Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 12 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code. - Question numbers 13 to 22 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 23 to 32 in Part III are of four marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 33 to 35 in Part IV are of seven marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 75
Part – I
(i) Answer all the questions. [12 × 1 = 12]
(ii) Choose the most suitable answer and write the code with the corresponding answer.
Question 1.
If the Earth shrinks to 50% of its real radius its mass remaining the same, the weight of a body on the Earth will ______.
(a) decrease by 50%
(b) increase by 50%
(c) decrease by 25%
(d) increase by 300%
Answer:
(c) decrease by 25%
Question 2.
The refractive index of four substances A, B, C and D are 1.31, 1.43, 1.33, 2.4 respectively. The speed of light is maximum in ______.
(a) A
(b)B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(a) A
Question 3.
When a sound wave travels through air, the air particles ______.
(a) vibrate along the direction of the wave motion
(b) vibrate but not in any fixed direction
(c) vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave motion (id) do not vibrate
Answer:
(a) vibrate along the direction of the wave motion
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following represents 1 amu?
(a) mass of a C-12 atom
(b) mass of hydrogen atom
(c) 1/12th of the mass of a C-12 atom
(d) mass of 0-16 atom
Answer:
(c) 1/12th of the mass of a C-12 atom
Question 5.
______ is a relative periodic property.
(a) atomic radii
(b) Ionic radii
(c) Electron affinity
(d) Electron negativity
Answer:
(b) Ionic radii
Question 6.
Which of the following is the universal solvent?
(a) Acetone
(b) Benzene
(c) Water
(d) Alcohol
Answer:
(c) Water
Question 7.
Root hairs are ______.
(a) cortial cell
(b) projection of epidermal cell
(c) unicellular
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (b) and (c)
![]()
Question 8.
Polyphagia is a condition seen in ______.
(a) Obesity
(b) Diabetes mellitus
(c) AIDS
(d) Cancer
Answer:
(b) Diabetes mellitus
Question 9.
9 : 3: 3 : 1 ratio is due to ______.
(a) Segregation
(b) Independent Assortment
(c) Crossing over
(d) Recessive factors
Answer:
(b) Independent Assortment
Question 10.
rDNA is a ______.
(a) vector DNA
(b) circular DNA
(c) recombinant of vector DNA
(d) satellite DNA
Answer:
(c) recombinant of vector DNA
Question 11.
Biogenesis was speculated by ______.
(a) Louis pasteur
(b) Darwin
(c) Lamark
(d) Oparin
Answer:
(a) Louis pasteur
![]()
Question 12.
Green house effect refers to ______.
(a) cooling of earth
(b) warming of earth
(c) cultivation of plants
(d) trapping of UV rays
Answer:
(b) warming of earth
Part – II
Answer any seven questions. (Q.No: 22 is compulsory) [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 13.
State Newton’s laws of motion.
Answer:
Every body continues to be in its state of rest or the state of uniform motion along a straight line unless it is acted upon by some external force.
Question 14.
Why are traffic signals red in colour?
Answer:
- Red light has the highest wavelength.
- It is scattered by atmospheric particles.
- So red Tight in able to travel the longest distance through fog, rain etc.
Question 15.
What is co-efficient of apparent expansion?
Answer:
Coefficient of apparent expansion is defined as the ratio of the apparent rise in the volume of the liquid per degree rise in temperature to its unit volume. The SI unit of coefficient of apparent expansion is K-1.
Question 16.
Difference between atoms and molecules.
Answer:
Atom:
- An atom is the smallest particle of an element.
- Atom does not exist in free state except in a noble gas.
- Atoms does not have a chemical bond.
Molecules:
- A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound.
- Molecule exists in free state.
- Atoms in a molecule are held by chemical bonds.
Question 17.
Define Hydrated salt.
Answer:
The number of water molecules found in the crystalline substance or salts is called water of crystallization. Such salts are called hydrated salts.
![]()
Question 18.
What are synthetic auxins?
Answer:
Artificially synthesized auxins, that have the properties like auxins are called as synthetic auxins. Eg. 2,4-D (2, 4-Dichlorophenoxy Acetic acid)
Question 19.
Mention the Medicinal value of Leech.
Answer:
- They can be used to treat cardiovascular diseases.
- Biochemical substances derived from leech saliva are used for preparation of pharmaceutical drugs that can treat hypertension.
Question 20.
Define triple fusion.
Answer:
During double fertilization, one sperm fuses with the egg and forms a diploid zygote. The other sperm fuse with the secondary nucleus to form the primary endosperm, which is triploid in nature. This called triple fusion.
Question 21.
What are Analogous organs?
Answer:
The analogous organs look similar and perform similar functions but they have different origin and developmental pattern. E.g: The function of the wings of a bat, the wings of a bird and wings of an insect are similar, but their basic structures are different.
Question 22.
A current of 2A flows through a 12 V bulb then find resistance.
Answer:
Given: V = 12V; I = 2A
V = IR
R = \(\frac{V}{I}=\frac{12}{2}\)
R = 6 Ω
Part – III
Answer any seven questions (Q.No: 32 is compulsory) [7 × 4 = 28]
Question 23.
Deduce the equation of a force using Newton’s second law of motion.
Answer:
“The force acting on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force”.
Let, ‘m’ be the mass of a moving body, moving along a straight line with an initial speed ‘u’ After a time interval of ‘t’, the velocity of the body changes to ‘v’ due to the impact of an unbalanced external force F.
Initial momentum of the body Pi = mu
Final momentum of the body Pf = mv
Change in momentum Δp = Pf – Pi.
= mv – mu
By Newton’s second law of motion,
Force, F ∝ rate of change of momentum
F ∝ change in momentum / time
F ∝ \(\frac{m v-m u}{t}\)
F ∝ \(\frac{k m(v-u)}{t}\)
Here, k is the proportionality constant, k = 1 in all systems of units. Hence,
F = \(\frac{m(v-u)}{t}\)
