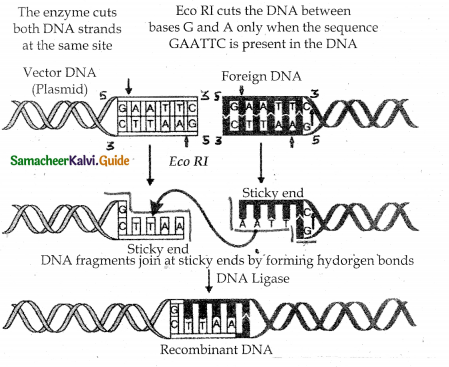
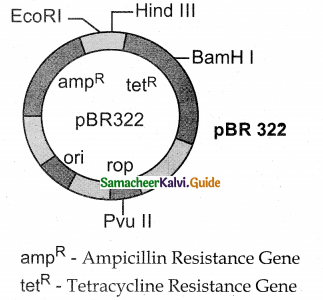
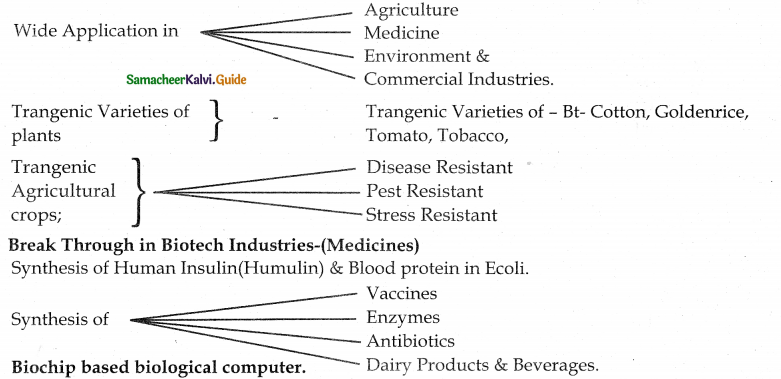
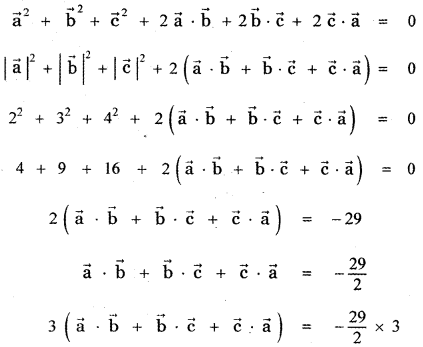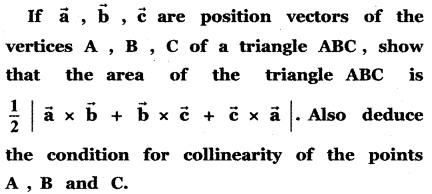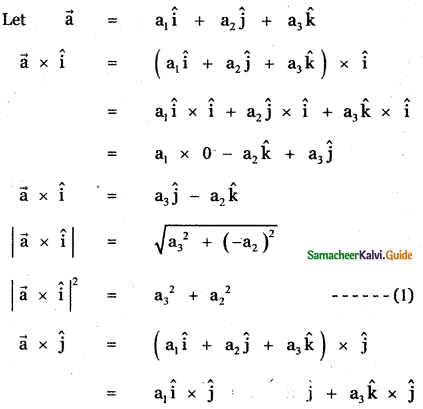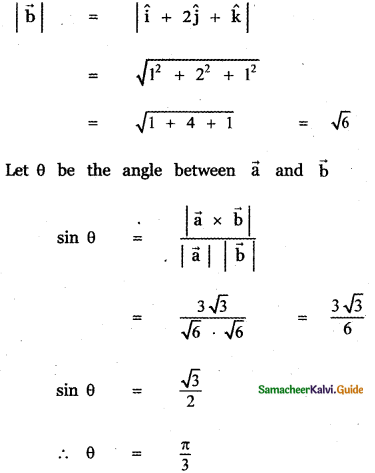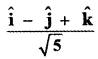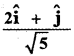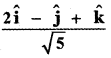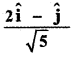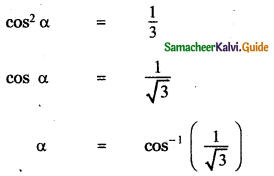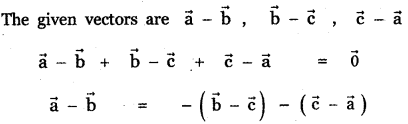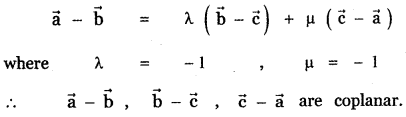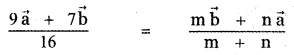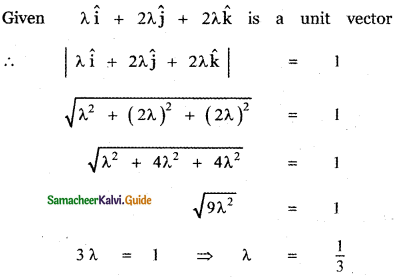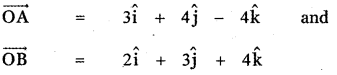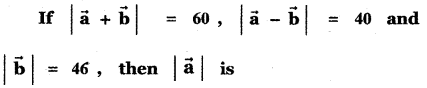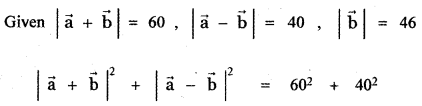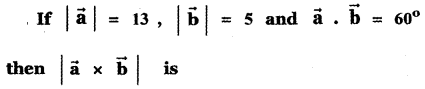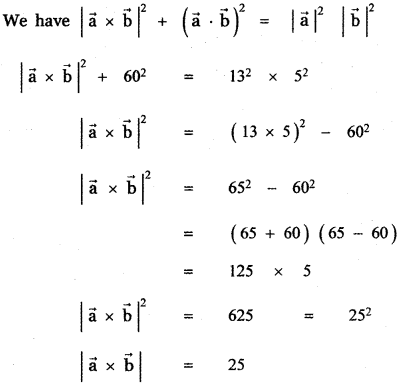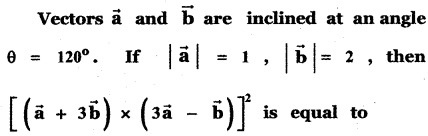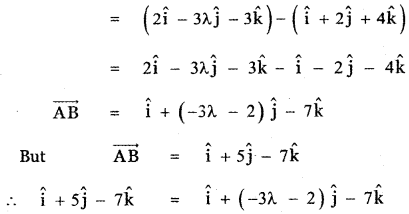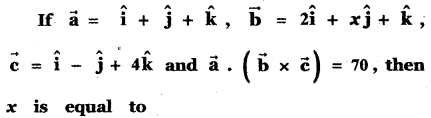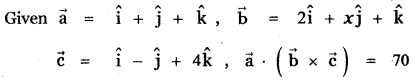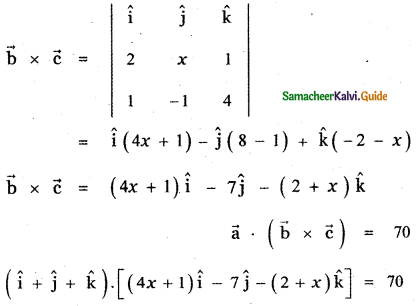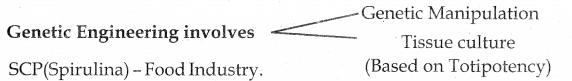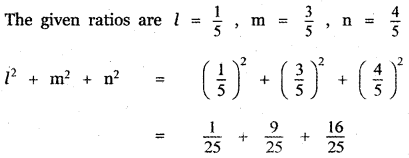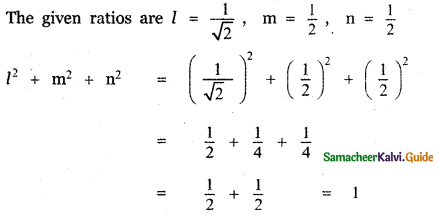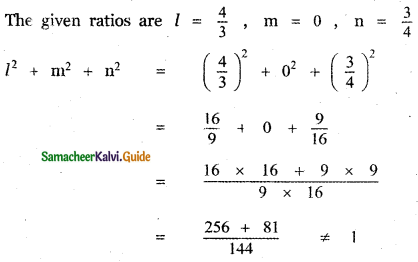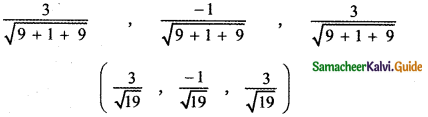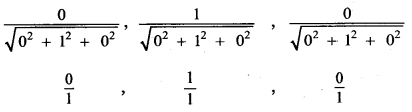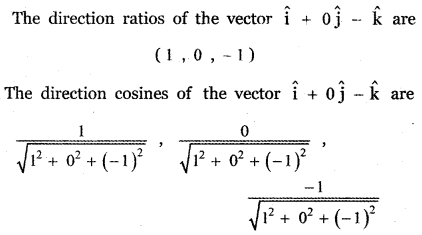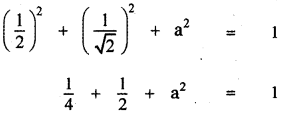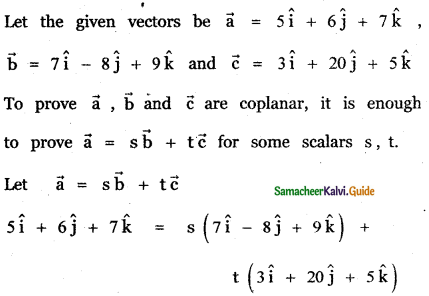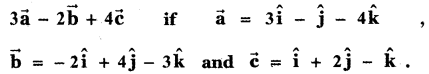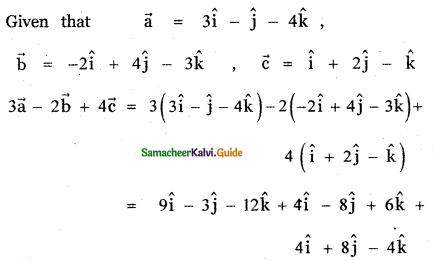Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 8 Vector Algebra – I Ex 8.3 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Vector Algebra – I Ex 8.3
Question 1.
