Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are of five marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are of Eight marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
Which country was expelled from the League of Nations for attacking Finland?
(a) Germany
(b) Russia
(c) Italy
(d) France
Answer:
(b) Russia
Question 2.
Who was the first Indian judge of the Madras High Court?
(a) T. Muthu Swamy
(b) P. S. Sivasamy
(c) V. S. Srinivasa Sastri
(d) G. A. Natesan
Answer:
(a) T. Muthu Swamy
Question 3.
Which American President followed the policy of containment of communism?
(a) Woodrow Wilson
(b) Truman
(c) Theodore Roosevelt
(d) Franklin Roosevelt
Answer:
(b) Truman
Question 4.
Which one of the following was launched by Haji Shariatullah in 1818 in East Bengal?
(a) Wahhabi Rebellion
(b) Farazi Movement
(c) Tribal uprising
(d) Kol Revolt
Answer:
(b) Farazi Movement
![]()
Question 5.
Who was arrested during the anti-Rowlatt protests in Amirtsar?
(a) Motilal Nehru
(b) Shaifuddin Kitchlew
(c) MohamedAli
(d) Raj Kumar Shukla
Answer:
(b) Shaifuddin Kitchlew
Question 6.
The North-South extend of India is ………………..
(a) 2,500 km
(b) 2,933 km
(c) 3,214 km
(d) 2,814 km
Answer:
(c) 3,214 km
Question 7.
Meteorology is the science of………………..
(a) Weather
(b) Social
(c) Political
(d) Human
Answer:
(a) Weather
Question 8.
The Soil which is rich in iron oxides is ………………..
(a) Alluvial
(b) Black
(c) Red
(d) Alkaline
Answer:
(c) Red
Question 9.
The latitudinal extent of Tamil Nadu is………………..
(a) 8°4’N to 13°35’N
(b) 8°5’S to 13°35’S
(c) 8°0’N to 13°5’N
(d) 8°0’S to 13°05’S
Answer:
(a) 8°4’N to 13°35’N
Question 10.
Pick out the odd one………………..
(a) Inundational canals
(b) Perennial canals
(c) Tanks
(d) Canals
Answer:
(c) Tanks
![]()
Question 11.
Under which article financial emergency can be proclaimed?
(a) Article 352
(b) Article 356
(c) Article 360
(d) Article 368
Answer:
(c) Article 360
Question 12.
Which Minister plays a vital role in molding foreign policy of our country?
(a) Defense Minister
(b) Prime Minister
(c) External Affairs Minister
(d) Home Minister
Answer:
(c) External Affairs Minister
Question 13.
…………….. is the only state in India to adopt universal PDS
(a) Kerala
(b) Andhra Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(c) Tamil Nadu
Question 14.
GNP equals………………..
(a) NNP adjusted for inflation
(b) GDP adjusted for inflation
(c) GDP plus net property income from abroad
(d) NNP plus net property income or abroad
Answer:
(c) GDP plus net property income from abroad
Part – II
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 × 2 = 20]
Question 15.
Mention the four articles of faith laid down by Maharishi Debendranath Tagore?
Answer:
Maharashi Debendranath Tagore laid down the following four articles of faith –
- In the beginning, there was nothing. The one Supreme Being alone existed who created the Universe.
- He alone is the Good of truth, Infinite Wisdom, Goodness and Power, eternal, omnipresent, the One without second.
- Our salvation depends on belief in him and in his worship in this world and the next.
- Belief consists in loving him and doing his will.
Question 16.
Mention the important clauses of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany.
Answer:
Here are the important clauses of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany:
- Germany was forced to give up territories to the west, north and east of the German border.
- Germany had to disarm and was allowed to retain a very restricted armed force (army, navy and air force);
- As reparations for the War, Germany was expected to pay for the military and civilian cost of the War to the Allied nations. .
Question 17.
What were the duties of a Palayakkarars?
Answer:
The Palayakkarars carried on the following duties:
- They collected revenue, administered the territory control, settled disputes and maintained law and order.
- On many occasions the Palayakkarars helped the Nayak rulers to restore the kingdom to them.
Question 18.
Write a note on Bhagat Singh.
Answer:
1. Bhagat Singh was an Indian socialist revolutionary whose two acts of dramatic violence against the British in India and the execution at the age of 23 made him a folk hero of the Indian Independence Movement.
2. Bhagat Singh along with B. K. Dutt threw a smoke bomb inside the Central Legislative Assembly in 1929. It was not intended to hurt anyone. They threw pamphlets and shouted Tnquilab Zindabad’ and ‘Long Live the Proletariat’.
3. He along with Rajguru was arrested and sentenced to death. Bhagat Singh’s daring act fired the imagination of the youth across India and he became popular.