Since, acceleration = change in velocity / time, a = (v – u)/t. Hence, we have
F = m x a
Force = mass x acceleration
- No external force is required to maintain the motion of a body moving with uniform velocity.
- When the net force acting on a body is not equal to zero, then definitely the velocity of the body will change.
- Thus, change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force. The change may take place either in magnitude or in direction or in both.
![]()
Question 24.
Differentiate the eye defects: Myopia and Hypermetropia.
Answer:
Myopia:
- Myopia, also known as short sightedness, occurs due to the lengthening of eye ball.
- With this defect, nearby objects can be seen clearly but distant objects cannot be seen clearly.
- The focal length of eye lens is reduced or the distance between eye lens and retina increases.
- The far point will not be infinity for such eyes and the far point has come closer.
- Due to this, the image of distant objects are formed before the retina.
- This defect can be corrected using a concave lens.
Hypermeteropia:
- Hypermeteropia, also known as long sightedness, occurs due to the shortening of eye ball.
- With this defect, distant objects can be seen clearly but nearby objects cannot be seen clearly.
- The focal length of eye lens is increased or the distance between eye lens and retina decreases.
- Hence, the near point will not be at 25 cm for such eyes and the near point has moved farther.
- Due to this, the image of nearby objects are formed behind the retina.
- This defect can be corrected using a convex lens.
Question 25.
(i) Define electric potential and potential difference.
Answer:
Electric Potential: The electric potential at a point is defined as the amount of work done in moving a unit positive charge from infinity to that point against the electric force.
Electric Potential Difference: The electric potential difference between two points is defined as the amount of work done in moving a unit positive charge from one point to another point against the electric force.
(ii) How does a fuse wire protect electrical appliances?
Answer:
- The fuse wire is connected in series, in an electric circuit.
- When a large current passes through the circuit, the fuse wire melts due to Joule’s heating effect and hence the circuit gets disconnected.
- Therefore, the circuit and the electric appliances are saved from any damage.
- The fuse wire is made up of a material whose melting point is relatively low.
Question 26.
Give the salient features of “Modern atomic theory”.
Answer:
The salient features of “Modem atomic theory” are,
- An atom is no longer indivisible.
- Atoms of the same element may have different atomic mass.
- Atoms of different elements may have same atomic masses.
- Atoms of one element can be transmuted into atoms of other elements. In other words, atom is no longer indestructible.
- Atoms may not always combine in a simple whole number ratio.
- Atom is the smallest particle that takes part in a chemical reaction.
- The mass of an atom can be converted into energy [E = mc2].
![]()
Question 27.
(i) How will you classify Hydrocarbons?
Answer:
Hydrocarbons are classified into three classes such as Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes.
(a) Alkenes:
These are hydrocarbons, which contain only single bonds. They are represented by the general formula CnH2n + 2 (where n = 1,2, 3) Ex: Methane (CH4)
(b) Alkenes:
The hydrocarbons, which contain one or more C = C bonds are called alkenes. These are unsaturated compounds. They are represented by the general formula CnH2n.
Ex: Ethylene (C2H4)
(c) Alkynes:
The hydrocarbons containing carbon to carbon triple bond are called alkynes. They have the general formula CnH2n – 2 Ex: Acetylene (C2H2)
(ii) Write the characteristic of hydrocarbons.
Answer:
- Lower hydrocarbons are gases at room temperature E.g. methane, ethane are gases.
- Alkanes are least reactive when alkynes are most reactive due to presence triple bond.
- Alkanes are saturated whereas alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated.
- They are insoluble in water.
Question 28.
Which acts as a link between the nervous system and endocrine system?
Answer:
Hypothalamus, acts as a link between nervous system and endocrine system. It lies at the base of the thalamus. It controls involuntary functions like hunger, thirst, sleep, sweating, sexual desire, anger, fear, water balance, blood pressure etc. It acts as a thermo regulatory (temperature control) center of the body. It controls the secretion of hormones from anterior Pituitary gland.
Question 29.
(i) What are heart sounds? How are they produced?
(ii) What is Aneuploidy?
Answer:
(i) The rhythmic closure and opening of the valves causes heart sounds.
The first sound ‘LUBB’ is of longer duration and is produced by the closure of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves after the beginning of ventricular systole.
The second sound ‘DUPP’ is of a shorter duration and produced by the closure of semilunar valve at the end of ventricular systole.
(ii) Aneuploidy is the loss or gain of one or more chromosomes in a set. It is of three types. Monosomy (2n – 1), Trisomy (2n + 1)andNullisomy (2n – 2).
Question 30.
Discuss the importance of biotechnology in the field of medicine.
Answer:
Using genetic engineering techniques, medicinally important pharmaceutical products for the treatment of various diseases have been developed.
- Insulin used in the treatment of diabetes.
- Human growth hormone used for treating children with growth deficiencies.
- Blood clotting factors are developed to treat haemophilia.
- Development of vaccines against various diseases like Hepatitis B and rabies
- Tissue plasminogen activator is used to dissolve blood clots and to prevent heart attack.
![]()
Question 31.
What are the phases of menstrual cycle? Indicate, the changes in the ovary and uterus.
Answer:
The four phases of the menstrual cycle are:
- Menstrual or Destructive phase
- Follicular or Proliferative phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal or secretory phase
Events of menstrual cycle and changes in ovary and changes in uterus.