Find \(\vec{a}\) . \(\vec{b}\) when
(i) \(\vec{a}\) = î – 2ĵ + k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 3î – 4ĵ – 2k̂
(ii) \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + 2ĵ – k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 6î – 3ĵ + 2k̂
Answer:
(i) \(\vec{a}\) = î – 2ĵ + k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 3î – 4ĵ – 2k̂
\(\vec{a}\) . \(\vec{b}\) = (î – 2ĵ + k̂) . (3î – 4ĵ – 2k̂)
= (1) (3) + (-2) (-4) + (1) (-2)
= 3 + 8 – 2
= 9
![]()
(ii) \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + 2ĵ – k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 6î – 3ĵ + 2k̂
\(\vec{a}\) . \(\vec{b}\) = (2î + 2ĵ – k̂) . (6î – 3ĵ + 2k̂)
= (2) (6) + (2) (-3) + (-1) (2)
= 12 – 6 – 2 = 12 – 8 = 4
Question 2.
Find the value λ for which the vectors \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are perpendicular, where
(i) \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + λĵ – k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = î – 2ĵ + 3k̂
(ii) \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + 4ĵ – k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 3î – 2ĵ + λk̂
Answer:
When \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are ⊥r then \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = 0
\(\vec{a}\) ⊥r \(\vec{b}\) ⇒ \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = 0
(i) (2) (1) + (λ) (-2) + (1) (3) = 0 ⇒ λ = 5/2
(ii) (2) (3) + (4) (-2) + (-1) (λ) = 0
6 – 8 – λ = 0
-λ – 2 = 0 ⇒ -λ = 2 ⇒ λ = -2
![]()
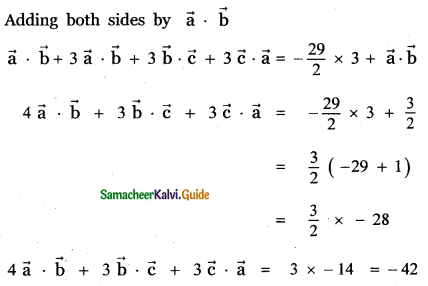
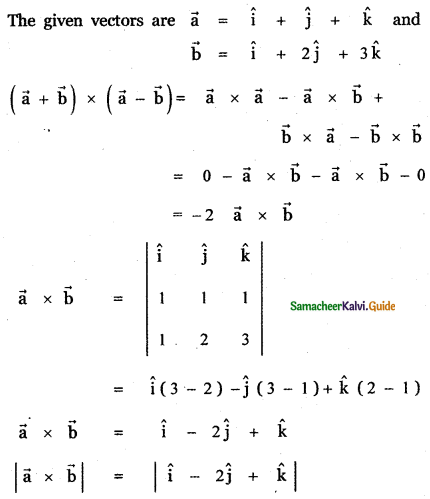
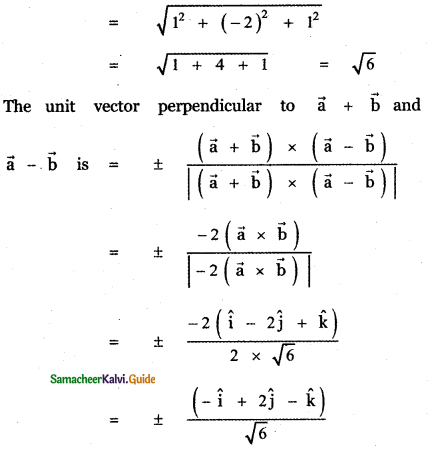
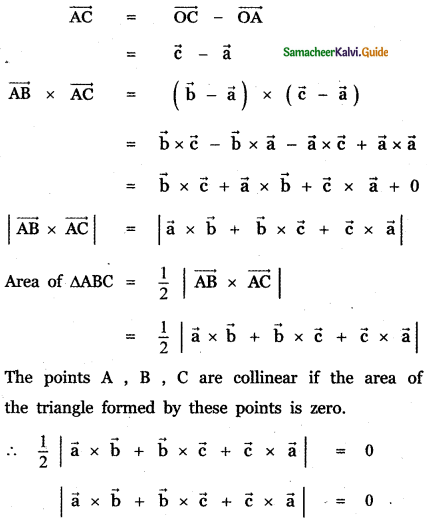
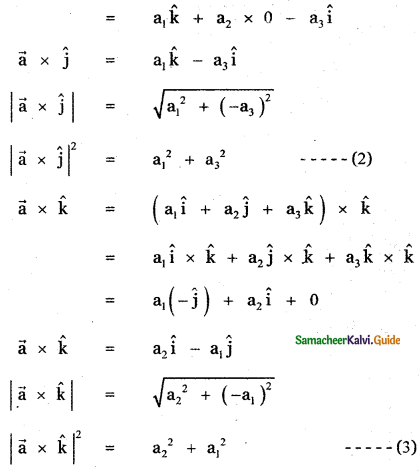
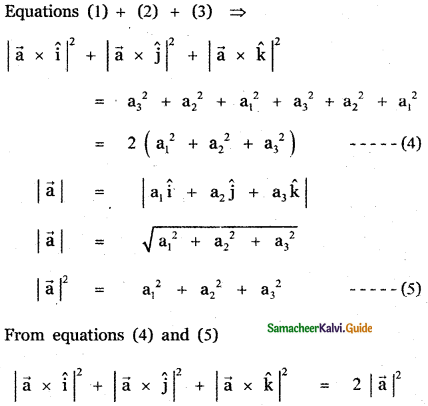
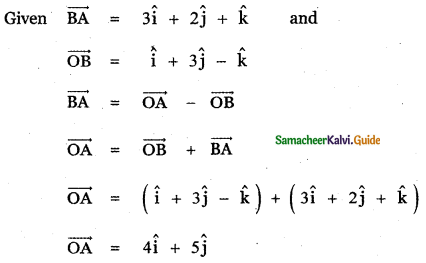
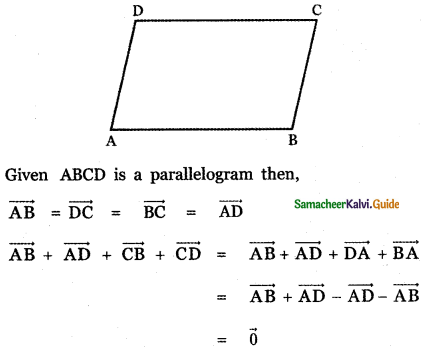
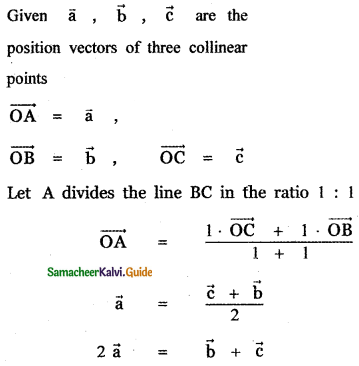
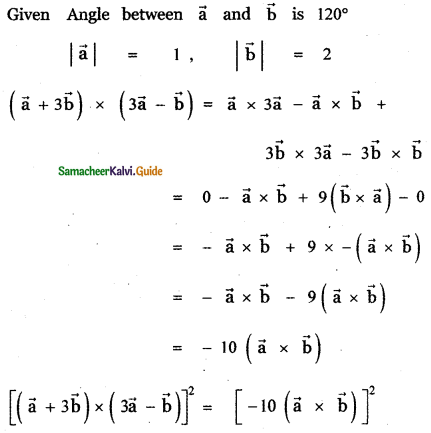
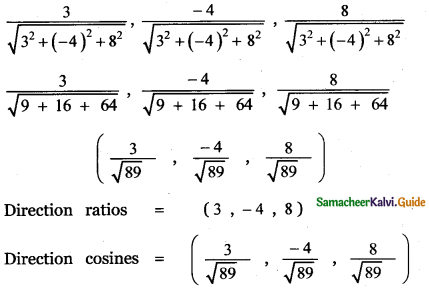
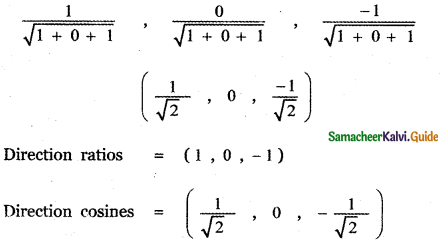
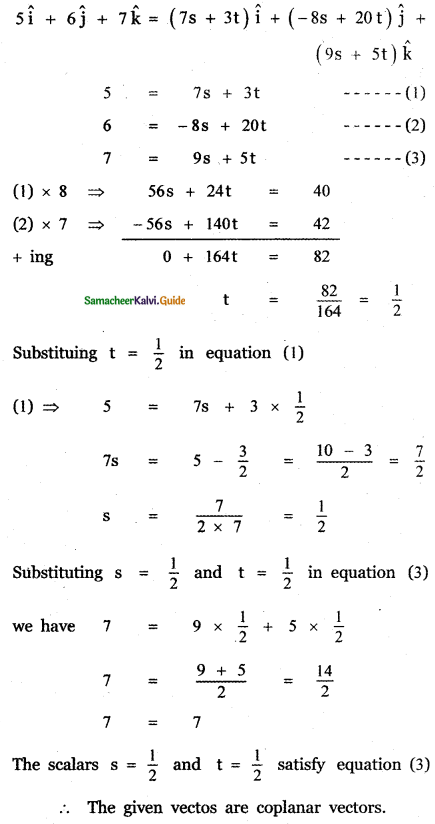
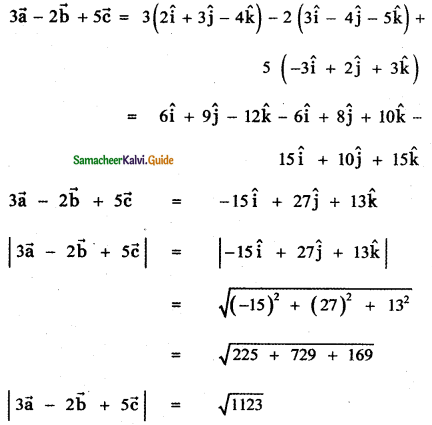
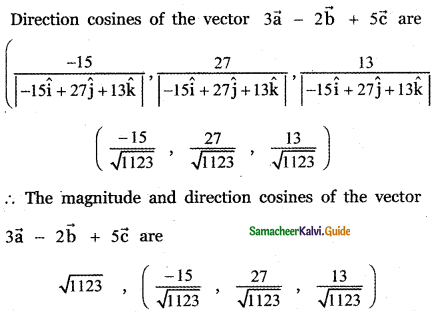
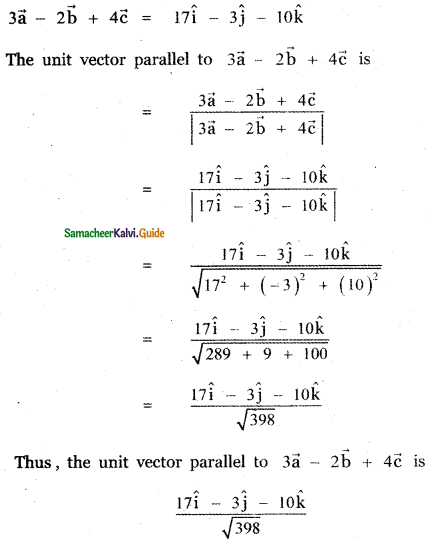
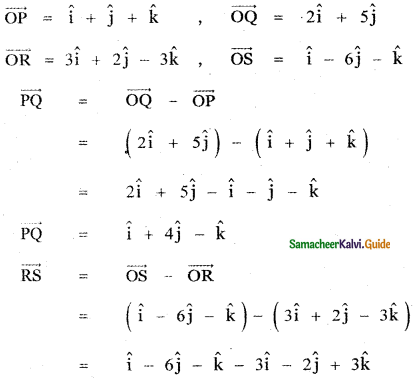
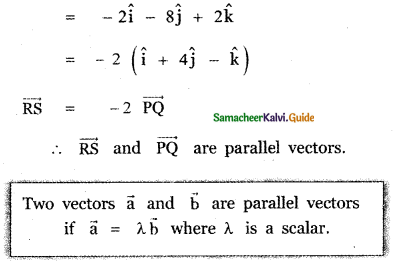
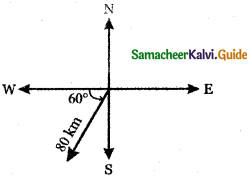
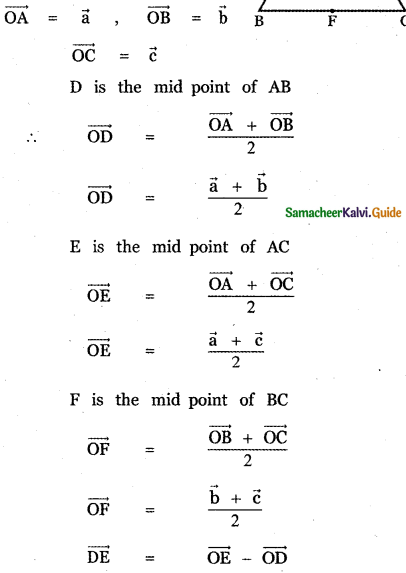
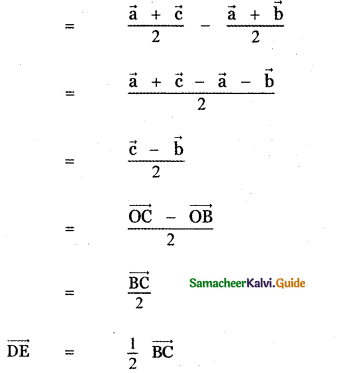
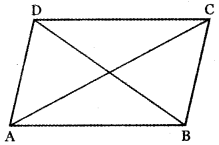
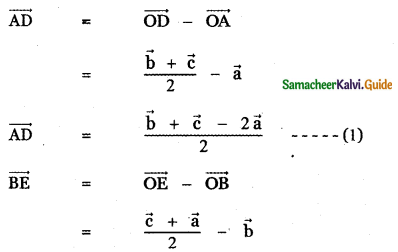
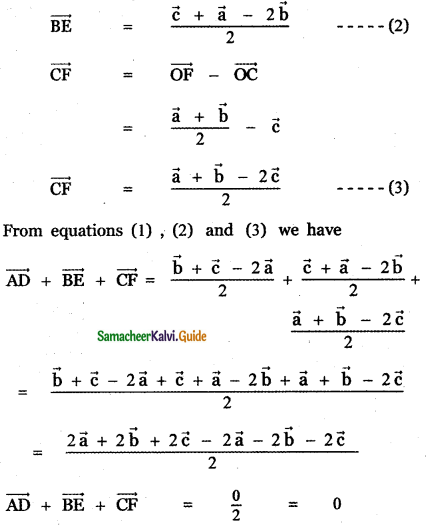
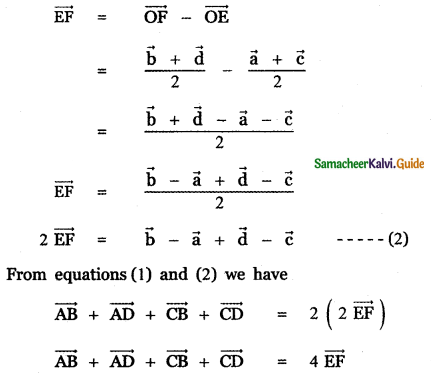
Question 3.