![]()
Question 19.
Name the distinct seasons of India.
Answer:
- Winter or cold weather season (Jan-Feb)
- Pre Monsoon or Summer (March-May)
- Southwest Monsoon or rainy season (June-September)
- Northeast Monsoon season (October-December)
Question 20.
Define Agriculture.
Answer:
Agriculture is the process of producing food for people, fodder for cattle, fiber and many other desired products by the cultivation of certain plants and the raising of domesticated animals.
Question 21.
Name the different types of coal with their carbon content.
Answer:
- Anthracite : contains 80 to 90% Carbon
- Bituminous : contains 60 to 80% Carbon
- Lignite : 40 to 90% Carbon
- Peat : contains less than 40% Carbon
Question 22.
List out the air ports and sea ports of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Airports:
- Chennai International Airport
- Coimbatore International Airport
- Madurai International Airport
- Tiruchirapalli International Airport
Domestic Airports:
Tuticorin and Salem
Sea Port: Major Sea Ports are:
- Chennai
- Ennore
- Tuticorin
Intermediate port at Nagapattinam and 15 minor ports.
Question 23.
List out any five global groupings in which India is a member.
Answer:
India is a member of formal groupings like UNO, NAM, S AARC, G20 and the Commonwealth.
Question 24.
List out any two special powers of the Attorney General of India?
Answer:
1. The Attorney General of India has the right to speak and to take part in the proceedings of both Houses of the Parliament or their joint sitting and any committee of the Parliament of which he may be named as a member, but without a right to vote.
2. In the performance of his official duties, Attorney General of India has the right of audience in all Courts in the territory of India.
![]()
Question 25.
What are the qualifications for the appointment of Governor?
Answer:
Qualifications of the Governor is given below
- He should be a citizen of India.
- He must have completed 35 years of age.
- He should not be a member of Parliament or any State legislature.
- He should not hold any other profitable occupation.
Question 26.
Write the name of economic policies of India.
Answer:
Name of economic policies in India are:
- Agriculture Policy
- Industrial Policy
- New Economic Policy
- Trade Policy
- Employment Policy
- Currency and Banking Policy
- Fiscal and Monetary Policy
- Wage Policy
- Population Policy
Question 27.
What is meant by black money?
Answer:
Black money is funds earned on the black market on which income and other taxes have not been paid. The unaccounted money that is concealed from the tax administrator is called black money.
Question 28.
Name any five biosphere reserves in India.
Answer:
- Agasthyamalai
- Dibru Saikhowa
- Dihang Dibang
- Great Nicobar
- Gulf of Mannar
- The Nilgiris
- Sundarbans
Part – III
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 × 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks
(i) In 1918, the society for the study of Marxism was fortned in ………………..University.
(ii) ………………..is the Tamil Nadu state animal.
(iii) ………………..is a small Himalyan Kingdom.
(iv) ………………..is the value of currency expressed in terms of the amount of goods and services
that one unit of money can buy.
(v) The difference between the value of exports and imports is called ………………..
Answers
(i) Peking
(ii) Nilgiri Thar
(iii) Bhutan
(iv) Purchasing power
(v) Balance of trade
Question 30.
Match the following

Answers:

![]()
Question 31.
Match the following

Answers:

Question 32.
(a) Distinguish between
(i) Jute industry and Sugar industry.
(ii) Internal Trade and International Trade.
Answer:
(a) (i) Jute industry and Sugar industry:
Jute industry :
- The Jute industry is concerned mainly with the production of gunny bags, canvas, pack sheets, jute web, carpets, cordage, hessian and twines.
- West Bengal, Titagarh, Jagatdat, Budge- budge, Haora and Bhadreshwar are the chief centres of jute industry.
Sugar industry :
- Sugar can be produced from sugarcane, sugar-beets, or any other crop which have sugar content.
- Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Bihar, Punjab, Gujarat, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh.
(ii) Internal Trade and International Trade:
Internal Trade
- Internal trade is also known as local trade. It is carried on within the domestic territory of a country.
- Land transport plays a major role in the movement of goods.
- This trade is mostly fixed on the nation’s currency.
- This internal trade helps to promote balanced regional growth in the country. This trade leads to rapid economic progress of a country.
International Tirade :
- International trade is also known as External trade. It is a trade carried on between two or more countries.
- Ocean transport plays major role in the movement of goods.
- This trade is carried on foreign currency.
- This trade leads to rapid economic progress of a country.
(b) Give reason: Cities are densely populated than the villages.
Answer:
Agriculture, job opportunities and industrial development are the main causes of population density in the cities then the villages.
Question 33.
Assess the structure and the activities of the UN.
