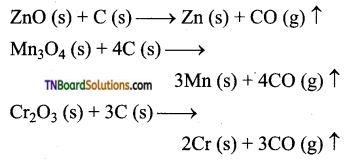
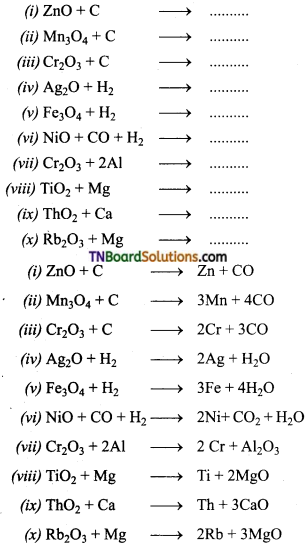
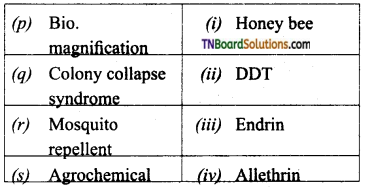
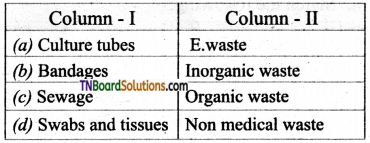
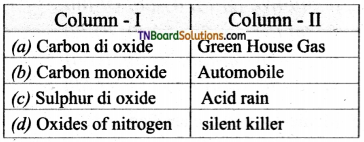
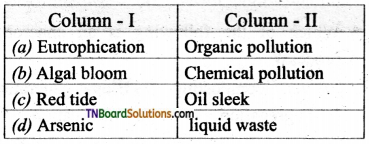
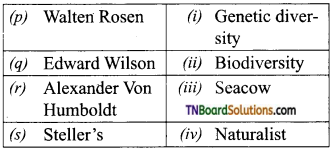
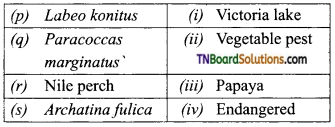
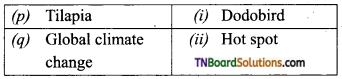
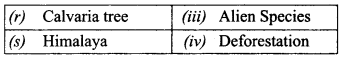
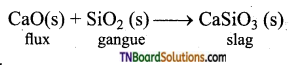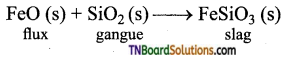Students get through the TN Board 11th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 1 Living World which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 1 Living World
Answer the following short answers.
Question 1.
Define Biosphere.
Answer:
Earth has formed some 4.6 billion years ago. It is a life-supporting planet with landforms like mountains, plateaus, glaciers, etc., Life on earth exists within a complex structure called the biosphere.
Question 2.
What is the role of the DNA molecule?
Answer:
DNA is essential for the regulation of life and is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and thus nonliving and living things exist together to make our planet unique.
Question 3.
What is consciousness?
Answer:
AH organisms are capable of sensing their environment and respond to various physical, chemical, and biological stimuli. Animals sense their surroundings by sense organs. This is called consciousness.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain Prions.
Answer:
Prions were discovered by Stanley B.Prusiner in the year 1982 and are proteinaceous infectious particles. They are the causative agents for about a dozen fatal degenerative disorders of the central nervous system of humans and other animals. For example Creutzfeldt – Jakob Disease (CJD), Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) – commonly known as mad cow disease and scrapie disease of sheep.
Question 5.
What is Plasmid?
Answer:
Plasmids are extrachromosomal double-stranded, circular, self-replicating, autonomous elements. They contain genes for fertility, antibiotic-resistant and heavy metals. It also helps in the production of bacteriocins and toxins which are not found in the bacterial chromosome.
Question 6.
Mention the need for classification?
Answer:
Classification is essential to achieve the following needs:
- To relate things based on common characteristic features.
- To define organisms based on the salient features.
- Helps in knowing the relationship amongst different groups of organisms.
- It helps in understanding the evolutionary relationship between organisms.
Question 7.
What is Pili?
