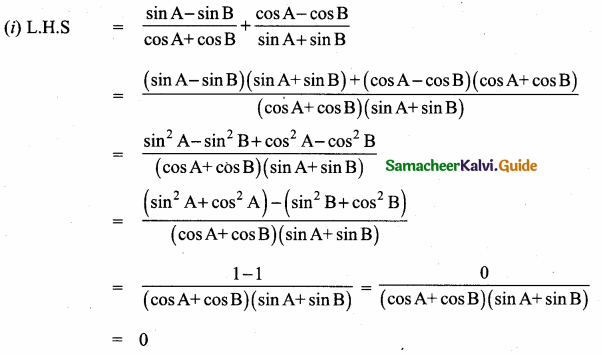
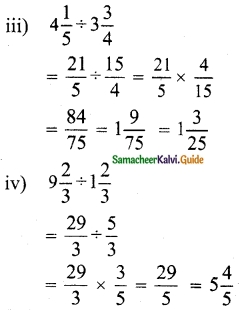
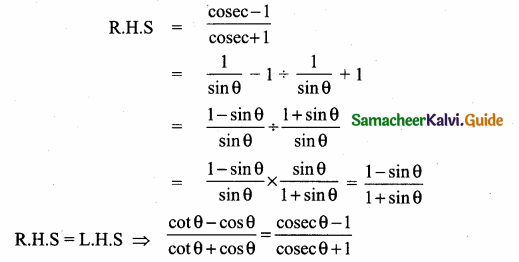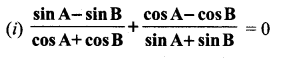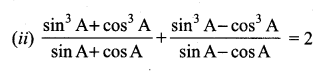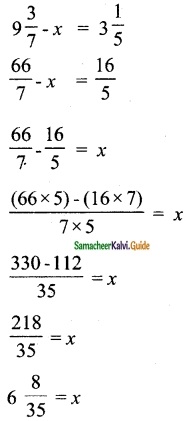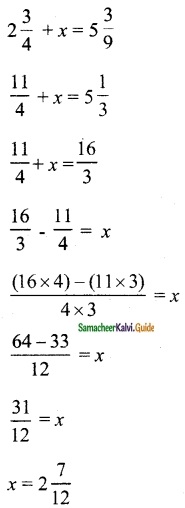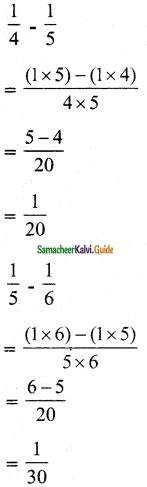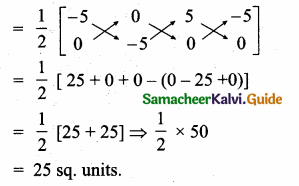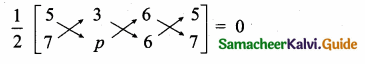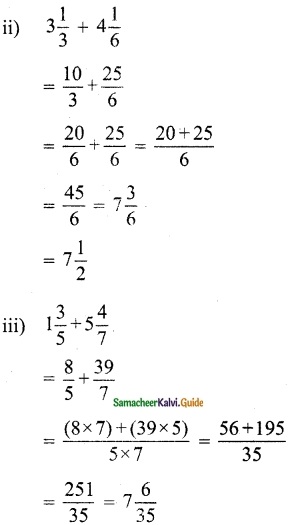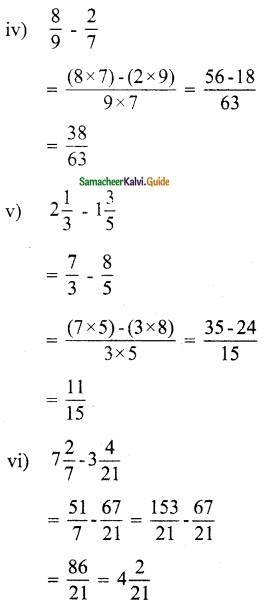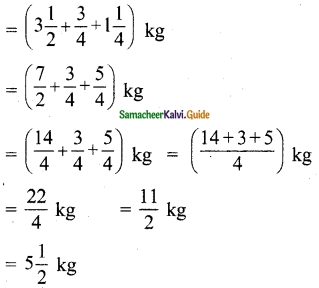Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.2 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.2
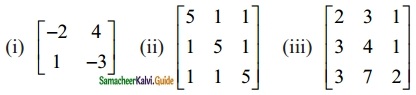
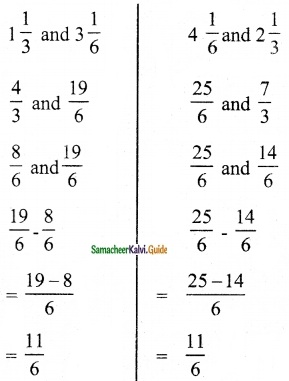
Question 1.
Find the rank of the following matrices by minor method:
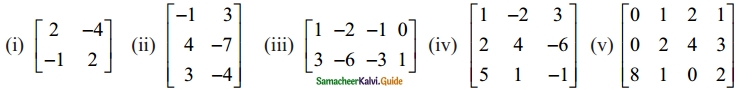
Solution:
(i) A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -4 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)
A is a matrix of order 2 × 2 and p(A) ≤ 2
Second order minor
|A| = \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -4 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)
= 4 – 4 = 0
∴p(A) ≠ 2
First order minor is non vanishing
p(A) = 1
(ii) A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
-1 & 3 \\
4 & -7 \\
3 & -4
\end{array}\right]\)
A is a matrix of order 3 × 2 and p(A) ≤ 2
Second order minor
\(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 3 \\ 4 & -7 \end{bmatrix}\)
= 7 – 12 = -5 ≠ 0
∴ p(A) = 2
(iii) A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1 & -2 & -1 & 0 \\
3 & -6 & -3 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
A is a matrix of order 2 × 4 and p(A) ≤ 2
Second order minor
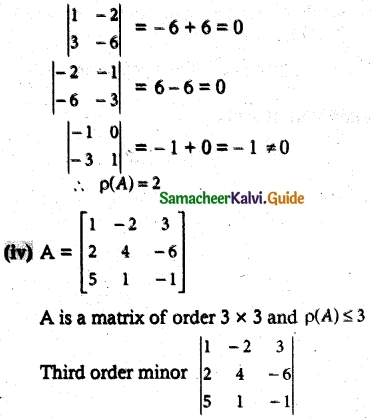
= 1(-4 + 6) + 2(-2 + 30) + 3(2 – 20)
= 2 + 56 – 54 = 4 ≠ 0
∴p(A) = 3
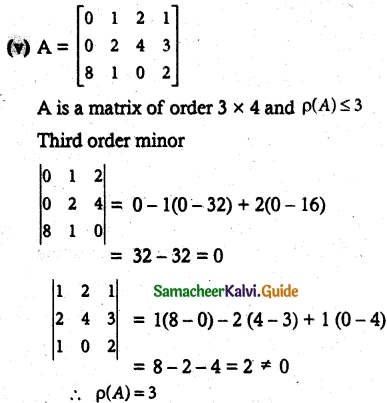
![]()
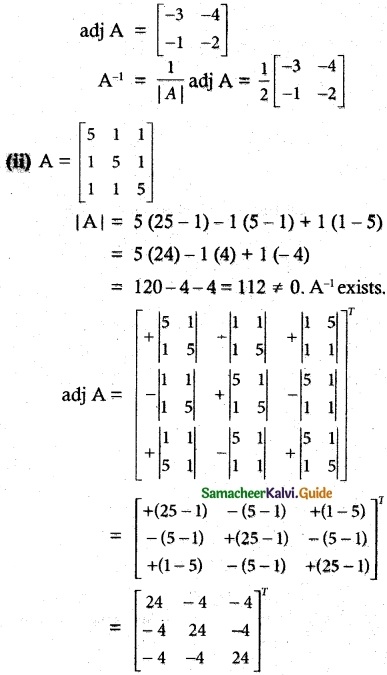
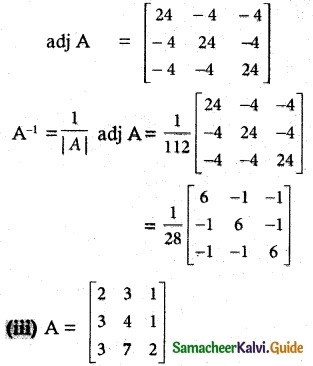
Question 2.
Find the rank of the following matrices by row reduction method:
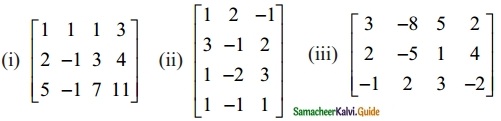
Solution:
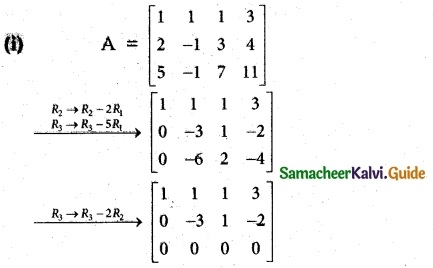
The last equivalent matrix is in row echelon form. It has two non-zero rows.
∴ p(A) = 2
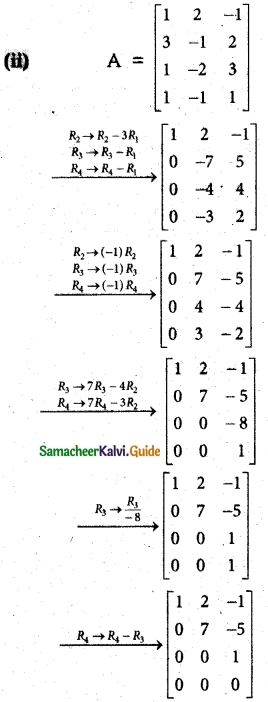
The last equivalent matrix is in row echelon form. It has three non-zero rows.
∴ p(A) = 3
![]()
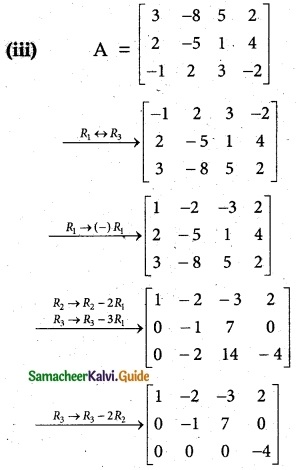
The last equivalent matrix is in row echelon form. It has three non-zero rows.
∴ p(A) = 3
![]()
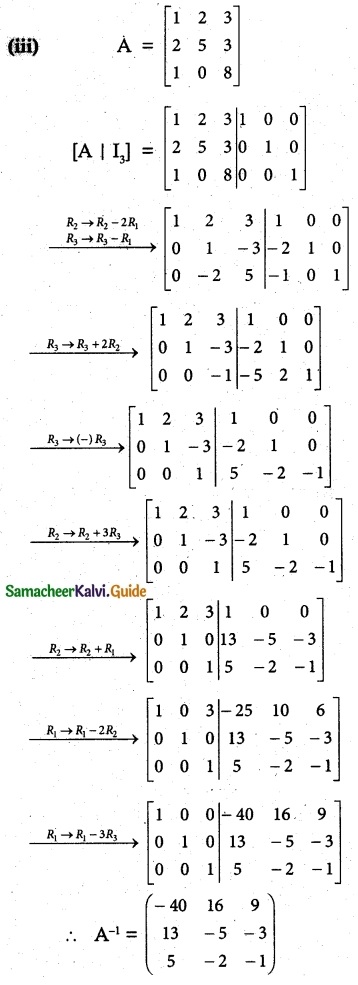
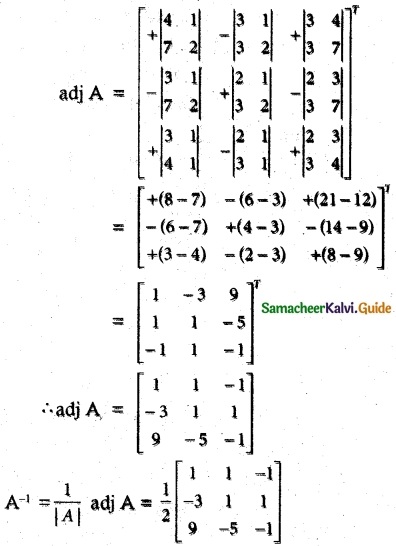
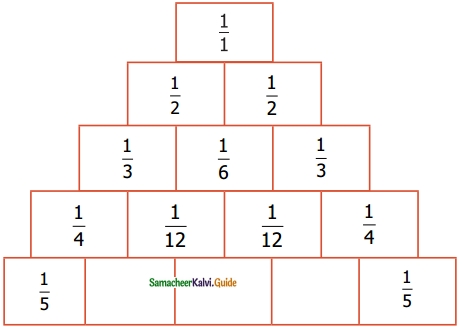
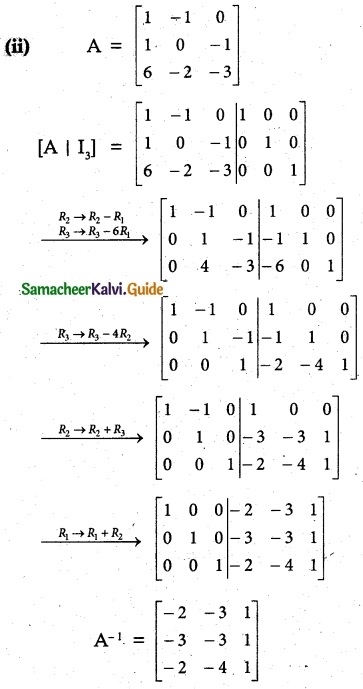
Question 3.
Find the inverse of each of the following by Gauss-Jordan method:
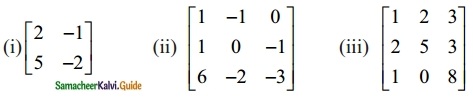
Solution:
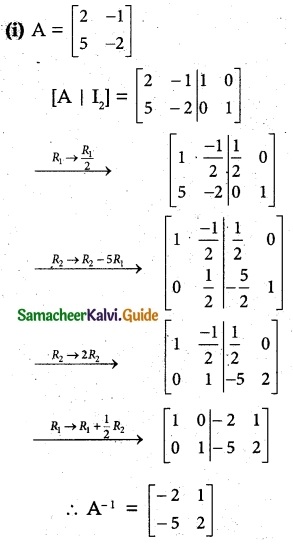
![]()
![]()