Answer:
The United Nations came into existence in the year 1945 to achieve lasting peace among all nations which were inter-dependent. It functions like any government, through its principal organs which are similar to the legislative, executive and judicial wings of a state.
- The General Assembly is the body in which each member state is represented. It meets once a year and issues of interest and points of conflict are discussed in the Assembly.
- The Security Council has fifteen members, five of them (the USA, Britain, France, Russia and China) are permanent members. The other ten temporary members are elected in .rotation from different parts of the world. Each of the permanent members has the right to veto any decision by the other members of the Security Council.
- The UN Secretariat is headed by the Secretary General, who is elected by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council.
- The International Court of Justice is the Judicial wing of the United Nations. Its headquarter is at The Hague.
- The fifth organ of the UN is the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). It is responsible for coordinating all the economic and social work of the United Nations.
Activities of the United Nations:
Human rights, the problems of refugees, climate change, gender equality are all within the ambit of the activities of the United Nations. The UN Peace-keeping force has acted in many areas of conflict all over the world.
Question 34.
Discuss the response to Swadeshi Movement in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
1. During the Swadeshi movement, public meetings were organised in various parts of Tamil Nadu, and they were attended by thousands of people. Tamil was used for the first time to mobilise people.
2. Many journals came into existence to spread Swadeshi ideals. Students and youth participated widely in the movement. Some lectures were delivered by Bipin Chandra Pal, while Subramania Bharati’s patriotic songs stirred patriotic emotions in people.
![]()
Question 35.
Explain the importances of satellite communication in India.
Answer:
1. Satellite images are used for weather forecasting, monitory of natural calamities, surveillance of border areas etc. The communication through satellites emerged as a new era in communication in our country after the establishment of Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) in 1969.
2. Satellite systems in India can be grouped into two on the basis of two satellites namely
“Indian National Satellite” (INSAT) and “Indian Remote Sensing Satellite” (IRS). These satellites collect data in several spectral band and transmit there to ground stations for various uses.
3. The communication and remote sensing satellites INSAT and IRS have revolutionized India’s communication system. Metrological studies and natural resource management. The National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA) at Hyderabad provides facilities for acquisition of data and its processing.
4. There is no doubt that India has irrefatably arrived as a space power in the world. The INSAT series are used for relaying signals to television, telephone, radio, mobile phone.
5. It is also useful in weather detection, internet. The INSAT series GSAT series, GSAT series KALPANA -1, HAMS AT, EDUSAT are the major communication satellite used for communication purpose. GSAT – 7A is the recent launch for communication programs. INSAT – IB launched on 30th August, 1983 is the first communication satellite in INSAT series.
Question 36.
Bring out the types and distribution of soils in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Types of Soils Distribution of Soil in Tamil Nadu
Alluvial Soil : It is found in river valley regions and coastal plains. Thanjavur, Tiruvarur, Nagapattinam, Villupuram, Cuddalore, Tirunelveli and Kanniyakumari
Black Soil : Coimbatore, Madurai, Virudhunagar, Tirunelveli and Thoothukudi
Red Soil : Sivagangai and Ramanathapuram
Laterite Soil : Kancheepuram, Tiruvallur and Thanjavur districts and source patches over the mountain region in the Nilgiris
Saline Soil : Saline soils in Tamil Nadu are confined to the Coromandel coast and Vedaranyam
Question 37.
Mention OPEC missions and how does it help other countries?
Answer:
OPEC’s mission:
- To coordinate oil policies in its member countries
- Help stabilise oil markets
- To secure fair and stable income to petroleum producers
- An efficient, economic and regular supply of oil to consuming nations
- A fair return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry
How does OPEC help other countries:
The OPEC Fund for International Development (OPID) is an institution that helps finance projects with low interest loans. It also provides grants to social and humanitarian projects. OPEC has an Information Centre with over 20,000 volumes including books, reports, maps and conference proceedings related to petroleum, energy and the oil market. The Information Centre is open to the public and is often used by researchers and students. ,
Question 38.
Write the differences between the growth and development.
Answer:
Differences between the Economic growth and Economic development:
Economic Growth :
- It is the positive quantitative change in the output of an economy in a particular time period
- Economic growth is the ‘narrower’ concept.
- Quantitative in nature.
- Rise in parameters like, GDP, GNP, FDI, FII etc.
- Short term in nature.
- It is applicable in developed nations.
- It is measured by increase in national income.
- It occurs in a certain period of time.
Economic Development :
- It consider the rise in the output in an economy along with the advancement of HDI index which considers a rise in living standards, advancement in technology and overall happiness index of a nation.
- Economic development is the ‘broader’ concept.
- Qualitative in nature.
- Rise in life expectancy rate, infant, improvement in literacy rate, infant mortality rate and poverty rate etc.
- Long-term in nature.
