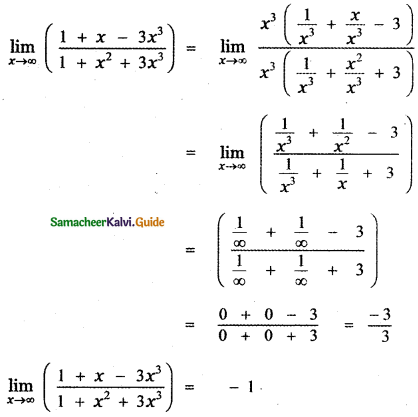
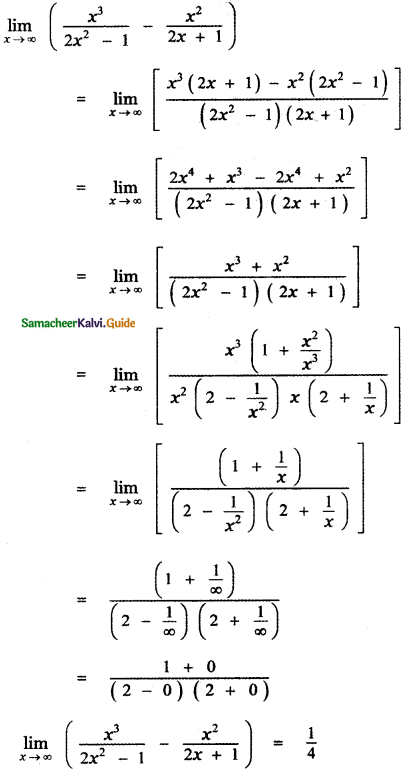
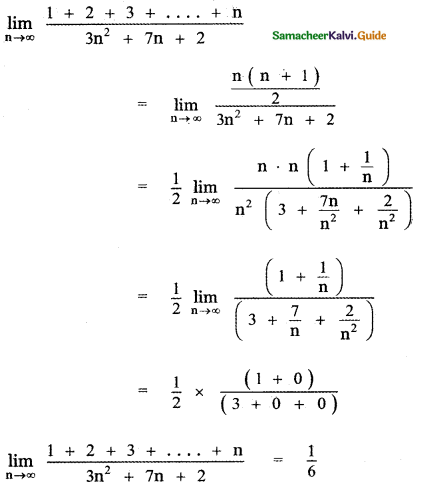
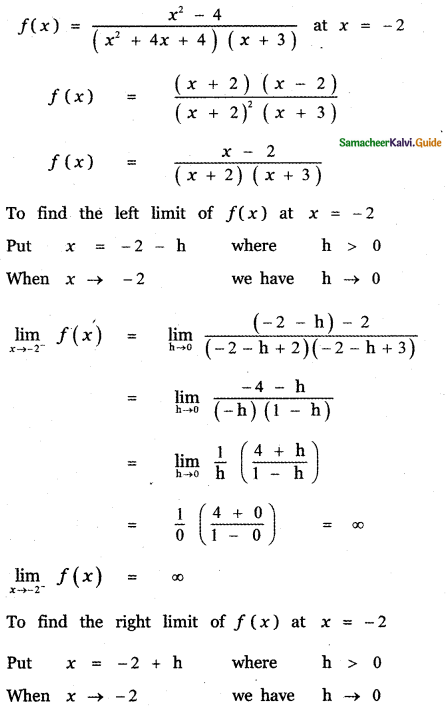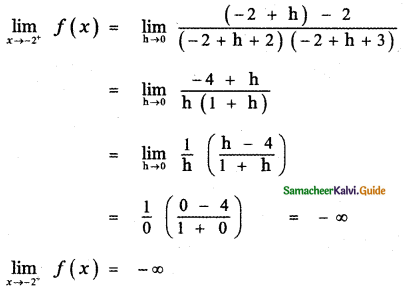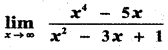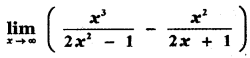Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Guide Pdf Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
12th Bio Zoology Guide Principles of Inheritance and Variation Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Haemophilia is more common in males because it is a………………
(a) Recessive character carried by Y-chromosome
(b) Dominant character carried by Y-chromosome
(c) Dominant trait carried by X-chromosome
(d) Recessive trait carried by X-chromosome
Answer:
(d) Recessive trait carried by X-chromosome
Question 2.
ABO blood group in man is controlled by …………………….
(a) Multiple alleles
(b) Lethal genes
(c) Sex linked genes
(d) Y-linked genes
Answer:
(a) Multiple alleles
![]()
Question 3.
Three children of a family have blood groups A, AB and B. What could be the genotypes of their parents?
(a) IAIB and ii
(b) IA1O and IBIO
(c) IB IB and IAIA
(d) IAIA and ii
Answer:
(b) IA1O and IBIO
Question 4.
Which of the following is not correct?
(a) Three or more alleles of a trait in the population are called multiple alleles.
(b) A normal gene undergoes mutations to form many alleles
(c) Multiple alleles map at different loci of a chromosome
(d) A diploid organism has only two alleles out of many in the population
Answer:
(c) Multiple alleles map at different loci of a chromosome
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following phenotypes in the progeny are possible from the parental combination
(a)AandB only
(b) A,B andAB only
(c) AB only
(d) A,B,AB and O
Answer:
(d) A,B,AB and O
Question 6.
Which of the following phenotypes is not possible in the progeny of the parental genotypic combination IAIO x lAlB ?
(a) AB
(b) O
(c) A
(d) B
Answer:
(b) O
Question 7.
Which of the following is true about Rh factor in the offspring of a parental combination DdXDd (both Rh positive)?
(a) All will be Rh positive
(b) Half will be Rh positive
(c) About 3/4 will be Rh negative
(d) About one fourth will be Rh negative
Answer:
(d) About one fourth will be Rh negative
![]()
Question 8.
What can be the blood group of offspring when both parents have AB blood group?
(a) AB only
(b) A, B and AB
(c) A, B, AB and O
(d) A and B only
Answer:
(b) A, B and AB
Question 9.
If the childs blood group is ‘O’ and fathers blood group is ‘A’ and mother’s blood group is ‘B’ the genotype of the parents will be …………….
