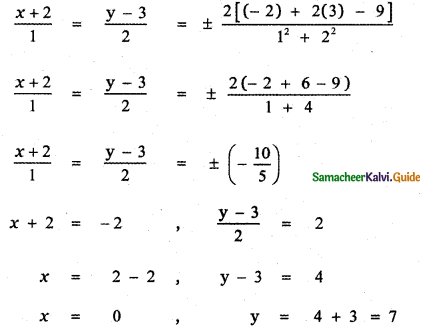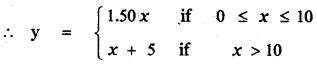Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th English Guide Pdf Supplementary Chapter 6 Remember Caesar (Play) Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th English Solutions Supplementary Chapter 6 Remember Caesar (Play)
12th English Guide Remember Caesar (Play) Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Textual Questions:
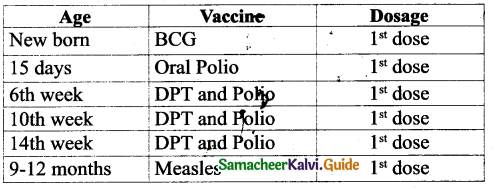
1. Complete the summary of the play, choosing the appropriate words from the list given below the passage: (Text Book Page No. 206)
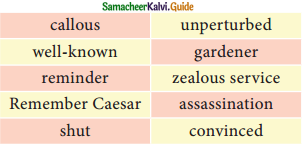
Lord Weston was a (1) _____ judge in England. Being pompous and vain, he told his secretary Roger that he had attained glory by hard work and (2) ____. He expressed his displeasure over Roger’s request for a half-holiday. Suddenly, he discovered a piece of paper with the words (3) _____ in his pocket, and he feared that the message was a warning conveyed by his enemies who had received legal punishments from him. As the message was sent on the 15th of March, (the day Julius Caesar was assassinated), he was (4) ______ that someone affected by his fair judgement was plotting his murder. Sensing the definite attack, Lord Weston ordered his secretary to (5)______ all the doors and windows. But his wife remained (6) ______ by the threat. So, Lord Weston was angered by her (7) ______ reaction. He ordered Roger to send the cook and the (8) ______ away. Both Weston and Roger took elaborate precautionary measures to thwart the (9) ______ attempt. Finally, Weston was able to recollect that he had written the message “Remember Caesar” himself as a (10) ______. Caesar was actually a gardener who had an appointment to visit Weston’s garden. The play revolves around Weston’s absent-mindedness which is the crux of the play.
Answers:
- well-known
- zealous service
- Remember Caesar
- Convinced
- shut
- unperturbed
- callous
- gardener
- assassination
- reminder
![]()
2. Based on your understanding of the text, answer the following questions briefly: (Text Book Page No. 206)
Question a.
How did Lord Weston describe himself?
Answer:
Lord Weston claimed that he had won his honours by hard work and zealous service. He is acknowledged as the most impartial judge in England.
Question b.
How did Roger react to Lord Weston’s advice?
Answer:
Roger was not very serious in listening to Lord Weston’^advice. While talking to Roger, Weston discovered his misplaced diligence.
Question c.
What made Lord Weston think that his life was in danger?
Answer:
Question d.
Why was the speaker keen to know what day it was?
Answer:
The speaker was keen to know what day it was and he was told the fifteenth of March by Roger. When he heard the day, he was looking at the paper in a horrified manner and thought of’The Ides of March’ how, Julius Caesar was assassinated.
Question e.
Mention the immediate steps taken by Lord Weston to protect himself from his assassination.
Answer:
Weston along with Roger takes such precautions that they almost ruined the floors, shut all the entries, drowned some newly bought Velvet Cloak along with some precious books, and even drew the pistol out to attack the intruders. Thus Lord Weston has taken immediate steps in order to protect himself from his assassination.
![]()
Question f.
Do you think that Lady Weston did not care about the threat to her husband? State reasons.
Answer:
Lady Weston did not care about the threat to her husband. It was so evident that when Weston informed her of the danger and threat of assassination, she seemed to be unaffected and undisturbed. She reminded him of his panic sometimes and then laughed at his fears. She said that he didn’t value to anything to be assassinated.
Question g.
How did Lord Weston ‘defuse’ the ‘infernal machine’?
Answer:
Lord Weston wanted the pail to submerge the suspicious-looking parcel in the water to deactivate it if it contained explosives. So he told Roger to pick the wet cloth off the edge of the pail, dropping it on the carpet, and plunges the books into the water, which very naturally overflows at this new incursion. This is how Weston planned to defuse the ‘infernal machine’.
Question h.
Whose life was of ‘great value’ to England? In what way?
Answer:
According to Roger, Lord Weston’s life was of great value to England. When Weston asked Roger to open the window in order to throw the suspicious-looking parcel outside, he told Weston to keep away from the danger and he would handle the thing. Because he said that life was not more important than Lord Weston.
Question i.
Why did the speaker consider his lifeless important?
Answer:
The speaker considered his lifeless important because he has already had his life. When Roger told that his life was nothing and Weston’s life was of great value to England, he stopped him to say so, and made Roger to feel for a long life as he was too younger than Weston. He also told him that there were many great things for him to do in the world.
Question j.
Who reminded Lord Weston about Mr. Caesar?
Answer:
Roger reminded Lord Weston about Mr. Caesar whom he met on Tuesday at Hampton and has come to see him just to discuss rose trees.
Question k.
What was the truth about the crumpled piece of paper?
Answer:
Weston has found a scrap of paper while searching for a fill for his pipe in his pocket with a warning – “Remember Caesar”. Actually, it was written by Weston himself as a reminder of Mr. Caesar whom he, met at Hampton. Since he was absent-minded, he totally forgot about Mr. Caesar and (Disconnected the statement with the historical king Julius Caesar.
Question l.
Bring out the irony in the message “Remember Caesar”.
Answer:
The irony that keeps the reader on the point of suspense is the message, On seeing Remember Caesar Scribbled on a paper, Lord Weston suspects that it was a message for him from someone. Who had made all preparations to assassinate him? In fact, it was all due to a misunderstanding brought in by a slip of memory.
![]()
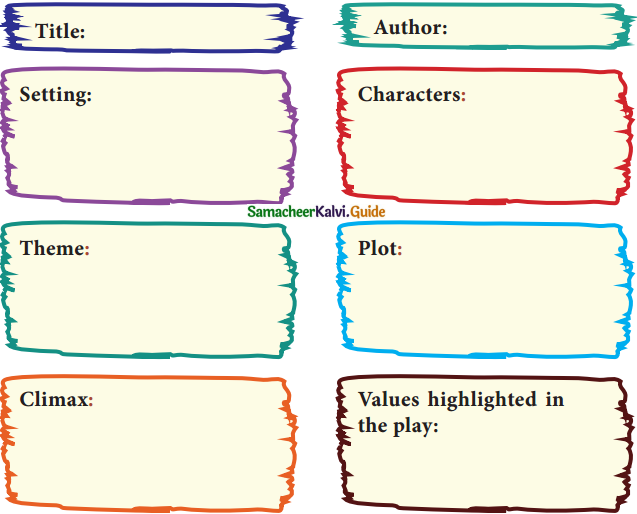
3. Based on your understanding of the play, complete the Graphic Organiser (GO) suitably: (Text Book Page No. 206)
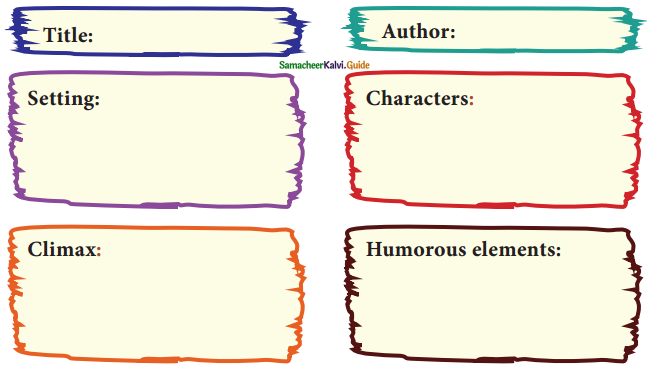
Title:
Remember Caesar
Author:
Gordon Daviot
Setting:
The play is set in a way, Lord Weston is seated by the fireplace, talking to Roger with a table of books and papers beside him.
Characters:
Lord Weston, Roger Chetwynd, Lady Weston.
Climax:
At the end of the story, the real Caesar enters. It was Mr. Caesar, a gardener who had agreed to visit Weston’s garden that morning.
Humorous elements:
The message was handwritten by Weston himself, as a reminder but the entire confusion was created by Weston because of his absent-mindedness.