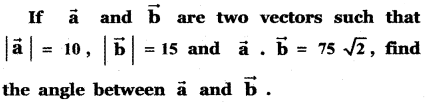
Answer:
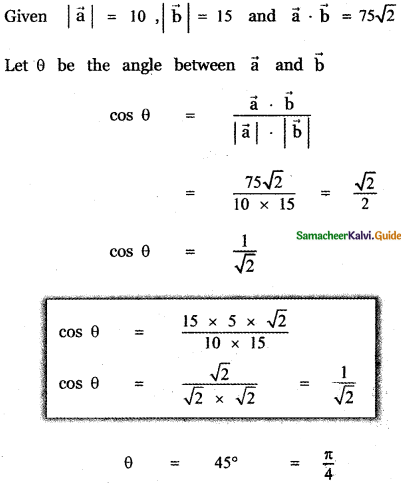
Question 4.
Find the angle between the vectors
(i) 2î + 3ĵ – 6k̂ and 6î – 3ĵ + 2k̂
(ii) î – ĵ and ĵ – k̂
Answer:
(i) 2î + 3ĵ – 6k̂ and 6î – 3ĵ + 2k̂
Let θ be the angle between the given vectors, then
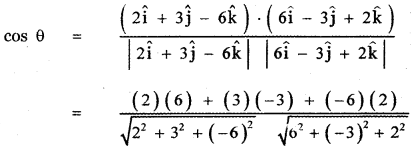
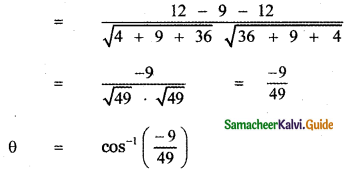
![]()
(ii) î – ĵ and ĵ – k̂
Let θ be the angle between the given vectors, then
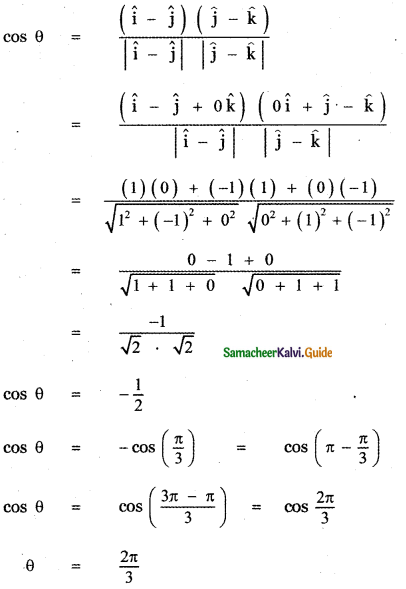
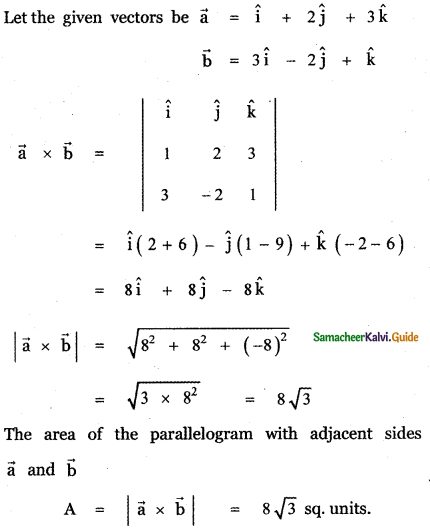
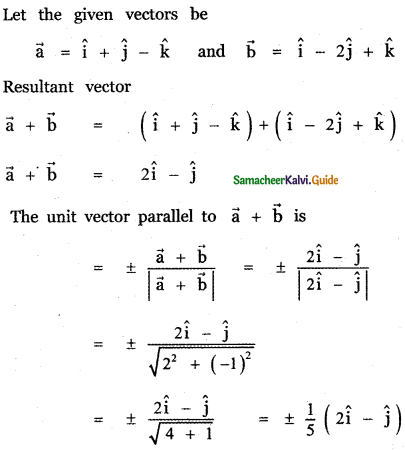
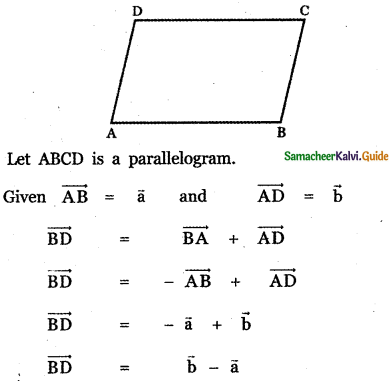
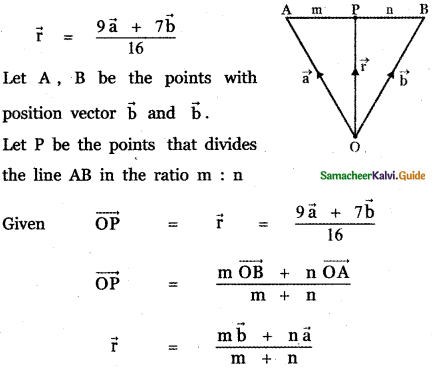
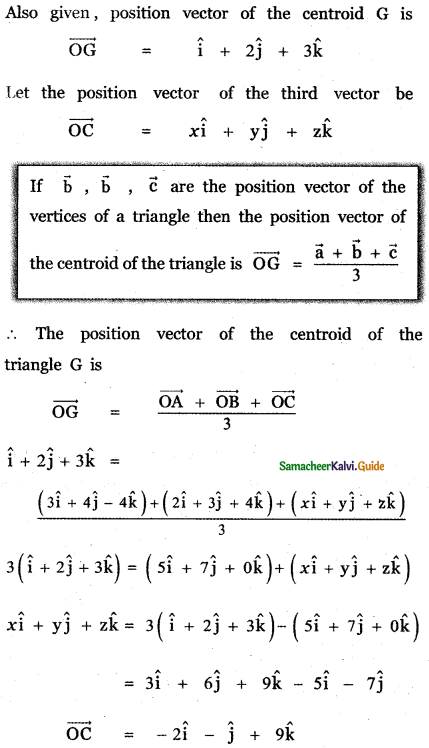
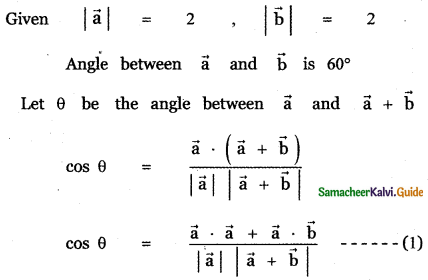
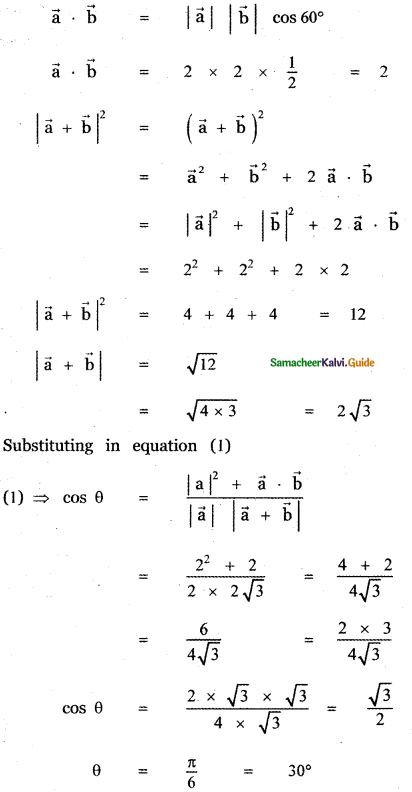
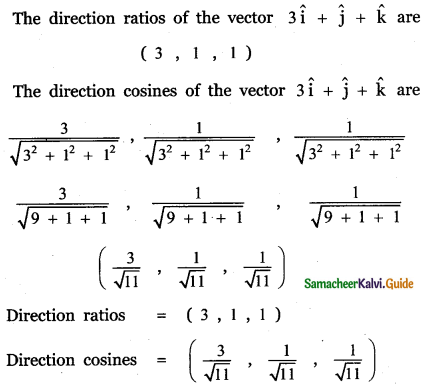
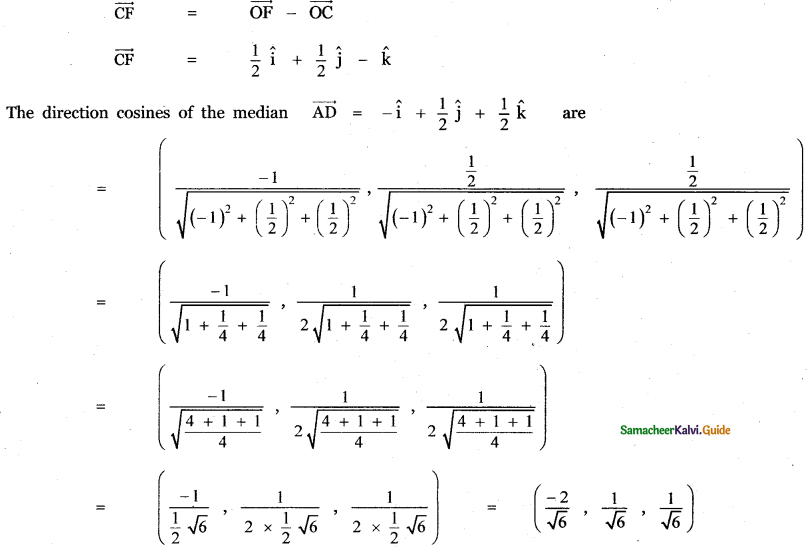
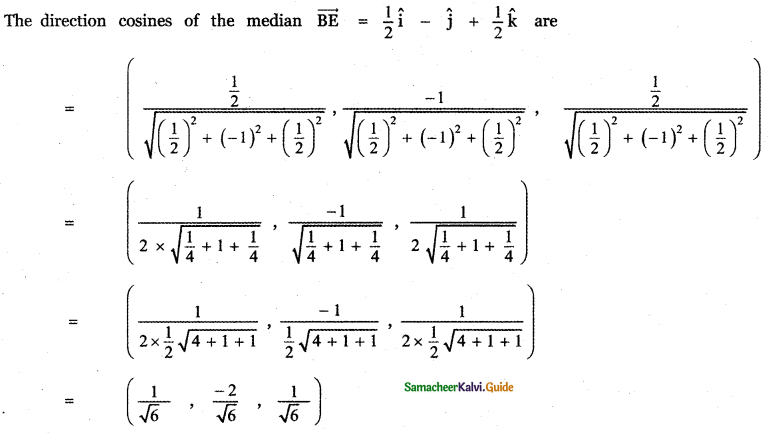
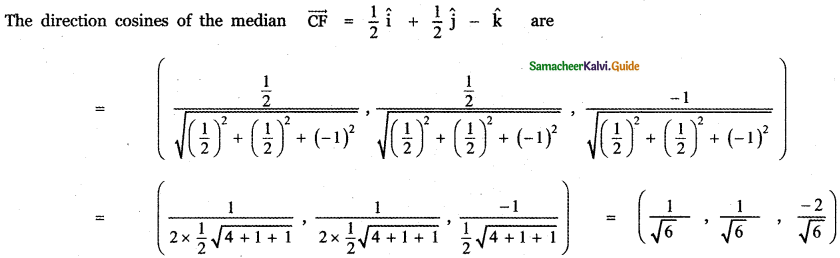
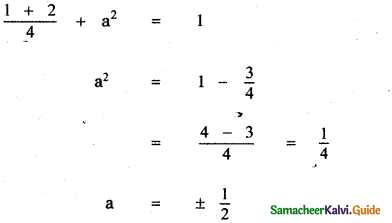
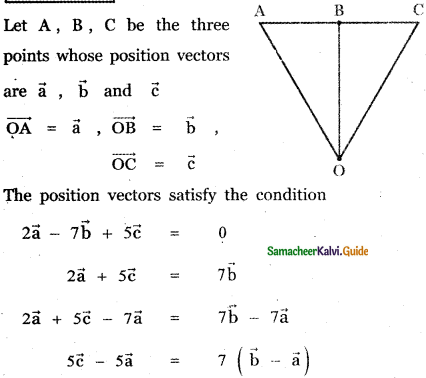
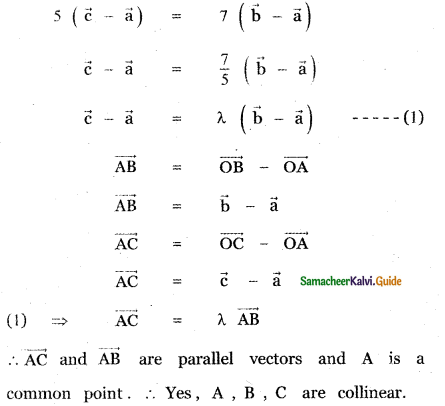