(a) IAIA and IBIO
(b) IAIO and IBIO
(c) IAIO and IOIO
(d) IOIO and IBIB
Answer:
(b) IAIO and IBIO
Question 10.
XO type of sex determination and XY type of sex determination are examples of …………………
(a) Male heterogamety
(b) Female heterogamety
(c) Male homogamety
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(a) Male heterogamety
![]()
Question 11.
In an accident there is great loss of blood and there is no time to analyse the blood group Question which blood can be safely transferred?
(a) ‘O’ and Rh negative
(b) ‘O’ and Rh positive
(c) ‘B’ and Rh negative
(d) ‘AB’ and Rh positive
Answer:
(a) ‘O’ and Rh negative
Question 12.
Father of a child is colourblind and mother is carrier for colourblindness, the probability of the child being colourblind is ………………
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 100%
(d) 75%
Answer:
(b) 50%
Question 13.
A marriage between a colourblind man and a normal woman produces
(a) All carrier daughters and normal sons
(b) 50% carrier daughters, 50% normal daughters
(c) 50% colourblind sons, 50% normal sons
(d) All carrier offsprings
Answer:
(a) All carrier daughters and normal sons
![]()
Question 14.
Mangolism is a genetic disorder which is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome number.
(a) 20
(b) 21
(c) 4
(d) 23
Answer:
(b) 21
Question 15.
Klinefelters’ syndrome is characterized by a karyotype of………………
(a) XYY
(b) XO
(c) XXX
(d) XXY
Answer:
(d) XXY
Question 16.
Females with Turners’syndrome have………………
(a) Small uterus
(b) Rudimentary ovaries
(c) Underdeveloped breasts
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
![]()
Question 17.
Pataus’ syndrome is also referred to as………………
(a) 13-Trisomy
(b) 18-Trisomy
(c) 21-Trisomy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) 13-Trisomy
Question 18.
Who is the founder of Modem Eugenics movement?
(a) Mendel
(b) Darwin
(c) Fransis Galton
(d) Karl pearson
Answer:
(c) Fransis Galton
Question 19.
Improvement of human race by encouraging the healthy persons to marry early and produce large number of children is called………………
(a) Positive eugenics
(b) Negative eugenics
(c) Positive euthenics
(d) Positive euphenics
Answer:
(a) Positive eugenics
Question 20.
The ……………… deals with the control of several inherited human diseases especially inborn errors of metabolism.
(a) Euphenics
(b) Eugenics
(c) Euthenics
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Euphenics
![]()
Question 21.
“Universal Donor” and “Universal Recipients” blood group are ……………… and ……………… respectively.
(a) AB, O
(b) O, AB
(c) A, B
(d) B, A
Answer:
(b) O, AB
Question 22.
ZW-ZZ system of sex determination occurs in………………
(a) Fishes
(b) Reptiles
(c) Birds
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 23.
A co-dominant blood group is
(a) A
(b) AB
(c) B
(d) O
Answer:
(b) AB
Question 24.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding ZW-ZZ type of sex determination?
(a) It occurs in birds and some reptiles
(b) Females are homogametic and males are heterogametic
(e) Male produce two types of gametes
(d) It occurs in gypsy moth
Answer:
(b) Females are homogametic and males are heterogametic
![]()
Question 25.
What is haplodiploidy?
Answer:
In haplodiploidy, the sex of the offspring is determined by the number of sets of chromosomes it receives. Fertilized eggs develop into females (Queen or Worker) and unfertilized eggs develop into males (drones) by parthenogenesis. It means that the males have half the number of chromosomes (haploid) and the females have double the number (diploid).
Question 26.
Distinguish between heterogametic and homogametic sex determination systems.
Answer:
Heterogametic Sex :
- Organisms producing two different types of gametes.
- Example: Human male.
Sperm with X chromosome
Sperm with Y chromosome
Homogametic Sex :
- Organisms producing only one type of gametes.
- Example: Human female.
Every egg produced contain X chromosomes.
Question 27.
What is Lyonisation?
Answer:
Lyonisation is a process of inactivation of one of the X chromosomes in some females.
![]()
Question 28.
What is criss-cross inheritance?
Answer:
Inheritance of genes from a male parent to female child and then to male grandchild or female parent to male child and then to female grandchild. E.g., X-linked gene inheritance.
Question 29.
Why are sex-linked recessive characters more common in male human beings?
Answer:
Sex linked inherited traits are more common in males than females because, males are hemizygous and therefore express the trait when they inherit one mutant allele.
Question 30.
What are holandric genes?
Answer:
The genes present in the differential region of the Y chromosome are called Y- linked or holandric genes. The Y linked genes have no corresponding allele in X chromosome.
Question 31.
Mention the symptoms of Phenylketonuria.
Answer:
Severe mental retardation, light pigmentation of skin and hair. Phenylpyruvic acid is excreted in the urine.
Question 32.
Mention the symptoms of Down’s syndrome.
Answer:
Severe mental retardation, defective development of the central nervous system, increased separation between the eyes, flattened nose, ears are malformed, mouth is constantly open and the tongue protrudes.
![]()
Question 33.
Differentiate Intersexes from Supersexes.
Answer:Intersexes:
Intersexes refers to the individuals having the characteristics of both female and male sexes and their sexual anatomy does not seem to fit the typical definition of male or female.
Supersexes:
Supersexes ar formed as a result of an abnormal combination of sex chromosomes.
Example: Super males in humans human beings have 44+XYY chromosomes.
Question 34.
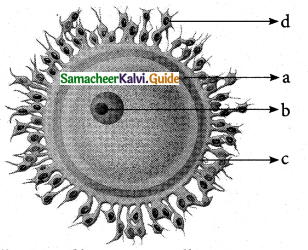
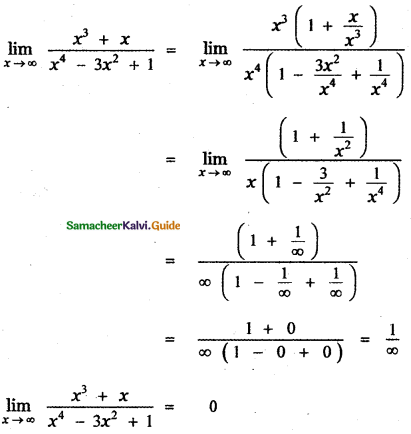
Explain the genetic basis of ABO blood grouping in man.
