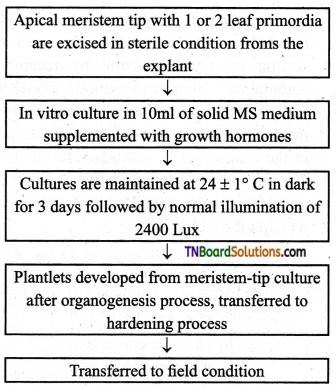
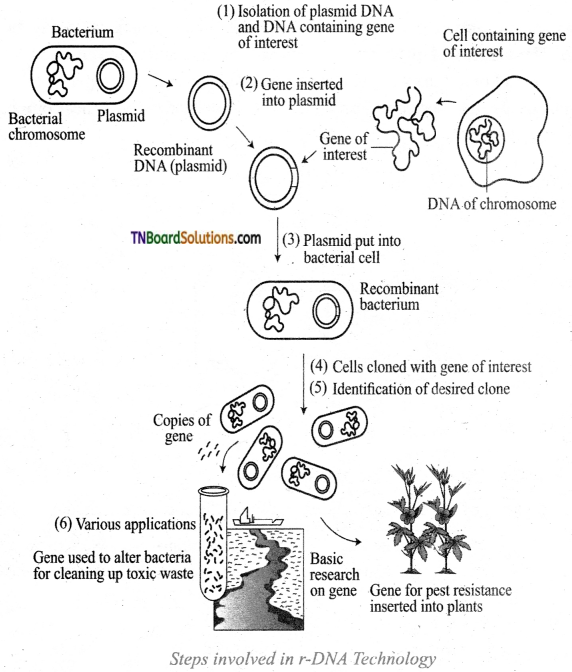
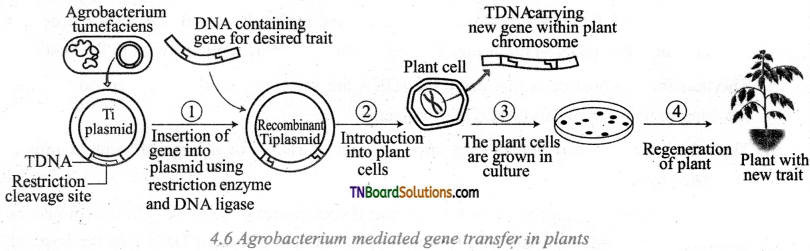
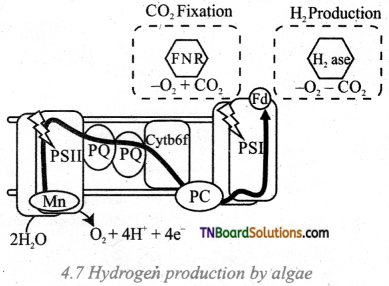
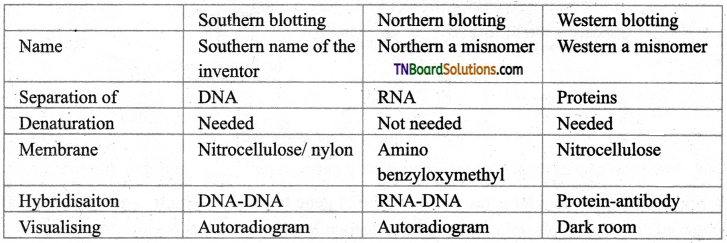
Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 10 Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 10 Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is meant by pseudo-cereal?
Answer:
Pseudo cereal refers to the foods that are prepared and eaten as a whole grain but are from grasses. Eg. Quinoa.
Question 2.
Give the scientific names of two bowls of cereal.
Answer:
- Paddy – Oryza sativa
- Wheat – Triticum aestivum
![]()
Question 3.
Mention any two examples of minor millets.
Answer:
- Foxtail millet – Setaria italica.
- Kodo millet – Paspalum scorbiculatum.
Question 4.
Define Pulses.
Answer:
Pulses are the edible seeds that are harvested from the fruits of the Fabaceae family. They ‘provide a vital source of plant-based protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Question 5.
Mention the nativity of black gram and green gram.
Answer:
- Black gram – India
- Green gram – India.
Question 6.
Define sugar.
Answer:
Sugar refers to the generic name of sweet tasting soluble carbohydrate that is used in foods and beverages.
Question 7.
Mention any two uses of Palmyra.
Answer:
- Palm sugar is prepared from the exudate from the inflorescence of Palmyra.
- Germinated seeds have elongated embryos surrounded by fleshy scale leaf, which is edible.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain briefly the property of coffee.