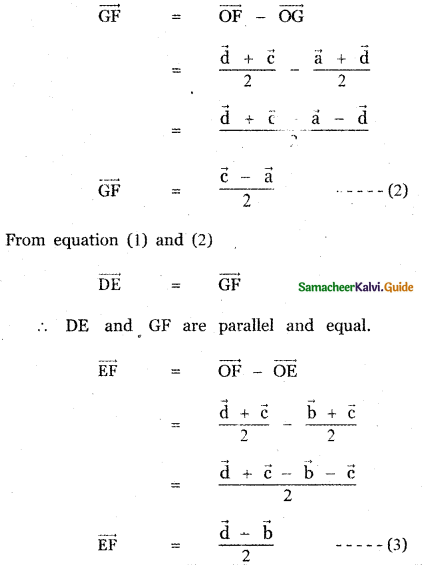
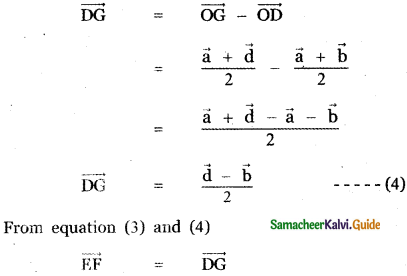
Question 5.
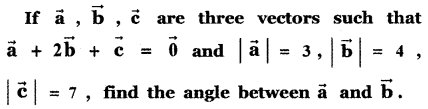
Answer:
![]()
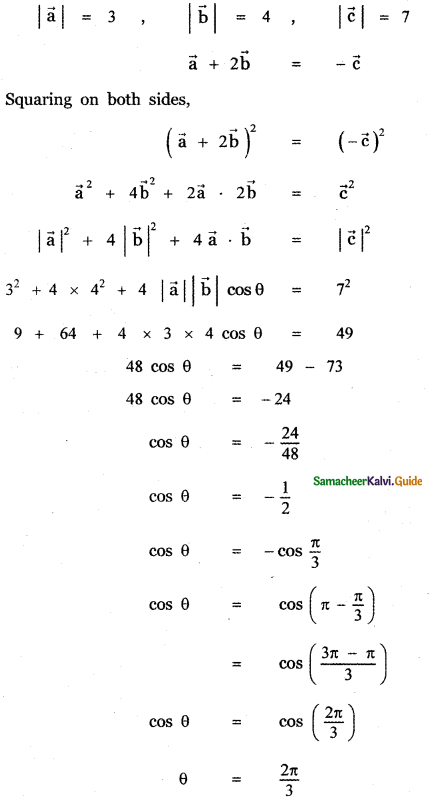
![]()
Question 6.
Show that the vectors \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + 3ĵ + 6k̂ \(\vec{b}\) = 6î + 2ĵ – 3k̂ and \(\vec{c}\) = 3î – 6ĵ + 6k̂ are mutually orthogonal.
Answer:
Given \(\vec{a}\) = 2î + 3ĵ + 6k̂ \(\vec{b}\) = 6î + 2ĵ – 3k̂ and \(\vec{c}\) = 3î – 6ĵ + 6k̂
\(\vec{a}\) . \(\vec{b}\) = (2î + 3ĵ + 6k̂) . (6î + 2ĵ – 3k̂)
= (2) (6) + (3) (2) + (6) (-3)
= 12 + 6 – 18
= 0
∴ \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{a}\) are perpendicular.
\(\vec{b}\) . \(\vec{c}\) = (6î + 2ĵ – 3k̂) . (3î – 6ĵ + 6k̂)
= (6) (3) + (2) (- 6) + (-3) (2)
= 18 – 12 – 6
= 0
∴ \(\vec{b}\) and \(\vec{c}\) are perpendicular.
\(\vec{c}\) . \(\vec{a}\) = (3î – 6ĵ + 6k̂) . (2î + 3ĵ + 6k̂)
= (3) (2) + (-6) (3) + (2) (6)
= 6 – 18 + 12
= 0
∴ \(\vec{c}\) and \(\vec{a}\) are perpendicular.
Hence \(\vec{a}\), \(\vec{b}\), \(\vec{c}\) are mutually perpendicular vectors.