Answer:
Multiple allele inheritance of ABO blood groups
Blood differs chemically from person to person. When two different incompatible blood types are mixed, agglutination (clumping together) of erythrocytes (RBC) occurs. The basis of these chemical differences is due to the presence of antigens (surface antigens) on the membrane of RBC and epithelial cells. Karl Landsteiner discovered two kinds of antigens called antigen ‘A’ and antigen ‘B’ on the surface of RBC’s of human blood. Based on the presence or absence of these antigens three kinds of blood groups, type ‘A’, type ‘B’, and type ‘O’ (universal donor) were recognized. The fourth and the rarest blood group ‘AB’ (universal recipient) was discovered in 1902 by two of Landsteiner’s students Von De Castelle and Sturli.
Bernstein in 1925 discovered that the inheritance of different blood groups in human beings is determined by a number of multiple allelic series. The three autosomal alleles located on chromosome 9 are concerned with the determination of blood group in any person. The gene controlling blood type has been labeled as ‘L’ (after the name of the discoverer, Landsteiner) or I (from isoagglutination). The I gene exists in three allelic forms, IA, IB and IO. IA specifies A antigen. IB allele determines B antigen and IO allele specifies no antigen. Individuals who possess these antigens in their fluids such as the saliva are called secretors.
Each allele (IA and IB) produces a transferase enzyme. IA allele produces N-acetyl galactose transferase and can add N-acetyl galactosamine (NAG) and IB allele encodes for the enzyme galactose transferase that adds galactose to the precursor (i.e. H substances). In the case of IO/IO allele no terminal transferase enzyme is produced and therefore called “null” allele and hence cannot add NAG or galactose to the precursor.
From the phenotypic combinations it is evident that the alleles IA and IB are dominant to 1°, but co-dominant to each other (IA = IB). Their dominance hierarchy can be given as (IA=IB> 1O). A child receives one of three alleles from each parent, giving rise to six possible genotypes and four possible blood types (phenotypes). The genotypes are IAIA , IAIO, IBIB, IBIO, IAIB and IOIO.
Question 35.
How is sex determined in human
Answer:
Genes determining sex in human beings are located on two sex chromosomes, called allosomes. In mammals, sex determination is associated with chromosomal differences between the two sexes, typically XX females and XY males. 23 pairs of human chromosomes include 22 pairs of autosomes (44A) and one pair of sex chromosomes (XX or XY). Females are homogametic producing only one type of gametes (egg), each containing one X chromosome while the males are heterogametic producing two types of sperms with X and Y chromosomes. An independently evolved XX: XY system of sex chromosomes also exist in Drosophila.
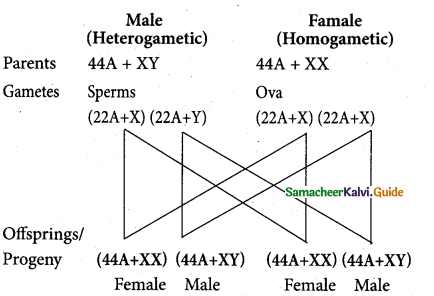
![]()
Question 36.
Explain male heterogamety.
Answer:
Male heterogamety (XY males) is a type of sex determination in which males produce two different types of gametes. For example, human males produce two kinds of sperms that is sperm with X-chromosome and sperms with Y-chromosome.
Question 37.
Brief about female heterogamety.
Answer:
Female heterogamety (ZO females) refers to the condition, where female produces two types of egg cells. Some with Z chromosome and some without Z chromosome.
Question 38.
Give an account of genetic control of Rh factor?
Answer:
Genetic control of Rh factor
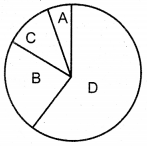
Fisher and Race hypothesis: Rh factor involves three different pairs of alleles located on three different closely linked loci on the chromosome pair. This system is more commonly in use today, and uses the ‘Cde’ nomenclature.
In the given figure, three pairs of Rh alleles (Cc, Dd and Ee) occur at 3 different loci on homologous chromosome pair-1. The possible genotypes will be one C or c, one D or d, one E or e from each chromosome. For e.g. CDE/cde; CdE/cDe; cde/cde; CDe/CdE etc. All genotypes carrying a dominant ‘D’ allele will produce Rh+positive phenotype and double recessive genotype ‘dd’ will give rise to Rh negative phenotype.
Wiener Hypothesis
Wiener proposed the existence of eight alleles (R1, R2, R0, Rz, r, r1, r11, ry) at a single Rh locus. All genotypes carrying a dominant ‘R allele’ (R1, R2 ,R0 ,Rz) will produce ‘Rh-positive’ ^phenotype and double recessive genotypes (rr, rr1, rr11, rry) will give rise to Rh-negative phenotype.
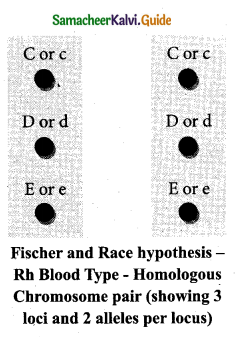
![]()
Question 39.
Explain the mode of sex determination in honeybees.
Answer:
In hymenopteran insects such as honeybees, ants and wasps, a mechanism of sex determination called haplodiploidy mechanism of sex determination is common. In this system, the sex of the offspring is determined by the number of sets of chromosomes it receives. Fertilized eggs develop into females (Queen or Worker) and unfertilized eggs develop into males (drones) by parthenogenesis. It means that the males have half the number of chromosomes (haploid) and the females have double the number (diploid), hence the name haplodiploid for this system of sex determination.
This mode of sex determination facilitates the evolution of sociality in which only one diploid female becomes a queen and lays the eggs for the colony. All other females which are diploid having developed from fertilized eggs help to raise the queen’s eggs and so contribute to the queen’s reproductive success and indirectly to their own, a phenomenon known as Kin Selection. The queen constructs their social environment by releasing a hormone that suppresses fertility of the workers.