Answer:
Pili or fimbriae are hair-like appendages found on the surface of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria (eg. Enterobacterium). The pili are 0.2 to 20 pm long with a diameter of about 0.025pm. In addition to normal pili, special types of pili that help in conjugation called sex pili are also found.
![]()
Question 8.
Define “Pruteen”.
Answer:
“Pruteen” is a single cell protein derived from Methylophilus and Methylotropus.
Question 9.
What are Mycobiont and Phycobiont?
Answer:
The symbiotic association between algae and fungi is called lichens. The algal partner |is called Phycobiont or Photobiont and the fungal partner is called Mycobiont. Algae provide nutrition for fungal partners in turn fungi provide protection and also help to fix the thallus to the substratum through rhizines. Asexual reproduction takes place through fragmentation, Soredia, and Isidia. Phycobionst reproduces by akinetes, hormogonia, aplanospore, etc., Mycobionts undergo sexual reproduction and produce ascocarps.
Question 10.
Define Homeostasis.
Answer:
Property of self-regulation and tendency to maintain a steady-state within an external environment which is liable to change is called Homeostasis. It is essential for the living organism to maintain internal conditions to survive in the environment.
Question 11.
Mention any four living characteristics of viruses.
Answer:
- Presence of nucleic acid and protein.
- Capable of mutation
- Ability to multiply within living cells.
- Able to infect and cause diseases in living beings.
Question 12.
Explain the term Viroid.
Answer:
Viroid is a circular molecule of ssRNA without a capsid and was discovered by T.O.Diener in the year 1971. The RNA of viroid has a low molecular weight. Viroids cause citrus exocytic and potato spindle tuber disease in plants.
![]()
Question 13.
What is meant by red tide?
Answer:
Red tide is caused by the toxic bloom of Dinoflagellates like Gymnodinium breve and Gonyaulax tamarensis. A major red tide incident in the west coast of Florida in the year 1982 killed hundreds and thousands of fishes.
Question 14.
What are Polysomes?
Answer:
The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. The number of ribosomes per cell varies from 10,000 to 15,000. The ribosomes are 70S type and consist of two subunits (50S and 30S). The ribosomes are held together by mRNA and form polyribosomes or polysomes.
Question 15.
Write briefly on purple sulfur bacteria.
Answer:
For bacteria belonging to this group, the hydrogen donor is Thiosulphate and Bacteriochlorophyll. Chlorophyll containing chlorosomes are present, eg. Chromatium.
Question 16.
Match the following:
| (i) Xanthomanas oryzae | (a) Apple |
| (ii) Erwiria caratovora | (b) Citrus |
| (iii) Erwiria amylovera | (c) Rice |
| (iv) Xanthomnas citri | (d) Carrot |
Answer:
(i)-(c);
(ii)-(a);
(iii)-(d);
(iv)-(b)
![]()
Question 17.
What is meant by aflatoxin?
Answer:
Aspergillus, Rhizopus, Mucor, and Penicillium ate involved in the spoilage of food materials. Aspergillus flavus infest dried foods and produce a carcinogenic toxins called aflatoxin.
Question 18.
Explain the term mycorrhizae.
Answer:
The Symbiotic association between fungal mycelium and roots of plants is called mycorrhizae. In this relationship, fungi absorb nutrition from the root, and in turn, the hyphal network of mycorrhizae forming fungi helps the plant to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil.
Question 19.
Name any two fungal diseases of plants and their causative organism.
Answer:
- A blast of Paddy: Magnaporthe grisea.
- Red rot of sugarcane: Colletotrichum falcatum.
Question 20.
Explain Oomycetes with an example.
Answer:
Coenocytic mycelium is present. The cell wall is made up of Glucan and Cellulose. Zoospore with one whiplash and one tinsel flagellum is present. Sexual reproduction is Oogamous. eg. Albugo.
![]()
Answer In brief.
Question 1.
Differentiate extrinsic and intrinsic.
Answer:
| Extrinsic | Intrinsic |
| Growth in non-living objects is extrinsic. | Growth in living things is intrinsic. |
| Mountains, boulders, and sand mounds grow by simple aggregation of material on the surface. | Living cells grow by the addition of new protoplasm within the cells. |
Question 2.
List out the classification of viruses.
