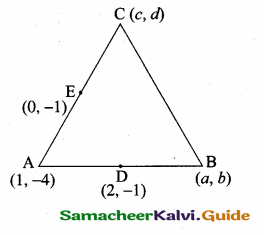
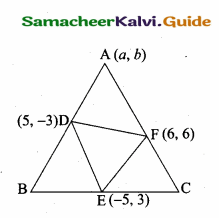
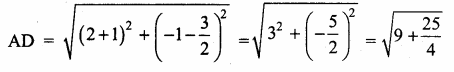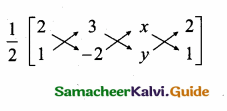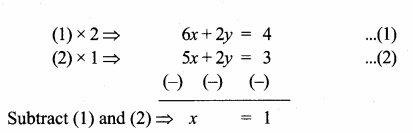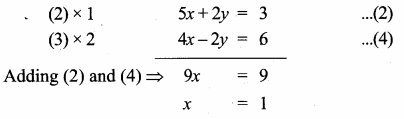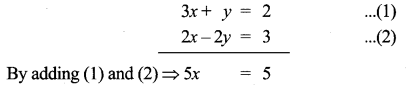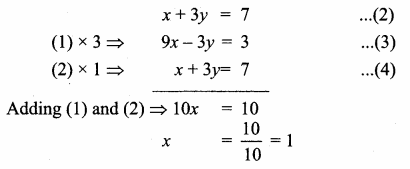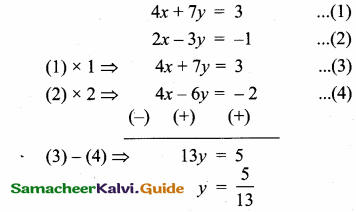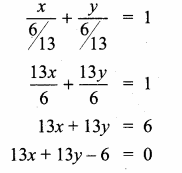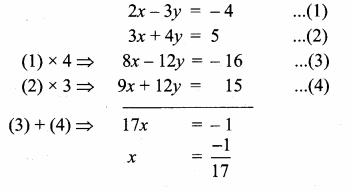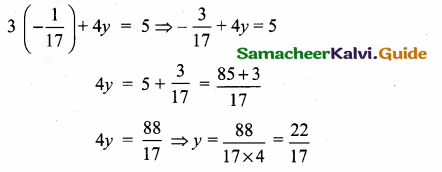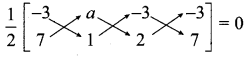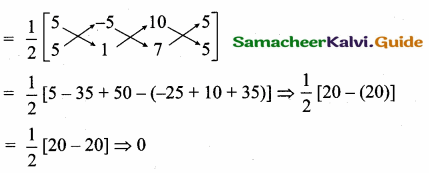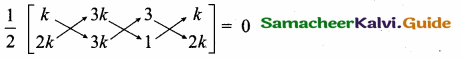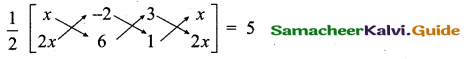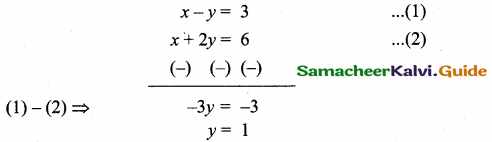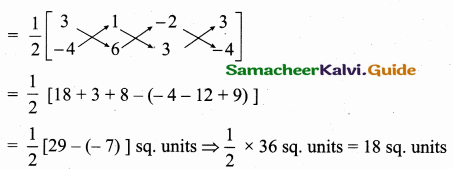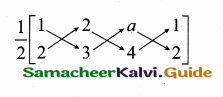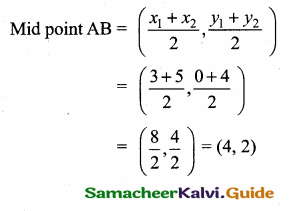