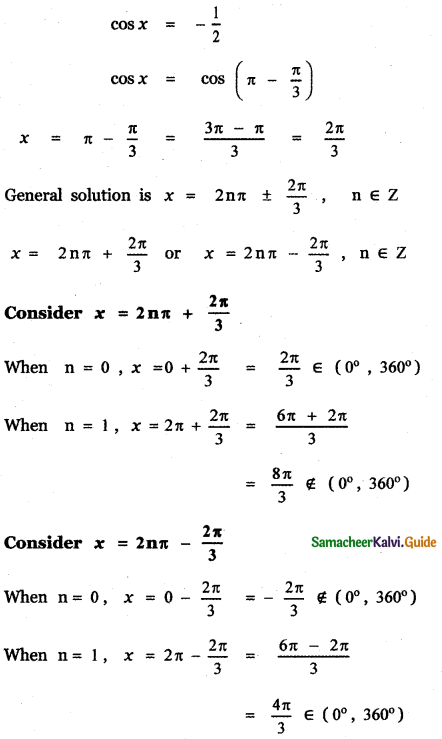
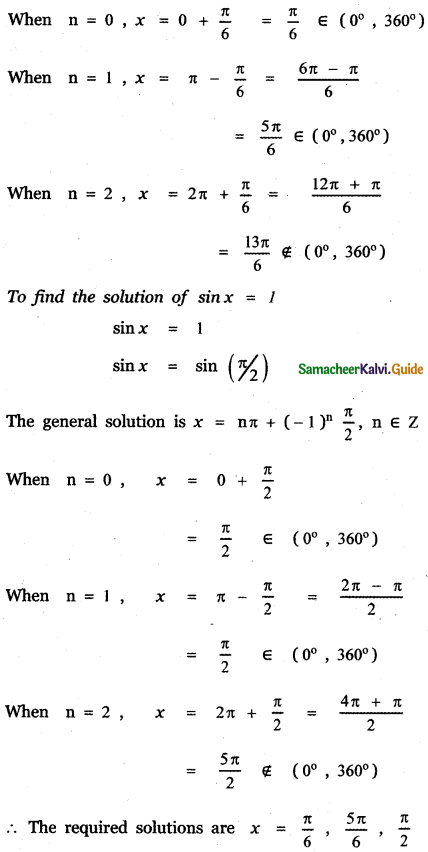
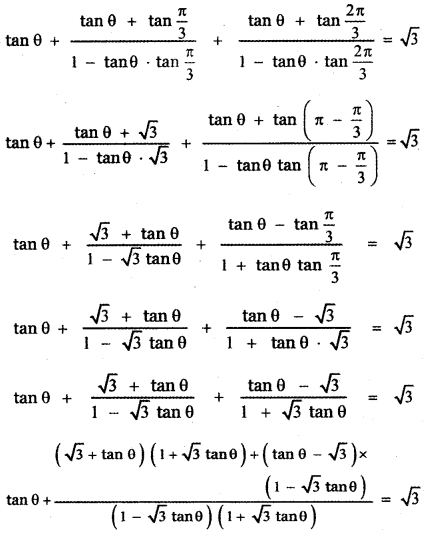
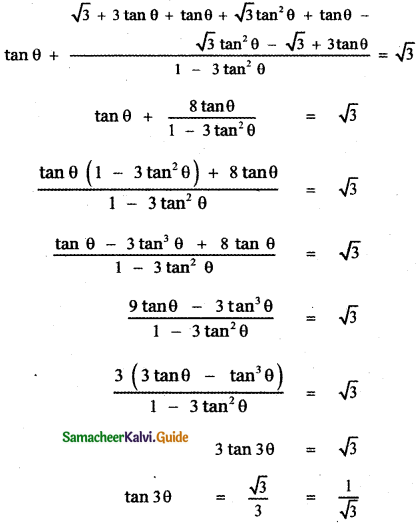
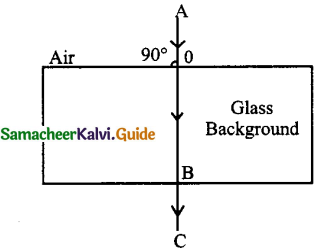
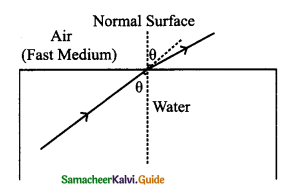
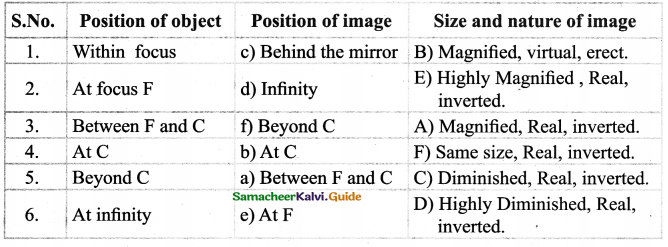
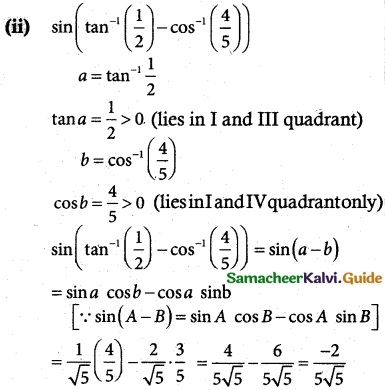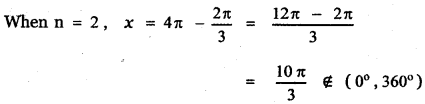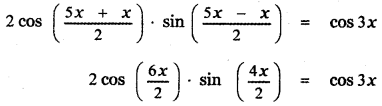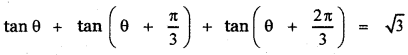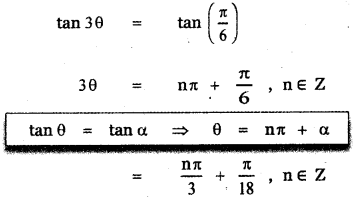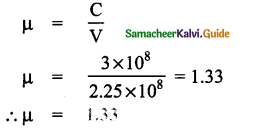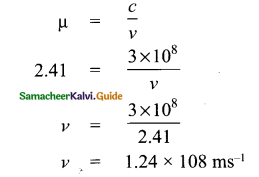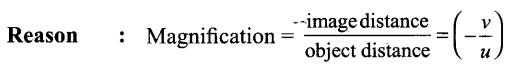Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 7 Heat Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 7 Heat
9th Science Guide Heat Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Calorie is the unit of
(a) heat
(b) work
(c) temperature
(d) food
Answer:
(a) heat
Question 2.
SI unit of temperature is
(a) fahrenheit
(b) joule
(c) Celsius
(d) kelvin
Answer:
(d) kelvin
![]()
Question 3.
Two cylindrical rods of same length have the area of cross section in the ratio 2:1. If both the rods are made up of same material, which of them conduct heat faster?
(a) Both rods
(b) Rod-2
(c) Rod-1
(d) None of them
Answer:
(c) Rod-1
Question 4.
In which mode of transfer of heat, molecules pass on heat energy to neighbouring molecules without actually moving from their positions?
(a) Radiation
(b) Conduction
(c) Convection
(d) Both B and C
Answer:
(a) Radiation
Question 5.
A device in which the loss of heat due to conduction, convection and radiation is minimized is
(a) Solar cell
(b) Solar cooker
(c) Thermometer
(d) Thermos flask
Answer:
(d) Thermos flask
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The fastest mode of heat transfer is ……………………….
Answer:
radiation
2. During day time, air blows from ……………………… to………………………
Answer:
sea to land
![]()
3. Liquids and gases are generally ……………………… conductors of heat.
Answer:
poor
4. The fixed temperature at which matter changes state from solid to liquid is called………………………
Answer:
melting point
III. Assertion and Reason type questions :