Answer:
| Different Classes of viruses | |
| Class | Example |
| Class 1 – Viruses with dsDNA | Adenoviruses |
| Class 2 – Viruses with (+) sense ssDNA | Parvo viruses |
| Class 3 – Viruses with dsRNA | Reo viruses |
| Class 4 – Viruses with (+) sense ssRNA | Toga viruses |
| Class 5 – Viruses with (-) antisense ssRNA | Rhabdo viruses |
| Class 6 – Viruses with (+) sense ss RNA- RT that replicate with DNA intermediate in the life cycle. | Retroviruses |
| Class 7 – Viruses with ds DNA – RT that replicate with RNA intermediate in the life cycle. | Hepadna viruses |
Question 3.
Name any three plant, animal, and human diseases caused by viruses.
Answer:
Plant diseases: (i) Tobacco mosaic, (ii) Cauliflower mosaic, (iii) Sugarcane mosaic.
Animal diseases: (i) Foot and mouth disease of cattle, (ii) Rabies of dog, (iii) Encephalomyelitis of horse
Human diseases: (i) Common cold, (ii) Hepatitis B, (iii) Cancer.
![]()
Question 4.
Distinguish catabolism and anabolism.
Answer:
| Anabolism | Catabolism |
| Building up process. | Breaking down process. |
| Smaller molecules combine together to form larger molecules. | Larger molecules break into smaller units. |
| Chemical energy is formed and stored, eg. Synthesis of proteins from amino acids. | The stored chemical energy is released and used. eg. Breaking down of glucose to C02 and water. |
Question 5.
List out any three methods of sexual reproduction, in fungi.
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction is present but sex organs are absent. Somatogamy or spermatisation results in plasmogamy.
- Karyogamy is delayed and the dikaryotic phase is prolonged.
- Karyogamy takes place in basidium and it is immediately followed by meiotic division.
Question 6.
Describe briefly the Viral genome.
Answer:
- Each virus possesses only one type of nucleic acid either DNA or RNA. The nucleic acid may be in a linear or circular form.
- Generally nucleic acid is present as a single unit but in wound tumor virus and in influenza virus it is found in segments.
- The viruses possessing DNA are called ‘Deoxyviruses’ whereas those possessing RNA are called ‘Riboviruses’. The majority of animal and bacterial viruses are DNA viruses (HIV is the animal virus that possesses RNA).
- Plant viruses generally contain RNA (Cauliflower Mosaic virus possesses DNA). The nucleic acids may be single-stranded or double-stranded. On the basis of the nature of nucleic acid, viruses are classified into four categories. They are Viruses with ssDNA (Parvoviruses), dsDNA (Bacteriophages), ssRNA (TMV), and dsRNA(wound tumour virus).
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the structure of T4 bacteriophage.
Answer:
- The T4 phage is tadpole-shaped and consists of head, collar, tail, base plate, and fibers.
- The head is hexagonal which consists of about 2000 identical protein subunits.
- The long helical tail consists of an inner tubular core that is connected to the head by a collar.
- There is a base plate attached to the end of the tail. The base plate contains six spikes and tail fibers. These fibers are used to attach the phage to the cell wall of the bacterial host during replication.
- A dsDNA molecule of about 50 pm is tightly packed inside the head. The DNA is about 1000 times longer than the phage itself.
Question 8.
Draw and label the ultrastructure of a bacterial cell.
Answer:
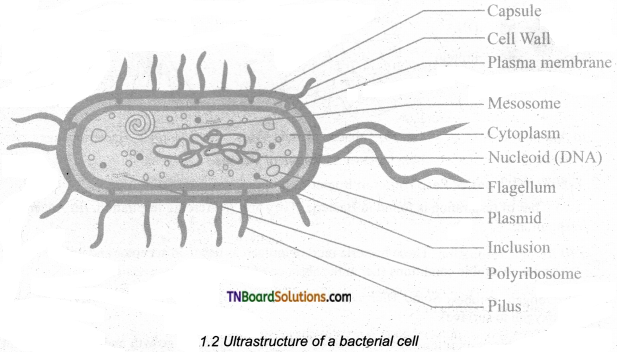
Question 9.
