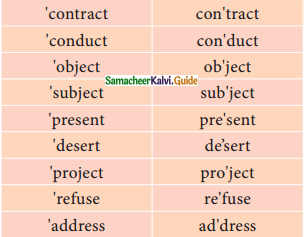
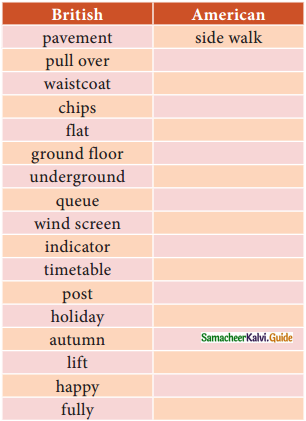
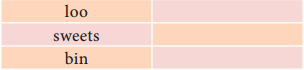
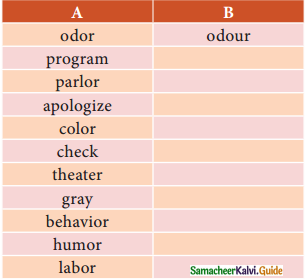
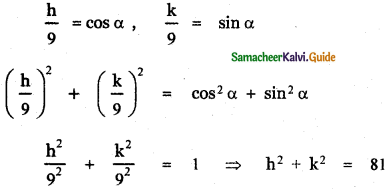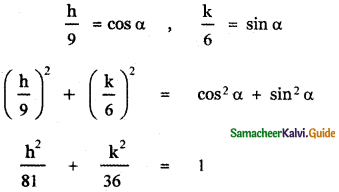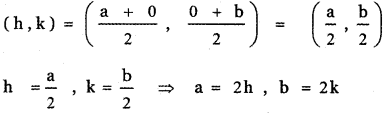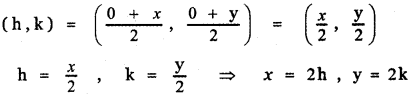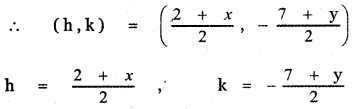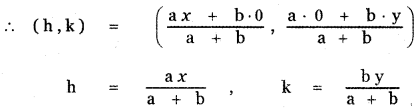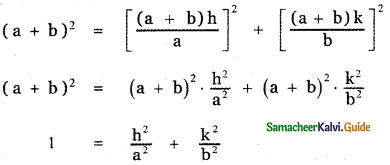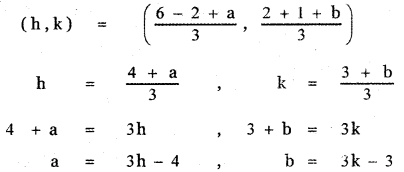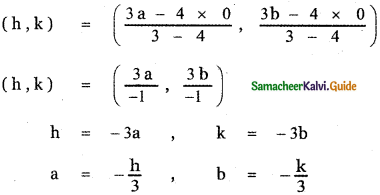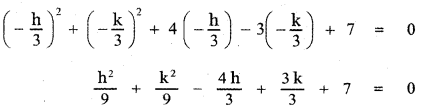Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Two Dimensional Analytical Geometry Ex 6.2 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Two Dimensional Analytical Geometry Ex 6.2
Question 1.
Find the equation of the lines passing through the point (1, 1):
(i) with y – intercept – 4
(ii) with slope 3
(iii) and (-2, 3)
(iv) and the perpendicular from the origin makes an angle 60° with x – axis.
Answer:
(i) with y – intercept – 4
The equation the line with slope m and having y – intercept b is y = mx + b ——- (1)
Given b = – 4
∴ (1) ⇒ y = m x – 4
Given this line passes through the point (1, 1)
∴ 1 = m 1 – 4 ⇒ m = 5
∴ The required equation is y = 5x – 4
![]()
(ii) Slope m = 3, passing through (x1, y1) = (1, 1)
Equation of the line is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
(i.e) y- 1 = 3(x – 1) ⇒ y – 1 = 3x – 3 ⇒ 3x – y = 2
(iii) (-2, 3)
The equation of line joining the two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is
![]()
Given (x1, y1) = (1, 1), (x2, y2) = (- 2, 3)
∴ The equation of the required line is
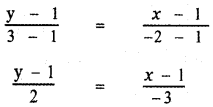
– 3 (y – 1) = 2 (x – 1)
– 3y + 3 = 2x – 2
2x + 3y – 2 – 3 = 0
2x + 3y – 5 = 0
(iv) The perpendicular from the origin makes an angle 60° with x – axis
The equation of the line in the normal form is x cos α + y sin α = p ——- (1)
Given α = 60°
∴ cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\) , sin 60° = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
(1) ⇒ x . \(\frac{1}{2}\) + y . \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) = p
x + √3 = 2p —— (2)
This line passes through the point (1,1)
∴ 1 + √3 = 2p
Substituting for p in equation (2)
∴ The required equation is x + √3y = 1 + √3
![]()
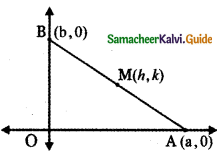
Question 2.