- It is applicable in developing co countries.
- It is measured by increase in real national income, i.e., per capita income.
- It is a continuous process.
![]()
Question 39.
Write the challenges of Globalization.
Answer:
The following are the challenges of globalization.
- To ensure that the benefits of globalization extent to all countries. That will certainly not happen automatically.
- To deal with the fear that globalization leads to stability, which is particularly marked in the developing world. .
- To address the very real fear in the industrial world that increased global competition will lead memorably to a race to the bottom in wages, labour rights, employment practices, and the environment.
- Globalization and all of the complicated problems related to it must not be used as excuses to avoid searching for new ways to cooperate in the over all interest of countries and people.
- People have started consuming more junk foods. This has badly affected their health.
Question 40.
Name some industrial development agencies and explain them.
Answer:
The following are some agencies that have played a key role in industrialization in the state.
SIPCOT: (State Industries Promotion Corporation of Tamil Nadu), 1971:
It was formed in the year 1971 to promote industrial growth in the state by setting up industrial estates.
TANSIDCO: (Tamil Nadu Small Industries Development corporation), 1970:
TANSIDCO is a state-agency of the state of TN established in the year 1970 to promote smallscale industries in the state. It gives subsidies and provide technical assistance for new firms in the small scale sector.
TIDCO (Tamil Nadu Industrial Development Corporation), 1965:
TIDCO is another government agency to promote industries in the state and to establish industrial estates.
TIIC (Tamil Nadu Industrial Investment Corporation Ltd.), 1949:
