TN State Board 12th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 25 Government Schemes for Entrepreneurial Development
Question 1.
Name any four Governmental Entrepreneurial schemes.
Answer:
- Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme(M-SIPS)
- New Gen Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development Centre(New Gen IEDc) .
- Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (iv) Single Point Registration Scheme (SPRS).
Question 2.
Give a note on ‘Digital India’.
Answer:
The Digital India initiative has been launched to modernize the Indian economy to make all Government services available electronically. The initiatives aims at transforming India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy with universal access to goods and services.
![]()
Question 3.
State any three entrepreneurial development schemes of Government of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
The three schemes among the entrepreneurial schemes of Government of Tamilnadu is
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
- Self – Help Group (SHG)
- New Entrepreneur – Cum – Enterprise Development Scheme (NEEDS)
Question 4.
List down the two types of finance.
Answer:
- Long term: which are needed for acquiring fixed assets.
- hort term: which are meant for meeting working capital needs.
Question 5.
Mention the time period of Provision Registration Certificate.
Answer:
Entrepreneur has to apply for provisional registration certificate. It will be issued to entrepreneur after the fulfilment of certain conditions for a period of 12 months duration subject to renewal of two periods of six months.
![]()
Question 6.
What is ‘Startup India’?
Answer:
Through the start up India initiative, Government of India promotes entrepreneurship by monitoring, nurturing and facilitating startups through out their life cycle. Since its launch in January 2016, the initiative has successfully given a head start to numerous aspiring entrepreneurs. A “Fund of Funds” has been created to help startups gain access to funding.
Question 7.
Expand the following: STEP, JAM, TREAD, NI-SIPS, SEED and New Gen IEDC.
Answer:
STEP- Support to Training and Employment Program for Women
JAM – Jan dhan – Aadhaar – Mobile
TREAD – Trade Related Entrepreneurship Assistance and Development
M-SIPS – Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme
SEED – Science for Equity Empowerment and Development
New Gen IEDC – New Gen Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development Centre.
Question 8.
Write a short note on the following:
(a) Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme.
(b) Project report.
Answer:
(a) Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme aims at helping entrepreneurs in the field of Agriculture, pets and animals, and social impact to set up small diary farms and incentives are provided to cover the cost of the required equipment or establishment of the facility.
(b) Project reports needs to be prepared according to the format prescribed in the loan application form of term lending institutions. An entrepreneur can get the report prepared either by technical consultancy organization or by auditors or by consultants or by development agencies. This report should cover aspects like sources of labour and raw materials, market potential and profitability.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the procedure for getting power connection for an Entrepreneurial venture?
Answer:
An entrepreneur has to make application to assistant divisional engineer of state electricity board for power connection after paying Security Deposit and fulfiling the official formalities prescribed.
Question 10.
Explain any five Government Entrepreneurial schemes.
Answer:
In order to support and strengthen, the start up culture in India, the Government has launched various schemes. They are as follows:
Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS):
The M-SIPS scheme provides capital subsidy of 20% in SEZ and 25% subsidy in non – SEZ for business units engaged in manufacturing of electronics in the fields of the internet of things, aeronautical, aerospace and defence, automotive, renewable energy, non – renewable energy, technology, green technology and nano – technology.
New Gen Innovations and Entrepreneurship Development Centre (New Geh IEDC):
New Gen IEDC provides a limited one – time, non – recurring financial assistance to entrepreneurs upto 25 Lakhs in the field of chemicals, technology hardware, healthcare and life sciences, aeronautics/aerospace and defence, agriculture, AI ( artificial intelligence) , AR/VR ( augmented + virtual reality), automotive, telecommunication and networking.
Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS):
Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme aims at helping entrepreneurs in the field of agriculture, pets and animals, and social impact to set up small dairy farms and incentives are provided to cover the cost of the required equipment or establishment of the facility.
Single Point Registration Scheme (SPRS):
A great scheme for micro and small enterprises, which provides an exemption from payment of Earnest Money Deposit (EMD). Under this scheme, the tenders are issued free of cost.
Atal incubation centres (AIC):
The Government of India has setup the AIC scheme at NITI Aayog in 2016 with the over arching purpose of promoting a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country. This has been set up to provide high class incubation facilities across various parts of India in terms of capital equipment, operating facilities, along with sectoral experts for monitoring startups, especially in transport.
![]()
Question 11.
Describe the steps promoting Entrepreneurial venture.
Answer:
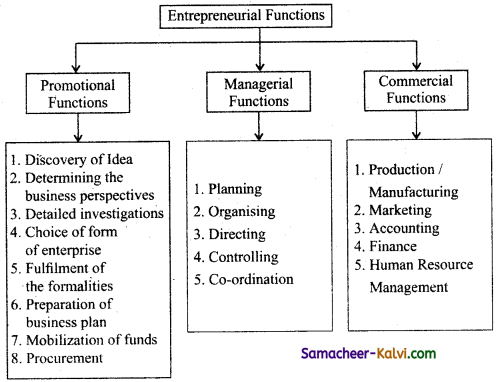
(i) Selection of the Product:
An entrepreneur may select a product according to his aspiration, capacity and motivation after a thorough scrutinity of micro and macro environment of business. He/she may select a brand, new product or may like to select imitation one or he/she may improve upon an existing product in terms of additional features like comforts, convenience, ease of operation, lower price etc., An entrepreneur has to conduct economic viability of the project.
