Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 9 Introduction to C++ Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 9 Introduction to C++
11th Computer Science Guide Introduction to C++ Text Book Questions and Answers
Book Evaluation
Part I
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Who developed C++?
a) Charles Babbage
b) Bjarne Stroustrup
c) Bill Gates
d) Sundar Pichai
Answer:
b) Bjarne Stroustrup
Question 2.
What was the original name given to C++?
a) CPP
b) Advanced C
c) C with Classes
d) Class with C
Answer:
c) C with Classes
![]()
Question 3.
Who coined C++?
a) Rick Mascitti
b) Rick Bjarne
c) Bill Gates
d) Dennis Ritchie
Answer:
a) Rick Mascitti
Question 4.
The smallest individual unit in a program is:
a) Program
b) Algorithm
c) Flowchart
d) Tokens
Answer:
d) Tokens
Question 5.
Which of the following operator is extraction operator of C++?
a) >>
b) <<
c) <>
d) AA
Answer:
a) >>
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following statements is not true?
a) Keywords are the reserved words convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
b) Reserved words or keywords can be used as an identifier name.
c) An integer constant must have at least one digit without a decimal point.
d) Exponent form of real constants consists of two parts
Answer:
b) Reserved words or keywords can be used as an identifier name.
Question 7.
Which of the following is a valid string literal?
a) ‘A’
b) ‘Welcome’
c) 1232
d) “1232”
Answer:
d) “1232”
Question 8.
A program written in high level language is called as ………………………
a) Object code
b) Source code
e) Executable code
d) All the above
e) Executable code
Answer:
b) Source code
![]()
Question 9.
Assume a=5, b=6; what will be result of a & b?
a) 4
b) 5
c) 1
d) 0
Answer:
a) 4
Question 10.
Which of the following is called as compile time operators?
a) size of
b) pointer
c) virtual
d) this
Answer:
a) sizeof
![]()
Part – II
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
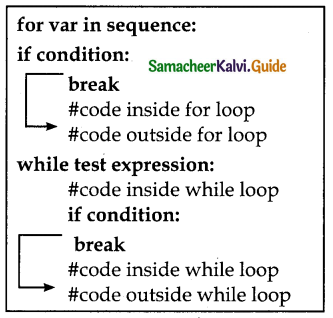
What is meant by a token? Name the token available in C++.
Answer:
C++ program statements are constructed by many different small elements such as commands, variables, constants, and many more symbols called operators and punctuators. Individual elements are collectively called Lexical units or Lexical elements or Tokens.
C++ has the following tokens:
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Literals
- Operators
- Punctuators
Question 2.
What are keywords? Can keywords be used as identifiers?
Answer:
Keywords:
Keywords are the reserved words which convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
They are the essential elements to construct C++ programs.
Example:
int / float / auto / register Reserved words or keywords cannot be used as an identifier name.
![]()
Question 3.
The following constants are of which type?
- 39
- 032
- OXCAFE
- 04.14
Answer:
- 39 – Decimal
- 032 – Octal
- OXCAFE – Hexadecimal
- 04.14 – Decimal
Question 4.
Write the following real constants into the exponent form:
i) 23.197
ii) 7.214
iii) 0.00005
iv) 0.319
Answer:
i) 23.197 : 0.23197 E2 (OR) 2.3197 E1 (OR) 23197E-3
ii) 7.214 : 0.7214 E1 (OR) 72.14 E-1 (OR) 721.4 E-2 (OR) 7214E-3
iii) 0.00005 : 5E-5
iv) 0.319 : 3.19 E-l (OR) 31.9 E-2 (OR) 319 E-3
Question 5.
Assume n=10; what will be result of n>>2;?
Answer:
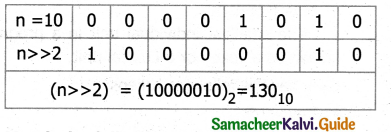
![]()
Question 6.
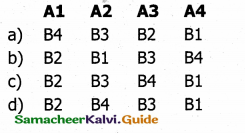
Match the following:
|
A |
B |
| (a) Modulus | (1) Tokens |
| (b) Separators | (2) Remainder of a division |
| (c) Stream extraction | (3) Punctuators |
| (d) Lexical Units | (4) get from |
Answer:
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 1
Part – III
Short Answers
Question 1.
Describe the differences between keywords and identifiers.
Answer:
Keywords:
- Keywords are the reserved words which convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
- They are essential elements to construct C++ programs.
- Most of the keywords are common to C, C++, and Java.
Identifiers:
- Identifiers are the user-defined names given to different parts of the C++ program.
- They are the fundamental building blocks of a program.
- Every language has specific rules for naming the identifiers.
Question 2.
Is C++ case sensitive? What is meant by the term “case sensitive”?
Answer:
Yes. C++ is case sensitive as it treats upper and lower-case characters differently.
Example: NUM, Num, num are different in C++.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate “=” and “==”.
Answer:
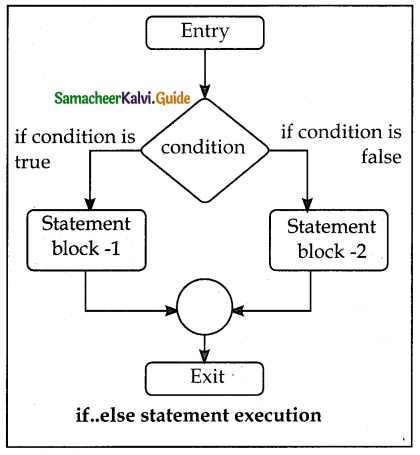
- ‘=’ is an assignment operator which is used to assign a value to a variable which is on the left hand side of an assignment statement.
- ‘=’operator copies the value at the right side
of the operator to the left side variable. Ex. num = 10; means 10 assign to the variable num. - ‘= =’ is a relational operator. It is used to compare both operands are same or not.
- Ex. num = = 10 means it compare num value with 10 and returns true(l) if both are same or returns false(0)
Question 4.
Assume a=10, b=15; What will be the value of a∧b?
Answer:
Bitwise XOR (∧) will return 1 (True) if only one of the operand is having a value 1 (True). If both are True or both are False, it will return 0 (False).
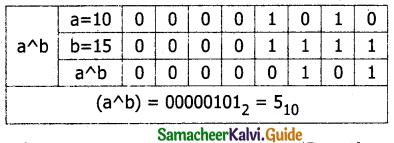
Question 5.
What is the difference between “Run time error” and “Syntax error”?
Answer:
Run time Error:
- A run time error occurs during the execution of a program. It occurs because of some illegal operation that takes place.
- For example, if a program tries to open a file which does not exist, it results in a run-time error.
Syntax Error:
- Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated.
- For example: if you type as follows, C++ will throw an error.
cout << “Welcome to Programming in C++”
![]()
Question 6.
What are the differences between “Logical error” and “Syntax error”?
Answer:
- A Program has not produced the expected result even though the program is grammatically correct. It may be happened by the wrong use of variable/operator/order of execution etc. This means, the program is grammatically correct, but it contains some logical error. So, a Semantic error is also called a “Logic Error”.
- Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated.
Question 7.
What is the use of a header file?
Answer:
Header files contain definitions of Functions and Variables, which are imported or used into any C++ program by using the preprocessor #include statement. Header files have an extension “.h” which contains C++ function declaration and macro definition.
Example: #include
Question 8.
Why is main function special?
Answer:
Every C++ program must have a main function. The main() function is the starting point where all C++ programs begin their execution. Therefore, the executable statements should be inside the main() function.
Question 9.
Write two advantages of using include compiler directive.
Answer:
- The program is broken down into modules, thus making it more simplified.
- More library functions can be used, at the same time size of the program is retained.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the following in real constants.
- 15.223
- 211.05
- 0.00025
Answer:
- 15.223 → 1.5223E1 → 0.15223E2 → 15223E-3
- 211.05 → 2.1105E2 → 21105 E-2
- 0.00025 → 2.5E-4
Part – IV
Explain In Detail
Question 1.
Write about Binary operators used in C++.
Answer:
Binary Operators require two operands:
Arithmetic operators that perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division (+, -, *, %, /), etc. are binary operators which require a minimum of two operands.
Relational operators are used to determining the relationship between its operands. The relational operators (<, >, >=, <=, ==, !=) are applied on two operands, hence they are binary operators. AND, OR (logical operator) both are binary operators. The assignment operator is also a binary operator (+=, – =, *=, /=, %=).
Question 2.
What are the types of Errors?
Answer:
COMMON TYPES OF ERRORS
| Type of Error |
Description |
| Syntax Error | Syntax is a set of grammatical rules to construct a program. Every programming language has unique rules for constructing the sourcecode. Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated. Example: if we type as follows, C++ will throw an error. cout << “Welcome to C++” |
| As per grammatical rules of C++, every executable statement should terminate with a semicolon. But, this statement does not end with a semicolon. | |
| Semantic error’ | A Program has not produced expected result even though the program is grammatically correct. It may be happened by the wrong use of variable/operator/order of execution etc. This means, the program is grammatically correct, but it contains some logical error. So, Semantic error is also called a “Logic Error”. |
| Run time error | A run time error occurs during the execution of a program. It occurs because of some illegal operation that takes place. For example, if a program tries to open a file which does not exist, it results in a run-time error. |
![]()
Question 3.
Assume a=15, b=20; What will be the result of the following operations?
a) a&b
b) a|b
c) aAb
d)a>>3
e) (~b)
Answer:
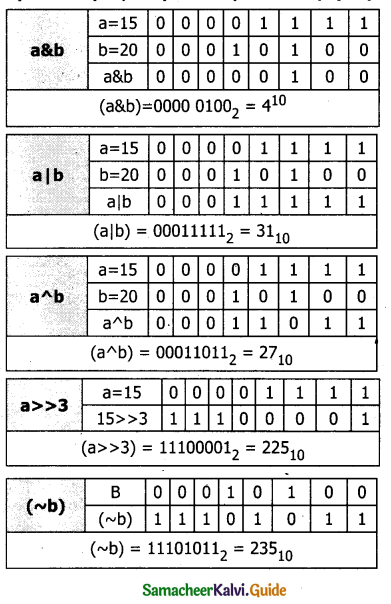
11th Computer Science Guide Introduction to C++ Additional Questions and Answers
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
The latest standard version published in December 2017 as ISO/IEC …………….. which is informally known as C++ 17.
(a) 14882 : 1998
(b) 14883 : 2017
(c) 14882 : 2017
(d) 14882 : 2000
Answer:
(c) 14882 : 2017
Question 2.
C++ language was developed at ……………….
a) Microsoft
b) Borland International
c) AT & T Bell Lab
d) Apple Corporation
Answer:
c) AT & T Bell Lab
Question 3.
An integer constant is also called……………..
(a) fixed point constant
(b) floating-point constant
(c) real constants
(d) Boolean literals
Answer:
(a) fixed point constant
![]()
Question 4.
C++supports ………… programming paradigms.
a) Procedural
b) Object-Oriented
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 5.
…………….. relational operators are binary operators.
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 6
(d) 2
Answer:
(c) 6
Question 6.
C++ is a superset (extension) of …………….. language.
a) Ada
b) BCPL
c) Simula
d) C
Answer:
d) C
![]()
Question 7
…………….. used to label a statement.
(a) colon
(b) comma
(c) semicolon
(d) parenthesis
Answer:
(a) colon
Question 8.
The name C++ was coined by …………….
a) Lady Ada Lovelace
b) Rick Mascitti
c) Dennis Ritchie
d) Bill Gates
Answer:
b) Rick Mascitti
Question 9.
IDE stands for ……………..
(a) Integrated Development Environment
(b) International Development Environment
(c) Integrated Digital Environment
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Integrated Development Environment
![]()
Question 10.
Till 1983, C++ was referred to as …………………
a) New C
b) C with Classes
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 11.
…………….. data type signed more precision fractional value.
(a) char
(b) short
(c) long double
(d) signed doubles
Answer:
(c) long double
Question 12.
C# (C-Sharp), D, Java, and newer versions of C languages have been influenced by ………………. language.
a) Ada
b) BCPL
c) Simula
d) C++
Answer:
d) C++
![]()
Question 13.
…………….. manipulator is the member of iomanip header file.
(a) setw
(b) setfill
(c) setf
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 14.
C++is ……………… language.
a) Structural
b) Procedural
c) Object-oriented
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Object-oriented
Question 15.
C++ includes ………………..
a) Classes and Inheritance
b) Polymorphism
c) Data abstraction and Encapsulation
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 16.
C language does not allow ………………
a) Exception handling
b) Inheritance
c) Function overloading
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 17.
……………. is a set of characters which are allowed to write a C++ program.
a) Character set
b) Tokens
c) Punctuators
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Character set
Question 18.
A character represents any …………………..
a) Alphabet
b) Number
c) Any other symbol (special characters)
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 19.
Most of the Character set, Tokens, and expressions are very common to C based programming languages like ………………..
a) C++
b) Java
c) PHP
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 20.
…………… is a white space.
a) Horizontal tab
b) Carriage return
c) Form feed
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 21.
C++ program statements are constructed by many different small elements called……………….
a) Lexical units
b) Lexical elements
c) Tokens
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 22.
…………… is a C++token.
a) Keywords
b) Identifiers and Literals
c) Punctuators and Operators
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 23.
The smallest individual unit in a program is known as a ……………
a) Token
b) Lexical unit
c) Token or a Lexical unit
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Token or a Lexical unit
Question 24.