TIIC is intended to provide low-cost financial support for both setting up new units and also for expansion of existing units. Though it is meant to meet the requirements of all types of firms, 90% of support goes to micro, small and medium enterprises.
TANSI (Tamil Nadu Small Industries Corporation Ltd.), 1965:
TANSI was formed in 1965 to take over the small scale-units that were set up and run by the Department of Industries and Commerce. It is supposed to be the first industrial corporation operating in the domain for small enterprises.
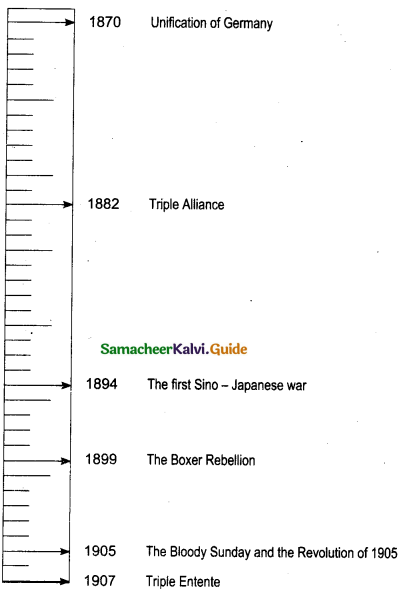
Question 41.
Draw a time line for the following:
Write any five important events between 1920-1940
Year – Events
1920 – Non Co-operation Movement
1921 – Ahmedabad Congress Session
1922 – Chauri Chaura incident / Suspension of Non Co-operation movement
1923 – Birth of Swaraj Party
1924 – Formation of Hindustan Republican Army
1925 – Death of C.R. Das / Swaraj Party dissolved
1927 – Formation of Simon Commission
1928 – Arrival of Simon Commission to India / The Nehru Report
1929 – Lahore Congress
1930 – Salt Satyagraha / Civil Disobedience Movement / Dandi. March / First Round Table Conference
1931 – Gandhi Irwin Pact / Second Round Table Conference
1932 – Poona Pact / The Communal Award / Third Round Table Conference
1935 – Government of India Act
1937 – Provincial Elections
1939 Second World War started
1940 – Jinnah’s demand for separate nation – Pakistan / August offer
![]()
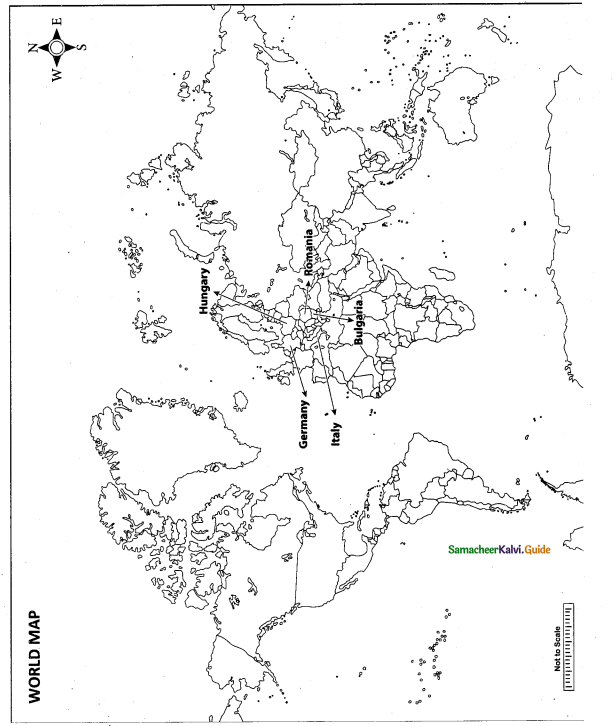
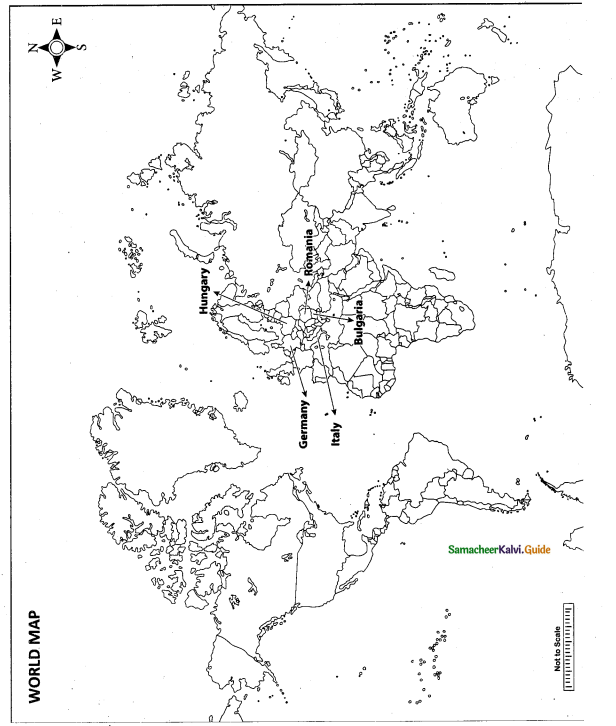
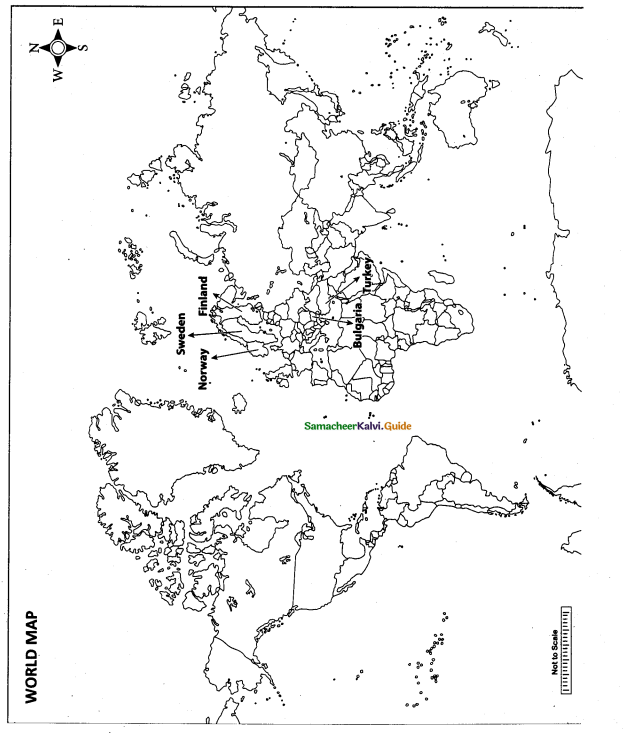
Question 42.
Mark the following places on the world map.
(i) Norway
(ii) Sweden
(iii) Finland
(iv) Bulgaria
(v) Turkey
Answer:
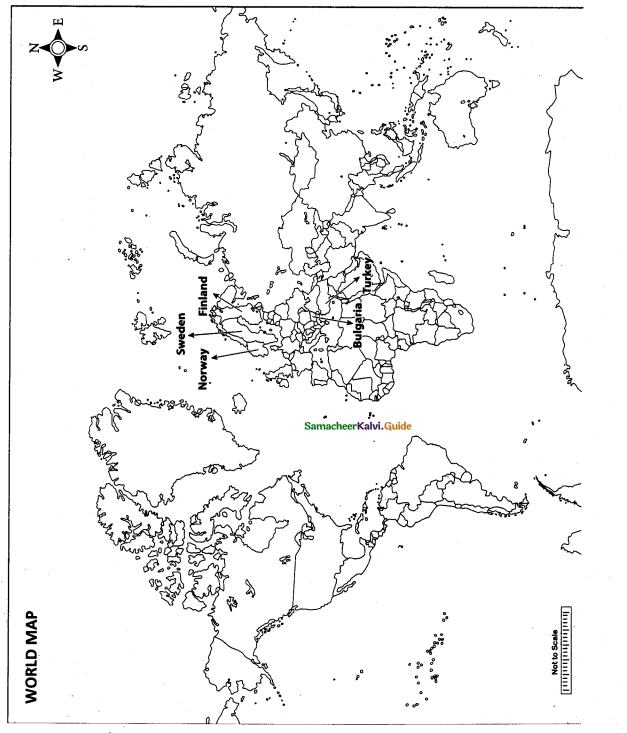
Part – IV
Answer both questions. [2 × 8 = 16]
Question 43. (a) Anti-Colonial Struggle in Indo-China (*) Define the concept of decolonisation.