Question 32.
(i) Explain how the loss of heat (or transfer of heat) due to modes of transfer of heat is minimised in a thermos flask.
Answer:
Transfer of heat is thermos is minimised as under.
(1) By conduction:
As in conduction heat can transfer by contact of material medium. In thermos air is evacuated between the walls so heat transfer in stopped by conduction mode.
(2) By convection:
As convection mode also require material (fluid) medium and there is nothing between the walls of thermos so heat does not transfer by connection mode.
(3) By Radiation:
As Ag polish is coated opaque on inner and outer walls of thermos radiation obeys the laws of refraction and reflection so no refraction takes place through opaque wall. Reflection of outer radiation goes outside of innerwall goes inside. So the transfer of heat is minimised by polishing.
(ii) Briefly write any four characteristics of group in the periodic table.
Answer:
- The element present in a group have the same valency.
- The element present in a group have identical chemical properties.
- The physical properties of the elements in the group vary gradually.
- The atomic radii of the elements present in a group increases downwards
Part – IV
(1) Answer all the questions. [3 × 7 = 21]
(2) Each question carries seven marks.
(3) Draw diagram wherever necessary.
Question 33.
(a) (i) State Ohm’s law.
Answer:
According to Ohm’s law, at a constant temperature, the steady current ‘I’ flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference ‘V’ between the two ends of the conductor.
I ∝ V.
∴V = IR
(ii) With the help of a circuit diagram derive the formula for the resultant resistance of three resistances connected in parallel.
Answer:
Resistors in Parallel:
A parallel circuit has two or more loops through which current can pass. If the circuit is disconnected in one of the loops, the current can still pass through the other loop(s). The wiring in a house consists of parallel circuits.