If P (r, c) is mid point of a line segment between the axes then show that \(\frac{x}{\mathbf{r}}+\frac{\mathbf{y}}{\mathbf{c}}\) = 2
Answer:
Let AB be the line segment intercepted between the axes. Let A be (a, 0) and B be (0, b)
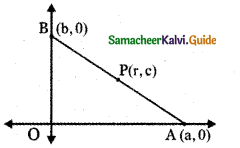
Given P (r, c) is the mid point of AB
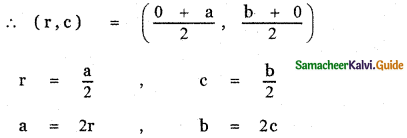
The equation of the line AB having x-intercept a and y-intercept b is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}\) = 1
Substituting for a, b in the above equation, we have

Question 3.
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (1, 5) and also divides the line segment between the coordinate axes in the ratio 3 : 10.
Answer:
Let the line divide the coordinate axis in the ratio 3 : 10.
∴ x-intercept = 3k
y-intercept = 10k
∴ The equation of the straight line is \(\frac{x}{3 k}+\frac{y}{10 k}\) = 1
This line passes through the point P (1, 5).

∴ The required equation is
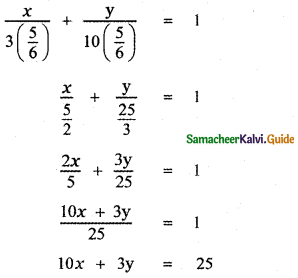
![]()
Question 4.
If p is length of perpendicular from origin to the line whose intercepts on the axes are a and b, then show that \(\frac{1}{\mathbf{p}^{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathbf{a}^{2}}+\frac{1}{\mathbf{b}^{2}}\)
Answer:
The equation of the line with x – intercept a and y – intercept b is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}\) = 1 ——- (1)
The length of the perpendicular from the origin (0, 0) to the line (1) is
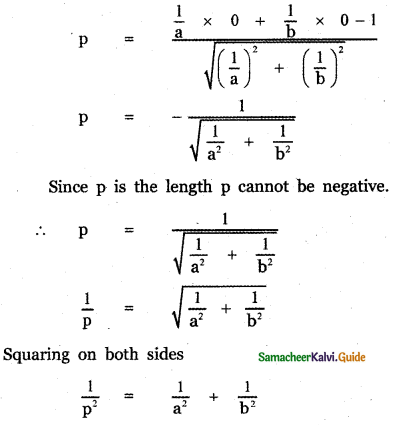
Question 5.
The normal boiling point of water is 100° C or 212° F and the freezing point of water is 0° C or 32° F.
(i) Find the linear relationship between C and F. Find
(ii) the value of C for 98.6° F and
(iii) the value of F for 38° C.
Answer:
(i) Choose Celsius degree along the x-axis and Fahrenheit degree along the y-axis.
Given a Freezing point in Celsius = 0°C
The freezing point in Fahrenheit degree = 32° F
∴ The Freezing point is (0°, 32°)
Also given Boiling point in Celsius = 100°C
The boiling point in Fahrenheit = 212° F
∴ The Boding point is (100°, 212°)
Let C denote the Celsius degree and F denote the Fahrenheit degree.
The equation of the path connecting the freezing point (0°, 32°) and the boiling point (100°, 212° ) is
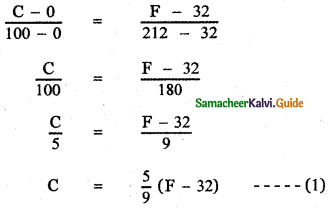
which is the required relation connecting C and F.
