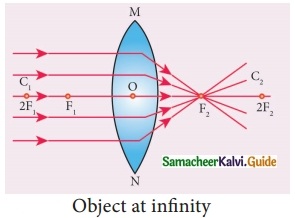
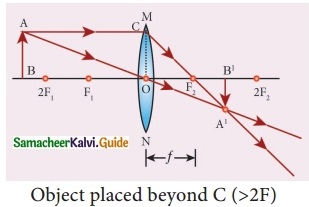
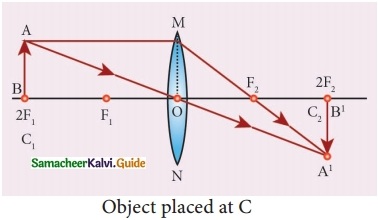
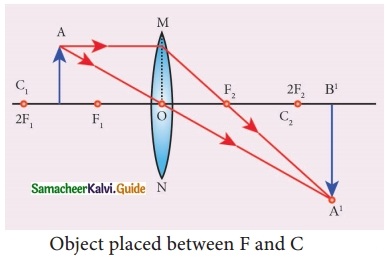
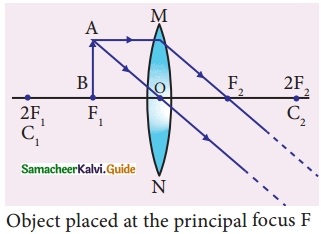
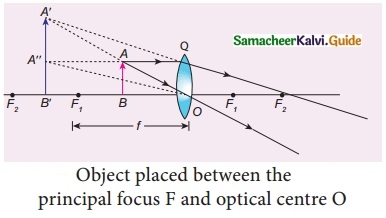
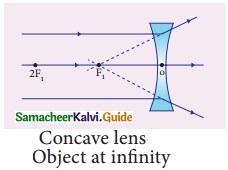
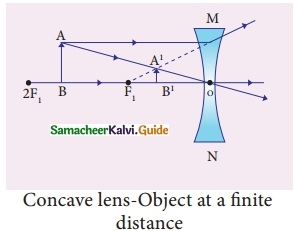
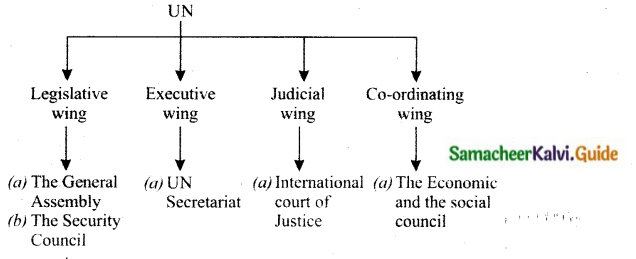
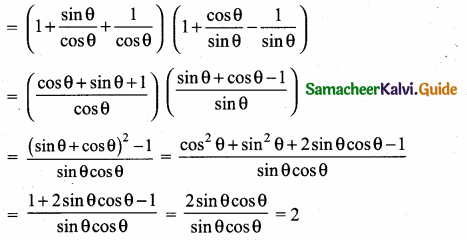
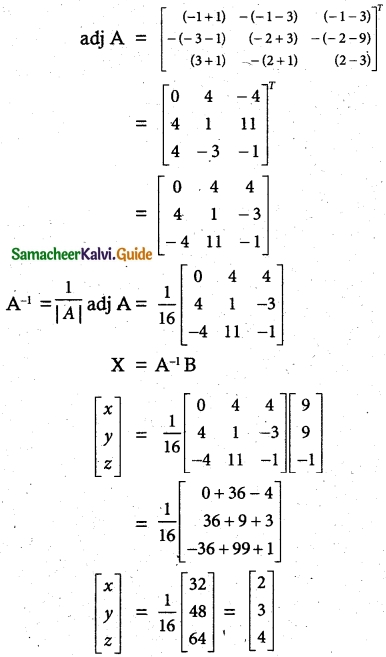
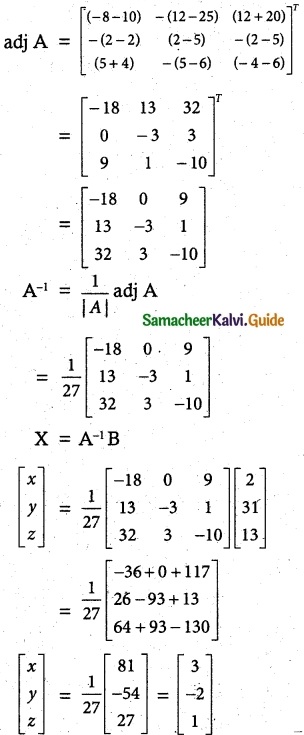
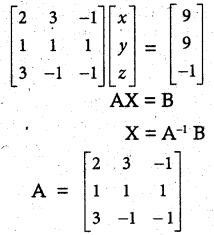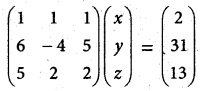Students can download 10th Social Science History Chapter 4 The World after World War II Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions History Chapter 4 The World after World War II
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science The World after World War II Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Who was the first director of Whampoa Military Academy?
(a) Sun Yat-Sen
(b) Chiang Kai-Shek
(c) Michael Borodin
(d) Chou En Lai
Answer:
(b) Chiang Kai-Shek
Question 2.
Which American President followed the policy of containment of Communism?
(a) Woodrow Wilson
(b) Truman
(c) Theodore Roosevelt
(d) Franklin Roosevelt
Answer:
(b) Truman
![]()
Question 3.
When was People’s Political Consultative Conference held in China?
(a) September 1959
(b) September 1948
(c) September 1954
(d) September 1949
Answer:
(d) September 1949
Question 4.
The United States and European allies formed to resist any Soviet aggression in Europe.
(a) SEATO
(b) NATO
(c) SENTO
(d) Warsaw Pact
Answer:
(b) NATO
Question 5.
Who became the Chairman of the PLO’s Executive Committee in 1969?
(a) Hafez al-Assad
(b) Yasser Arafat
(c) Nasser
(d) Saddam Hussein
Answer:
(b) Yasser Arafat
Question 6.
When was North and South Vietnam united?
(a) 1975
(b) 1976
(c) 1973
(d) 1974
Answer:
(b) 1976
Question 7.
Where was Arab League formed?
(a) Cairo
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Syria
Answer:
(a) Cairo
![]()
Question 8.
When was the Warsaw Pact dissolved?
(a) 1979
(b) 1989
(c) 1990
(d) 1991
Answer:
(d) 1991
II. Fill in the blanks
- ………………. was known as the “Father of modern China”.
- in 1918, the society for the study of Marxism was formed in ………………. University.
- After the death of Dr. Sun Yat-Sen, the leader of the Kuomintang party was ……………….
- ……………….. treaty is open to any Arab nation desiring peace and security in the region.
- The treaty of ………………. provided for mandates in Turkish -Arab Empire.
- Germany joined the NATO in ……………….
- ………………. was the Headquarters of the Council of Europe.
- ………………. treaty signed on February 7,1992 created the European Union.
Answers:
- Dr. Sun Yat-Sen
- Peking
- Chiang-Kai-Sheik
- Central Treaty organisation
- Versailles
- 1955
- Strasbourg
- Maastricht
III. Choose the correct statement / statements
Question 1.
(i) In China (1898) the young emperor, under the influence of the educated
minority, initiated a series of reforms known as the 100 days of reforms.
(ii) The Kuomintang Party represented the interests of the workers and peasants.
(iii) Yuan Shih-Kai had lost prestige in the eyes of Nationalists, when he agreed to the demand of Japan to have economic control of Manchuria and Shantung.
(iv) Soviet Union refused to recognize the People’s Republic of China for more than two decades.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) In 1948, the Soviets had established left wing government in the countries of Eastern Europe that had been liberated by the Soviet Army.
(ii) The chief objective of NATO was to preserve peace and security in the North Atlantic region.
(iii) The member countries of SEATO were committed to prevent democracy from gaining ground in the region.
(iv) Britain used the atomic bomb against Japan to convey its destructive capability to the USSR.
(a) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): America’s Marshall Plan was for reconstruction of the war¬. ravaged Europe.
Reason (R): The US conceived the Marshal Plan to bring the countries in the Western Europe under its influence.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A)and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
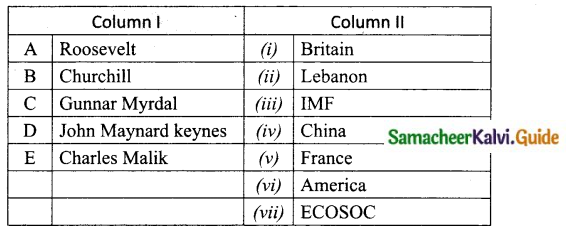
IV. Match the following

Answer:
A. (ii)
B. (iii)
C. (iv)
D. (v)
E. (i)
V. Answer briefly
Question 1.
Write any three causes for the Chinese Revolution of 1911.
Answer:
Three causes of the Chinese Revolution of 1911 are
- The government of Manchu dynasty began to disintegrate with the death of the Empress Dowager Cixi in 1908. The new emperor was two-years old and the provincial governors began to assert their independence. In October 1911 the local army mutinied and the revolt spread.
- There were a few middle class leaders. Dr. Sun Yat-sen was one among them. He took part in the rising against the Manchus in 1895. The rising failed and Sun Yat-Sen was sent in the prison. But he continued to spread nationalist ideas.
- Yuan Shih-Kai, who had earlier served as a minister in the Manchu administration, persuaded those responsible for the ascension of the young Emperor to prevant on him to abdicate.
Question 2.
Explain how in 1928 Kuomintang and Chiang-Kai Shek established Central Government in China.
Answer:
Chiang Kai-shek started conquering China. Starting from Canton, in 1928, he captured Peking and also removed all communists in the Kuomintang party. Thus, he established Central government in China.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on Mao’s Long March.
Answer:
Mao was an active leader who had gained full control of the Chinese Communist Party, by 1933. In 1934, he organised communist army of about 100,000 and set out on a long March. The marchers were continually harassed by Kuominatang forces, by local war lords and by unfriendly tribesmen of the 100,000 who set out, only 20,000 finally arrived in northern Shemi in late 1935, after crossing nearly 6000 miles. They were soon poined by other communist armies. By 1937, Mao had become the leader of over 10 million people. Mao’s Long March, as it is called so, has become legendary in the history of China.
Question 4.
What do you know of Baghdad Pact?
Answer:
In 1955, Turkey, Iraq, Great Britain, Iran and Pakistan signed a pact known as Baghdad pact. In 1958, when United States joined, then it was called as Central Treaty organization. The treaty was open to any Arab nation desiring peace and security in their region. It was dissolved in 1979.
Question 5.
What was the Marshall Plan?
Answer:
The Marshall Plan was an American initiative passed in 1948 to and Western Europe, in which the United States gave over $12 Billion in economic assistance to help rebuild Western European economies after the end of World War II. It operated for four years beginning in April 1948. The goals of the United States were to rebuild war-tom regions, modernise industry and improve European prosperity.
Question 6.
The Suez Canal crisis confirmed that Israel had been created to serve the cause of western interests-Elaborate.
Answer:
In 1956, Egypt invaded Suez Canal under Colonel Nasser and nationalized it. With the failure of diplomacy, Britain and France decided to use force. They bombed Egyptian air fields as well as Suez Canal area. However, United States and United Nations pressure, all the three invaders withdrew from Suez Canal.
Question 7.
Write a note on Third World Countries.
Answer:
The capitalist countries led by the US were politically designated as the First Worlds, while the communist states led by the Soviet Union came to be known as the Second World states, outside these two were called third World. During the Cold War, third World consisted of the developing world the former colonies of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. With the break up of the Soviet Union in 1991, and the process of globalisation, the term Third World has lost its relevance.
Question 8.
How was the Cuban missile crisis defused?
Answer:
In April 1961, on the island of Bay of Pigs, U.S bombed Cuban airfields and surrounded Cuba, with their warships. At the same time, USSR was secretly installing nuclear missiles in Cuba. Finally when Soviet President Khrushchev agreed to withdraw the missiles, the Cuban missile-crisis defused.
![]()
VI. Answer all the questions under each caption
Question 1.
Cold War
(a) Name the two military blocs that emerged in the Post-World War II.
Answer:
United States and the Soviet Union were the two military blocs that emerged in the post World War-II.
(b) Who coined the term “Cold War” and who used it first?
Answer:
The term Cold war was first coined by the English writer George Orwell in 1945 and it was used for the first time by Bernard Baruch, a multimillionaire from USA.
(c) What was the response of Soviet Russia to the formation of NATO?
Answer:
Warsaw Pact was the response of Soviet Russia to the formation of NATO.
(d) What was the context in which Warsaw Pact was dissolved?
Answer:
With the Break-up of USSR in 1991, the Warsaw Pact was dissolved.
Question 2.
Korean War
(a) Who was the President of North Korea during the Korean War?
Answer:
Kim II was the President of North Korea during the Korean War.
(b) Name the southern rival to the President of North Korea.
Answer:
Syngman Rhee
(c) How long did the Korean War last?
Answer:
The Korean War lasted three years
(d) What was the human cost of the War?
Answer:
The human cost was enormous, there were 500,000 western casualties and three times that number on the other side. Approximately two million Korean civilian died.
Question 3.
Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)
(a) When and where was the first conference on Non-Aligned Movement held?
Answer:
At Belgrade, in 1961, the first conference on NAM was held.
(b) Who were the prominent personalities present in the first conference?
Answer:
The prominent personalities present in the first conference were Tito (Yugoslavia), Nasser (Egypt), Nehru (India), Nikrumah (Ghana), Sukrano (Indonesia),.
(c) What were the objectives of NAM?
Answer:
Peaceful co-existence, commitment to peace and security.
(d) List out any two basic principles of Non-Alignment Movement enunciated in the Belgrade Conference.
Answer:
- Non-Alignment with any of the two super powers (USA/USSR).
- Fight all forms of colonialism and Imperialism.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Estimate the role of Mao Tse tung in making China a communist country.
Answer:
- Mao was greatly influenced by the ideas of Max and Lenin. He wanted to make China a communist country. So, he became active in the political activities of Hunan from the year 1912.
- After the death of Sun Yat-Sen in 1925, The Kuomintang was organised under the leadership of Chang Kai-Shek. Being an avowed critic of communists, Chiang removed all the important position holders in the Communist Party including Mao Tse Tung to weaken the party. However, the communists continued to influence the workers and peasants the Kuomintang represented the interests of landlords and capitalists.
- Mao had understood that the Kuomintang grip on the towns was too strong. So, he started organising the peasantry. When the relationships between Kuomintang and Communist Party broke, a few hundred Communist-led by Mao retreated into the wild mountains on the border between the provinces of Kiangsi and Hunan. The Kuomintang could not penetrate the mountains.
- Meanwhile, the campaign against the communists got distracted as Chiang Kai-Shek had to deal with the constant threat from Japan.
- By 1933 Mao had gained full control of the Chinese Communist Party. In 1934, he set out on a long march with the help of about 100,000 communist army. He also got support of other communist armies.
- By 1937, Mao had become the leader of over 10 million people. He organised workers and peasants councils in villages of Shensi and Kansu and finally got success in making China a communist country.
![]()
Question 2.
Attempt an essay on the Arab-lsraeii wars of 1967 and 1973.
Answer:
- Before the creation of the State of Israel in 1948, all Arabs and their . descendants lived in the Palestine.
- Ever since the formation, the Palestinian Liberation organisation (PLO). Israel came to be attacked by the Palestinian Guerrilla groups based in Syria, Lebanon and Jordan.
- Israel resorted to violent military force .
- In November 1966, an Israeli strike on the village of Al-Samu in the west bank of Jordan killed 18 people and wounded 54 people.
- Israel’s air battle with Syria in April 1967 ended in the shooting down of six Syrian MIG fighter jets.
- After air battle with Syria, when Arab States were mobilized by Nasser on June 5th Israel staged a sudden air strike that destroyed more than, 90% of Egypt’s air force on the tarmac.
- Later, Egypt and Syria under Presidents Anwar Sadat and Hafez-al- Assad respectively concluded a secret agreement in January 1973 to bring their armies under one command.
- When peace deals did not work out with Israel, Egypt and Syria launched a sudden and surprise attack on the Yom Kippur religious holiday on 6th October 1973.
- Though Israel suffered heavy casualities, it finally pushed back the Arab forces.
- Due to U.N intervention, Israel was forced to return and Arabs gained nothing.
- U.S succeeded in showing their control on their region and oil resource, led to U. S led war against Iraq in 1991.
Question 3.
Narrate the history of transformation of Council of Europe into an European Union.
Answer:
(i) After World War II, it was decided to integrate the states of western Europe. One of the chief objectives was to prevent further European wars by ending the rivalry between France and Germany. In May 1949, ten countries met in London and signed a form called Council of Europe
(ii) Since the Council of Europe had no real power, a proposal to set up two European organisations were made. Accordingly, the European Defence Community (EDC) and the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) were established. Six countries belonging to ECSC signed the treaty of Rome which established the European Economic Community (EEC) or the European Common Market, with headquarters at Brussels.
(iii) The EEC facilitated the elimination of barriers to the movement of goods and services, capital, and labour. It also prohibited public policies or private agreements that restricted market comptetion. Throughout the 1970s and 80s the EEC kept expanding its membership.
(iv) The single European Act came into force on July 1, 1987. It significantly expanded the EEC’s scope giving the meetings of the EPC a legal basis. It also called for more intensive coordination of foreign policy among member countries. According to the SEA each member was given multiple votes, depending on the countries population.
(v) The Maastricht (Netherlands) Treaty signed on February 7, 1992, created the European Union (EU). Today the European Union has 28 member states, and is functioning from its headquarters at Brussels, Belgium.
![]()
VIII. Activity
Question 1.
Divide the class into two groups. Let one group act as supporters of USA and the other group act as supporters of Soviet Union, Organise a debate.
Answer:
One group of students act as the supports of USA and the other group act as supporters of Soviet Union on their role in the cold war era.
(Students can have debate based on the following aspects)
During the time of cold war, the two super powers that emerged was USA and USSR.
Strengths of USA:
- Strongest navy both the Pacific and Atlantic.
- Continued and strong economic position that the USA held in the beginning till the end.
- Foreign policy of the USA. The actions of USA during the cold war era, very powerful and could guarantee others the strong power of the nation is to prevent communism spreading elsewhere.
- The country was able to generate the vast amount of wealth necessary to sustain the investment in weapons, technology and other operations.
- USA was also technologically powerful in target finding, tracking, sensors etc.
- The Truman’s doctrine was used throughout the war time. The doctrine helped USA to negotiate with other states to adopt capitalism.
Strengths of USSR:
- Strongest land based military, especially tanks.
- USSR developed air defense equipment and networks.
- Spread of Communism joined together backed USSR.
- As against NATO, USSR also formed military block, the Warsaw pact.
- With Western European countries USSR facilitated trade relations.
- Highly strengthened space exploration.
In the end of cold war, the Soviet Union fell, and the Communism expired.
Question 2.
Involving the entire class, an album may be prepared with pictures relating to Korean, Arab-lsraeli and Vietnam Wars to highlight the human sufferings in terms of death and devastation.
Answer:
Students should go to the search engine in google and type “The War’s impact on the Korean peninsula and trace the article of the journal of America – East Asia Relations” for a detailed Report.
Korean War: To give a sample answer: According to a U.S. Department of state publication, the number of killed, wounded and missing from the Armed forces of the Republic of Korea exceeded 4,00.000. From the U.S. side, 1,42,000. In addition, the heavy toll in death and injuries to the civilian population as well as wide property damage.
Arab-Israel War: Students should trace the answer from the google search engine as: The U.N. Report on Israel’s Gaza War.
To give a sample answer: From the 183 page report of the U.N. report, it is very clear that many civilians died. More than 6,000 Israeli airstrikes, 14,500 tank shells and 35,000 artillery shells led to the destruction of about 18,000 dwellings in Gaza. Nearly 1,462 Palestinian civilians, 299 women and 551 children were killed (According to U.N. Investigation). In Israel six civilians and 67 soldiers were killed.
Vietnam War: Students should trace the answer in the google search engine as “The War’s effect on the Vietnamese Land and People” for a detailed report.
To give a sample answer: About 58,000 American soldiers were killed and another 3,04,000 were wounded. Since most of the fighting took place in Vietnam, an estimated 4 million Vietnamese were killed on both sides including as many as 1 -3 million civilians. Many Vietnamese in country side turned into homeless refuges. Many forms and forests were destroyed.
Along with the detailed report, students should collect pictures showing Korea, Arab-Israel and Vietnam War, highlighting human sufferings. Students should click to google search engine and go to → Images → then type Korean War pictures / Arab Israel War pictures / Vietnam War pictures, download it take a print out of its and paste it in a A4 sheet paper or an a chart paper neatly and create an album.
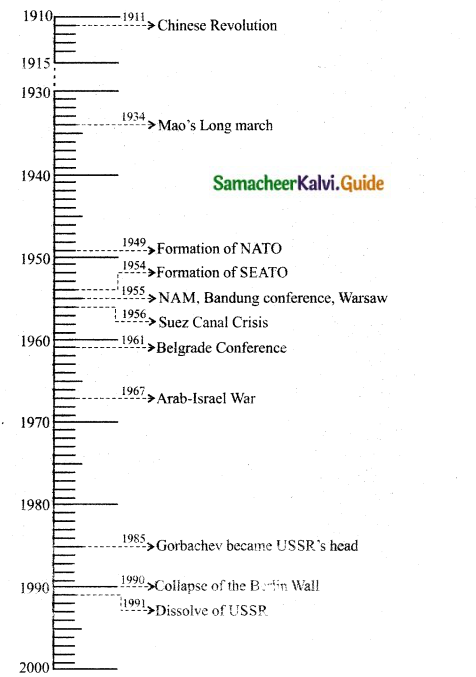
Timeline:
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science The World after World War II Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The emergence of ……………. and ……………. as super powers resulted in the division of the World into two block after World War II.
(a) Japan, USA
(b) USA, USSR
(c) China, Japan
(d) USA, Germany
Answer:
(b) USA, USSR
Question 2.
Dr.Sun yat-sen was born in a poor family near ………
(a) Canton
(b) France
(c) Spain
Answer:
(a) Canton
Question 3
……………. was called the father of modern China.
(a) Chiang-Kai-Shek
(b) Yuan-Shi-Kai
(c) Mao-Tse-Tung
(d) Dr. Sun Yat-Sen
Answer:
(d) Dr. Sun Yat-Sen
Question 4.
Mao was born in ……… in South – East China.
(a) Cambodia
(b) Vietnam
(c) Hunan
Answer:
(c) Hunan
Question 5.
Yuan-Shi-Kai died in the year …………….
(a) 1912
(b) 1913
(c) 1915
(d) 1916
Answer:
(d) 1916
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a part of Indo – China?
(a) Cambodia
(b) China
(c) Vietnam
Answer:
(b) China
Question 7.
The Historical Long March set out in China in …………….
(a) 1935
(b) 1937
(c) 1934
(d) 1936
Answer:
(c) 1934
Question 8.
In which of the following was indentured Vietnamese labour widely used?
(a) Rice cultivation
(b) Rubber plantation
(c) Industry
Answer:
(b) Rubber plantation
![]()
Question 9.
……………. was the leader of the people’s Republic of China.
(a) Marshall
(b) Truman
(c) Mao-Tse-Tung
(d) Chiang-Kai-shek
Answer:
(c) Mao-Tse-Tung
Question 10.
Ho Chi Minh means ………
(a) He, Who enlightens
(b) Enlightenment
(c) The Enlightened one
Answer:
(a) He, Who enlightens
Question 11.
The Idea of European self-help programme financed by the United States was called as …………….
(a) NATO
(b) SEATO
(c) ECA
(d) Marshall plan
Answer:
(d) Marshall plan
Question 12.
EURATOM was established by the ………
(a) Treaty of Nanking
(b) Treaty of Rome
(c) Treaty of London
Answer:
(b) Treaty of Rome
Question 13.
The term ‘cold war’ was first coined by the English writer …………….
(a) Shakespeare
(b) George Orwell
(c) William Dexter
(d) Peter Alphonse
Answer:
(b) George Orwell
Question 14.
As a part of Marshall plan financing, European nations received nearly ……………. billion in aid.
(a) $ 12
(b) $ 11
(c) $ 15
(d) $ 13
Answer:
(d) $ 13
Question 15.
Greece and Turkey joined NATO in the year …………….
(a) 1945
(b) 1947
(c) 1952
(d) 1955
Answer:
(c) 1952
Question 16.
……………. was otherwise called as pact.
(a) NATO
(b) CENTO
(c) SEATO
(d) EC SC
Answer:
(d) EC SC
Question 17
……………. are included as member countries in NATO.
(a) Canada, Belgium
(b) U.K., Portugal
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 18.
NATO had ……………. members by the year 2017.
(a) 30
(b) 51
(c) 29
(d) 24
Answer:
(c) 29
Question 19.
In December 1954, a conference of eight European nations took place in Moscow. This was called as …………….
(a) Warsaw pact
(b) Counter to NATO
(c) SEATO
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 20.
The headquarters of the Warsaw pact was …………….
(a) Belgium
(b) Poland
(c) Moscow
(d) Romania
Answer:
(c) Moscow
![]()
Question 21.
The Korea was partitioned into North and South Korea in the year …………….
(a) 1944
(b) 1945
(c) 1946
(d) 1947
Answer:
(b) 1945
Question 22.
With the collapse of the ……………. the idea of non-alignment lost relevance.
(a) Berlin
(b) CIA
(c) ECA
(d) Soviet Union
Answer:
(d) Soviet Union
Question 23.
The NAM held its first conference at ……………. in 1961.
(a) Bandung
(b) Belgrade
(c) Thailand
(d) Philippine
Answer:
(b) Belgrade
Question 24.
The World Zionist Organisation was founded in the year …………….
(a) 1857
(b) 1887
(c) 1897
(d) 1867
Answer:
(c) 1897
Question 25.
Castro nationalised the U.S. owned ……………. companies.
(a) cotton
(b) sugar
(c) oil
(d) petrol
Answer:
(b) sugar
Question 26.
The Cuban Missile crisis was defused by ……………. as the agreed to withdraw the missiles.
(a) Khrushchev
(b) Fidel Castro
(c) Leumi
(d) Stem Gang
Answer:
(a) Khrushchev
![]()
Question 27.
In the Arab World, it is treated as the ……………. when large number of Arabs become refugees.
(a) Catastrophe
(b) Nakbah
(c) Negev and (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 28.
For resolving the Suez Canal Crisis, ……………. from Indian played a crucial role.
(a) Gandhi
(b) Nehru
(c) Bose
(d) Tilak
Answer:
(b) Nehru
Question 29.
Arab-lsrael war took place in the years …………….
(a) 1967,69
(b) 1969,74
(c) 1967,73
(d) 1972,73
Answer:
(c) 1967,73
Question 30.
……………. became the first president of the state of Palestine in 1989.
(a) Anwar Sadat
(b) Yasser Arafat
(c) Nasser Arafat
(d) Nasser Hussain
Answer:
(b) Yasser Arafat
Question 31.
By the end of second world war, ……………. controlled the northern half of Vietnam.
(a) Vietminh
(b) Ho-Chi-Minh
(c) Ngo Dinh Diem
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Vietminh
Question 32.
……………. controlled the southern half of the Vietnam.
(a) Viet Minh
(b) Bao Dai
(c) Ngo Dinh Diam
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Bao Dai
Question 33.
The North and the South Vietnam were formally united as one country in …………….
(a) 1973
(b) 1976
(c) 1975
(d) 1974
Answer:
(b) 1976
Question 34.
In May 1949, ten countries met in ……………. and signed to form a council of Europe.
(a) Japan
(b) Syria
(c) London
(d) France
Answer:
(c) London
Question 35.
To prevent further European War ……………. was founded.
(a) Council of Europe
(b) Council of Trent
(c) ECSC
(d) EU
Answer:
(a) Council of Europe
![]()
Question 36.
……………. did not join the EEC, when it was formed.
(a) U.K
(b) U.S.A
(c) USSR
(d) Italy
Answer:
(a) U.K
Question 37.
Britain, voted to exit the EU in the year …………….
(a) 2015
(b) 2014
(c) 2017
(d) 2019
Answer:
(c) 2017
Question 38.
West Berlin was supported by …………….
(a) USA
(b) UK
(c) USSR
(d) Germany
Answer:
(a) USA
Question 39.
East Berlin was supported by …………….
(a) USA
(b) UK
(c) USSR
(d) Germany
Answer:
(c) USSR
Question 40.
Germany was officially united on …………….
(a) 1987
(b) 1989
(c) 1990
(d) 2003
Answer:
(c) 1990
Question 41.
in 1985, ……………. became the head of the USSR.
(a) Mikhai Gorbachev
(b) Reagen
(c) Stalin
(d) Kohl
Answer:
(a) Mikhai Gorbachev
Question 42.
The Chernobyl disaster took place in the year …………….
(a) 1987
(b) 1984
(c) 1986
(d) 2006
Answer:
(c) 1986
Question 43.
Gorbachev announced his resignation on …………….
(a) 21st November
(b) 25th December
(c) 2nd October
(d) 15th August
Answer:
(b) 25th December
Question 44.
USSR dissolved formally In the year …………….
(a) 31st Dec. 1990
(b) 30th Dec. 1991
(c) 31st Dec. 1991
(d) 28,h Feb. 1991
Answer:
(c) 31st Dec. 1991
![]()
Question 45.
……………. was an ally of Gorbachev.
(a) Yeltsin
(b) Brezhnev
(c) Khrushchev
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Yeltsin
II. Fill in the blanks
- ………………… and ………………… were the Superpowers after the World War II.
- The cold war period ended with the fall of …………………
- Empress Dowager died in ………………… led to the disintegration of the Manchu dynasty.
- Kuomintang party of China was otherwise called as ………………… party.
- ………………… was the ultimate aim of Dr. Sun Yat-sen’s party.
- The Chinese revolution broke out in the year …………………
- The first director of the Whampoa Military academy was …………………
- The campaign against the communists led by Chiang-Kai-Shek was distracted by ………………… and warlords.
- By ………………… Mao became the leader of the Chinese people.
- Over ………………… delegates from various countries attended the people’s political consultative conference.
- When Japanese surrendered in 1945, the Japanese areas were occupied by the …………………
- By the year …………………, communist control has been established over most parts of China.
- The two mighty communist powers in the world were ………………… and …………………
- The term cold war was first coined by …………………
- ………………… nations became a part of Marshall’s plan of self-help programme.
- The Marshall plan funding ended in …………………
- ………………… was created to resist Soviet aggression in Europe.
- NATO means …………………
- NATO was formed in the year …………………
- The members of NATO agreed that, any armed attack on any one of them would be considered attack on …………………
- For the collective security of the South-east Asia, ………………… was formed in 1954.
- Member of SEATO were committed to prevent …………………
- SEATO was formed in 1954, after signing of the …………………
- ………………… was formed by Soviet Union as a counter to NATO.
- ………………… European nations attended the Warsaw pact in December 1954.
- The treaty on Warsaw pact was concluded on …………………
- The Warsaw pact was dissolved in …………………
- The Warsaw pact dissolved because of the break-up of …………………
- The Baghdad pact was otherwise called as …………………
- Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Pakistan and Great Britain signed a treaty in 1955, known as …………………
- When U.S.A joined the Baghdad pact, it was called by name …………………
- USA joined the Baghdad pact in the year …………………
- CENTO was dissolved in the year …………………
- Korea was partitioned as North Korea and South Korea in the year …………………
- The president of North Korea was …………………
- The party of Kim II was called as …………………
- The president of the South Korea was …………………
- The party of Syngman Rhee was …………………
- Korean War lasted for ………………… years.
- NAM refers to the …………………
- NAM was signed in ………………… at the ………………… conference.
- Bandung is a city in …………………
- With the collapse of ………………… the idea of NAM lost importance.
- CIA is a Central Intelligence Agency of …………………
- The Act of ………………… in Cuba, threatened American economic interests.
- USA bombed Cuban ………………… with the aim of overthrowing Castro’s regime.
- ………………… was the president of USSR, when the Cuban Missile crisis took place.
- Cuba was helped by …………………
- When USSR remove missile from Cuba, USA had to agree to remove missile from ………………… and …………………
- ………………… was a Zionist Terrorist Organisation.
- The Zionist Para-military organization was called as …………………
- The World Zionist organization was founded in the year …………………
- Jews living outside their ancient home scattered around North America and Europe was called as …………………
- ………………… Nationalised Suez Canal.
- India represented by ………………… played a crucial role in resolving the crisis.
- The Arab-lsraeli War took place in the years ………………… and …………………
- PLO refers to …………………
- PLO was formed in …………………
- ………………… was the prominent leader of Palestine.
- By the end of the Second World War, ………………… Controlled the northern half of Vietnam.
- South Vietnam was ruled by …………………
- America supported troops of ………………… Vietnam.
- The city of ………………… was renamed as Ho-Chi-Minh city.
- To create a United Europe to resist any threat from Soviet Russia, ………………… was formed.
- European Economic Community was otherwise called as …………………
- SEA refers to …………………
- According to the SEA, each member was given ………………… votes.
- The ………………… Treaty created the European Union.
- Maastricht is in …………………
- EU was created on Maastricht treaty signed on …………………
- The headquarters of the EU is at …………………
- Brussels is at …………………
- ………………… Germany was prosperous.
- ………………… Germany was suffering from lack of democracy and freedom.
- Germany was officially reunited on …………………
- Glasnost means …………………
- Perestroika means …………………
- ………………… was introduced by Gorbachev to restructure Soviet economic and political system.
- After Gorbachev, power fell into the hands of …………………
- For ………………… days, Soviet Union, continued to exist only in name.
- Soviet Union dissolved formally on 31st December …………………
- USSR split into ………………… countries.
- ………………… was the president of the newly independent Russian State.
- U.S.A. troops used ………………… weapons in their war against Vietnam.
- Napalm and Agent Orange are the names of incendiary …………………
Answers:
- USA and USSR
- Berlin Wall
- 1908
- National People’s Party
- Socialism
- 1911
- Chiang-Kai-Shek
- Japan
- 1937
- 650
- Kuomintang
- 1948
- Soviet Union, People’s Republic of China
- George Orwell
- Sixty
- 1951
- NATO
- North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
- 1949
- NATO
- SEATO
- Communism
- Manila Pact
- Warsaw Pact
- 8 (eight)
- May 14, 1955
- 1991
- USSR
- Central Treaty Organisation
- Baghdad Pact
- Central Treaty Organisation
- 1958
- 1979
- 1945
- Kim II
- People’s Republic of Korea
- Syngman Rhee
- The Republic of Korea
- three
- Non-Aligned Movement
- 1955, Bandung
- Indonesia
- Soviet Union
- America
- Castro
- Airfields
- Khrushchev
- USSR
- Turkey, Italy
- Stem Gang
- Irgun Zvai Leumi
- 1897
- Diaspora
- Colonel Nasser
- Nehru
- 1967, 1973
- Palestine Liberation Organisation
- 1948
- Yasser Arafat
- Viet Minh
- Ngo Dinh Diem
- South
- Saigon
- Council of Europe
- European Common Market
- Single European Act
- multiple
- Maastricht
- Netherlands
- Feb 7, 1992
- Brussels
- Belgium
- West Berlin’s
- East Berlin
- 3rd October 1990
- openness
- restructuring
- Perestroika
- Boris Yeltsin
- Six 81.1991
- 15
- Boris Yeltsin
- Bacteriological
- bombs
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement / statements
Question 1.
(i) The cold war period ended with the fall of Berlin Wall
(ii) Mao concentrated mainly on organizing the peasantry.
(iii) In 1937, the communist army of about 100,000 set out on the Long march.
(iv) Marshall plan funded nearly $ 15 billion.
(a) (ii and (ii) are correct
(b) (i) and (iii) are correct
(c) (ii and (iv) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct.
Answer:
(a) (ii and (ii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) The USSR was much concerned about the destruction caused by the Second World War.
(ii) The South East Asia Treaty organization was organised for the collective security of countries in South East Asia.
(iii) The Communist States led by the Soviet Union came to be known First World Countries.
(iv) The Capitalist countries led by the U.S.A. were politically designated as Second World Countries.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (iii), (iv) are wrong
(c) (i) and (iv) are correct
(d) (ii) and (iii) are correct.
Answer:
(b) (i), (iii), (iv) are wrong
Question 3.
(i) NAM refers to the Non-Aligned Movement.
(ii) The Single European Act of the EU as called as SEA.
(iii) Anwar Sadat was the president of the Palestine in 1989.
(iv) The fighters of South Vietnam were trained in guerrilla warfare.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (iii), (iv) are wrong
(c) (i) and (iv) are correct
(d) (ii) and (iii) are correct.
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 4.
(i) The Third World principally consist of the developing World.
(ii) With the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, and the process of globalization, the term has lost its relevance.
(iii) The former colonies of Asia, Africa, and Latin America were called as Third World Countries.
(iv) The division of Germany into West and East led to glaring differences in living standards.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are correct
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
(d) All the four are correct.
Answer:
(d) All the four are correct.
Question 5.
(i) Yeltsin worked as a Mayor of Moscow.
(ii) Yeltsin was returned to power with overwhelming support of a Moscow in 1899.
(iii) For twelve days, the Soviet Union continued to exist only in name.
(iv) On 28th February 1991, USSR was formally dissolved.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are correct
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
(d) All the four are correct.
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
![]()
Question 6.
(i) CENTO was otherwise called as Manila pact.
(ii) As a counter to SEATO, NATO was formed.
(iii) The Korean war helped to bring down the intensity of the Cold war.
(iv) The EEC eliminated barriers to the movement of goods, Capital and labour.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are wrong
(c) (i) and (iv) are correct
(d) All the four are correct.
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are wrong
Question 7.
(i) The Berlin Wall was just a physical barrier.
(ii) Berlin Wall divided East Germany and West Germany.
(iii) USA supported East Berlin.
(iv) USSR supported West Berlin.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are wrong
(c) (i) and (iv) are correct
(d) All the four are wrong.
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Yuan Shih-Kai of China lost prestige in his country.
Reason (R): He agreed to the demand of Japan to have economic control of Manchuria and Shantung.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Assertion (A): The rivalry that developed after World War 11 is referred to as “Cold War”.
Reason (R): This war did not take recourse to weapons.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Assertion (A): There was High military expenditure on both sides of USA and USSR.
Reason (R): Soviet Union tested the nuclear bomb and America used the nuclear bomb against Japan.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The U.S. and its European allies formed the NATO to wage war against Vietnam.
Reason (R): As a counter to the NATO, Soviet Union organised the Warsaw pact.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R.) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): A small country had succeeded in winning Independence and the greatest power of the World-The country Vietnam.
Reason (R): The help given to Vietnam by the Socialist Countries, the political support given by Asia and Africa is evident.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Sun Yat-sen sent Chiang Kai-shek to Moscow, in Russia. The Russians in turn sent Michael Borodin to China.
Reason {R): Chiang Kai-shek started conquering China from Canton.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 7.
Assertion (A): U.S.A. supported Diem government in South Vietnam. Reason (R): U.S. wanted to establish a strong government in South Vietnam.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
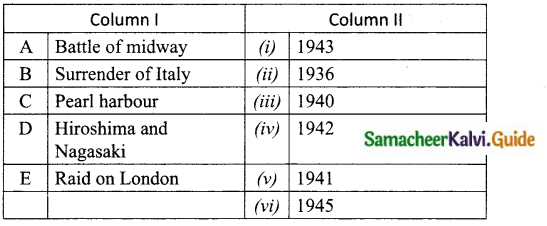
V. Match the following
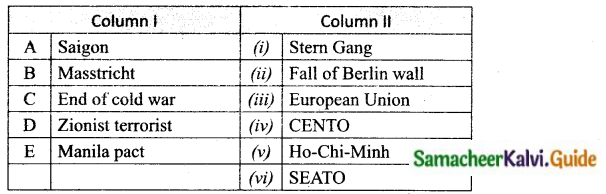
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iii)
C. (ii)
D. (i)
E. (vi)
![]()
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.

Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (vi)
VI. Answer briefly
Question 1.
Describe about Zionist movement.
Answer:
(i) In Palestine, the ancient home of Jews, only a few thousand Jews were living in 1900.
(ii) Some 15 million were scattered around Europe and North America.
(iii) These Jews had been subjected to systematic persecution for centuries.
(iv) But in the late nineteenth century, the persecution in Russia (Where two-thirds of the world’s jews lived), France and Germany was intense.
(v) Some Jews emigrated to Palestine, while many more went to the United States and Britain.
(vi) In 1896, Thodore Herzel, a Viennese journalist, published a pamphlet called the Jewish state in which he called for the creation of a Jewish national home. In 1897 the world zionist organisation was founded.
Question 2.
What was Truman’s policy?
Answer:
Truman, the president of USA announced a policy of containment of communism. This implies U.S. would support those countries which were threatened by USSR to spread communism.
Question 3.
Mention the initial member countries of the EU.
Answer:
- Belgium
- France
- Italy
- Luxemburg
- Netherlands
- West Germany
Question 4.
What is meant by SEA?
Answer:
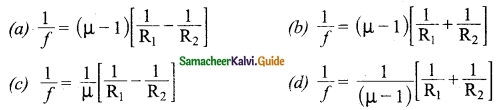
SEA refers to the single European Act which came into force on July 1,1987. According to the SEA, each member was given multiple votes depending on the country’s population. Its main aim is establishing a single market.
Question 5.
Name the organs of the EU.
Answer:
- European parliament
- Council of the European Union
- European commission
- Court of Justice
- Court of Auditors
![]()
Question 6.
Write a note on European Union.
Answer:
On February 7, 1992, the Maastricht Treaty that signed in Netherlands created the European Union. All the member countries of the EU will use common currency Euro, a single market and common Act. EU at present has 28 members with head quarters at Brussels, Belgium.
Question 7.
How was the European union formed?
Answer:
According to the Merger Treaty of 1967, the three communities namely the European coal and steel community, the European Economic community and the European Atomic Energy community were merged together to form the European union.
VII. Answer all the questions under each caption
Question 1.
People’s Republic of China
(a) Who was the leader of the People’s Republic of China?
Answer:
Mao Tse-Tung was the leader of the People’s Republic of China.
(b) Name the two mighty Communist powers of the world?
Answer:
The Soviet-Union and the people’s Republic of China.
(c) Who did not recognise People’s Republic of China and for how long?
Answer:
The UNO refused to recognise people’s Republic of China for more than twenty years.
(d) How did the government of Taiwan got recognition?
Answer:
The government of Chiang Kai-shek in Taiwan was given recognition ‘ due to the pressure from USA.
Question 2.
Achievements of EU
(a) What is the symbol of the Euro?
Answer:
The symbol of the Euro is €.
(b) What did the Euro eliminate?
Answer:
The Euro eliminated foreign exchange hurdles encountered by companies doing business across European border.
(c) How many members are there in the EU at present?
Answer:
At present, there are 28 members in the EU.
(d) Who allocates funds to European research projects?
Answer:
The European Research council.
Question 3.
Disintegration of The Soviet Union.
(a) Who became the head of USSR in 1985?
Answer:
Mikhail Gorbachev became the head of the USSR in 1985.
(b) What is meant by “thaw”?
Answer:
The “Thaw” refers to the period from the early 1950’s and 1960’s when repression and censorship in the Soviet Union was relaxed and millions of political prisioners were released. It was the period of Khrushchev’s reign.
(c) What is meant by Glasnost?
Answer:
Glasnost means openness. It was the policy of more transperancy and openness in the government policy of former Soviet Russia introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev.
(d) What is meant by Perestroika?
Answer:
Perestroika means restructuring. It refers to the programme introduced by Mikhail Gorbhachev to restructure Soviet economic and political system.
Question 4.
Berlin Wall
(a) Who constructed a wall which virtually cut off West Berlin and East Berlin? and when?
Answer:
East German began to construct a wall in 1961 which virtually cut off West Berlin and East Berlin.
(b) How was it guarded?
Answer:
It was guarded with watchtowers and other lethal impediments to stop people from the east.
(c) What does the Berlin wall symbolise?
Answer:
It was symbolic boundary between Communism and Capitalism.
(d) What happened with the fall of the Berlin wall?
Answer:
With the fall of the Berlin wall , followed by the collapse of the Soviet Union, the cold war came to an end.
VIII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Write a brief account of the life and achievements of Ho Chi Minh.
Answer:
He was born in a small town in Central Vietnam. He studied in French school that produced great leaders. After his studies he worked on a French liner operating between Saigon and Marseilles. He was greatly inspired by European communist parties, became member of commintem and was instrumental in bringing together competing nationalists groups to form the Vietnamese communist party in 1930. It was later renamed the Indo-Chinese communist party. After spending 30 years abroad in Europe, China Thailand, he returned to Vietnam in 1941. He became President of the Vietnam Democratic Republic in 1943.
After the split of Vietnam, he and the communists took control of North Vietnam. With the help of his government, National Liberation Front in the south fought for unification of the country. He fought hard to maintain the autonomy of Vietnam and till the end proved true to his name. Ho Chi Minh meaning He, Who Enlightens.
![]()
Question 2.
Illustrate the cold war developments in case of the Vietnam war. Narrate how North and South Vietnam unified as Independent Nation.
Solution:
- By 1945, the end of the second world war, Viet Minh controlled the northern half of Vietnam, led by Ho-chi- Minh.
- Viet Minh and french reached an agreement by which North Vietnam would be a free state.
- While French was helped by America, Viet Minh was helped by the new Chinese communist government.
- War broke out between them. Eventually , France troops were defeated.
- The Geneva conference that met on Korea and Indo China in 1954, decided that of Laos. Combodia and Vietnam. The independent states would be Laos and Cambodia. Vietnam, temporarily divided.
- While North Vietnam controlled by Viet Minh with leader Ho-Chi-Minh and south Vietnam would be under the leadership of Bao Dai.
- At the same time, South Vietnam was ruled by Ngo Dinh Diem.
- When U.S wanted to establish a strong Non-communist government in South Vietnam. In 1965, marines landed on Danang naval base and namely 2,10,000 traps in the country, j (ix) The U.S bombed both North and South.
- The fighters of North Vietnam trained in Guerrilla warfare sustained.
- America suffered heavy casualties , vast devastated and many were killed.
- The youth rebelled against the horrors of the war.
- The protest against the war spread all over the world.
- By 1975, the armies of the North and the only one party of South Vietnam called National Liberation front of South Vietnam attacked America.
- By 30th April 1975, all the American troops had withdrawn and capital of South Vietnam Saigon was liberated.
- North Vietnam and South Vietnam formally united as one country in 1976.
- The city of Saigon was renamed as the Ho-Chi-Minh city .
- Thus, the emergence of Vietnam as a united and Independent nation was an historic event.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the breakup of the Soviet Union.
Answer:
- In the middle of 1980’s Soviet Union economy was suffering.
- In 1985, Mikhail Gorbachev took over as the president of USSR.
- Gorbachev spoke about the need for openness (Glasnost) and Perestroika (restructuring).
- But his ideas of reform did not work out for him because, to compete with U.S, USSR need to allocate more funds to the military.
- The economic stagnation of the Soviet Union aggrevated tension and promoted nationalist feelings.
- In the year 1988, Mass protest broke out in Armenia and in the Baltic states.
- Gorbachev made attempts to stabilize his position by relying on conservative forces in 1989, 1991.
- But the massive miner’s strike interrupted. The series of worker’s strike under mined the communist regimes first in Poland, then in Hungary.
- The fall of Berlin wall in Germany, encouraged people to be united.
- Gorbachev made a last attempt to take a hard line against miner’s strike and huge demonstrations in Moscow in 1991.
- In response, the conservative forces in his government used troops in Moscow and held Gorbachev under house arrest.
- Power fell into the hands of Boris Yeltsin.
- In November 1991, eleven republics announced that they would establish a common wealth of independent states.
- On 25th Dec 1991 , Gorbachev resigned.
- For six days, the Soviet Union continued to remain only in name and at midnight on 31st December 1991 it was formally dissolved.
- The USSR was no more.