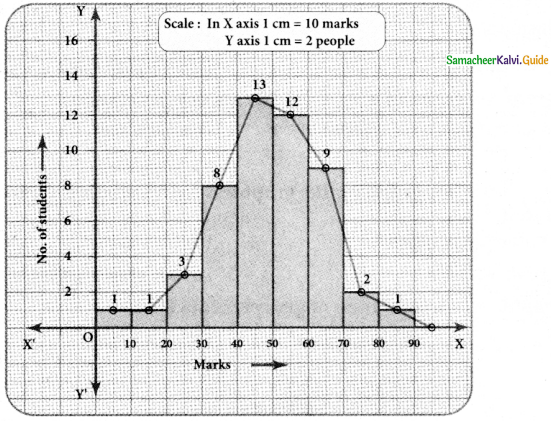
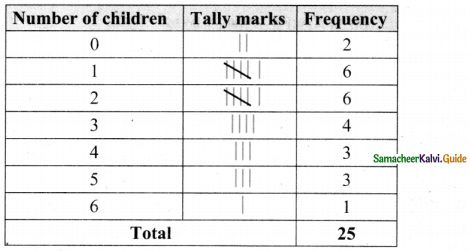
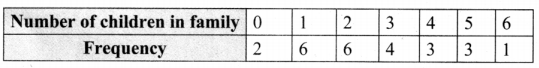
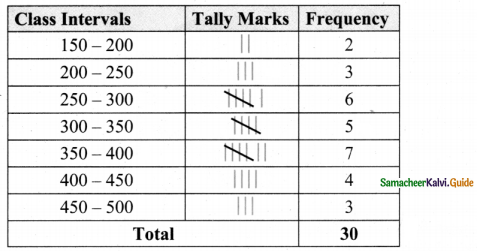
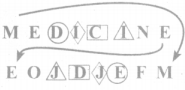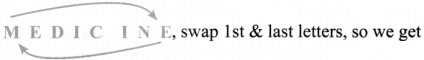Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 7 Information processing Ex 7.4 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Information processing Ex 7.4
Question 1.
Find the best buy of the following purchases:
(i) A pack of 5 chocolate bars for ₹ 175 or 3 chocolate bars for ₹ 114?
Answer:
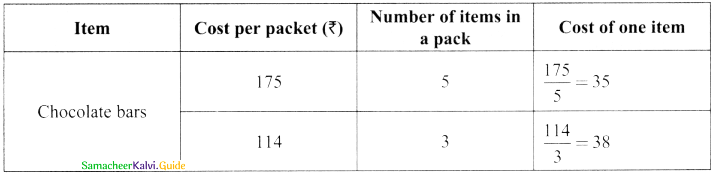
Best buy is a packet of 5 chocolate bars for ₹ 175
![]()
(ii) Basker buy 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) dozen of eggs for 81 and Aruna buy 15 eggs for ₹ 64.50?
Answer:
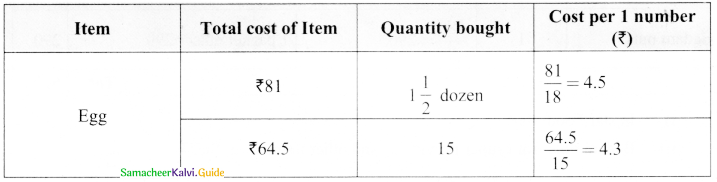
Best buy is 15 eggs for ₹ 64.5
Question 2.
Using the given picture find the total special offer price of fresh sweets and bakery products to buy \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) kg laddu, 1 kg cake, 6 pockets of bread.

