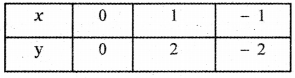
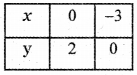
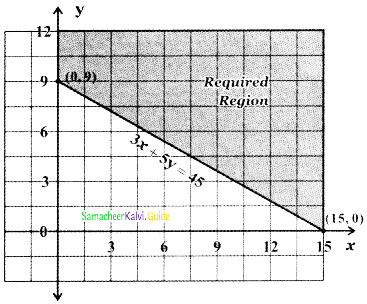
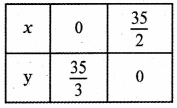
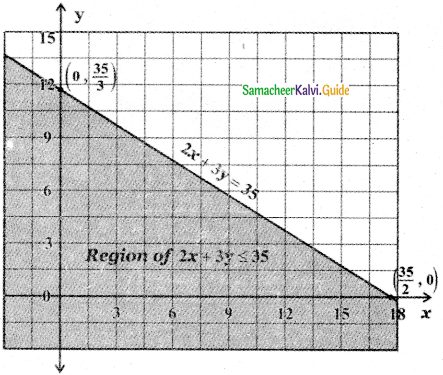
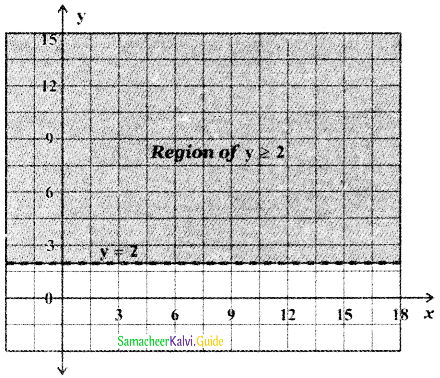
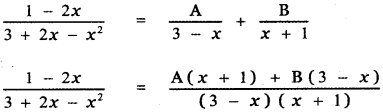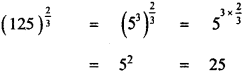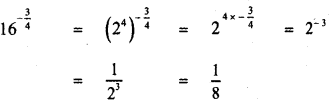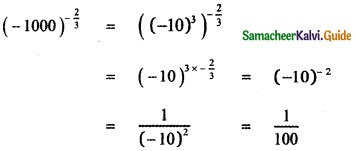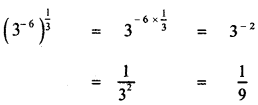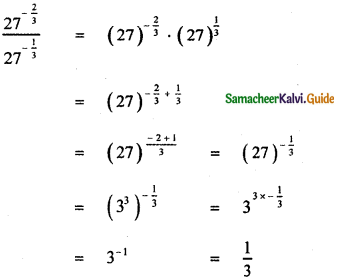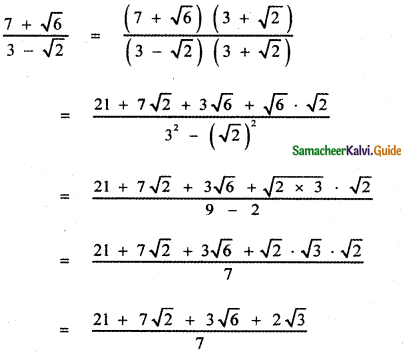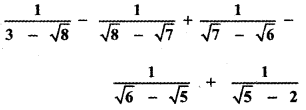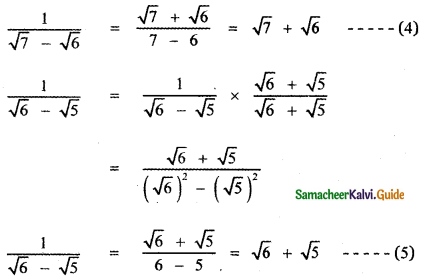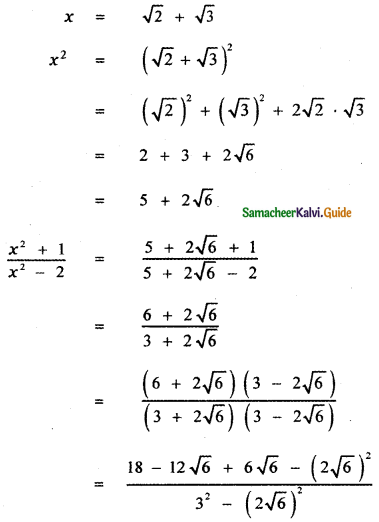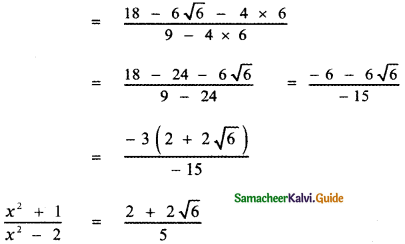Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Guide Pdf Term 3 Supplementary Chapter 3 The Case of the Missing Water Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Solutions Term 3 Supplementary Chapter 3 The Case of the Missing Water
5th English Guide The Case of the Missing Water Text Book Back Questions and Answers
A. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
The tank in Divya’s village was almost ______.
a) full
b) dry
c) half full
Answer:
b) dry
Question 2.
Divya loved solving ______.
a) problem
b) sums
c) mysteries
Answer:
c) mysteries
Question 3.
Divya and Rani decided to draw a ______.
a) goat
b) mountain
c) map
Answer:
c) map
Question 4.
Elephants were visiting ______ field. (Not in the text)
a) paddy
b) ragi
c) sugar cane
Answer:
c) sugar cane
Question 5.