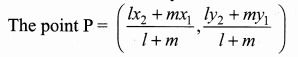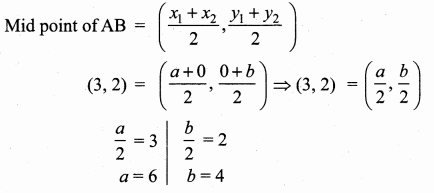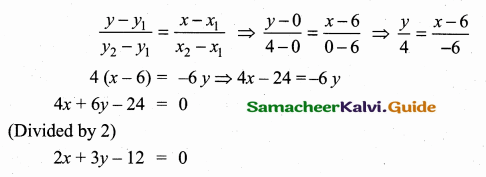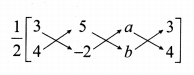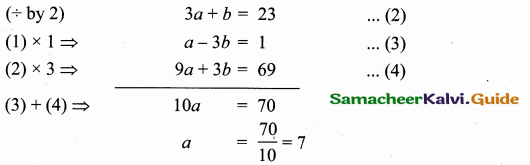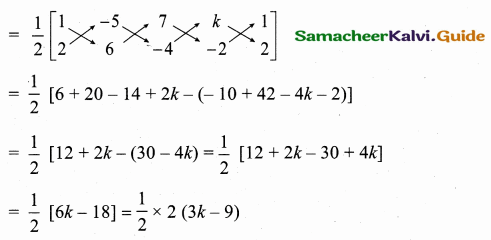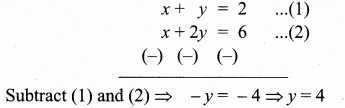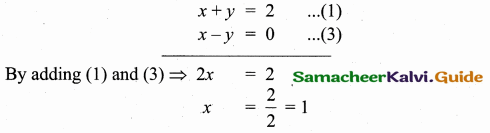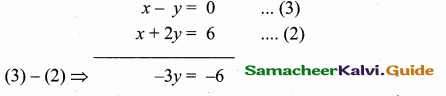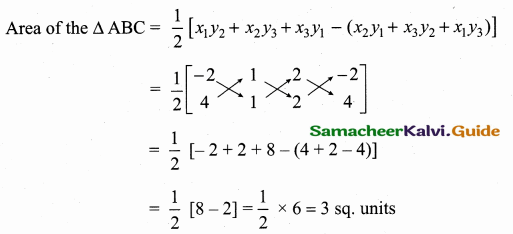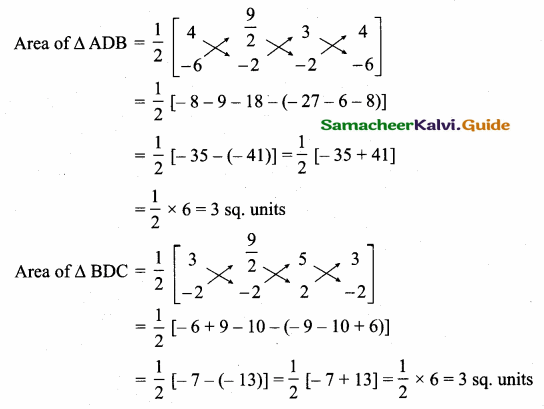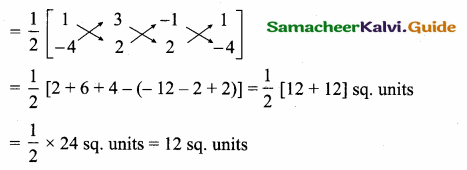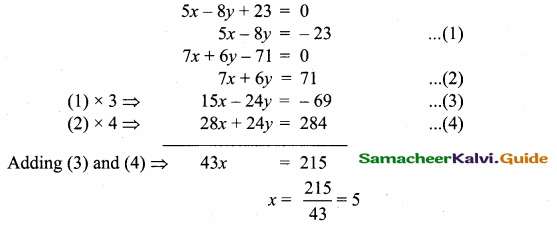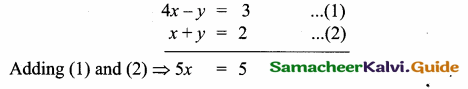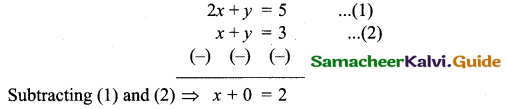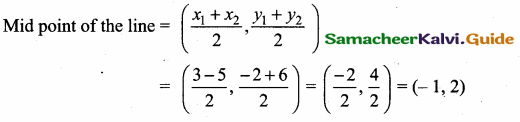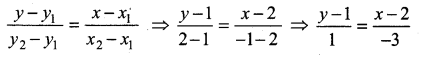Students can download Maths Chapter 5 Coordinate Geometry Ex 5.4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Coordinate Geometry Ex 5.4
Question 1.
Find the slope of the following straight lines.
(i) 5y – 3 = 0
(ii) 7x – \(\frac { 3 }{ 17 } \) = 0
Solution:
(i) 5y – 3 = 0
5y = 3 ⇒ y = \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
Slope = 0
(ii) 7x – \(\frac { 3 }{ 17 } \) = 0 (Comparing with y = mx + c)
7x = \(\frac { 3 }{ 17 } \)
Slope is undefined
![]()
Question 2.
Find the slope of the line which is
(i) parallel to y = 0.7x – 11
(ii) perpendicular to the line x = -11
Solution:
(i) y = 0.7x – 11
Slope = 0.7 (Comparing with y = mx + c)
(ii) Perpendicular to the line x = – 11
Slope is undefined (Since the line is intersecting the X-axis)
Question 3.
Check whether the given lines are parallel or perpendicular
(i) \(\frac { x }{ 3 } \) + \(\frac { y }{ 4 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 } \) = 0 and \(\frac { 2x }{ 3 } \) + \(\frac { y }{ 2 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) = 0
(ii) 5x + 23y + 14 = 0 and 23x – 5x + 9 = 0
Solution:
(i) \(\frac { x }{ 3 } \) + \(\frac { y }{ 4 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 } \) = 0 ; \(\frac { 2x }{ 3 } \) + \(\frac { y }{ 2 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) = 0
Slope of the line (m1) = \(\frac { -a }{ b } \)
= – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) ÷ \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) = –\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) × \(\frac { 4 }{ 1 } \) = – \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)
Slope of the line (m2) = – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) ÷ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) = –\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) × \(\frac { 2 }{ 1 } \) = – \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)
m1 = m2 = – \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)
∴ The two lines are parallel.
(ii) 5x + 23y + 14 = 0 and 23x – 5x + 9 = 0
Slope of the line (m1) = \(\frac { -5 }{ 23 } \)
Slope of the line (m2) = \(\frac { -23 }{ -5 } \) = \(\frac { 23 }{ 5 } \)
m1 × m2 = \(\frac { -5 }{ 23 } \) × \(\frac { 23 }{ 5 } \) = -1
∴ The two lines are perpendicular
![]()
Question 4.
If the straight lines 12y = -(p + 3)x + 12, 12x – 7y = 16 are perpendicular then find ‘p’
Solution:
Slope of the first line 12y = -(p + 3)x +12
y = \(-\frac{(p+3) x}{12}+1\) (Comparing with y = mx + c)
Slope of the second line (m1) = \(\frac { -(p+3) }{ 12 } \)
Slope of the second line 12x – 7y = 16
(m2) = \(\frac { -a }{ b } \) = \(\frac { -12 }{ -7 } \) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 7 } \)
Since the two lines are perpendicular
m1 × m2 = -1
\(\frac { -(p+3) }{ 12 } \) × \(\frac { 12 }{ 7 } \) = -1 ⇒ \(\frac { -(p+3) }{ 7 } \) = -1
-(p + 3) = -7
– p – 3 = -7 ⇒ -p = -7 + 3
-p = -4 ⇒ p = 4
The value of p = 4
![]()
Question 5.
Find the equation of a straight line passing through the point P(-5,2) and parallel to the line joining the points Q(3, -2) and R(-5,4).
Solution:
Slope of the line = \(\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
Slope of the line QR = \(\frac { 4+2 }{ -5-3 } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ -8 } \) = \(\frac { 3 }{ -4 } \) ⇒ – \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 } \)
Slope of its parallel = – \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 } \)
The given point is p(-5, 2)
Equation of the line is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 2 = – \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 } \) (x + 5)
4y – 8 = -3x – 15
3x + 4y – 8 + 15 = 0
3x + 4y + 7 = 0
The equation of the line is 3x + 4y + 7 = 0
Question 6.
Find the equation of a line passing through (6, -2) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (6, 7) and (2, -3).
Solution:
Let the vertices A (6, 7), B (2, -3), D (6, -2)
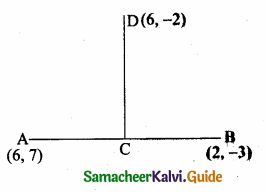
Slope of a line = \(\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
Slope of AB = \(\frac { -3-7 }{ 2-6 } \) = \(\frac { -10 }{ -4 } \) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)
Slope of its perpendicular (CD) = – \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 } \)
Equation of the line CD is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y + 2 = –\(\frac { 2 }{ 5 } \) (x – 6)
5(y + 2) = -2 (x – 6)
5y + 10 = -2x + 12
2x + 5y + 10 – 12 = 0
2x + 5y – 2 = 0
The equation of the line is 2x + 5y – 2 = 0
![]()
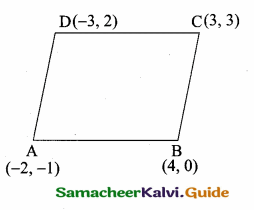
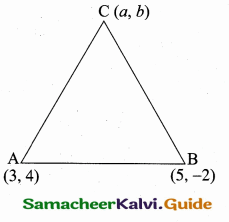
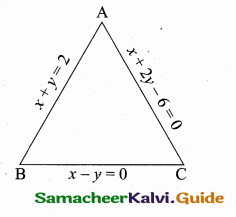
Question 7.
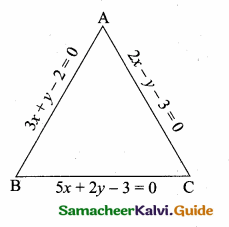
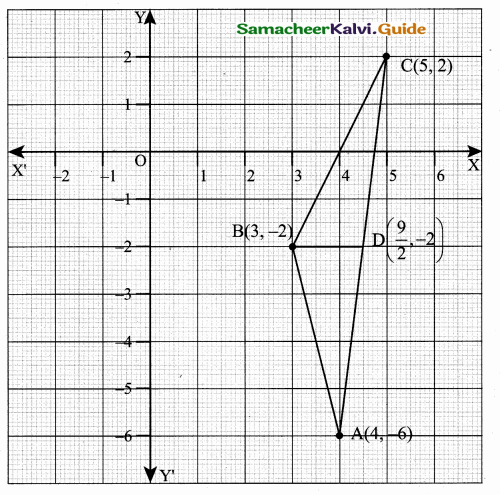
A(-3,0) B(10, -2) and C(12,3) are the vertices of ∆ABC. Find the equation of the altitude through A and B.
Solution:
To find the equation of the altitude from A.
The vertices of ∆ABC are A(-3, 0), B(10, -2) and C(12, 3)
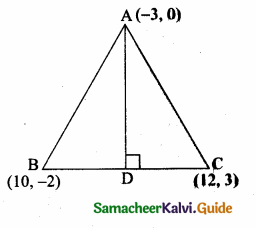
Slope of BC = \(\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
= \(\frac { 3+2 }{ 12-10 } \) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)
Slope of the altitude AD is – \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 } \)
Equation of the altitude AD is
y – y1 = m (x – x1)
y – 0 = – \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 } \) (x + 3)
5y = -2x -6
2x + 5y + 6 = 0
Equation of the altitude AD is 2x + 5y + 6 = 0
Equation of the altitude from B
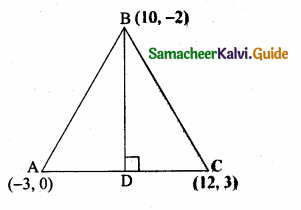
Slope of AC = \(\frac { 3-0 }{ 12+3 } \) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 15 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 } \)
Slope of the altitude AD is -5
Equation of the altitude BD is y – y1= m (x – x1)
7 + 2 = -5 (x – 10)
y + 2 = -5x + 50
5x + 7 + 2 – 50 = 0 ⇒ 5x + 7 – 48 = 0
Equation of the altitude from B is 5x + y – 48 = 0
![]()
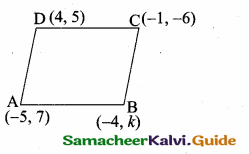
Question 8.
Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the points A(-4,2) and B(6, -4).
Solution:
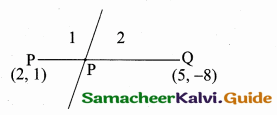
“C” is the mid point of AB also CD ⊥ AB.
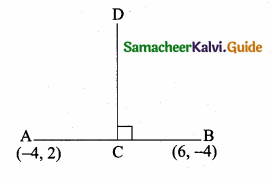
Slope of AB = \(\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
= \(\frac { -4-2 }{ 6+4 } \) = \(\frac { -6 }{ 10 } \) = – \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
Slope of the ⊥r AB is \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \)
Mid point of AB = (\(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}, \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\))
= (\(\frac { -4+6 }{ 2 } \),\(\frac { 2-4 }{ 2 } \)) = (\(\frac { 2 }{ 2 } \),\(\frac { -2 }{ 2 } \)) = (1,-1)
Equation of the perpendicular bisector of CD is
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y + 1 = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) (x – 1)
5(x – 1) = 3(y + 1)
5x – 5 = 3y + 3
5x – 3y – 5 – 3 = 0
5x – 3y – 8 = 0
Equation of the perpendicular bisector is 5x – 3y – 8 = 0
![]()
Question 9.
Find the equation of a straight line through the intersection of lines 7x + 3y = 10, 5x – 4y = 1 and parallel to the line 13x + 5y + 12 = 0.
Solution:
Given lines are.
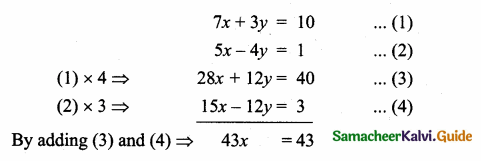
x = \(\frac { 43 }{ 43 } \) = 1
Substitute the value of x = 1 in (1)
7(1) + 3y = 10 ⇒ 3y = 10 – 7
y = \(\frac { 3 }{ 3 } \) = 1
The point of intersection is (1,1)
Equation of the line parallel to 13x + 5y + 12 = 0 is 13x + 5y + k = 0
This line passes through (1,1)
13 (1) + 5 (1) + k = 0
13 + 5 + k = 0 ⇒ 18 + k = 0
k = -18
∴ The equation of the line is 13x + 5y – 18 = 0
Question 10.
Find the equation of a straight line through the intersection of lines 5x – 6y = 2, 3x + 2y = 10 and perpendicular to the line 4x – 7y + 13 = 0.
Solution:
Given lines are.
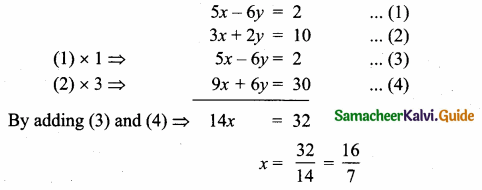
Substitute the value of x = \(\frac { 16 }{ 7 } \) in (2)
3 × \(\frac { 16 }{ 7 } \) + 2y = 10 ⇒ 2y = 10 – \(\frac { 48 }{ 7 } \)
2y = \(\frac { 70-48 }{ 7 } \) ⇒ 2y = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)
y = \(\frac{22}{2 \times 7}\) = \(\frac { 11 }{ 7 } \)
The point of intersect is (\(\frac { 16 }{ 7 } \),\(\frac { 11 }{ 7 } \))
Equation of the line perpendicular to 4x – 7y + 13 = 0 is 7x + 4y + k = 0
This line passes through (\(\frac { 16 }{ 7 } \),\(\frac { 11 }{ 7 } \))
7 (\(\frac { 16 }{ 7 } \)) + 4 (\(\frac { 11 }{ 7 } \)) + k = 0 ⇒ 16 + \(\frac { 44 }{ 7 } \) + k = 0
\(\frac { 112+44 }{ 7 } \) + k = 0 ⇒ \(\frac { 156 }{ 7 } \) + k = 0
k = – \(\frac { 156 }{ 7 } \)
Equation of the line is 7x + 4y – \(\frac { 156 }{ 7 } \) = 0
49x + 28y – 156 = 0
![]()
Question 11.
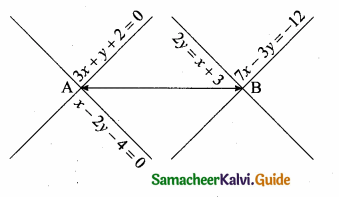
Find the equation of a straight line joining the point of intersection of 3x + y + 2 = 0 and x – 2y -4 = 0 to the point of intersection of 7x – 3y = -12 and 2y = x + 3.
Solution:
The given lines are.
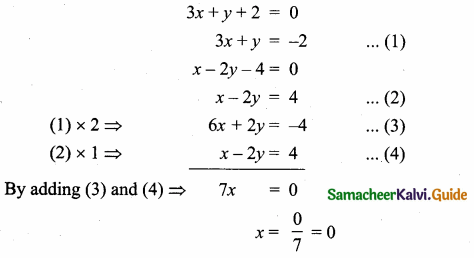
Substitute the value of x = 0 in (1)
3 (0) + y = -2
y = -2
The point of intersection is (0, -2).
The given equation is
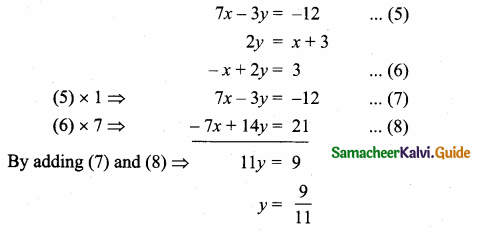
Substitute the value of y = \(\frac { 9 }{ 11 } \) in (6)
– x + 2 (\(\frac { 9 }{ 11 } \)) = 3 ⇒ -x + \(\frac { 18 }{ 11 } \) = 3
-x = 3 – \(\frac { 18 }{ 11 } \) = \(\frac { 33-18 }{ 11 } \) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 11 } \)
x = – \(\frac { 15 }{ 11 } \)
The point of intersection is (-\(\frac { 15 }{ 11 } \),\(\frac { 9 }{ 11 } \))
Equation of the line joining the points (0, -2) and (-\(\frac { 15 }{ 11 } \),\(\frac { 9 }{ 11 } \)) is
![]()
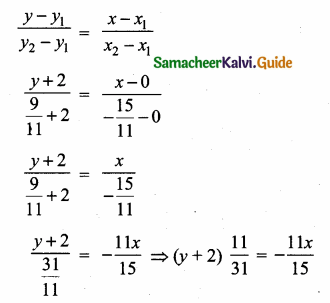
31 × (- 11x) = 11 × 15 (y + 2) = 165 (y + 2)
– 341 x = 165 y + 330
– 341 x – 165 y – 330 = 0
341 x + 165 y + 330 = 0
(÷ by 11) ⇒ 31 x + 15 y + 30 = 0
The required equation is 31 x + 15 y + 30 = 0
![]()
Question 12.
Find the equation of a straight line through the point of intersection of the lines 8JC + 3j> = 18, 4JC + 5y = 9 and bisecting the line segment joining the points (5, -4) and (-7,6).
Solution:
Given lines are.
8x + 3y = 18 …..(1)
4x + 5y = 9 …..(2)
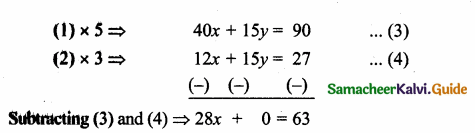
x = \(\frac { 63 }{ 28 } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \)
Substitute the value of x = \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \) in (2)
4 (\(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \)) + 5y = 9
9 + 5y = 9 ⇒ 5y = 9 – 9
5y = 0 ⇒ y = 0
The point of intersection is (\(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \),0)
Mid point of the points (5, -4) and (-7, 6)
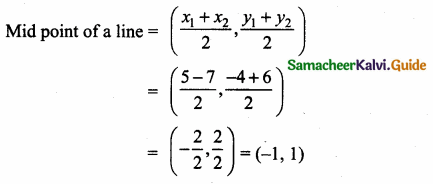
Equation of the line joining the points (\(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \),0) and (-1,1)
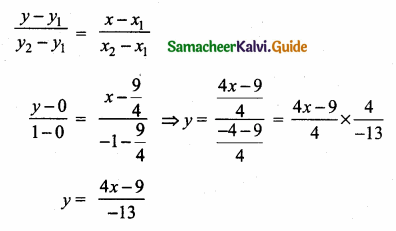
-13y = 4x – 9
-4x – 13y + 9 = 0 ⇒ 4x + 13y – 9 = 0
The equation of the line is 4x + 13y – 9 = 0