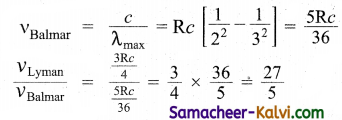
TN State Board 12th Computer Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Data Abstraction
Question 1.
What is abstraction?
Answer:
The process of providing only the essentials and hiding the details is known as abstraction.
Question 2.
What is Data Abstraction? Give examples.
Answer:
Data Abstraction is a powerful concept in computer science that allows programmers to treat code as objects.
Eg: Car, pencil, people are objects.
![]()
Question 3.
What is wishful thinking?
Answer:
Wishful thinking is the formation of beliefs and making decisions according to what might be pleasing to imagine instead of by appealing to reality.
Question 4.
What is a main difference between table and list?
Answer:
The main difference between table and list is that you cannot change the elements of a table once it is assigned, whereas in a list elements can be changed.
Question 5.
How will you support Data abstraction by defining an abstract data type?
Answer:
- Data abstraction is supported by defining an abstract datat type (ADT), which is a collection of constructors and selectors.
- Constructors create an object, bundling together different pieces of information, while selectors extract individual pieces of information from the object.
- The basic idea of data abstraction is to structure programs so that they operate on abstract data.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a example for Representation of Tuple as a pair.
Answer:
Representation of Tuple as a pair
num : = (1 ,2)
nums [0]
1
nums [1]
2
Here, the square bracket notation is used to access the data you stored in the pair.
The data is zero indexed, access the first element with nums [0] and the secondelement with nums [1].
Question 7.
Write a pseudo code in the following list to represent student as class.
Answer:
student – [‘Selvan’, ‘Kumar’, ‘100012345’, ‘[email protected]’]
code:
class student:
creation ( )
first Name: = “ ”
last Name : = “ ”
Id: = “ ” .
email
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the Representing Rational numbers using List? Give example.
Answer:
The rational number as a pair of two integers in pseudo code that is a numerator and a denominator.
Anyway of bundling two values together into one can be considered as a pair.
List are a common method to do so. Therefore List can be called as Pairs.
Eg: rational (n,d):
return [n,d]
return (x):
return x[o]
denom (x):
return x[1]
![]()
Question 9.
What is abstract data type?
Answer:
(i) Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a type for objects whose behavior is defined by a set of value and a set of operations.
(ii) Abstraction provides splitting a program into many modules.
Question 10.
Differentiate constructors and selectors.
Answer:
| Constructors |
Beleetprs |
| Constructors are function that build the abstract data type | Selectors are functions that retrieve information from the data type. |
| Eg: city = make city (name, lat, Ion). Where, city is called an abstract data type. | Eg: get name (city) getlat (city) |
![]()
Question 11.
What is a Pair?
Give an example.
Answer:
Bundling two values together into one can be considered as a pair.
Eg: 1st: =5 [10, 20]
Question 12.
What is a List? Give an example.
Answer:
List is constructed by placing expressions within square brackets separated by commas,
Eg: 1st: – [10, 20]
Question 13.
What is a Tuple? Give an example.
Answer:
Python language provides a compound Structure called pair which is made up of list or tuple.
Eg: colour = (‘red’, ‘blue’, ‘green’)
![]()
Question 14.
Differentiate Concrete data type and abstract datatype.
Answer:
|
Concrete datatype |
Abstract data type |
| A concrete data type is a data type whose representation is known. | In abstract data type the representation of a data type is unknown. |
| A concrete data type representation is defined. | The basic idea of data abstraction is Structured programs. |
| It is an independent part of the program. | Our programs should use data in such a way, as’ to make a few assumptions about the data as possible. |
Question 15.
Which strategy is used for program designing? Define that Strategy.
Answer:
We are using a powerful strategy for designing programs ‘Wishful thinking’.
Wishful Thinking is the formation of beliefs and making decisions according to what might be pleasing to imagine instead of by appealing to reality.
![]()
Question 16.
Identify Which of the following are constructors and selectors?
Answer:
(a) N1=number( )
Constructors
(b) accetnum(n1)
Selectors
(c) dispiaynum(n1)
Selectors
(d) eval(a/b)
Selectors
(e) x,y= makeslope (m) makeslope(n) Constructors
(f) display( )
Selectors
Question 17.
What are the different ways to access the elements of a list? Give example.
Answer:
(i) There are two different ways to access the elements of a list.