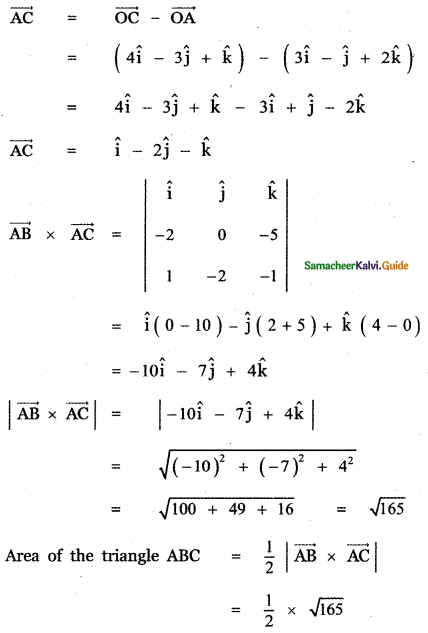
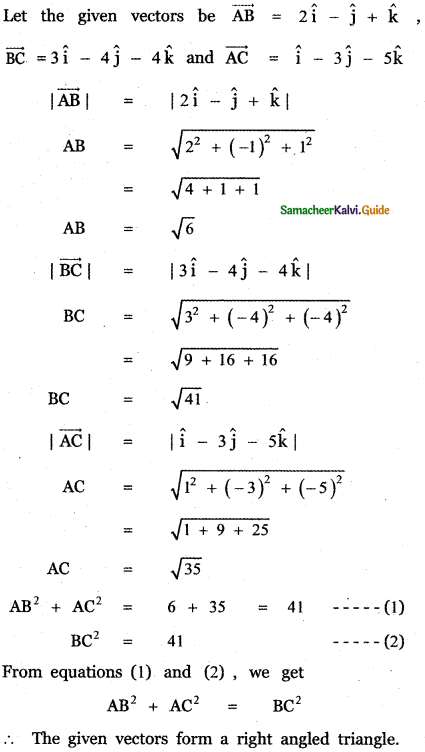
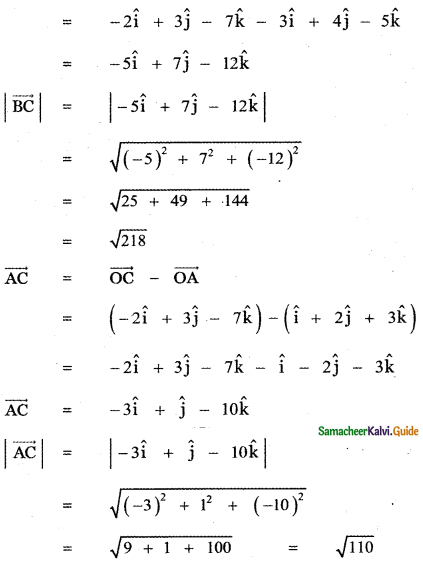
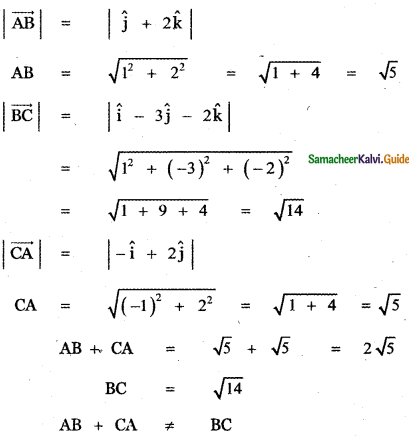
Question 7.
Show that the vectors – î – 2ĵ – 6k̂, 2î – ĵ + k̂ and – î + 3ĵ + 5k̂ from a right-angled triangle.
Answer:
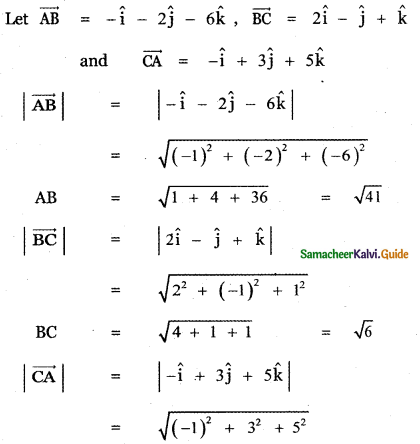
CA = \(\sqrt{1+9+25}\) = \(\sqrt{35}\)
AB ≠ BC + CA
∴ The given vectors form a triangle, Also
AB2 = 41, BC2 = 6, CA2 = 35
AB2 = BC2 + CA2
∴ ∆ ABC is a right angled triangle.
![]()
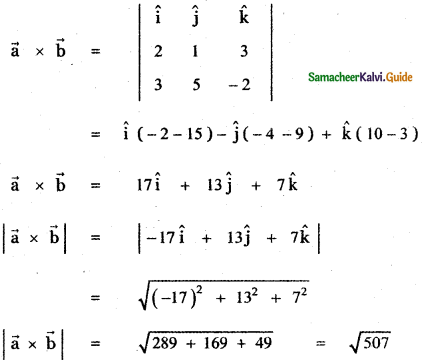
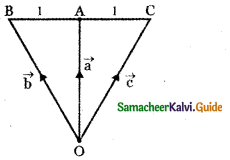
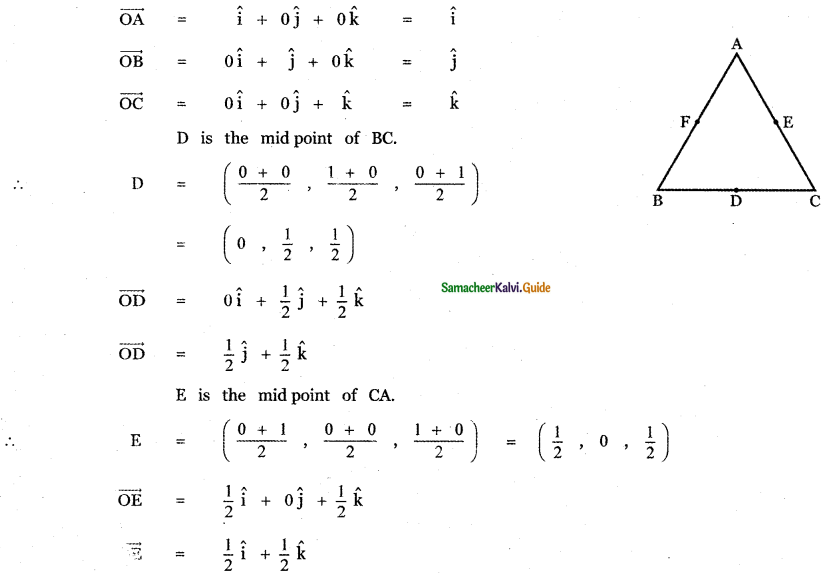
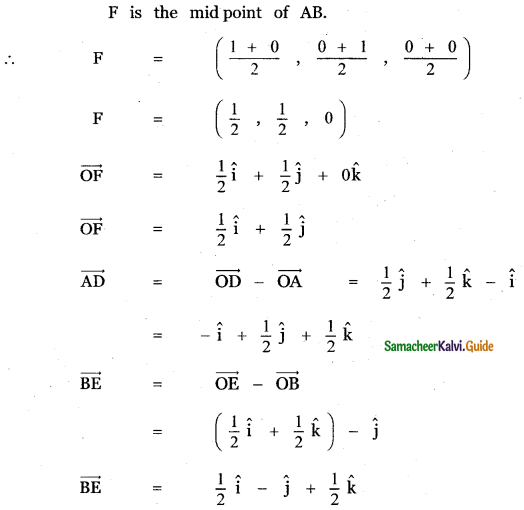
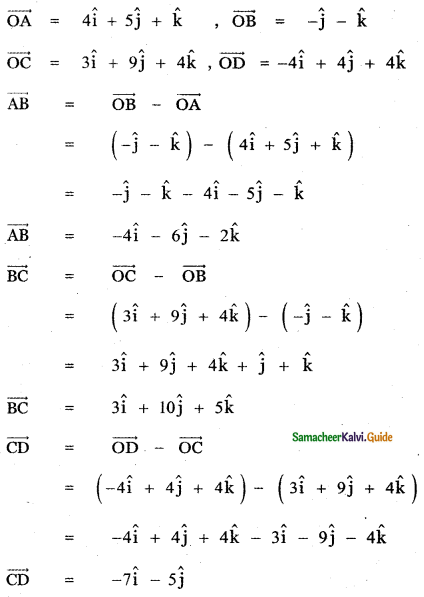
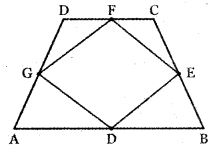
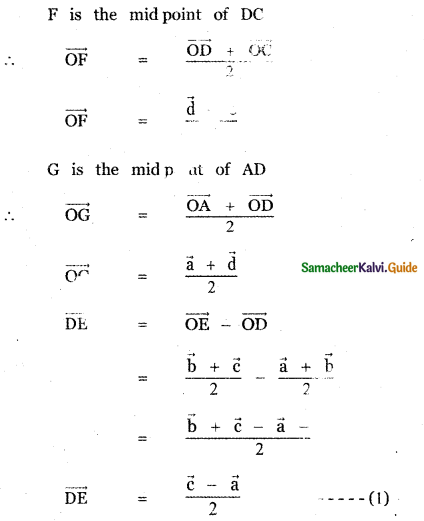
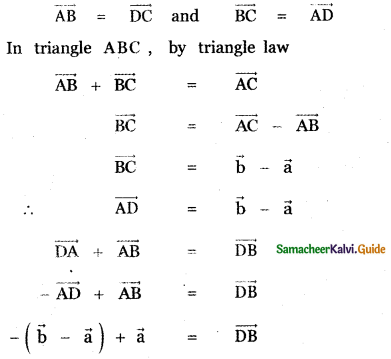
Question 8.