(if) What were the three States that formed Indo-China.
(iii) How did Communist ideas help in developing the spirit of anti-colonialism.
(iv) Which was the mainstream political party in Indo-China?
Answer:
(a) Anti-Colonial Struggle in Indo-China
(i) Decolonisation is a process through which colonial powers transferred institutional and legal control over their colonies to indigenous nationalist government.
(if). Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam.
(iii) Communist ideas from mainland China helped in developing the spirit of anti-colonalism in Indo-China. Many became convinced that the considerable wealth of Indo-China was benefiting only the colonial power. This aroused the feeling of nationalism which resulted in violence. In 1916 there was a major anti-colonial revolt which was crushed brutally. There were also guerrilla activities in Tongking.
(iv) The mainstream political party in Indo-China was the Vietnam Nationalist Party. It was composed of the wealthy and middle class sections of the population.
(b) Vellore Revolt
(i) When did Vellore Revolt break out?
(ii) Who introduced new military regulation?
(iii) Who was the first victim of the revolt?
(iv) Who was proclaimed by the rebels as their new rules?
Answer:
(b) Vellore Revolt
(i)10th July 1806 .
(ii) Commander in Chief Sir John Cradock.
(iii) Colonel Fancourt
(iv) Fateh Hyder
[OR]
(c) Velunachiyar
(i) Who was the military chief of Velunachiyar?
(ii) What were the martial arts in which she was trained?
(iii) Whom did she marry?
(iv) What was the name of her daughter?
(c) Velunachiyar
(i) Gopala Nayaker
(ii) The martial arts in which she was trained were valari, stick fighting and to wield weapons.
(iii) She was married to Muthu Vadugar, the Raja of Sivagangai.
(iv) Her Daughter’s name was Vellachinachiar.
(d) Self Respect Movement
(i) Who started the Self Respect Movement? ’
(ii) Why did he start?
(iii) When was it started?
(iv) Name the laws passed by the government due to the constant struggle of Self Respect Movement.
Answer:
(d) Self Respect Movement
(i) E.V. Ramaswamy Periyar started the self respect movement.
(ii) He started it in order to spread and execute his ideas and policies.
(iii) It was started in 1925.
(iv) Widow Remarriage Act, Women’s Right to property Act and abolition of Devadasi Act.
![]()
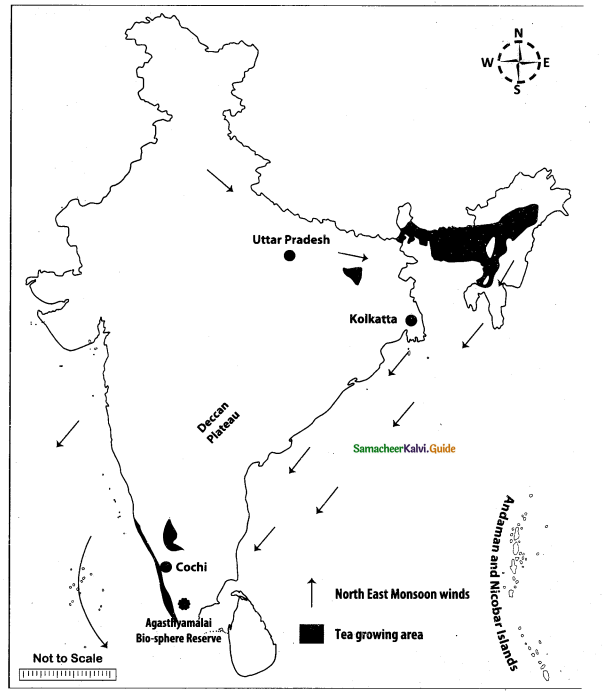
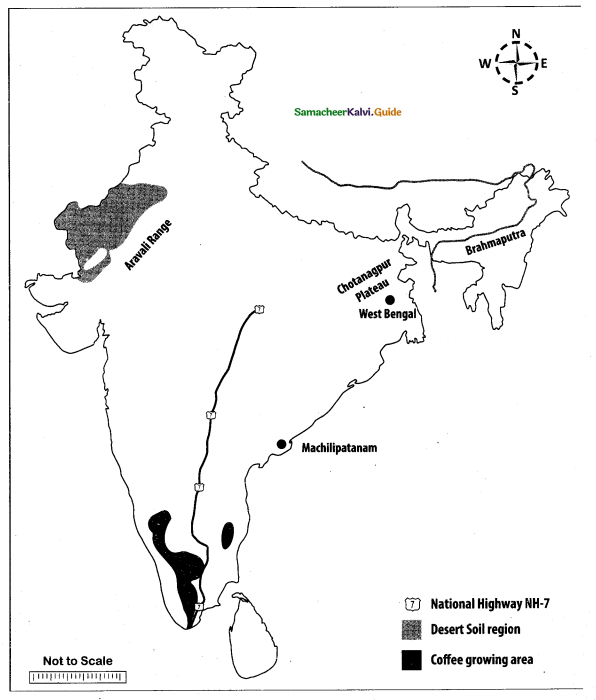
Question 44.
