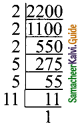
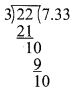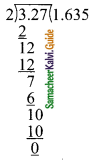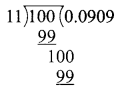Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.2 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.2
Question 1.
Find the value of the polynomial f(y) = 6y – 3y2 + 3 at
(i) y = 1
(ii) y = -1
(iii) y = 0
Solution:
(i) When y = 1
f(y) = 6y – 3y2 + 3
f(1) = 6(1) – 3(1)2 + 3
= 6 – 3 + 3 = 6
(ii) When y = – 1
f(y) = 6y – 3y2 + 3
f(-1) = 6(-1) – 3(-1)2 + 3
= – 6 – 3 + 3
= – 6
(iii) When y = 0
f(y) = 6y – 3y2 + 3
f(0) = 6(0) – 3(0)2 + 3
= 0 – 0 + 3
= 3
![]()
Question 2.
If p(x) = x2 – 2√2x + 1, find p(2√2).
Solution:
p(x) = x2 – 2√2x + 1
p(2√2) = (2√2)2 – 2√2 (2√2) + 1
= 8 – 8 + 1
= 0 + 1
= 1
Question 3.
Find the zeros of the polynomial in each of the following.
(i) P(x) = x – 3
Solution:
p( 3) = 3 – 3
= 0
p(3) is the zero of p(x)
(ii) p(x) = 2x + 5
Solution:
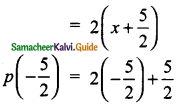
= -5 + 5
= 2(0)
= 0
Hence –\(\frac{5}{2}\) is the zero of p(x).
![]()
(iii) q(y) = 2y – 3
Solution:

= 2 × 0
= 0
Hence \(\frac{3}{2}\) is the zero of q(y).
(iv) f(z) = 8z
Solution:
f(0) = 8 × 0
= 0
Hence 0 is the zero of f(z)
(v) p(x) = ax when a ≠ 0
Solution:
p(0) = a(0)
= 0
Hence, 0 is the zero of p(x)
(vi) h(x) = ax + b, a ≠ 0, a, b∈R
Solution:

Hence –\(\frac{b}{a}\) is the zero of h(x).
![]()
Question 4.
Find the roots of the polynomial equations.
(i) 5x – 6 = 0
Solution:
5x = 6
x = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
\(\frac{6}{5}\) is the root of the polynomial.
(ii) x + 3 = 0
Solution:
x = -3
-3 is the root of the polynomial.
![]()
(iii) 10x + 9 = 0
Solution:
10x = -9
x = –\(\frac{9}{10}\)
–\(\frac{9}{10}\) is the root of the polynomial.
(iv) 9x – 4 = 0
Solution:
9x = 4
x = \(\frac{4}{9}\)
\(\frac{4}{9}\) is the root of the polynomial.
![]()
Question 5.
Verify whether the following are zeros of the polynomial, indicated against them,or not.
(i) p(x) = 2x – 1, x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution:
p (\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = 2(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) – 1
= 1 – 1
= 0
∴ \(\frac{1}{2}\) is the zero of the polynomial.
(ii) p(x) = x3 – 1, x = 1
Solution:
p(1) = 13 – 1
= 1 – 1
= 0
∴ 1 is the zero of the polynomial
![]()
(iii) p(x) = ax + b, x = \(\frac{-b}{a}\)
Solution:
p(\(\frac{-b}{a}\)) = a(\(\frac{-b}{a}\)) + b
= -b + b
= 0
∴ \(\frac{-b}{a}\) is the zero of the polynomial. a
(iv) p(x) = (x + 3) (x – 4); x = -3, x = 4
Solution:
P(-3) = (-3 + 3) (-3 – 4)
= (0) (-7)
= 0
P( 4) = (4 + 3) (4 – 4)
= (7) (0)
= 0
∴ -3 and 4 are the zeros of the polynomial.
![]()
Question 6.
Find the number of zeros of the following polynomials represented by their graphs.
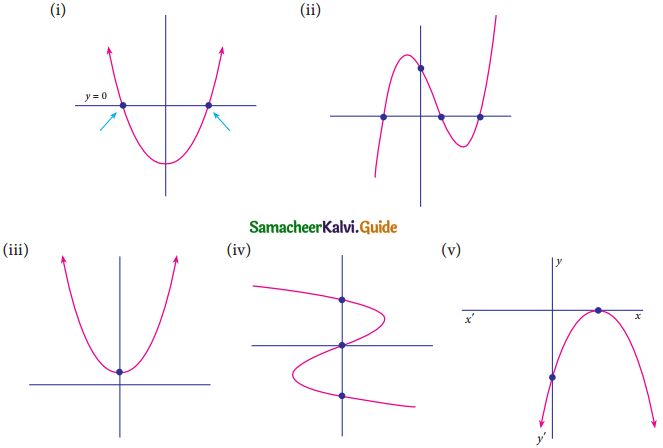
Solution:
(i) Number of zeros = 2 (The curve is intersecting the x-axis at 2 points)
(ii) Number of zeros = 3 (The curve is intersecting the x-axis at 3 points)
(iii) Number of zeros = 0 (The curve is not intersecting the x-axis)
(iv) Number of zeros = 1 (The curve is intersecting at the origin)
(v) Number of zeros = 1 (The curve is intersecting the x-axis at one point)