What is meant by Ammonification? Explain the bacteria involved in the process.
Answer:
| Bacterial aspects | Bacteria | Role |
| Ammonification | (i) Bacillus ramosus
(ii) Bacillus mycoides |
Convert complex proteins in the dead bodies of plants and animals into ammonia which is later converted into ammonium salt |
![]()
Question 10.
Explain Actinomycetes with an example.
Answer:
Actinomycetes are also called ‘Ray fungi’ due to their mycelia-like growth. They are anaerobic or facultative anaerobic microorganisms and are gram-positive. They do not produce an aerial mycelium. Their DNA contains high guanine and cytosine content (eg. Streptomyces).
Answer In detail.
Question 1.
Draw the structure of different types of viruses and explain.
Answer:
Viruses are ultramicroscopic particles. They are smaller than bacteria and their diameter range from 20 to 300 nm (1 nm = 10-9 meters). Bacteriophage measures about 10 – 100 nm in size. The size of TMV is 300 x 20 nm.
Generally, viruses are of three types based on shape and symmetry.
- Cuboid symmetry – eg. Adenovirus, Herpes virus.
- Helical symmetry – eg. Influenza virus, TMV.
- Complex or Atypical – eg. Bacteriophage, Vaccinia virus.
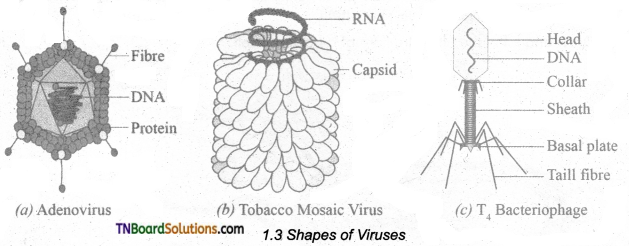
Question 2.
Explain the types of Respiration in Bacteria.
Answer:
Two types of respiration are found in Bacteria. They are (i) Aerobic respiration, (ii) Anaerobic respiration.
- Aerobic respiration These bacteria require oxygen as a terminal acceptor and will not grow under anaerobic conditions (i.e. in the absence of O2) eg. Streptococcus.
Obligate aerobes: Some Micrococcus species are obligate aerobes (i.e. they must have oxygen to survive), - Anaerobic respiration: These bacteria do not use oxygen for growth and metabolism but obtain their energy from fermentation reactions, eg. Clostridium.
Facultative anaerobes: There are bacteria that can grow either using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor or anaerobically using fermentation reaction to obtain energy. When a facultative anaerobe such as E. coli is present at a site of infection like an abdominal abscess, it can rapidly consume all available 02 and change to anaerobic metabolism producing an anaerobic environment and thus allow the anaerobic bacteria that are present to grow and cause disease, eg. Escherichia coli and Salmonella.
Capnophilic Bacteria: Bacteria that require CO2 for their growth are called as capnophilic bacteria, eg. Campylobacter.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the various steps in Gram’s staining procedure.
Answer:

Question 4.
Give a concise account of asexual reproduction in bacteria.
Answer:
Bacteria reproduce asexually by Binary fission, conidia, and endospore formation. Among these Binary fission is the most common one.
Binary fission: Under favorable conditions, the cell divides into two daughter cells. The nuclear material divides first and it is followed by the formation of a simple median constriction which! finally results in the separation of two cells.
Endospores: During unfavorable conditions bacteria produce endospores. Endospores are produced in Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus sphaericus, and Clostridium tetani. Endospores are thick-walled resting spores. During the favorable conditions, they germinate and form bacteria.
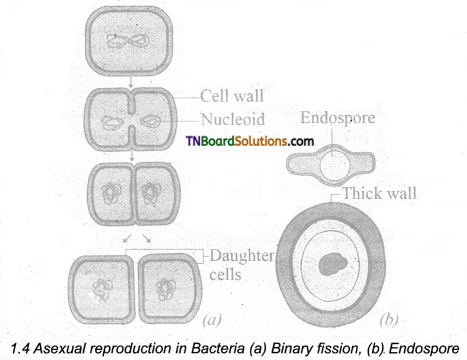
![]()
Question 5.