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion : Food can be cooked faster in vessels with copper bottom.
Reason : Copper is the best conductor of heat.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Question 2.
Assertion : Maximum sunlight reaches earth’s surface during the noon time.
Reason : Heat from the sun reaches earth’s surface by radiation.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Reason : When the sun is at its highest point, the earth’s surface absorbs more heat and retains. This heat is slowly radiated out causing increase in temperature.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion : When water is heated up to 100° C, there is no raise in temperature until all water gets converted into water vapour.
Reason : Boiling point of water is 10° C.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but the reason is false
Reason : When a substance changes from one state to another, a considerable amount of heat energy is absorbed or liberated. This energy is called latent heat.
IV. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Define conduction.
Answer:
The process of transfer of heat in solids from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature without the actual movement of molecules is called conduction.
Question 2.
Ice is kept in a double-walled container. Why?
Answer:
An ice-box is made of double wall and the space between the walls is filled with some non-conducting materials to provide heat insulation, so that the loss of heat can be minimized. Hence ice is kept in a double-walled container.
![]()
Question 3.
How does the water kept in an earthen pot remain cool?
Answer:
An earthen pot consists of small pores from which the water inside the pot constantly seeps out and gets evaporated due to the presence of high temperatures around it. The evaporation process requires heat which is acquired from the surface of the pot, hence making the water and the pot cooler.
Question 4.
Differentiate convection,and radiation.
Answer:
Convection
- The process of transfer of heat in which the heated molecules of a liquid (or gas) themselves move to carry heat from the hot to the cold end is called convection.
- Ex : Land and sea breeze.