(ii) The first way is multiple assignment, which unpacks a list into its elements and binds each element to a different name.
Eg: lst:= [10,20]
x,y:= 1st
(iii) The second method for accessing the elements in a list is by the element selection operator, with square brackets. Eg: 1st [0].
![]()
Question 18.
Identify Which of the following are List, Tuple and class ?
Answer:
(a) arr [1, 2, 34]
List
(b) arr (1,2, 34)
Tuple
(c) student [mo, name, mark] class
(d) day= (‘sun’, ‘mon’, ‘tue’, ‘wed’)
Tuple
(e) x= [2, 5, 6.5, [5, 6], 8.2]
List
(f) employee [eno, ename, esal, eaddress]
class
Question 19.
How will you facilitate data abstraction. Explain it with suitable example.
Answer:
(i) To facilitate data abstraction, you will need to create two types of functions: Constructors and Selectors.
(ii) Constructors are functions that build the abstract data type.
(iii) For example city= make city (name, lat, Ion)
(iv) Selectors are functions that retrieve information from the data type.
(v)get name (city), get lat (city), get Ion (city) are the selectors, because these functions extract information of this city object.
(vi) Constructors create an object, bundling together different pieces of information.
(vii) Selectors extract individual pieces of information from the object.
![]()
Question 20.
What is a List? Why List can be called as Pairs. Explain with suitable example.
Answer:
(i) List is constructed by placing expressions within square brackets separated- by comma.
(ii) Any way of bundling two values together into one can be considered as a pair.
(iii) List are a common method to do so. Therefore list can be called as pairs.
Eg: for list 1st: = [10,20] x, y: = 1st
Here x will become 10 and y will become 20.
(iv) Example for pair
1st [(0, 10), (1, 20)], Here 0 is a index position and 10 is a value.
1 is a index position and 20 is a value.
(v) List can store multiple values! Each value can be of any type and can even be another list.
Question 21.
How will you access the multi-item? Explain with example.
Answer:
(i) Multi-item means a multiple-item object where each item is a named thing.
Eg: class person:
creation ( )
Name: = “ ”
ID: – “ ”
email: = “”
![]()
Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Which is a poweful concept in Computer science that allows programmers to treat code as objects?
(a) Data abstraction
(b) Memory
(c) Mapping
(d)Accessibility
Answer:
(a) Data abstraction
Question 2.
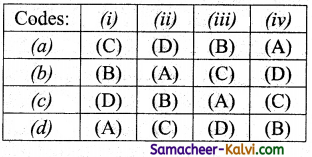
Match the following:
| (i) Constructors | (A) Comma – separated |
| (ii) Selectors | (B) Square brackets |
| (iii) List | (C) Extract individual |
| (iv)Tuple | (D) Bundling together |
(a) (i) – D, (ii) – A, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
(b) (i) – D (ii) – C, (iii) – B, (iv) – A
(c) (i) – B, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – A
(d) (i) – B, (ii) – D, (iii) – A, (iv) – C
Answer:
(b) (i) – D (ii) – C, (iii) – B, (iv) – A
![]()
Question 3.
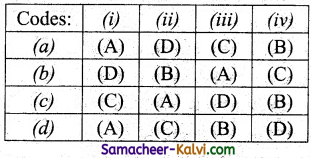
Match the following:
| (i) Compound structure | (A) Pair |
| (ii) Bundling two values | (B) Functions |
| (iiii) Multi – item object | (C) Pair |
| (iv) Constructors | (D) Classes |
(a) (i) – A, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – B
(b) (i) – A (ii) – D, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
(c) (i) – D, (ii) – B, (iii) – C, (iv) – A
(d) (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – A, (iv) – B
Answer:
(a) (i) – A, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – B
Question 4.
Assertion (A):
The basic idea of data abstraction is to structure program.
Reason (R):
Abstract Data Type is a type for objects whose behaviour is defined by a set of value and a set of operations.
(a) Both A and R are True and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are True but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is True, but R is False.
(d) A is False, but R is True.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are True and R is the correct explanation for A.
![]()
Question 5.
Choose the incorrect Pair:
(a) ADT – Abstract Data Type
(b) Classes – Structures
(c) Abstraction – Modularity
(d) List – Immutable
Answer:
(d) List – Immutable
Question 6.