(ii) Selection of Form of Ownership:
Entrepreneur has to choose the form of organization suitable and appropriate for his venture namely family ownership, partnership and private limited company. Family ownership and partnership forms of organization are suited for exercising unified control over the venture while the company form of organization may be preferred for pooling of more financial resources, managerial and technical skills and business experience for carrying on medium to large venture.
(iii) Selection of Site:
Entrepreneur has to choose suitable plot for accommodating his venture. He has four options open to him for housing his venture. They are as below:
(a) State Development Corporation like SIDCO, SIPCOT, MMDA, TNHB and Directorate of industries may allot plot of entrepreneur.
(b) Entrepreneur can have a factory sheds constructed by State Industrial Development Agency.
(c) Entrepreneur can start ventures in the land development by private developers.
(d) Entrepreneur may buy private land and develop it for industrial use.
(iv) Following things may be considered in choosing the site namely:
(a) Nearness to Native place.
(b) Incentives provided by the Government.
(c) Nearness to Market
(d) Availability of Labour and Raw Materials in a particular area
(e) Infrastructure facilities.
(v) Designing Capital Structure:
Entrepreneur has to determine the source of finance for funding the venture. He/she may mobilize funds from his own savings, loans from friends and relatives, term loans from banks and financial institutions.
(vi) Acquisition of Manufacturing Know-How:
Entrepreneur can acquire manufacturing know-how from Government research laboratories, research and development divisions of industries, and individual consultants. At times, main units may supply manufacturing know-how to entrepreneurs starting ancillary units or plant and machinery suppliers may provide this facility to entrepreneurs.
(vii) Preparation of Project Reports:
Project reports needs to be prepared according to the format prescribed in the loan application form of term lending institutions.
![]()
Question 12.
Discuss the preparation of a project report.
Answer:
An entrepreneur can get the report prepared either by technical consultancy organization or by auditors or by consultants or by development agencies. This report should cover aspects like sources of finance, technical know-
how, sources of labour and raw materials, market potential and profitability.
The project report should include the following.
(i) Technical feasibility: It should mention the following:
(a) Description of product specification
(b) Raw materials availability
(c) Manufacturing process
(d) Quality control measures
(e) Availability of water, power, transport and communicate facilities.
(ii) Economic Viability:
It is essentially involves compilation of demand for domestic and export market installed capacity of machines, market, share, revenue expected and suitable price structure.
(iii) Financial Viability: It should cover the aspect like
(a) Non-recurring cost such as Land and Building, Plant and Machinery etc.
(b) Recurring expenses like wages, salaries and overheads etc.
(c) Probable cost of production
(d) Profit on expected sales
(iv) Managerial competency:
Entrepreneur has to include the mechanism for managing the venture in the project report. In the case of small sized ventures, the owners or partners may take care of managerial activities while a team of managerial personnel is to be brought in for manning various managerial positions across different levels of management in the case of corporate form of organization.
(v) Provisional Regional Certificate:
Entrepreneur has to apply for Provisional Regional Certificate. It will be issued to entrepreneur after the fulfilment of certain conditions for a period of one year subject to renewal of two periods of six months duration further extension will not be granted.
(vi) Permanent Registration Certificate:
Once the venture has commenced production or when it is ready to commence production, it is eligible to get permanent registration certificate.
(vii) Statutory License:
Entrepreneur has to obtain Municipal License from the authority concerned. Then the entrepreneur has to register the unit with the Central and Sales Tax Department. If a unit comes within the provisions of factories act, he/she has to register the unit under the shops and Establishment Act.
(viii) Power Connection:
Entrepreneurs has to make application to Assistant Divisional Engineer of State Electricity Board for power connection after paying Security Deposit and fillfiling the official formalities prescribed. (ix) Arrangement of finance: Entrepreneurs requires two types of finance namely long and short term while long term requirements are needed for acquiring fixed assets, short term requirement are meant for making meeting working capital needs.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The _________ initiative was launched to modernize the Indian economy to make all Governments services available electronically.
(a) Standup India
(b) Startup India
(c) Digital India
(d) Make in India
Answer:
(c) Digital India
Question 2.
___________ is designed to transform India to a global design and manufacturing hub.
(a) Digital India
(b) Make in India
(c) Startup India
(d) Design India.
Answer:
(b) Make in India
![]()
Question 3.
__________ is the Government of India’s endeavour to promote culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
(a) AIM
(b) STEP
(c) SEED
(d) AIC
Answer:
(a) AIM
Question 4.
__________ should cover aspects like sources of finance, technical know-how, source of labour and raw material, market potential and profitability.
(a) Technical Report
(b) Finance Report
(c) Project Report
(d) Progress Report
Answer:
(c) Project Report
![]()
Question 5.
_________ has to include the mechanism for managing venture in the project
report.
(a) Banker
(b) Government
(c) Lending Institutions
(d) Entrepreneur
Answer:
(d) Entrepreneur