- Convection need matter to be present.
![]()
Radiation
- The process of transfer of heat in which a material medium is not necessary and heat is directly transferred from the hot body to the cold body is called radiation.
- Ex : Transfer of heat energy from the sun.
- Radiation can occur even in a vacuum.
Question 5.
Why do people prefer wearing white clothes during summer?
Answer:
People prefer white or light coloured clothes during summer as they are good reflectors of heat and hence, they keep us cool.
Question 6.
What is specific heat capacity?
Answer:
Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1°C or 1 K.
Question 7.
Define thermal capacity.
Answer:
- Heat capacity or thermal capacity is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a body by 1°C. It is denoted by ‘C’.
- C = Q/t, where C’ is the heat capacity, ‘Q’ is the quantity of heat required and ‘f’ is rise in temperature.
- SI unit of heat capacity is J/K. It is also expressed in cal/°C, kcal/°C or J/°C.
Question 8.
Define specific latent heat capacity.
Answer:
Specific latent heat is the amount of heat energy absorbed or liberated by unit mass of a substance during change of state without causing any change in temperature.
![]()
V. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Explain convection in daily life.
Answer:
Convection is the flow of heat through a fluid from places of higher temperature to places of lower temperature by movement of the fluid itself.
Hot air balloons:
Air molecules at the bottom of the balloon get heated by a heat source and rise. As the warm air rises, cold air is pushed downward and it is also heated. When the hot air is trapped inside the balloon, it rises.
Breeze :
During day time, the air in contact with the land becomes hot and rises. Now the cool air over the surface of the sea replaces it. It is called sea breeze. During night time, air above the sea is warmer. As the warmer air over the surface of the sea rises, cooler air above the land moves towards the sea. It is called land breeze.
Chimneys :
Tall chimneys are kept in kitchen and industrial furnaces. As the hot gases and smoke are lighter, they rise up in the atmosphere.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the changes of state in water? Explain.
Answer:
- The process of changing of a substance from one physical state to another at a definite temperature is defined as change of state.
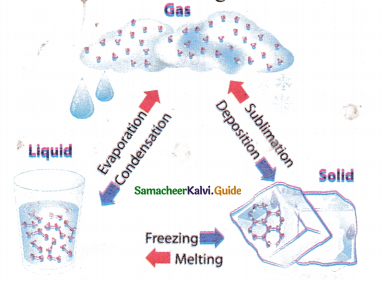
- For example, water molecules are in liquid state at normal temperature.
- When water is heated to 100°C, it becomes steam which is a gaseous state of matter. On reducing the temperature of the steam it becomes water again.
- If we reduce the temperature further to 0°C, it becomes ice which is a solid state of water. Ice on heating, becomes water again.
- Thus, water changes its state when there is a change in temperature.
- The process in which a solid is converted to liquid by absorbing heat is called melting or fusion.
- The process in which a liquid is converted to solid by releasing heat is called freezing.
- The process in which a liquid is converted to vapor by absorbing heat is called boiling or vaporization.
- The process in which a vapour is converted to liquid by releasing heat is called condensation.
- The process in which a solid is converted to gaseous state is called sublimation.
Question 3.
How can you experimentally prove water is a bad conductor of heat? How is it possible to heat water easily while cooking?
Answer:
Answer:
(a) Half fill a test tube with cold water. Wrap a piece of ice in wire gauze and drop it in the tube.
(i) It will sink to the bottom.
(ii) Now heat the top end of the test tube.
(iii) The water soon begins to boil at the top but the ice below has still not fully melted.
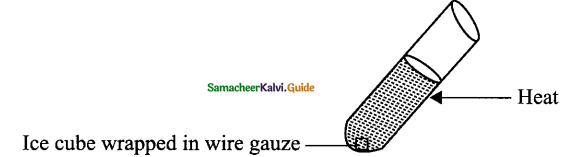
This activity shows that water is a bad conductor of heat. It does not easily conduct heat from the top to the bottom of the test tube.
![]()
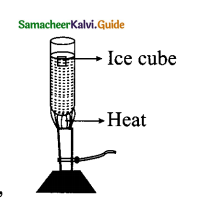
(b) It is possible to heat water easily while cooking:
- ill a test tube with cold water.
- Drop an ice-cube in this water.
- Now heat the water from below.
- You will find that the ice melts quickly.
This shows that though water is a bad conductor of heat, heat easily flows upwards in it. This method of transfer of heat is called convection. This method is involved in cooking.
VI. Numerical Problems.
Question 1.