![]()
4. Answer the following questions in a paragraph about 150 words each: (Text Book Page No. 207)
Question a.
“Remember Caesar” is a light-hearted comedy. Discuss the statement in a group and identify various aspects such as title, plot, and characterization that contribute to the humour in the play.
Answer:
The play “Remember Caesar” is actually a light-hearted comedy. Here, the play centers around the ides of March, that is the 15th of March, the day Julius Caesar was assassinated. It is about a pompous and proud judge who fears a life threat after he discovers a message ‘Remember Caesar’ scribbled on a piece of paper in his pocket.
He exhorts his assistant Roger to remain alert to foil the possible attempt of the assassin. He is panic-stricken and makes his assistant engage in elaborate precautionary measures. The title indeed is very apt to the plot, and as far as the characterization is concerned, it brings out a lot of humorous elements, especially by Lord Weston and Roger.
Even Weston’s wife Frances makes fun of his foolishness when he takes his pistol out to protect him from enemies. Though the plot gives us the suspense of what comes next, it focuses on the absent-minded Weston. Only because of Weston’s forgetfulness fullness, the story continues and has a lot of comical elements in it.
Question b.
Compare the character traits of Lord Weston and his wife.
Answer:
Lord Weston is a judge. He is always busy, giving advices to his servants, particularly to his assistant Roger. He is a man of ambitious and hard-working personality and always focussed on his own achievements in life. He expects Roger to follow the same in order to get success in his life.
The only weakness of Weston is his absent-mindedness. Due to the slip of his memory, he wasted his valuable time in taking precautionary measures from his enemies. It is all happened just because of his forgetfulness and of the habit of taking a note in a piece of paper. On the other hand, Weston’s wife Frances is an excellent lady and a total contrast of her husband.
It goes to her credit that the lady behaved at the sight of their daffodils. At the same time, she pokes fun at her pompous husband with a view to correct him as a patient mother does. In general, Lord Weston is absent-minded whereas lady Weston is steadily minded in the play “Remember Caesar”.
![]()
Paragraph:
Introduction:
The play “Remember Caesar” is actually a light-hearted comedy. Here, the play centers around the ides of March, that is the 15th of March, the day Julius Caesar was assassinated.
Plot:
Lord Weston is a pompous and proud judge and absent-minded who fears a life threat after he discovers a message ‘Remember Caesar’ scribbled on a piece of paper in his pocket. He exhorts his assistant Roger to remain alert to foil the possible attempt of the assassin. He is panic-stricken and makes his assistant engage in elaborate precautionary measures.
Characterization:
The title indeed is very apt to the plot, and as far as the characterization is concerned, it brings out a lot of humorous elements, especially by Lord Weston and Roger. Even Weston’s wife Frances makes fun of his foolishness when he takes his pistol out to protect him from enemies. Though the plot gives us the suspense of what comes next, it focuses on the absent-minded Weston. Only because of Weston’s forget fullness, the story. continues and has a lot of comical elements in it. Finally, Roger reminds Lord Weston about Mr. Caesar whom he met on Tuesday at Hampton. He has come to see him just to discuss rose trees.
Question C.
Group Work: (Text Book Page No. 207)
The play revolves around a ‘perceived threat’ and how Lord Weston and Lady Weston react to it. Let’s reverse their roles. Imagine a panic-stricken Lady Weston and a frivolous Lord Weston. Read the following piece of dialogue from the play and rewrite it to suit the changing roles.
Weston: My dear, your husband’s life is in grave danger.
Lady Weston: The last time it was in danger you had been eating game pie. What is it this time?
Weston : (annihilating her flippancy with one broadside): Assassination!
Lady Weston: Well, well! You always wanted to be a great man and now you have got your wish!
Weston: What do you mean?
Lady Weston: They don’t assassinate anybody.
Weston and Lady Weston in reversed roles:
Lady Weston: Dear husband. Look at this paper. Your life is in danger.
Weston: No dear, You thought my life was in danger when I ate game pie last time. What is this time?
Lady Weston: You may be assassinated?
Weston: Assassination It is silly.
Lady Weston: Don’t be so careless.
Weston: They don’t assassinate anybody. Particularly not me. You know. I am the most respected judge close to the king. Don’t worry.
![]()
ஆசிரியரைப் பற்றி:
கோர்டன் டேவியாட் (Gordon Daviot) (1896-1952) என்ற புனை பெயரைக் கொண்ட மிஸ் எலிசபத் மேக்கின்டோஷ் (Elizabeth McKintosh) ஸ்காட்லாந்தில் பிறந்த நாவலாசிரியர் (novelist) மற்றும் நாடக ஆசிரியர் (Playwright) ஆவார்.
இங்கிலாந்திலும் (England), ஸ்காட்டலாந்திலும் (Scotland) கல்வியாளராகவும், உடற்பயிற்சி ஊக்குனராகவும் (Physical Education Instructor) பணியாற்றி பின்னர் pseudonym Josephine Tey என்பவரின் தலைமையின் கீழ் கதைகள், நாவல் எழுதுவதிலும் தன்னை ஈடுபடுத்திக் கொண்டார்.
கதைச் சுருக்கம்:
ஜீலியஸ் சிசர் (Julius Caesar) ஒரு அற்புதமான இராணுவ ஜெனரல் மற்றும் பெரிய ரோமன் (Roman) மன்னர் ஆவார். அவர் கி.மு 100-ல் ஜீலை 13-ம் தேதி பிறந்தார். இன்றைய காலண்டரை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்ட ஜீலியன் நாட்காட்டியை அவர் உருவாக்கியுள்ளார். அவர் 44 கி.மு (பொ,ச,மு) இல் ரோமன் செனட்டர்களின் குழுவினால் படுகொலை செய்யப்ட்டார்.
ஜீலியஸ் சீசர் கொலை செய்யப்பட்ட மார்ச் 15-ம் நாள் பண்டைய ரோபிஸ் ஐட்ஸ் ஆஃப் மார்ச் (Ides of March) என அழைக்கப்பட்டது. இங்கு மார்ச் மாதங்கள் பற்றி இந்நாடகம் சுழல்கிறது. (ஜீலியஸ் சீசர் படுகொலை செய்யப்பட்ட நாள் மார்ச் 15).
வெஸ்டன் பிரபு (Lord Weston) ஒரு நீதிபதி. அவர் ஞாபக மறதி உள்ளவர். தன் சட்டை (Coat Pocket) பையில் ஒரு காகிதத்துண்டைக் காண்கிறார். அதில் “சீஸரை நினைவு கொள்” (Remember Caesar) என்று எழுதப்பட்டிருக்கிறது. ஒரு ஜோதிடரால் எச்சரிக்கப்பட்ட (ரோமானிய) ஜீலியஸ் சீசர் நினைவால் வெஸ்டன் அதிர்ச்சியடைகிறார்.
இது தன் உயிருக்கு அச்சுறுத்தல் என எண்ணுகிறார். ஒரு நபர் இந்த சீட்டை தம் கோட்டுப் பையில் திணித்திருக்கலாம் என்று சந்தேகப்படுகிறார். அவர் தன் உதவியாளரை வீட்டிலுள்ள எல்லா கதவுகளையும் மூடச் சொல்லுகிறார்.
தோட்டக்காரனையும் சமையல்காரரையும் வெளியே அனுப்பி விடச் சொல்கிறார். உண்மையில் சீசர் என்பது ஒரு தோட்டக்காரன் பெயர். சீசரை நினைவுகொள் என்று எழுதியதும் அவரே. அவருக்கு நேரம் ஒதுக்கியதை நினைவுகொள்ள தன் கைப்பட வெஸ்டன் எழுதிய சீட்டுதான் அது. நாடகத்தின் முடிவை வாசித்துக் காண்போம்.
![]()
| கதாபாத்திரங்கள் (Characters) | அவர்களின் பங்கு (Role/Part) |
| Lord Weston | Judge (நீதிபதி) |
| Roger Chetwynd | Weston’s Secretary (வெஸ்டனின் உதவியாளர்) |
| Lady Weston | Weston’s Wife (வெஸ்டனின் மனைவி) |
Remember Caesar (Play) Summary in Tamil
ஜீலியஸ் சீஸர் கொலையுண்ட “இட்ஸ் ஆஃப் மார்ச்” (மார்ச் 15 ஆம் நாளைச்) சுற்றி அமைந்த நாடகம் இதோ இங்கேயுள்ளது. ‘சீஸரை நினைவு கொள்’ என்ற இந்த நாடகம் ஆடம்பரமான, கர்வம் கொண்ட நீதிபதியைப் பற்றியது. தம்முடைய கோட்டுப்பையில் “சீஸரை நினைவுகொள்” என்ற வாசகம் எழுதிய செய்தியைக் கண்டபிறகு தன்னுடைய உயிருக்கு ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்ட அச்சுறுத்தல் என அவர் அஞ்சினார்.