………………… are the reserved words which convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
a) Keywords
b) Identifiers and Literals
c) Punctuators and Operators
d) All the above
Answer:
a) Keywords
![]()
Question 25.
………………. are the essential elements to construct C++ programs.
a) Keywords
b) Identifiers and Literals
c) Punctuators and Operators
d)All the above
Answer:
a) Keywords
Question 26.
Most of the keywords are common to …………… languages.
a) C, and C++
b) C++ and Java
c) C, C++ and Java
d) None of these
Answer:
c) C, C++ and Java
Question 27.
……………. is a case sensitive programming language.
a) C, and C++
b) C++ and Java
c) C, C++ and Java
d) None of these
Answer:
c) C, C++ and Java
![]()
Question 28.
In ……………. language, all the keywords must be in lowercase.
a) C, and C++
b) C++ and Java
c) C, C++ and Java
d) None of these
Answer:
c) C, C++ and Java
Question 29.
……………… is a new keyword in C++.
a) using
b) namespace
c) std
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 30.
…………….. is a new keyword in C++.
a) bal
b) static_cast
c) dynamic_cast
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 31.
………….. is a new keyword in C++.
a) true
b) false
c) Both A and B
c) None of these
Answer:
c) None of these
Question 32.
Identifiers are the user-defined names given to …………..
a) Variables and functions
b)Arrays
c) Classes
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 33.
Identifiers containing a …………. should be avoided by users.
a) Double underscore
b) Underscore
c) number
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Double underscore
![]()
Question 34.
The first character of an identifier must be an ………….
a) Alphabet
b) Underscore (_)
c) Alphabet or Underscore (_)
c) None of these
Answer:
c) Alphabet or Underscore (_)
Question 35.
Only …………… is permitted for the variable name.
a) Alphabets
b) Digits
c) Underscore
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 36.
Identify the correct statement from the following.
a) C++ is case sensitive as it treats upper and lower-case characters differently.
b) Reserved words or keywords cannot be used as an identifier name.
c) As per ANSI standards, C++ places no limit on its length.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 37.
ANSI stands for …………..
a) All National Standards Institute
b) Advanced National Standards Institute
c) American National Standards Institute
d) None of these
Answer:
c) American National Standards Institute
Question 38.
Identify the invalid variable name from the following.
a) num-add
b) this
c) 2myfile
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 39.
Identify the odd one from the following.
a) Int
b) _add
c) int
d) tail marks
Answer:
c) int
![]()
Question 40.
……………… are data items whose values do not change during the execution of a program.
a) Literals
b) Constants
c) Identifiers
d) Both A and B
Answer:
d) Both A and B
Question 41.
…………. is a type constant in C++.
a) Boolean constant
b) Character constant
c) String constant
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 42.
…………… is a type of numeric constant.
a) Fixed point constant
b) Floating-point constant
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
![]()
Question 43.
……………. are whole numbers without any fractions.
a) Integers
b) Real constant
c) Floating-point constant
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Integers
Question 44.
In C++, there are …………….. types of integer constants.
a) Two
b) Three
c) Four
d) Six
Answer:
b) Three
Question 45.
In C++, ……………… is a type of integer constant.
a) Decimal
b) Octal
c) Hexadecimal
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 46.
Any sequence of one or more digits (0 …. 9) is called ……………… integer constant.
a) Decimal
b) Octal
c) Hexadecimal
d) All the above
Answer:
a) Decimal
Question 47.
Any sequence of one or more octal values (0 …. 7) that begins with 0 is considered as a(n) …………… constant.
a) Decimal
b) Octal
c) Hexadecimal
d) All the above
Answer:
b) Octal
Question 48.
When you use a fractional number that begins with 0, C++ has consider the number as ………………..
a) An integer not an Octal
b) A floating-point not an Octal
c) An integer not a Hexadecimal
d) None of these
Answer:
a) An integer not an Octal
![]()
Question 49.
Any sequence of one or more Hexadecimal values (0 …. 9, A …. F) that starts with Ox or OX is considered as a(n) ………….. constant.
a) Decimal
b) Octal
c) Hexadecimal
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Hexadecimal
Question 50.
Identify the invalid octal constant,
a) 05,600
b) 04.56
c) 0158
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 51.
Identify the valid hexa decimal constant
a) 0X1,A5
b) 0X.14E
c) CAFE
d) CPP
Answer:
c) CAFE
![]()
Question 52.
The suffix ………….. added with any constant forces that to be represented as a long constant.
a) L or I
b) U or u
c) LO
d) Lg
Answer:
a) L or I
Question 53.
The suffix …………… added with any constant forces that to be represented as an unsigned constant.
a) L or I
b) U or u
c) US
d) us
Answer:
b) U or u
Question 54.
A _______ constant is a numeric constant having a fractional component.
a) Real
b) Floating point
c) Real or Floating point
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Real or Floating point
![]()
Question 55.
……………. constants may be written in fractional form or in exponent form.
a) Real
b) String
c) Character
d) Integer constant
Answer:
a) Real
Question 56.
Exponent form of real constants consists of ………….. parts.
a) three
b) two
c) four
d) five
Answer:
b) two
Question 57.
Exponent form of real constants consists of ……………. part.
a) Mantissa
b) Exponent
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
![]()
Question 58.
The mantissa must be a(n) …………. constant.
a) Integer
b) Real
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 59.
58.64 can be written as …………….
a) 5.864E1
b) 0.5864E2
c) 5864E-2
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 60.
Internally boolean true has value ……………
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) None of these
Answer:
b) 1
![]()
Question 61.
Internally boolean false has value …………….
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 0
Question 62.
A character constant is any valid single character enclosed within ………….. quotes.
a) Double
b) Single
c) No
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Single
Question 63.
Identify the odd one from the following,
a) ‘A’
b) ‘2’
c) ‘$’
d) “A”
Answer:
d) “A”
![]()
Question 64.
The value of a single character constant has an equivalent ………….. value.
a) BCD
b) ASCII
c) Nibble
d) None of these
Answer:
b) ASCII
Question 65.
The ASCII value of ‘A’ is …………..
a) 65
b) 97
c) 42
d) 75
Answer:
a) 65
Question 66.
The ASCII value of ‘a’ is ……………
a) 65
b) 97
c) 42
d) 75
Answer:
b) 97
![]()
Question 67.
C++ allows certain non-printable characters represented as ……………. constants.
a) Integer
b) Real
c) Character
d) String
Answer:
c) Character
Question 68.
The non-printable characters can be represented by using …………………………
a) Escape sequences
b) String
c) Boolean
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Escape sequences
Question 69.
An escape sequence is represented by a backslash followed by …………. character(s).
a) One
b) Two
c) One or Two
d) None of these
Answer:
c) One or Two
![]()
Question 70.
______ is escape sequence for audible or alert bell.
a) \a
b)\b
c) \n
d)\f
Answer:
a) \a
Question 71
_______ is escape sequence for backspace.
a)\a
b)\b
c) \n
d) \f
Answer:
b)\b
Question 72.
______ is escape sequence for form feed.
a)\a
b)\b .
c) \n
d) \f
Answer:
d) \f
![]()
Question 73.
______ is escape sequence for new line or line feed.
a) a
b)\b
c)\n
d)\f
Answer:
c)\n
Question 74.
……………. is escape sequence for carriage return.
a)\r
b)\c
c)\n
d)\cr
Answer:
a)\r
Question 75.
______ is escape sequence for horizontal tab.’
a)\a ‘
b)\b
c)\t
d)\f
Answer:
c)\t
![]()
Question 76.
_______ is escape sequence for vertical tab.
a)\v
b)\b
c) \t
d) \f
Answer:
a)\v
Question 77.
………………. is escape sequence for octal number.
a) \On
b) \xHn
c)\O
d)O
Answer:
a) \On
Question 78.
______ is escape sequence for hexadecimal number.
a) \On
b) \xHn
c)\O
d)\O
Answer:
b) \xHn
![]()
Question 79
______ ¡s escape sequence for Null character.
a) \On
b) \xHn
c)\O
d)\n
Answer:
c)\O
Question 80.
______ ¡s escape sequence for Inserting?
a) \?
b) \\
c)\’
d)\”
Answer:
a) \?
Question 81.
______ is an escape sequence for inserting a single quote.
a)\?
b)\\
c) \‘
d) \“
Answer:
c) \‘
![]()
Question 82.
______ is escape sequence for inserting double quote.
a)\?
b)\\
c) \‘
d) \“
Answer:
d) \“
Question 83.
______ is escape sequence for inserting
a)\?’
b)\\
c) \‘
d) \“
Answer:
b)\\
Question 84.
ASCII was first developed and published in 1963 by the …………. Committee, a part of the American Standards Association (ASA).
a) X3
b) A3
c) ASA
d) None of these
Answer:
a) X3
![]()
Question 85.
Sequence of characters enclosed within ………. quotes are called as String literals,
a) Single
b) Double
c) No
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Double
Question 86.
By default, string literals are automatically added with a special character………..at the end.
a) ‘\0’ (Null)
b) ‘\S’
c) V
d) None of these
Answer:
a) ‘\0’ (Null)
Question 87.
Identify the valid string constant from the following.
a) “A”
b) “Welcome”
c) “1234”
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 88.
The symbols which are used, to do some mathematical or logical operations are called as ………………
b) Operands
d) None of these
a) Operators
c) Expressions
Answer:
a) Operators
Question 89.
The data items or values that the operators act upon are called as ……………
a) Operators
b) Operands
c) Expressions
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Operands
Question 90.
In C++, the operators are classified as ………… types on the basis of the number of operands,
a) two
b) three
c) four ,
d) five
Answer:
b) three
![]()
Question 91.
………….. operators require only one operand.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Unary
Question 92.
…………… operators require two operands.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Binary
Question 93.
………… operators require three operands.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Ternary
![]()
Question 94.
C++ operators are classified as …………… types
a) 7
b) 3
c) 10
d) 4
Answer:
a) 7
Question 95.
…………… operators perform simple operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.
a) Logical
b) Relational
c) Arithmetic
d) Bitwise
Answer:
c) Arithmetic
Question 96.
…………… operator is used to find the remainder of a division.
a) /
b) %
c) *
d) **
Answer:
b) %
![]()
Question 97.
…………….. operator is called as Modulus operator.
a) /
b)%
c) *
d) **
Answer:
b)%
Question 98.
An increment or decrement operator acts upon a …………….. operand and returns a new value,
a) Single
b) Two
c) Three
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Single
Question 99.
………….. is a unary operator.
a) ++
b) —
c) Both ++ and —
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both ++ and —
![]()
Question 100.
The increment operator adds …………….. to its operand.
a) 1
b) 0\
c) -1
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 1
Question 101.
The decrement operator subtracts …………… from its operand.
a) 1
b) 0\
c) -1
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 1
Question 102.
The …………….. operators can be placed either as prefix (before) or as postfix (after) to a variable.
a) ++
b) –
c) ++or–
d) None of these
Answer:
c) ++or–
![]()
Question 103.
With the prefix version, C++ performs the increment/decrement………….. using the operand.
a) Before
b) After
c) When required
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Before
Question 104.
With the postfix version, C++ performs the increment/decrement…………….. using the operand.
a) Before
b) After
c) When required
d) None of these
Answer:
b) After
Question 105.
With the postfix version, C++ uses the value of the operand in evaluating the expression …………… incrementing /decrementing its present value.
a) Before
b) After
c) When required
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Before
![]()
Question 106.
……………… operators are used to determining the relationship between its operands.
a) Logical
b) Relational
c) Arithmetic
d) Bitwise
Answer:
b) Relational
Question 107.
When the relational operators are applied on two operands, the result will be a …………… value.
a) Boolean
b) Numeric
c) Character
d) String
Answer:
a) Boolean
Question 108.
C++ provides …………. relational operators.
a) Seven
b) six
c) Eight
d) Five
Answer:
b) six
![]()
Question 109.
All six relational operators are ……………
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Binary
Question 110.
A logical operator is used to evaluate …………… expressions.
a) Logical and Relational
b) Logical
c) Relational
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Logical and Relational
Question 111.
Which logical operator returns 1 (True), if both expressions are true, otherwise it returns 0 (false)?
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
a) AND
![]()
Question 112.
Which logical operator returns 1 (True) if either one of the expressions is true. It returns 0 (false) if both the expressions are false?
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
b) OR
Question 113.
Which logical operator simply negates or inverts the true value?
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
c) NOT
Question 114.
AND, OR both are ……………. operators.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Binary
![]()
Question 115.
NOT is a(n) …………… operator.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Unary
Question 116.
Identify the correct statement from the following.
a) The logical operators act upon the operands that are themselves called logical expressions.
b) Bitwise operators work on each bit of data and perform the bit-by-bit operations.
c) There are two bitwise shift operators in C++, Shift left (<<) & Shift right (>>).
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 117.
In C++, there are …………… kinds of bitwise operator.
a) Three
b) Four
c) Two
d) Five
Answer:
a) Three
Question 118.
…………. is a type of bitwise operator.
a) Logical bitwise operators
b) Bitwise shift operators
c) One’s compliment operators
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 119.
______ will return 1 (True) if both the operands are having the value 1 (True); Otherwise, it will return 0 (False).
a) Bitwise AND (&) .
b) Bitwise OR (|)
c) Bitwise Exclusive OR(A)
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Bitwise AND (&)
Question 120.