Choose the correct Pair:
(a) Constructors – Retrieve data
(b) Selectors – Build the data
(c) Pair – Compound structure
(d) Classes – Single-item object
Answer:
(c) Pair – Compound structure
Question 7.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Python provides a compound structure called Pair.
(b) A tuple is a semicolon(;) separated sequence of values surrounded with Parantheses.
(c) List is constructed by placing expressions within square brackets.
(d) The elements of a list can be accessed in two ways.
Answer:
(b) A tuple is a semicolon(;) separated sequence of values surrounded with Parantheses.
![]()
Question 8.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) The class construct defines the form for multi-part objects that represent a Person
(b) Constructor? are functions that build the concrete data type.
(c) Selectors are functions that build the data.
(d) ADT (Abstract Data Type) does specify how data will be organised in Memory.
Answer:
(a) The class construct defines the form for multi-part objects that represent a Person
Question 9.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) List
(b) Constructor
(c) Pair
(d) Tuple
Answer:
(b) Constructor
Question 10.
Expand ADT:
(a) Abstract Data Type
(b) Add Data Type
(c) Application,Data Type
(d) Absolute Data Type
Answer:
(a) Abstract Data Type
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following provides modularity?
(a) Function
(b) Class
(c) Object
(d) Variable
Answer:
(c) Object
Question 12.
Which of the following are functions that build the abstract data type?
(a) Function
(b) Selectors
(c) Constructors
(d) Destructors
Answer:
(c) Constructors
Question 13.
Which of the following extract the information of the object?
(a) Function
(b) Selectors
(c) Constructors
(d) Destructors
Answer:
(b) Selectors
![]()
Question 14.
Which data representation, a definition for each function is known?
(a) Concrete
(b) Abstract
(c) User defined
(d) Built in
Answer:
(a) Concrete
Question 15.
Which is contracted by placing expressions within square brackets separated by comma?
(a) Tuple
(b) List
(c) Dictionary
(d) Set
Answer:
(b) List
Question 16.
List can be called as:
(a) Tuple
(b) List
(c) Set
(d) Pairs
Answer:
(d) Pairs
![]()
Question 17.
Which of the following representation for Abstract Data Types?
(a) Classes
(b) Tuples
(c) Lists
(d) Pairs
Answer:
(a) Classes
Question 18.
Which data representation is defined as an independent part of the program?
(a) Abstract
(b) Concrete
(c) Tuple
(d) List
Answer:
(b) Concrete
![]()
Question 19.
Which of the following is a comma separated values surrounded with parentheses?
(a) List
(b) Dictionary
(c) Set
(d) Tuple
Answer:
(d) Tuple
Question 20.
Which of the following functions that build the abstract data type ?
(a) Constructors
(b) Destructors
(c) Recursive
(d) Nested
Answer:
(a) Constructors
Question 21.
Which of the following functions that retrieve information from the data type?
(a) Constructors
(b) Selectors
(c) Recursive
(d) Nested
Answer:
(b) Selectors
![]()
Question 22.
The data structure which is a mutable ordered sequence of elements is called:
(a) Built in
(b) List
(c) Tuple
(d) Derived data
Answer:
(b) List
Question 23.
A sequence of immutable objects is called:
(a) Built in
(b) List
(c) Tuple
(d) Derived data
Answer:
(c) Tuple
Question 24.
The data type whose representation is known are called:
(a) Built in datatype
(b) Derived datatype
(c) Concrete datatype
(d) Abstract datatype
Answer:
(c) Concrete datatype
![]()
Question 25.
Hie data type whose representation is unknown are called:
(a) Built in datatype
(b) Derived datatype
(c) Concrete datatype
(d) Abstract datatype
Answer:
(d) Abstract datatype
Question 26.
Which of the following is a compound structure?
(a) Pair
(b) Triplet
(c) Single
(d) Quadrat
Answer:
(a) Pair
Question 27.
Bundling two values together into one can be considered as:
(a) Pair
(b) Triplet
(c) Single
(d) Quadrat
Answer:
(a) Pair
![]()
Question 28.
Which of the following allow to name the various parts of a multi-item object?
(a) Tuples
(b) Lists
(c) Classes
(d) Quadrats
Answer:
(c) Classes
Question 29.
Which of the following is constructed by placing expression? within square brackets?
(a) Tuples
(b) Lists
(c) fel Glasses
(d) Quadrats
Answer:
(b) Lists