Question 40.
Discuss the genic balance mechanism of sex determination with reference to Drosophila?
Answer:
XX-XY type (Lygaeus Type) sex determination is seen in Drosophila. The females are homogametic with XX chromosomes, while the males are heterogametic with X and Y chromosomes. Homogametic females produce only one kind of egg, each with one X chromosome, while the heterogametic males produce two kinds of sperms some with X chromosome and some with Y chromosome.
The sex of the embryo depends on the fertilizing sperm. An egg fertilized by an ‘X’ bearing sperm produces a female, if fertilized by a ‘Y’ bearing sperm, a male is produced.
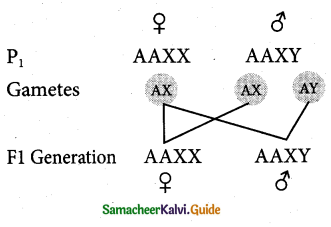
Question 41.
What are the applications of Karyotyping?
Answer:
- Karyotyping helps in gender identification.
- It is used to detect the chromosomal aberrations like deletion, duplication, translocation, non-disjunction of chromosomes.
- It helps to identify the abnormalities of chromosomes like aneuploidy.
- It is also used in predicting the evolutionary relationships between species.
- Genetic diseases in human beings can be detected by this technique.
![]()
Question 42.
Explain the inheritance of sex linked characters in human being.
Answer:
Haemophilia is commonly known as bleeder’s disease, which is more common in men than women. This hereditary disease was first reported by John Cotto in 1803. Haemophilia is caused by a recessive X-linked gene. A person with a recessive gene for haemophilia lacks a normal clotting substance (thromboplastin) in blood, hence minor injuries cause continuous ’bleeding, leading to death. The females are carriers of the disease and would transmit the disease to 50% of their sons even if the male parent is normal. Haemophilia follows the characteristic criss-cross pattern of inheritaitce.
Question 43.
What is extra chromosomal inheritance? Explain with an example.
Answer:
The cytoplasmic extra nuclear genes have a characteristic pattern of inheritance which does not resemble genes of nuclear chromosomes and are known as Extrachromosomal/ Cytoplasmic inheritance.
Question 44.
Comment on the methods of Eugenics.
Answer:
Eugenics refers to the study of the possibility of improving the qualities of human population.
Methods of Eugenics:
- Sex-education in school and public forums.
- Promoting the uses of contraception.
- Compulsory sterilization for mentally retarded and criminals.
- Egg donation.
- Artificial insemination by donors.
- Prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders and performing MTP
- Gene therapy
- Cloning
- Egg/sperm donation of healthy individuals.
![]()
12th Bio Zoology Guide Principles of Inheritance and Variation Additional Important Questions and Answers
12th Bio Zoology Guide Principles of Inheritance and Variation One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1
If a colorblind female marries a normal male, their sons will be ………………
(a) All normal visioned
(b) All color blinded
(c) One half normal visioned other half colorblind
(d) Three fourth colorblind one fourth normal
Answer:
(c) One half normal visioned other half colorblind
Question 2
Excess hair growth on pinna is a feature noticed only in males because ……………
(a) Males produce more testosterone
(b) gene responsible for the character is located in Y-chromosome
(c) Estrogen suppresses the character in females
(d) females act only as a carriers for this character
Answer:
(b) gene responsible for the character is located in Y-chromosome
Question 3.
ABO blood group is a classical example for ………………..
(a) Multiple allelism
(b) Pleotropism
(c) Incomplete dominance
(d) Polygenic mechanism
Answer:
(a) Multiple allelism
![]()
Question 4
Unit of heredity is ……………….
(a) allele
(b) allelomorph
(c) trait
(d) gene
Answer:
(d) gene
Question 5.
Identify the proper dominance hierarchy.
(a) IA = IO > IB
(b) IA = IB > O
(b) IA = IB > O
(d) IB = IA > O
Answer:
Question 6
Haemophilia is more common in human males than human females. The reason is due to
(а) X-linked dominant gene
(b) X-linked recessive gene
(c) Y-linked recessive gene
(d) Allosomal abnormality
Answer:
(b) X-linked recessive gene
Question 7.
Identify the correct statement.
(a) Homozygous sex chromosome (XX) produce males in Drosophila
(b) Homozygous sex chromosome (ZZ) determine female sex in birds
(c) Heterozygous sex chromosome (XO) determine male sex in grasshopper
(d) Heterozygous sex chromosome (ZW) determine male sex in gypsy moth
Answer:
(c) Heterozygous sex chromosome (XO) determine male sex in grasshopper
![]()
Question
Which blood group doesnot possess antibodies?
(a) IAIB
(b) IOIO
(c) IAO
(d) IBIB
Answer:
(a) IAIB
Question 9.
Assertion (A): On diagnosis, Ramu is reported to have underdeveloped testis and gynecomastia.
Reason (R): His karyotype reveals XXY condition.
(а) A is right but R is wrong
(b) R explains A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) Both and R are right but R is not the correct explanation of A
Answer:
(b) R explains A
Question 10.
Pick out the odd man.
(a) Klinefelter’s syndrome
(b) Turner’s syndrome
(c) Huntington’s chorea
(d) 13-Trisomy
Answer:
(c) Huntington’s chorea
![]()
Question 11.
Pick the odd one out regarding Mendelian disorder.
(a) Thalassemia
(b) phenylketonuria
(c) Albinism
(d) Huntington’s chorea
Answer:
(d) Huntington’s chorea
Question 12.
Match the following:
| A Down’s syndrome | i. 44AA + XXY |
| B Patau’s syndrome | ii. 45AA + XY |
| C Klinefelter’s syndrome | ii. 44AA + XO |
| D Turner’s syndrome | iv. 45AA+XX |
(a) A – iv, B – ii, C – i, D – iii
(b)A – ii, B – iv, C – iii, D – i
(a)A – iii, B – i, C – ii, D – iv
(c) A – i, B – iv, C – iii, D – iii
Answer:
(a) A – iv, B – ii, C – i, D – iii
![]()
Question 13.