Mark the following places on the given outline map of India.
(i) Aravalli
(ii) Brahmaputra
(iii) Chotanagpur plateau
(iv) West Bengal
(v) Desert soil region
(vi) Coffee growing area
(vii) Machillipatnam
(viii) National Highway NH-7
Answer:
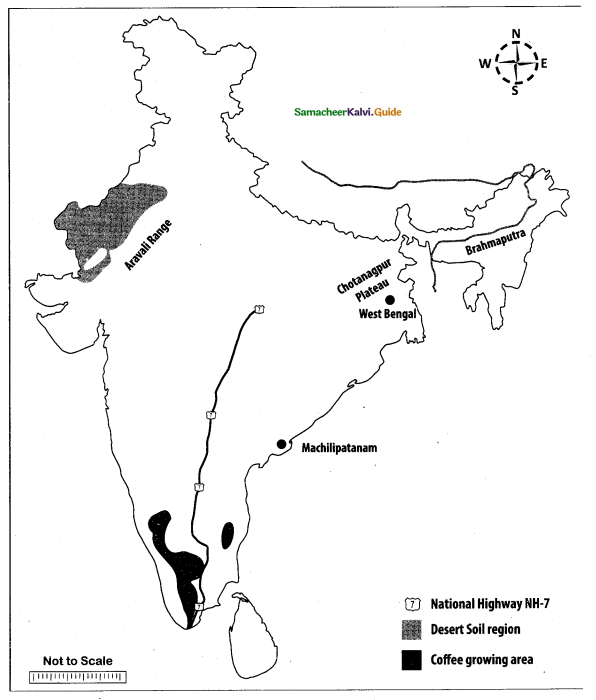
[OR]
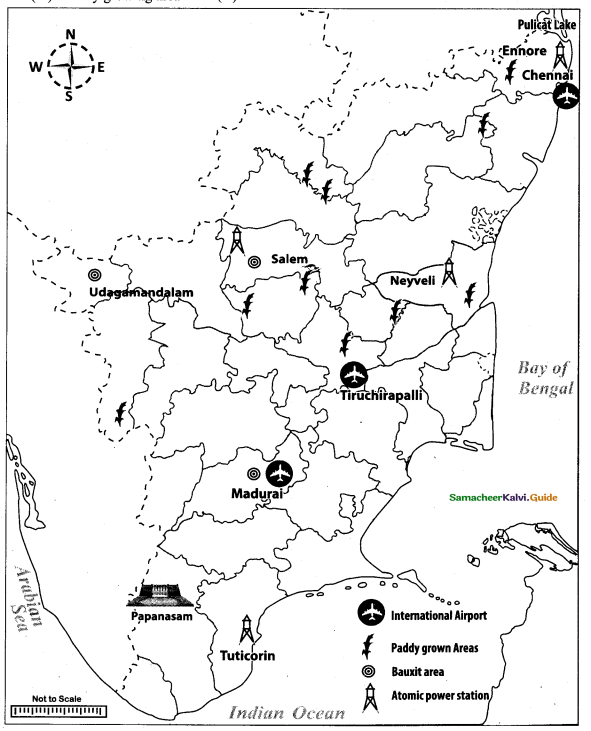
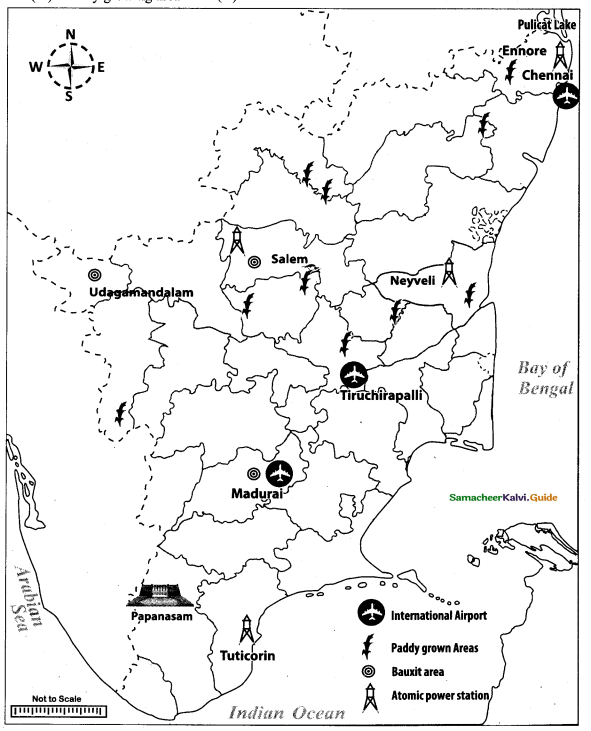
Mark the following places on the given outline map of Tamil Nadu.
