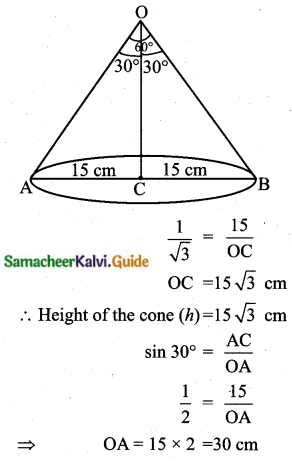
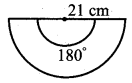
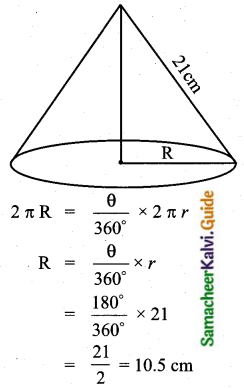
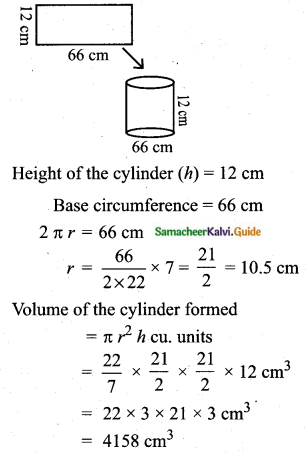
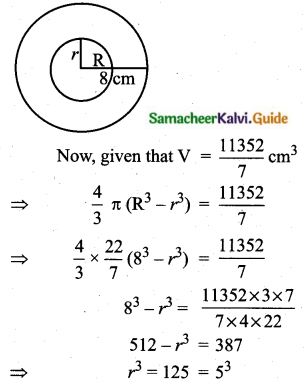
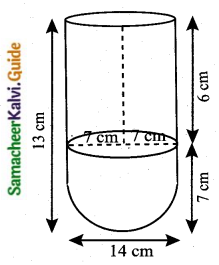
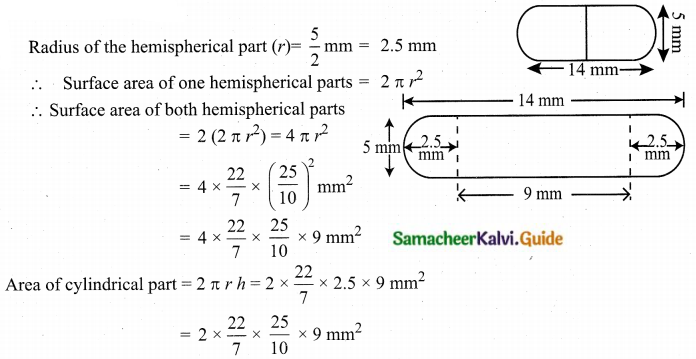
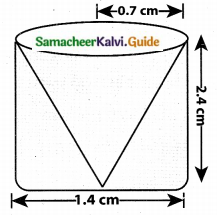
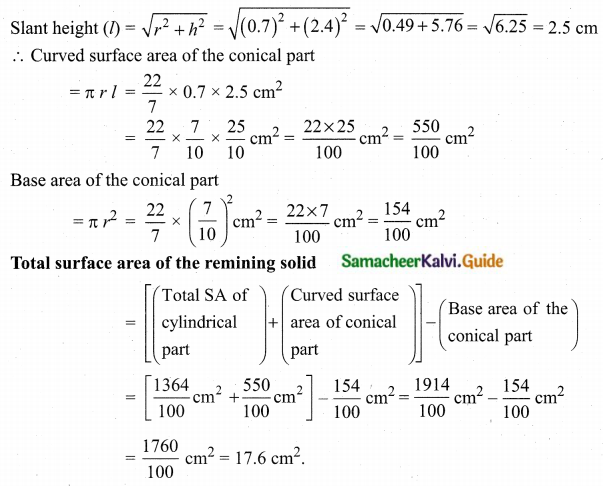
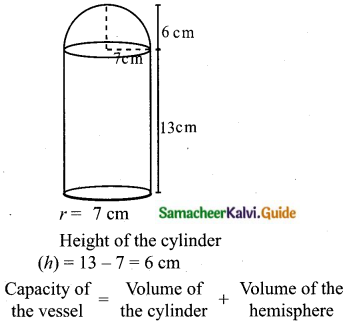
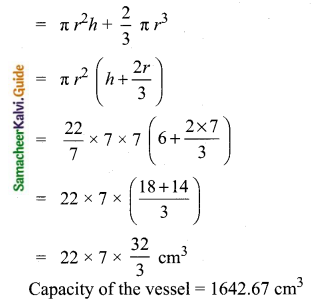
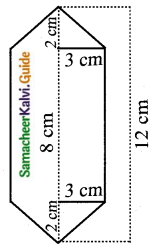
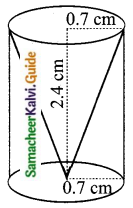
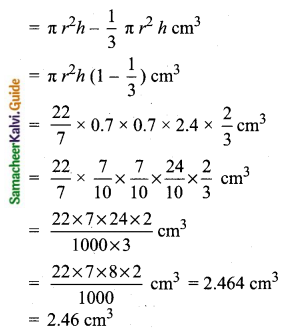
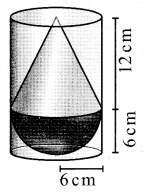
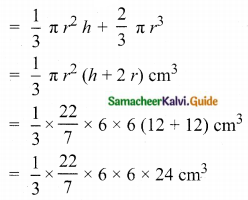
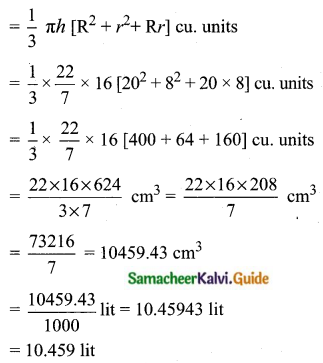
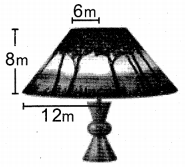
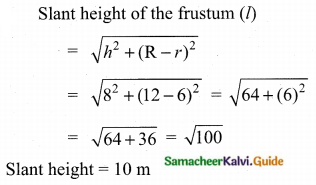