கொலை முயற்சியை முறியடிக்க கவனமாக இருக்குமாறு தன் உதவியாளர் ரோஜரை வலியுறுத்துகிறார். அச்சத்தால் பீதியடைந்த அவர், விரிவான முன்னெச்சரிக்கை நடவடிக்கைகளில் தீவிரமாக இறங்குமாறு தன் உதவியாளரை அறிவுறுத்துகிறார். வெஸ்டன் பிரபுவும் ரோஜரும் அந்தக் கொலை முயற்சியை முறியடிக்கிறார்களா இல்லையா என்பதை அறிய நாடகத்தைப் படிப்போமாக.
வெஸ்டன் பிரபு தீ மாடத்தின் அருகே அமர்ந்துள்ளார். அவர் அருகே புத்தகங்களும், தாள்களும் கொண்ட ஒரு மேஜை உள்ளது. பேசிக் கொண்டிருக்கிறார். அவருக்கு நேர் எதிரே, ஒல்லியான, உண்மையாளரான, மறதி நிறைந்த, மனசாட்சி மிக்க இளைஞர் திரு. ரோஜர் செட்விண்ட் அமர்ந்துள்ளார். எந்த அளவுக்கு மனசாட்சிமிக்கவர் என்றால் விடுமுறையில் இருந்தாலும் தன் எஜமானரின் வேலைகளில் நினைவு தவறியவராகவே இருப்பார்.
அவர் தன் எஜமானரின் பேச்சை (அவர் சொல்லச்சொல்ல குறிப்பெடுப்பதற்காக) கேட்கத் துவங்கி இருக்கிறார். ஆனால் வேலையின் வசீகரம் படிப்படியாக அதிகரித்துக் கொண்டே செல்கிறது. எஜமானர் சொல்லும் வரையறுக்கப்பட்ட சொற்கள் அவரை நோக்கிப் பாய்ந்து வந்தபோது, அவர் ஒரு தாளிலிருந்து மற்றொரு தாளுக்கு எழுதிக் கொண்டு இருந்தார். அவருடைய உதடுகளும் சொற்றொடர்களை அமைத்துக் கொண்டே இருந்தன.
வெஸ்டன்: ரோஜர் இது கடமையின் கேள்வி மட்டுமல்ல. உலகத்தில் உன்னுடைய சொந்த வெற்றியை நிர்ணயிப்பதாகும். உன் வாழ்க்கை முழுவதும் செயலாளராக இருப்பது உன் எண்ணம் இல்லை, இல்லையா? இல்லை. மிகவும் நல்லது. புத்திக் கூர்மையும், விளக்கங்களுக்கான மதிப்பும் உன்னுடைய கவனத்தில் இருக்க வேண்டும். நான் சோம்பலாக இருந்து கொண்டும், அபிமானங்களை நம்பிக் கொண்டும் வெஸ்டன் பிரபுவாக வரவில்லை.
கடும் உழைப்பினாலும், அக்கறையுடன் பணியாற்றியதாலும் நான் மரியாதையாக வென்றேன். இன்று இங்கிலாந்து நாட்டில் நான் மிகவும் புகழ்பெற்ற நடுநிலையான நீதிபதியாக இருக்கின்றேன் மற்றும் மாண்புமிகு இரண்டாம் சார்லஸ் மன்னருடைய அபிமானமுள்ள ஊழியனாக இருக்கின்றேன். அன்புள்ள ரோஜர் நான் நீ கற்றுக் கொள்வதற்கான எடுத்துக்காட்டாக இருக்கிறேன். அரைநாள் விடுமுறை கேட்பது உனக்கு ஏற்றதல்ல.
![]()
ஆனால் அது உன்னுடைய தகுதிக்குச் சரியில்லை. நான் அஞ்சுகிறேன்….. (தன் செயலாளரை நோக்கி அவர் திரும்புகின்றார். தன்னுடைய அறிவுக்கூர்மை தவறான வைக்கப்பட்டிருப்பதாகக் (தவறான நபரிடம் சொல்லப்படுவதற்காகக்) கண்டறிகின்றார். ஒரு இடைவெளிக்குப் பின் மிகவும் ஆர்வமில்லாமல்) நீ என்னுடைய சொற்பொழிவைக் கேட்காமல் இருக்கிறாய். திரு. செட்விண்ட் அவர்களே இப்படி இருக்க முடியுமா?
ரோஜர் : (அந்த வார்த்தையின் இசை நிறுத்தப்பட்டதால் சகஜ நிலைக்குக் கொண்டுவரப்படுகிறார்) என்ன, சொன்னீர்கள் எஜமானரே? ஓ…. இல்லை, ஆமாம், நிச்சயமாகக் நான் கேட்டுக் கொண்டு இருக்கிறேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : நான் எதைப் பற்றி பேசிக் கொண்டு இருந்தேன்?
ரோஜர் : உங்களைப் பற்றி ஐய்யா (திருத்திக் கொண்டு அதாவது வெற்றியை நோக்கி, தங்களின் எழுச்சி எஜமானே (இது அடிக்கடிக் கேட்கப்பட்ட கதை என்பது தெளிவாகிறது)
வெஸ்டன் : அரை நாள் விடுமுறைக்காக நீ அசாதாரணமாக வேண்டிக் கொண்டதைப் பற்றி நாம் பேசிக் கொண்டு
இருந்தோம். சென்ற மாதம் நீ ஒரே ஒரு நாள் மட்டும் விடுமுறை எடுத்திருந்தாய். உன்னுடைய இந்த புதிய கோரிக்கையை, பொருளற்ற ஓய்வை கேட்க, நான் விசாரிக்க இருந்ததால் அது உனக்கு சகஜமான சிரமம்தானே?
ரோஜர் : உங்களுக்கு ஒருவேளை இந்தப் பிற்பகலில் என்னுடைய தேவை இல்லாமல் இருந்தால், நான் விருது வழங்கும் குழுவின் எழுத்தாளரை நேரடியாகச் சந்தித்து அவன் ஏன் அந்த ஆவணத்தை அனுப்பவில்லை என்று கண்டறியலாம்.
வெஸ்டன் : (சிறிதளவு வியப்படைந்தவராக) ஓ….. ஓ நிச்சயமாக.
ரோஜர் : அது இல்லாத குறைதான் மெதுவாக வேலை நடக்கிறது. அது என்னுடைய வேலையை நிறுத்தி வைக்கிறது. பாருங்கள், இந்த மிகவும் சுவாரசியமான தருணத்தில், (ஆசையுடன் அவர் பார்வை அவர் மேஜையை நோக்கிச் செல்கின்றது)
வெஸ்டன் : அது நிச்சயமாக ஒரு வேறுபட்ட விசயம். காலநிலை நன்றாக இருந்தால் நீ திரு. கிளே வீட்டிற்கு இந்தப் பிற்பகலில் நடந்து செல்லக் கூடாது என்பதில் நான் காரணம் காணவில்லை .
உயர்ந்து வரும் ஒரு இளைஞனாக உன்னுடைய சிந்தனைகள் முக்கிய விஷயங்களில் செல்வதைக் கண்டு நான் மிகவும் விலகியுள்ளேன். புத்திக்கூர்மை, ஊக்கம், விளக்கத்தில் கவனம் இந்த மூன்றும் உனக்குத் தேவை. முறையான மனமின்றி இன்றி எந்த மனிதனும் நம்பிக்கை கொள்ள முடியாது.
(ரோஜர் தம் பணியைச் செய்யத் திரும்பப் போகிறார்) கற்றறிந்த எந்த தொழிலையும் திறம்படச் செய்வதற்கு ……. (அவர் நசுக்கப்பட்ட ஒரு காகிதத்துண்டை தன்னுடைய சட்டைப் பையில் காண்கிறார். அதை மென்மையாக வெளியே எடுக்கின்றார். விருப்பம் இல்லாமல் அதை சாதாரண தாளாக வைக்கிறார்).
விளக்கம், என் அன்புள்ள ரோஜர் விளக்கத்திற்கு கவனம் அதுதான், உயர்வின் தொடக்கம். அது….. சிறிது கஷ்டத்துடன் அந்த காகிதத்துண்டில் என்ன எழுதியிருக்கின்றது என்பதை தானே படிக்கின்றார். (சீஸரை நினைவுகொள்) தெளிவற்ற உற்சாகத்தோடு மீண்டும் படிக்கிறார்.