Answer:
Coffee, a non-alcoholic beverage, contains an alkaloid that stimulates the central nervous system. It also possess milS diuretic property.
Question 9.
What is the queen of spices? Write the areas of its cultivation in India.
Answer:
The queen of spices is cardamom. It is cultivated in the Western Ghats and North-Eastern India.
Question 10.
What is meant by red pepper?
Answer:
The red pepper is otherwise called as chilies and used in the preparation of sauces, curry powder, and pickles. The active ingredient is capsaicin.
Question 11.
Mention any two properties of teak wood.
Answer:
- The heartwood of teak is golden yellow to golden brown in color and changes into darker when exposed to light.
- It is durable, as it is resistant to the attack of termites and fungi.
Question 12.
Who invented paper production?
Answer:
Paper production is a Chinese invention. They prepared paper from the inner bark of paper mulberry in 105 A.D.
Question 13.
What is folk medicine?
Answer:
Folk medicine refers to the system of medicine practiced by ethnic communities through oral communication without any written documents.
![]()
Question 14.
Name any two medicinal plants.
Answer:
- Keezhanelli – Phyllanthus amarus
- Nilavembu – Andrographis paniculata.
Question 15.
Define Entrepreneurial Botany.
Answer:
Entrepreneurial Botany is defined as the study of how new businesses are created using plant resources. Eg. the Timber industry, the Rubber industry, etc.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Mention the uses of wheat.
Answer:
- In the Northern part of India Wheat is the staple food.
- Bread and other bakery products are produced from wheat flour.
- Alcoholic beverages and nutritive drinks are made from malted wheat.
Question 2.
Distinguish between a black gram and green gram.
Answer:
| Black gram | Green gram |
| The outer coat is black in colour. | The outer coat is green in colour. |
| The botanical name is Vigna mungo | The Botanical name is Vigna radiate. |
| Uttar Pradesh, Chaattisgarh and Karnataka are major states of cultivation. | Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are the major states of Cultivation. |
Question 3.
What are the national fruits of India? Explain its varieties and uses.
Answer:
The national fruit of India is mango.
The major varieties of mango in India are Alphonsa, Banganapalli, Neelam, and Malkova.
Mango is rich in beta carotenes and forms major table fruit in India. Unripe mangoes are used in chutneys, pickles, side dishes, or maybe eaten raw with salt and chili. Jelly is made from mango pulp. The aerated or non-aerated soft drinks are produced from mango pulp.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the origin and area of cultivation of sugar cane.
Answer:
Sugar cane, Saccharum officinarum is originated from New Guinea.
All districts of Tamil Nadu except Kanyakumari and Nilgiris cultivate sugar cane.
Question 5.
Write down the importance of groundnut.
Answer:
Brazil is the native of groundnut. The nuts contain 45% oil. Kernels are a rich source of phosphorous and vitamins.
It gives the premium cooking oil as it does not smoke. This oil is used in the manufacture of soaps and lubricants.
Question 6.
What is the king of spices? Mention its uses.
Answer:
The king of spices is black pepper, which is otherwise known as “Black Gold of India”. In the preparation of sauces, soups, curry powder, and pickles, it is used as a flavoring agent. It is also used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for enhancing salivary and gastric secretions. Pepper enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
Question 7.
List the various uses of rubber.
Answer:
- 70% of the rubber is being consumed by tire and other automobile manufacturing companies.
- Rubber is used in the manufacture of footwear, wire and cable insulations, raincoats, household and hospital goods, erasers, adhesives, and rubber bands. Concentrated latex is used for making gloves, balloons, and condoms. Cushion, pillows, and life belts are manufactured from foamed latex.
Question 8.
What is a psychoactive drug? Explain any one of such drugs.
Answer:
Psychoactive drug refers to a drug from some plants, which alters an individual’s perceptions of mind by producing hallucination.
One of the examples is cannabis or marijuana, the botanical name being Cannabis sativa. Marijuana is native of China and now it is legally cultivated in the states of Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarkhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh of India as industrial hemp. The active principle, which possesses medicinal properties is trans- tetrahydro cannabinol (THC).
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Write down the attributes of cereals as food plants?
Answer:
- Their greater adaptability and successful colonization on every type of habitat.
- The relative ease of cultivation is another important quality of cereals.
- They produce a higher yield per unit area due to their tillering property.
- The grains can be easily handled because the grains are dry and compact. They can easily be transported and stored without spoilage.
- They provide energy to the consumer due to their high calorific value.
Question 2.
Write about the importance of vegetables with examples.
Answer:
Vegetables are an important part of healthy eating. They provide many nutrients, including vitamins, potassium, fiber and folic acid. Vitamins A, E and C are abundant is vegetables.