Answer:
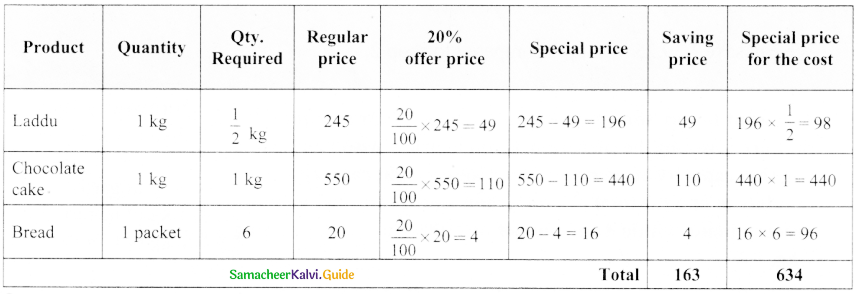
![]()
Question 3.
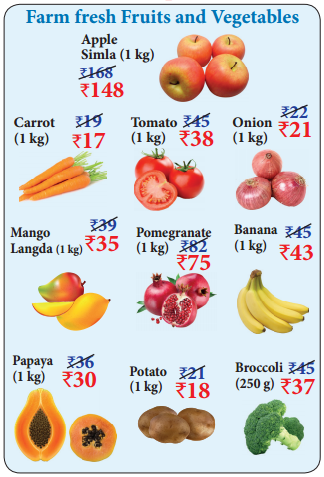
Using the given picture prepare a price list.
Suppose you planto buy 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) kg of apple, 2 kg of pomegranate, 2 kg of banana, 3 kg of mango, \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) kg of papaya, 3 kg of onion, \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) kg of tomato, and 1 kg of carrot in shop 1, how much will you save compared to shop 2.
Shop 1

Shop 2
Answer:
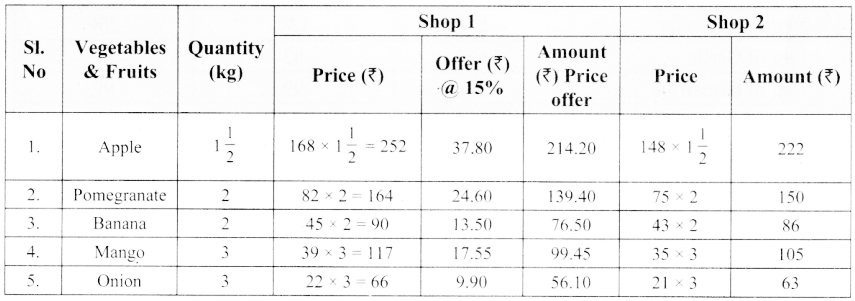
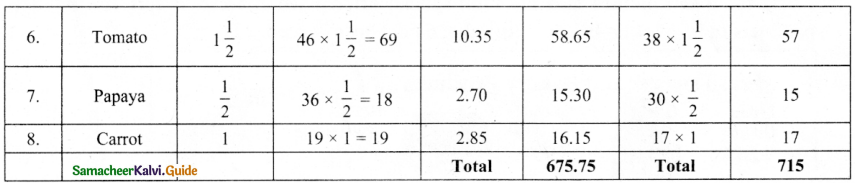
Price in shop 2 – Shop 1 = 715 – 675.75
= ₹ 39.25
We can save ₹ 39.25 in shop 1 compared to shop 2.
![]()
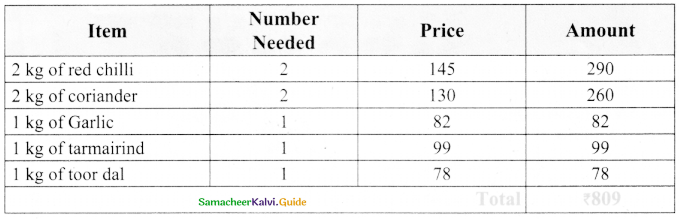
Question 4.
You want to buy some grocery items as per your shopping list that are given in the picture with their price. Also you have a bag that capacity of carrying 7 kg. Using weight ratio approach tabulate to find the total price and how much can
you buy more grocery items within your budget of ₹ 1000 and not exceeding 7 kg.
Shopping list
1. 2kg of red chili
2. 2 kg of coriander
3. 1 kg of garlic
4. 1 kg of tamarind
5. 2 kg of toor dal
Red chilli

₹ 141/1 kg
Coriander

₹ 130/1 kg
Garlic

₹ 82/1 kg
Tamarind

₹ 99/1 kg
Toor dal

₹ 78/1 kg
Answer:
![]()
Objective Type Questions
Question 5.
Online or television advertisements influence people on spending decisions by
(a) using special music
(b) making them think that they need the item
(c) using attractive pictures
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 6.
When I go shopping, I will buy
(a) something that looks attractive
(b) something my friend has
(c) something that I need to purchase
(d) the first thing I see in the store
Answer:
(c) something that I need to purchase
![]()
Question 7.
The best shopping choice is to
(a) shop at brand name stores always buy
(b) compare the choices before buying
(c) the same thing my friends bought
(d) buy at a regular shop always
Answer:
(b) compare the choices before buying