ஏதோ இழந்தவரைப் போல அந்தத்தாளை முன்னும் பின்னுமாகத் திருப்பிப் பார்க்கின்றார். அதன்பின் ஒரு பயங்கரமான கருத்து அவருக்குத் தோன்றுகிறது. ரோஜரை நோக்கி, இன்று என்ன தேதி? (மீண்டும் ரோஜர் தன்னுடைய பணியில் மூழ்கி இருக்கிறார். பதில் அளிக்கவில்லை ) ரோஜர்,,,,, நான் கேட்டேன் இது மாதத்தின் எந்த நாள்?
ரோஜர் : (சிரமத்துடன் இடைவெளி விட்டு இது 15வது நாள் எஜமானரே.
வெஸ்டன் : 15வது? மார் இன் 15 வது நாள் “இட்ஸ் ஆஃப் மார்ச் (மீண்டும் காகிதத்தாளை பார்த்துக் கொண்டு பயங்கரமான தாழ்ந்த குரலில்) சீஸரை நினைவுகொள் (உரத்தக்குரலில்) ஆஹா அவர்கள் என்னைக் கொல்ல நினைக்கிறார்கள்? அவர்கள் என்னை கொல்ல நினைக்கிறார்கள்? (ரோஜர் வியப்புடன் அந்த இடத்திற்கு வருகிறார்.
மக்களுக்கு நீதிபதியாக இருந்தாலே இப்படிதான். (அவருடைய பெருமை கிளர்ச்சியில் கரைந்து விடுகிறது) நீதியின் ஒரு கருவியாக இருந்தாலே இப்படித்தான். விரைவிலோ, தாமதமாகவோ, தெருக்களில் பழி தீர்த்தல் கிடக்கிறது. ஒரு நீதிபதி, நீதிபதியாக இருக்க அதிக அளவு அச்சமற்றவராக இருக்க வேண்டும். (வியப்பில் ஆழ்ந்த ரோஜரின் முகத்தில் அந்த காகிதத் துண்டை வீசுகிறார்) அந்த அளவுக்கு வெறுப்பு நிலவுகிறது.
ரோஜர் : பிரபுவே இது என்ன? இது என்ன?
![]()
வெஸ்டன் : நான் கவனத்துடன் இல்லாவிட்டால், (இது ஒரு மரணதண்டனை நிறைவேற்றும் ஆணை. நாம் எந்த வழக்குகளைப் பெற்று இருந்தோம்? தேசத்துரோக வழக்கில் கையூட்டுப் பெற நான் மறுத்துவிட்டேன். (இந்த தற்பெருமை அவருக்கு ஆறுதல் அளிக்கிறது) கடற்கொள்ளையர் இரு தரப்பினரும் என்னை வெறுக்கின்றார்கள் அல்லது அந்த பாதசாரி கொள்ளைக்காரனா.
ரோஜர் : இந்த காகிதத்தாள் ஓர் அச்சுறுத்தலா? எங்கே இருந்து இது வந்தது?
வெஸ்டன் : இது என் கோட் பையில் இருந்தது. யாரோ இதை… ஆம், இப்பொழுது நான் நினைத்துப் பார்க்கிறேன். நேற்று நான் நீதிமன்றத்தை விட்டு வரும்போது ஒரு மனிதன் என்னை உரசிக் கொண்டு போனான். அவன் குள்ளமான, தீயபார்வை கொண்ட மிகவும் அச்சமூட்டுபவன்.
ரோஜர் : இந்த காகிதத்தாள் என்ன சொல்கிறது?
வெஸ்டன் : (தன்னுடைய செயலாளரின் ஆவலைக் கவனித்த வகையில் தன்னுடைய தலைவிதியைப் பற்றிய நினைவில் மூழ்கியவராக) இது கதவின் சற்று அருகில் நடந்தது. மன்னிப்புக் கோருவதற்காக அவன் காத்திருக்கவில்லை. எனக்கு நினைவு இருக்கின்றது. நன்று. அவர்களின் எச்சரிக்கைக்காக, நான் நன்றி மட்டும் செலுத்த முடியும். என்னால் உதவி செய்ய முடியுமானால் நான் என்னுடைய காலத்திற்கு முன்னதாகவே இறந்து விடலாம்.
ஆனால், இன்று இல்லை. உடனே கீழே செல். எல்லாக் கதவுகளையும் பூட்டி விடு. தாழ் போட்டு விடு. சங்கிலி போட்டு விடு மற்றும் என் மனைவியை உடனே என்னிடம் வருமாறு சொல். உடனே. நில் வீட்டில் அறிமுகமற்றவர்கள் யாராவது இருக்கிறார்களா? வேலை ஆட்கள் அல்லது அத்தகையவர்கள்?
ரோஜர் : தோட்டக்காரன் ஜோயல் மட்டும்தான் பிரபுவே. அவன் கீழ் தளத்தில் ஜன்னல்களை சுத்தம் செய்து கொண்டு இருக்கிறான். (ஜோயல் சற்றுமுன் வெளியே போகிறான் என்று தன் தலையால் சுட்டிக் காட்டுகிறான்)
வெஸ்டன் : உடனே அவனை வெளியே அனுப்பி விடு. அவனிடம் ஒவ்வொன்றையும் விட்டுச் செல்ல சொல்லிவிடு போ. அவன் வெளியே போனவுடன் கதவைப் பூட்டி விடு. ஜன்னல்களும் மூடி இருப்பதை பார்த்துக் கொள்.
கொலைகாரன் இருப்பதாக நினைத்துக் கொண்டு…..
வெஸ்டன் : (துப்பாக்கி ஏந்தியவாறு அலமாரியை நோக்கி வெளியே வா. நான் சொல்கிறேன் வெளியே வா! (நிசப்தம்) உன் ஆயுதத்தைக் கீழே போடு. வெளியே வா. இல்லாவிடில் இப்பொழுது நான் உன்னை சுட்டு விடுவேன்.
(இன்னும் நிசப்தம் நிலவுவதால் தானாகவே அலமாரியின் கதவுக்கு அருகில் செல்கின்றார். அது காலியாக உள்ளது. நிம்மதி கிடைத்தவுடன் வெட்கப்படுகிறார். அவசரமாக துப்பாக்கியை மேஜை டிராயரில் திரும்பப் போடுகிறார்).
![]()
மகிழ்ச்சியான மற்றும் குறிக்கோளுடன் கூடிய திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் பிரவேசிக்கின்றார். ஒரு கவர்ச்சி மிக்க படைப்பு. அவர் ஒரு மிகச்சிறந்த இல்லத்தரசி என்பதை ஒரே பார்வையில் ஒருவர் அறிந்து கொள்ளலாம். அவர் எந்த அளவு புத்திசாலி என்பதையும் அவருடைய செயல்ரீதியான எளிமை, அவருடைய இனிமையான தீய எண்ணத்திற்கு பின்னால் அமைந்திருப்பதை யாரும் உறுதியாகச் சொல்ல முடியாது.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : (உள்ளே வரும் போதே பின்னால் பார்த்துக் கொண்டு, தோட்டக்காரன் ஜோயல் கீழ் தளத்தில் தண்ணீர் பாத்திரங்களை விட்டுச் செல்லக் கூடாது என்று நான் விரும்புகின்றேன்! என்ன இது. ரிச்சர்ட்?
வெஸ்டன் : என் அன்புக்குரியவளே. உன் கணவனின் உயிர் மிக்க ஆபத்தில் உள்ளது.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : சென்ற முறை வேட்டையாடப்பட்ட மாமிசத்துண்டை நீங்கள் சாப்பிட்டுக் கொண்டு இருக்கும் போது ஆபத்தில் இருந்தீர்கள். இந்த முறை என்ன?
வெஸ்டன் : (அவளுடைய கேலிப்பேச்சை அறியாதவராக) ஒரு கொலை!
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : நன்று. நன்று! நீங்கள் எப்பொழுதும் ஒரு பெரிய மனிதராக வர விரும்பினீர்கள். இப்பொழுது உங்கள் விருப்பத்தை பெற்று இருக்கிறீர்கள். ஏதோ ஒரு கொலை வழக்கு நினைத்துக் கொண்டு பேசுகிறாள்).
வெஸ்டன் : நீ என்ன கருதுகிறாய்?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : அவர்கள் யாரையும் கொலை செய்யவில்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : (காகிதத்தாளை அவளுக்குக் காட்டியவாறு அதைப்படி. உன்னால் சிரிக்க முடிந்தால் பார்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : நான் சிரித்துக் கொண்டு இருக்கவில்லை. (படிக்க முயற்சித்தவாறு எவ்வளவு பயங்கரமான கிறுக்கல்.
வெஸ்டன் : ஆமாம், ஒரு மூர்க்கனின் நச்சு நிறைந்த கிறுக்கல்கள்.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : (புரிந்துகொண்டவாறு “சீஸரை நினைவுகொள்“ இது ஒரு புதிரா?