(ii) To find the value of C for 98.6° F
(1) For 98.6° F To find C.

(iii) To find the value of F for 38° C,
For 38° C To find F
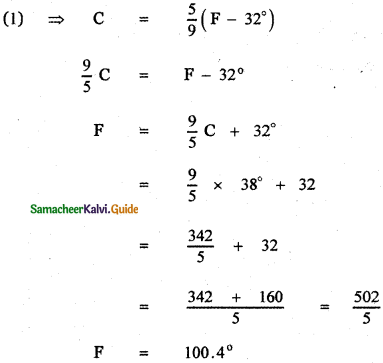
![]()
Question 6.
An object was launched from a place P in constant speed to hit a target. At the 15th second, it was 1400 m from the target, and at the 18th second 800 m away. Find
(i) the distance between the place and the target
(ii) The distance covered by it in 15 seconds
(iii) time taken to hit the target.
Answer:
Let us take the time T along the x-axis and the Distance D along the y-axis.
Given when time T = 15 s , the distance D = 1400 m
The corresponding point is (15, 1400)
Also when time T = 18 s , the distance D = 800 m.
The corresponding point is (18, 800)
(i) The distance between the place and the target:
∴ The relation connecting T and D is the equation of the straight line joining the points (15, 1400) and (18, 800)

To find the distance between the target and the place, Put T = 0 in equation (1)
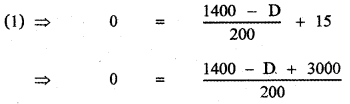
4400 – D = 0 ⇒ D = 4400 m.
Required distance = 4400 m.
(ii) The distance covered by it in 15 seconds:
Put T = 15 in the above equation
15 = \(\frac{1400-\mathrm{D}}{200}\) + 15
∴ \(\frac{1400-\mathrm{D}}{200}\) = 0 ⇒ D = 1400 m.
(iii) Time taken to hit the Target:
When the target is reached D = 0
∴ (1) ⇒ T = \(\frac{1400-0}{200}\) + 15
T = \(\frac{1400}{200}\) + 15
T = 7 + 15 = 22 seconds
∴ The time taken to hit the target is 22 seconds
![]()
Question 7.
The population of the city in the years 2005 and 2010 are 1, 35, 000 and 1, 45, 000 respectively. Find the approximate population in the year 2015. (assuming that the growth of population is constant).
Answer:
Let us choose the year along the x-axis and the population of the city along the y-axis.
Given In the year 2005 population is 1,35,000
The corresponding point is (2005, 1,35,000)
In the year 2010, population is 1,45,000
The corresponding point is (2010, 1,45,000)
Let Y denote the year and P denote the population.
The relation connecting Y and P is the equation of the straight line joining the points (2005, 1,35,000) and (2010, 1,45,000)
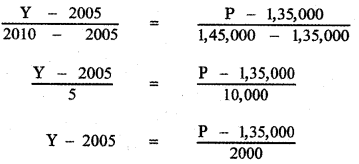
When y = 2015
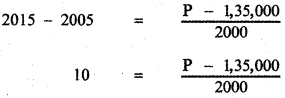
P = 1,35,000 + 10 × 2,000
P = 1,35,000 + 20,000 = 1,55,000
∴ The population in the year 2015 is 1,55,000
Question 8.
Find the equation of the line if the perpendicular drawn from the origin makes an angle 30° with x – axis and its length is 12.
Answer:
Given length of the perpendicular p = 12
Angle made by the perpendicular α = 30°
The equation the straight line in the normal form is
x cos α + y sin α = p
∴ The required equation of the straight line is
x cos 30° + y sin 30° = 12
x\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) + y × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 12
√3x + y = 24
![]()
Question 9.
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through (8, 3) and having intercepts whose sum is 1.
Answer:
Let a and b be the x and y-intercepts of the line.
Given a + b = 1
b = 1 – a —— (1)
The equation of the straight line is
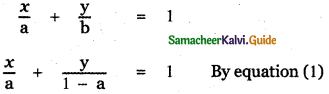
The line passes through the point (8, 3)
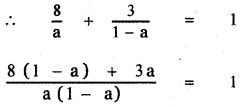
8(1 – a) + 3a = a(1 – a)
8 – 8a + 3a = a – a2
a2 – 5a + 8 – a = 0
a2 – 6a + 8 = 0
a2 – 4a – 2a + 8 = 0
a(a – 4) – 2(a – 4) = 0
(a- 4) (a – 2) = 0
a = 4 or a = 2
When a = 2, b = 1 – 2 = – 1
When a = 4, b = 1 – 4 = – 3
∴ The equation of the straight lines are
x – 2y = 2 and 3x – 4y = 12
Question 10.
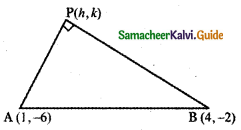
Show that the points (1, 3), (2, 1) and \(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\) are collinear, by using
(i) concept of slope
(ii) using a straight line and
(iii) any other method.
Answer:
Let the given points be A (1 , 3), B (2 , 1) and \(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\)
(i) Slope Method:
A (1 , 3 ), B (2 , 1 ), C\(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\)
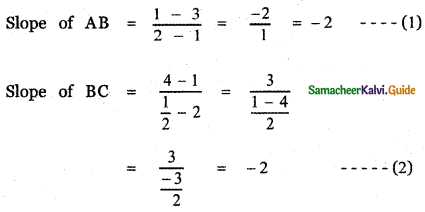
From equations (1) and (2)
Slope of AB = Slope of BC
∴ The given points A, B, C are collinear.
![]()
(ii) Using a straight line
A(1 , 3) , B(2 , 1) , C\(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\)
The equation of the straight line joining the points
A( 1 , 3) , B(2 , 1) is
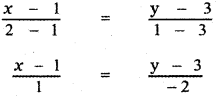
-2(x- 1) = y – 3
– 2x + 2 = y – 3
2x + y – 2 – 3 = 0
2x+ y – 5 = 0 ——- (2)
Substituting the third point C \(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\) in equation (2)
we have 2\(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\) + 4 – 5 = 0
1 + 4 – 5 = 0
0 = 0
∴ The third point C\(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\) lies on the straight line AB.
Hence the points A , B , C are collinear.
(iii) Distance method:
A(1 , 3) , B(2 , 1) , C\(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 4\right)\)
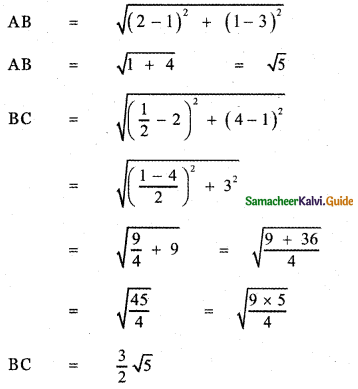
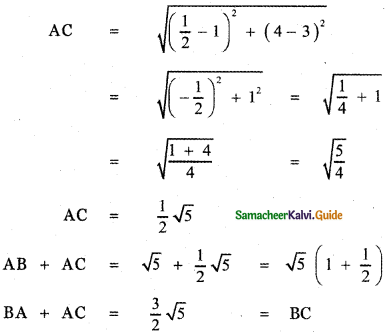
Thus BA + AC = BC
∴ The points A, B, C are collinear.
![]()
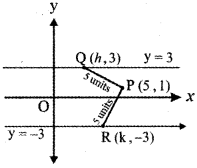
Question 11.
A straight line is passing through the point A (1, 2) with slope \(\frac{5}{12}\). Find the points on the line which are 13 units away from A.
Answer:
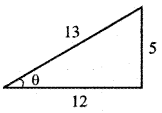
Slope of the line m = tan θ = \(\frac{5}{12}\)
sin θ = \(\frac{5}{13}\), cos θ = \(\frac{12}{13}\)
The parametric equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2) making angle θ with x – axis is
![]()
Any point on this line is
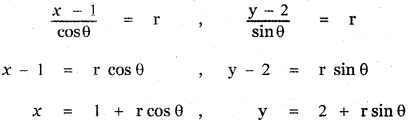
(1 + r cos θ, 2 + r sin θ) ……… (1)
where r is the distance of any point from A (1, 2) on the line.
To find the point which is 13 units away from A (1, 2) on the line.
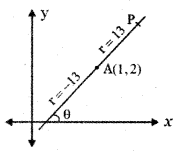
Substitute r = ± 13, cos θ = \(\frac{12}{13}\), sin θ = \(\frac{5}{13}\) in equation (1)
Required point = \(\left(1 \pm 13\left(\frac{12}{13}\right), 2 \pm 13\left(\frac{5}{13}\right)\right)\)
= (1 ± 12, 2 ± 5)
= (1 + 12, 2 + 5)
= (1 + 12, 2 + 5) or (1 – 12, 2 – 5)
= (13, 7) or (- 11, – 3)
Question 12.
A 150 m long train is moving with a constant velocity of 12.5 m/s.
(i) The equation of motion of the train.
(ii) Time taken to cross a pole.
(iii) The time to cross the bridge of length 850m is?
Answer:
Length of the train = 150 m
Constant velocity of the train = 12.5 m/s
(i) The equation of motion of the train:
Take time in seconds along the x-axis and distance in meters along the y-axis.
Let the train be at the origin.
∴ Length of the train = 150 m is the negative y-intercept
b = -150
The slope of the motion of the train m = 12.5 m/s
The equation of the line with slope-intercept form is
y = mx + b
∴ y = 12.5x – 150
which is the required equation of motion of the train.
![]()
(ii) Time taken to cross a pole:
The equation of motion is y = 12.5 x – 150
To find the time taken to cross the pole, Put y = 0
0 = 12.5 x – 150 ⇒ 12.5 x = 150
⇒ x = \(\frac{150}{12.5}\) = 12 sec
(iii) The time taken to cross the bridge of length 850 m
The equation of motion is y = 12.5 x – 150
To find the time taken to cross the bridge of length 850 m, put y = 850
850 = 12.5 x – 150
12.5 x = 850 + 150 = 1000
x = \(\frac{1000}{12.5}=\frac{10000}{125}\) = 80 sec
Question 13.
A spring was hung from a hook in the ceiling. A number of different weights were attached to the spring to make it stretch, and the total length of the spring was measured each time shown in the following table.
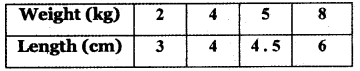
(a) Draw a graph showing the results.
(b) Find the equation relating the length of the spring to the weight on it.
(c) What is the actual length of the spring?
(d) If the spring stretches to 9 cm long, how much weight should be added?
(e) How long will the spring be when 6 kilograms of weight on it?
Answer:
Choose the weight along the x-axis and Length along the y-axis.
(a)
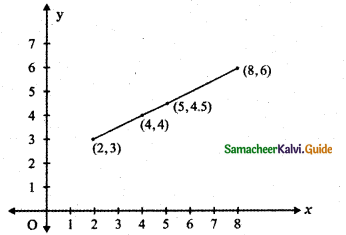
(b) The points are(2, 3), (4, 4), (5, 4.5), (8, 6) The relation connecting weight and Length is the equation of the straight line joining the points (2, 3) and (4, 4)
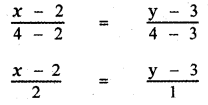
x – 2 = 2(y – 3)
x – 2 = 2y – 6
x – 2y + 6 – 2 = 0
x – 2y + 4 = 0 —– (1)
which the required relation connecting weight and length.
(c) To find the actual length of the spring, put weight x = 0 in equation (1)
0 – 2y + 4 = 0 ⇒ 2y = 4 ⇒ y = 2
∴ The actual length of the spring is 2 cm.
(d) If the spring stretch to 9 cm long, To find the required weight, put y = 9, in equation (1)
(1) ⇒ x – 2 (9) + 4 = 0
x – 18 +4 = 0 ⇒ x = 14
Weight to be added is 14 kg.
(e) Next we find the length of the string when a weight of 6 kg is added.
Put x = 6 in equation (1)
6 – 2y + 4 = 0 ⇒ 2y = 10 ⇒ y = 5cm
∴ Required length is 5 cm.
![]()
Question 14.
A family is using Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) of weight 14.2 kg for consumption. (Full weight 29.5 kg includes the empty cylinders tare weight of 15.3 kg.). If it is used at a constant rate, then it lasts for 24 days. Then the new cylinder is replaced
(i) Find the equation relating the quantity of gas in the cylinder to the days,
(ii) Draw the graph for the first 96 days.
Answer:
(i) Find the equation relating the quantity of gas in the cylinder to the days.
Given Total weight of cylinder = 29.5 kg
Weight of the gas inside the cylinder = 14.2 kg
Let x denote the number of days of consumption of the gas, y denote the quantity of gas inside a cylinder.
Initially x = 0 then y = 14.2
The corresponding point is (0, 14.2)
The gas inside the cylinder lasts for 24 days
∴ When x = 24, we have y = 0
The corresponding point is (24, 0)
∴ The linear relation between the quantity of gas in the cylinder to the number of days of consumption is the equation of the line joining the points (0, 14.2 ) and (24, 0).
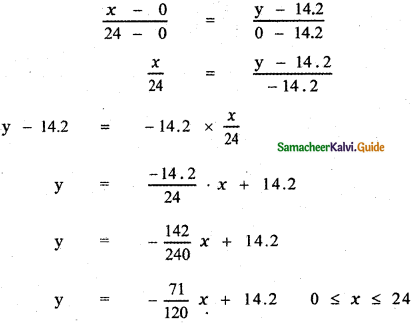
which is the required relation
(ii) Draw the graph for the first 96 days:
The relation connecting the quantity of gas to the number of days of consumption is
y = –\(\frac{71}{120}\)x + 14.2
Let f(x) = –\(\frac{71}{120}\) x + 14.2
Here f(x) is a periodic function of period 24
∴ f(x + 24) = f(x)
When x = 0
f(0) = –\(\frac{71}{120}\) × 0 + 14.2 ⇒ y = 14.2
The corresponding point is (0, 14.2)
When x = 24
f(24) = –\(\frac{71}{120}\) × 0 + 14.2 ⇒ y = 14.2
⇒ f(24) = –\(\frac{71}{5}\) + 14.2
= – 14.2 + 14.2 = 0 ⇒ y = 0
Corresponding point is (24 , 0)
When x = 48
f(48) = f(24 + 24 + 0) = f(24 + 0)
= f(o) = o
Corresponding point is (48, 0)
When x = 72
f(72) = f(24 + 24 + 24 + 0)
= f(24 + 24 + 0) = f(24 + 0)
= f(0) = 0
Corresponding point is (72, 0)
The required graph is
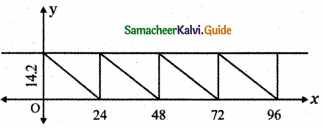
![]()
Question 15.
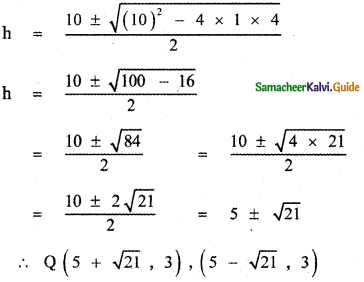
In the shopping mall, there is a hall of cuboid shape with dimension 800 x 800 x 720 units, which needs to be added the facility of an escalator in the path as shown by the dotted line in the figure. Find
(i) the minimum total length of the escalator
(ii) the height at which the escalator changes its direction
(iii) the slopes of the escalator at the turning points.
Answer:
Give the dimension of the cube = 800 × 800 × 720
(i) Minimum total length of the escalator:
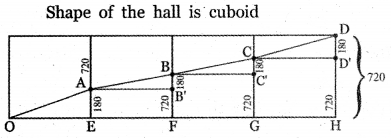
The path of the escalator is
from OA to AB to BC to CD
OE = 800, EA = \(\frac{1}{4}\) × height of the building
EA = \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 720 = 180
Since there are four steps for the escalator
∴ OA2 = OE2 + EA2
= 8002 + 1802
= (40 × 20)2 + (9 × 20)2
= 402 × 202 + 92 × 202
= 202 (402 + 92)
= 202 ( 1600 + 81)
= 202 × 1681
OA2 = 202 × 412
OA = \(\sqrt{20^{2} \times 41^{2}}\) = 20 × 41 = 820
Since ∆OAE ≡ ∆ ABB’ ≡ ∆ BCC ≡ ∆ CDD’
We have OA = AB = BC = CD
Total length of the escalator
= OA + AB + BC + CD
= 820 + 820 + 820 + 820
= 4 × 820
= 3280
Minimum length of the escalator = 3280 units
(ii) Lengths at which the escalator changes its direction:
The heights at which the escalator changes its direction
First step EA = \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 720 = 180 unis
Second step FB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 720 = 360 units
Third step GC = \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 720 = 540 units
![]()
(iii) The slopes of the escalator at the turning points.
In the right angle ∆ OAE
OE = 800, EA = 180
Let ∠ AOE = θ
The slope of the escalator OE 180
![]()
∴ Slope at each turning points is \(\frac{9}{40}\)