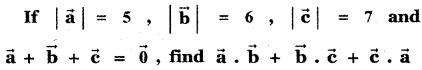
Answer:
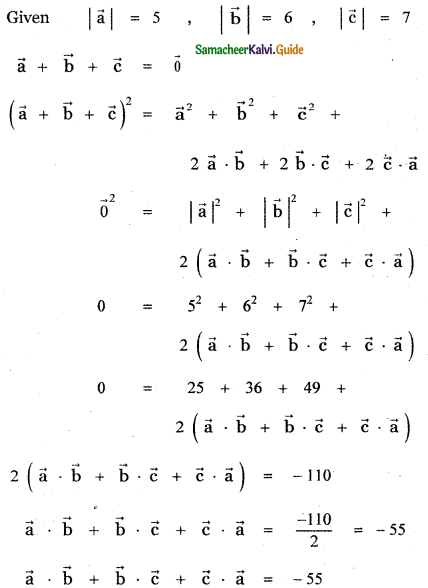
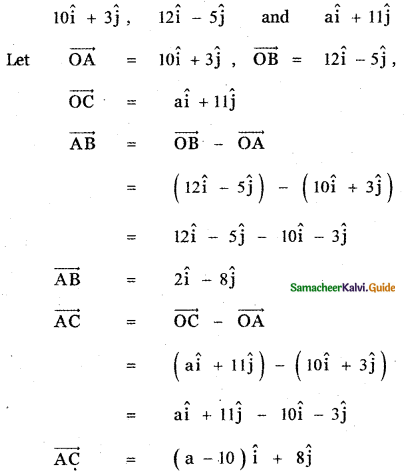
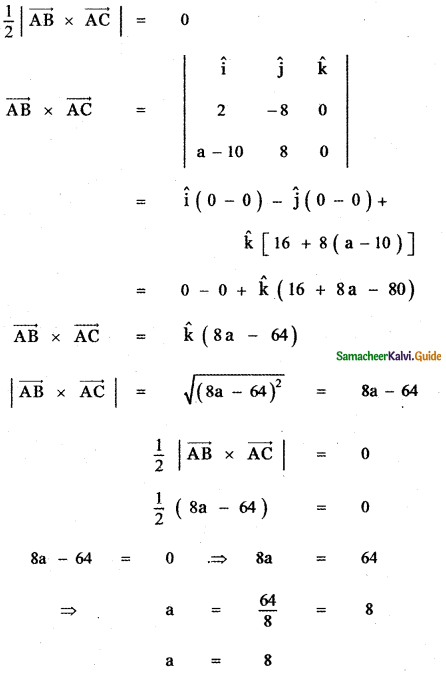
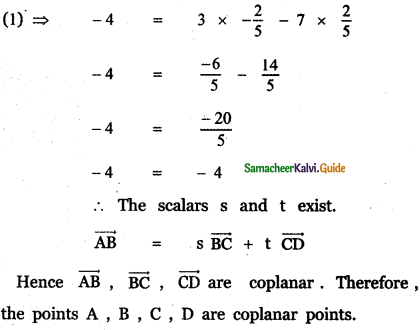
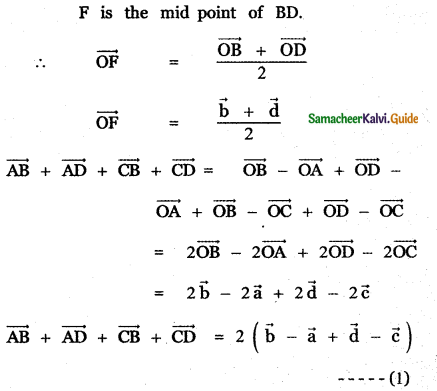
Question 9.
Show that the points (2, – 1, 3), (4, 3, 1), and (3, 1, 2) are collinear.
Answer:
Let the given points be
A (2, -1, 3), B (4, 3, 1) and C (3, 1, 2)
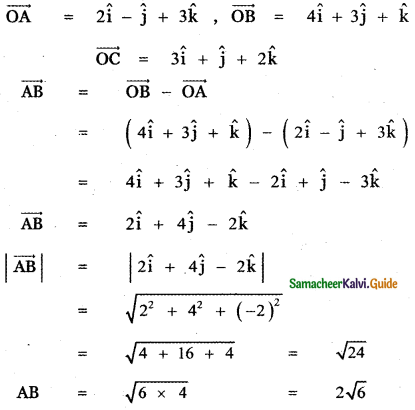
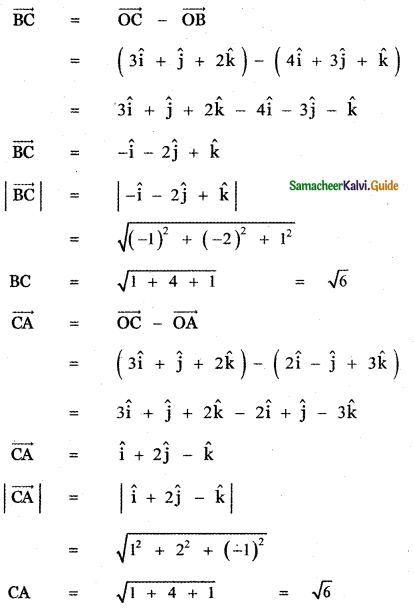
AB = 2√6, BC = √6, CA = √6
BC + CA = √6 + √6 = 2√6
∴ BC + CA = BA = 2√6
Hence the given points A, B, C are collinear.
![]()
Question 10.
If \(\vec{a}\), \(\vec{b}\) are unit vectors and θ is the angle between them, show that
(i) ![]()
(ii)![]()
(iii) 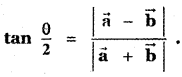
Answer:
Given \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are unit vectors.