வெஸ்டன் : இது ஒரு மரண அழைப்பு. இன்று என்ன நாள் என்று உனக்குத் தெரியுமா?
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : வியாழக்கிழமை
வெஸ்டன் : மாதத்தின் என்ன நாள்?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : அநேகமாக 12. நான் யூகிக்கின்றேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : (பொருள்பட) இது பதினைந்து மார்ச்.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : கடவுள் இரக்கம் காட்டுவாராக. உங்கள் அன்புச் சகோதரியின் பிறந்த நாள். நாம் அவளுக்கு தேவையான குவளைமலர்களைக் கூட பரிசாக அனுப்பவில்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : நான் முன்பே கைவிட்டு விட்டேன். பிரான்ஸிஸ். உன்னுடைய உள்ளத்தில் தீர்க்கமுடியாத வியாதி அது. மார்ச் 15 அன்று சீஸர் சட்டமன்றத்தில் கொல்லப்பட்டார்.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : ஆமாம். நிச்சயமாக எனக்கு நினைவு இருக்கிறது. அவர்கள் சீஸரின் புகழுக்கு நிகராக நிற்க முடியவில்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : (நிரூபித்க் காட்டியவாறு அவர் ஒரு மாபெரும் மனிதராக இருந்தார்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (இரக்கத்துடன்) ஆம் என் அன்புமிக்கவரே. நிச்சயமாக அவர் இருந்தார். (மீண்டும் அந்த காகிதத் துண்டைப் பார்த்தவாறு) யாரோ ஒருவர் உங்களைக் கொலை செய்ய நினைத்துக் கொண்டு இருக்கிறாரா?
வெஸ்டன் : தெள்ளத் தெளிவாக.
![]()
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : நீண்ட நாட்களுக்கு முன்னதாகவே யாரும் இதை செய்யவில்லை என்று ஆச்சர்யப்படுகிறேன். (அவர் கண்ணில் வியப்பு நிறைந்த பார்வை ஏற்படும் முன்) பெரும்பாலான மக்கள் நீதிபதிகளை வெறுக்க வேண்டும். நீங்கள் ஒரு கண்டிப்பான நீதிபதி என்று அவர்கள் சொல்கின்றார்கள்.
வெஸ்டன் : கண்டிப்பாக இருப்பது சட்டம்தான். நான் ஒரு நீதிபதி. அன்புள்ள பிரான்ஸிஸ், வித்தைக்காரன் இல்லை. மக்கள் கூட்டத்தை மகிழ்விக்க நான் சட்டத்தை திரித்துக் கூறவில்லை. அவர்கள் விருப்பப்படும் நாளன்று இறந்து நான் அவர்களை மகிழ்விக்க மாட்டேன்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : இல்லை, நிச்சயமாகவே இல்லை. இன்று நீங்கள் வீட்டைவிட்டு வெளியே போகமாட்டீர்கள். அழகிய லேசான விருந்து மற்றும் ஒரு டம்ளர்….
வெஸ்டன் : நான் எல்லாக் கதவுகளையும் வழியையும் அடைத்து தடைசெய்ய ரோஜர்-ஐ அனுப்பியுள்ளேன். தரைதளத்தையும் மூடுவது புத்திசாலிதனம் என்று நான் நினைக்கின்றேன். அவைகள் யாருக்காகவும், திறக்கப்படாமல் இருக்கப் பார்த்துக் கொள்ள வேண்டும்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : பிரெஞ்சுக்காரர்களையும். டச்சுக்காரர்களையும் ஒரு சேர நீங்கள் எதிர்பார்த்துக் கொண்டு இருக்கிறீர்களா? இது காலை நேரம். திரு. காம்மென்ஸ்-ஸின் பையன் மளிகைப் பொருட்கள் கொண்டு வருவான். நான் எப்படி வாங்குவது)…..
வெஸ்டன் : உனக்கு, உன் கணவனின் உயிரைவிட சிறிதளவு மிளகு பெரியதா, அன்பே?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : இது சிறிதளவு மிளகு அல்ல. பெருமளவு மாவு. ரொட்டி பற்றாக்குறையாகிவிட்டால், குழம்பு தண்ணீர் மாதிரி இருந்தால் நீங்கள்தான் குறை கூறுவீர்கள். (காகிகத் துண்டை அவரிடம் திரும்பக் கொடுத்து இந்த சிறிய காகிதத் துண்டு உங்களைத்தான் குறிக்கின்றது என எப்படி தெரியும்?
வெஸ்டன் : ஏனெனில் அது என் பாக்கெட்டில் இருந்தது. என் புகைக்குழாயைப் பற்ற வைக்க ஏதோ ஒன்றைப் பார்த்துக் கொண்டிருக்கும்போது இதை நான் கண்டேன். (பொருள்பட) அங்கே (பையில்) ஓட்டைகள் இல்லை.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : ஓட்டைகள் இல்லையா. பின்னே என்ன மறுபடியும்? ரிச்சர்ட் நீங்கள் அளவுக்கு மீறி புகைக்கிறீர்கள்.
வெஸ்டன் : (அவசரமாகத் தொடர்ந்து) நேற்று என்னை உரசிக் கொண்டு போன மனிதனால் இது என் பாக்கெட்டில் நழுவவிடப்பட்டது. ஒரு கருத்த ஒல்லியான கெட்ட முகமுடைய மனிதன்.
![]()
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : அவன் மிகவும் தீமையானவன் என்று நான் கருதவில்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : இதைப்பற்றி உனக்கு என்ன தெரியும்! (ஒரு நாற்காலியில் சாய்ந்தவாறு நிறுத்து பிரான்ஸிஸ் நிறுத்து! இது என்னை மனம் உடையச் செய்கிறது….. (வீட்டைச் சுற்றி ஓடோடிப் பார்த்தப்பின் ரோஜர் பிரவேசிக்கிறார்).
வெஸ்டன் : ஹாய் ரோஜர்! நீ எல்லாவற்றையும் பார்த்து விட்டாயா? ஒவ்வொரு கதவும் பூட்டப்பட்டதா? ஒவ்வொரு ஜன்னலும் பூட்டப்பட்டதா? பணியாளர் எல்லாம் வெளியேறிவிட்டார்களா?
ரோஜர் : (சற்று சஞ்சலப்பட்டவனாக) எல்லா கதவுகளும், சமையலறை கதவு ஒன்றைத் தவிர. பிரபுவே!
வெஸ்டன் : (கோபத்துடன்) ஏன் சமையலறை ஒன்று மட்டும் பூட்டவில்லை?
ரோஜர் : (உளறிக்கொண்டு சமையல்காரி நினைக்கிறாள்…. அதாவது…. அவள் சொன்னாள்.
வெஸ்டன் : சரி. பேசு, அவள் என்ன சொன்னாள். சமையலறைக் கதவை நான் பூட்டச்சொன்னதைப் பற்றி அவள் என்ன நினைக்கிறாள்?
ரோஜர் : (வேகத்துடன்) தான் ஒரு மரியாதைக்குரிய பெண் என்றும் தன் வாழ்நாளில் தாழிடுவதில்லை என்றும், தன் வயதில் (தவறு செய்ய துவங்க வில்லையென்றும்) சமையலறைக் கதவு பக்கம் யார் வந்தாலும் சமாளிக்க முடியும் என்று அவள் சொன்னாள்.
வெஸ்டன் : அவளை தன் பொருட்களைக் கட்டிக் கொண்டு வீட்டைவிட்டு உடனே வெளியேறச் சொல்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : உங்கள் அபிமான உணவுகளை யார் சமைப்பது? நீங்கள் சொன்னபடி எல்லாக் கதவுகளும் மூடப்படுவதை நான் பார்க்கிறேன். எப்பொழுதும் நாம் மேல் ஜன்னல் வழியாக (ஒரு வேளை மளிகை சாமான்கள் கொண்டு வரப்பட்டால்) மளிகைச் சாமான்களை இழுக்க முடியும்.
வெஸ்டன் : (தம்மைத்தாமே கட்டுப் படுத்திக்கொண்டு ஆவல் மிகுந்த இந்த நேரத்தில் இத்தகைய கீழ்த்தரமான யோசனை ஏற்றதல்ல. பிரான்ஸிஸ். நீ மோசமானவள்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : உங்களுக்கு இது கீழ்த்தரமானதாகத் தோன்றவில்லையா? என்ன விசித்திரம்? (கதவுகளை) சுவர்களை மூடி மேற்கூரை வழியாக அனுமதிப்பது புதுமையானது என நான் நினைத்தேன். எப்படியோ! (அவள் மீண்டும் அறைக்குள் வருகிறாள். அறையின் வெவ்வேறு இடங்களிலிருந்து இரண்டு மெழுகுவர்த்தித் தாங்கிகளை எடுக்கிறாள் கதவு பக்கம் போகிறாள்).