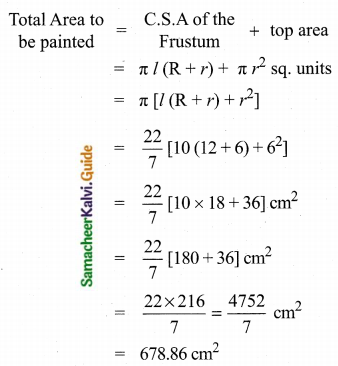
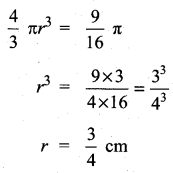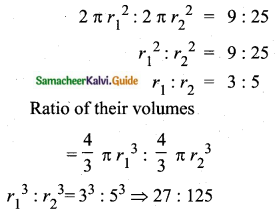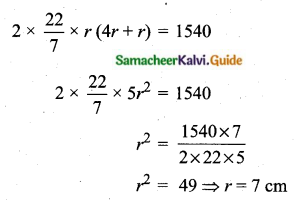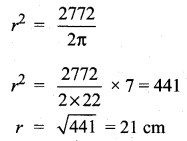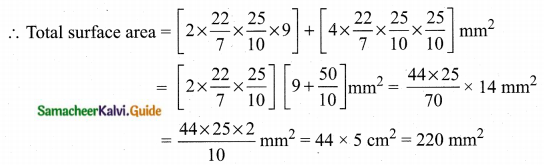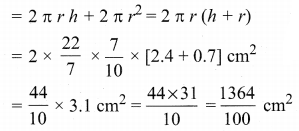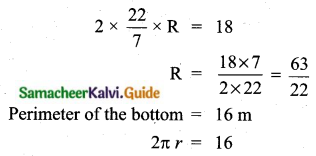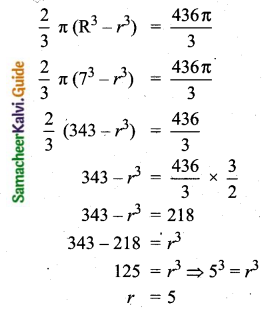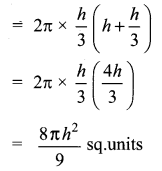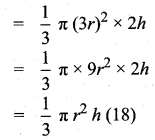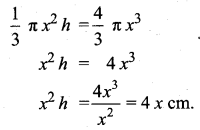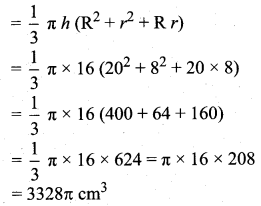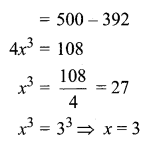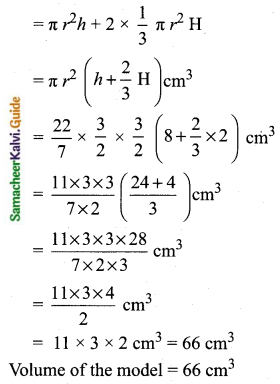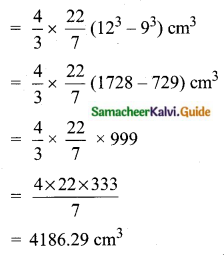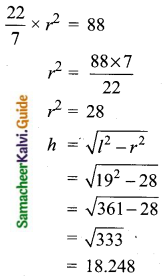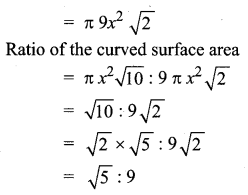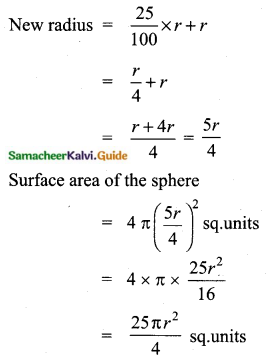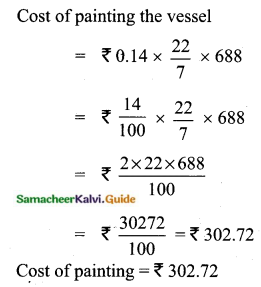Students can download Maths Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Ex 8.1 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Ex 8.1
Question 1.
Find the range and coefficient of range of the following data.
(i) 63, 89, 98, 125, 79, 108, 117, 68
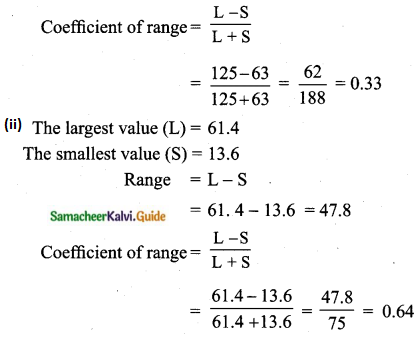
(ii) 43.5, 13.6, 18.9, 38.4, 61.4, 29.8
Answer:
(i) Here the largest value (L) = 125
The smallest value (S) = 63
Range = L – S = 125 – 63 = 62
Question 2.
If the range and the smallest value of a set of data are 36.8 and 13.4 respectively, then find the largest value.
Solution:
If the range = 36.8 and
the smallest value = 13.4 then
the largest value = L = R + S
= 36.8 + 13.4 = 50.2
Question 3.
Calculate the range of the following data.
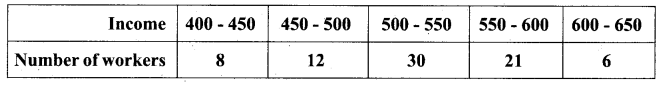
Answer:
Smallest value (S) = 400
Largest value (L) = 650
Range = L – S = 650 – 400 = 250
![]()
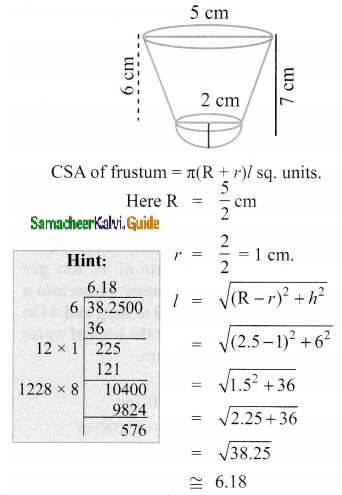
Question 4.
A teacher asked the students to complete 60 pages of a record notebook. Eight students have completed only 32, 35, 37, 30, 33, 36, 35 and 37 pages. Find the standard deviation of the pages yet to be completed by them.
Answer:
The remaining number of pages to be completed is 60 – 32; 60 – 35; 60 – 37; 60 – 30; 60 – 33; 60 – 36; 60 – 35 and 60 – 37
The pages to be completed are, 28, 25, 23, 30, 27, 24, 25, and 23
Arrange in ascending order we get, 23, 23, 24, 25, 25, 27, 28 and 30

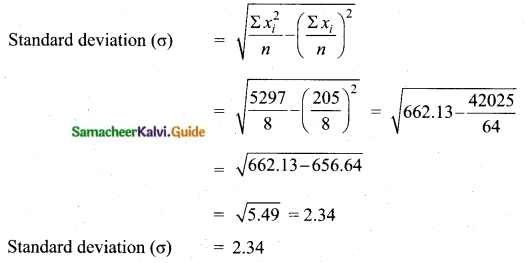
Question 5.
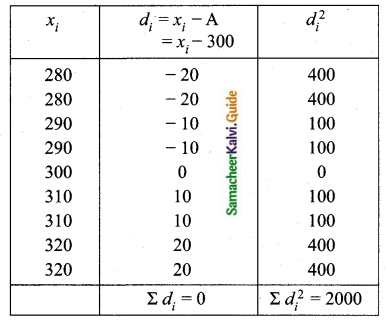
Find the variance and standard deviation of the wages of 9 workers given below:
₹ 310, ₹ 290, ₹ 320, ₹ 280, ₹ 300, ₹ 290, ₹ 320, ₹ 310, ₹ 280.
Answer:
Arrange in ascending order we get,
280, 280, 290, 290, 300, 310, 310, 320 and 320
Assumed mean = 300
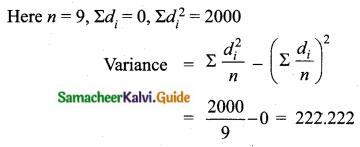
Variance = 222.222
Standard deviation = √Variance = √222.222 = 14.907 = 14.91
Variance = 222.22
Standard deviation = 14.91
Question 6.
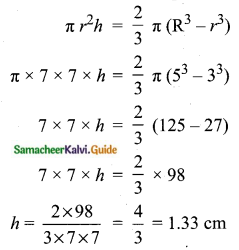
A wall clock strikes the bell once at 1 o’clock, 2 times at 2 o’clock, 3 times at 3 o’clock and so on. How many times will it strike in a particular day? Find the standard deviation of the number of strikes the bell make a day.
Answer:
Wall clock strikes the bell in 12 hours
1, 2, 3, 4, 5,… ,12
Wall clock strikes in a day (24 hours)
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24.
Assumed mean = 14
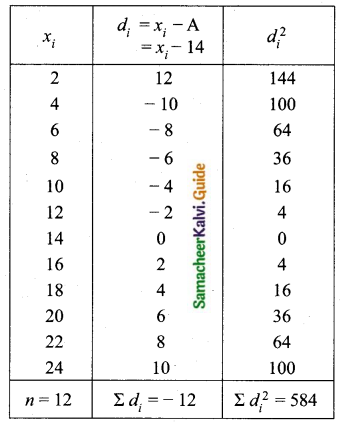
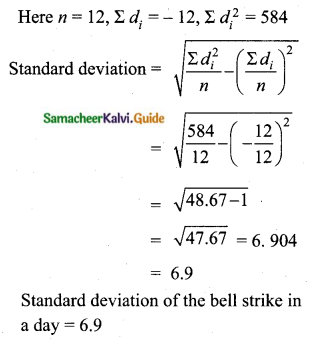
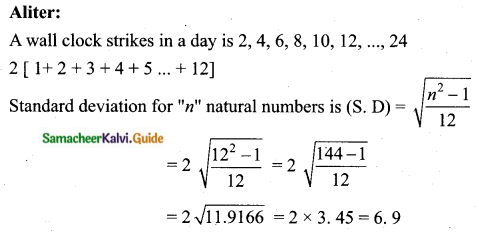
The standard deviation of bell strike in a day is 6.9
![]()
Question 7.
Find the standard deviation of the first 21 natural numbers.
Answer:
Here n = 21
The standard deviation of the first ‘n’ natural numbers,
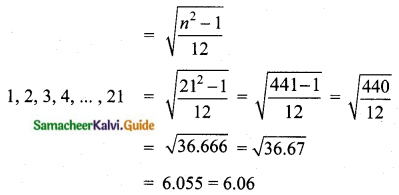
The standard deviation of the first 21 natural numbers = 6.06
Question 8.
If the standard deviation of a data is 4.5 and if each value of the data is decreased by 5, then find the new standard deviation.
Solution:
If the standard deviation of a data is 4.5 and each value of the data decreased by 5, the new standard deviation does not change and it is also 4.5.
Question 9.
If the standard deviation of a data is 3.6 and each value of the data is divided by 3, then find the new variance and new standard deviation.
Answer:
The standard deviation of the data = 3.6
Each value of the data is divided by 3
New standard deviation = \(\frac{3.6}{3}\) = 1.2
New Variance = (1.2)2 = 1.44 [∴ Variance = (S.D)2]
New standard Deviation = 1.2
New variance = 1.44
Question 10.
The rainfall recorded in various places of five districts in a week are given below.

Find its standard deviation.
Answer:
Assumed mean = 60
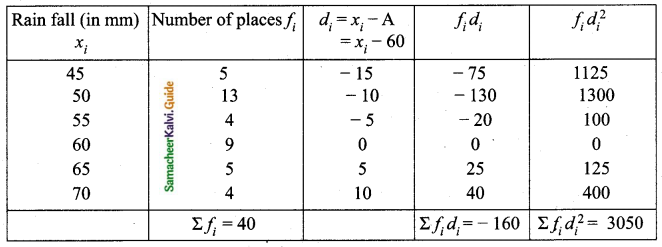
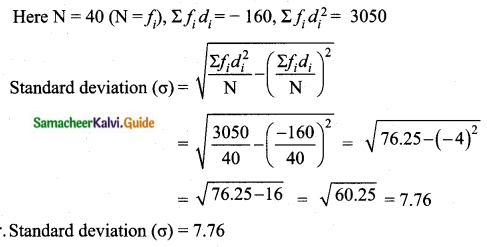
![]()
Question 11.
In a study about viral fever, the number of people affected in a town were noted as
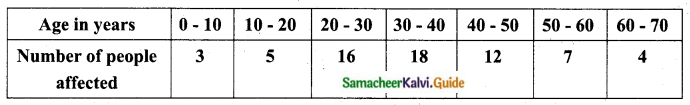
Find its standard deviation.
Answer:
Assumed mean = 35
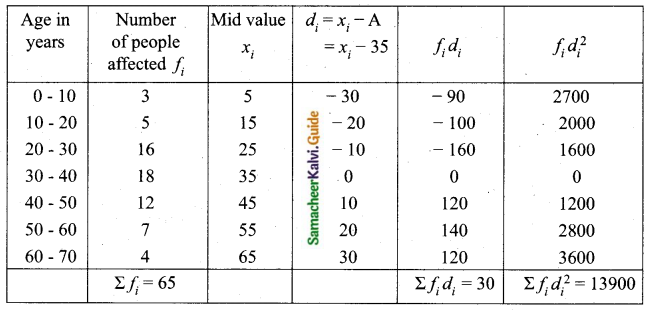
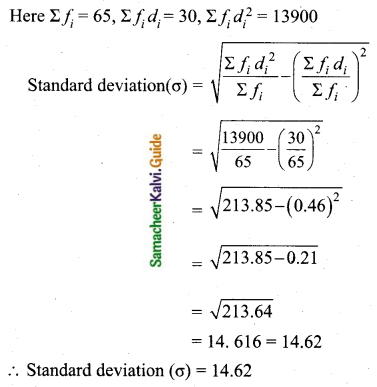
Question 12.
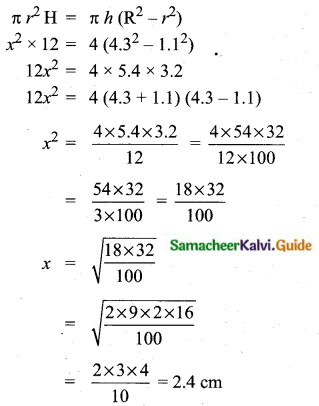
The measurements of the diameters (in cms) of the plates prepared in a factory are given below. Find the standard deviation.

Answer:
Assumed mean = 34.5
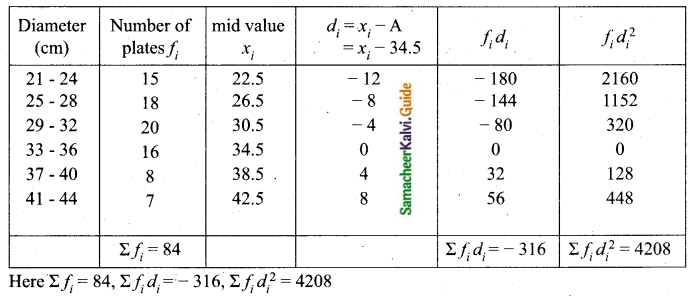
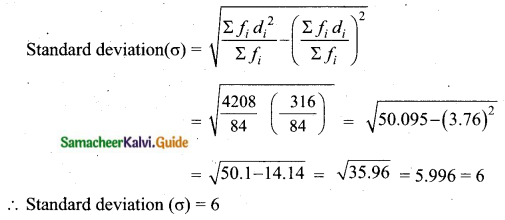
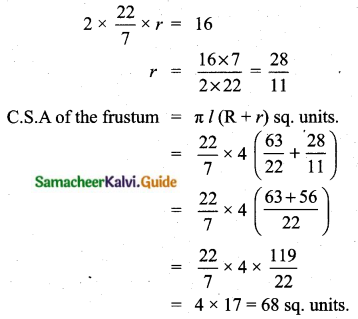
Question 13.
The time taken by 50 students to complete a 100 meter race are given below. Find its standard deviation.

Answer:
Assumed mean = 11
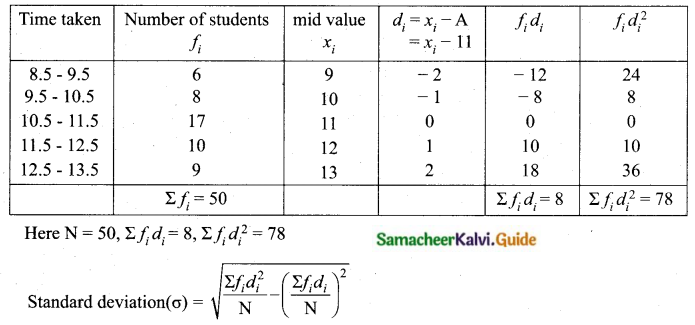
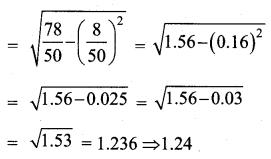
Standard deviation (σ) = 1.24
Question 14.
For a group of 100 candidates, the mean and standard deviation of their marks were found to be 60 and 15 respectively. Later on, it was found that the scores 45 and 72 were wrongly entered as 40 and 27. Find the correct mean and standard deviation.
Answer:
Number of candidates = 100
n = 100
Mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = 60
standard deviation (σ) = 15
Mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = \(\frac{\Sigma x}{n} \Rightarrow 60=\frac{\Sigma x}{100}\)
Σx = 6000
Correct total = 6000 + (45 – 40) + ( 72 – 27) = 6000 + 5 + 45 = 6050
Correct mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = \(\frac{6050}{100}\) = 60.5
Given standard deviation = 15
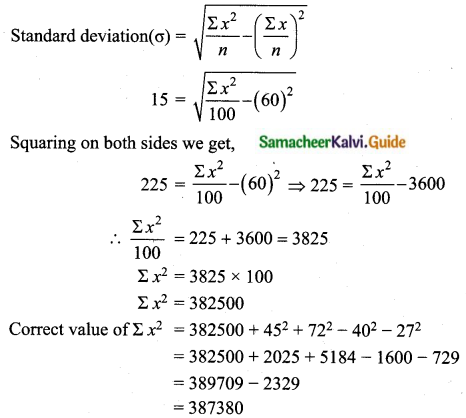
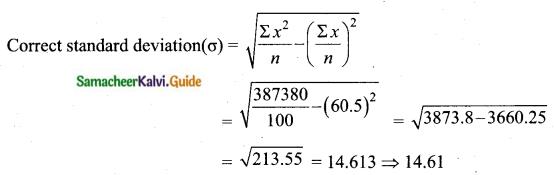
Correct mean = 60.5
Correct standard deviation (σ) = 14. 61
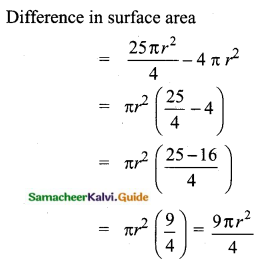
![]()
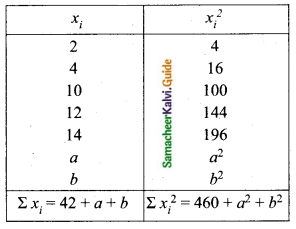
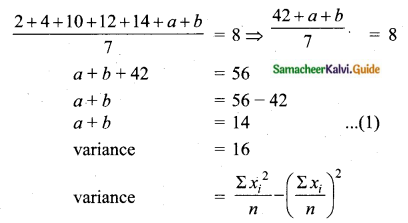
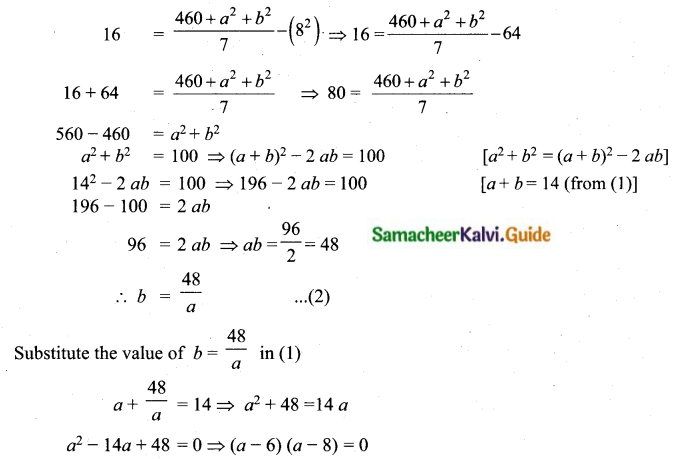
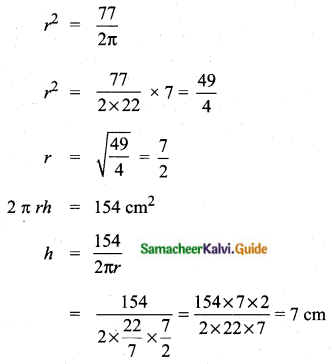
Question 15.
The mean and variance of seven observations are 8 and 16 respectively. If five of these are 2, 4, 10, 12 and 14, then find the remaining two observations.
Answer:
Let the missing two observations be ‘a’ and ‘b’
Arithmetic mean = 8