One of the examples of a vegetable is okra, Abelmoschus esculantus. It is otherwise known as Lady’s finger, which is a native of tropical Africa. Lady’s finger is grown in Assam, Maharashtra, and Gujarat in large quantities. In Tamil Nadu, Coimbatore, Dharmapuri, and Vellore are the major districts, which cultivate okra.
The fresh and tender fruits are used as vegetables. It has the most important nutrients, especially phosphorous.
Question 3.
List out the uses of red chilies.
Answer:
- Red chilies are crushed and powdered to use as condiments.
- Chilies are used in the manufacture of sauces, curry powders, and preparation of pickles.
- The active ingredient of chilies is capsaicin.
- It has pain-relieving properties and used in pain-relieving balms.
- Chillies are a good source of vitamins C, A, and E.
![]()
Question 4.
Write about the folk system of medicine.
Answer:
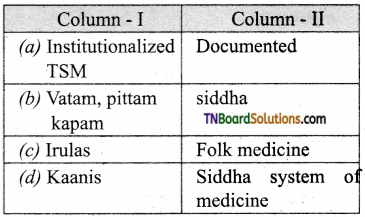
The rural communities of India are practicing this system of medicine through oral tradition without any authenticated written documents. Ministry of Environment and Forestry launched a program of All India Coordinated Research project on ethnobotany to document the plants used as medicine by ethenic groups in India. About 8000 plant species have been documented as the result of this project.
Irulas, Malayalis, Kurumbas, Paliyans, and Kannis are the tribal groups in Tamil Nadu, who are known for their medicinal knowledge. Some of the important medicinal plants they use include keezhanelli and nilavembu, which are now brought for medicinal use.
Choose the correct answers.