(i) Consider that three resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected across two common points A and B.
(ii) The potential difference across each resistance is the same and equal to the potential difference between A and B. This is measured using the voltmeter.
(iii) The current I arriving at A divides into three branches I1, I2 and I3 passing through R1, R2 and R3 respectively.
According to the Ohm’s law, we have,

The total current through the circuit is given by
I = I1 + I2 + I3
Using equations (1), (2) and (3), we get

Let the effective resistance of the parallel combination of resistors be Rp. Then,
I = \(\frac{V}{R_{p}}\) …….(5)
Combining equations (4) and (5), we have

Thus,
(iv) When a number of resistors are connected in parallel, the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances is equal to the reciprocal of the effective or equivalent resistance.
(v) When ‘n’ resistors of equal resistances Rare connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is \(\frac{R}{n}\)

Hence, Rp = \(\frac{R}{n}\)
(vi) The equivalent resistance in a parallel combination is less than the lowest of the individual resistances.
(OR)
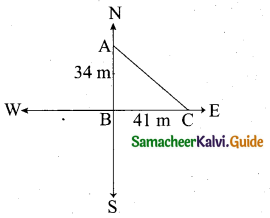
(b) (i) A man is standing between two vertical walls 680 m apart. He claps his hands and hears two distinct echoes after 0.9 seconds and 1.1 second respectively. What is the speed of sound in the air?
Answer:
Given Data
d = 680 m
t1 = 0.9 s
t2 = 1.1 s
v = ?

(ii) An electric heater of resistance 5 Ω is connected to an electric source. If a current of 6 A flows through the heater, then find the amount of heat produced in 5 minutes.
Answer:
Given resistance R = 5 Ω, Current I = 6 A,
Time t = 5 minutes = 5 × 60 s = 300 s
Amount of heat produced, H = I2Rt
H = 62 × 5 × 300. Hence, H = 54000 J
![]()
Question 34.
(a) (i) Calculate the gram molecular mass of NH3.
Answer:
Atomic mass of N = 14
H = 1
Gram molecular mass of NH3 = (14 × 1) + (1 × 3)
= 14 + 3 = 17 g
(ii) Calculate the percent by mass of glucose in a solution made by dissolving 500 g of glucose in 50 g of water.
Answer:

(iii) Calculate the number of water molecule present in one drop of water which weights 0.18.
Answer:

Number of molecules = No. of moles x Avogadro number
= 0.01 × 6.023 × 1023
= 0.06023 × 1023
= 6.023 × 1021 molecules
(OR)
(b) (i) How does pH play an important role in everyday life?
Answer:
- The pH of blood is almost 7.4. Any increase or decrease in this value leads to diseases.
- Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
- If pH of rain water becomes less than 7, it becomes acid rain which is harmful in day-to-day life.
- pH changes cause tooth decay.
- During indigestion the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation.
(ii) Classify the following compounds based on the pattern of carbon chain and give their structural formula: (i) Propane (ii) Benzene (iii) Cyclobutane (iv) Furan
Answer:
(i) Propane is open chain or a cyclic compound because it contains an open chain.
CH3 – CH3 – CH3 [Propane]
(ii) Benzene is a carbocyclic compound because it contains carbon atoms cyclic ring of 6 atoms.

(iii) Cyclobutane is a carbocyclic compound.

(iv) Furan is a hetrocyclic compound because in the cyclic chain one atom is oxygen atom.

![]()
Question 35.
(a) (i) What is Scratch?
(ii) Differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus
(iii) Why fossil fuels are to be conserved?
Answer:
(i) ‘Scratch’ is a software used to create animations, cartoons and games easily. Scratch, on the other hand, is a visual programming language.
(ii)
Type-1 Diabetes mellitus:
- People with type-1 diabetes do not produce Insulin in pancreas.
- Immune system destroys insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Cannot be controlled without taking insulin.
- Diagnosed in childhood
- Not associates with excess body weight
Type-2 Diabetes mellitus:
- People with type-2 diabetes do not respond to insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes are Insulin Resistant.
- Possible to treat initially without medication or treating with tablets.
- Diagonsed over 30 years old.
- Associated with excess body weight.
(iii) Formation of fossil fuels is a very slow process and takes very long period of time for renewal. Hence to be conserved.
[OR]
(b) (i) Write the dental formula of rabbit.
Answer:
(i) Dental formula is (I\(\frac{2}{1}\), C\(\frac{0}{0}\), PM\(\frac{3}{2}\), M\(\frac{3}{2}\)) in Rabbit, which is written as \(\frac{2033}{1023}\)
I – Incisors
PM – Premolar
C – Canines
M – Molars
(ii) With a neat labelled diagram explain the techniques involved in gene cloning.
Answer:
Gene cloning:

The carbon copy or more appropriately, a clone means to make a genetically exact copy of an organism.
In gene cloning, a gene or a piece of DNA fragment is inserted into a bacterial cell, where DNA will be multiplied (copied) as the cell divides.
Techniques involved in gene cloning:
- Isolation of desired DNA fragment by using restriction enzymes.
- Insertion of the DNA fragment into a suitable vector (plasmid) to make rDNA.
- Transfer of rDNA into bacterial host cell (Transformation).
- Selection and multiplication of recombinant host cell to get a clone.
- Expression of cloned gene in host cell.