Rani thought of herself as a ______ engineer.
a) civil
b) mechanical
c) sanitary
Answer:
c) sanitary
Question 6.
Rani and divya informed the happening to the ______.
a) police
b) friends
c) elders
Answer:
c) elders
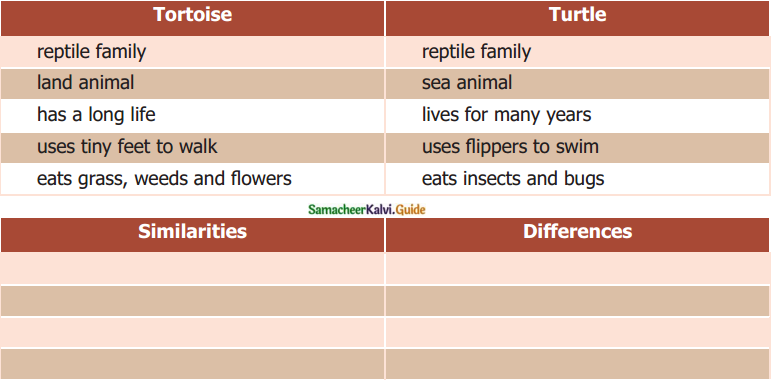
![]()
B. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Why did Manju’s parents leave the village?
Answer:
Manju’s parents left the village because there was no water in the village.
Question 2.
What kind of water did Divya use to brush her teeth?
Answer:
Divya brushed her teeth with muddy tank water.
Question 3.
What did Rani want to become?
Answer:
Rani wanted to become a sanitary engineer in the future.
Question 4.
Where did the tanker man take the water from the village?
Answer:
The tanker man took the water to the city from the village.
Question 5.
Do you think it is okay for the tanker to take water? Why?
Answer:
No. When the whole village is suffered without water, it is not fair for the tanker to take water to the city.
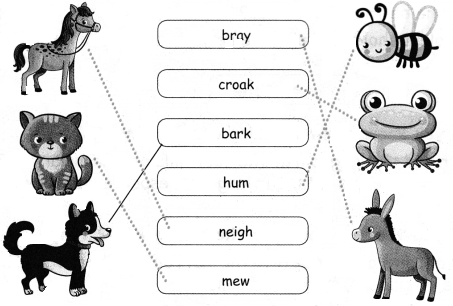
![]()
C. Try your own:
Answer:
![]()
D. Speak and win:
Join in any group. Support or oppose using 4 to 5 sentences to win.

I support Divya:
- Divya had a social responsibility.
- Divya roamed everywhere to find how the water was lost and became tired.
- Divya fought with her friend Rani for her concern to know how the water was lost.
- Her determination to solve a mystery is to be appreciated.
I oppose Divya:
- Divya always pokes her nose in other matters.
- Small girl Divya need not strain to find herself how the water was lost.
- Divya unnecessarily had a difference of opinion with her friend.
- Divya should not command the tanker man. She should inform the village people about him.
![]()
Let us read aloud:
A. Read the passage 3 times and colour a dustbin each time:
I am Mani. I have to take a bus to nearby city. I crossed the road to reach the bus stand. I got the bus and sat down and took out a book to read. Before I started to read, I just looked at the people around me. The two men sitting next to me were talking loudly. Some were listening to music on their phone. I was unable to focus on reading. The men were talking about cleaning the city. As they were talking, they opened a pack of biscuits to eat. After some time I dozed off. When I opened my eyes, the bus had reached the city. The two men were not there but pieces of the biscuits and wrappers were there. I cleaned the wrappers and put them in the dustbin.
![]()
Question 1.
What did Mani take out?
Answer:
Mani took out a book to read.
Question 2.
What did Mani find on the seat when he woke up?
Answer:
When Mani woke up, he found pieces of the biscuits and wrappers on the seat.
Question 3.
If you were Mani, what would you do?
Answer:
If I were Mani, I would have asked my fellow passengers to talk softly in public and to keep clean the surroundings.
![]()
Let us write:
Creative writing with suspense:
In the dark cold winter night in 1950, Rani and his brother Raj were waiting at the old open railway station showering in fear and in cold. They wanted to go to the next station for half an hour distance but the train was one hour late. They kept their eyes and early open to hear the engine sound. But nothing came. Suddenly Raj saw the smoke coming from far and a streak of fire too.
Still, the train did not come. They started walking toward the direction of the ‘train’ seeing the smoke. Oh! what a surprise. The ‘train’ was actually a tribal man smoking cigar covering himself with a black blanket. Rani seamed with fear. The friendly tribal man understood their need and took them to the next station in his bullock cart. Rani and Raj understood brotherly have from an uncultured tribal man that day.
Writing a Story with suspense:
Words that help you create suspense:
suddenly, just then, at that moment, all of a sudden, silently, in alarm, scared, from the shadows, dark, unexpectedly, etc.
Let us use these words to write a paragraph on “A day in the forest”:
A day in the forest
Suddenly in a distance, I noticed some paws on the mud. My head turned red with fear and I silently stepped back. Just then, I saw a big brown furry animal with green eyes coming out of the shadows. In that moment, I didn’t know what I had to do. I screamed and ran. All of a sudden, I heard a howl. behind me. I turned to see two wolves chasing me.
![]()
Write a story with suspense:
That Night In Beach It was on December 26th. Sinha and Tiwari came from Barauni to Chennai to attend an important office duty. Their work was completed in the evening. They planned to leave Chennai the next day evening. So, that day night they went to the beach at around 9.00 pm. It was a no moon day and there was complete darkness. They walked along the beach and sat near a boat.
Nobody was there in that place. Suddenly, the boat started moving towards the Bay of Bengal. They looked inside the boat, but there was nobody. Both of them frightened. They started to run but they could not move their legs. They screamed in fear. All of a sudden, a voice instructed them to move towards the water and drown into the sea. Then their legs started to go to the sea.
By the time, a man was running towards them at a distance. He shouted at them not to go to the sea. He called the police over the phone. Police came. At that time, Sinha and Tiwari were walking in knee-deep water. Police rescued them. The man told that some years back, hundreds of people lost their lives in that place. Some ghosts are still wandering there during that particular day. Sinha and Tiwari could not recollect what had happened to them. They thanked the police and the man who helped them.
![]()
I can do:
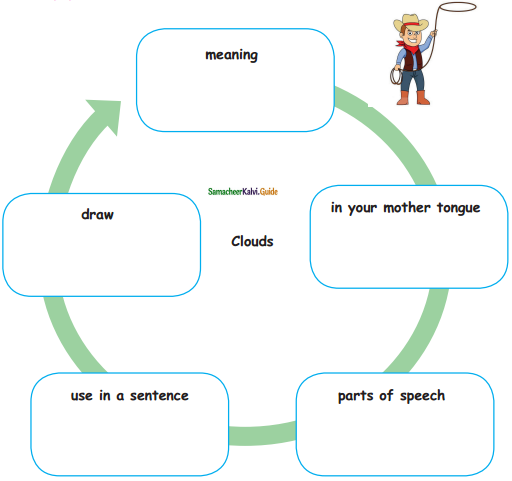
A. Answer the following:

Question 1.
Name of the object
Answer:
Tanker
Question 2.
In your mother tongue
Answer:
தண்ணீர் வாகனம்
Question 3.
Use in a sentence
Answer:
My uncle is a tanker driver
![]()
B. Write the animals and their young ones:
Question 1.

Answer:
calf
Question 2.

Answer:
cub
Question 3.

Answer:
chick
![]()
C. Match the rhyming word:
| 1. green | a. can |
| 2. society | b. care |
| 3. man | c. clean |
| 4. welfare | d. inability |
Answer:
| 1. green | a. clean |
| 2. society | b. inability |
| 3. man | c. can |
| 4. welfare | d. care |
![]()
D. Recite the poem with correct intonation:
This activity to be done by students.
E. Choose the correct one show past perfect tense:
Question 1.
we ______ (see) the movie last week.
a) have seen
b) saw
c) had seen
Answer:
(c) had seen
Question 2.
I ______ (meet) him before.
a) had met
b) meet
c) have met
Answer:
(a) had met
F. Choose the correct one to show future perfect tense:
Question 1.
I ______ (finish) this book.
(a) had finished
(b) have finished
(c) will have finished
Answer:
(c) will have finished
Question 2.
By this time tomorrow, we ______ (arrive) in Chennai.
(a) will have arrived
(b) have arrived
(c) would have arrived
Answer:
(a) will have arrived
![]()
Grammar – Textual Exercise:
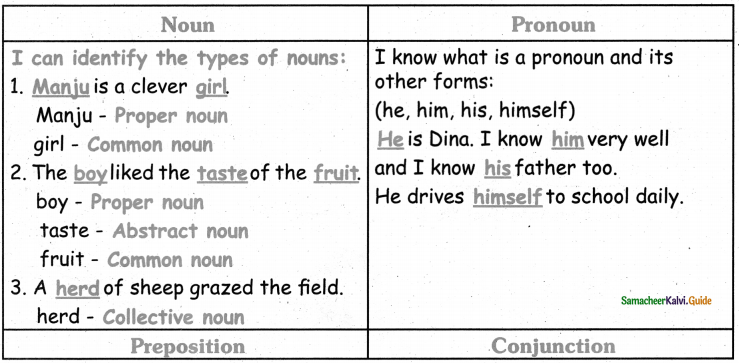
A. I am a 5th student and I know all these.
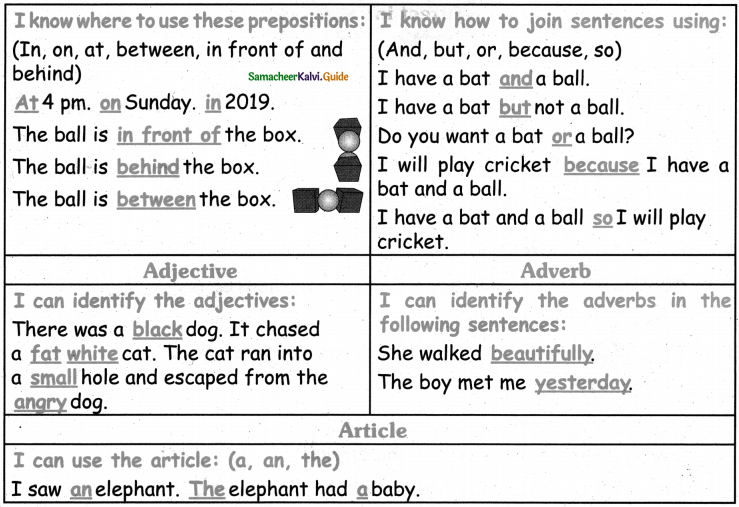
I know where to use these prepositions:
B. I know three tenses and I can write all tenses.
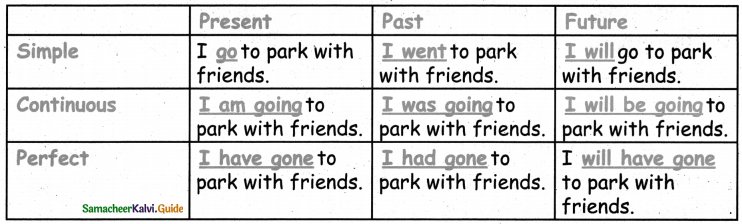
![]()
5th English Guide The Case of the Missing Water Additional Questions and Answers
I. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Divya followed her parents to the stream.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Divya collapsed into the boat with Rani.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Divya had an idea. She hugged the pump.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Rani may be we shouldn’t have missed the village.
Answer:
False
![]()
II. Identify the character/speaker :
Question 1.
“We just need enough until the rains arrive”.
Answer:
Appa
Question 2.
“Further up, then?”
Answer:
goatherd
Question 3.
“Manju’s parents left the village”.
Answer:
Divya
Question 4.
“You can’t change anything”.
Answer:
Tanker man
Question 5.
“Like real Sanitary Engineers”.
Answer:
Rani
![]()
III. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What did Divya’s Ammachi, Amma, and Appa do when the village tank was almost dry?
Answer:
When the village tank was almost dry, Divya’s Ammachi prayed for rain. Her Amma collected water in all the buckets, pots, and vessels in the home. Appa took his tools to dig a little deeper.
Question 2.
What mystery did Divya solve at home?
Answer:
At home when Ammachi couldn’t find her reading glasses, Divya would help her find them from the book she was reading.
Question 3.
Who were the three people Divya asked ‘where the water had gone?
Answer:
Divya asked the fisherman, goatherd, and Rani about where the water had gone.
Question 4.
Where all did Divya go to find where the water had gone?
Answer:
First Divya went to the tank and then to the other side of the tank, she followed the dry stream bed down the hill and came to the bottom tank.
Question 5.
Why was the glass half empty?
Answer:
The class was half empty because the children had left the areas with their families as there was no water.
Question 6.
What do sanitary engineers do?
Answer:
Sanitary engineers build pipes, tanks, and drains.
Question 7.
What did Divya and Rani draw? Why?
Answer:
Divya and Rani drew the map of their village showing all its tanks and streams.
Question 8.
Where did the water go?
Answer:
The water was pumped and taken to the tanker below the bund to be carried to the city.
Question 9.
How did Divya and Rani stop the tanker man to take the water in the village?
Answer:
Divya and Rani tried to stop the tanker man from taking the water to the city by hugging the pump.
Question 10.
What happened when the monsoon came?
Answer:
When the monsoon came, it rained heavily, the bund overflowed and the stream rushed down the hill.
![]()
The Case of The Missing water Summary in English and Tamil
The tank in Divya’s village was almost dry. Ammachi began to pray for rain. Amma collected all the buckets and pots and vessels in the house and filled them up.. “We need to store as much water as we can,” she said. Appa collected tools to dig a little deeper. “We just need enough until the rains arrive,” he said.
திவ்யாவின் கிராமத்திலிருந்த குளம் பெரும்பாலும் வறண்டு விட்டது. அம்மாச்சி மமை வரவேண்டுமென பிரார்க்கனை செய்தார். வீட்டிலிருந்த வாளிகள், பானைகள், பாத்திரங்கள் எல்லாவற்றையும் எடுத்து, அவற்றில் நீரை நிரப்பி
வைத்தாள் அம்மா. “நம்மால் முடிந்த அளவுக்கு தண்ணீரை சேமிக்க வேண்டிய தேவை ஏற்பட்டுவிட்டது”, என்றாள் அம்மா. கொஞ்சம் ஆழமாகத் தோண்டு வதற்கான கருவிகளை அப்பா சேகரித்தார். “மழை வரும் வரையில் நமக்கு இது தேவை”, என்றார் அவர்.
Divya got out her notebook and pencil. She put on her thinking cap and followed her parents to the tank. She examined the tank bed closely. It was cracked and dusty.
திவ்யா ‘ தனது நோட்டு புத்தகத்தையும் பென்சிலையும் எடுத்துக் கொண்டாள். தனது பெற்றோரை பின்தொடர்ந்தபடி குளத்திற்குச் சென்றாள். வெகு அருகிலிருந்தபடி குளத்தை அவள் ஆய்வு செய்தாள். நிலத்தில் பிளவு ஏற்பட்டு, தூசி படிந்திருந்தது.
Divya wondered, “Where did the water in the tank go? Did it run away? Was it stolen? This is a mystery!” Divya loved solving mysteries: Like the time Ammachi couldn’t find her reading glasses. Divya had found them in her book, marking the page she was reading. “I’ll find that water,” Divya muttered to herself.
திவ்யா ஆச்சர்யப்பட்டாள். “குளத்திலிருந்த தண்ணீர் எங்கே போனது? அது ஓடிவிட்டதா? திருடப்பட்டுவிட்டதா? இது ஒரு மர்மம்”, என்றாள். மர்மங்களுக்கு தீர்வு காண்பதை திவ்யா விரும்பினாள். படிப்பதற்கான கண் கண்ணாடியை அம்மாச்சி கண்டுபிடிக்க முடியாமல் போன சமயத்தில் நடந்ததைப் போல.
அவருடைய புத்தகத்தில், படித்த பக்கத்தை குறிப்பிட வேண்டி, அது வைக்கப்பட்டிருந்ததை திவ்யா கண்டுபிடித்துக் கொடுத்தாள். “அந்த தண்ணீரையும் நான் கண்டுபிடிப்பேன்,” என திவ்யா தனக்குள் முணுமுணுத்துக் கொண்டாள்.
![]()
Divya walked to the other side of the tank, past dead fish and dried reeds. “Do you know where the water could have gone?” Divya asked a fisherman. “Downstream?” the fisherman suggested. Divya followed the dry stream bed down the hill. At the bottom was another tank. It had lots of goats, but no water.
திவ்யா குளத்தின் மறுகரைக்கு நடந்தாள். இறந்து போன மீன்களையும், காய்ந்து போன நாணல்களையும் கடந்தாள். “தண்ணீ ர் எங்கே போயிருக்க முடியுமென உங்களுக்கு தெரியுமா?” என ஒரு மீனவரைதிவ்யா கேட்டாள்.
“கீழ்மட்டத்திற்கு போயிருக்கலாம்,” என்றார் மீனவர். குன்றின் அடியிலிருந்த, வறண்டு போன நீரோடையில் திவ்யா நடந்தாள். கீழே இன்னொரு குளம் இருந்தது. அங்கு பல ஆடுகள் மேய்ந்த படி இருந்தன, ஆனால் நீர் இல்லை.
Divya asked the goatherd, “Do you know where the water might be?” “Upstream,” the goatherd suggested. I “That’s where I came from,” Divya said. “No water there.” “Further up, then?” the goatherd said. “That’s where your water comes from.”
திவ்யா ஆடு மேய்ப்பவரிடம், “தண்ணீ ர் எங்கே போயிற்று என உங்களுக்குத் தெரியுமா?” என கேட்டாள். ஆடுமேய்ப்பவர், “மேல் மட்டத்திற்கு போயிருக்கலாம்” என்றார். “அங்கிருந்து தான் நான் வருகிறேன், அங்கு தண்ணீர் இல்லை” என்றாள் திவ்யா. “அதற்கும் மேலே. அங்கிருந்துதான் தண்ணீர் வருகிறது”, என்றார் ஆடு மேய்ப்ப வர்.
Divya climbed up to the tank. Then she climbed up some more to a tank further up the hill. There was no water, no birds. There was only one person there. “Rani, I can’t find any water. Any idea where it’s gone?” Divya called to her. She knew Rani from school.
“Downstream,” Rani called back. Divya was suddenly angry. She stomped her foot. “No!” she shouted. “It’s not. I
have searched and searched. It’s not upstream or downstream. Got it?”.
திவ்யா குளத்தை நோக்கி குன்றின் மேலே ஏறினாள். அங்கு இருந்த ஒரு குளத்தில் தண்ணீ ரும் இல்லை, பறவைகளும் இல்லை. ஒரே ஒரு பெண் மட்டும் இருந்தாள். “ராணி, தண்ணீரையே பார்க்க முடியவில்லை. அது எங்கே போயிற்று என்று ஏதாவது ஐடியா இருக்கிறதா?”
என திவ்யா அவளைக் கேட்டாள். பள்ளியிலிருந்தே ராணியை அவளுக்குத் தெரியும். “கீழ் மட்டத்தில்”, என்றாள் ராணி. திவ்யா திடீரென கோபப்பட்டாள். தரையை காலால் தட்டினாள்.
“இல்லை” என கூச்சலிட்டாள். “அங்கே இல்லை. நானும் தான் தேடினேன்-தேடினேன். அது மேல்மட்டத்திலும் இல்லை, கீழ்மட்டத்திலும் இல்லை. புரிந்ததா?”
![]()
“How about up there?” Rani suggested. Divya and Rani looked up at the sky.” The sun glared back at them. Everything was white-hot and dusty. “No,” they agreed together. “No water there. Divya collapsed into the boat with Rani and gnawed on a lotus stem. She was hot and tired.
அது இன்னும் உயரே சென்றிருக்கலாம்,” என்றாள் ராணி. திவ்யாவும், ராணியும் வானத்தைப் பார்த்தனர். சூரியன் அவர்களின் மீது ஒளியை பாய்ச்சியது. எல்லாமே வெள்ளையாக-வெப்பமாகவும், தூசியுடனும் இருந்தன. “இல்லை, அங்கே தண்ணீர் இல்லை”, அவர்கள் இருவருமே ஒரு சேர ஒப்புக் கொண்டனர். திவ்யா, ராணியுடன் படகில் சாய்ந்தபடி, ஒரு தாமரைத் தண்டை கடித்தாள். அவள் உடம்பு வெப்பத்தால் தகித்தது. அவள் களைப்படைந்தாள்.
“Manju’s parents left the village, “Divya said. “They went to the city” where they have water. Maybe we should all go.” “You go,” Rani snapped. “No one asked you to be here.” “Fine,” Divya said. And she stomped back home. But it wasn’t fine! There was still no water, still no rain.
மஞ்சுவின் பெற்றோர் இந்த கிராமத்தை விட்டுச் சென்று விட்டனர். நகரத்துக்குப் போய் விட்டனர். அங்கு அவர்களுக்கு தண்ணீ ர் கிடைக்கும். நாம் எல்லோரும் போக வேண்டி வரலாம்”, என்றாள் திவ்யா. “நீபோ, இங்கேயே இருக்கவேண்டுமென உன்னை
யாரும் கேட்டுக் கொள்ளப் போவதில்லை”, என்றாள் ராணி. “நல்லது” என்றாள் திவ்யா. அவள் வீட்டுக்குத் திரும்பினாள் ஆனால் அங்கு சூழ்நிலை சரியில்லை. இன்னும் அங்கு தண்ணீர் இல்லை, மழையும் இல்லை.
The next day, Divya brushed her teeth with muddy tank water in a tiny glass. “Thooo!” she spat. In school, the class was half-empty. More families had left the area. She missed all her friends! In the middle of Environmental Studies class, she turned and ran out of school. She ran and ran until she was panting. She finally sat at the side of the road.
அடுத்த நாள். சேறுகலந்த குளத்து நீரை ஒரு சிறிய கிளாஸில் வைத்துக் கொண்டு, திவ்யா பல் துலக்கினாள். “த்தூ!” என அவள் துப்பினாள். பள்ளியில் பாதி வகுப்பு காலியாக இருந்தது. அந்தப் பகுதியிலிருந்து மேலும் பல குடும்பங்கள் சென்று விட்டிருந்தனர்.
அவள் தன் எல்லா நண்பர்களையும் இழந்தாள். வகுப்பில், சுற்றுச்சூழல் பாடத்தின் நடுவே, அவள் எழுந்து, பள்ளியை விட்டு ஓடினாள். மூச்சிறைக்கும் வரை அவள் ஓடினாள். இறுதியில், சாலையின் ஒரு புறத்தில் அவள் அமர்ந்தாள்.
![]()
“I have to find the water!” she huffed. “Can I help?” said a voice. It was Rani who had seen Divya running away” from school. Divya beamed. “Yes!” “We have to do this properly,” Rani said. “Like real Sanitary Engineers.” “Like who…?” Divya asked. “Sanitary Engineers build pipes and tanks and drains. I am going to be one when I grow up,” Rani said. Divya and Rani decided to draw a map of their village and all its tanks and streams, showing all the places where the water might have flowed.
தண்ணீர் எங்கே போனது என நான் கண்டுபிடிக்க வேண்டும்”, என்று ஒரு வித கோபத்துடன் “உனக்கு உதவட்டுமா”, என்றது ஒரு குரல், அது ராணி தான். பள்ளியிலிருந்து திவ்யா ஓடிவந்ததை அவள் பார்த்தாள். “சரி”, என்றாள் திவ்யா.”சுகாதாரப் பொறியாளர்களைப் போல, நாம் இதை சரியாகச் செய்ய வேண்டும்”, என்றாள் ராணி. “யார் அவர்கள்?”, என்று திவ்யா கேட்டாள்.
“குழாய்கள், தொட்டிகள், வடிகால் வாய்க்கால்களை கட்டுகிறார்களே அவர்கள் தான். நான்பெரியவளாக வளர்ந்த பிறகு சுகாதாரப் பொறியாளராவேன்,” என்றாள் ராணி. அவர்களின் கிராமத்தின் வரைபடத்தை அவர்கள் இருவரும் வரைய தீர்மானித்தனர். மேலும் தண்ணீர் செல்லக்கூடிய வழித்தடங்கள், குளங்கள், ஓடைகள் எல்லாவற்றையும் வரைபடத்தில் குறிக்கவும் முடிவு செய்தனர்.
Where could the water possibly have gone? Finally, they sat back and pored over the map. “We haven’t seen that tank yet,” Divya pointed to one of the tanks they had drawn. “Let’s go,” Rani agreed. Divya and Rani began climbing up the hill. The stream here was dry as well.
தண்ணீ ர் எங்கே போயிருக்க கூடும்? இறுதியாக, அவர்கள் தரையில் அமர்ந்து, வரைபடத்தை கூர்ந்து ஆராயத்தொடங்கினர். “அந்தக் குளத்தை இதுவரை நாம் பார்க்கவில்லை, அவர்கள் வரைந்த குளங்களில் ஒன்றை சுட்டிக்காட்டியபடி, திவ்யா இவ்வாறு கூறினாள். “நாம் போகலாம்”, ராணி சம்மதித்தாள். ஏறத் தொடங்கினர். அந்த ஓடையும் வறண்டு திவ்யாவும், ராணியும் அந்தக் குன்றின் மீது போயிருந்தது.
“Maybe we shouldn’t have missed school. This tank is probably dry as well,” Rani said sadly. When they reached the tank, Divya” and Rani realised they were wrong. This tank was full! Rani pointed at a small pump at the end of the lake. There was a tanker just below the bund, collecting water as it flowed. A man stood by, guiding the tanker. “Mystery solved,” said Divya angrily.
நாம் பள்ளிக்குச் செல்வதை தவற விட்டிருக்கக் கூடாது. இந்தக் குளமும் வறண்டிருக்கிறது”, என்றாள் ராணி வருத்தமாக. குளத்தை அவர்கள் அடைந்தபோது, திவ்யா, ராணி இருவருமே தங்களது யூகம் தவறு என உணர்ந்த னர். அந்தக் குளத்தில் தண்ணீ ர் நிரம்பியிருந்தது.
அங்கு ஏரியின் முடிவில் ஒரு சிறு பம்ப் இருந்ததை ராணி சுட்டிக்காட்டினாள். கரைக்குக் கீழே ஒரு டேங்கர் (நீர் ஏற்றிச் செல்லும் வாகனம்) இருந்தது. அதில் தண்ணீர் நிரப்பப்பட்டுக் கொண்டிருந்தது. அதனருகில் ஒரு மனிதன் நின்றிருந்தான். “மர்மம் தீர்க்கப்பட்டது”, என்றாள் திவ்யா கோபத்துடன்.
![]()
“Where are you taking our water?” Divya wanted to know. “The city,” the man said. “I need to supply nine-thousand litres today!” “That’s not fair!” Rani said. The man shrugged, “That’s how it is.” “My friend is a Sanitary Engineer, Divya yelled. “She knows what’s fair.” The man laughed.” Sanitary Engineer it seems! You’re just children!” Rani said quietly, “Yes, but I know you can’t just take our water away.”
“எங்கள் தண்ணீ ரை எங்கே எடுத்துப் போகிறீர்?” என்று திவ்யா கேட்டாள். “நகரத்திற்கு, இன்றைக்கு நான் 9,000 லிட்டர் தண்ணீ ரை சப்ளை செய்தாக வேண்டுமே”, என்றான் அந்த மனிதன். “அது நியாயமல்ல”, என்றாள் ராணி.” “அது அப்படித்தான்,” என்றான் அவன் தன் தோள்பட்டையை உயர்த்தியபடி, “என் நண்பர் ஒரு சுகாதாரப் பொறியாளர்.
அவருக்கு எது நியாயமெனத் தெரியும்,” என்று திவ்யா சத்தமிட்டாள். அந்த மனிதன் சிரித்தான். “துப்புரவாளர் என்று தோன்றுகிறது. நீங்கள் எல்லாம் குழந்தைகள்தான்,” என்றான் அவன். “ஆம். ஆனால், நீங்கள் எங்கள் தண்ணீ ரை எடுத்துச் செல்ல முடியாது,” என்று ராணி அமைதியாகச் சொன்னாள்.
“Go home,” the man said. “You can’t change anything!” Divya had an idea. She hugged the pump. “You can’t turn it on now!” Rani ran up to hug the pump too. “Hey!” said the man. Now he was really angry. “Just go home,” he said.
“வீட்டுக்குப் போங்கள், உங்கள் இருவரால் எதையும் மாற்றிடவிட முடியாது”, என்றான் அவன். திவ்யாவுக்கு ஒரு யோசனை தோன்றியது. அவள் அந்த “பம்ப்”-ஐ கட்டி அணைத்துக் கொண்டாள். “இப்போது உங்களால் இந்த பம்ப்-ஐ திருப்ப முடியாது.” ராணியும் ஓடிச்சென்று’ பம்ப்-ஐ அணைத்துக் கொண்டாள். இப்போது அந்த மனிதன் உண்மையிலேயே கோபப்பட்டான். “வீட்டிற்குப் போய் விடுங்கள்”, என்றான்.
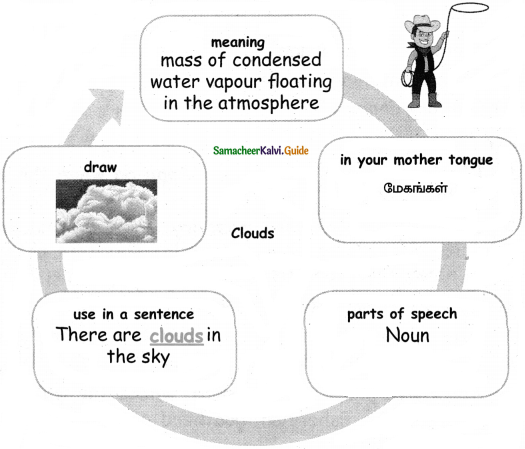
That was when the clouds broke, and rain poured. “The ‘monsoon is here!” Divya shouted. “I’m going home, even if you aren’t, the tanker man said. It rained and rained. WOOSH, the bund overflowed, and the stream rushed down, splashing them.
அப்போது மேகங்கள் உடைந்து, மழை பெய்தது. “பருவமழை இங்கே ஆரம்பம்”, திவ்யா சத்தமிட்டாள். “நீங்கள் போகாவிட்டாலும், நான் வீட்டிற்குப் போகிறேன்”, என்று அந்த டேங்கர் மனிதன் கூறினான். மழை தொடர்ந்து பெய்தது. ஊஷ், குளம் நிரம்பி வழிந்தது. நீரோடையில் தண்ணீர் பாய்ந்து அவர்கள் மீது, தெறித்தபடி, கீழ்நோக்கி ஓடியது.
“The water has been found! Mystery solved!” Divya said. “WOOOOOO!” They yowled with joy.
“தண்ணீர் கண்டுபிடிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது! மர்மம் தீர்ந்தது”, என்றாள் திவ்யா. “ஊ…” அவர்கள் மகிழ்ச்சியுடன் குரல் எழுப்பினர்.
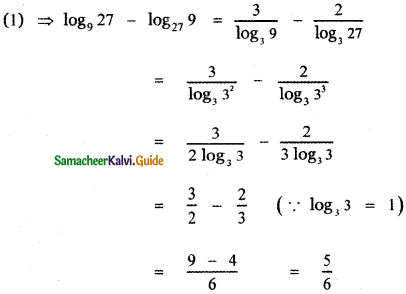
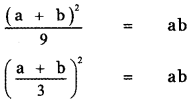
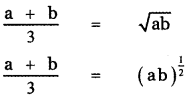
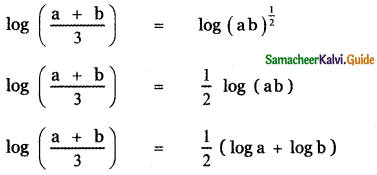
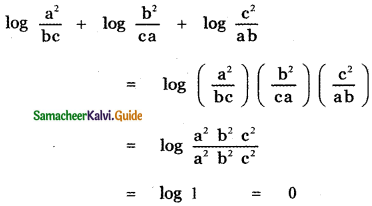
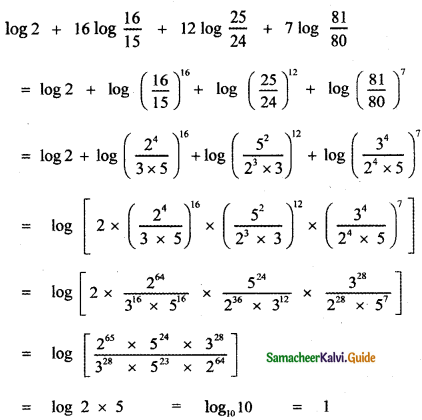
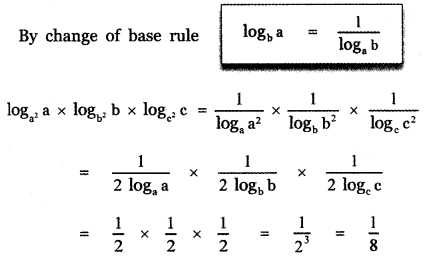
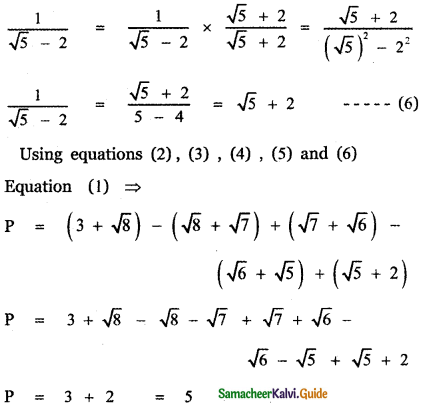
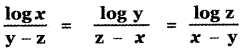 , then prove that xyz = 1
, then prove that xyz = 1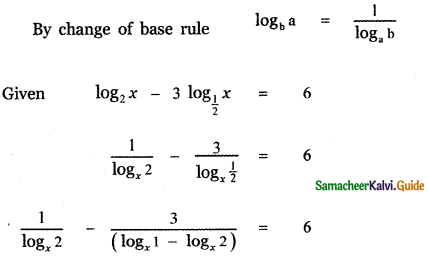

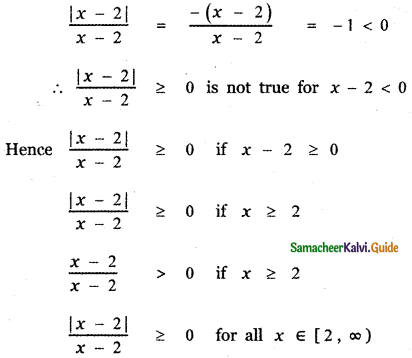
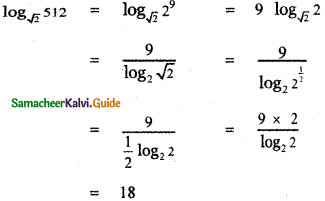
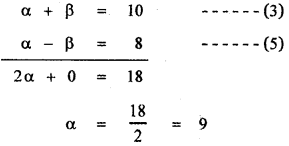
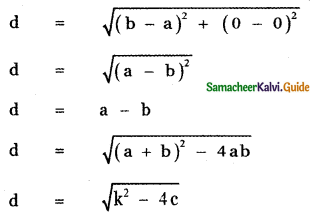
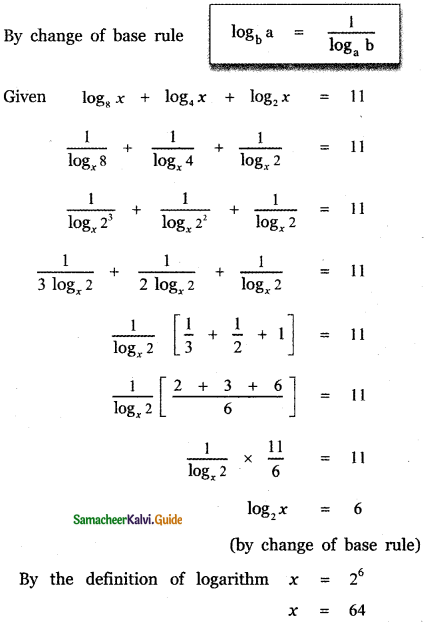
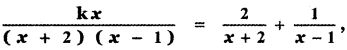 then the value of k is
then the value of k is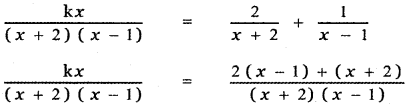
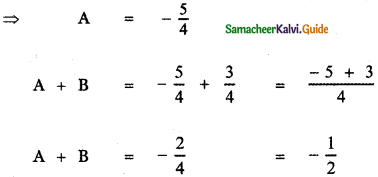
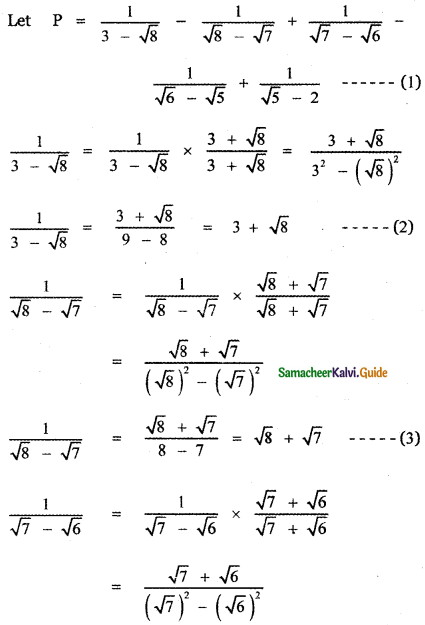
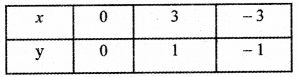
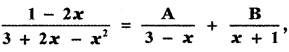 , then the value of A + B is
, then the value of A + B is