………… will return 1 (True) if any one of the operands is having a value 1 (True); It returns 0 (False) if both the operands are having the value 0 (False)
a) Bitwise AND (&)
b) Bitwise OR (|)
c) Bitwise Exclusive OR(A)
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Bitwise OR (|)
Question 121.
…………. will return 1 (True) if only one of the operand is having a value 1 (True).If both are True or both are False, it will return 0 (False).
a) Bitwise AND (&)
b) Bitwise OR (|)
c) Bitwise Exclusive OR(A)
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Bitwise Exclusive OR(A)
![]()
Question 122.
There are …………… bitwise shift operators in C++.
a) Three
b) Two
c) Four
d) Five
Answer:
b) Two
Question 123.
……………. is a type of * .wise shift operator in
C++.
a) Shift left
b) Shift right
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 124.
……………. is a type of bitwise shift left operator in C++.
a) <<
b) >>
c) &&
d) ||
Answer:
a) <<
![]()
Question 125.
…………. is a type of bitwise shift right operator in C++.
a) <<
b) >>
c) &&
d) ||
Answer:
b) >>
Question 126.
The value of the left operand is moved to the left by the number of bits specified by the right operand using …………. operator.
a) <<
b) >>
c) &&
d) ||
Answer:
a) <<
Question 127.
The value of the left operand is moved to right by the number of bits specified by the right operand using …………. operator.
a) <<
b) >>
c) &&
d) ||
Answer:
b) >>
![]()
Question 128.
Right operand should be an unsigned integer for …………… operator.
a) Arithmetic
b) Relational
c) Bitwise Shift
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Bitwise Shift
Question 129.
………… is the bitwise one’s complement operator.
a) <<
b) >>
c) &&
d) ~
Answer:
d) ~
Question 130.
The bitwise ………….. operator inverts all the bits in a binary pattern, that is, all l’s become 0 and all 0’s become 1.
a) Shift left
b) Shift right
c) One’s complement
d) None of these
Answer:
c) One’s complement
![]()
Question 131.
…………… is a unary operator.
a) Shift left
b) Shift right
c) Bitwise one’s complement
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Bitwise one’s complement
Question 132.
………….. operator is used to assigning a value to a variable which is on the left-hand side of an assignment statement.
a) Assignment
b) Logical
c) Bitwise
d) Conditional
Answer:
a) Assignment
Question 133.
…………. is commonly used as the assignment operator in all computer programming languages.
a) :=
b) ==
c) =
d) None of these
Answer:
c) =
![]()
Question 134.
…………… operator copies the value at the right side of the operator to the left side variable,
a) Assignment
b) Logical
c) Bitwise
d) Conditional
Answer:
a) Assignment
Question 135.
The assignment operator is a(n) ……………….. operator.
a) Unary
b) Binary
c) Ternary
d) Conditional
Answer:
b) Binary
Question 136.
How many conditional operators are used in C++?
a) one
b) two
c) three
d) four
Answer:
a) one
![]()
Question 137.
…………….. operator is a Ternary Operator.
a) Assignment
b) Logical
c) Bitwise
d) Conditional
Answer:
d) Conditional
Question 138.
…………… operator is used as an alternative to if … else control statement.
a) Assignment
b) Logical
c) Bitwise
d) Conditional
Answer:
d) Conditional
Question 139.
……………. is a pointer to a variable operator.
a) &
b) *
c) →
d) → *
Answer:
b) *
![]()
Question 140.
…………… is an address operator.
a) &
b) *
c) →
d) →*
Answer:
a) &
Question 141.
……………. is a direct component selector operator.
a) .(dot)
b) *
c) →
d) →*
Answer:
a) .(dot)
Question 142.
…………… is an indirect component selector operator.
a) .(dot)
b) *
c) →
d) →*
Answer:
c) →
![]()
Question 143.
…………. is a dereference operator.
a) . (dot)
b) .*
c) →
d) →*
Answer:
b) .*
Question 144.
……………… is a dereference pointer to class member operator.
a) . (dot)
b) .*
c) →
d) →*
Answer:
d) →*
Question 145.
……………. is a scope resolution operator.
a) .(dot)
b) .*
c) : :
d) →*
Answer:
c) : :
![]()
Question 146.
The operands and the operators are grouped in a specific logical way for evaluation is called as………………
a) Operator precedence
b) Operator association
c) Hierarchy
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Operator association
Question 147.
Which operator is lower precedence?
a) Arithmetic
b) Logical
c) Relational
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Logical
Question 148.
Which operator is higher precedence?
a) Arithmetic
b) Logical
c) Relational
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Arithmetic
![]()
Question 149.
Which operator is the lowest precedence?
a) Assignment
b) Comma
c) Conditional
d) Arithmetic
Answer:
b) Comma
Question 150.
In C++, asterisk ( * ) is used for ……………… purpose.
a) Multiplication
b) Pointer to a variable
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 151.
……………. punctuator indicates the start and the end of a block of code.
a) Curly bracket { }
b) Paranthesis ()
c) Sqaure bracket [ ]
d) Angle bracket < >
Answer:
a) Curly bracket { }
![]()
Question 152.
……………. punctuator indicates function calls and function parameters.
a) Curly bracket { }
b) Paranthesis ()
c) Square bracket [ ]
d) Angle bracket < >
Answer:
b) Paranthesis ()
Question 153.
……………. punctuator indicates single and multidimensional arrays.
a) Curly bracket { }
b) Paranthesis ()
c) Square bracket [ ]
d) Angle bracket < >
Answer:
c) Square bracket [ ]
Question 154.
……………… punctuator is used as a separator in an expression.
a) Comma,
b) Semicolon;
c) Colon :
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Comma,
![]()
Question 155.
Every executable statement in C++ should terminate with a ………..
a) Comma,
b) Semicolon;
c) Colon:
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Semicolon;
Question 156.
……………… punctuator is used to label a statement.
a) Comma,
b) Semicolon;
c) Colon:
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Colon:
Question 157.
………….. is a single line comment.
a) /I
b) /* ……..*/
c) \\
d) None of these
Answer:
a) /I
![]()
Question 158.
……………… is a multi line comment.
a) //
b) /* */
c) \\
d) None of these
Answer:
b) /* */
Question 159.
C++ provides the operator to get input. .
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
a) >>
Question 160.
…………….. operator extracts the value through the keyboard and assigns it to the variable on its right.
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
a) >>
![]()
Question 161.
………………. operator is called as “Stream extraction” or “get from” operator.
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
a) >>
![]()
Question 162.
Get from operator requires …………….. operands.
a) three
b) two
c) four
d) five
Answer:
b) two
Question 163.
…………….. is the operand of get from the operator.
a) Predefined identifier cin
b) Variable
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 164.
To receive or extract more than one value at a time ………… operator should be used for each variable.
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
a) >>
![]()
Question 165.
……………. is called cascading of operator.
a) >>
b) <<
c) 11 .
d) Both A and B
Answer:
d) Both A and B
Question 166.
C++ provides …………… operator to perform output operation. a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
b) <<
Question 167.
The operator ………….. is called the “Stream insertion” or “put to” operator.
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
b) <<
![]()
Question 168.
…………… operator is used to send the strings or values of the variables on its right to the object on its left. a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
b) <<
Question 169.
The second operand of put to operator may be a …………….
a) Constant
b) Variable
c) Expression
d) Either A or B or C
Answer:
d) Either A or B or C
Question 170.
To send more than one value at a time …………… operator should be used for each constant/ variable/expression.
a) >>
b) <<
c) ||
d) &&
Answer:
a) >>
![]()
Question 171.
The compiler ignores …………… statement.
a) Comment
b) Input
c) Output
d) Assignment
Answer:
a) Comment
Question 172.
Usually all C++ programs begin with include statements starting with a ……………… symbol.
a) $
b) #
c) {
d) %
Answer:
b) #
Question 173.
The symbol …………… is a directive for the preprocessor.
a) $
b) #
c) {
d) %
Answer:
b) #
![]()
Question 174.
_____ means, statements are processed before the compilation process begins.
a) Preprocessor
b) Include
c) Header file
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Preprocessor
Question 175.
The header file ……………… should include in every C++ program to implement input/output functionalities.
a) iostream
b) stdio
c) conio
d) math
Answer:
a) iostream
Question 176.
………….. header file contains the definition of its member objects cin and cout.
a) iostream
b) stdio
c) conio
d) math
Answer:
a) iostream
![]()
Question 177.
Namespace collects identifiers used for …………..
a) Class
b) Object
c) Variables
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 178.
…………….. provides a method of preventing name conflicts in large projects.
a) namespace
b) header files
c) include
d) None of these
Answer:
a) namespace
Question 179.
Every C++ program must have a …………… function.
a) user defined
b) main( )
c) Library .
d) None of these
Answer:
b) main( )
![]()
Question 180.
The …………….. function is the starting point where all C++ programs begin their execution.
a) user-defined
b) main ( )
c) Library
d) None of these
Answer:
b) main ( )
Question 181.
The executable statements should be inside the ………… function.
a) user-defined
b) main ( )
c) Library
d) None of these
Answer:
b) main ( )
Question 182.
The statements between the …………… braces are executable statements.
a) Curly bracket { }
b) Paranthesis ()
c) Square bracket [ ]
d) Angle bracket < >
Answer:
a) Curly bracket { }
![]()
Question 183.
For creating and executing a C++ program, one must follow ……………. important steps.
a) two
b) three
c) five
d) four
Answer:
d) four
Question 184.
For creating and executing a C++ program, one must follow ……….. step.
a) Creating source code and save with .cpp extension
b) Compilation
c) Execution
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 185.
………………. links the library files with the source code and verifies each and every line of code.
a) Interpreter
b) Compiler
c) Loader
d) Assembler
Answer:
b) Compiler
![]()
Question 186.
If there are no errors in the source code, …………… translates the source code into a machine-readable object file.
a) Interpreter
b) Compiler
c) Loader
d) Assembler
Answer:
b) Compiler
Question 187.
The compiler translates the source code into machine-readable object file with an extension…………..
a) .cpp
b) .exe
c) .obj *
d) None of these
Answer:
c) .obj *
Question 188.
The object file becomes an executable file with extension ……………
a) .cpp
b) .exe
c) .obj
d) None of these
Answer:
b) .exe
![]()
Question 189.
………….. files can run without the help of any compiler or IDE.
a) Source
b) Object
c) Executable
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Executable
Question 190.
…………… makes it easy to create, compile and execute a C++ program.
a) Editors
b) IDE
c) Compilers
d) None of these
Answer:
b) IDE
Question 191.
IDE stands for …………….
a) Integrated Development Environment
b) Integrated Design Environment
c) Instant Development Environment
d) Integral Development Environment
Answer:
a) Integrated Development Environment
![]()
Question 192.
……………. is open-source C++ compiler.
a) Dev C++ / Geany / Sky IDE
b) Code Lite / Code::blocks / Eclipse
c) Ner Beans / Digital Mars
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 193.
Dev C++ is written in …………
a) Delphi
b) C++
c) C
d) Pascal
Answer:
a) Delphi
Question 194.
………….. error is possible in C++.
a) Syntax
b) Semantic
c) Run-time
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 195.
………….. error occurs because of some illegal operation that takes place.
a) Syntax
b) Semantic
c) Run-time
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Run-time
Question 196.
Semantic error is called as ……………error.
a) Syntax
b) Logic
c) Run-time
d) All the above
Answer:
b) Logic
Question 197.
If a program tries to open a file which does not exist, it results in a …………. error.
a) Syntax
b) Logic
c) Run-time
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Run-time
Question 198.
……………. errors occur when grammatical rules of C++are violated.
a) Syntax
b) Logic
c) Run-time
d) All the above
Answer:
a) Syntax
![]()
Very Short Answers (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Mention any two benefits of C++.
Answer:
- C++ is a highly portable language and is often the language of choice for multi-device, multi-platform app development.
- C++ is an object-oriented programming language and includes classes, inheritance, polymorphism, data abstraction, and encapsulation.
Question 2.
What is a character?
Answer:
A character represents any alphabet, number, or any other symbol (special characters) mostly available in the keyboard.
Question 3.
What are the types of C++ operators based on the number of operands?
Answer:
The types of C++ operators based on the number of operands are:
- Unary Operators – Require only one operand
- Binary Operators – Require two operands
- Ternary Operators – Require three operands
![]()
Question 4.
What are the recent keywords included in C++?
Answer:
The recent list of keywords includes: using, namespace, bal, static_cast, const_cast, dynamic_cast, true, false.
Question 5.
What is a stream extraction operator?
Answer:
C++ provides the operator >> to get input. It extracts the value through the keyboard and assigns it to the variable on its right; hence, it is called as “Stream extraction” or “get from” operator.
Question 6.
Why the following identifiers are invalid?
a) num-add
b) this
c) 2myfile
Answer:
a) num-add – It contains spedal character (-) which ¡s not permitted
b) this – It is a keyword in C++. Keyword can not be used as identifier
c) 2myflle – Name must begin with an alphabet or an underscore.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the main types of C++ datatypes?
Answer:
In C++, the data types are classified into three main categories
- Fundamental data types
- User-defined data types
- Derived data types.
Question 8.
What are Boolean literals?
Answer:
Boolean literals are used to represent one of the Boolean values (True or false). Internally true has value 1 and false has value 0.
Question 9.
What are string literals?
Answer:
The sequence of characters enclosed within double quotes is called String literals. By default, string literals are automatically added with a special character ‘\0’ (Null) at the end. Valid string Literals: “A” “Welcome” “1234” Invalid String Literals : ‘Welcome’,’1234′
![]()
Question 10.
Differentiate Operators and Operands.
Answer:
The symbols which are used to do some mathematical or logical operations are called as Operators.
The data items or values that the operators act upon are called as Operands.
Question 11.
What are the classifications of C++ operators based on operand requirements?
Answer:
In C++, the operators are classified on the basis of the number of operands as follows:
i) Unary Operators – Require only one operand
ii) Binary Operators – Require two operands
iii) Ternary Operators – Require three operands
Question 12.
List the C++ operators.
Answer:
C++ Operators are classified as:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Conditional Operator
- Other Operators ,
![]()
Question 13.
Write note on increment and decrement operators.
Answer:
++ (Plus, Plus) Increment operator
– (Minus, Minus) Decrement operator
An increment or decrement operator acts upon a single operand and returns a new value. Thus, these operators are unary operators. The increment operator adds 1 to its operand and the decrement operator subtracts 1 from its operand.
Example:
x++ is the same as x = x+1; It adds 1 to the present value of x.
X– is the same as x = x—1; It subtracts 1 from the present value of x.
Question 14.
Write a note on bitwise operators.
Answer:
Bitwise operators work on each bit of data and perform the bit-by-bit operation.
In C++, there are three kinds of bitwise operators, which are:
- Logical bitwise operators
- Bitwise shift operators
- One’s compliment operator
Question 15.
Write about bitwise one’s compliment operator.
Answer:
The Bitwise one’s compliment operator:
The bitwise One’s compliment operator ~(Tilde), inverts all the bits in a binary pattern, that is, all l’s become 0 and all 0’s become 1. This is a unary operator.
Example:
If a = 15; Equivalent binary values of a is 0000 1111
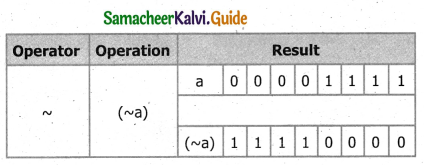
![]()
Question 16.
Write about assignment operator.
Answer:
Assignment Operator:
The assignment operator is used to assigning a value to a variable which is on the left-hand side of an assignment statement. = (equal to) is commonly used as the assignment operator in all computer programming languages. This operator copies the value at the right side of the operator to the left side variable. It is also a binary operator.
Question 17.
What are the shorthand assignment operators? Give example.
Answer:
|
Operator |
Name of Operator Example | |
| += | Addition Assignment | a = 10; c = a+= 5; (ie, a = a+5) c = 15 |
| -= | Subtraction Assignment | a = 10; c = a-= 5; (ie, a = a-5) c = 5 |
| * = | Multiplication Assignment | a = 10; c = a*= 5; (ie, a = a*5) c = 50 |
| /= | Division Assignment | a = 10; c – a/= 5; (ie, a = a/5) c = 2 |
| %= | Modulus Assignment | a = 10; c = a%= 5; (ie, a = a%5) c = 0 |
![]()
Question 18.
Write note on conditional or ternary operator.
Answer:
In C++, there is only one conditional operator is used. ?: is a conditional Operator. This is a Ternary Operator. This operator is used as an alternative to if… else control statement.
Question 19.
Write note on comma (, ) operator.
Answer:
The comma (,) is an operator in C++ used to bring together several expressions. The group of expressions separated by a comma is evaluated from left to right.
Question 20.
What are the pointer operators?
Answer:
* – Pointer to a variable operator
& – Address of operator
Question 21.
What are the component selection operators?
Answer:
. – Direct component selector operator
-> – Indirect component selector operator
![]()
Question 22.
What are the class member operators?
Answer:
:: – Scope access / resolution operator
.* – Dereference operator
->* – Dereference pointer to class member operator
Question 23.
What is operator association?
Answer:
The operands and the operators are grouped in a specific logical way for evaluation. This logical grouping is called as an Association.
Question 24.
What are the cascading operators?
Answer:
Get from (>>) and Put to (<<) operators are cascading operators.
Question 25.
What are the popular C++ Compilers with IDE.
Answer:
|
Compiler |
Availability |
| Dev C++ | Open-source |
| Geany | Open-source |
| Code:: blocks | Open source |
| Code Lite | Open-source |
| Net Beans | Open-source |
| Digital Mars | Open-source |
| Sky IDE | Open-source |
| Eclipse | Open-source |
![]()
Short Answers (3 Marks)
Question 1.
What are the benefits of C++?
Answer:
Benefits of learning C++:
- c++ ¡s a highly portable language and ¡s often the language of choice for multi-device, multi- platform app development.
- C++ is an object-oriented programming language and includes classes, inheritance, polymorphism, data abstraction and encapsulation.
- C++ has a rich function library.
- C++ allows exception handling, inheritance and function overloading which are not possible in C.
- C++ is a powerful, efficient and fast language.
It finds a wide range of applications — from GUI applications to 3D graphics for games to real-time mathematical simulations.
Question 2.
What are the characters used In C++?
Answer:
C++ accepts the following characters:
| Alphabets | A …. Z, a…. z |
| Numeric | 0 …. 9 |
| Special Characters | + – * / ~ ! @ # $ % A& [ ] ( ) {} = ><_\l?.,:'”; |
| White space | Blank space, Horizontal tab (->), Carriage return (), Newline, Form feed |
| Other characters | C++ can process any of the 256 ASCII characters as data. |
Question 3.
What are Automatic conversion and Type promotion?
Answer:
Implicit type conversion is a conversion performed by the compiler automatically. So, the implicit conversion is also called “Automatic conversion”. This type of conversion is applied usually whenever different data types are intermixed in an expression. If the type of the operands differs, the compiler converts one of them to match with the other, using the rule that the “smaller” type is converted to the “wider” type, which is called “Type Promotion”.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the rules for naming an identifier/variable?
Answer:
Rules for naming an identifier:
- The first character of an identifier must be an alphabet or an underscore (-).
- Only alphabets, digits, and underscore are permitted. Other special characters are not allowed as part of an identifier.
- c++ is case sensitive as it treats upper and lower-case characters differently.
- Reserved words or keywords cannot be used as an identifier name.
Question 5.
List the kinds of literals in C++.
Answer:
C++ has several kinds of literals. They are:
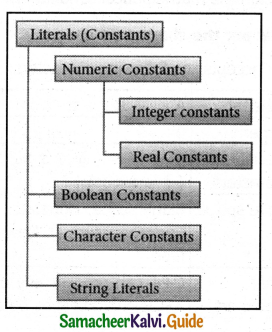
Question 6.
What are the types of C++operators?
Answer:
C++ Operators are classified as:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Conditional Operator
- Other Operators
![]()
Question 7.
Write a note on character constants.
Answer:
A character constant is any valid single character enclosed within single quotes. A character constant in C++ must contain one character and must be enclosed within a single quote.
Valid character constants : ‘A’, ‘2\ ‘$’
Invalid character constants : “A”
The value of a single character constant has an equivalent ASCII value. For example, the value of’A’ is 65.
Question 8.
What are escape sequences? Explain.
Answer:
Escape sequences (or) Non-graphic characters:
C++ allows certain non-printable characters represented as character constants. Non-printable characters are also called non-graphical characters. Non-printable characters are those characters that cannot be typed directly from a keyboard during the execution of a program in C++.
For example: backspace, tabs etc. These non-printable characters can be represented by using escape sequences. An escape sequence is represented by a backslash followed by one or two characters.
Example: \t \On \xHn
Question 9.
Tabulate the escape sequence characters.
Answer:
|
Escape sequence |
Non-graphical character |
| \a | Audible or alert bell |
| \b | Backspace |
| \f | Form feed |
| \n | Newline or linefeed |
| \r | Carriage return |
| \t | Horizontal tab |
| \v | Vertical tab |
| \\ | Backslash |
| \’ | Single quote |
| \” | Double quote |
| \? | Question Mark |
| \On | Octal number |
| \xHn | Hexadecimal number |
| \o | Null |
![]()
Question 10.
Write a note on arithmetic operators.
Answer:
Arithmetic operators perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.
|
Operator |
Operation |
Example |
| + | Addition | 10 + 5 = 15 |
| – | Subtraction | 10 – 5 = 5 |
| * | Multiplication | 10 * 5 = 50 |
| / | Division | 10 / 5 = 2 (Quotient of the division) |
| % | Modulus (To find the reminder of a division) | 10 % 3 = 1 (Remainder of the division) |
Question 11.
What are the relational operators in C++? Give examples.
Answer:
Relational operators are used to determining the relationship between its operands. When the relational operators are applied on two operands, the result will be a Boolean value i.e 1 or 0 to represents True or False respectively. C++ provides six relational operators. They are:
| Operator | Operation | Example |
| > | Greater than | a > b |
| < | Less than | a < b |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | a >= b |
| <= | Less than or equal to | a <= b |
| == | Equal to | a == b |
| j= | Not equal | a != b |
- In the above examples, the operand ‘a’ is compared with ‘b’ and depending on the relation, the result will be either 1 or 0. i.e., 1 for true, 0 for false.
- All six relational operators are binary operators.
![]()
Question 12.
What are the logical operators used in C++? Explain its operation.
Answer:
A logical operator is used to evaluate logical and relational expressions. The logical operators act upon the operands that are themselves called as logical expressions. C++ provides three logical operators.
table
|
Operator |
Operation |
Description |
| && | AND | The logical AND combines two different relational expressions into one. It returns 1 (True), if both expressions are true, otherwise, it returns 0 (False). |
| II | OR | The logical OR combines two different relational expressions into one. It returns 1 (True) if either one of the expressions is true. It returns 0 (False) if both the expressions are false. |
| ! | NOT | NOT works on a single expression/operand. It simply negates or inverts the truth value, i.e., if an operand/expression is 1 (True) then this operator returns 0 (False) and vice versa. |
AND, OR both are binary operators where as NOT is a unary operator.
Example:
a = 5, b = 6, c = 7;
|
Expression |
Result |
| (a<b) && (b<c) | 1 (True) |
| (a>b) && (b<c) | 0 (False) |
| (a<b) || (b>c) | 1 (True) |
| !(a>b) | 1 (True) |
Question 13.
What are the logical bitwise operators? Explain its operation.
Answer:
Logical bitwise operators:
- & Bitwise AND (Binary AND)
- | Bitwise OR (Binary OR)
- ∧ Bitwise Exclusive OR (Binary XOR)
- Bitwise AND (&) will return 1 (True)if both the operands are having the value 1 (True); Otherwise, it will return 0 (False).
- Bitwise OR (|) will return 1 (True) if any one of the operands is having a value 1 (True); It returns 0 (False) if both the operands are having the value 0 (False).
- Bitwise XOR(A) will return 1 (True) if only one of the operand is having a value of 1 (True). If both are True or both are False, it will return 0 (False).
The truth table for bitwise operators (AND, OR, XOR)
| A | B | A & B | A | B | A ∧ B |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
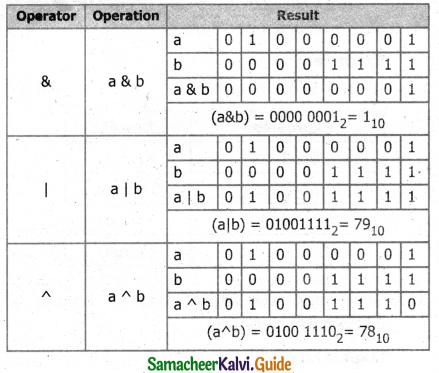
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Example:
If a = 65, b=15
Equivalent binary values of 65 = 0100 0001; 15 = 0000 1111
![]()
Question 14.
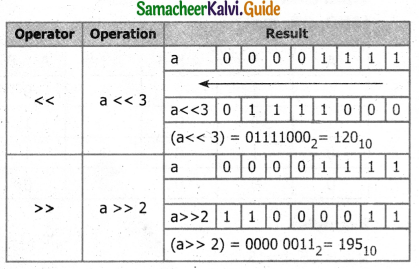
What are the bitwise shift operators? Explain its operation.
Answer:
The Bitwise shift operators:
There are two bitwise shift operators in C++, Shift left (<<) and Shift right (>>).
- Shift left (<<) – The value of the left operand is moved to the left by the number of bits specified by the right operand. The right operand should be an unsigned integer.
- Shift right (>>) – The value of the left operand is moved to the right by the number of bits specified by the right operand. The right operand should be an unsigned integer.
Example:
If a =15; the Equivalent binary value of a is 0000 1111
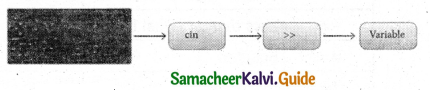
Question 15.
What is input operator in C++? Explain.
Answer:
C++ provides the operator >> to get input. It extracts the value through the keyboard and
assigns it to the variable on its right; hence, it is called as “Stream extraction” or “get from” operator.
It is a binary operator i.e., it requires two operands. The first operand is the pre-defined identifier cin that identifies keyboard as the input device. The second operand must be a variable.
Working process of cin
Example:
cin>>num; — Extracts num value
cin>>x>>y; — Extracts x and y values
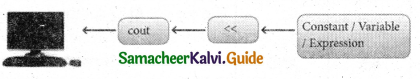
Question 16.
What is an output operator in C++? Explain.
Answer:
C+ + provides << operator to perform output operation. The operator << is called the “Stream insertion” or “put to” operator. It is used to send the strings or values of the variables on its right to the object on its left. << is a binary operator.
The first operand is the pre-defined identifier cout that identifies monitor as the standard output object. The second operand may be a
constant, variable or an expression.
Working process of cout
Example:
cout<<“Welcome”; – Display Welcome on-screen cout<<“The Sum =”<
![]()
Explain in Detail 5 Marks
Question 1.
Explain Integer Constants. (or) Fixed point constants In detail.
Answer:
Integers are whole numbers without any fractions. An integer constant must have at least one digit without a decimal point. It may be signed or unsigned. Signed integers are considered as negative, commas and blank spaces are not allowed as part of it.
In C++, there are three types of integer constants:
- Decimal
- Octal
- Hexadecimal
i) Decimal
Any sequence of one or more digits (0 …. 9).
|
Valid |
Invalid |
| 725 | 7,500 (Comma is not allowed) |
| -27 | 66 5 (Blank space is not allowed) |
| 4.56 | 9$ (Special Character not allowed) |
If we assign 4.56 as an integer decimal constant, the compiler will accept only the integer portion of 4.56 ie. 4. It will simply ignore .56.
ii) Octal:
Any sequence of one or more octal values (0 ….7) that begins with 0 is considered as an Octal constant.
|
Valid |
Invalid |
| 012 | 05,600 (Comma is not allowed) |
| -027 | 04.56 (A decimal point is not allowed)** |
| +0231 | 0158 (8 is not a permissible digit in the octal system) |
iii) Hexadecimal:
Any sequence of one or more Hexadecimal values (0 …. 9, A …. F) that starts with Ox or OX is considered as a Hexadecimal constant.
|
Valid |
Invalid |
| 0x123 | 0x1,A5 (Comma is not allowed) |
| 0X568 | 0x.l4E (Decimal point is not allowed like this) |
![]()
Question 2.
Explain Real Constants. (or) Floating-point constants in detail.
Answer:
Real Constants (or) Floating-point constants:
A real or floating-point constant is a numeric constant having a fractional component. These constants may be written ¡n fractional form or ¡n exponent form.
The fractional form of a real constant is a signed or unsigned sequence of digits including a decimal point between the digits.
It must have at least one digit before and after a decimal point. It may have a prefix with the + or – sign.
A real constant without any sign will be considered positive.
Exponent form of real constants consists of two parts:
- Mantissa
- Exponent
The mantissa must be either an integer or a real constant. The mantissa followed by a letter E or e and the exponent. The exponent should also be an integer.
For Example:
58000000.00 may be written as 0.58 x 108 or 0. 58E8.
|
Mantissa (Before E) |
Exponent (After E) |
| 0.58 | 8 |
Example:
5.864 E1 → 5.864 x 101 → 58.64
5864 E-2 → 5864 x 10-2 → 58.64
0.5864 E2 → 0.5864 x 102 → 58.64
Question 3.
Explain the prefix and postfix operators’ working process with suitable examples.
Answer:
The ++ or – operators can be placed either as prefix (before) or as postfix (after) to a variable. With the prefix version, C++ performs the increment / decrement before using the operand.
For example: N1=10, N2=20;
S = ++N1 + ++N2;
The following Figure explains the working process of the above statement.
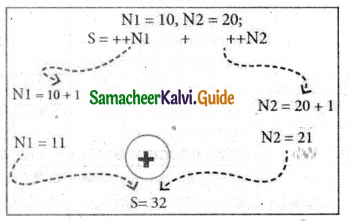
In the above example, the value of num is first incremented by 1, then the incremented value is assigned to the respective operand.
With the postfix version, C++ uses the value of the operand in evaluating the expression before incrementing /decrementing its present value.
For example: N1=10, N2=20;
S = N1++ + ++N2;
The following Figure explains the working process of the above statement.
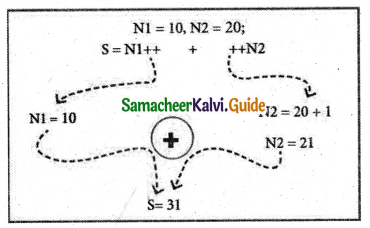
In the above example, the value assigned to operand N1 is taken into consideration, first and then the value will be incremented by 1.
![]()
Question 4.
What are punctuators/separators? List the punctuators and their operations.
Answer:
Punctuators are symbols, which are used as delimiters while constructing a C++ program. They are also called “Separators”. The following punctuators are used in C++.
| Curly braces { } | Opening and closing curly braces indicate the start and the end of a block of code. A block of code containing more than one executable statement. These statements together are called as “compound statement”. | int main () {int x=10, y=20, sum; sum = x + y; cout << sum; } |
| Parenthesis () | Opening and closing parenthesis indicate function calls and function parameters. | clrscr(); add (5, 6); |
| Square brackets [ ] | It indicates single and multidimensional arrays. | int num[5]; charname[50]; |
| Comma (,) | It is used as a separator in an expression. | int x=10, y=20, sum; |
| Semicolon ; | Every executable statement in C++ should terminate with a semicolon. | int main ()
{ |
| Colon : | It is used to label a statement. | private: |
| Comments ///* *1 |
Any statement that begins with // are considered a comments. Comments are simply ignored by compilers, i.e., compiler does not execute any statement that begins with a // // Single line comment /* ………….. / Multiline comment |
/* This is written By myself to learn CPP */ int main () { intx=10, y=20, sum; // to sum x and y sum = x + y; cout << sum; } |
![]()
Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
What is meant by literals? How many types of integer literals available in C++?
Answer:
Literals are data items whose values do not change during the execution of a program. Literals are called as Constants.
In C++, there are three types of integer literals (constants). They are:
- Decimal
- Octal
- Hexadecimal
Question 2.
What kind of constants is following?
i) 26
ii) 015
iii) 0xF
iv) 014.9
Answer:
i) 26 : Decimal constant
ii) 015 : Octal constant
iii) 0xF : Hexadecimal constant
iv) 014.9 : Integer Constant. (A fractional number that begins with 0, C++ has consider the number as an integer not an Octal)
Question 3.
What is the character constant in C++?
Answer:
A character constant is any valid single character enclosed within single quotes. A character constant in C++ must contain one character and must be enclosed within a single quote.
Valid character constants: ‘A’, ‘2’, ‘$’
Invalid character constants: “A”
![]()
Question 4.
How are non-graphic characters represented in C++?
Answer:
Non-printable characters are also called as non-graphical characters.
Non-printable characters are those characters that cannot be typed directly from a keyboard during the execution of a program in C++, for example, backspace, tabs, etc. These non-printable characters can be represented by using escape sequences.
An escape sequence is represented by a backslash followed by one or two characters.
|
Escape Sequence |
Non-graphical character |
| \a | The audible or alert bell |
| \b | Backspace |
| \f | Form feed |
| \n | Newline or linefeed |
| \r | Carriage return |
| \t | Horizontal tab |
| \v | Vertical tab |
| \\ | Backslash |
| V | Single quote |
| \” | Double quote |
| \On | Octal number |
| \xHn | Hexadecimal number |
| \0 | Null |
Even though an escape sequence contains two characters, they should be enclosed within single quotes because, C++ consider escape sequences as character constants and allocates one byte in ASCII representation.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the following real constants into exponent form:
i) 32.179
ii) 8.124
iii) 0.00007
Answer:
i) 32.179 → 3.2179E1 (OR) 0.32179E2 (OR) 32178E-3
ii) 8.124 → 0.8124E1 (OR) 8124E-3
iii) 0.00007 → 7E-5
Question 6.
Write the following real constants into fractional form:
i) 0.23E4
ii) 0.517E-3
iii) 0.5E-5
Answer:
i) 0.23E4 → 2300
ii) 0.517E-3 → 0.000517
iii) 0.5E-5 → 0.000005
Question 7.
What is the significance of the null (\0) character in a string?
Answer:
By default, string literals are automatically added with a special character ‘\0’ (Null) at the end. It is called as an end of string character.
The string “welcome” will actually be represented as “welcome\0” in memory and the size of this string is not 7 but 8 characters i.e., inclusive of the last character \0.
![]()
Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
What is the use of operators?
Answer:
Operators are the symbols which are used to do some mathematical or logical operations on their operands.
Question 2.
What are binary operators? Give examples.
Answer:
Arithmetic binary operators.
Binary Operators – Require two operands.
The arithmetic operators addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(*), division(/) and Modulus(%) are binary operators which requires two operands.
Example:
|
Operator |
Operation |
Example |
| + | Addition | 10 + 5 = 15 |
| – | Subtraction | 10 – 5 = 5 Slfil.r |
| * | Multiplication | 10 * 5 = 50 |
| / | Division | 10 / 5 = 2 (Quotient of the division) |
| % | Modulus (To find the reminder of a division) | 10 % 3 = 1 (Remainder of the division) |
Question 3.
What does the modulus operator % do?
Answer:
The modulus operator is used to find the remainder of a division.
Example:
10%3 will return 1 which is the remainder of the division.
![]()
Question 4.
What will be the result of 8.5 % 2?
Answer:
The following error will appear while compiling the program.
Invalid operands of types ‘double’ and ‘int’ to binary ‘operator%’.
The reason is % operator operates on integer operands only.
Question 5.
Assume that R starts with a value of 35. What will be the value of S from the following expression? S=(R–)+(++R)
Answer:
S = 70
Question 6.
What will be the value of j = – – k + 2k. if k is ‘ 20 initially?
Answer:
The value of j will be 57 and k will be 19.
C++ Code;
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int k=20,j;
j=–k+2*k;
cout<< “Vlaue of j=”<<j<< “\nVlaue of
k =”<<k;
return 0;
}
Out put

![]()
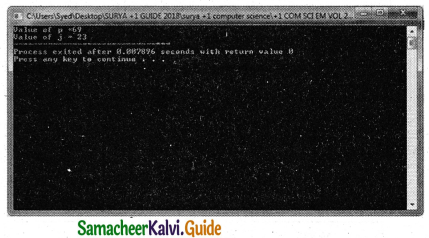
Question 7.
What will be the value of p = p * ++j where j is 22 and p = 3 initially?
Answer:
The value of p is 69 and j is 23.
C++ program:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int j=22, p=3;
P = P * ++j;
cout<< “Value of p =”<<p<< “\nValue of
j =”<<j;
return 0;
}
Out put
Question 8.
Give that i = 8, j = 10, k = 8, What will be result of the following expressions?
i) i < k
ii) i < j
iii) i > = k
iv) i = = j
v) j ! = k
Answer:
|
Expression |
Result |
| i < k | 0 (False) |
| i < j | 1 (True) |
| i >= k | 1 (True) |
| i == j | 0 (False) |
| j != k | 1 (True) |
![]()
Question 9.
What will be the order of evaluation for the following expressions?
i) i + 3 > = j – 9
ii) a +10 < p – 3 + 2 q
Answer:
Question 10.
Write an expression involving a logical operator to test, if marks are 75 and grade is ‘A’.
Answer:
(marks == 75) && (grade == ‘A)
Hands On Practice
Type the following C++ Programs in Dev C++ IDE and execute, if the compiler shows any errors, try to rectify it and execute again and again till you get the expected result.
Question 1.
C++ Program to find the total marks of three
subjects.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m1, m2, m3, sum;
cout << “\n Enter Mark 1:”; cin >> m1;
cout << ”\n Enter Mark 2: “; cin >> m2;
cout << “\n Enter Mark 3: “; cin >> m3;
sum = m1 + m2 + m3;
cout << “\n The sum = ” << sum;
}
Make changes in the above code to get the average of all the given marks.
Answer:
Modified Program:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m1, m2, m3, sum;
float avg;
cout << “\n Enter Mark 1: “;
cin >> m1;
cout << “\n Enter Mark 2: “;
cin >> m2;
cout << “\n Enter Mark 3: “;
cin >> m3;
sum = m1 + m2 + m3;
avg = (float)sum / 3;
cout << “\n The sum = ” << sum;
cout << “\n The average = ” << avg;
}
Output
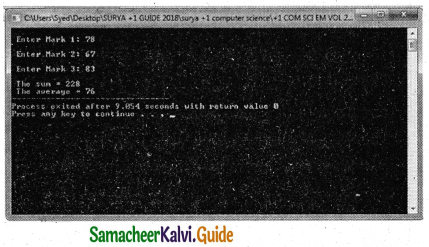
![]()
Question 2.
C++ program to find the area of a circle.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int radius;
float area;
cout << “\n Enter Radius: “;
cin<< radius;
area = 3.14 * radius * radius;
cout << “\n The area of circle =“ <<area;
}
Output

Question 3.
Point out the errors in the following program:
Using namespace std;
int main( )
{
cout << “Enter a value”
cin << numl >> num2
num+num2=sum;
cout >> “\n The Sum= ” >> sum;
Answer:
|
Given code |
Error |
| Using namespace std; | The keyword must be in lowercase. So, Using should be written as using. Header file is missing. |
| int main() | No Error |
| No Error | |
| cout << “Enter a value “; | Prompt should be “Enter two values” because cin contains two variables. |
| cin << numl >> num2 | Variables are not declared. It should be declared first, cin must followed by Extraction operator(>>).
Semicolon is missing at the end of the statement. |
| num+num2=sum; | Improper assignment statement and undefined variable name used. It should be replaced as sum=numl + num2; |
| cout >> “\n The Sum= ” >> sum; | cout must followed by put to the operator. Return 0; statement is missing. Close bracket} missing. |
The correct program is given below:
using namespace std;
#include
int main()
{
int num1,num2,sum;
cout << “Enter two values”; cin >> numl >> num2;
sum= num+num2;
cout << “\n The Sum= “<< sum;
return 0;
}
![]()
Question 4.
Point out the type of error in the following program:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int h=10; w=12;
cout << “Area of rectangle ” << h+w; >
Answer:
Syntax error exists. Ie. int h=10;w=12; should written as int h=10,w=12;
There is also a logical error in the above program.
The formula for rectangle area is given wrong. This error will not indicate by the compiler.
MODIFIED PROGRAM:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int h=10, w=12;
cout << “Area of rectangle ” << h*w;
}
Output

DATATYPES, VARIABLES AND EXPRESSIONS
Book Evaluation
Part -I
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
How many categories of data types available in C++?
a) 5
b) 4
c) 3
d) 2
Answer:
c) 3
Question 2.
Which of the following data types is not a fundamental type?
a) signed
b) int
c) float
d) char
Answer:
a) signed
![]()
Question 3.
What will be the result of following statement?
char ch= ‘B’;
cout << (int) ch;
a) B
b) b
c) 65
d) 66
Answer:
d) 66
Question 4.
Which of the character is used as suffix to indicate a floating point value?
a) F
b) C
c) L
d) D
Answer:
a) F
Question 5.
How many bytes of memory allocates for the following variable declaration if you are using Dev C++? short int x;
a) 2
b) 4
c) 6
d) 8
Answer:
a) 2
![]()
Question 6.
What is the output of the following snippet?
char ch = ‘A’;
ch= ch + 1;
a) B
b) A1
c) F
d) 1A
Answer:
a) B
Question 7.
Which of the following Is not a data type modifier?
a) signed
b) int
c) long
d) short
Answer:
b) int
Question 8.
Which of the following operator returns the size of the data type?
a) size of( )
b) int ( )
c) long ( )
d) double ( )
Answer:
a) size of( )
![]()
Question 9.
Which operator to be used to access a reference of a variable?
a) $
b) #
c) &
d) !
Answer:
c) &
Question 10.
This can be used as an alternate to end command:
a) \t
b) \b
c) \0
d) \n
Answer:
c) \0
![]()
Part II
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
Write a short note const keyword with an example.
Answer:
const is the keyword used to declare a constant, const keyword modifies/restricts the accessibility of a variable. So, it is known as an Access modifier.
Example:
const int num =100; indicates that the variable num can not be modified. It remains constant.
Question 2.
What is the use of setw( ) format manipulator?
Answer:
setw ( ):
setw manipulator sets the width of the field assigned for the output. The field width determines the minimum number of characters to be written in the output.
Syntax:
setw(number of characters)
Example:
cout << setw(25) << “Net Pay : ” << setw(10)
<< np << endl;
Question 3.
Why is char often treated as an integer data type?
Answer:
Character data type is often said to be an integer type since all the characters are represented in memory by their associated ASCII Codes.
![]()
Question 4.
What is a reference variable? What is its use?
Answer:
A reference provides an alias for a previously defined variable. Declaration of a reference consists of base type and an & (ampersand) symbol; reference variable name is assigned the value of a previously declared variable.
Syntax:
<&reference_variable> =
Example:
#include
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int num;
int &temp = num; //declaration of a reference variable temp
num = 100;
cout << “\n The value of num =” << num;
cout << “\n The value of temp =” << temp;
}
Output
The value of num = 100
The value of temp = 100
Question 5.
ConsIder the following C++ statement Are they equivalent?
char ch=67;
char ch=’C’;
Answer:
Yes. Both are equivalent. Both assignment statements will store character C’ in the variable ch.
Question 6.
what Is the difference between 561 and 56?
Answer:
- 56 indIcate an Integer
- 56L indicates Long Integer The suffix L indicates Long. So it stores a long integer
![]()
Question 7.
Determine which of the following are valid constant? And specify their type,
i) 0.5
ii) ‘Name’
iii) ‘\t’
iv) 27,822
Answer:
i) 0.5 : Valid. Floating-point constant
ii) ‘Name’ : Invalid. String constant must be enclosed within double-quotes.
iii) ‘\t’ : Valid. Character constant.
iv) 27,822 : Invalid. Comma not allowed with integer constant.
Question 8.
Suppose x and y are two double-type variables that you want add as integers and assign to an integer variable. Construct a C++ statement for doing so.
Answer:
double x, y;
int sum;
x = 12.64;
y = 13.56;
sum = (int) x + (int) y;
The variable sum will have the value of 25 due to explicit casting.
Question 9.
What will be the result of following if num=6 initially?
Answer:
a) cout << num;
6
b) cout << (num==5);
0
![]()
Question 10.
Which of the following two statements are valid? Why? Also write their result, int a;
i) a=3,014;
ii) a =(3,014);
Answer:
i) a=3,014; – Invalid. Special character comma(,) not allowed.
ii) a=(3,014); – Valid. 014 is an octal constant. It will be converted into decimal and then stored in a. So, a will hold 12 as its value.
Part – III
Short Answers
Question 1.
What are arithmetic operators in C++? Differentiate unary and binary arithmetic operators. Give example for each of them.
Answer:
Arithmetic Operators:
Arithmetic operators perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc.
| Operator | Operation | Example |
| + | Addition | 10 + 5-15 |
| – | Subtraction | 10-5-5 |
| * | Multiplication | 10 * 5 = 50 |
| / | Division | 10 / 5 = 2 (Quotient of the division) |
| % | Modulus (To find the reminder of a division) | 10 % 3 = 1 (Remainder of the division) |
The above-mentioned arithmetic operators are binary operators which require a minimum of two operands.
Unary arithmetic operators:
– (Unary) – The unary minus operator changes the sign of its argument. A positive number ‘ becomes negative and negative number becomes
positive, int a = 5;
a = -a; // a becomes -5
+ (Unary) – The unary plus operator keeps the sign of its argument,
int a = -5;
a = +a; // a still have the value same value -5
(No change)
a = 5;
a = +a; // a stil have the same value 5
(No change)
Unary Minus is different from – (Binary) ie. subtraction operator requires two operands.
Unary Plus is different from + (Binary) ie. addition operator requires two operands.
#include
mt mamo
{
mt x=10;
intÿ= -10;
inta = -10;
‘nt b = 10;
y=+y;
a= -a;
b=+b;
cout«”\nx = “«X;
cout«”\ny = “«y;
cout«”\na = “«a;
cout«”\nb = “«b;
return 0;

![]()
Question 2.
Evaluate x+= x + ++x; Let x=5;
Answer:
x=18
Code:
using namespace std;
#include
int main ()
{
int x;
x = 5;
x+= x + ++x;
cout «x;
return O;
}
Out put

Question 3.
How relational operators and logical operators related to one another?
Answer:
Both relational and logical operators will give the evaluation result as Boolean constant value 1 (True) or 0(False).
Question 4.
Evaluate the following C++ expressions where x, y, z are integers and m, n are floating
point numbers. The value of x = 5, y = 4 and
m=2.5;
i) n=x+y/x;
n=5
ii)z=m*x+y;
z=16
iii) z = (x++) * m + X;
z = 18
Code:
using namespace std;
#include
int main()
{
int x,y,z1,z2;
float m,n;
x=5;
y=4;
m=2.5;
n = x + y / X;
z1=m*x+y;
z2 = (x++) * m + X;
cout<<”\nN = “<<n;
còut<<”\nzl =<<z1;
cout<<”\nz2 =<<z2;
return 0;
}
output

![]()
11th Computer Science Guide Introduction to C++ Additional Questions and Answers
Choose The Correct Answer 1 Mark
Question 1.
Every programming language has _____ fundamental element.
a) Data types
b) Variables
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 2.
c++ provides a predefined set of data types for handling the data item is known as …………….. data type.
a) Fundamental
b) Built-in data types
c) User-defined
d) Either A or B
Answer:
d) Either A or B
Question 3.
A programmer can create his own data types called as ______ data types.
a) Fundamental
b) Built-in data types
c) User defined
d) Either A or B
Answer:
c) User defined
![]()
Question 4.
In a programming language, fields are referred as ……………
a) Variables
b) Data
c) File
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Variables
Question 5.
In a programming language, values are referred to as ……………
a) Variables
b) Data
c) File
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Data
Question 6.
In C++, the data types are classified as ______ main categories.
a) three
b) four
c) two
d) five
Answer:
a) three
![]()
Question 7.
In C++, ______ is a data type category.
a) Fundamental
b) Derived
c) User defined
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 8.
The ………….. are the named memory locations to hold values of specific data types.
a) Literals
b) Variables
c) Constants
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Variables
Question 9.
There are ………….. fundamental (atomic) data types in C++.
a) two
b) three
c) four
d) five
Answer:
d) five
![]()
Question 10.
…………… is an atomic data type in C++,
a) char / int
b) float / double
c) void
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 11.
………….. are whole numbers without any fraction.
a) Integers
b) Characters
c) Strings
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Integers
Question 12.
Identify the correct statement from the ; following.
a) Integers can be positive or negative.
b) If you try to store a fractional value in an int type variable it will accept only the integer portion of the fractional value.
c) If a variable is declared as an int, C++ compiler allows storing only integer values into it.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 13.
……….. data type accepts and returns all valid \ ASCII characters.
a) Character
b) float
c) void
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Character
Question 14.
Character data type is often said to be an …………… type.
a) float
b) string
c) void
d) int
Answer:
d) int
Question 15.
……………… means significant numbers after decimal point.
a) Precision
b) Digit
c) Floating point
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Precision
![]()
Question 16.
The _____ data type is larger and slower than type float.
a) Char
b) double
c) void
d) int
Answer:
b) double
Question 17.
The literal meaning for void is …………….
a) Empty space
b) Nothing
c) Blank
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Empty space
Question 18.
In C++, the ……………. data type specifies an empty set of values.
a) Char
b) double
c) void
d) int
Answer:
c) void
![]()
Question 19.
……………. is used as a return type for functions that do not return any value.
a) Char
b) double
c) void
d) int
Answer:
c) void
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement from the following.
a) One of the most important reason for declaring a variable as a particular data type is to allocate appropriate space in memory.
b) As per the stored program concept, every data should be accommodated in the main memory before they are processed)
c) C++ compiler allocates specific memory space for each and every data handled according to the compiler’s standards.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 21.
char data type needs ……………. bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
d) 1
![]()
Question 22.
int data type needs ………….. bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
c) 2
Question 23.
float data type needs …………….. bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
b) 4
Question 24.
double data type needs ………… bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
a) 8
![]()
Question 25.
The range of char data type is ………………
a) -127 to 128
b) -32,768 to 32,767
c) 3.4 x 10-38 to 3.4 x 1038 -1
d) 1.7 x 10-308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Answer:
a) -127 to 128
Question 26.
The range of int data type is …………..
a) -127 to 128
b) -32,768 to 32,767
c) 3.4 x HT38 to 3.4 x 1038-1
d) 1.7 x 10-308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Answer:
b) -32,768 to 32,767
Question 27.
The range of float data type is ……………
a) -127 to 128
b) -32,768 to 32,767
c) 3.4 x 10-38 to 3.4 x 1038 -1
d) 1.7 x lO”308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Answer:
c) 3.4 x 10-38 to 3.4 x 1038 -1
![]()
Question 28.
The range of double data type is …………….
a) -127 to 128
b) -32,768 to 32,767
c) 3.4 x 10″38 to 3.4 x 1038-1
d) 1.7 x 10-308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Answer:
d) 1.7 x 10-308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Question 29.
…………….. can be used to expand or reduce the memory allocation of any fundamental data type.
a) Modifiers
b) Access specifiers
c) Promoters
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Modifiers
Question 30.
………….. are called as Qualifiers.
a) Modifiers
b) Access specifiers
c) Promoters
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Modifiers
![]()
Question 31.
There are …………….modifiers used in C++.
a) five
b) four
c) three
d) two
Answer:
b) four
Question 32.
……………… is a modifier in C++,
a) signed / unsigned
b) long
c) short
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 33.
short data type needs …………. bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
c) 2
![]()
Question 34.
unsigned short data type needs ………….. bytes of memory. .
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
c) 2
Question 35.
signed short data type needs…………… bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
c) 2
Question 36.
signed long data type needs ……………. bytes of memory.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
b) 4
![]()
Question 37.
The range of unsigned short is …………..
a) -32,768 to 32768
b) 0 to 65535
c) -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
d) 0 to 4,294,967,295
Answer:
b) 0 to 65535
Question 38.
The range of unsigned long is ……………..
a) -32,768 to 32768
b) 0 to 65535
c) -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
d) 0 to 4,294,967,295
Answer:
d) 0 to 4,294,967,295
Question 39.
The range of signed long is ……………..
a) -32,768 to 32768
b) 0 to 65535
c) -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
d) 0 to 4,294,967,295
Answer:
c) -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
![]()
Question 40.
The range of unsigned char is …………….
a) -32,768 to 32768
b) 0 to 65535
c) 0 to 255
d) 0 to 4,294,967,295
Answer:
c) 0 to 255
Question 41.
The range of long double data type is ……………..
a) -127 to 128
b) -32,768 to 32,767
c) 3.4 x 10^932 to 1.1 x 104932 -1
d) 1.7 x 10~308 to 1.7 x 10308 -1
Answer:
c) 3.4 x 10^932 to 1.1 x 104932 -1
Question 42.
int data type needs …………. bytes of memory in Dec C++.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
b) 4
Question 43.
unsigned int data type needs ……………… bytes of memory in Dec C++.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
b) 4
![]()
Question 44.
signed int data type needs …………… bytes of memory in Dec C++.
a) 8
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Answer:
b) 4
Question 45.
long double data type needs…………… memory in Dec C++.
a) 10
b) 8
c) 2
d) 12
Answer:
d) 12
Question 46.
long double data type needs…………… memory in Turbo C++.
a) 10
b) 8
c) 2
d) 12
Answer:
a) 10
![]()
Question 47.
…………….. is an operator which gives the size of a data type.
a) sizeof()
b) byteof()
c) datatype()
d) None of these
Answer:
a) sizeof()
Question 48.
The suffix……………. is used for floating point values
a) U
b) L
C) F
d) None of these
Answer:
C) F
Question 49.
The suffix ……………… is used for long int values.
a) U
b) L
C) F
d) None of these
Answer:
b) L
Question 50.
The suffix ………….. is used for unsigned int
a) U
b) L
C) F
d) None of these
Answer:
a) U
![]()
Question 51.
……………… are user-defined names assigned to specific memory locations in which the values are stored.
a) Literals
b) Variables
c) Operators
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Variables
Question 52.
There are ………….. values associated with a symbolic variable
a) two
b) three
c) four
d) five
Answer:
a) two
Question 53.
…………… is data stored in a memory location.
a) L-value
b) R-value
c) T-value
d) B-value
Answer:
b) R-value
![]()
Question 54.
…………… is the memory address in which the R-value is stored.
a) L-value
b) R-value
c) T-value
d) B-value
Answer:
a) L-value
Question 55.
The memory addresses are in the form of ……………. values.
a) Binary
b) Octal
c) Decimal
d) Hexadecimal
Answer:
d) Hexadecimal
Question 56.
Every …………. should be declared before they are actually used in a program.
a) Variable
b) Operand
c) Literals
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Variable
![]()
Question 57.
If we declare a variable without any initial value, the memory space allocated to that variable will be occupied with some unknown value is called as ………….. values.
a) Junk
b) Garbage
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 58.
A variable can be initialized during the execution of a program is known as ……………..
a) Dynamic initialization
b) Static initialization
c) Random initialization
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Dynamic initialization
Question 59.
………….. is the keyword used to declare a constant.
a) constant
b) const
c) cons
d) None of these
Answer:
b) const
![]()
Question 60.
…………… keyword modifies / restricts the accessibility of a variable.
a) constant
b) const
c) cons
d) None of these
Answer:
b) const
Question 61.
……………….. is known as Access modifier of a variable.
a) constant
b) const
c) cons
d) None of these
Answer:
b) const
Question 62.
Declaration of a reference consists of ……………..
a) Base type
b) An 8i (ampersand) symbol
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
![]()
Question 63.
……………. are used to format the output of any
C++ program,
a) Qualifiers
b) Modifiers ‘
c) Manipulators
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Manipulators
Question 64.
ManIpulators are functions specifically designed to use with the ______ operators.
a) Insertion («)
b) Extraction(»)
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 65.
Commonly used manipulator is …………..
a) endl and setw
b) setfill
c) setprecision and setf
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 66.
endl manipulator is a member of ………………….. header file.
a) iomanip
b) iostream
c) manip
d) conio
Answer:
b) iostream
Question 67.
setw, setfihl, setprecision and setf manipulators are members of______ header file.
a) iomanip
b) iostream
c) manip
d) conio
Answer:
a) iomanip
Question 68.
______ is used asa line feeder in C++.
a) setw
b) setfill
c) endi
d) setf
Answer:
c) endi
![]()
Question 69.
______ can be used as an alternate to ‘sn’.
a) setw
b) setfill
c) endi
d) setf
Answer:
c) endi
Question 70.
______ inserts a new line and flushes the buffer.
a) setw
b) setfill
c) endi
d) setf
Answer:
c) endi
Question 71.
______ manipulator sets the width of the field assigned for the output.
a) setw
b) setñhl
c) endi
d) setf
i.) IIUI
U) SeIT
Answer:
a) setw
![]()
Question 72.
_______ manipulator is usually used after setw.
a) endl
b) setfill
c) endl
d) setf
Answer:
b) setfill
Question 73.
______ is used to display numbers with fractions In specific number of digits.
a) ‘endI
b) setfill i1
c) endl
d) setprecision
Answer:
d) setprecision
Question 74.
setf() manipulator may be used in form…………..
a) Fixed
b) Scientific
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
![]()
Question 75.
An expression ¡s a combination of ……………………… arranged as per the rules of C++.
a) Operators
b) Constants
c) Variables
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 76.
InC++,there are ………………………….. types of expressions used.
a) four
b) five
c) seven
d) two
Answer:
c) seven
Question 77.
The process of converting one fundamental type into another is called as …………………………
a) Type Conversion
b) Compiling
c) Inverting
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Type Conversion
![]()
Question 78.
c++ provides …………………… types of conversions
a) three
b) two
c) four
d) five
Answer:
b) two
Question 79.
C++ provides _____types of conversion.
a) Implicit
b) Explicit
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 80.
A(n) ………………………. type conversion is a conversion performed by the compiler automatically.
a) Implicit
b) Explicit
c) BothAandB
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Implicit
Question 81.
______conversion is also called as Automatic conversion.
a) Implicit ‘
c) BothAandB
b) Explicit
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Implicit ‘
![]()
Question 82.
Data of smaller type converted to the wider type, which is called is as ………………
a) Type Promotion
c) Type extended
b) Type upgrade
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Type Promotion
Question 83.
c++ allows explicit conversion of variables or expressions from one data type to another specific data type by the programmer Is called as ………….
a) Type Promotion
b) Type upgrade
c) Type casting
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Type casting
Very Short Answers 2 Marks
Question 1.
What are the classification of data types?
Answer:
In C++, the data types are classified as three main categories.
- Fundamental data types
- User-defined data types and
- Derived data types.
Question 2.
Define: Variable.
Answer:
The variables are the named memory locations to hold values of specific data types.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the syntax for declaring a variable with an example.
Answer:
Syntax for declaring a variable:
Example:
int num1;
int num1, num2, sum;
Question 4.
What a the fundamental/atomic data types in C++?
Answer:
Fundamental (atomic) data types are predefined data types available with C++. There are five fundamental data types in C++: char, int, float, double and void.
Question 5.
Write about int data type.
Answer:
Integers are whole numbers without any fraction. Integers can be positive or negative. Integer data type accepts and returns only integer numbers.
If a variable is declared as an int, C++ compiler allows storing only integer values into it.
If we try to store a fractional value in an int type variable it will accept only the integer portion of the fractional value.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the advantages of using float data type?
Answer:
There are two advantages of using float data types.
- They can represent values between the integers.
- They can represent a much greater range of values.
Question 7.
What is the disadvantage of using float data type?
Answer:
The floating point operations takes more time to execute compared to the integer type ie., floating point operations are slower than integer operations. This is a disadvantage of floating point operation.
Question 8.
What do you mean by precision?
Answer:
Precision means significant numbers after decimal point of floating point number.
Question 9.
Tabulate the memory allocation for fundamental data types?
Answer:
Memory allocation for fundamental data types
| Data type |
Space in memory |
|
| in terms of bytes | in terms of bits | |
| char | 1 byte | 8 bits |
| int | 2 bytes | 16 bits |
| float | 4 bytes | 32 bits |
| double | 8 bytes’ | 64 bits |
![]()
Question 10.
Tabulate the range of value for fundamental data types?
Answer:
|
Data type |
Range of value |
| char | -127 to 128 |
| int | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| float | 3.4×10--38 to 3.4×1038 -1 |
| double | 1.7×10--308 to 1.7xl0308-1 |
Question 11.
What is modifier?
Answer:
Modifiers can be used to modify the memory allocation of any fundamental data type. They are also called as Qualifiers.
Question 12.
What are the modifiers in C++?
Answer:
There are four modifiers used in C++.
They are;
- signed
- unsigned
- long
- short
Question 13.
What are the two values associated with a variable?
Answer:
There are two values associated with a symbolic variable; they are R-value and L-va!ue.
- R-value is data stored in a memory location.
- L-value is the memory address in which the R-value is stored.
![]()
Question 14.
How memory addresses are represented?
Answer:
The memory addresses are in the form of Hexadecimal values.
Example: .
0x134e represents a memory address.
Question 15.
What are garbage or junk values?
Answer:
If we declare a variable without any initial value, the memory space allocated to that variable will be occupied with some unknown value. These unknown values are called as “Junk” or “Garbage” values.
Question 16.
What do you mean by dynamic ¡nitialization
Answer:
A variable can be initialized during the execution of a program. It is known as “Dynamic
initiaIization’
For example: .
int sum = num1+num2;
This initializes sum using the known values of num1 and num2 during the execution.
Question 17.
What is the difference between reference and pointer variable?
Answer:
A reference is an alias for another variable whereas a pointer holds the memory address of a variable.
Question 18.
What is the purpose of manipulators in C++?
Answer:
Manipulators are used to format the output of any C++ program. Manipulators are functions specifically designed to use with the insertion (<<) and extraction>>) operators.
![]()
Question 19.
What are the manipulators used in C++?
Answer:
Commonly used manipulators are:
endl, setw, setfill, setprecision and setf.
Question 20.
Write about the endl manipulator.
Answer:
endl (End the Line)
endl is used as a line feeder in C++. It can be used as an alternate to ‘\n’. In other words, endl inserts a new line and then makes the cursor to point to the beginning of the next line.
Example:
cout << “The value of num = ” << num <<endl;
Question 21.
What is the difference between endl and \n.
Answer:
There is a difference between endl and ‘\n’, even though they are performing similar tasks.
endl – Inserts a new line and flushes the buffer (Flush means – clean)
‘\n’ – Inserts only a new line.
Question 22.
Write about setw( ) manipulator.
Answer:
setw ( ) :
setw manipulator sets the width of the field assigned for the output. The field width determines the minimum number of characters to be written in output.
Syntax: ‘
setw(number of characters)
Example:
cout<< setw(25) << “Basic Pay :”<< setw(10)<< basic<< endl;
![]()
Question 23.
What is the use of setfill( ) manipulator? setfill ():
Answer:
This manipulator is usually used after setw. If the presented value does not entirely fill the given width, then the specified character in the setfill argument is used for filling the empty fields.
Syntax:
setfill (character);
Example:
cout<<“\n H.R.A :”<<setw(10)< For example, if we assign 1200 to hra, setw accommodates 1200 in a field of width 10 from right to left and setfill fills p in the remaining 6 spaces that are in the beginning. The output will be, 0000001200.
Question 24.
What is the purpose of setprecision() manipulator?
Answer:
setprecision ( ):
This is used to display numbers with fractions in specific number of digits.
Syntax:
setprecision (number of digits);
Example:
float hra = 1200.123;
cout << setprecision (5) << hra;
In the above code, the given value 1200.123 will be displayed in 5 digits including fractions. So, the output will be 1200.1
setprecision ( ) prints the values from left to right. For the above code, first, it will take 4 digits and then prints one digit from fractional portion.
Question 25.
WhIch of the following statements are valid? Why? Also write their result
Inta; .
i) a – (014,3);
ii) a = (5,017)
iii) a = (3,018)
Answer:
i) a = (014,3); – Valid. A will hold 3. (The second value)
ii) a = (5,017) – Valid. 014 ¡s an octal constant. It will be converted into decimal and then stored in a. So, a will hold 15 as its value.
iii) a = (3,018) – Invalid. Because 8 is not an octal digit. (A number starts with 0 is considered as an octal)
![]()
Question 26.
Which of the following statements are valid? Why? Also write their result.
inta;
i) a = (3,0xA);
ii) a = (5,0xCAFE)
iii) a = (OXCAFE,0XF)
iv) a = (0XCAFE,0XG)
Answer:
i) a = (3,0xA):
Valid. OxA is a hexadecimal constant. It will be converted into decimal and then stored in a. So, a will hold 10 as its value.
ii) a = (5,0xCAFE):
Valid. OxCAFE is a hexadecimal constant. It will be converted into decimal and then stored in a. So, a will hold 51966 as its value.
iii) a = (OXCAFE,0XF):
Valid. 0XF is a hexadecimal constant. It will be converted into decimal and then stored in a. So, a will hold 15 as its value.
iv) a= (OXCAFE,0XGAB):
Invalid. Because G is not a hexadecimal digit in OXGAB.\
Short Answer 3 Marks
Question 1.
LIstthedattypesinC++.
Answer:
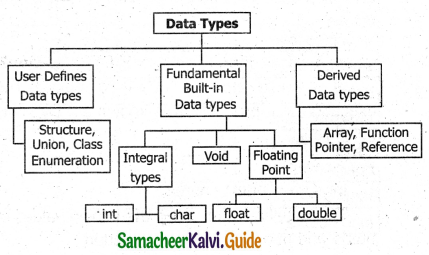
Question 2.
Write about character data type.
Answer:
Character data type accepts and returns all valid ASCII characters. Character data type is often said to be an integer type, since ail the characters are represented in memory by their associated ASCII Codes.
If a variable is declared as char, C++ allows storing either a character or an integer value.
Example:
char c=65;
char ch = ‘A’; Both statements will assign ‘A’ to c and ch.
![]()
Question 3.
Write note on double data type.
Answer:
double data type:
This data type is for double precision floating point numbers. The double is also used for handling floating point numbers. But, this type occupies double the space than float type. This means, more fractions can be accommodated in double than in float type.
The double is larger and slower than type float. The double is used in a similar way as that of float data type.
Question 4.
Compare memory allocation by Turbo C++ and Dev C++.
Answer:
| Data type | Memory size in bytes | |
| Turbo C++ | Dev C++ | |
| short | 2 | 2 |
| unsigned short | 2 | 2 |
| signed short | 2 | 2 |
| int | 2 | 4 |
| unsigned int | 2 | 4 |
| signed int | 2 | 4 |
| long | 4 | 4 |
| unsigned long | 4 | 4 |
| signed long | 4 | 4 |
| char | 1 | 1 |
| unsigned char | 1 | 1 |
| signed char | 1 | 1 |
| float | 4 | 4 |
| double | 8 | 8 |
| long double | 10 | 12 |
![]()
Question 5.
What is the purpose of number suffix in C++?
Answer:
There are different suffixes for integer and floating point numbers. Suffix can be used to assign the same value as a different type.
For example, if we want to store 45 in an int, long, unsigned int and unsigned long int, you can use suffix letter L or U (either case) with 45 i.e. 45L or 45U.
This type of declaration instructs the compiler to store the given values as long and unsigned.
‘F’ can be used for floating point values, example: 3.14F
Question 6.
How setprecision( ) is used to set the number of decimal places?
Answer:
setprecision can also be used to set the number of decimal places to be displayed. In order to do this task, we will have to set an ios flag within setf( ) manipulator.
This may be used in two forms:
(i) fixed and
(ii) scientific.
These two forms are used when the keywords fixed or scientific are appropriately used before the setprecision manipulator.
Example:
#include
#indude
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout << setprecision(2)<<0.1;
}
In the above program, ios flag is set to fixed type; it prints the floating point number in fixed notation. So, the output will be, 0.10
cout.setf(ios: scientific); cout << setprecision(2) << 0.1;
In the above statements, ios flag is set to scientific type; it will print the floating point number in scientific notation. So, the output wiil
be, 1.00e-001
![]()
Explain In Detail 5 Marks
Question 1.
What is an expression? Explain its types with suitable example.
Answer:
An expression is a combination of operators, constants and variables arranged as per the rules of C++.
An expression may consist of one or more operands, and zero or more operators to produce a value. In C++, there are seven types of expressions as given below.
|
Expression |
Description |
Example |
| 1.Constant Expression | Constant expression consist only constant values | int num=100; |
| 2. Integer Expression | The combination of integer and character values and/or variables with simple arithmetic operators to produce integer results. | sum = num1 +
num2; avg=sum/5; |
| 3. Float Expression | The combination of floating point values and/or variables with simple arithmetic operators to produce floating point results. | Area=3.14*r*r; |
| 4. Relational Expression | The combination of values and/or variables with relational operators to produce bool(true means 1 or false means 0) values as results. | x>y;
a+b==c+d; |
| 5. Logical Expression | The combination of values and/or variables with Logical operators to produce bool values as results. | (a>b)&& (c= = 10); |
| 6. Bitwise Expression | The combination of values and/or variables with Bitwise operators. | x>>3;
a<<2; |
| 7. Pointer Expression | A Pointer is a variable that holds a memory address. Pointer declaration statements. | int *ptr; |
![]()
Question 2.
Explain type conversion in detail.
Answer:
The process of converting one fundamental type into another is called as “Type Conversion”. C++ provides two types of conversions.
- Implicit type conversion
- Explicit type conversion
Implicit type conversion:
An Implicit type conversion is a conversion performed by the compiler automatically. So, implicit conversion is also called as “Automatic
conversion “.
This type of conversion is applied usually whenever different data types are intermixed in an expression. If the type of the operands differs, the compiler converts one of them to match with the other, using the rule that the “smaller” type is
converted to the “wider” type, which is called as “Type Promotion”
Example:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=6;
float b =3.14;
cout << a+b
}
In the above program, operand ‘a’ ¡s an mt type and ‘b’ is a float type. During the execution of the program, ‘mt’ is converted into a ‘float because a float is wider than mt.
Hence, the output of the above program will be: 9.14
Explicit type conversion:
C++ allows explicit conversion of variables
or expressions from one data type to another
specific data type by the programmer. It is called
as “type casting”.
Syntax:
(type-name) expression;
Where type-name is a valid C++ data type to which the conversion is to be performed.
Example:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
float varf=78.685;
cout << (int) varf;
}
In the above program, variable varf is declared as a float with an initial value 78.685. The value of varf is explicitly converted to an int type in cout statement. Thus, the final output will be 78.
During explicit conversion, if we assign a value to a type with a greater range, it does not cause any problem. But, assigning a value of a larger type to a smaller type may result in loosing or loss of precision values.
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double varf= 178.25255685;
cout << (float) varf < < endl;
cout << (int) varf << endl;
}
Output
178.253
178
![]()
Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
What do you mean by fundamental data types?
Answer:
C++ provides a predefined set of data types for handling the data items. Such data types are known as fundamental or built-in data types.
Question 2.
The data type char is used to represent characters. Then why is it often termed as an integer type?
Answer:
Character data type is often said to be an integer type, since all the characters are represented in memory by their associated ASCII Codes.
Question 3.
What is the advantage of floating point numbers over integers?
Answer:
Advantages of using float data types.
- They can represent values between the integers.
- They can represent a much greater range of values.
Question 4.
The data type double is another floating point type. Then why is it treated as a distinct data type?
Answer:
The double is also used for handling floating point numbers. But, this type occupies double the space than float type. This means, more fractions can be accommodated in double than in float type.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the use of void data type?
Answer:
The literal meaning for void is ’empty space’. In C++, the void data type specifies an empty set of values. It is used as a return type for functions that do not return any value.
Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
What is modifiers? What is the use of modifiers?
Answer:
Modifiers are used to modify the storing capacity of a fundamental data type except void type.
For example, int data type can store only two bytes of data. In reality, some integer data may have more length and may need more space in memory. In this situation, we should modify the memory space to accommodate large integer values. .
Modifiers can be used to modify the memory allocation of any fundamental data type. They are also called as Qualifiers.
Question 2.
What is wrong with the following C++ statement?
Answer:
long float x;
The modifier long must be associated with only double.
Question 3.
What Is variable? Why a variable called symbolic variable?
Answer:
Variables are user-defined names assigned to specific memory locations in which the values are stored. Variables are also identifiers; and hence,
the rules for naming the identifiers should be followed while naming a variable.
These are called as symbolic variables because these are named locations.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by dynamic initialization of a variable? Give an example.
Answer:
A variable can be initialized during the execution of a program. It is known as Dynamic
initialization.
For example:
int sum = num1+num2;
This initializes sum using the known values of num1 and num2 during the execution.
Question 5.
What is wrong with the following statement?
Answer:
const int x ;
In the above statement x must be initialized. It is missing. It may rewritten as
const mt x =10;
Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
What is meant by type conversion?
Answer:
The process of converting one fundamental type into another is called as “Type Conversion”. C++ provides two types of conversions.
- Implicit type conversion
- Explicit type conversion
Question 2.
How implicit conversion different from explicit conversion?
Answer:
An Implicit type conversion is a conversion performed by the compiler automatically. Implicit conversion is also called as “Automatic conversion”.
An explicit conversion of variables or expressions from one data type to another specific data type is by the programmer. It is called as “type casting”.
![]()
Question 3.
What is difference between endl and \n?
Answer:
There is a difference between endl and ‘\n’ even though they are performing similar tasks.
endl – Inserts a new line and flushes the buffer (Flush means – dean)
‘\n’ – Inserts only a new line.
Question 4.
What is the use of references?
Answer:
A reference provides an alias for a previously defined variable. Declaration of a reference consists of base type and an & (ampersand) symbol; reference variable name is assigned the value of a previously declared variable.
Syntax:
<&reference_variable>=
Question 5.
What is the use of setprecision ( )?
Answer:
setprecision ( ):
This is used to display numbers with fractions in specific number of digits.
Syntax:
setprecision (number of digits);
Example:
float hra = 1200.123;
cout << setprecision (5) << hra;
The given value 1200.123 will be displayed in 5 digits including fractions. The output will be 1200.1
![]()
Hands On Practice
Question 1.
Write C++ programs to interchange the values of two variables.
a) Using with third variable C++PROGRAM:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
intx,y,t;
cout<<“\nEnter two numbers”; cin>>x>>y;
cout<<“\nValues before interchage
x=”<<x<<“\ty=”<<y;
t=x;
x=y;
y=t;
cout<<“\nValues after interchage x=”<<x<<“\ty=”<<y;
return 0;
}
Output
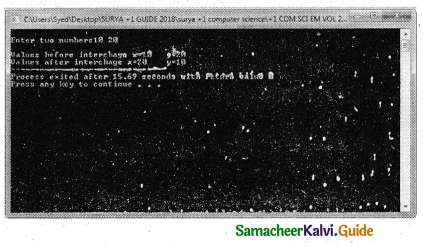
b) Without using third variable C++ PI OGRAM:
#include
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int x,y;
cout<<“\nEnter two numbers”; cin>>x>>y;
cout<<“\nValues before interchage
x=”<<x<<“\ty=”<<y;
//interchage process without using third
variable
x=x+y;
y=x-y;
x=x-y;
cout<<“\nValues after interchage x=”<<x<<“\ty=”<<y;
return 0;
}
Output
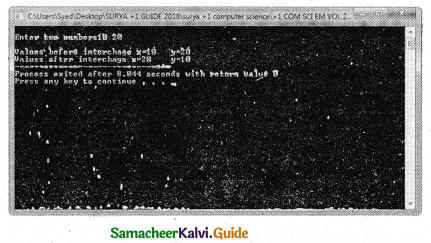
![]()
Question 2.
Write C++ programs to do the following:
a) To find the perimeter and area of a quadrant.
C++ PROGRAM:
#include
using namespace std;
int mainQ()
{
float ppm,area;
cout<<“\nEnter radius cin>>r;
area = 3.14 * r * r / 4;
pm = 3.14 * r / 2;
cout<<“\nQuadrant Area = “<<area;
cout<<“\n\nQuadrant Perimeter = “<<pm;
return 0;
}
OutPut
b) To find the area of triangle.
C++ PROGRAM 1:
(Area of triangle when b and h values are known)
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float b,h,area;
cout<<“\nEnter b and h value of triangle cin>>b>>h;
// Area of triangle when b and h values are known
area = b * h / 2;
cout<<“‘\nBase value = “<<b<<“Height = “<<h<<“Triangle Area = “<<area;
return 0;
}
OutPut

C++ PROGRAM 2:
(Area of triangle when three sides are known)
#inciude
#include using namespace std;
int main()
{
float a,b,c,area,s;
cout<<“\nEnter three sides of triangle cin>>a>>b>>c;
//Area of triangle when three sides are known
s = (a+b+c)/2;
area = sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
cout<<“\n Sidel value = “<<a<<“Side2
value = “<<b<<” Side3 value =”<<c;
cout<<“\nTriangie Area = “<<area;
return 0;
}
Output

c. To convert the temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
C++ PROGRAM:
//Convertion of the temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float c,f;
cout<<”\nEnter Celsius value “; cin>>c;
f=9*c/5+32;
cout«”\nTemperature in Celsius = “<<C;
cout < <“\nTemperature in Fahrenheit =
“<<f;
return 0;
}
Output

![]()
Question 3.
Write a C++ to find the total and percentage of marks you secured from 10th Standard Public Exam. Display all the marks one-by- one along with total and percentage. Apply formatting functions.
C++ PROGRAM:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int rnain()
{
int tarn,enm,mam,som,scm,total,avg; char name[30];
cout<<“\nEnter name of the student cin>>name;
cout<<“\nEnterTamil mark”; cin>>tam;
cout<<“\nEnter English mark”; cin>>enm;
cout<<“\nEnter Maths mark “; cin>>mam;
cout<<“\nEnter Science mark “; cin>>scm;
cout<<“\nEnter Social Science mark”; cin>>som; .
total = tarn + enm + mam + scm + som; avg = total / 5;
cout<<“\n\t\tlOth Standard Public Exam Mark”<<end!<<endl;
cout<<setw(30)<<“Name of the student «name<<endk<endl;
cout<<setw(30)<<setfill(“)<<“Tamil mark
< <setw(3)< <setfill(‘0’)< <tam< cout<<setw(30)<<setfillC ‘)<<“English
mark “<setw(3)<<setfill(‘0’)<<enm< cout<<setw(30)<<setfillC ‘)<<“Maths mark
< <setw(3)< <setfillCO’)< <mam< <endl< <endl;
cout<<setw(30)<<setfillC ‘)<<“Science
mark :”<<setw(3)<<setfill(‘0’)<<scm< cout< < setw(3G) < < setfi 11C ‘) < < “Soda I
Science mark :”<<setw(3)<<setfillC0’)< cout<<setw(30)<<setfillC ‘)«’Total Marks <<setw(3)<<setfillC0’)<<totak<endk<endl;
cout<<setw(30)«setfillC ‘)«”Average mark:”
<<setw(3)<<setfill(‘0’)< return 0;
}
Output