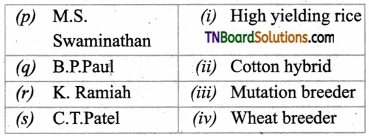
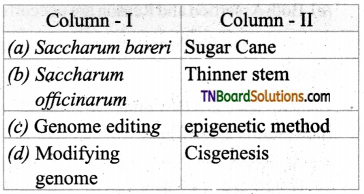
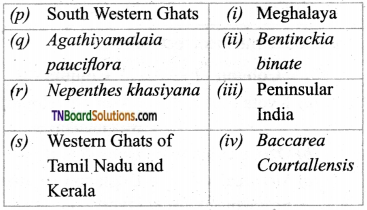
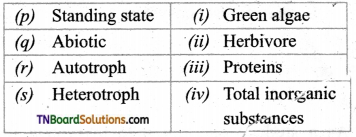
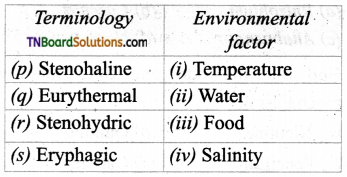
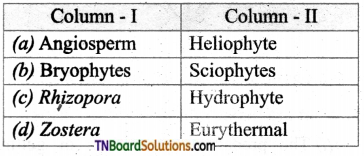
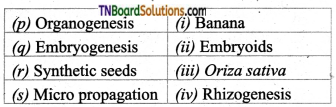
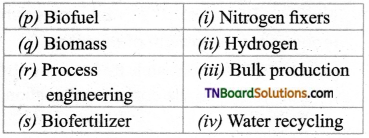
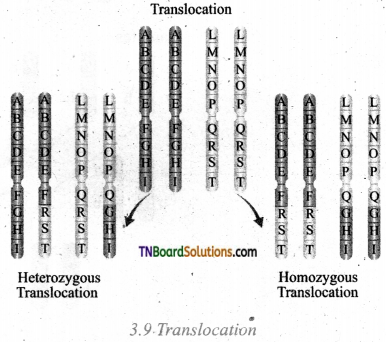
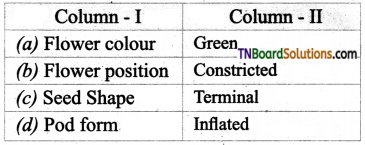
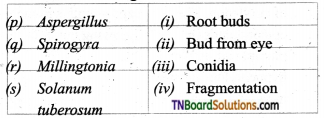
1. Match the following.
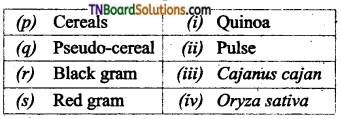
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(ni); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
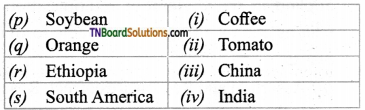
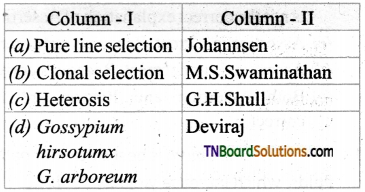
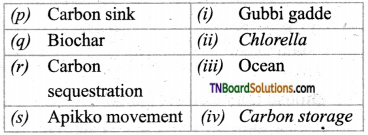
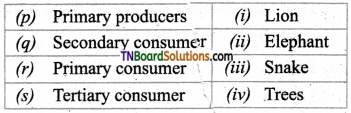
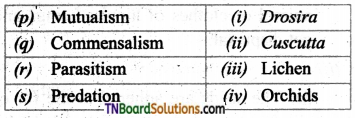
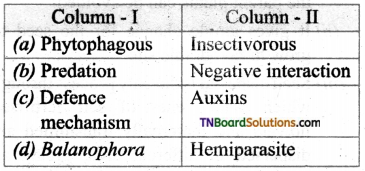
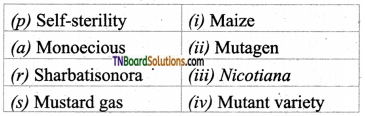
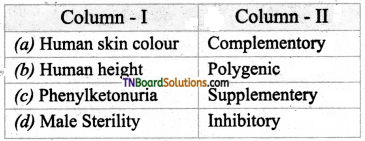
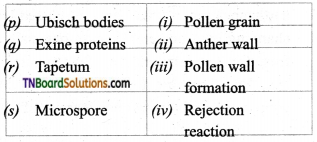
2. Match the following.
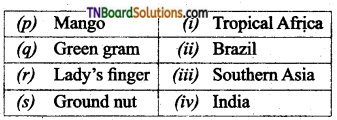
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
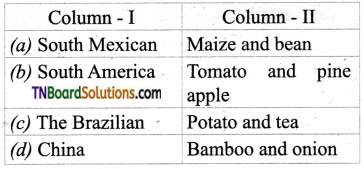
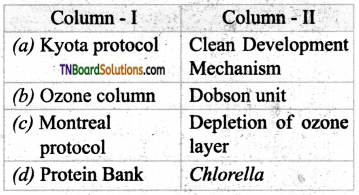
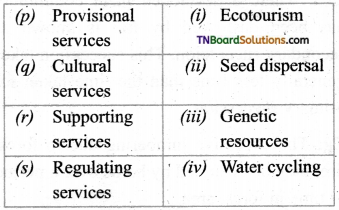
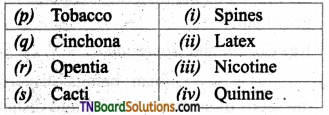
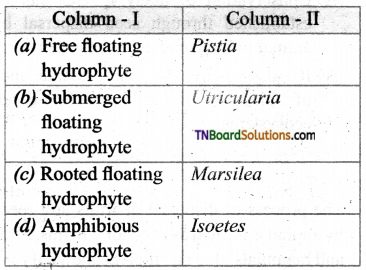
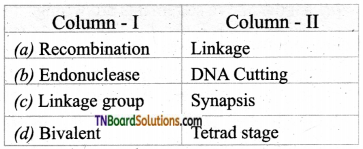
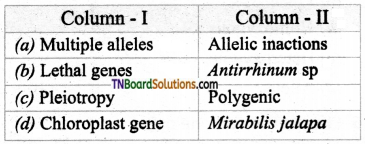
3. Match the following.

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
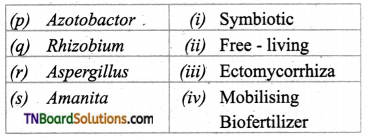
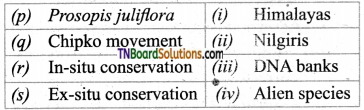
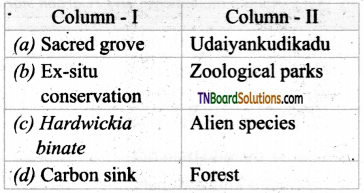
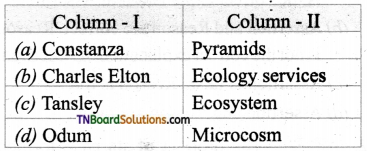
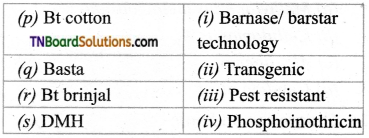
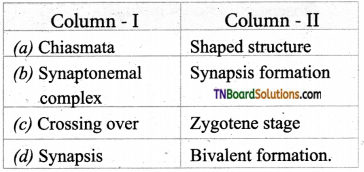
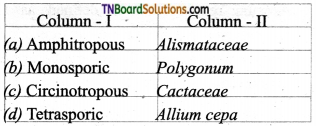
4. Match the following.
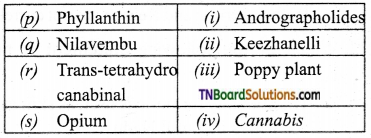
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); fr)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); fr)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
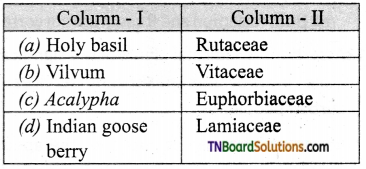
5. Which one is called as holy basil?
(a) Phyllanthus emblica
(b) Acalypha indica
(c) Ocimum sanctum
(d) Aegle marmelos
Answer:
(c) Ocimum sanctum
6. Marijuana is included under the family:
(a) Solanaceae
(b) Cannabiaceae
(c) Acanthaceae
(d) Euphorbiaceae
Answer:
(b) Cannabiaceae
![]()
7. Which of the following is used as Bio-pest repellent:
(a) Azadirachata indica
(b) Acalypha indica
(c) Vinca rosea
(d) Aegle marmelos
Answer:
(a) Azadirachata indica
8. Chenopodium quinoa is coming under:
(a) Pulses
(b) Cereals
(c) Nuts
(d) Pseudo-cereals
Answer:
(d) Pseudo-cereals
9. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Black gram
(b) Sorghum
(c) Pigeon gram
(d) Green gram
Answer:
(b) Sorghum
10. Choose the odd one:
(a) Coffea arabica
(b) Elettaria cardamomum
(c) Piper nigrum
(d) Cumcuma longa
Answer:
(a) Coffea arabica
![]()
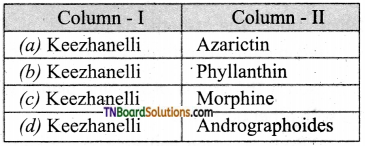
11. Find out the odd one.
(a) Phyllanthin
(b) Azadictin
(c) Gibberillin
(d) Morphine
Answer:
(c) Gibberillin
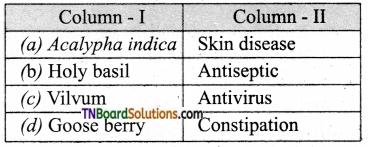
12. Indicate the odd one.
(a) Nilavembu
(b) Garlic
(c) Indian gooseberry
(d) Vilvum
Answer:
(b) Garlic
13. Choose the correct one.
Answer:
(c)
14. Which of the following is not a correct pair?
Answer:
(d)
15. Which of the following is the correct pair?
Answer:
(b)
![]()
16. Choose the incorrect pair.
Answer:
(c)
17. Assertion: Phyllanthus is a well-known hepato protective plant used for the treatment of jaundice.
Reason: It has been scientifically proved that the extract of Pamarus is effective against hepatitis B virus.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Assertion is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Assertion is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Assertion is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
18. Assertion: Medicinal plants play a significant role in providing healthcare services to urban people.
Reason: They serve as the therapeutic agents as well as important raw material for ’ the manufacture of traditional and modern medicines.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
19. Assertion: The essential oil from Jasmine is used in modern perfumery and cosmetics.
Reason: The aroma of Jasmine blends well with other perfumes.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
20. Assertion: An orange dye “Henna” is obtained from the roots of Law Sonia inermis.
Reason: The principal colouring matter lacosone obtained from the root is harmless.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
21. Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) Traditionally turmeric is used as skin care cosmetics in Tamil Nadu.
(b) Aloe vera is an antioxidant.
(c) Perfumes are manufactured from essential oil.
(d) All the above statement are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above statement are not correct.
22. Choose the correct statement.
(a) Black pepper is known as the queen of spices.
(b) Cardamom is called as the king of spices.
(c) Black pepper is called as the ‘black gold of India’.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Black pepper is called as the ‘black gold of India’.
23. Indicate the incorrect statement.
(a) The origin of red mango is Southern Asia
(b) The origin of red gram is Southern Irtdia.
(c) Lady’s finger is a native of Tropical Africa.
(d) Kodo millet is originated from Asia.
Answer:
(d) Kodo millet is originated from Asia.
![]()
24. Identify the correct statement.
(a) Rice is the chief source of carbohydrate.
(b) Wheat is the chief sources of protein.
(c) Edible oil is extracted from the husks of paddy.
(d) Rice bran is used as a fuel.
Answer:
(a) Rice is the chief source of carbohydrate.