![]()
வெஸ்டன் : இவற்றால் நீ என்ன செய்ய விரும்புகிறாய்?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : தரைத்தளத்தில் இருளில் மூழ்கி கிடப்போமானால் நாம் எல்லா மெழுகுவர்த்திகளையும் சேகரிக்க
விரும்புவோம் வெளியேறுதல்).
வெஸ்டன் : பெண்களின் புத்தி தொடர்பற்ற கருதப்படாத செயல்களில் ஈடுபடுவது எனக்கு முடிவற்ற வியப்பாக தோன்றுகிறது. (தான் என்ன செய்கிறோம் என்பதைக் கவனிக்காமல் தீமாடத்தின் பக்கம் நகர்கின்றார்.
புகைக்கூண்டில் தலையை ஒட்டி வைத்து அதன் அகலத்தை பார்ப்பதைப் போல இருக்கிறார். தலையை திரும்ப எடுத்தவாறு ரோஜர் நின்று கொண்டு கவனிப்பதை அறிகிறார்) நீ உன் வேலையை மறுபடியும் தொடராமலிருக்க, எந்த காரணத்தையும் நான் காணவில்லை, ரோஜர்.
ரோஜர் : எஜமானரே, நீங்கள் ஆபத்தில் சிக்கி இருக்கும்போது, வேலை செய்வது என் அதிகாரத்துக்கு அப்பாற்பட்டது. என்னால் செய்ய முடிந்த எதுவும் இல்லையா?
வெஸ்டன் : (மிகவும் முகஸ்துதி செய்யப்பட்டவராக) முட்டாள். என் அன்பு ரோஜர், முட்டாள். எனக்கு எதுவும் நடக்கப் போவதில்லை.
ரோஜர் : ஒருவேளை நான் சென்று அதிகாரிகளை தடுத்து எச்சரிக்கிறேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : (மிகவும் வீரமாக) இல்லை , இல்லை, இல்லை. என் காலடியில் ஒரு பாதுகாவலரை வைத்து என் மீதி வாழ்க்கையை கழிக்க வேண்டுமா? உன் வேலையைத் தொடர்ந்து செய் மற்றும் ….. (அவர் கண்கள், வலதுபுறச் சுவரில் ஒரு நாற்காலியில் கிடக்கும் பார்சலைப் பார்த்து, ஒளிர்கின்றன. சுமார் 18 ஓ 10 ஒ 4 அங்குல அளவுள்ள கன செவ்வகப் பெட்டி அது. ஒரு மெல்லிய கயிற்றால் கட்டப்பட்டுள்ளது. தீவிரமாக) என்ன இது?
ரோஜர் : இன்று காலை அது உங்களுக்காக வந்தது ஐயா,
வெஸ்டன் : என்ன அது?
ரோஜர் : (தன் குரலில் லேசான துவக்கச் சந்தேகத்துடன்) எனக்குத் தெரியாது, பிரபு. இதை எடுத்துக்
கொண்டு வந்தவர் இன்று இதை பெறுவது உங்களுக்கு மிகவும் முக்கியம் என்று சொன்னார்.
வெஸ்டன் : நீ அது என்னவென்று கேட்கவில்லையா, முட்டாள்.
![]()
ரோஜர் : (பணிவுடன்) அது என்னுடைய வேலையாக எனக்குத் தோன்றவில்லை. நான் ஒரு போதும் தங்களுடைய விசயத்தைப் பற்றி கேட்பதில்லை. தங்களுக்கு இந்த பார்சலை காட்டிவிட்டேன். இது வந்த போது அங்கேயே விட்டுவிடு என்று சொன்னீர்கள்.
வெஸ்டன் : (அந்த பொருளின் மீது, அதிகரிக்கும் அசாதாரண மனநிலையுடன் எட்டிப் பார்த்தவாறு இதைக் கொண்டு வந்தவன் என்ன விதமான மனிதன்? அவன் குட்டையாக, கருப்பு நிறமாக இருந்தானா?
ரோஜர் : (அதைப்பற்றித் தெளிவாக கவனிக்காமல் இருந்ததால்) அவன் குட்டையாக இருந்தான் என நினைக்கிறேன். ஆனால் கருப்பாக இல்லை அவன் தொப்பி முகத்தை மறைத்துவிட்டது. நான் நினைக்கிறேன், அவன் மேவாய்க் கட்டையில் ஒரு மச்சம் இருந்தது. ஆனால் நான்…. இது ஒரு ……..
வெஸ்டன் : மச்சமா? (அவர் கற்பனை வேலை செய்கிறது) ஒரு மச்சம் ஆம். ஆம். அந்த மனிதனுக்கும் ஒரு மச்சம் தாடையில் வலது புறம். அவன் இங்கே நின்று இருப்பது போல் நான் பார்க்கிறேன். நாம் இதில் இருந்து உடனே விடுபட வேண்டும்.
ரோஜர் : இது ஓர் நரக கொல்லும்) இயந்திரம் என்று நினைக்கிறீர்களா அய்யா? நாம் இதை வைத்து என்ன செய்வோம்?
வெஸ்டன் : (பக்கவாட்டு ஜன்னலைச் சுட்டிக் காட்டி ஜன்னலைத் திற, நான் இதை என்னால் முடிந்த அளவுக்கு தோட்டத்தில் தூக்கி எறிகின்றேன்.
ரோஜர் : ஆனால் அது வெடித்து விடலாம், ஐயா நாம் அதை எறிந்தோமானால்.
வெஸ்டன் : நாம் எறியாவிட்டால் அது வெடித்து விடலாம், என்பது நிச்சயம். அது எவ்வளவு நேரமாக இங்கே
இருக்கிறது?
ரோஜர் : சுமார் 9 மணிக்கு அது வந்தது, அய்யா.
வெஸ்டன் : (மன வேதனையுடன்) சுமார் மூன்று மணி நேரத்துக்கு முன். ரோஜர், ஜன்னலைத் திற
ரோஜர் : இல்லை அய்யா. நீங்கள் ஜன்னலைத் திறங்கள், நான் அதைக் கையாளுகிறேன். என் உயிர் ஒன்றுமில்லை. உங்கள் உயிர் இங்கிலாந்து நாட்டுக்கு மதிப்பு மிக்கது.
வெஸ்டன் : இல்லை. ரோஜர் இல்லை. நீ இளைஞன். நான் என் வாழ்க்கையைக் கழித்து விட்டேன். உலகில் நீ இன்னும் செய்ய வேண்டிய பெரும்பணிகள் உள்ளன. நீ வாழ வேண்டும். என் வாழ்க்கையை வருங்கால சந்ததியருக்கு எழுதிவிடு.
நான் சொல்வதைச் செய். நீ மிகுந்த கவனத்துடன் கையாள நான் வாக்குறுதி தருகின்றேன். (ரோஜர் ஜன்னல் பக்கம் விரைந்து ஓடுகிறான்) இல்லை. காத்திரு. ஒரு சிறந்த யோசனை. தோட்டக்காரனின் வாளி, அது இன்னும் படிக்கட்டில்தான் உள்ளது?
![]()
ரோஜர் : ஆம். ஆம். நிச்சயமாக (அவன் அறையை விட்டுச் செல்கிறான்) ஒரு நொடியில் திரும்ப வரும் போது, சுத்தப்படுத்தும் கந்தல் துணி தொங்கிக் கொண்டிருக்கும் தண்ணீர் நிரம்பிய மரவாளியை எடுத்துக் கொண்டு வருகிறான்.

வெஸ்டன் : பின்னால் நில். (அவர் அச்சத்துடன் பார்சலை எடுக்கின்றார்) என்ன நடக்கும் என்று நமக்கு தெரியாது. (அவர் பார்சலை நீளவசமாக பாத்திரத்தில் இடுகிறார், தம்முடைய கையை முழு நீளத்திற்குப் பயன்படுத்துகிறார். தலையைப் பின்னோக்கி வைக்கிறார். கண்களின் ஓரங்களில் இருந்து பார்க்கின்றார். போதியளவு தண்ணீர் இல்லை. அதை (பார்சலை) மறைக்கும் அளவுக்கு இல்லை.