Identify the proper ratio of normal visioned individuals against colorblind individuals, if colorblind carrier female marries a normal male.
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 3:1
(c) 1 : 3
(d) All four are normal visioned
Answer:
(c) 1 : 3
Question 14.
Pick out the correct statement.
(i) Karyotyping helps in gender identification
(ii) Holandric genes are located on X-chromosome
(iii) Trisomy-21 is an allosomal abnormality
(iv) Cooley’s anemia is an autosomal recessive disorder
(a) i, iii, iv are correct
(c) i and iv are correct
Answer:
(c) i and iv are correct
![]()
Question 15.
DOPA stands for ……………….
(a) 3,4- dihydroxy phenylacetate
(b) 3, 4 – dihydroxy phenylalanine
(c) 3,4- dihydroxy phenyl aspartate
(d) 3, 4- dihydroxy phenol aldehyde
Answer:
(b) 3,4 – dihydroxy phenylalanine
Question 16.
The type of antibody generated against Rh antigen is ….
(a)IgE
(b) IgG
(c) IgA
(d) IgB
Answer:
(b) IgG
Question 17.
Which of the following symbol is used in the pedigree analysis to represent unspecified sex?

Answer:
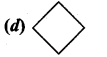
Question 18:
A colorblind man marries a woman with normal sight who has no history of color blindness in her family. What is the probability of their grandson being colorblind?
(a) 1/4
(b) 3/4
(c) 2/4
(d) 4/4
Answer:
(a) 1/4
![]()
Question 19.
Multiple alleles are located……………………
(a) at different loci on homologous chromosome
(b) at same locus on homologous chromosome
(c) at different loci on non-homologous chromosome
(d) at different chromosomes
Answer:
(b) at same locus on homologous chromosome
Question 20.
Identify the incorrect statement regarding haplodiploidy.
(g) Haplodiploidy is noticed in honeybees and drosophila
(b) Unfertilized eggs develop into drones
(c) Fertilized eggs develop into queen and worker bees
(d) Males have half the total chromosomal number
Answer:
(a) Haplodiploidy is noticed in honeybees and drosophila
Question 21.
IA and IB genes of ABO blood group are
(a) Co-dominant
(b) Pleotropic
(c) Dominant and recessive
(d) Epistatic
Answer:
(a) Co-dominant
Question 22.
Which one of the following crosses show 3 : 1 ratio of normal visioned versus carrier blind?
(a) XCXC x X+Y
(b) X+ XC x XC Y–
(c) X+XC x X+Y–
(d) X+X+ x XCY–
Answer:
(c) X+XC x X+Y–
12th Bio Zoology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define multiple allelism.
Answer:
When three or more alleles of a gene that control a particular trait occupy the same locus on the homologous chromosome of an organism, they are called multiple alleles and their inheritance is called multiple allelism.
![]()
Question 2.
Name the discoverers of antigen A, B and AB.
Answer:
Antigens A and Antigen B was discovered by Karl Landsteiner. Antigen AB was discovered by Von De Castelle and Sturli.
Question 3.
What happens if type A blood is injected to a person having B blood group? Explain the reason.
Answer:
When two different incompatible blood types are mixed, agglutination (clumping together) of erythrocytes (RBC) occurs. The basis of these chemical differences is due to the presence of antigens (surface antigens) on the membrane of RBC and epithelial cells.
Question 4.
State the allelic forms of I gene and mention its chromosomal location.
Answer:
The I gene exists in three forms: IA, IB and IO. The alleles are located on chromosome 9.
Question 5.
Write the possible genotypes for a person having a B-blood group.
Answer:
The possible genotypes of a B-blood group person are IBIB or IBIO.
Question 6.
State Wiener Hypothesis on Rh-factor.
Wiener proposed the existence of eight alleles (R1, R2, R0, Rz, r, r1, r11, ry) at a single Rh locus. All genotypes carrying a dominant ‘R allele’ (R1, R2 ,R0 ,Rz) will produce ‘Rh-positive’ phenotype and double recessive genotypes (rr, rr1, rr11, rry) will give rise to Rh-negative phenotype.
![]()
Question 7.
Distinguish between homogametic and heterogametic condition with example.
Answer:
Homogametic organism:
- Organism producing only one type of gametes.
- e.g. Human female (Only X)
Heterogametic organism :
- Organism producing two different types of gametes.
- e.g. Human Male (X and Y)
Question 8.
Name any four organism expressing ZW-ZZ type of sex determination.
Answer:
Gypsy moth, fishes, reptiles and birds.
Question 9.
Expand (a) SRY (b) TDF
Answer:
SRY – Sex Determining region Y
TDF – Testes Determining Factor
![]()
Question 10.
Define Barr body.
Answer:
In 1949, Barr and Bertram first observed a condensed body in the nerve cells of female cat which was absent in the male. This condensed body was called sex chromatin by them and was later referred as Barr body.
Question 11.
Based on Lyon’s hypothesis, mention the number of Barr bodies in XXY males, XO females.
Answer:
XXY males – One Barr body.
XO females – No Barr body.
Question 12.
State Lyon’s hypothesis.
Answer:
Lyon’s hypothesis states that in mammals the necessary dosage compensation is accomplished by the inactivation of one of the X chromosomes in females so that both males and females have only one functional X chromosome per cell.
Mary Lyon suggested that Barr bodies represented an inactive chromosome, which in females becomes tightly coiled into a heterochromatin, a condensed and visible form of chromatin (Lyon’s hypothesis). The number of Barr bodies observed in cell was one less than the number of X-Chromosome. XO females have no Barr body, whereas XXY males have one Barr body.
Question 13.
Mention few X-linked inherited diseases.
Answer:
Red-green colour blindness or daltonism, haemophilia and Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy.
![]()
Question 14.
Define Karyotyping.
Answer:
Karyotyping is a technique through which a complete set of chromosomes is separated from a cell and the chromosomes are arranged in pairs. An idiogram refers to a diagrammatic representation of chromosomes.
Question 15.
Explain the inheritance pattern of Y-linked genes for example.