What is the heat in joules required to raise the temperature of 25 grams of water from 0°C to 100°C? What is the heat in Calories? (Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C)
answer:
Given : Mass of water m = 25g
Initial temperature T1 = 0°C
Final temperature T1 = 100°C
Change in temperature ΔT = (T2 – T1)
= (100 – 0)°C [ΔT= 100°C]
Specific heat of water C = 4.18 J/g°C
Solution:
The heat required H (in joules) = m × c × ΔT
= 25 × 4.18 × 100
= 25 × 418
= 10450 J
Heat required in calories = 1 calorie = 4.18 J
10450 J = 2497.60 calories
![]()
Question 2.
What could be the final temperature of a mixture of 100 g of water at 90°C and 600 g of water at 20°C.
Answer:
Mass of water m1 = 100 g = 0.1 kg
Specific heat capacity of water c = 4186 J
Temperature = 90°C
Mass of water m2 = 600 g = 0.6 kg
Temperature = 20°C
Solution:
Heat lost by hot water = Heat gained by cold water
m1 × c × θ1 = m2 × c × θ2
0.1 × 4186 x (90 – TF) = 0.6 × 4186 × (TF – 20)
0.1 × (90 – TF) = (TF – 20) × 0.6
9 – 0.1 TF = 0.6TF – 12
0.7TF = 21
TF = 30°C
Final temperature of a mixture = 30°C
Question 3.
How much heat energy is required to change 2 kg of ice at 0°C into water at 20°C? (Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 3,34,000J/kg, Specific heat capacity of water = 420OJKg-1K-1
Solution:
Mass of ice m = 2 kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of water = L = 3, 34, 000 J/kg
Change in temperature ΔT = (T2 – T1)
= (20 – 0)° C
ΔT = 20° C
Specific heat capacity of water C = 4200 J Kg-1K-1
Heat energy required= m × c × ΔT + m × L
= 2 × 4,200 × 20 + 2 × 3,34,000
= 1,68,000 + 6,68,000
Heat Energy required = 8,36,000 J
![]()
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY – 1
Take a glass of water and put some ice cubes into it. Observe it for some time. What happens? The ice cubes melt and disappear. Why did it happen? It is because heat energy in the water is transferred to the ice.
Aim:
To demonstrate transfer of heat.
Material required :
A glass of water, ice cubes.
Procedure:
Take a glass of water and put some ice cubes into it. Observe it for some time. What happens?
Observation :
The ice cubes melt and disappear. It is because heat energy in the water is transferred to the ice.
Conclusion :
Heat transfer takes place when heat energy flows from the object of higher temperature to an object with lower temperature.
[End of the activity]
![]()
ACTIVITY – 2
Take metal rods of copper, aluminum, brass and iron. Fix a match stick to one end of each rod using a little melted wax. When the temperature of the far ends reach the melting point of wax, the matches drop off. It’s observed that the match stick on the copper rod would fall first, showing copper as the best conductor followed by aluminum, brass and iron.
Aim :
To compare the conducting powers of various metals.
Materials required :
Metal roads of copper, aluminium, brass and iron, match stick, melted wax.
Procedure :
Fix a match stick to one end of each rod using the little melted wax. When the temperature of the far ends reach the melting point of wax, the matches drop. Observe what happens?
Observation :
The match stick on the copper rod would fall first, showing copper as the best conductor followed by aluminum, brass and then iron.
Conclusion:
Metals are good conductors of heat. Copper is the best conductor of heat.
[End of the activity]
![]()
ACTIVITY – 3
Drop a few crystals of potassium permanganate down to the bottom of a beaker containing water. When the beaker is heated just below the crystals, by a small flame, purple streaks of water rise upwards and fan outwards.
Aim :
To demonstrate transfer of heat through convection in liquids.
Materials required :
Crystals of potassium permanganate, beaker containing water.
Procedure :
Drop a few crystals of potassium permanganate down to the bottom of a beaker containing water, heat it with a small flame.
Observation :
When the beaker is heated, just below the crystals purple streaks of water rise upwards and fan outward.
Conclusion :
Water molecules at the bottom of the beaker receive heat energy and move upward and replace the molecules at the top.
This activity shows that the flow of heat through a fluid from places of higher temperature to places of lower temperature by movement of the fluid itself.
[End of the activity]
![]()
ACTIVITY – 4
Take some crushed ice cubes in a beaker and note down the temperature using thermometer. It will be 0°C. Now heat the ice in the beaker. You can observe that ice is melting to form water. Record the temperature at regular intervals and it will remain at 0°C until whole ice is converted to liquid. Now heat the beaker again and record the temperature. You can notice that the temperature will rise up to 100°C and it will retain the same even after continuous heating until the whole mass of water in the beaker is vaporized.
Aim :
To understand latent heat of the water.
Materials Required :
Crushed ice cubes, beaker and thermometer.
Procedure :
Take some crushed ice cubes in a beaker and note down the temperature using thermometer. It will be 0°C. Now heat the ice in the beaker, (i) Observe and record the temperature at regular intervals. Heat the beaker again and record the temperature.
Observation :
- Ice is melting to form water.
- Water will remain at 0°C until the whole ice is converted to liquid.
- On further heating, we can observe that the temperature will rise up to 100°C and the temperature will be at 100°C even after continuous heating until the whole mass of water in the beaker is vapourized.
Conclusion :
In this activity, the temperature is constant at 0°C until entire ice is converted into liquid and again constant at 100°C until all the water is converted into vapour.
It is because, when a substance changes from one state to another, a considerable amount of heat energy is absorbed or liberated. This energy is called latent heat.
9th Science Guide Heat Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Water is used as a coolant because it ………………….
(a) is inexpensive
(b) is easily available
(c) is a good conductor of heat
(d) has a high specific heat capacity
Answer:
(d) has a high specific heat capacity
![]()
Question 2.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature through 1°C is called………………………
(a) thermal energy
(b) calorie
(c) heat capacity
(d) specific heat capacity
Answer:
(c) heat capacity
Question 3.
The temperature at which a liquid gets converted into its vapour state is called its………………………
(a) melting point
(b) boiling point
(c) dew point
(d) freezing point
Answer:
(b) boiling point
![]()
Question 4.
Sweating causes cooling because water has a………………………
(a) high specific heat
(b) low specific heat
(c) high latent heat of fusion
(d) high latent heat of vaporisation
Answer:
(d) high latent heat of vaporisation
Question 5.
Which of the following is true?
(a) 1 J = 412 calorie
(b) 1 J = 0.24 calorie
(c) 1 calorie = 4.2 J
(d) Both b and c
Answer:
(c) 1 calorie = 4.2 J
Question 6.
Ice does not melt rapidly because of
(a) high specific heat capacity
(b) high latent of fusion
(c) high heat capacity
(d) high latent heat of fusion
Answer:
(d) high latent heat of fusion
![]()
Question 7.
Which one of the following scales has a lower fixed point at 0°C?
(a) Kelvin scale
(b) Fahrenheit scale
(c) Celsius scale
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Celsius scale
Question 8.
When we heat one end of an iron rod, its other end also gets heated. Can you say, Which one of the following is behind this?
(a) Convection of heat
(b) Radiation of heat
(c) Insulation of heat
(d) Conduction of heat
Answer:
(d) Conduction of heat
Question 9.
In which of the following, chemical energy is converted into heat energy?
(a) Heater
(b) Refrigerators
(c) Candle
(d) Motor
Answer:
(c) Candle
![]()
Question 10.
On a cold day, it is hard to open the lid of a tight container. But when you gently heat the neck you can easily open the lid. why?
(a) On heating glass expands and lid contracts
(b) On heating lid expands more than the neck and thus slides easily
(c) Neck becomes slippery on heating
(d) Lid of the bottle cannot bear the heat.
Answer:
(b) On heating lid expands more than the neck and thus slides easily
Question 11.
Warm air is ………………………
(a) lighter than cold air
(b) heavier than cold air
(c) both have equal weights
(d) cannot be said
Answer:
(a) lighter than cold air
![]()
Question 12.
The phenomenon involved in the sea breeze and the land breeze is ………………………
(a) convection
(b) conduction
(c) radiation
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) convection
Question 13.
A liquid changes into a gas at a constant temperature known as its………………………
(a) absolute zero
(b) boiling point
(c) evaporation point
(d) dew point
Answer:
(b) boiling point
Question 14.
Copper and Iron are good conductors of heat. Which one of the following is not a good conductor of heat?
(a) Soil
(b) Aluminium
(c) Tungsten
(d) Steel
Answer:
(a) Soil
![]()
Question 15.
The specific heat capacity of water is
(a) 4200 Jkg-1K-1
(b) 420 Jg-1K-1
(c) 0.42 Jg-1K-1
(d) 4.2 Jkg-1K-1
Answer:
(a) 4200 Jkg-1K-1
Question 16.
Two cylinders of equal height and radius are made of copper and aluminum. Which of them conducts heat faster?
(a) Copper rod
(b) Aluminium rod
(c) Both of them
(d) None of them
Answer:
(a) Copper rod
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. ………………………is a process which is just reverse of melting.
Answer:
Freezing
2. While a substance is undergoing a change of state, the temperature of the body remains ………………………
Answer:
same
3. A change of state is a change of a substance from………………………
Answer:
one physical state to another
4. ………………………is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
Answer:
Temperature
![]()
5. The solid, liquid, gaseous phases of water can coexist in equilibrium at………………………
Answer:
273.16K
6. The sum of the kinetic and potential energy is called the ………………………of the molecules.
Answer:
internal energy
7. ……………………… is greater for liquids than that for solids and maximum in case of gases.
Answer:
Expansion
8. When heat energy is added to a substance, the kinetic energy of its particles and so the particles ……………………… move at a higher speed.
Answer:
increase
9. When a dog keeps out its tongue and breathes hard, the moisture on the tongue turns into ………………………and it evaporates.
Answer:
water
![]()
10. Black marks appearing on the ceiling above a lamp or fan caused by dust being carried upwards in the air are due to………………………
Answer:
convection currents
11. ………………………is the method of heat transfer that does not require particles to carry the heat energy.
Answer:
Radiation
12. Radiation consists of ………………………waves travelling at the speed of light.
Answer:
electromagnetic
13. We can observe all the three ways of heat transfer while………………………
Answer:
burning wood
![]()
14. ……………………… is known as an absolute scale.
Answer:
Kelvin
15. Specific latent heat L =………………………
Answer:
Q/m
III. Match the following :
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Heat | a) Heat gained or lost in the change of state with out any change in temperature |
| 2. m × L. | b) Heat gained or lost when there is no change of state |
| 3. Temperature | c) Form of energy |
| 4. m × s × t | d) SI unit of specific latent heat |
| 5. J/Kg | e) degree of hotness or coldness |
Answer:
1-c, 2 -a, 3 — e, 4-b, 5-d
![]()
II.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Specific heat capacity of water | a) 0°C |
| 2. Latent heat of fusion of ice | b) 2260 J/g |
| 3. Latent heat of vaporisation of water | c) 100°C |
| 4. Melting point of ice | d) 4.2 J/g°C |
| 5. Boiling point of water | e) 336 J/g |
Answer:
1-d, 2 -e, 3 – b, 4-a, 5-c
IV. Assertion and Reason type questions :
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Temperature is the measure of heat energy.
Reason (R) : Energy is the capacity to do work.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Reason: It is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Radiation is a process of transfer of heat in which a material medium is not necessary.
Reason (R): The heat from the sun reaches us through millions of miles of empty space by convection.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
Reason : All hot bodies radiate’ heat, therefore from the sun the heat comes to us by radiation.
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Heat energy is transferred from one body to another due to a
temperature difference between them.
Reason (R) : Heating a substance causes a rise in temperature.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Reason : Heat energy is more in hot substances and less in cold substances and flows from hot substances to cold substances.
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : When a very hot liquid is poured into a thick glass tumbler it cracks.
Reason (R) : Unequal expansion of the inner and outer glass walls causes the glass to crack.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
V. Very short answer type questions.
Question 1.
What is the other name of heat capacity?
Answer:
Thermal capacity.
Question 2.
Define one calorie.
Answer:
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g water by 1°C is called one calorie.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the relation between calorie and Joule?
Answer:
1 Calorie = 4.186 J
= 4.2 J
Question 4.
Name a device that prevents loss of energy (or gain) by conduction, convection and radiation.
Answer:
Thermos flask.
Question 5.
Which factor determines the direction of flow of heat from one body to another?
Answer:
Temperature.
Question 6.
Who introduced the term latent heat?
Answer:
Joseph Black in 1750.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the minimum possible temperature? Is there also a maximum possible temperature?
Answer:
The minimum possible temperature is OK. There is no limit to maximum temperature.
VI. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Heat gained by a body depends upon which factors?
Answer:
- Mass of the body
- Change in temperature of the body
- Nature of the material of the body.
Question 2.
Water is used as a coolant in car radiators. Why?
Answer:
Water is used as a coolant in car radiators because it has high specific heat capacity. As a result, it can absorb large amounts of heat from the car engine without any substantial increase in its temperature.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by thermal equilibrium?
Answer:
When two bodies at different temperatures are kept in contact with each other, then heat energy flows from the hot body to the colder one.
It means that the hot body will lose heat and the cold body will gain heat till they reach a common temperature. This state is called thermal equilibrium.
Question 4.
Define latent heat of fusion?
Answer:
Heat energy is absorbed by a solid during melting and an equal amount of heat energy ‘ is liberated by the liquid during freezing, without any temperature change. It is called latent heat of fusion.
Question 5.
Why are burns caused by steam more painful than those caused by boiling water at the same temperature?
Answer:
- When steam hits our skin, it condenses to water and then cools down to the temperature of skin.
- Now, the energy released will be due to latent heat and fall in temperature.
- Whereas when boiling water hits our skin, there is no phase transition but only fall in temperature and the heat transferred to skin will be only due to cooling.
- Also, the loss of energy that is released from steam hitting our skin occurs quickly and in a small localized area, therefore causing damage to our cells.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by solidification or deposition?
Answer:
Solidification is the process in which a gas directly condenses into its solid state without going into liquid state Ex : Carbon dioxide gas gets converted into dry ice.
Question 7.
Define absolute zero.
Answer:
The temperature at which the pressure and volume of a gas theoretically reaches zero is called absolute zero.
Question 8.
Give some practical applications of conduction in daily life.
Answer:
- Metals are good conductors of heat. So, aluminium is used for making utensils to cook food quickly.
- Mercury is used in thermometers because it is a good conductor of heat.
- We wear woolen clothes in winter to keep ourselves warm. Air, which is a bad conductor, does not allow our body heat to escape.
![]()
Question 9.
Give some practical applications of radiation.
Answer:
- White or light colored clothes are good reflectors of heat. They keep us cool during summer.
- The bottom surface of cooking utensils is blackened because the black surface absorbs more heat from the surrounding.
- The surface of the airplane is highly polished because it helps to reflect most of the heat radiation from the sun.
Question 10.
Can convection take place in solids? Why?
Answer:
No. The molecules in a solid are only free to vibrate about their fixed positions. For convection to take place, the molecules need to move to carry the heat with them. Hence, convection cannot take place in solids.
Question 11.
In winters, when the sun suddenly goes behind the clouds we feel cold, can you say why?
Answer:
The clouds cut off the radiant heat from the sun.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Give the difference between heat and temperature.
Answer:
Heat
- Heat is a form of energy due to which we feel hot or cold.
- Its SI unit is joule (J)
- It depends upon mass, nature and temperature of the body.
- It is a form of energy.
- It is measured by a calorimeter.
Temperature :
- The degree of hotness or coldness of a body is known as temperature.
- Its SI unit is kelvin (K).
- It does not depend upon mass, nature and temperature of the body.
- It is a condition that determines the direction of flow of heat.
- It is measured by a thermometer.
Question 2.
Give some practical applications of specific latent heat of ice.
Answer:
Specific latent heat of ice is very high (i.e.) 336 J/g.
- Due to high specific latent heat of ice, snow on mountains do not melt as a whole, but melts gradually into water with the heat of the sun.
If the specific latent heat of ice would not have been so high, all the snow would have melted very quickly and there would have been floods in the rivers. - All the water in lakes and ponds in cold places do not freeze all at the same time. If freezes slowly and keeps the surrounding moderate.
- Drinks are cooled more effectively by ice pieces at 0°C and not by water at 0°C. This is because 1 g of ice takes away 336 J of heat from the drink to melt into water at 0°C.
![]()
Question 3.
600 g of copper at 50°C is mixed with lOOOg water at 20°C. Find the final temperature of the mixture. Specific heat capacity of copper is 0.4 Jg-1°C-1 and that of water is 4.2 Jg-1°C-1
Solution :
Let final temperature of the mixture of copper and water = x °C
For copper:
Mass of copper m1 = 600g
Specific heat capacity of copper c1 = 0.4Jg-1°C-1
Initial temperature of copper t1 = 50°C
Final temperature of copper t2 = x°C
Fall in temperature Δt = (50 – x)°C
Heat lost by copper = m1 × c1 × t
= 600 × 0.4 × (50 – x)
For water :
Mass of water m2 = 1000g
Specific heat capacity of water c2 = 4.2Jg-1°C-14
Initial temperature of water t1 = 20°C
Final temperature of water t2 = x°C
Rise in temperature Δt = (x – 20)°C
Heat gained by water = m2 × c2 × t
= 100 × 4.2 × (x – 20)
According to the principle of calorimetry,
Heat lost by copper = Heat gained by water
600 × 0.4 × (50 – x) =1000 x 4.2 x (x – 20)
240 × (50 – x) = 4200 ( x- 20)
12,000 – 240x = 4200x-84000
4200x + 240x =12000 + 84000
4440 = 96000
x = \(\frac{96000}{4440}=21.6\)
So, final temperature of mixture of water and copper x = 21.6°C
![]()
Question 4.
Compare heat capacity and specific heat capacity.
Answer:
Specific heat capacity :
- It is the heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance through 1°C.
- It does not depend on the mass of the body It depends on the mass of the body
- Its unit is Jkg-1 °C-1
Heat capacity
- It is the heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of substance through 1°C.
- It depends on the mass of the body
- Its unit is J°C-1.
Question 5.
Explain the following effects of heat.
(i) Expansion
(ii) Change in temperature
(iii) Change in state
(iv) Chemical changes.
Answer:
(i) Expansion:
When heat is added to a substance, the molecules gain energy and vibrate and force other molecules apart. As a result, expansion takes place. You would have seen some space being left in railway tracks. It is because, during summer time, more heat causes expansion in tracks. Expansion is greater for liquids than for solids and maximum in case of gases.
(ii) Change in temperature :
When heat energy is added to a substance, the kinetic energy of its particles increases and so the particles move at higher speed. This causes rise in temperature. When a substance is cooled, that is, when heat is removed, the molecules lose heat and its temperature falls.
(iii) Change in state :
When you heat ice cubes, they become water and water on further heating changes into vapour. So, solid becomes liquid and liquid becomes gas, when heat is added. The reverse takes place when heat is removed.
(iv) Chemical changes :
Since heat is a form of energy it plays a major role in chemical changes. In some cases, chemical reactions need heat to begin and also heat determines the speed at which reactions occur. When we cook food, we light the wood and it catches fire and the food particles become soft because of the heat energy. These are all the chemical changes taking place due to heat.
![]()
VIII. Numerical Problems
Question 1.
What is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 5 kg of iron from 30°C to 130°C? Specific heat capacity of iron = 483 Jkg-1C-1.
Solution :
Mass of iron m = 5kg
Initial temperature t1 = 30°C
Final temperature t2 = 130°C
Rise is temperature Δt = (t2 -t1) = 130 – 30 = 100°C
Specific heat capacity of iron c = 483Jkg-1°C-1
Q = m × c × Δt
= 5 × 483 × 100
= 2,41,500J
Question 2.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 200g of ice at 0°C into the water at 0°C Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg-1
Solution :
Mass of ice m = 200g
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice L = 336Jg-1
Heat required Q = mL
= 200 × 336
Q = 67,200 J
![]()
Question 3.
2875 J of heat is required to melt 115 g of lead at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat capacity of fusion of lead.
Solution:
Mass of lead m = 115 g
Heat required Q = 2875 J
Specific latent heat of lead L =?
We know that Q = m L
L = \(\frac{Q}{m}=\frac{2875}{115}\)
= 25 Jg-1
Question 4.
What will be the final temperature if 1,68,000 J of heat is absorbed by 2 kg of water at 30°C?
Solution :
Heat absorbed Q = 1,68,000 J
m = 2kg
Initial temperature t1 = 30°C
Let final temperature t2 = x°C
Rise is temperature Δt = (t2 – t1)
= (x – 30)°C
Specific heat capacity of water C = 4200 J kg-1°C-1
We know that Q = m × c × Δt
1,68,000 = 2 × 4200 × (x – 30 )
x – 30 = \(\frac{1,68,000}{2 \times 4200}\)
x- 30 = 20
x = 30 + 20
= 50°C
So, the final temperature of water = 50°C
![]()
Question 5.
A metal ball of heat capacity 50J/°C loses 2000 J of heat. By how much will its temperature fall?
Solution :
Heat capacity of ball = 50 J °C-1
Heat lost Q = 200 J
Fall in temperature t =?
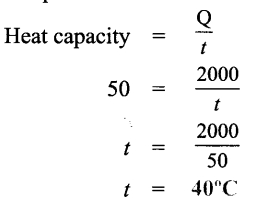
IX. Convert the following
1. 100°F to °C
Solution:
T(°C) = (T(°F) – 32) /1.8
T(°C) = (100°F – 32)
T(°C) = 37.7 °C
2. 40°C to Fahrenheit (°F)
Solution :
T(°F) = (T(°F) × 1.8) + 32
= 40°C × 1.8 + 32
= 72 + 32
T(°F) = 104°F
3. 35°C to Kelvin
Solution :
T(K) = T(°C) +273.15
= 35 + 273.15
T(K) = 308.15 K
4. 80°K to °C
Solution :
T(°C) = T(K) – 273.15
T(°C) = 80-273.15
T(°C) = 193.I5 °C
![]()
X. Define the following :
1. Heat: Heat is a form of energy which transfers from the higher temperature region to the lower temperature region of a body.
2. Conduction: The process of transfer of heat in solids from a region of higher temperature
to a region of lower temperature without the actual movement of molecules is called conduction.
3. Convection: Convection is the flow of heat through fluid from places of higher temperature to places of lower temperature by the movement of the fluid itself.
4. Radiation: Radiation is a method of heat transfer that does not require particles to carry the heat energy.
5. Temperature: Temperature is the degree of hotness or coolness of a body.
6. Specific heat capacity: Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1° C or 1 K.
7. Heat capacity or thermal capacity: Heat capacity is the heat required to raise the temperature of the entire mass of the body by 1° C.
8. Change of state: The process of changing of a substance from one physical state to another at a definite temperature is known as change of state.
9. Melting or fusion: The process in which a solid is converted to a liquid by absorbing heat is called melting or fusion.
10. Boiling: Th e process in which a liquid is converted to vapor by absorbing heat is called boiling or vaporization.
11. Sublimation: Th e process in which a solid is converted to a gaseous state is called sublimation.
12. Latent heat: Thus, latent heat is the amount of heat energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical states without any change in its temperature.
13. Specific latent heat: Specific latent heat is the amount of heat energy absorbed or liberated by the unit mass of a substance during a change of state without causing any change in temperature.