ரோஜர் : ஒரு வினாடிக்குள் நான் கொஞ்சம் தண்ணீர் கொண்டு வருகிறேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : இல்லை போகாதே. அந்த மலர்கள் (மலர்த் தொட்டியைச் சுட்டிக்காட்டுகிறார்)
ரோஜர் : நிச்சயமாக (மலர் தொட்டியில் அமைக்கப்பட்டிருந்த டாபடில்ஸ் மலர்களை இழுத்து ஆவேசமாக மேஜையின் பக்கம் எறிகின்றார். (அதிலிருந்த தண்ணீ ரை மரத்தொட்டியில் கொட்டுகிறார்) ஆ… வேலை முடிந்துவிட்டது.
வெஸ்டன் : (ரும்பிக்கை இழந்தவரா பார்சலில் இருந்து தம்முடைய கையை எடுக்கின்றார்) இப்பொழுது அது மிதக்கத் துவங்கும். அது முழுவதும் ஈரமாகிவிடும் அல்லது பயன் இல்லாமல் போகும்.
ரோஜர் : அது உள்ளே மூழ்குவதற்கு கீழே செல்வதற்கு நாம் அதன் மீது கனமான பொருளை வைக்க வேண்டும்.
வெஸ்டன் : ஆம். ஆம். ஏதாவது ஒன்றை எடுத்து வா.
வெஸ்டன் : நான் என்ன எடுப்பேன்?
வெஸ்டன் : ஏதாவது ஒன்று, கனமான தொட்டிக்குள் பொருத்தமான புத்தகங்கள். ஏதாவது ஒன்று.
ரோஜர் : (பயம் இல்லாவிட்டால் மட்டும், இவருக்கு புத்தகங்கள் மரியாதைக்குரிய பொருள்கள்) புத்தகங்களா ஐயா? ஆனால், அவைகள் மிகவும் நினைந்துவிடுமே, இல்லையா?
வெஸ்டன் : கடவுள் பெயரைச் சொல்லி அடுக்குகளில் உள்ள முதல் 6 புத்தகங்களைக் கொண்டு வா.
![]()
ரோஜர் : (புத்தகங்களை எடுத்துக்கொண்டு வருகிறார். இது உதவி செய்யாது என்று நான் கருதுகின்றேன். இத்தகைய அழகான பைண்டிங் செய்யப்பட்டவை. (மரத்தொட்டியின் மேல் இருந்த ஈரத்துணியை எடுத்து அதை தரை விரிப்பின் மீது போட்டு புத்தகங்களை (அதில் சுற்றி மூட்டையாக்கி தண்ணீரில் போடுகிறார். இதனால் இயல்பாக தண்ணீர் மேலே வழிகின்றது.
வெஸ்டன் : தன்னுடைய கைகளை வெளியே எடுத்து நிம்மதிப் பெருமூச்சுடன் பின்னோக்கி உட்காருகின்றார். நன்றாக, உண்மையாக மூழ்கிவிட்டது. (தம் நெற்றியைத் துடைக்கின்றார் ரோஜர் அருகிலுள்ள நாற்காலியில் அமர்கின்றார்) (திருமதி வெஸ்டன் ஒரு தட்டில் மதுபானமும், சில பிஸ்கட்டுகளும் வைத்துக் கொண்டு பிரவேசிக்கின்றார்)
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : (அவர்களின் விசித்திர (செயலைக்) தொழிலைக் கண்டு ரிச்சர்ட்! இந்த தொட்டியில் நீங்கள் என்ன வைத்திருக்கிறீர்கள்?
வெஸ்டன் : இன்று காலையில் வந்த பார்சல். இதைக் கொண்டு வந்தவன்தான் நேற்று என்னை உரசிக்கொண்டு என் பாக்கெட்டில் அந்தக் காகிதத் துண்டைப் போட்டவன். முட்டாள்கள்! நான் இதை திறந்து பார்ப்பேன் என்று எண்ணி இருந்தார்கள். (இப்பொழுது அவர் நிம்மதியாக இருக்க தொடங்குகின்றார்) ஆனால், அந்த பலருக்கு, நாம் ஒருவரே போதும்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (மிகவும் நம்பிக்கை இழந்தவராக) நீங்கள் அழகிய புத்தம் புதிய ஒன்றை …… கெடுத்துவிட்டீர்கள்….
வெஸ்டன் : (ஆத்திரத்துடன் இடைமறித்து) பிரான்ஸிஸ் (இடி இடிப்பதைப் போல் அவள் பெயர் சொன்னதால் அவள் பேச்சு அணைக்கப்படுகிறது.) நீ சொன்ன புத்தகம் என்ன புதிய பொருள். உன்னுடைய கணவனின் உயிர் ஆபத்தில் இருக்கும் போது தரைவிரிப்பு ஒரு பொருட்டா? நீ எனக்கு அதிர்ச்சி ஊட்டுகின்றாய்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (தரைவிரிப்பை பற்றி அவள் சொல்லவில்லை தரை விரிப்பா? (இடைவெளிக்குப் பின் நிதானமாக)
இல்லை. நிச்சயமாக இல்லை. நான் உங்கள் பாதுகாப்புக்கு எதிராக, ஆசியாவிலேயே மிக்க அழகிய எந்த ஒரு பொருளையும் எடைபோட கனவில் கூட நினைக்கவில்லை. உங்களுக்குத் தெரியும். நீங்கள் இப்படி இருப்பதை டாக்டர் ஏற்றுக் கொள்ளமாட்டார்.
வெஸ்டன் : ஒரு வேளை, வசந்தகால காலை நேரத்தில் டாக்டர் தன் கதவின் அருகே நரக எந்திரத்தை வைத்திருக்கமாட்டார்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (நிதானத்துடன் ஜன்னலுக்கு எதிராக தொங்கிய உருவப்படத்தின் மீது தன் கண்களைச் செலுத்தினார்) எங்கள் மூத்த அத்தை சிசிலியின் உருவப்படத்தை அகற்றுவது சிறந்தது என்று நீங்கள் நினைக்கிறீர்களா?
வெஸ்டன் : கடவுள் பெயரால், ஏன்?
![]()
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : ஜன்னல் வழியாக சுடப்படும் போது அவள் உருவப்படம் நேர்க்கோட்டில் அமைகிறது.
வெஸ்டன் : ஜன்னல் வழியாக ஏன் யாரும் சுட வேண்டும், நான் கேட்கலாமா?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (நிதானமாக அந்த குரலை ஆட்சேபனை செய்பவராக) நான் உங்கள் உடைமைகளை பற்றி சிந்தித்துக் கொண்டு இருந்தேன். என் அன்புமிக்க ரிச்சர்ட், யாராவது ஒருவர் அந்த அய்லெக்ஸ் மரத்தில் உட்கார்ந்து கொண்டு……
வெஸ்டன் : ஓடி வந்து) பிரான்ஸிஸ்! அய்லெக்ஸ் மரத்தைப் பற்றிச் சிந்திக்க உன்னைத் தூண்டியது எது?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : நான் அங்கே இருந்துதான் உங்களைச் சுட்டு இருப்பேன். அதாவது நான் உங்களை சுடப்போனால் அந்த மரத்தின் இலைகள் ஒருவரை மறைப்பதற்கு போதிய அளவு அடர்த்தியாக உள்ளன. இருப்பினும் அவர்களின் பார்வையை மறைக்க போதுமானது இல்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : அந்த ஜன்னலை விட்டு வந்து விடு.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : என்ன?
வெஸ்டன் : அந்த ஜன்னலிலிருந்து தூரமாக வா.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : (அவர் பக்கம் நகர்ந்து) என்னை யாரும் சுடப் போவதில்லை.
வெஸ்டன் : (அறைக்கு வெளியே ஓடி வந்து தரை தளத்திலிருந்து வரும் ரோஜரை அழைத்தவராக) ரோஜர்! ரோஜர்!
ரோஜர் : (வெகு தொலைவிலிருந்து) என் பிரபுவே?
வெஸ்டன் : தோட்டக்காரன் போய் விட்டானா?
ரோஜர் : இல்லை பிரபுவே. சமையலறை ஜன்னலுக்கு வெளியே சாப்பிட்டுக் கொண்டு இருக்கிறான்.
வெஸ்டன் : நான் சொல்லும் வரை அவனை அய்லெக்ஸ் மரத்தின் அடியில் உட்காரச் சொல்.
ரோஜர் : அய்லெக்ஸ் மரமா? சரி பிரபுவே. (வெஸ்டன் திரும்ப வந்து தன்னுடைய கைத்துப்பாக்கி வைத்திருந்த மேஜை டிராயர் பக்கம் போகின்றார்)
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : (அவர் கைத்துப்பாக்கியை வெளியே எடுக்கும்போது) அன்புள்ள ரிச்சர்ட், கவனமாக இருங்கள்.
அது மிகவும் ஆபத்தான ஆயுதம்.
வெஸ்டன் : அது மிகவும் ஆபத்தான ஆயுதம்.
