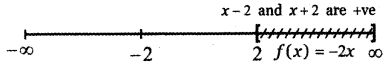
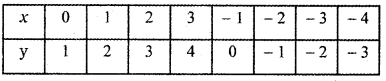
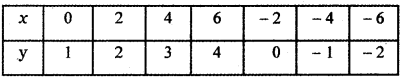
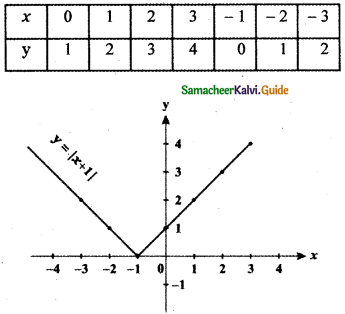
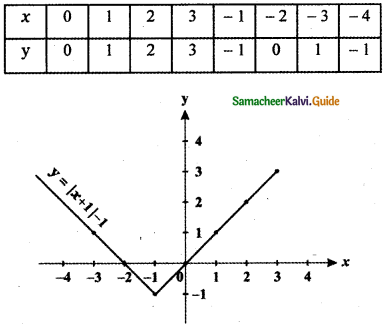
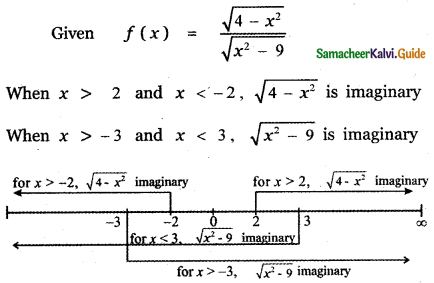
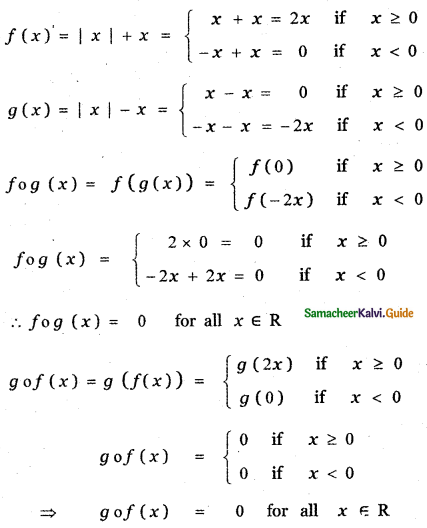
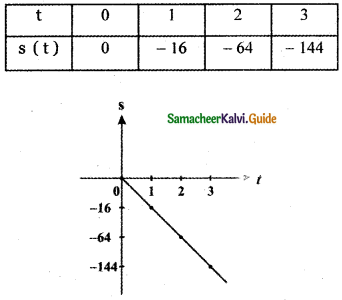
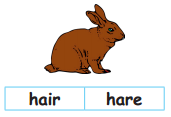
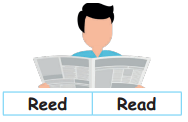
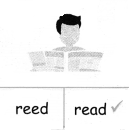
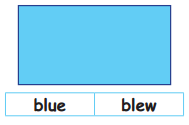
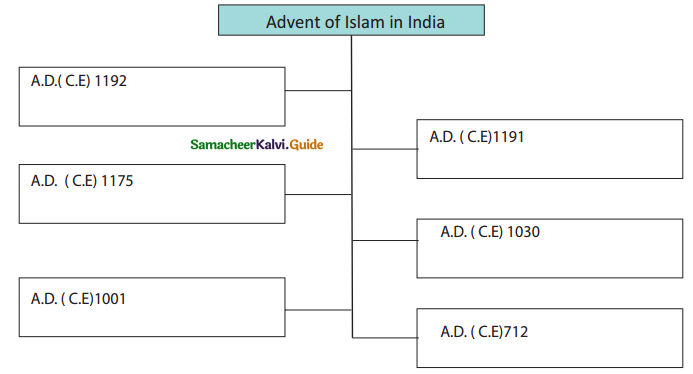
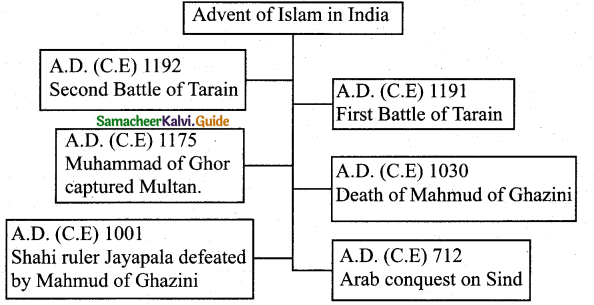
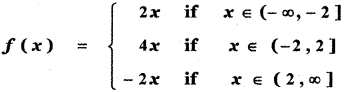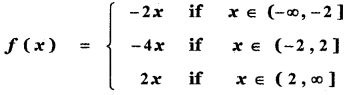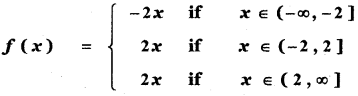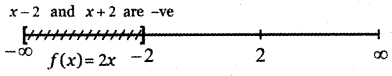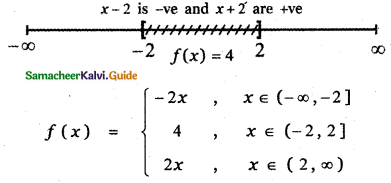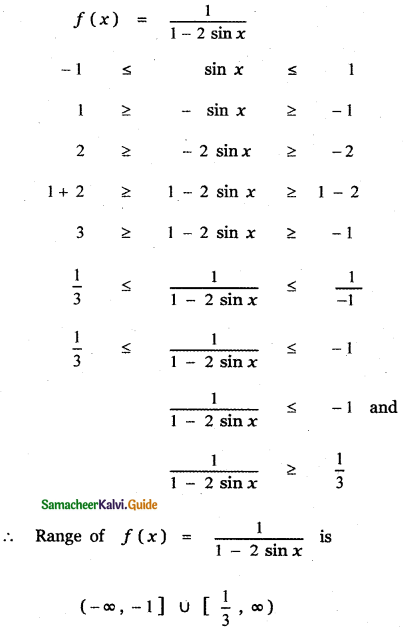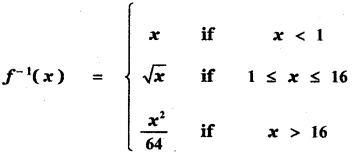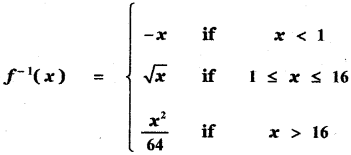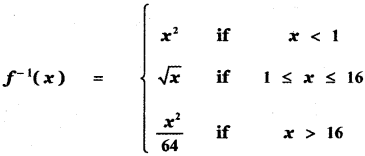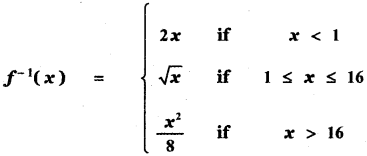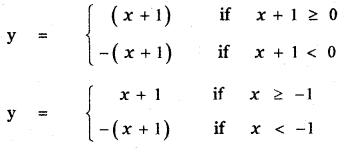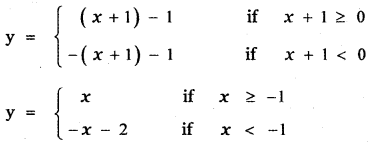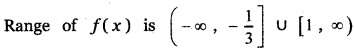Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Guide Pdf Term 3 Poem 1 Why Questions Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Solutions Term 3 Poem 1 Why Questions
5th English Guide Why Questions Text Book Back Questions and Answers
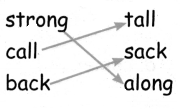
A. Match the rhyming words:
| 1. flow | a. know |
| 2. grow | b. week |
| 3. seek | c. blow |
Answer:
| 1. flow | a. blow |
| 2. grow | b. know |
| 3. seek | c. week |
![]()
B. List questions to which you seek answer using ‘Why?’:
Answer:
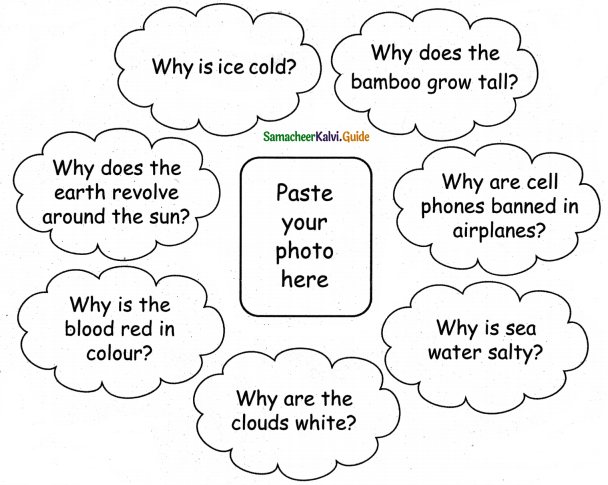
![]()
C. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Why should we ask questions?
Ans :
We should ask questions to know the answers. Thus we can improve our knowledge.
Question 2.
Do you love to seek answers to the questions?
Answer:
Yes.
![]()
Let Us Know:
Adverb:
Words that describe an action or verb are called adverbs.
How:
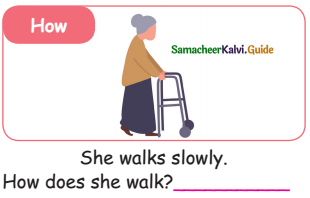
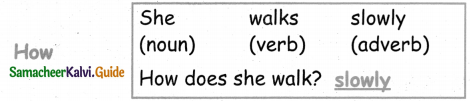
When:


Where:


How Often:


![]()
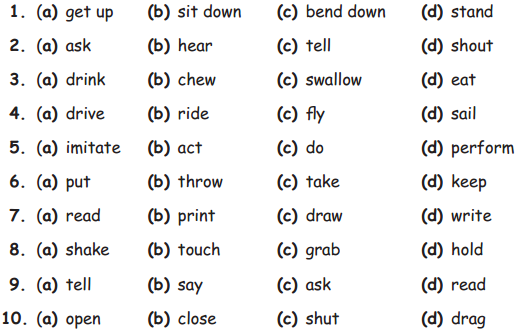
A. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
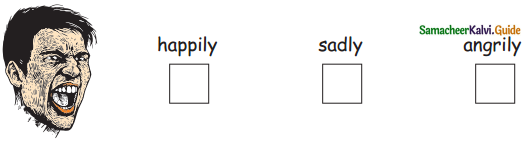
Answer:

Question 2.

Answer:

Question 3.

Answer:

Question 4.

Answer:

Question 5.
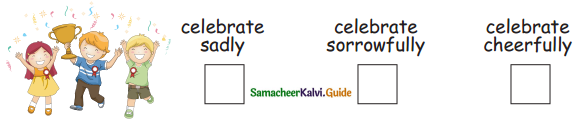
Answer:

![]()
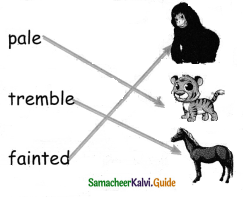
B. Circle and write the adverbs:
Question 1.
He laughed merrily.
Answer:
Merrily
Question 2.
We will leave today.
Answer:
Today
Question 3.
Suddenly the old man fainted.
Answer:
Suddenly
Question 4.
I’m waiting here.
Answer:
Here
Question 5.
I drink coffee thrice.
Answer:
Thrice
![]()
C. Pick and write the adverbs to complete the sentences:
(loudly, beautifully, brilliantly, bravely, cunningly)
Question 1.

My dog barks _______.
Answer:
My dog barks loudly.
Question 2.

She won the game _______.
Answer:
She won the game brilliantly.
Question 3.

She coloured the picture _______.
Answer:
She coloured the picture beautifully.
Question 4.

The lion fought _______.
Answer:
The lion fought bravely.
Question 5.

A jackal cheated the crow _______.
Answer:
A jackal cheated the crow cunningly.
![]()
Let us Listen:
Listen to the audio and fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
In North America football is known as _______.
Answer:
soccer
Question 2.
It is a game with two teams of _______ players.
Answer:
eleven
Question 3.
Fouls usually lead to a _______.
Answer:
yellow card
Question 4.
Two yellow cards are equal to one _______.
Answer:
red card
Question 5.
Yellow card is known as _______.
Answer:
caution
![]()
Let us speak:
How to deliver a speech?
There are 3 important steps to learn to deliver a speech.
Step 1: Connect
- Maintain eye contact with all.
- Move your hands to express
- Maintain your volume (everyone should be able to hear you)
Step 2: Construct
- Topic: Good day to one and all. Today, I am going to speak about _______.
- Opinion: I feel ___ (Express your opinion of the topic.)
- Examples: Give three examples to strengthen your opinion.
- Opinion: Tell your opinion again.
- Closing: Thank you all.
Step 3: Content
- Topic: _______ (What is your topic?)
- Opinion: _______ (How do you feel about the topic?)
- Example 1: _______ (Why do you feel so?)
- Example 2: _______ (Why do you feel so?)
- Example 3: _______ (Why do you feel so?)
- Opinion: _______ (How do you feel about the topic?)
- Closing: _______.
![]()
Pair up and speak to your partner on the topic “My favourite hero” for 30 seconds:
My favourite hero
Good day to one and all. Today, I am going to speak about my favourite hero, Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
He was a man from Rameshwaram who dreamt of touching the sky by becoming a pilot. He ended up being one of the most popular Presidents of India.
He was well known for his contributions to science. He was a motivational speaker. He was also an academician and wrote many inspirational books.
He developed missiles AGNI ( a ballistic missile) and PRITHVI (surface to surface missile). Thus he was known as the Missile Man of India.
He received doctorates from nearly 40 universities, including Edinburg University and Oakland University.
Switzerland commemorates May 26 as Science Day in memory of APJ Abdul Kalam as it was on this day in 2005 when he visited the country.
Even in his death, Dr. Kalam gave us a message worth remembering. He died doing what he loved the most – teaching and igniting young people’s minds with his words of wisdom. Thank you all for listening to my speech.
![]()
5th English Guide Why Questions Additional Questions and Answers
A. Match the following:
| 1. Sky | a. soft |
| 2. Earth | b. blue |
| 3. Silk | c. hot |
| 4. Fire | d. round |
Answer:
| 1. Sky | a. blue |
| 2. Earth | b. round |
| 3. Silk | c. soft |
| 4. Fire | d. hot |
B.
| 1. River | a. blow |
| 2. Wind | b. shine |
| 3. Sun | c. pour |
| 4. Rain | d. flow |
Answer:
| 1. River | a. flow |
| 2. Wind | b. blow |
| 3. Sun | c. shine |
| 4. Rain | d. pour |
![]()
Additional Grammar:
Adverb:
- Most adverbs are formed by adding ” – ly” to an adjective.
regular + ly → regularly
(adjective) (adverb) - If the adjective already ends in “-ly”, the “-y” usually changes to “-i”.
heavy → heavily (adjective) (adverb) - There are many common adverbs that do not end in “-ly”.
e.g. again, also, just, never, often, soon, today, too, very, well.
I. Use the adverbs and fill in the blanks:
(normally, never, gradually, always, regularly, generally)
Question 1.
Police men are _______ trained well.
Answer:
generally
Question 2.
Story books have _______ a fascinated me.
Answer:
always
Question 3.
I go to college _______.
Answer:
regularly
Question 4.
Mom _______ lets me stay up late.
Answer:
never
Question 5.
My fever _______ reduced.
Answer:
gradually
![]()
Additional Delivering A Speech:
Deliver a speech on “Healthy foods”:
Healthy foods
A very good morning to all present here. Today I am going to speak about healthy foods.
Eating the right foods keeps us healthy, without disease, and gives us long life. So it is essential to know about healthy foods.
Healthy foods are all naturally available foods around us. Most of them are cheap. Cereals, fruits, and vegetables are available everywhere. Most of them may be eaten raw to get all the nutrients present in them.
When natural foods are cooked in too much water, the nutrients are lost. When we remove the outer coats of fruits and vegetables, the high nutrients in them are lost.
There should be variety in the foods we eat. Seasonal fruits and vegetables are easily available and cheap too. They strengthen our organs.
When natural foods are healthy and tasty, we need not go for junk foods that are harmful and brings in problems like indigestion.
Let’s take a pledge today to eat healthy foods and keep away junk foods.
![]()
Why Questions Summary in English and Tamil
Why is the sky blue?
Why is the earth round?
Why is silk soft?
Why is fire hot?
Think! Why is it so?
வானம் ஏன் நீல நிறமாக உள்ளது?
பூமி ஏன் உருண்டையாக உள்ளது?
பட்டு ஏன் மென்மையாக உள்ளது?
நெருப்பு ஏன் சூடாக உள்ளது?
சிந்தியுங்கள்! அது ஏன் அப்படி உள்ளது?
Why does the river flow?
Why does the wind blow?
Why does the sun shine?
Why does the rain pour?
Think! Why is it so?
ஆறு ஏன் ஓடுகிறது?
காற்று ஏன் வீசுகிறது?
சூரியன் ஏன் ஒளி வீசுகிறது?
மழை ஏன் பெய்கிறது?
சிந்தியுங்கள் ! அது ஏன் அப்படி?
Let us seek,
With questions all week,
As we grow,
With answers to know,
Think!
நாம் தேடுவோமாக,
வாரம் முழுவதும் வினாக்களுடன்.
நாம் வளரும் போது,
விடைகளை அறிந்து கொள்ள,
சிந்தியுங்கள்!
![]()
Why Questions Glossary:
Blow – to move along (வீசுதல்)
Pour – flowing (பெய்தல்)
Shine – bright (ஒளிருதல்)
Soft – smooth (மென்மையான)