Enumerate the general characteristic features of fungi.
Answer:
- The majority of fungi are made up of thin, filamentous branched structures called hyphae. A number of hyphae get interwoven to form mycelium. The cell wall of fungi is made up of a polysaccharide called chitin (polymer of N-acetyl glucosamine).
- The fungal mycelium is categorized into two types based on the presence or absence of septa (figure). In lower fungi, the hypha is aseptate, multinucleate and is known as coenocytic mycelium (eg. Albugo). In higher fungi, a septum is present between the cells of the hyphae. eg. Fusarium:
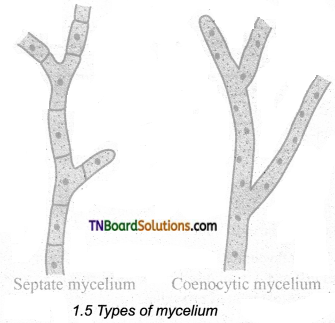
- The mycelium is organized into loosely or compactly interwoven fungal tissues called plectenchyma. It is further divided into two types prosenchyma and pseudoparenchyma. In the former type, the hyphae are arranged loosely but parallel to one another In the latter hyphae are compactly arranged and lose their identity.
- In holocarpic forms, the entire thallus is converted into reproductive structure whereas in Eucarpic some regions of the thallus are involved in the reproduction other regions remain vegetative. Fungi .reproduce both by asexual and sexual methods. The asexual phase is called Anamorph and the sexual phase is called Teleomorph. Fungi having both phases are called Holomorph.
- In general sexual reproduction in fungi includes three steps (a) Fusion of two protoplasts (plasmogamy), (b) Fusion of nuclei (karyogamy), and (c) Production of haploid spores through meiosis.
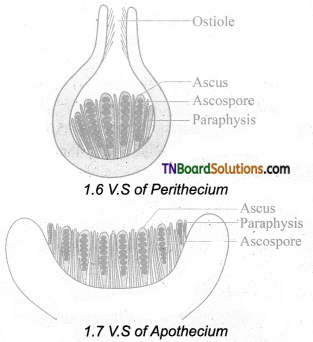
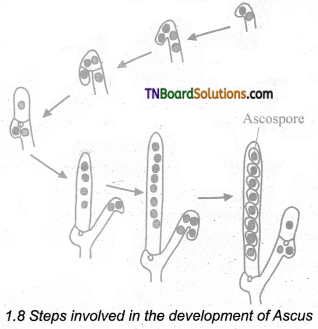
Question 6.
Write an essay on the Beneficial activities of fungi.
Answer:
Fungi provide delicious and nutritious food called mushrooms. They recycle the minerals by decomposing the litter thus adding fertility to the soil. The dairy industry is based on a single-celled fungus called yeast. They deteriorate the timber. Fungi cause food poisoning due to the production of toxins. The Beneficial and harmful activities of fungi are discussed below:
Beneficial activities:
- Food: Mushrooms likeLentinus edodes, Agaricusbisporus, Volvariella volvaceae are consumed ‘ for their high nutritive value. Yeasts provide vitamin B and Eremothecium ashbyii is a rich source of Vitamin B12.
- Medicine: Fungi produce antibiotics that arrest the growth or destroy the bacteria. Some of the antibiotics produced by fungi include Penicillin (Penicillium notatum), Cephalosporins,
(Acremonium chrysogenum), Griseofulvin (Penicillium griseofulvum). Ergot alkaloids (Ergotamine) produced by Claviceps purpurea are used as vasoconstrictors. - Industries: Production of organic acid: For the commercial production of organic acids fungi are employed in the Industries. Some of the organic acids and fungi which help in the production of organic acids are Citric acid and Gluconic-acid – Aspergillus niger, Itaconic acid – Aspergillus terreus, Kojic acid – Aspergilhis oryzae.
- Bakery and Brewery: Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is used for the fermentation of sugars to yield alcohol. Bakeries utilize yeast for the production of Bakery products like Bread, buns, rolls. etc. Penicillium roquefortii and Penicillium camemberti are employed in cheese production.
- Production of enzymes: Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger is employed in the production of enzymes like Amylase, Protease, Lactase etc., ’Rennet’ which helps in the coagulation of milk in cheese manufacturing is derived from Mucor spp.
- Agriculture: Mycorrhiza forming fungi like Rhizoctonia, Phallus, Scleroderma helps in the absorption of water and minerals. Fungi like Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae are used as Biopesticides to eradicate the pests of crops. Gibberellin, produced by a fungus Gibberella fujikuroi induce plant growth and is used as growth promoter.
![]()
Activity
Text Book Page No. 25
Collect some root nodules of leguminous crops. Draw diagram. Wash, it in tap water and prepare d smear by squeezing the content into a clean slide. Follow the Gram staining method and identify the bacteria.
Answer:
Azotobacter, Clostridium, rhizobium are observed.
Text Book Page No. 37
Get a button mushroom. Draw a diagram of the fruit body. Take a thin longitudinal section passing through the gill and observe the section under a microscope. Record your observations.
Answer:
Keep a slice of bread in a clean plastic tray or plate. Wet the surface with little water. Leave the setup for 3 or 4 days. Observe the moldy growth on the surface of the bread. Using .a needle removes some mycelium and place it on a slide and stain the mycelium using lactophenol blue. Observe the mycelium and sporangium under the microscope and Record your observation and identify the fungi and its group based on characteristic features:
The bread mold fungi such as Mucor, Rhizopus can be observed.
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. A sexual reproduction in living organism occurs by the production of:
(a) conidia formation
(b) budding
(c) binnary fission
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
2. Animal sense their surroundings by sense organ is called:
(a) Metabolism
(b) Irritability
(c) Consciounsness
(d) Anabolism
Answer:
(c) Consciounsness
3. Who obtained the crystalline protein sediment from infected tobacco juice?
(a) Edward Jennev
(b) W.M. Stanley
(c) Ivanowsky
(d) F.W. Twort
Answer:
(b) W.M. Stanley
4. Which of the following is the diameter of bacteriophage?
(a) 10 – 100 nm
(b) 20 – 100 nm
(c) 10 – 200 nm
(d) 20 – 30 nm
Answer:
(a) 10 – 100 nm
![]()
5. How many classes are there in viruses?
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 6
Answer:
(c) 1
6. The shape of TMV is:
(a) round shape
(b) cuboid shape
(c) cylindrical shape
(d) rod shape
Answer:
(d) rod shape
7. Identify the incorrect statement of living characters of viruses.
(a) Absence of metabolism
(b) Presence of nucleic acid
(c) Multiply within the cells
(d) Capable of mutation
Answer:
(a) Absence of metabolism
8. Cyanophages means:
(a) Viruses infecting red algae
(b) Viruses infecting brown algae
(c) Viruses infecting blue-green algae
(d) Viruses infecting green algae
Answer:
(c) Viruses infecting blue-green algae
9. Which one of the following is a bacterial disease?
(a) Common cold
(b) Cancer
(c) Rabies
(d) Tetanus
Answer:
(d) Tetanus
10. Who proposed the five kingdom classification?
(a) R.H. Whittaker
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Haeckel
(d) Aristotle
Answer:
(a) R.H. Whittaker
![]()
11. Actinomycetes, cyanobacteria are examples of:
(a) Protostar
(b) Fungi
(c) Monera
(d) Animalia
Answer:
(c) Monera
12. What are the three domains of life according to Carl Woese and co-workers?
(a) Prokaiyota, Eukaryota, Archaea
(b) Archaea, Bacteria, Protozoa
(c) Archaea, Fungi, Bacteria
(d) Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Answer:
(d) Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
13. Who coined the word Bacterium?
(a) Christian Gram
(b) C.G.Ehrenberg
(c) Griffith
(d) Lederberg
Answer:
(b) C.G.Ehrenberg
14. Eschrichia coli and Salmonella are examples of:
(a) Aerobes
(b) Obligate aerobes
(c) Facultative anaerobes
(d) Anaerobes
Answer:
(c) Facultative anaerobes
![]()
15. Which among the bacteria breakdown hydrocarbons?
(a) Pseudomonas putida
(b) Lacto bacillus
(c) Bifido bacterium
(d) Nitrosomonas
Answer:
(a) Pseudomonas putida
16. Match the following disease with their pathogen:
| Name of the disease | Name of the pathogen |
| (i) Bacterial blight | (a) Clavibactor michiganensis |
| (ii) Fire blight | (b) Xanthomonas citri |
| (Hi) Citrus canker | (c) Xanthomonas oryzae |
| (iv) Ring rot | (d) Erwinia amylvora |
(a) (i)-(d); (ii)-(c); (iii)-(b); (iv)-(a)
(b) (i)-(c); (ii)-(a); (iii)-(b); (iv)-(d)
(c) (i)-(a)-, (ii)-(d); (iii)-(b); (iv)-(c)
(d) (i)-(c); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(b); (iv)-(a)
Answer:
(d) (i)-(c); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(b); (iv)-(a)
17. PHB means:
(a) Poly Hexo Butyrate
(b) Poly Hydrolxl Butyle
(c) Poly -13 Hydroxl Butyrate
(d) Poly Hedfal Butyrate
Answer:
(c) Poly -13 Hydroxl Butyrate
![]()
18. Which of the statement is incorrect in blue-green algae?
(a) The thallus is unicellular
(b) The reserve food material is cyanophycean starch
(c) Absence of mucilage around the thallus
(d) Sexual reproduction is absent
Answer:
(c) Absence of mucilage around the thallus
19. Nostoc and Anabaena are examples of:
(a) Biofertilizer
(b) Biological fuel
(c) Biotic factor
(d) Pro-Biotic
Answer:
(a) Biofertilizer
20. Father of the Indian mycology is:
(a) P.A.Michali
(b) C.H.Blackley
(c) Sir Edwin John Butler
(d) A.F. Blakeshec
Answer:
(c) Sir Edwin John Butler
21. In Fungi reproduction sexual phase is called:
(a) Anamorph
(b) Holomorph
(c) Allelomorph
(d) Teleomorph
Answer:
(d) Teleomorph
22. Odd one out (Type of ascocarp):
(a) Deistothecium
(b) Perithecium
(c) Apothecium
(d) Basidium
Answer:
(d) Basidium
![]()
23. Which one of the following is a rich source of vitamin B12?
(a) Agaricus bisporus
(b) Aspergillus oryzae
(c) Eremothecium ashbyii
(d) Clavicepspurpurea
Answer:
(c) Eremothecium ashbyii
24. Pick out the incorrect pair:
(a) Blast of paddy – Magnaporthe grisea
(b) Red rot of sugarcane – Albugo Candida
(c) Rust of wheat – Pucciniagraminis
(d) peach of leaf curl – Taphrina deformans
Answer:
(b) Red rot of sugarcane – Albugo Candida
25. The symbiotic association between fungal mycelium and roots of higher plants is called:
(a) Lichen
(b) Symbiotic
(c) Monotropa
(d) Mycorrhizac
Answer:
(d) Mycorrhizac
26. Each virus posses only one type of nucleic acid:
(a) Either DNA or RNA
(b) DNA only
(c) Neither DNA nor RNA
(d) RNA only
Answer:
(a) Either DNA or RNA
![]()
27. Tobacco mosaic virus is a:
(a) rhomboid-shaped helical virus
(b) rod-shaped helical virus
(c) rectangular-shaped virus
(d) triangular shaped helical virus
Answer:
(b) rod-shaped helical virus
28. Indicate the correct statement:
(a) Virion is a circular molecule of ss RNA without a capsid
(b) Virion is a phage that injects linear DNA into the host cell
(c) Virion is an intact infective virus particle, which is non – replicating outside a host cell
(d) Virion is discovered by J.W Randles
Answer:
(c) Virion is an intact infective virus particle, which is non – replicating outside a host cell
29. Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another is called:
(a) Conjugation
(b) Transformation
(c) Transduction
(d) Binary fission
Answer:
(b) Transformation
![]()
30. Fusion of two somative cells of the hypae is called:
(a) Anisogamy
(b) Somatogamy
(c) Oogamy
(d) Isogamy
Answer:
(b) Somatogamy