வெஸ்டன் : (கம்பீரமாக) எனக்குத் தெரியும்
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : சரி, கொலைகாரனை முறியடிக்க இது ஒரு மோசமான வழி என்று நான் நினைக்கிறேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : எது?
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : ஒருவர் தம்மையே தாக்குவது. (டாபடில்ஸ் மலர்களின் கோப்பையை எடுத்துக் கொண்டு ரோஜர்
பிரவேசிக்கிறார்)
வெஸ்டன் : (அவர் உள்ளே வரும் போது அவரைச் சுற்றிப் பார்க்கின்றார்) ஜோயல் மரத்தின் அடியில் உட்கார
போய்விட்டானா?
![]()
ரோஜர் : ஆம், ஐயா, (மலர்க் கோப்பையை வைத்து விட்டு, பக்கவாட்டு ஜன்னலின் பக்கம் போகிறார்) நான் உங்கள் செய்தியை அவனுக்குச் சொல்லிவிட்டேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : அந்த ஜன்னலில் இருந்து விலகி நில். (ரோஜர் வியப்புடன் பார்க்க) அய்கெல்ஸ் மரத்தில் யாராவது
இருக்கலாம்.
ரோஜர் : ஆனால் அவர்கள் உங்களைச் சுடுவதற்கு முயற்சிப்பார்கள் என்று நீங்கள் நினைக்கின்றீர்களா. அத்துடன்……. (அவர் வாளியை சுட்டிக்காட்டுகிறார்)
வெஸ்டன் : யாருக்குத் தெரியும்? நீ ஒரு குற்றவாளி மனதுடன் இதைக் கையாளும் போது, நான் சொல்லும் வரையில் …. நீ தோட்டக்காரனிடம் பேசுவதற்கு கதவைத் திறந்தாயா?
ரோஜர் : இல்லை பிரபுவே. நான் ஷட்டர் வழியே பேசினேன்.
வெஸ்டன் : (கைத்துப்பாக்கியின் லாக்-கைத் தொட்டுக் கொண்டு இப்பொழுது மரத்தில் யாராவது இருக்கிறார்களா என்பதைப்பார்க்கப்போகிறோம். (ஜன்னல் பக்கம் நகர்கின்றனர், ஓரக்கண்ணால் எட்டிப்பார்க்கிறார்)
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : ரிச்சர்ட், அதை நீங்கள் சுடப்போனீர்களானால் தயவு செய்து நான் சொல்லும் வரையில் காத்திருங்கள். (கீழ் தளத்திலுள்ள முன் பக்க கதவிலிருந்து வேகமாக கதவு தட்டும் ஒசையால் அவள் பேசுவது இடைமறிக்கப்பட்டது. அங்கே உள்ள அனைவரும் முற்றிலும் தப்பித்துவிடும் அளவுக்கு எதிர்பாராத நிகழ்ச்சி. ரோஜர் முதலாவதாக அதிர்ச்சியில் இருந்து மீளுகின்றார்)
ரோஜர் : முன்கதவுப் பக்கம் யாரோ இருக்கிறார்கள். தெருவின் பக்கம் பார்க்க, வசதியாக பின்புறச் சுவரில் ஜன்னல் பக்கம் நகர்கின்றனர். கதவை திறக்கப் போகிறார். வெஸ்டன் பிரபு அவரைத் தடுக்கின்றார்)
வெஸ்டன் : (இன்னும் தீமாடத்தின் அருகே) அந்த ஜன்னலை திறக்காதே.
ரோஜர் : ஆனால் ஜன்னலைத் திறக்காவிட்டால் அங்கே யார் என்பதை எப்படிப் பார்க்க முடியும். வெஸ்டன் : நீ உன் தலையை அந்த ஜன்னலின் வழியே நீட்டினால், கேள்வி கேட்பதற்கு காத்து இருக்காமல்
அவர்கள் உன்னைச் சுட்டு விடுவார்கள்.
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : ஆனால், ரிச்சர்ட் அது முற்றிலும் குற்றமற்ற பார்வையாளராக இருக்கலாம். (கதவு தட்டப்படுவது
மீண்டும் கேட்கிறது)
ரோஜர் : நான் ஒரு நாற்காலியின் மீது நின்று கொண்டு இருந்தால்…. (அவர் ஜன்னலின் பக்கம் ஒரு நாற்காலியைக் கொண்டு வருகிறார் மற்றும் அதன் மீது நிற்கின்றார். ஆனால் முன் கதவருகில் காத்திருப்பது யார் என்பதைப் பார்ப்பதற்கு அவர் போதிய அளவு உயரமானவர் இல்லை)
வெஸ்டன் : நன்று! நன்று! அது யார் என்பதை உன்னால் சொல்ல முடியுமா?
ரோஜர் : நான் போதிய அளவு உயரமானவன் இல்லை பிரபுவே.
![]()
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : ஒரு ஸ்டூல் சேர்த்துக் கொள் ரோஜர். (ரோஜர் நாற்காலியின் மீது ஸ்டூல் சேர்க்கின்றார். அந்த
ஆபத்தான கட்டமைப்பில் ஏறுவதற்கு திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் உதவி செய்கின்றாள்).
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : இப்பொழுது நீ யாரையாவது பார்க்க முடிகின்றதா?
ரோஜர் : (பார்த்துவிட்டு, பிறகு கீழே இறங்கி வந்து) எல்லாம் நன்மைக்கே பிரபுவே. (மாடிப்படி கதவைத் திறந்து கீழே உள்ள ஒருவரை அழைக்கின்றார்) அது திருவாளர். சீஸர் (இந்தத் தகவல் ஒரு இடைவெளியால் தொடரப்படுகிறது?) அவரை நான் உள்ளே அனுமதிக்கலாமா?
வெஸ்டன் : உனக்கு யார் சொன்னது?
ரோஜர் : திரு. சீஸர், உங்களுக்கு நினைவு இருக்கிறதா, செவ்வாய்கிழமை ஹாம்ப்டனில் உங்களைச் சந்தித்தவர், பிரபு. ரோஜாச் செடிகளைப் பற்றி இன்று காலை உங்களைப் பார்க்க அவர் Mவரவேண்டி இருந்தது. நீங்கள் அதை குறிப்பு எடுத்துக் கொண்டீர்கள்.
வெஸ்டன் : (மயக்கமுற்று தன் பாக்கெட்டில் இருந்த நசுங்கிய காகிதத் துண்டை எடுத்து நான் குறிப்பு எடுத்தேனா? “சீஸரை நினைவுகொள்” இது என்னுடைய கையெழுத்தா? ஆமாம். இது என்னுடைய கையெழுத்தாகத்தான் இருக்க வேண்டும்.
திருமதி, வெஸ்டன் : (தயவுடன்) இது ஒரு மூர்க்கனின் நச்சு நிறைந்த கிறுக்கல் என்று நான் சொல்லி இருக்கக் கூடாது. ரோஜர் நீ கீழே போய் திரு. சீஸரை உள்ளே அழைத்து வருவது நல்லது. ரிச்சர்ட் கைத்துப்பாக்கியை தூரத்தில் வையுங்கள்.
உங்கள் பார்வையாளர் இதை தவறாக புரிந்துக் கொள்ளலாம். ஒரு குழந்தையிடம் பேசுவதைப்போல அவள் சந்தோஷமாகப் பேசுகிறாள். அவளிடம் வியப்பு காணப்படவில்லை. ஏனென்றால் இந்த குழப்பமான ஓசைகளும், சின்னஞ்சிறு நிகழ்வுகளுக்காக அவர் கணவர் பெரும் குழப்பத்தை ஏற்படுத்துவதும் சர்வசாதாரணம்)
![]()
வெஸ்டன் : திரு. சீஸர் (அவர் வாளியின் பக்கம் நகர்கின்றார்)
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : நிச்சயமாக. இத்தகைய பெயரை யாரும் எப்படி மறக்க முடியும்? இப்போ நீங்கள் என்னை மன்னித்தால்… இது என்னுடைய பரபரப்பான காலை நேரம்.
வெஸ்டன் : (கதவிற்கு வெளியே அவள் செல்வதைத் தடுத்து) பிரான்ஸிஸ் அந்த பார்சலில் என்ன இருந்தது என்று நீ நினைக்கிறாய்?
திருமதி. வெஸ்டன் : அது உங்களுடைய புதிய வெல்வட் மேலங்கி. அன்பே, நான் சொல்வதற்கு முயன்றேன். உங்களுக்கு தெரியுமா?
(திரை கீழே இறங்குகிறது. வெஸ்டன் பிரபு தண்ணீரிலிருந்து முற்றிலும் நனைந்துவிட்ட மேலங்கியை எடுக்கிறார்)