(i) International airport
(ii) Madurai
(iii) Paddy growing area
(iv) Atomic power station
(v) Bauxite area
(vi) Pulicat lake
(vii) Papanasam
(viii) Ennore
Answer:
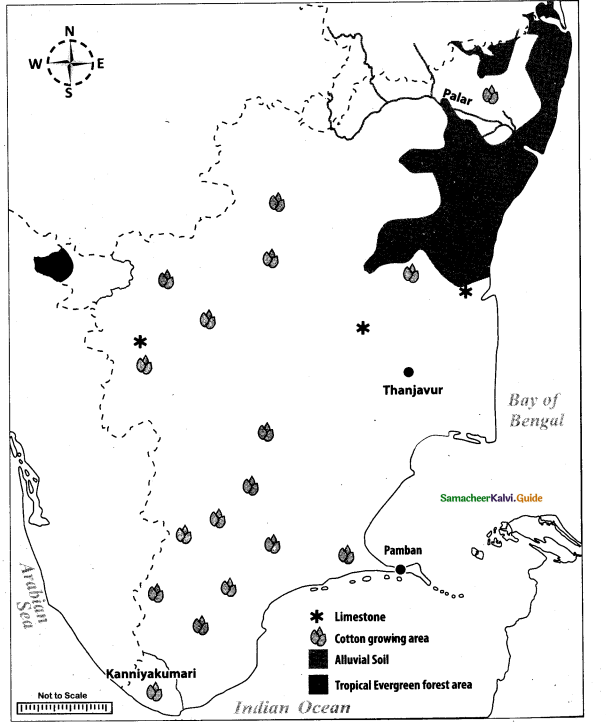
Map for Q. 42
(i) Norway
(ii) Sweden
(iii) Finland
(iv) Bulgaria
(v) Turkey
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
(i) Aravalli Range
(ii) River Brahmaputra
(iii) Chotanagpur plateau
(iv) West Bengal
(v) Desert soil region
(vi) Coffee growing area
(vii) Machillipatnam
(viii) National Highway NH-7
Answer:
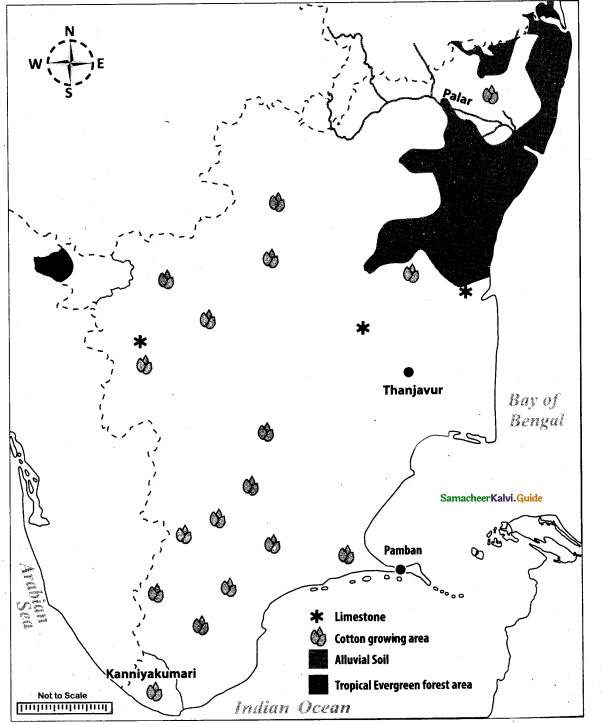
Map for Q. 44
(i) International airport
(ii) Madurai
(iii) Paddy growing area
(iv) Atomic power station
(v) Bauxite area
(vi) Pulicat lake
(vii) Papanasam
(viii) Ennore
Answer: