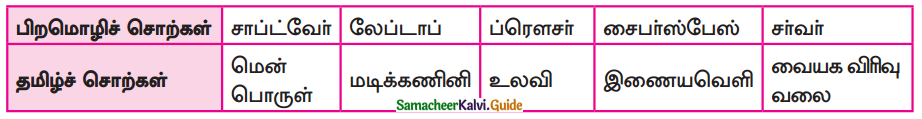
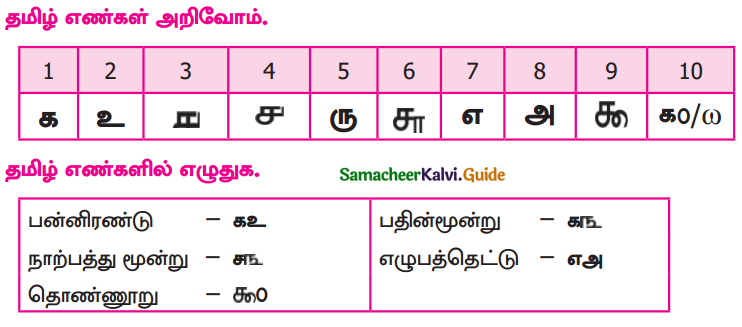
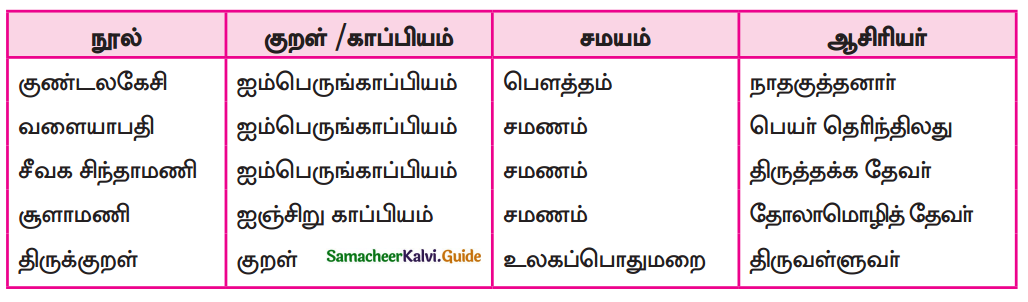
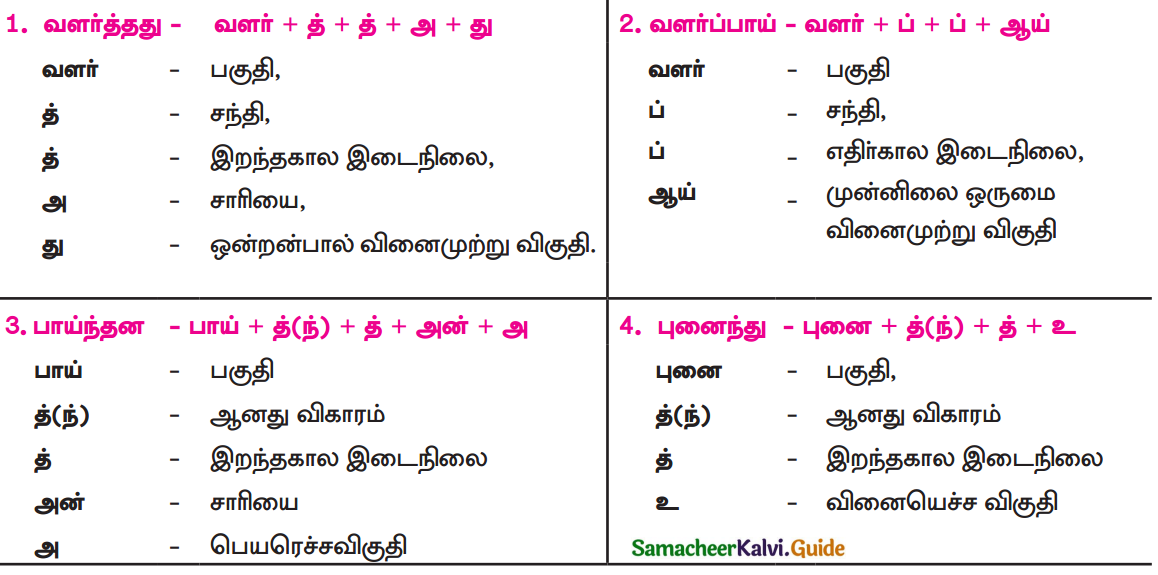
Students can Download 9th Tamil Chapter 2.1 நீரின்றி அமையாது உலகு Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Tamil Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Tamil Solutions Chapter 2.1 நீரின்றி அமையாது உலகு
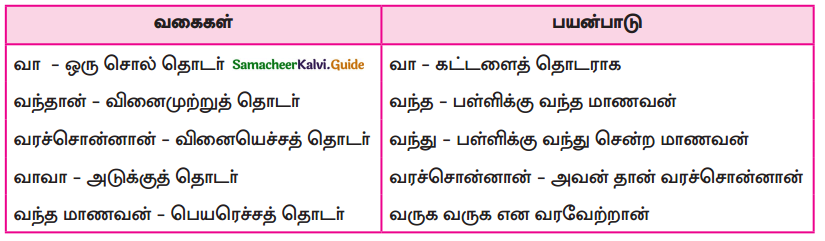
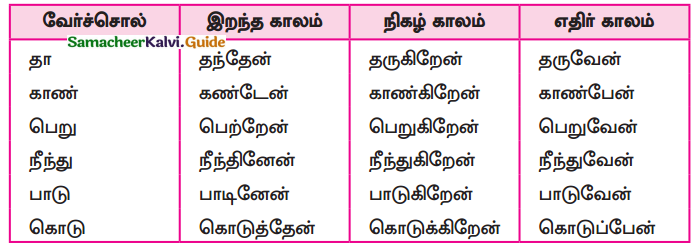
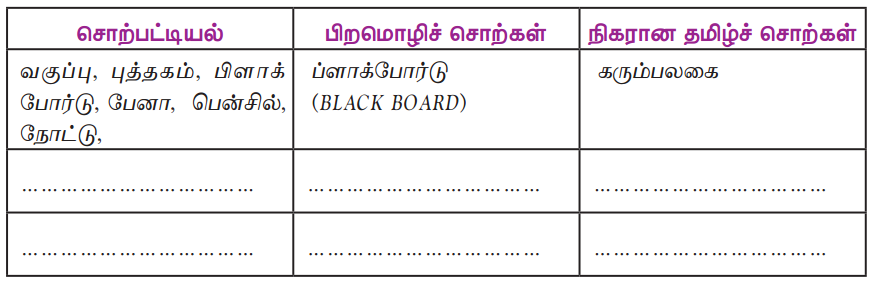
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
நீரின்று அமையாது உலகு, நீரின்று அமையாது யாக்கை இவ்விரண்டு தொடர்களையும் ஒப்புமைப்படுத்தி வகுப்பில் கலந்துரையாடுக.
Answer:

![]()
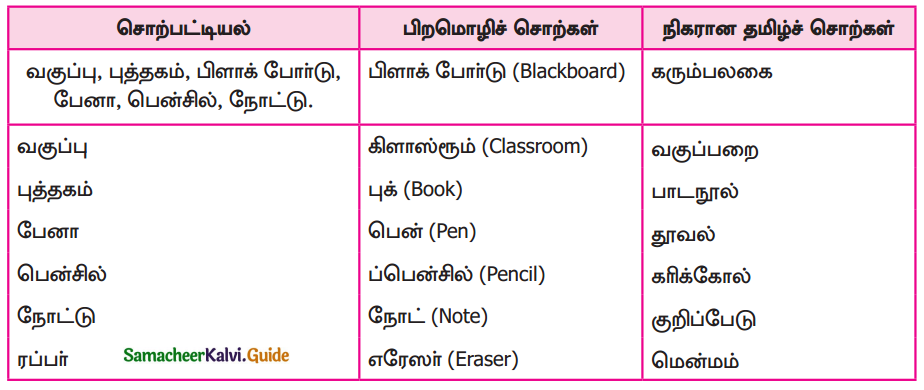
Question 2.
வீடுகளில் பயன்படுத்தப்படும் தண்ணீர் எங்கிருந்து கிடைக்கிறது? இதற்கான நீர் எங்கிருந்து வருகிறது? இன்னும் எவ்வளவு காலத்திற்குத் தண்ணீர் போதுமானதாக இருக்கும்? என்பவற்றுக்கான தகவல்களைத் திரட்டி ஒப்புடைவு உருவாக்குக.
Answer:
- நம் வீடுகளில் நாம் பயன்படுத்தும் தண்ணீ ருக்கு ஆதாரமாக இருப்பது நிலத்தடி நீர்,
- அணைகளில் தேக்கி வைக்கப்பட்டிருக்கும் நீர், கிணற்றுநீர் ஆகியவை ஆகும்.
- ஆழ்குழாயில் வரும் நீரின் வேகத்தைப் பொறுத்து அஃது எவ்வளவு நாள் வரும் என கணக்கிடப்படும்.
அணைகளின் கொள்ளளவை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்டு எவ்வளவு காலம் பயன்படுத்தலாம் என்று கூறுவர். அணைகளில் வெளியேறும் நீர்வரத்து நீரை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்டும், வானிலை அறிக்கை தெரிவிக்கும் மழையின் போக்கைக் கொண்டும், ஒரு மாதத்திற்கு போதுமானது….. எத்தனை நாட்களுக்கு பிரச்சனையின்றி நீர் வழங்கலாம் போன்றவை முடிவு செய்யப்படும்.
அதன் அடிப்படையில் மக்களின் குடிநீர், பயன்படுத்தும் நீரின் தேவை பூர்த்தி செய்யப்படும்.
![]()
பாடநூல் வினாக்கள்
பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
நீர் நிலைகளோடு தொடர்பில்லாதது எது?
அ) அகழி
ஆ) ஆறு
இ) இலஞ்சி
ஈ) புலரி
Answer:
ஈ) புலரி
![]()
Question 2.
பொருத்தமான விடையைத் தேர்க.
அ) நீரின்று அமையாது உலகு – திருவள்ளுவர்
ஆ) நீரின்று அமையாது யாக்கை – ஒளவையார்
இ) மாமழை போற்றுதும் – இளங்கோவடிகள்
i) அ, இ, ஆ
ii) ஆ, இ, அ
iii) ஆ, அ , இ
iv) அ, ஆ, இ
Answer:
iv) அ, ஆ, இ
குறுவினா
Question 1.
“கூவல்” என்று அழைக்கப்படுவது எது?
Answer:
உவர்மண் (களர்மண்) நிலத்தில் தோண்டப்படும் நீர்நிலைக்கு கூவல் என்று பெயர்.
![]()
Question 2.
உங்களது பள்ளியைச் சுற்றியுள்ள நீர்நிலைகளின் பெயர்களைக் குறிப்பிடுக.
Answer:
ஆழிக் கிணறு – கடலருகே தோண்டிக் கட்டிய கிணறு
இலஞ்சி – பலவகைக்கும் பயன்படும் நீர்த்தேக்கம்
ஊருணி – மக்கள் பருகு நீர் உள்ள நீர்நிலை
கேணி – அகலமும் ஆழமும் உள்ள பெருங்கிணறு
பூட்டைக் கிணறு – கமலை நீர்பாய்ச்சும் அமைப்புள்ள கிணறு
Question 3.
மணிநீரும் மண்ணும் மலையும் அணிநிழற்
Answer:
காடும் உடையது அரண்
– இக்குறள் கூறும் நாட்டின் அரண்கள் யாவை?
மணிபோல் தெளிவான நீரும், வெட்ட வெளியான நிலமும், ஓங்கி உயர்ந்த மலையும் நிழல் தருகிற காடும் ஆகிய நான்கும் அமைந்து இருப்பதே ஒரு நாட்டின் அரண் ஆகும்.
![]()
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
அடுத்த தலைமுறைக்கும் தண்ணீர் தேவை – அதற்கு நாம் செய்ய வேண்டியவற்றை எழுதுக.
Answer:
- ஐம்பூங்களுள் ஒன்று நீர். அது நிலம், காற்று, நெருப்பு வானம் ஆகிய நான்குடன் தொடர்பு
- கொண்டு இயங்கவல்லது. நம் முன்னோர் கிடைத்த நீரை அளவோடு பயன்படுத்தினர்.
- அதனால் நாமும், நீரை அளவோடு பயன்படுத்தி வரும் தலைமுறைக்கு பாதுகாத்து வைக்க வேண்டும்.
- ‘குளம் தொட்டு வளம் பெருக்கி வாழ்ந்தவர்கள் தமிழர். இன்றும் நீர்நிலைகளைப் பாதுகாத்துப் பராமரிக்க வேண்டும்.
- மழைநீரைப் பயன்படுத்தும் முறை அறியவேண்டும். இளம் தலைமுறையினர்க்கு நீர் மேலாண்மை பயிற்சி வழங்க வேண்டும்.
![]()
Question 2.
சோழர்காலக் குமிழித்தூம்பு எதற்காகப் பயன்படுத்தப்பட்டது?
Answer:
- குமிழித்தூம்பு என்பது ஏரியில் உள்ள நீரையும் சேறையும் வெறியேற்றுவதற்காகப் பயன்படுத்தப் பட்டன.
- சோழர்காலத்தில் நீர்நிரம்பி நிற்கும் ஏரிக்குள் நீந்தி கழிமுகத்தை (ஏரி நீர்க்கழிவு) அடைந்து குமிழித் தூம்பைத் தூக்கி விடுவார்கள்.
- குமிழித்தூம்பில் இரண்டு துளைகள் இருக்கும். மேலே இருக்கும் நீரோடித் துளையிலிருந்து
- நீர் வெளியேறும். கீழே இருக்கும் சேறோடித் துளையிலிருந்து நீர் சுழன்று சேற்றுடன் வெளியேறும். இதனால் தூர் வாரத் தேவையில்லை .
![]()
நெடுவினா
Question 1.
நீரின்று அமையாது உலகு – என்னும் வள்ளுவரின் அடி உணர்த்தும் பொருள் ஆழத்தை எடுத்துக் காட்டுடன் விவரி.
Answer:
முன்னுரை :
‘நீர்இன்று அமையாது உலகு எனின் யார்யார்க்கும்
வான்இன்று அமையாது ஒழுக்கு’
ஒழுக்கம் உயிரினும் சிறந்தது. எத்தகைய சிறப்புகளை உடையவர்களுக்கும் நீர் இல்லையேல் ஒழுக்கங்கள் அமையா. எனவே மழையின்றி ஒழுக்கம் நிலை பெறாது என்று திருவள்ளுவர் குறிப்பிடுகிறார். நம்முன்னோர்கள் பல்வேறு நீர்நிலை வடிவங்களை அமைத்து நீரைப் பாதுகாத்தனர். நாமும் இனிவரும் தலைமுறையினர்க்கு நீரைப் பாதுகாத்து வைக்க வேண்டும்.
மழை உழவுக்கு உதவுகிறது :
மழை உழவுத் தொழிலுக்கு உதவுகிறது. விதைத்து வாழ வேண்டும் என்னும் நோக்கில் வளர்கின்றன. ” நிலமும் மரமும் உயிர்களும் நோயின்றி வாழ வேண்டும் என்ற புலவர்களுள் ஒருவரான மாங்குடி மருதனார் கூறியதைப் புரிந்துகொள்ள வேண்டும்.
![]()
ஒவ்வொரு வட்டாரத்தின் நில அமைப்பு, மண்வளம், வடிவமைக்கப்பட்டிருந்தது, இதில் ஏரிகளும் குளங்களும் பாசனத்திற்கான எளிய வடிவங்களாகப் பயன்பட்டன.
உணவெனப் படுவது நிலத்தொடு நீரே:
உணவெனப்படுவது நிலத்தோடு நீரே என்னும் சங்கப்பாடல், நீரின் இன்றியமையாத் தேவையை எடுத்துரைக்கிறது.
‘மணிநீரும் மண்ணும் மலையும் அணிநிழற்
காடும் உடையது அரண்’
என்னும் குறளில் நாட்டின் சிறந்த அரண்களுள் நீருக்கே முதலிடம் தருகிறார்.
உலகச் சுகாதார நிறுவனம், “உலகம் விரைவில் குடிநீருக்கான கடும் சிக்கலை எதிர்கொள்ளும்” என எச்சரிக்கிறது. குடிநீரை விலை கொடுத்து வாங்கும் அவலம் தொடரும் நிலையை மாற்றியமைக்கத் திட்டமிட வேண்டியது உடனடித் தேவையாகும். ஆண்டுதோறும், பெறுகின்ற மழைப்பொழிவை ஆக்கநிலையில் பயன்படுத்தும் செயல் திட்டத்தை உருவாக்க வேண்டும்.
![]()
பல்லுயிர்ப் பாதுகாப்பு :
உலகின் பல்லுயிர்ப் பாதுகாப்பிற்கு அடிப்படை தண்ணீர் நமது முன்னோர்கள் கண்டுணர்ந்த வாழ்வியல் அணுகுமுறைகளைப் பின்பற்ற வேண்டும். குளம், ஏரி, கால்வாய், கிணறு போன்ற நீர்நிலைகளின் பாதுகாப்பு குறித்த விழிப்புணர்வை மக்களிடம் உருவாக்க வேண்டும். இதை ஒரு மக்கள் இயக்கமாக மாற்ற வேண்டும்.
நிறைவுரை :
உணவு உற்பத்திக்கு அடிப்படை நீரே. அந்த நீரே உணவாகவும் இருக்கிறது. இதை இரண்டாயிரம் ஆண்டுகளுக்கு முன்பே திருவள்ளுவர்,
“துப்பார்க்குத் துப்பாய துப்பாக்கித் துப்பார்க்குத்
துப்பாய தூஉம் மழை”
என்று கூறியுள்ளதைக் கருத்தில் கொண்டு செயல்படுவோம்.
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
பாண்டி மண்டலத்தில் ஏரியை ……….. என்று அழைப்பர்.
அ) ஊருணி
ஆ) கண்மாய்
இ) குளம்
ஈ) அகழி
Answer:
ஆ) கண்மாய்
![]()
Question 2.
உலகச் சுற்றுச்சூழல் தினம் கொண்டாடப்படும் நாள் ……..
அ) ஜுன் 5
ஆ) மார்ச் 20
இ) அக்டோபர் 5
ஈ) பிப்ரவரி 2
Answer:
அ) ஜுன் 5
![]()
Question 3.
‘நிலமும் மரமும் உயிர்கள் நோயின்றி வாழ வேண்டும் எனும் நோக்கில் வளர்கின்றன’ என்று கூறியவர் ………..
அ) மிளைகிழான் நல்வேட்டனார்
ஆ) கணிமேதாவியார்
இ) மாங்குடி மருதனார்
ஈ) நல்லந்துவனார்
Answer:
இ) மாங்குடி மருதனார்
Question 4.
‘இந்திய நீர்ப்பாசனத்தின் தந்தை’ என்று போற்றப்படுபவர் ………
அ) பென்னி குயிக்
ஆ) விஸ்வேஸ்வரய்யா
இ) சர்.பக்கிள்
ஈ) சர். ஆர்தர் காட்டன்
Answer:
ஈ) சர். ஆர்தர் காட்டன்
![]()
Question 5.
‘கிராண்ட் அணைக்கட்’ என்று அழைக்கப்படுவது …………
அ) பக்ரா நங்கல்
ஆ) ஹிராகுட்
இ) சர்தார் சரோவர்
ஈ) கல்லணை
Answer:
ஈ) கல்லணை
Question 6.
பொருந்தாத இணையைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
அ) குண்டு – குளிப்பதற்கேற்ற சிறுகுளம்
ஆ) அருவி – மலைமுகட்டுத் தேக்க நீர்
இ) அகழி – கோட்டைப்புறத்து நீர் அரண்
ஈ) கூவல் – மக்கள் பருகுநீர்நிலை
Answer:
ஈ) கூவல் – மக்கள் பருகுநீர்நிலை
![]()
Question 7.
திருமணம் முடிந்த பின் தொடர் நிகழ்வை ………. என்பர்.
அ) சனி நீராடு
ஆ) மஞ்சள் நீராட்டு
இ) கடலாடுதல்
ஈ) பூப்புனித நீராட்டு
Answer:
இ) கடலாடுதல்
Question 8.
பொருந்தாத இணையைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
அ) குண்டம் – குளிக்கும் நீர்நிலை
ஆ) கூவல் – உவர்மண் நிலத்தில் தோண்டப்படும் நீர்நிலை
இ) ஊருணி – மக்கள் பருகும் நீர்நிலை
ஈ) கண்மாய் – உவர் நீர்நிலை
Answer:
ஈ) கண்மாய் – உவர் நீர்நிலை
![]()
நிரப்புக
9. மழை பற்றிய பத்துக் குறட்பாக்கள் அடங்கிய அதிகாரம் ………….
Answer:
வான்சிறப்பு
10. மாமழை போற்றுதும் என்று போற்றியவர் ………..
Answer:
இளங்கோவடிகள்
11. கல்லணையின் கட்டுமான உத்தியைக் கொண்டு கட்டப்பட்ட அணை
Answer:
தௌலீஸ்வரம்
12. நாம் வாழும் தமிழ்நாடு……….. பகுதியில் உள்ளது.
Answer:
வெப்ப மண்டலப்
13. சனிநீராடு என்றவர் ………….
Answer:
ஔவையார்
![]()
14. அகலமும், ஆழமும் உள்ள பெருங்கிணறு ………….
Answer:
கேணி
15. தேக்கப்பட்ட பெரிய நீர்நிலை …………
Answer:
சிறை
16. பலவகைக்கும் பயன்படும் நீர்த்தேக்கம் ……….. எனப்படும்.
Answer:
இலஞ்சி
17. முல்லைப் பெரியாறு அணை கட்டியவர் …………
Answer:
ஜான் பென்னிகுயிக்
18. ஒரு நாட்டின் சிறந்த அரண்களுள் முதன்மையாகத் திகழ்வது …………
Answer:
நீர் அரண்
![]()
குறுவினா
Question 1.
நன்னீர் நிலைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
மழைநீர், ஆற்றுநீர், ஊற்றுநீர் மூலம் கிடைக்கும் நீர்நிலைகள்.
Question 2.
நீ அறிந்த தமிழகத்தின் மூன்று நீர்நிலைப் பெயர்களுக்கு விளக்கம் தருக.
Answer:
- ஆழிக்கிணறு : கடலருகே தோண்டிக் கட்டிய கிணறு.
- ஊருணி : மக்கள் பருகு நீர் உள்ள நீர்நிலை.
- உறைக்கிணறு : மணற்பாங்கான இடத்தில் தோண்டிச் சுடுமண் வளையமிட்ட கிணறு.
Question 3.
ஜான் பென்னி குயிக் – குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
தமிழகத்தில் மதுரை தேனி, திண்டுக்கல், சிவகங்கை, இராமநாதபுரம் ஆகிய மாவட்டங்களுக்குக் குடிநீருக்கும், விவசாயத்திற்கும் பயன்படும் முல்லைப் பெரியாறு அணையைக் கட்டியவர். ஆங்கில அரசாங்கம் கூடுதல் நிதி ஒதுக்க மறுத்த போது தனது சொத்துக்களை விற்று அணையைக் கட்டிமுடித்தார்.
![]()
Question 4.
நிலத்தடி நீர்வளம் குறைந்து வரும் நாடுகள் யாவை?
Answer:
அமெரிக்கா, இந்தியா, பாகிஸ்தான், சீனா.
Question 5.
கல்லணை பற்றிக் குறிப்பு தருக.
Answer:
- பல நூற்றாண்டுகளுக்கு முன் கரிகால் சோழன் காலத்தில் கட்டப்பட்டது.
- நீளம் – 1080 அடி, அகலம் – 40 முதல் 60 அடி, உயரம் – 15 முதல் 18 அடி.
- கல்லணை நம் முன்னோரின் திட்ப நுட்பத்திற்கும், தொழில் நுட்பத்திற்கும் சான்றாகத் திகழ்கிறது.
Question 6.
‘குளித்தல்’ என்பதன் பொருள் யாது?
Answer:
சூரிய வெப்பத்தாலும் உடல் உழைப்பாலும் வெப்பமடைந்த உடலைக் குளிரவைத்தலாகும். குளிர்த்தல் என்பதே குளித்தல் என்று ஆனது.
![]()
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
கல்லணையைக் கட்ட பயன்படுத்தப்பட்ட தொழில்நுட்பத்தை விவரி.
Answer:
காவிரி ஆற்றின் மீது பெரிய பாறைகளைக் கொண்டு வந்து போட்டனர். அந்தப் பாறைகளும் நீர் அரிப்பின் காரணமாகக் கொஞ்சம் கொஞ்சமாக மண்ணுக்குள் சென்றன.
அவற்றின் மேல் வேறொரு பாறையை வைத்து நடுவே தண்ணீரில் கரையாத ஒருவித ஒட்டும் களிமண்ணைப் புதிய பாறைகளில் பூசி, இரண்டையும் ஒட்டிக்கொள்ளும் விதமாகச் செய்தனர்.
![]()
இதுவே, கல்லணையைக் கட்டப் பயன்படுத்தப்பட்ட தொழில் நுட்பமாகக் கருதப்படுகிறது.