∴ |\(\vec{a}\)| = 1 and |\(\vec{b}\)| = 1
(i) ![]()

(ii) ![]()
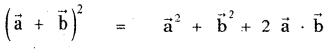
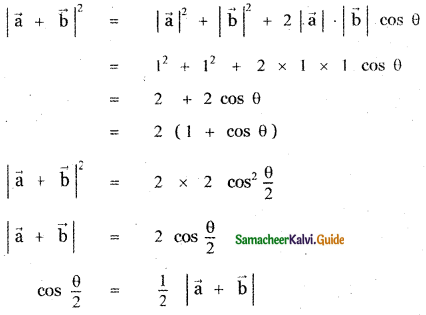
(iii) 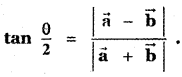
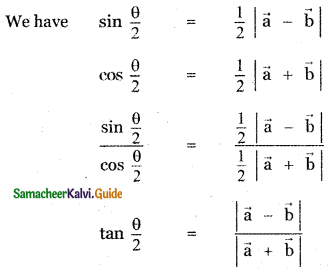
![]()
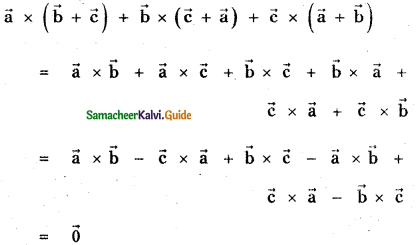
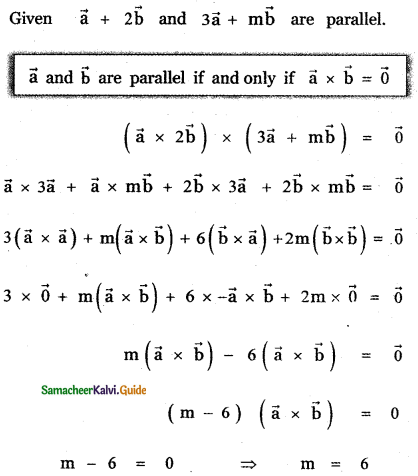
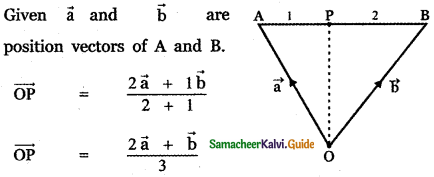
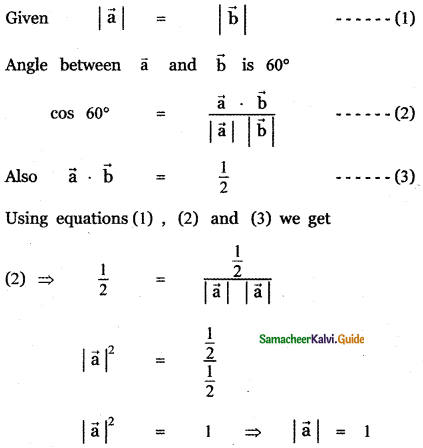
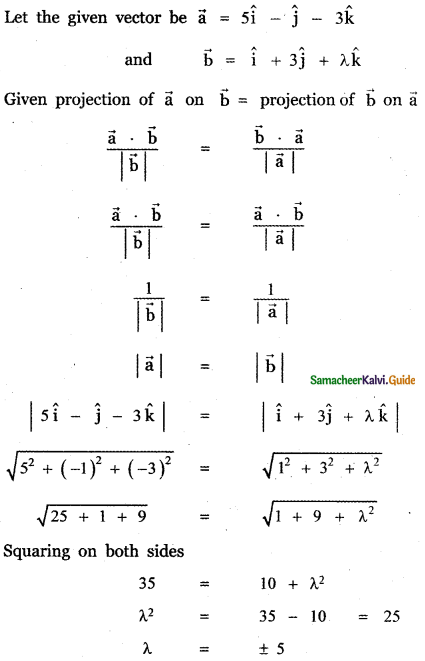
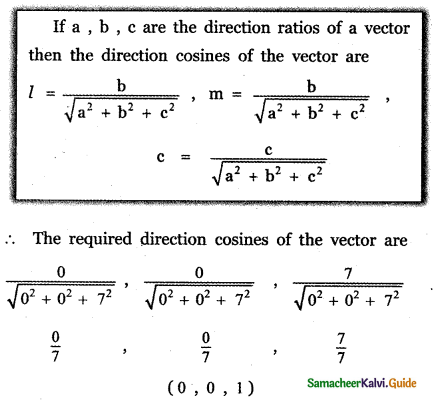
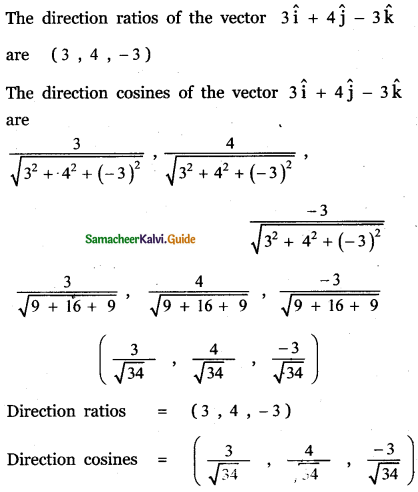
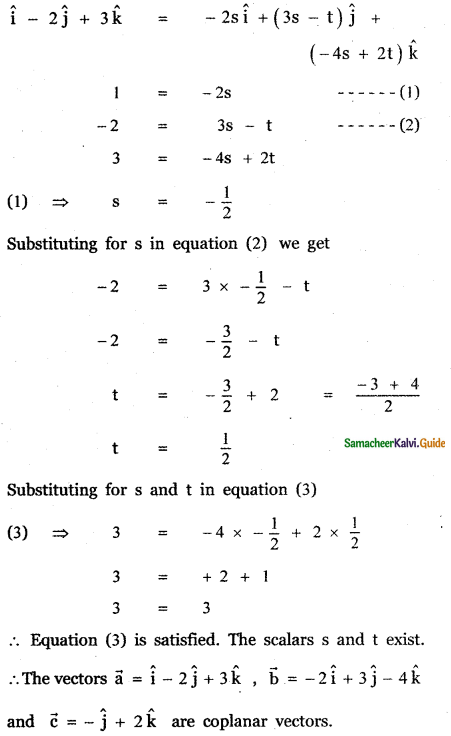
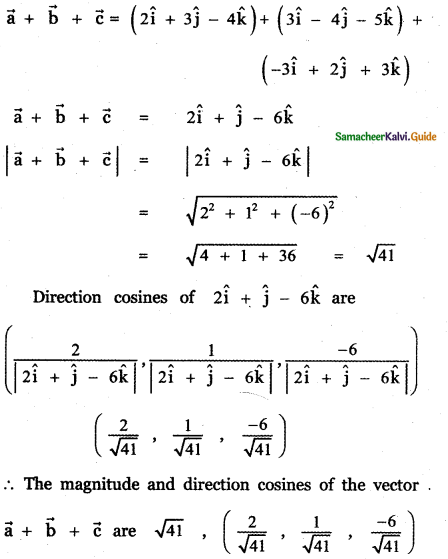
Question 11.
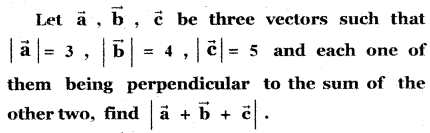
Answer:
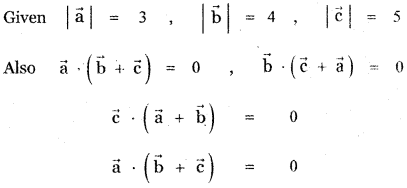

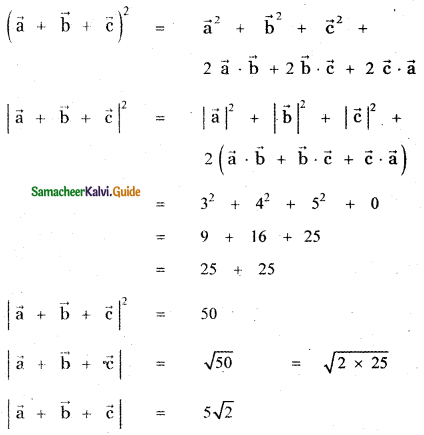
![]()
Question 12.
Find the projection of the vector î + 3ĵ + 7k̂ on the vector 2î + 6ĵ + 3k̂
Answer:
The given vectors are î + 3ĵ + 7k̂ and 2î + 6ĵ + 3k̂
Projection of î + 3ĵ + 7k̂ on 2î + 6ĵ + 3k̂ is
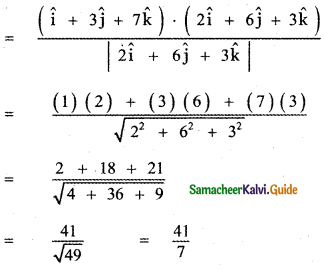
Question 13.
Find λ, when the projection \(\vec{a}\) = λî + ĵ + 4k̂ on \(\vec{b}\) = 2î + 6ĵ + 3k̂ is 4 units.
Answer:
The given vectors are
\(\vec{a}\) = λî + ĵ + 4k̂ , \(\vec{b}\) = 2î + 6ĵ + 3k̂
Also given that projection of \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) is 4 units.
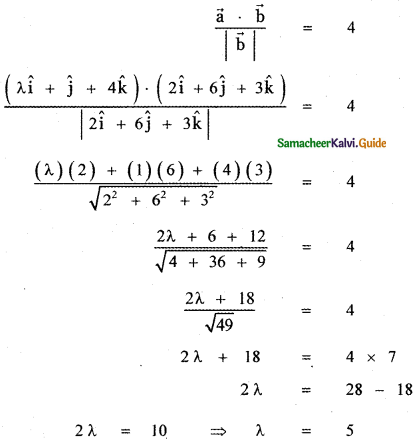
![]()
Question 14.
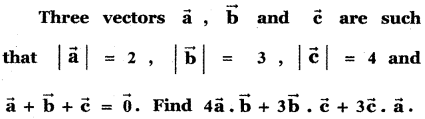
Answer: