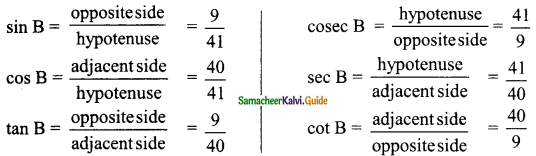
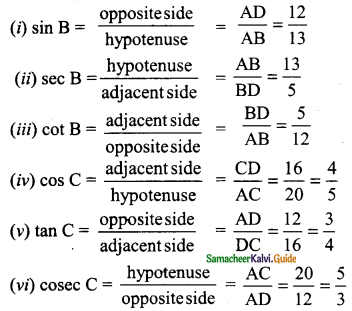
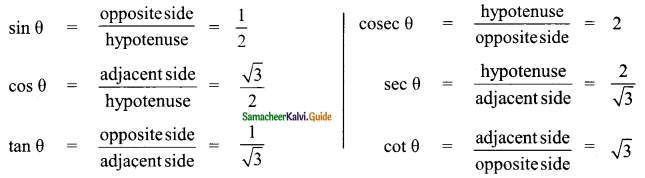
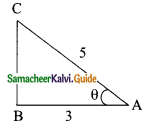
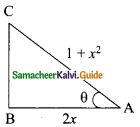
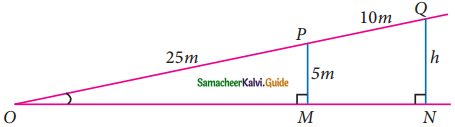
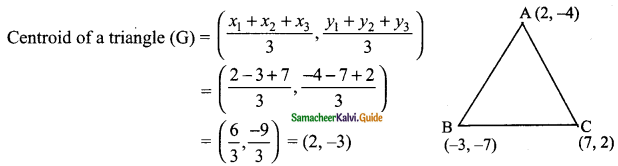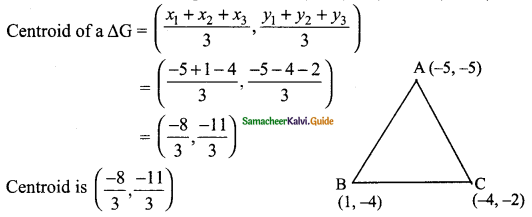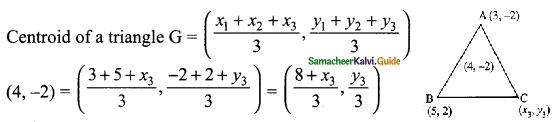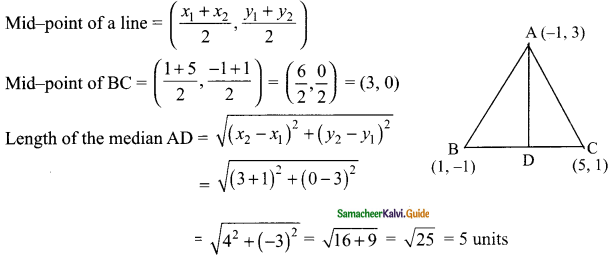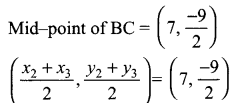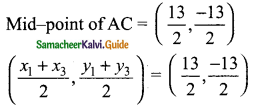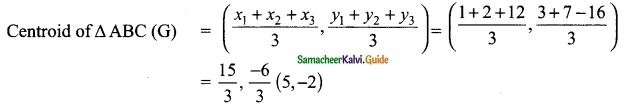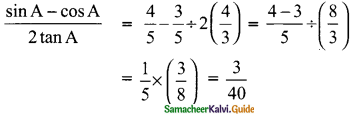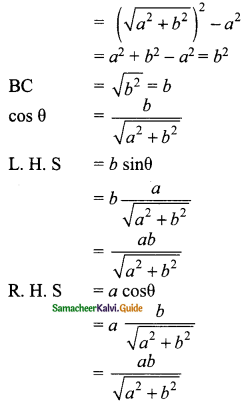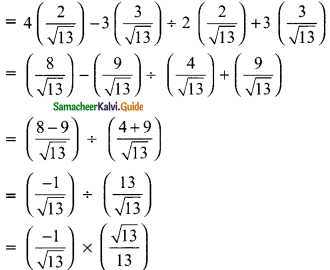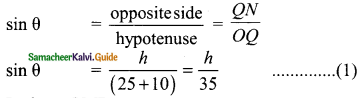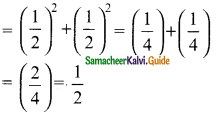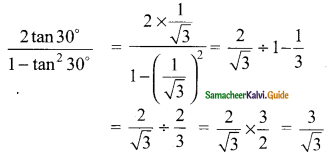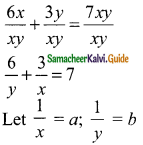Students can download Maths Chapter 6 Trigonometry Ex 6.2 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Trigonometry Ex 6.2
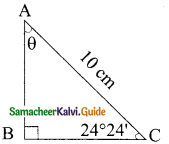
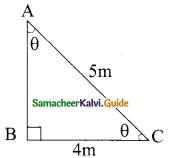
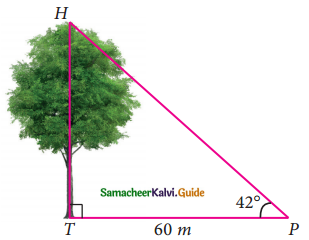
Question 1.
Verify the following equalities:
(i) sin² 60° + cos² 60° = 1
Solution:
sin 60° = \(\frac{√3}{2}\); cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
L.H.S = sin² 60° + cos² 60°
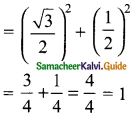
L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence it is proved.
![]()
(ii) 1 + tan² 30° = sec² 30°
Solution:
tan 30° = \(\frac{1}{√3}\); sec 30° = \(\frac{2}{√3}\)
L.H.S = 1 + tan² 30°
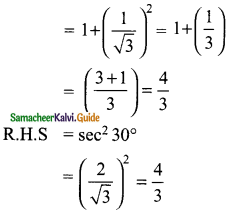
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence it is proved.
(iii) cos 90° = 1 – 2sin² 45° = 2cos² 45° – 1
Solution:
cos 90° = 0, sin 45° = \(\frac{1}{√2}\), cos 45° = \(\frac{1}{√2}\)
cos 90° = 0 ……. (1)
1 – 2 sin² 45° = 1 – 2 (\(\frac{1}{√2}\))²
= 1 – 2 × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 1 – 1 = 0 → (2)
2 cos² 45° – 1 = 2(\(\frac{1}{√2}\))² – 1
= \(\frac{2}{2}\) – 1
= \(\frac{2 – 2}{2}\) = 0 → (3)
From (1), (2) and (3) we get
cos 90° = 1 – 2 sin² 45° = 2 cos² 45° – 1
Hence it is proved.
![]()
(iv) sin 30° cos 60° + cos 30° sin 60° = sin 90°
Solution:
sin 30° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); cos 30° = \(\frac{√3}{2}\); sin 60° = \(\frac{√3}{2}\); sin 90° = 1
L.H.S = sin 30° cos 60° + cos 30° sin 60°
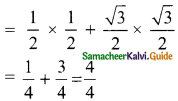
= 1
R.H.S = sin 90° = 1
L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence it is proved.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the value of the following:
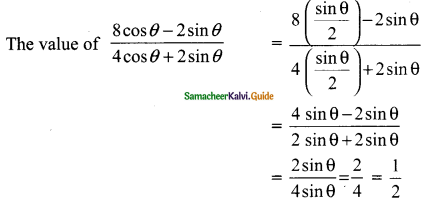
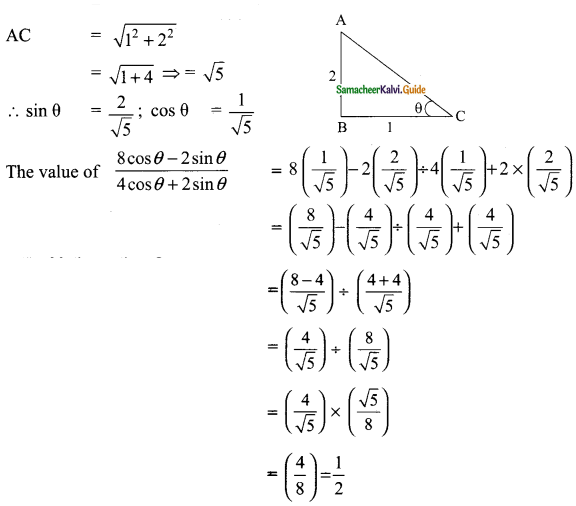
(i) \(\frac{tan 45°}{cosec 30°}\) + \(\frac{sec 60°}{cot 45°}\) – \(\frac{5 sin 90°}{2 cos 0°}\)
(ii) (sin 90° + cos 60° + cos 45°) × (sin 30° + cos 0° – cos 45°)
(iii) sin²30° – 2 cos³ 60° + 3 tan4 45°
Solution:
(i) tan 45° = 1, cosec 30° = 2; sec 60° = 2; cot 45° = 1; tan 45°, sin 90° = 1; cos 0° = 1
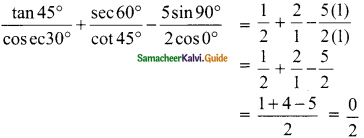
= 0
(ii) sin 90° = 1; cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); cos 45° = \(\frac{1}{√2}\); sin 30° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); cos 0° = 1
(sin 90° + cos 60° + cos 45°) × (sin 30° + cos 0° – cos 45°)
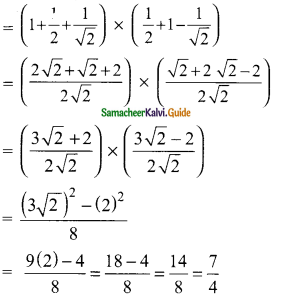
= \(\frac{7}{4}\)
![]()
(iii) sin 30° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\); tan 45° = 1
sin² 30° – 2 cos³ 60° + 3 tan4 45°
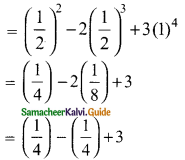
= 3
![]()
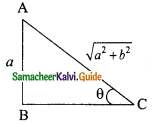
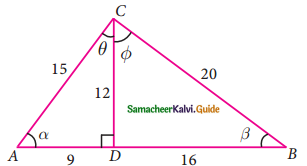
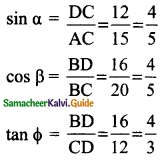
Question 3.
Verify cos 3 A = 4 cos³ A – 3 cos A, when A = 30°
Solution:
L.H.S = cos 3 A
= cos 3 (30°)
= cos 90°
= 0
R.H.S = 4 cos³ A – 3 cos A
= 4 cos³ 30° – 3 cos 30°
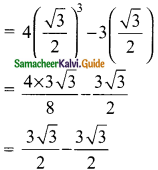
= 0
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence it is proved.
![]()
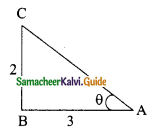
Question 4.
Find the value of 8 sin2x, cos 4x, sin 6x, when x = 15°.
Solution:
8 sin 2x cos 4x sin 6x = 8 sin 2 (15°) × cos 4 (15°) × sin (6 × 15°)
= 8 sin 30° × cos 60° × sin 90°
= 8 × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 1
= 2
![]()