Answer:
Genes in the non-homologous region of the Y-chromosome are inherited directly from male to male. In humans, the Y-linked or holandric genes for hypertrichosis (excessive development of hairs on pinna of the ear) are transmitted directly from father to son, because males inherit the Y chromosome from the father. Female inherits only X chromosome from the father and are not affected.
Question 16.
Observe the symbol used in pedigree analysis and give the proper terms they represent.
Answer:
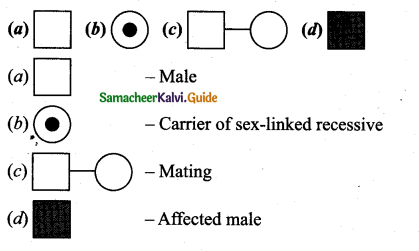
![]()
Question 17.
Write a brief note on pedigree analysis.
Answer:
Pedigree is a “family tree”, drawn with standard genetic symbols, showing the inheritance pathway for specific phenotypic characters. Pedigree analysis is the study of traits as they have appeared in a given family line for several past generations.
Question 18.
What do you mean by ‘Mendelian disorder’.
Answer:
Alteration or mutation in a single gene causes Mendelian disorders. These disorders are transmitted to the offsprings on the same line as the Mendelian pattern of inheritance. E.g., Thalassemia.
Question 19.
Name any four Mendelian disorders.
Answer:
(a) Thalassemia (b) Albinism (c) sickle cell anaemia (d) Huntington’s chorea
Question 20.
What is the phenotype of (a) IAIO (b) IOIO
Answer:
(a) IAIO – A blood group person
(b) IOIO – O blood group person
![]()
Question 21.
On which chromosomes does HBA1 gene and HBB genes are located?
Answer:
HBA1 gene is located on chromosome 16.
HBB gene is located on chromosome 11.
Question 22.
Complete the equation.
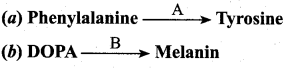
Answer:
(a) A = Phenylalanine hydroxylase
(b) B = Tyrosinase
Question 23.
Write a note on Huntington’s chorea.
Answer:
Huntington’s chorea is inherited as an autosomal dominant lethal gene in man. It is characterized by involuntary jerking of the body and progressive degeneration of the nervous system, accompanied by gradual mental and physical deterioration. The patients with this disease usually die between the age of 35 and 40.
Question 24.
Comment on Trisomy-21.
Answer:
Trisomic condition of chromosome – 21 results in Down’s syndrome. It is characterized by severe mental retardation, defective development of the central nervous system, increased separation between the eyes, flattened nose, ears are malformed, mouth is constantly open and the tongue protrudes.
![]()
Question 25.
Mention the genetic makeup of Turner’s syndrome person and Klinefelter’s syndrome , person.
Answer:
Klinefelter’s syndrome – 44AA+XXY
Turner’s syndrome – 44AA+XO
Question 26.
List out any four clinical symptoms of Klinefelter’s syndrome.
Answer:
Gynaecomastia, high pitched voice, under developed genetalia and tall with long limbs.
12th Bio Zoology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Three Marks Questions and Answers
Question 27.
Write the types of sex-determination mechanisms does the following crosses as shown. Give an example for each.
(a) Female XX with Male XO (6) Female ZW with Male ZZ
Answer:
(a) Male heterogamety. e.g., Human beings.
(b) Female heterogamety. e.g., Birds.
Question 28.
What are the enzymes encoded by the alleles IA, IB and IO?
Answer:
IA allele produces N-acetyl galactose transferase and can add N-acetyl galactosamine (NAG) and IB allele encodes for the enzyme galactose transferase that adds galactose to the precursor (i.e. H substances). In the case of IO/IO allele no terminal transferase enzyme is produced and therefore called “null” allele and hence cannot add NAG or galactose to the precursor.
![]()
Question 29.
Draw a tabular column representing various types of blood group in human beings, their phenotypes, genotypes, antigens and respective antibodies.
Answer:
Genetic basis of the human ABO blood groups:
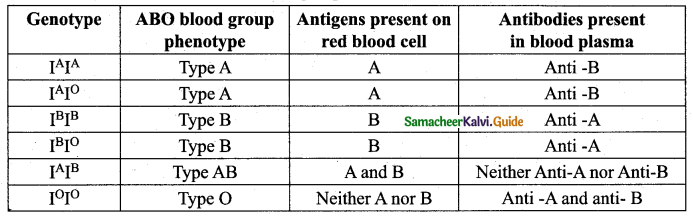
Question 30.
Give an account on Rhesus factor.
Answer:
Rhesus or Rh – Factor: The Rh factor or Rh antigen is found on the surface of erythrocytes. It was discovered in 1940 by Karl Landsteiner and Alexander Wiener in the blood of rhesus monkey, Macaca rhesus and later in human beings. The term ‘Rh factor’ refers to “immunogenic D antigen of the Rh blood group system. An individual having D antigen are Rh D positive (Rh+) and those without D antigen are Rh D negative (Rh”)”. Rhesus factor in the blood is inherited as a dominant trait.
Naturally occurring Anti D antibodies are absent in the plasma of any normal individual. However if an Rh” (Rh negative) person is exposed to Rh+ (Rh positive) blood cells (erythrocytes) for the first time, anti D antibodies are formed in the blood of that individual. On the other hand, when an Rh positive person receives Rh-negative blood no effect is seen.
![]()
Question 31.
How Erythroblastosis foetalis can be prevented?
Answer:
If thefmother is Rh negative and foetus is Rh positive, anti D antibodies should be administered to the mother at 28th and 34th week of gestation as a prophylactic measure. If the Rh-negative mother delivers Rh positive child then anti D antibodies should be administered to the mother soon after delivery. This develops passive immunity and prevents the formation of anti D antibodies in the mothers blood by destroying the Rh foetal RBC before the mother’s immune system is sensitized. This has to be done whenever the woman attains pregnancy.
Question 32.
Explain XX-XO type of sex determination.
Answer:
XX-XO method of sex determination is seen in bugs, some insects such as cockroaches and grasshoppers. Pi The female with two X chromosomes are homogametic Gametes (XX) while the males with only one X chromosome are heterogametic (XO). The presence of unpaired X chromosomes determines the male sex. The males PI Generation with unpaired ‘X’ chromosome produce two types of sperms, one half with X chromosome and other half without X chromosome. The sex of the offspring depends upon the sperm that fertilizes the egg.
