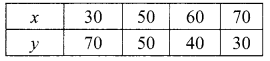
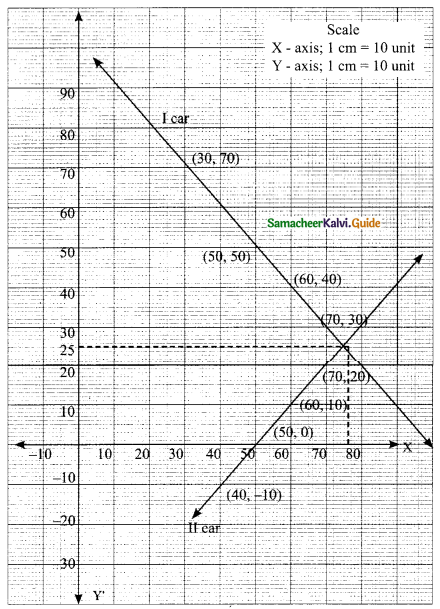
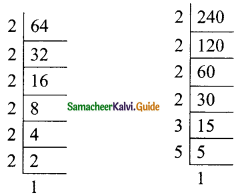
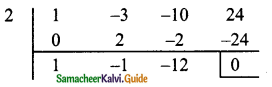
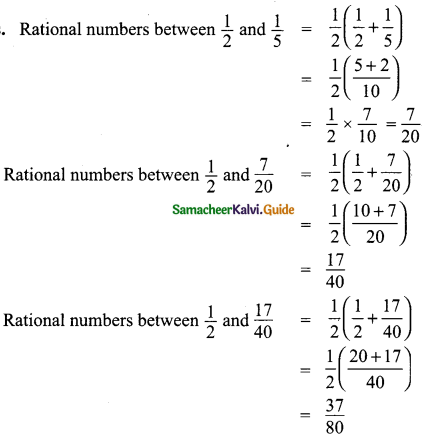
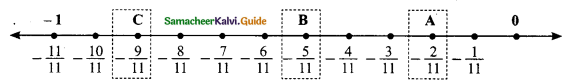
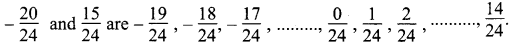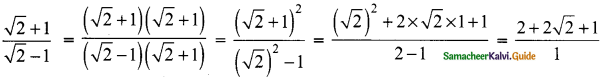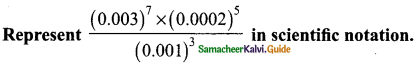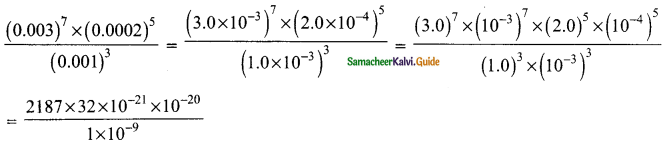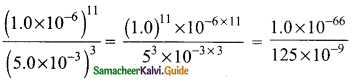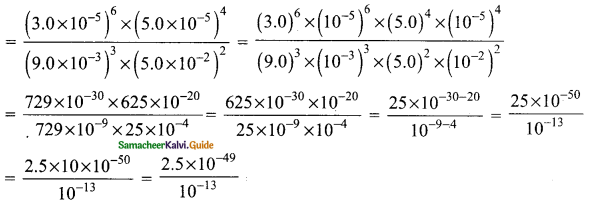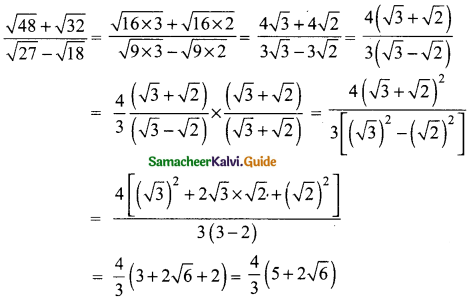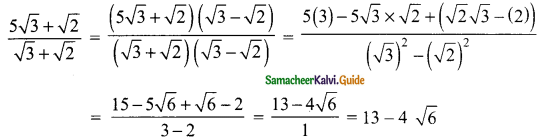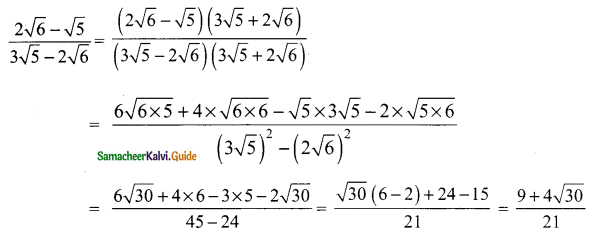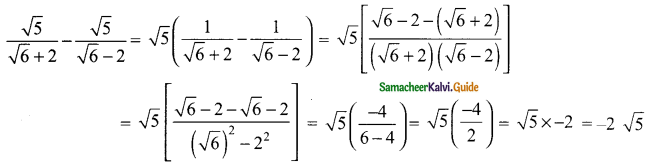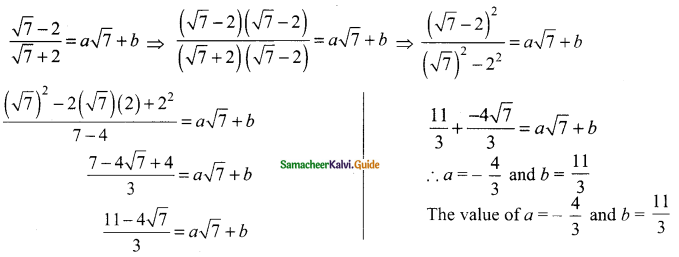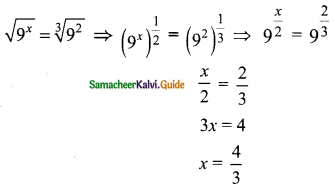Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.11 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.11
Question 1.
Solve, using the method of substitution.
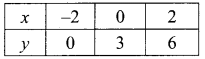
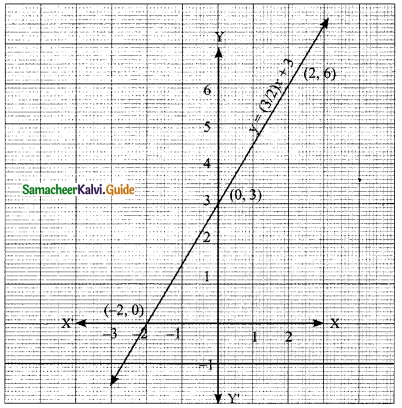
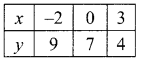
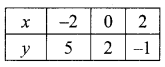
(i) 2x – 3y – 7; 5x + y = 9
Solution:
2x – 3y = 7 → (1)
5x + y = 9 → (2)
Equation (2) becomes
y = 9 – 5x
Substitute the value of y in (1)
2x – 3 (9 – 5x) = 7
2x – 27 + 15x = 7
17x = 7 + 27
17x = 34
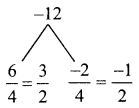
x = \( \frac{34}{17}\)
= 2
Substitute the value of x = 2 (in) (2)
y = 9 – 5 (2) = 9 – 10 = -1
∴ The value of x = 2 and y = -1
![]()
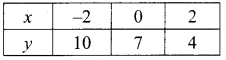
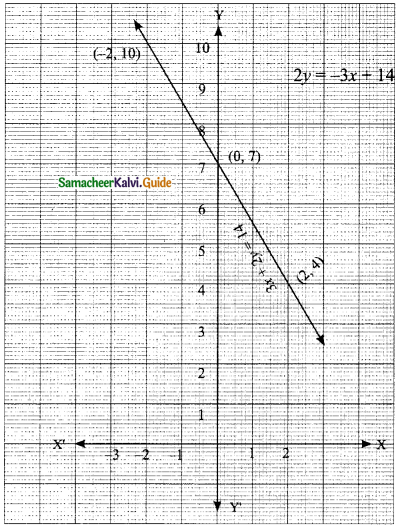
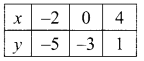
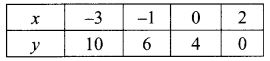
(ii) 1.5x + 0.1y = 6.2; 3x – 0.4y = 11.2
Solution:
1.5x + 0.1y = 6.2
Multiply by 10
15x + y = 62
y = 62 – 15x → (1)
3x – 0.4y = 11.2
Multiply by 10
30x – 4y = 112
divided by (2) we get
15x – 2y = 56 → (2)
Substitute the value of y in (2)
15x – 2(62 – 15x) = 56
15x – 124 + 30x = 56
45x = 56 + 124
45x = 180
x = \( \frac{180}{45}\)
= 4
Substitute the value of x = 4 in (1)
y = 62 – 15(4)
= 62 – 60
y = 2
∴ The value of x = 4 and y = 2
![]()
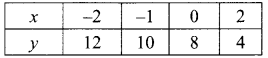
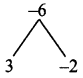
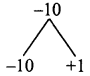
(iii) 10% of x + 20% of y = 24; 3x – y = 20
Solution:
\( \frac{10}{100}\) × x + \( \frac{20}{100}\) × y = 24
\( \frac{x}{10}\) + \( \frac{y}{5}\) = 24
Multiply by 10
x + 2y = 240 → (1)
3x – y = 20
– y = 20 – 3x
y = 3x – 20 → (2)
Substitute the value of y in (1)
x + 2 (3x – 20) = 240
x + 6x – 40 = 240
7x – 40 = 240
7x = 240 + 40
7x = 280
x = \( \frac{280}{7}\)
x = 40
Substitute the value of x = 40 in (2)
y = 3 (40) – 20 = 120 – 20
y = 100
∴ The value of x = 40 and y = 100
![]()
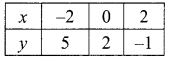
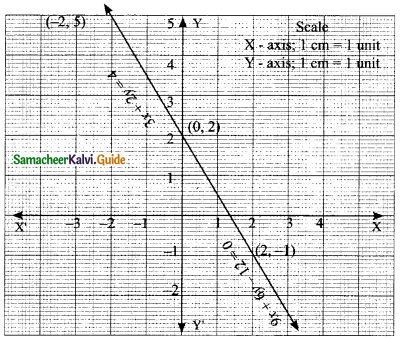
(iv) √2x – √3y = 1; √3x – √8y = 0
Solution:
√2x – √3y = 1
– √3y = 1 – √2x
√3y = √2x – 1
y = \(\frac{√2x-1}{√3}\) → (1)
√3x – √8y = 0 → (2)
Substitute the value of y in (2)
\(\sqrt{3x}-\frac{√8(√2x-1)}{√3}\)
multiply by √3
⇒ \(\frac{3x-√8(√2x-1)}{√3}\)
3x – √8(√2x – 1) = 0
3x – 4x + √8 = 0
-x = √8
Substitute the value of x in (1)
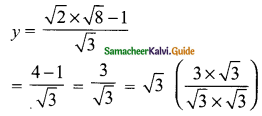
The value of x = √8 and y = √3
![]()
Question 2.
Raman’s age is three times the sum of the ages of his two sons. After 5 years his age will be twice the sum of the ages of his two sons. Find the age of Raman.
Solution:
Let Raman’s age be “x” years and the sum of the ages of two sons be “y” years.
By the given first condition
x = 3y
x – 3y = 0 → (1)
After 5 years Raman’s age is x + 5 years
Sum of sons age is (y + 10) years
(each son age increases by 5 years)
By the given second condition
x + 5 = 2 (y + 10)
x + 5 = 2y + 20
x – 2y = 20 – 5
x – 2y = 15 → (2)
Equation (1) becomes
x = 3y
Substitute the value of x in (2)
3y – 2y = 15
y = 15
Substitute the value of y = 15 in x = 3y
x = 3(15)
x = 45
∴ Raman’s age = 45 years
![]()
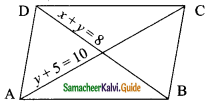
Question 3.
The middle digit of a number between 100 and 1000 is zero and the sum of the other digit is 13. If the digits are reversed, the number so formed exceeds the original number by 495. Find the number.
Solution:
Let the unit digit be and the 100 is digit be X. The number is XOY (100x + y)
By the given first condition
x + y = 13 ….(1)
If the digits are reversed the number is 100 y + x.
By the given second condition.
100y + x = 100x + y + 495
-99x + 99y = 495
-x + y = 5 …. (2)
x + y = 13 ….(1)
Add (1) and (2)
2y = 18
y = 9
Substitute the value of y = 9 in (1)
x + 9 = 13
x = 13 – 9
x = 4
∴ The number is 409
![]()