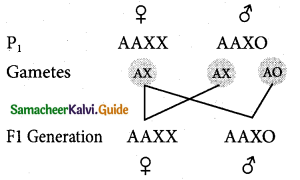
![]()
Question 33.
Name the type of sex-determination mechanism of the following organisms.
(a) Gypsy moth (A) Human beings (c) Butterflies
Answer:
(a) Gypsy moth -ZW – ZZ type (ZW-females, ZZ – males)
(b) Human beings – XX – XY type (XX-females, XY – males)
(c) Butterflies – ZO – ZZ type (ZO-females, ZZ – males)
Question 34.
Complete the following cross.
![]()
Answer:
Question 35.
Role of Y- chromosome is crucial for maleness – Justify.
Answer:
Current analysis of Y chromosomes has revealed numerous genes and regions with potential genetic function; some genes with or without homologous counterparts are seen on the X. Present at both ends of the Y chromosome are the pseudoautosomal regions (PARs) that are similar with regions on the X chromosome which synapse and recombine during meiosis.
The remaining 95% of the Y chromosome is referred as the Non-combining Region of the Y (NRY). The NRY is divided equally into functional genes (euchromatic) and non-functional genes (heterochromatic). Within the euchromatin regions, is a gene called Sex determining region Y (SRY). In humans, absence of Y chromosome inevitably leads to female development and this SRY gene is absent in X chromosome. The gene product of SRY is the testes determining factor (TDF) present in the adult male testis.
![]()
Question 36.
Color blindness is a perfect example for criss-cross of inheritance – Justify the statement.
Answer:
A marriage between a colour blind man and a normal visioned woman will produce normal visioned male and female individuals in F1 generation but the females are carriers. The marriage between a F1 normal visioned carrier woman and a normal visioned male will produce one normal visioned female, one carrier female, one normal visioned male and one colour blind male. Colour blind trait is inherited from the male parent to his grandson through carrier daughter, which is an example of criss-cross pattern of inheritance.
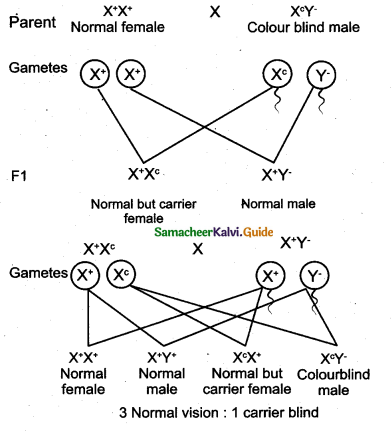
Question 37.
How the Karyotype of lymphocytes was prepared by Tjio and Levan?
Answer:
Preparation of Karyotype Tjio and Levan (1960) described a simple method of culturing lymphocytes from the human blood. Mitosis is induced followed by addition of colchicine to arrest cell division at metaphase stage and the suitable spread of metaphase chromosomes is photographed. The individual chromosomes are cut from the photograph and are arranged in an orderly fashion in homologous pairs. This arrangement is called a karyotype. Chromosome banding permits structural definitions and differentiation of chromosomes.
![]()
Question 38.
What is a genetic disorder? Mention its types?
Answer:
A genetic disorder is a disease or syndrome that is caused by an abnormality in an individual -DNA. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an entire chromosome or even a set of chromosomes. Genetic disorders are of two types namely, Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders.
Question 39.
Explain the genetic basis of Phenylketonuria.
Answer:
Phenylketonuria is an inborn error of Phenylalanine metabolism caused due to a pair of autosomal recessive genes. It is caused due to mutation in the gene PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase gene) located on chromosome 12 for the hepatic enzyme “phenylalanine hydroxylase”.
This enzyme is essential for the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine. Affected individual lacks this enzyme, so phenylalanine accumulates and gets converted to phenylpyruvic acid and other derivatives. It is characterized by severe mental retardation, light pigmentation of skin and hair. Phenylpyruvic acid is excreted in the urine.
![]()
![]()
Question 40.
Give an account of Patau’s syndrome.
Answer:
Trisomic condition of chromosome 13 results in Patau’s syndrome. Meiotic non-disjunction is thought to be the cause for this chromosomal abnormality. It is characterized by multiple and severe body malformations as well as profound mental deficiency. Small head with small eyes, cleft palate, malformation of the brain and internal organs are some of the symptoms of this syndrome.
Question 41.
Define aneuploidy.
Answer:
Failure of chromatids to segregate during cell division resulting in the gain or loss of one or more chromosomes is called aneuploidy. It is caused by the non-disjunction of chromosomes.
12th Bio Zoology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 42.
What do you mean by “syndrome”? Give two examples.
Answer:
Group of signs and symptoms that occur together and characterize a particular abnormality is called a syndrome, e.g., Down’s syndrome and Turner’s syndrome.
Question 42.
Explain in detail about Erythroblastosis foetalis.
Answer:
Rh incompatability has great significance in childbirth. If a woman is Rh-negative and the man is Rh positive, the foetus may be Rh positive having inherited the factor from its father. The Rh negative mother becomes sensitized by carrying Rh positive foetus within her body. Due to damage of blood vessels, during child birth, the mother’s immune system recognizes the Rh antigens and gets sensitized. The sensitized mother produces Rh antibodies. The antibodies are IgG type which are small and can cross placenta and enter the foetal circulation. By the time the mother gets sensitized and produce anti ‘D’ antibodies, the child is delivered.
Usually no effects are associated with exposure of the mother to Rh positive antigen during the first child birth, subsequent Rh positive children carried by the same mother, may be exposed to antibodies produced by the mother against Rh antigen, which are carried across the placenta into the foetal blood circulation. This causes haemolysis of foetal RBCs resulting in haemolytic jaundice and anaemia. This condition is known as Erythroblastosis foetalis or Haemolytic disease of the new bom (HDN).
![]()
Question 43.
Decribe female heterogamy and its types.
Answer:
Heterogametic Females:
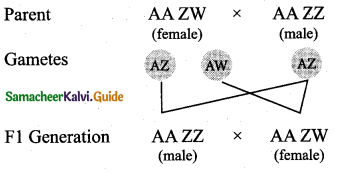
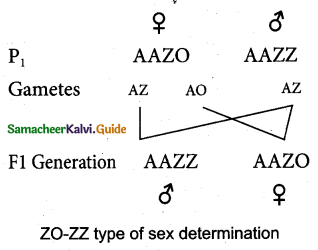
In this method of sex determination, the homogametic male possesses two ‘X’ chromosomes as in certain insects and certain vertebrates like fishes, reptiles and birds producing a single type of gamete; while females produce dissimilar gametes. The female sex consists of a single ‘X’ chromosome or one ‘X’ and one ‘Y’ chromosome. Thus the females are heterogametic and produce two types of eggs. Heterogametic females are of two types, ZO-ZZ type and ZW-ZZ type. ,
ZO-ZZ Type
This method of sex determination is seen in certain moths, butterflies and domestic chickens. In this type, the female possesses single ‘Z’ chromosome in its body cells and is heterogametic (ZO) producing two kinds of eggs some with ‘Z’ chromosome and some without ‘Z’ chromosome, while the male possesses two ‘Z’ chromosomes and is homogametic (ZZ).
ZW-ZZ type
This method of sex determination occurs in certain insects (gypsy moth) and in vertebrates such as fishes, reptiles and birds. In this method the female has one ‘Z’ and one ‘ W’ chromosome (ZW) producing two types of eggs, some carrying the Z chromosomes and some carry the W chromosome. The male sex has two ‘Z’ chromosomes and is homogametic (ZZ) producing a single type of sperm.
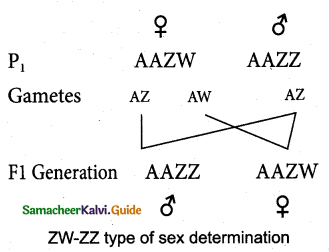
![]()
Question 44.
Write elaborately about the following Mendelian disorders.
(a) Thalassemia (b) Albinism
Answer:
(a) Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive disorder. It is caused by gene mutation resulting in excessive destruction of RBC’s due to the formation of abnormal haemoglobin molecules. Normally haemoglobin is composed of four polypeptide chains, two alpha and two beta globin chains. Thalassemia patients have defects in either the alpha or beta globin chain causing the production of abnormal haemoglobin molecules resulting in anaemia.
Thalassemia is classified into alpha and beta based on which chain of haemoglobin molecule _ is affected. It is controlled by two closely linked genes HBA1 and HBA2 on chromosome 16. Mutation or deletion of one or more of the four alpha gene alleles causes Alpha Thalassemia. In Beta Thalassemia, production of beta globin chain is affected. It is controlled by a single gene (HBB) on chromosome 11. It is the most common type of Thalassemia and is also known as Cooley’s anaemia. In this disorder, the alpha chain production is increased and damages the membranes of RBC.
(b) Albinism
Albinism is an inborn error of metabolism, caused due to an autosomal recessive gene. Melanin pigment is responsible for skin colour. Absence of melanin results in a condition called albinism. A person with the recessive allele lacks the tyrosinase enzyme system, which is required for the conversion of dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) into melanin pigment inside the melanocytes. In an albino, melanocytes are present in normal numbers in their skin, hair, iris, etc., but lack melanin pigment.

Question 45.
Discuss any two Allosomal anomalies in human.
Answer:
Allosomal abnormalities in human beings
Mitotic or meiotic non-disjunction of sex chromosomes causes allosomal abnormalities. Several sex chromosomal abnormalities have been detected. E.g. Klinefelter’s syndrome and Turner’s syndrome.
1. Klinefelter’s Syndrome (XXY Males)
This genetic disorder is due to the presence of an additional copy of the X chromosome resulting in a karyotype of 47,XXY. Persons with this syndrome have 47 chromosomes (44AA+XXY). They are usually sterile males, tall, obese, with long limbs, high pitched voice, under developed genetalia and have feeble breast (gynaecomastia) development.
2. Turner’s Syndrome (XO Females)
This genetic disorder is due to the loss of a X chromosome resulting in a karyotype of 45,X. Persons with this syndrome have 45 chromosomes (44 autosomes and one X chromosome) (44AA+XO) and are sterile females. Low stature, webbed neck, underdeveloped breast, rudimentary gonads lack of menstrual cycle during puberty, are the main symptoms of this syndrome.
![]()
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
On analysis, a person’s karyotype reveals an extra one chromosome of the twenty-first pair. What does this condition represent? which type of symptoms can be noticed in the person?
Answer:
Trisomy-21 or Down’s syndrome.
Symptoms – Mental retardation, malformed ears, protruded tongue, mouth is constantly open etc.
Question 2.
A female whose blood group is AB– got conceived and later it is diagnoised that her – foetus possess B+. What measures would be taken to prevent the foetus from Haemolytic disease of Newborn (HDN)
Answer:
If the mother is Rh-negative and foetus is Rh-positive, anti D antibodies should be administered to the mother at 28th and 34th week of gestation as a prophylactic measure. If the Rh-negative mother delivers a Rh-positive child then anti D antibodies should be administered to the mother soon after delivery. This develops passive immunity and prevents the formation of anti D antibodies in the mother’s blood by destroying the Rh foetal RBC before the mother’s immune system is sensitized. This has to be done whenever the woman attains pregnancy.
![]()
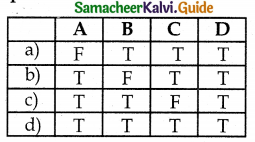
Question 3.
The following table shows the genotypes for ABO blood grouping and these phenotypes. Complete the table by filling the gaps.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
| IAIA | A |
| ? | A |
| ? | AB |
| IOIO | ? |
Answer:
2) IAIO
3) IAIB
4) O
Question 4.
Give one example for each of the following group of drugs, (a) Stimulants (b) Analgesic (c) Hallucinogens
Answer:
(a) Stimulants – Eg.: Nicotine
(b) Analgesic – Eg.: Opium
(c) Hallucinogens – Phencyclidine